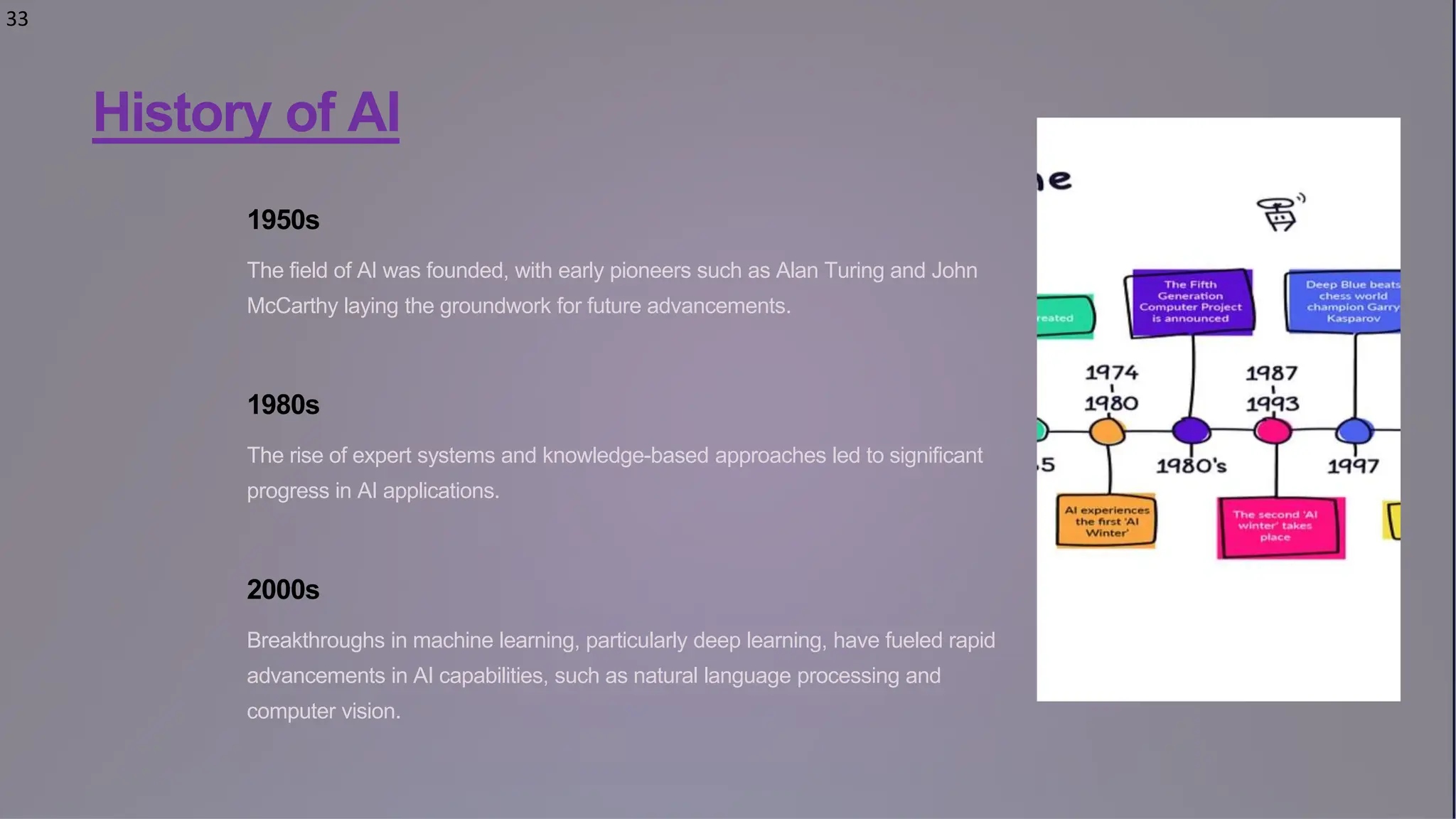
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly evolving field focused on creating machines that perform tasks requiring human intelligence, utilizing technologies like machine learning and natural language processing. The history of AI spans from the foundational work in the 1950s to recent advancements in deep learning and AI applications across various sectors including healthcare and autonomous vehicles. Future developments in AI will prioritize ethical considerations and aim to augment human intelligence rather than replace it.