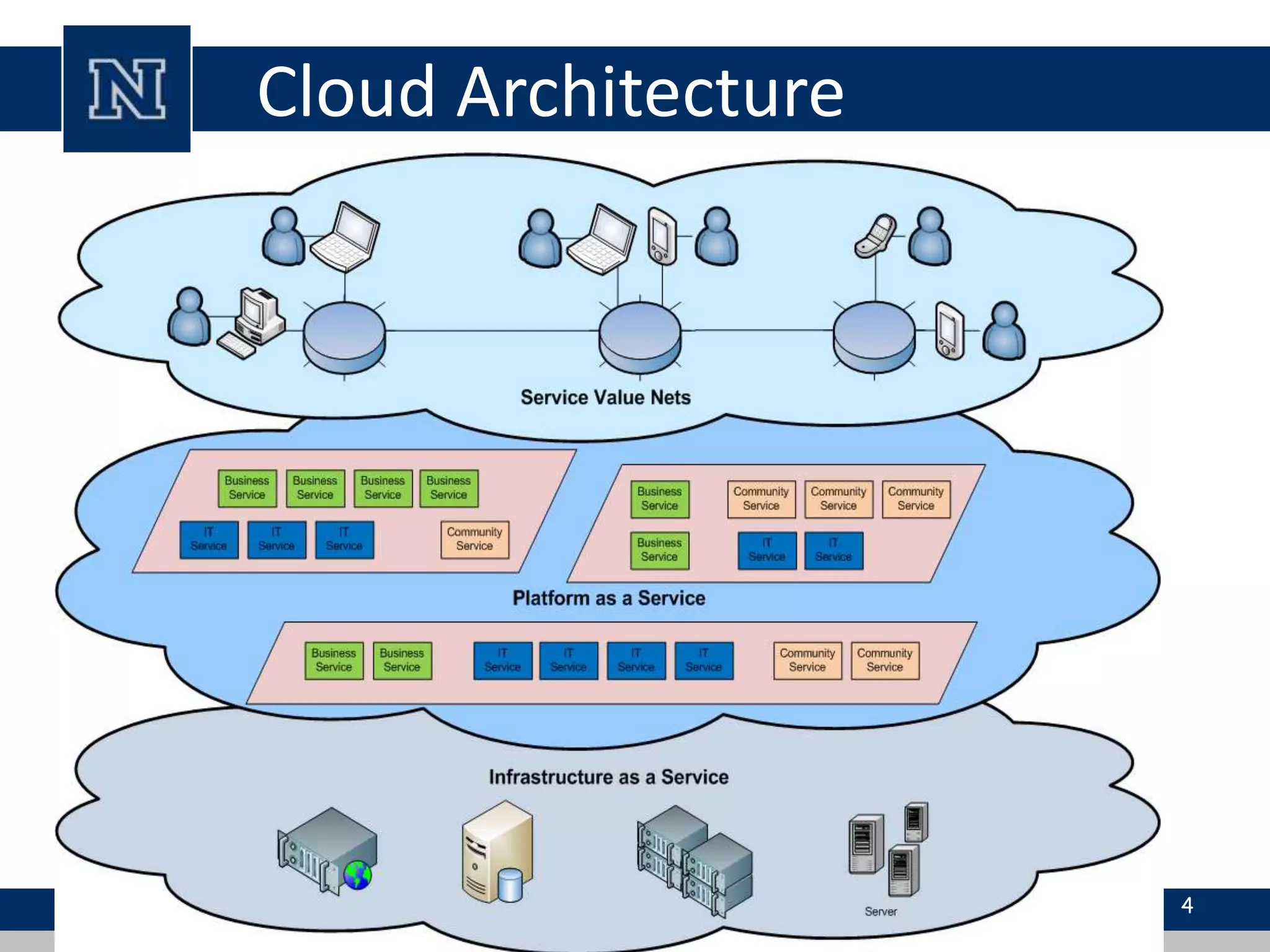
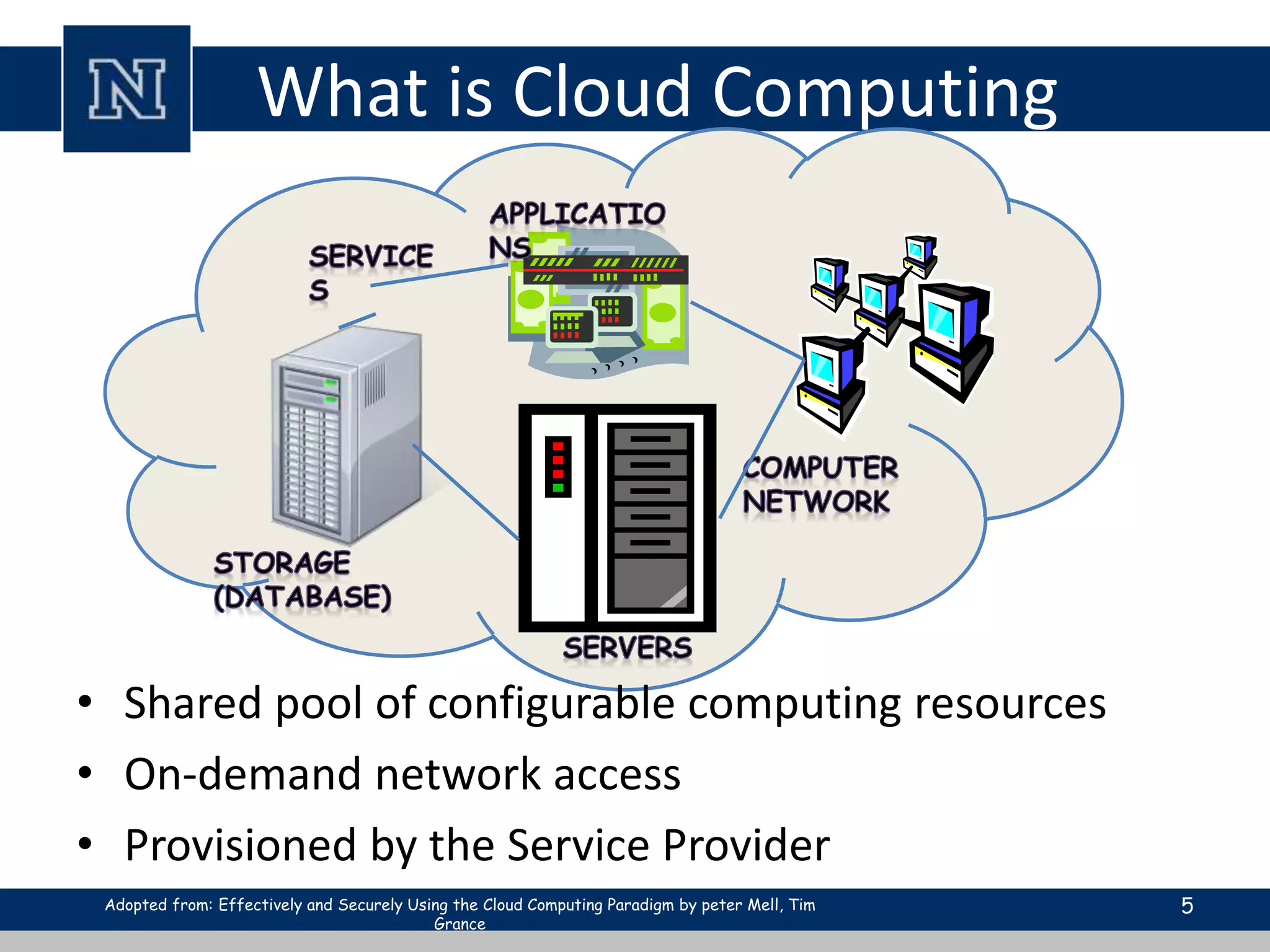
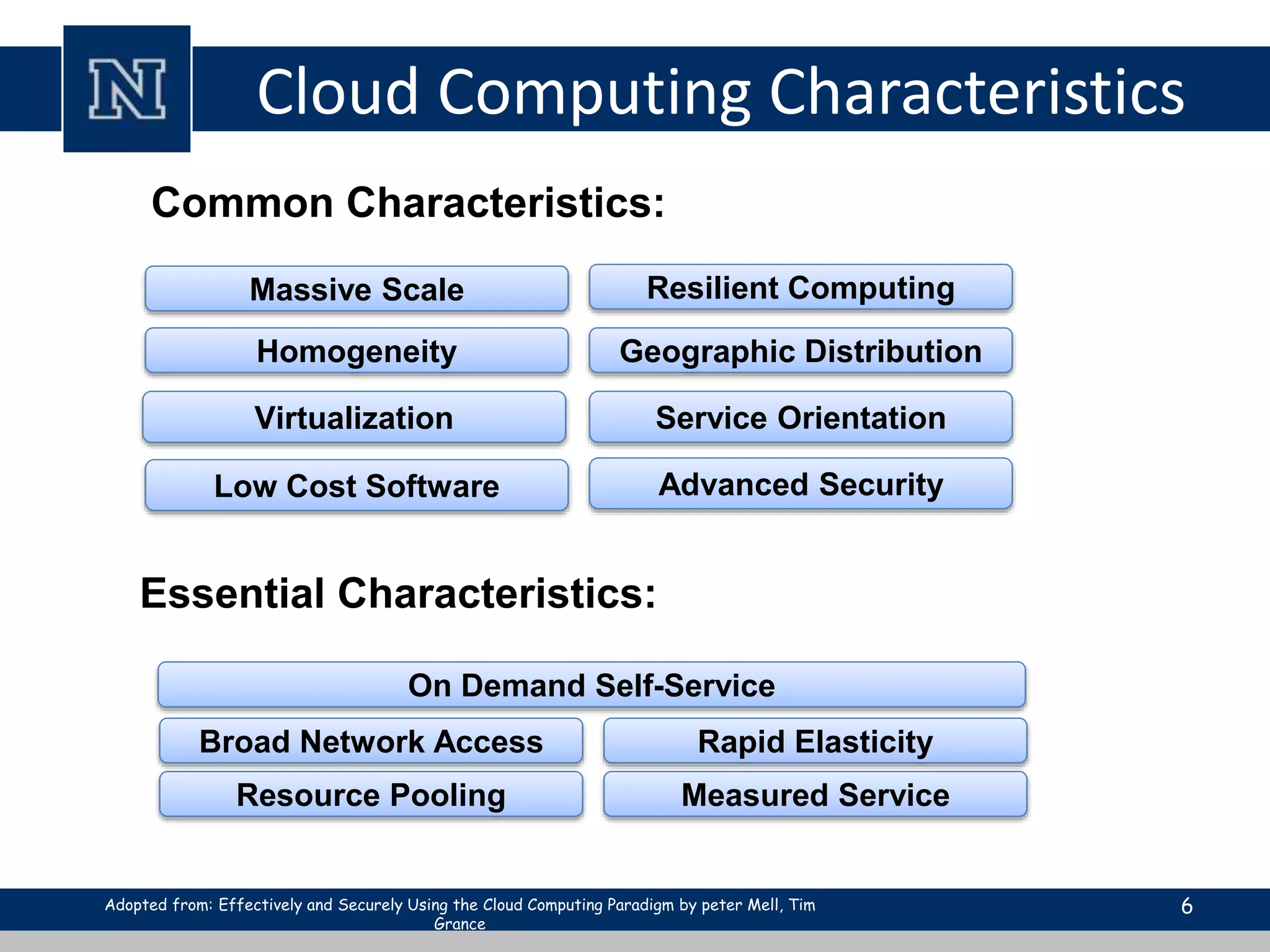
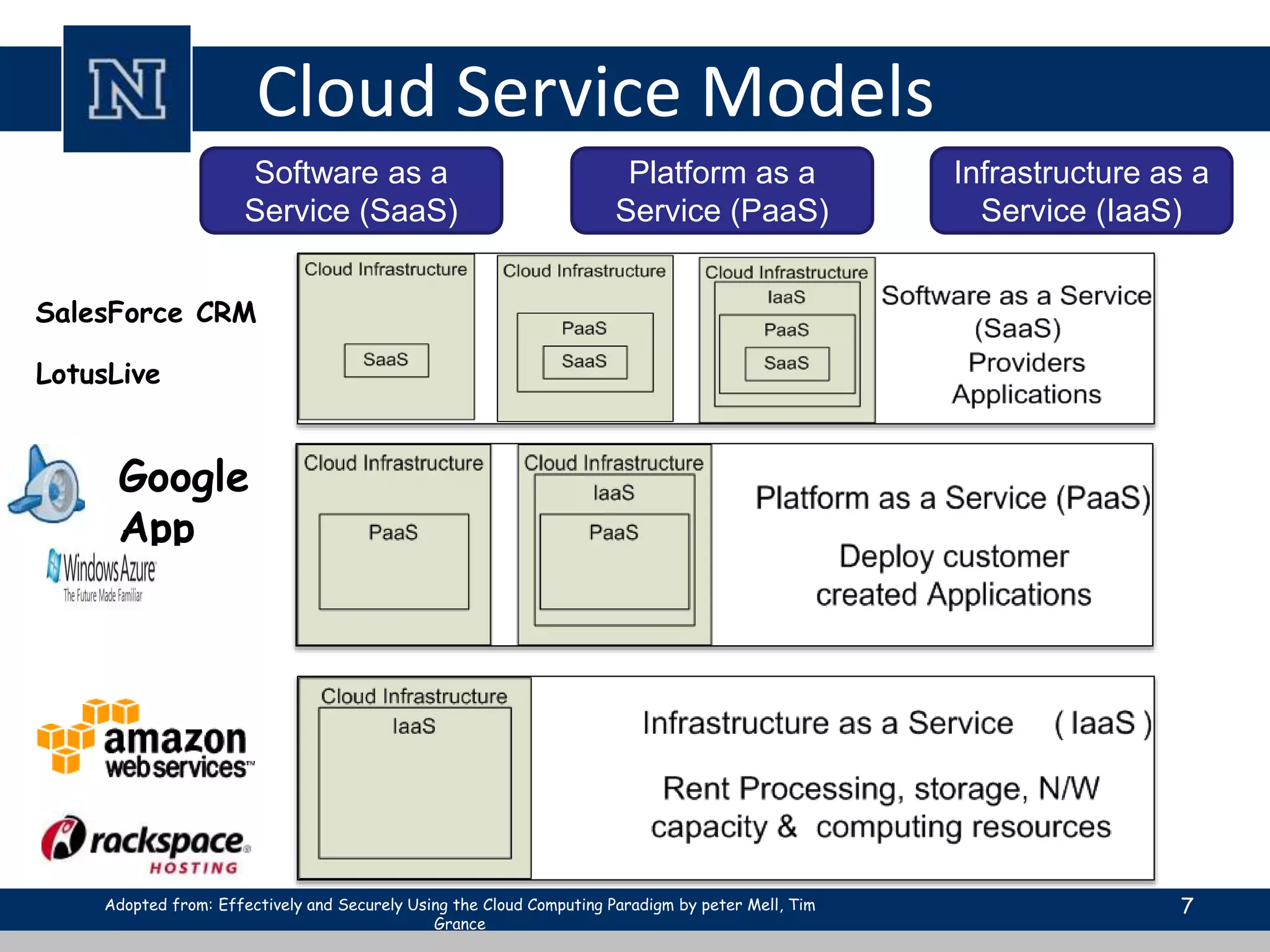
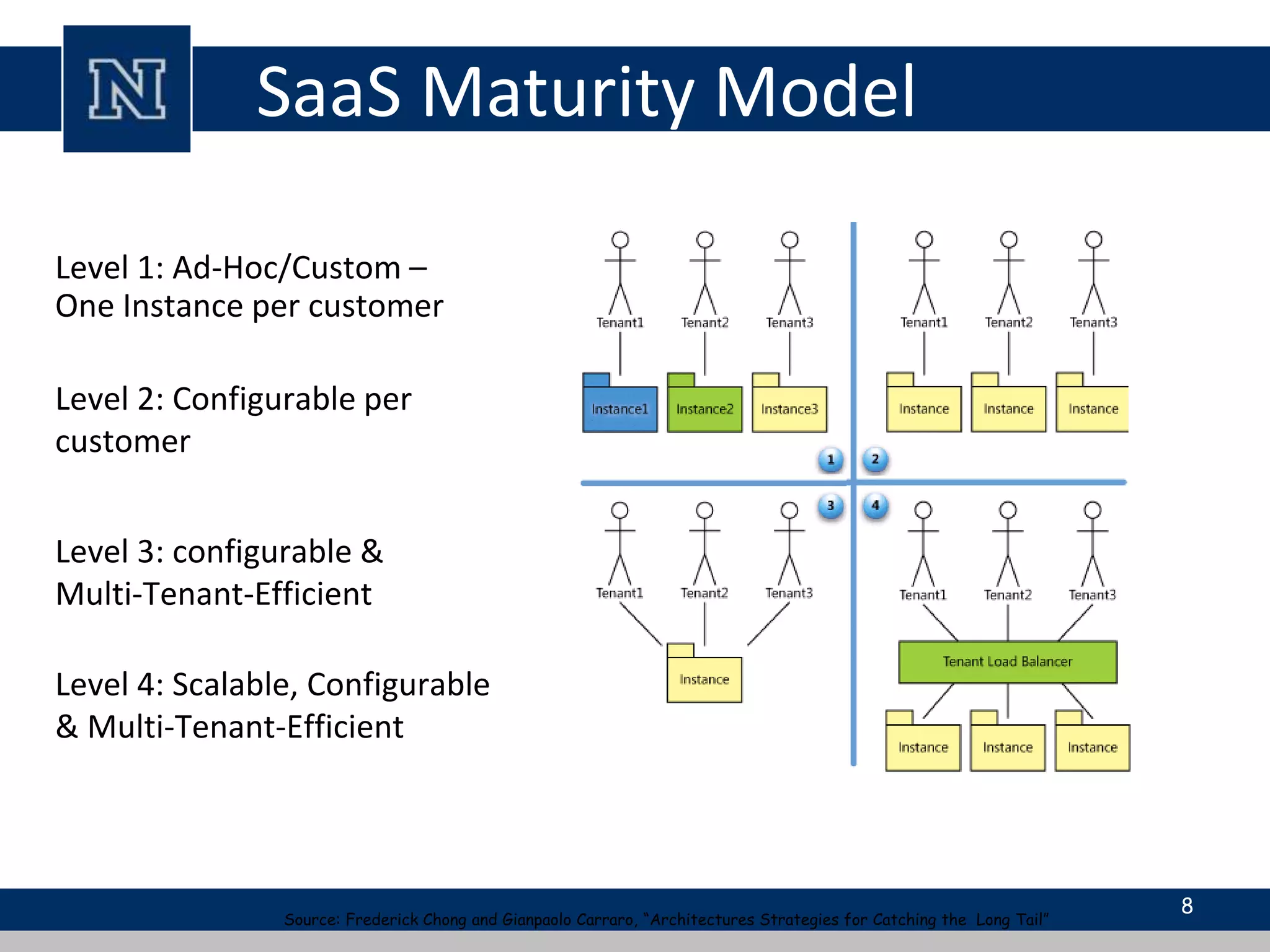
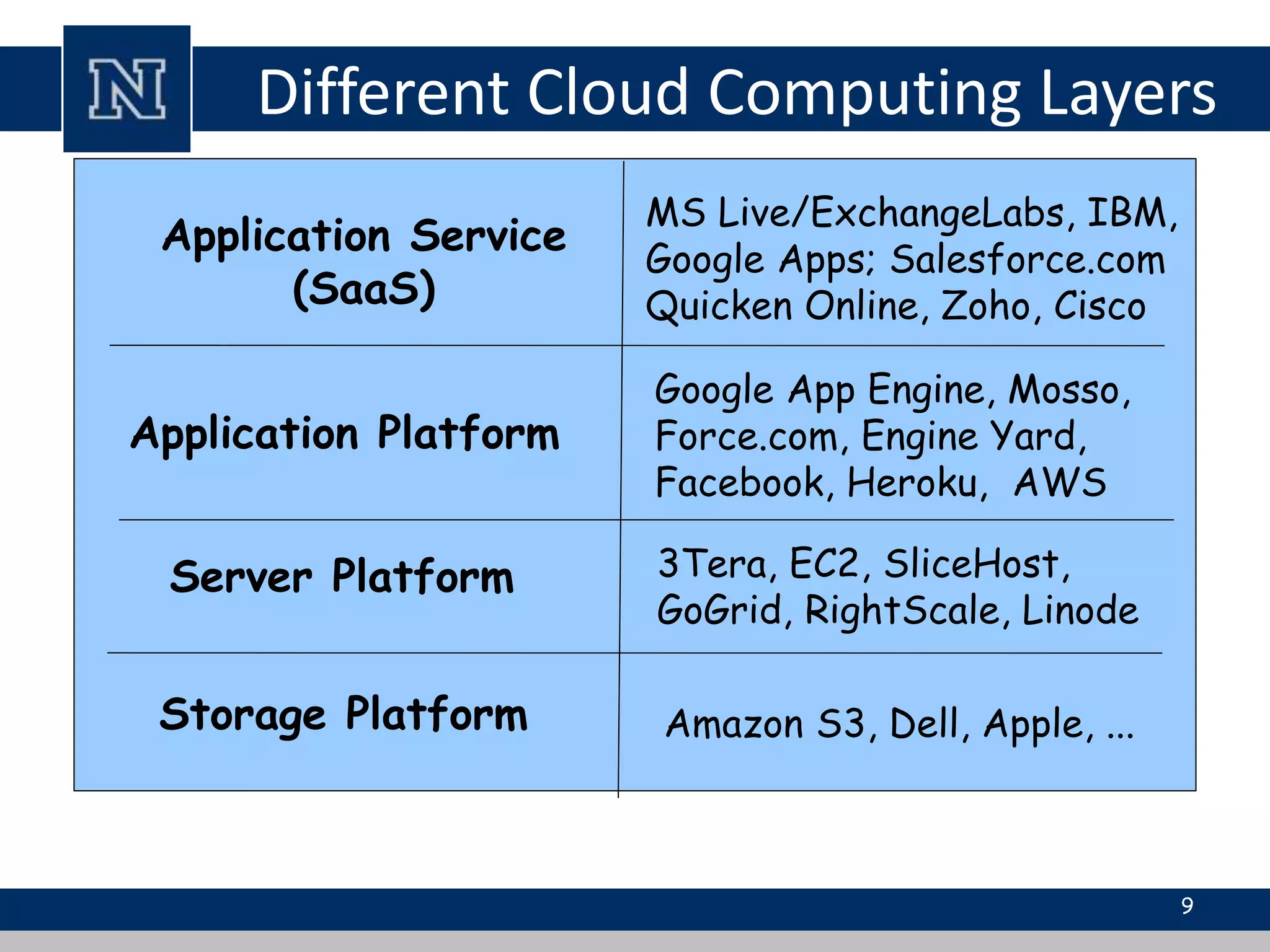
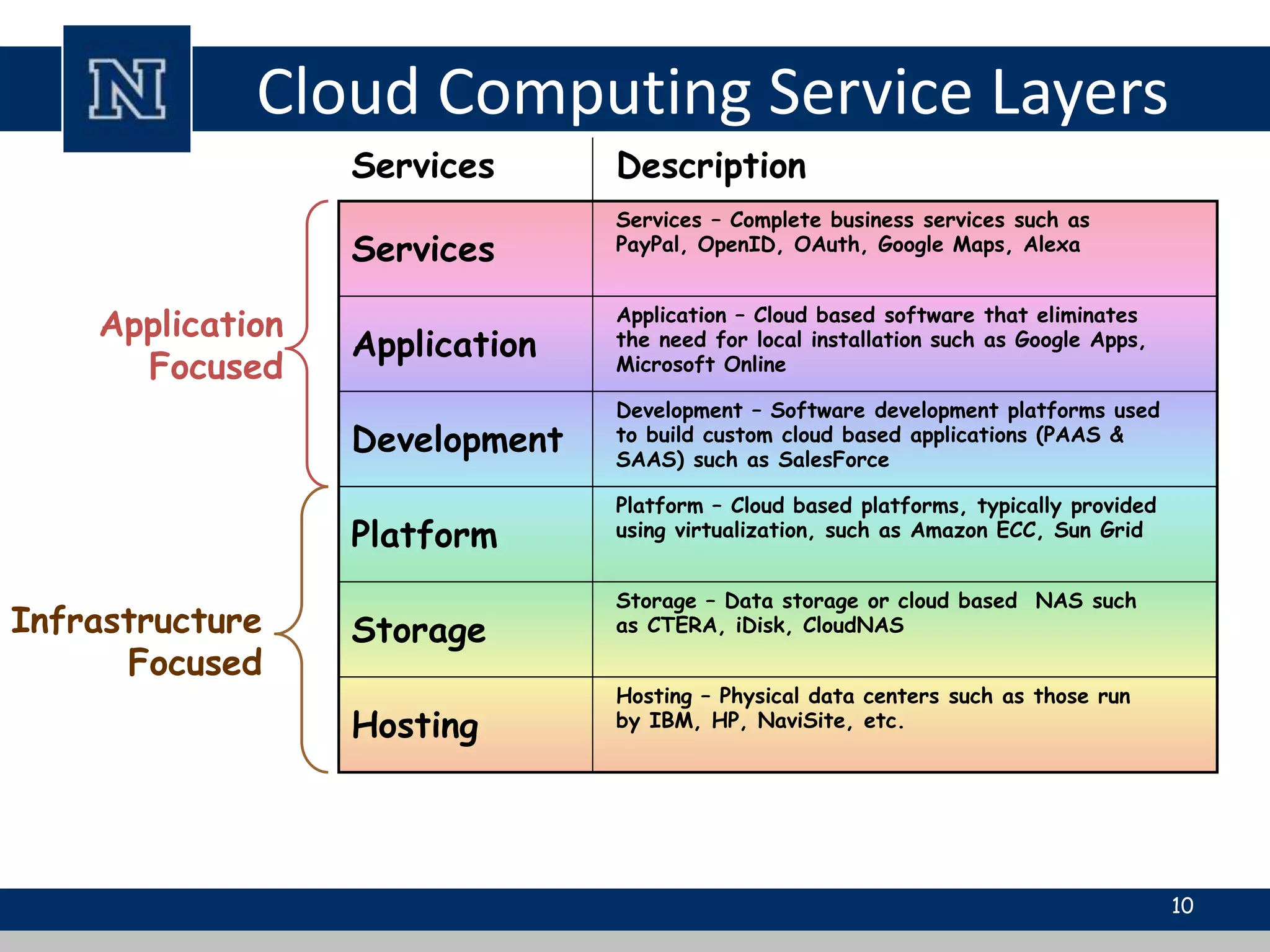
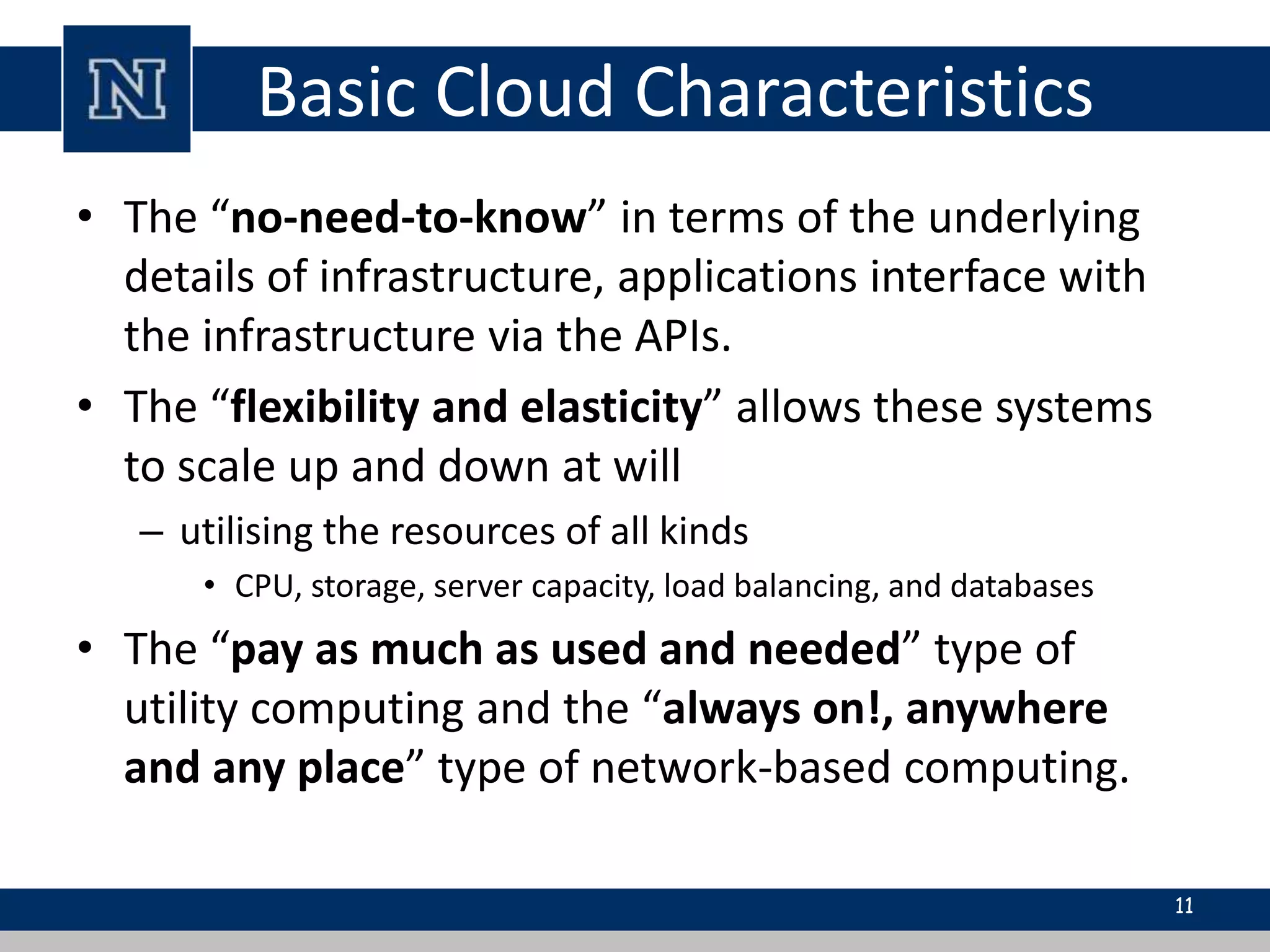
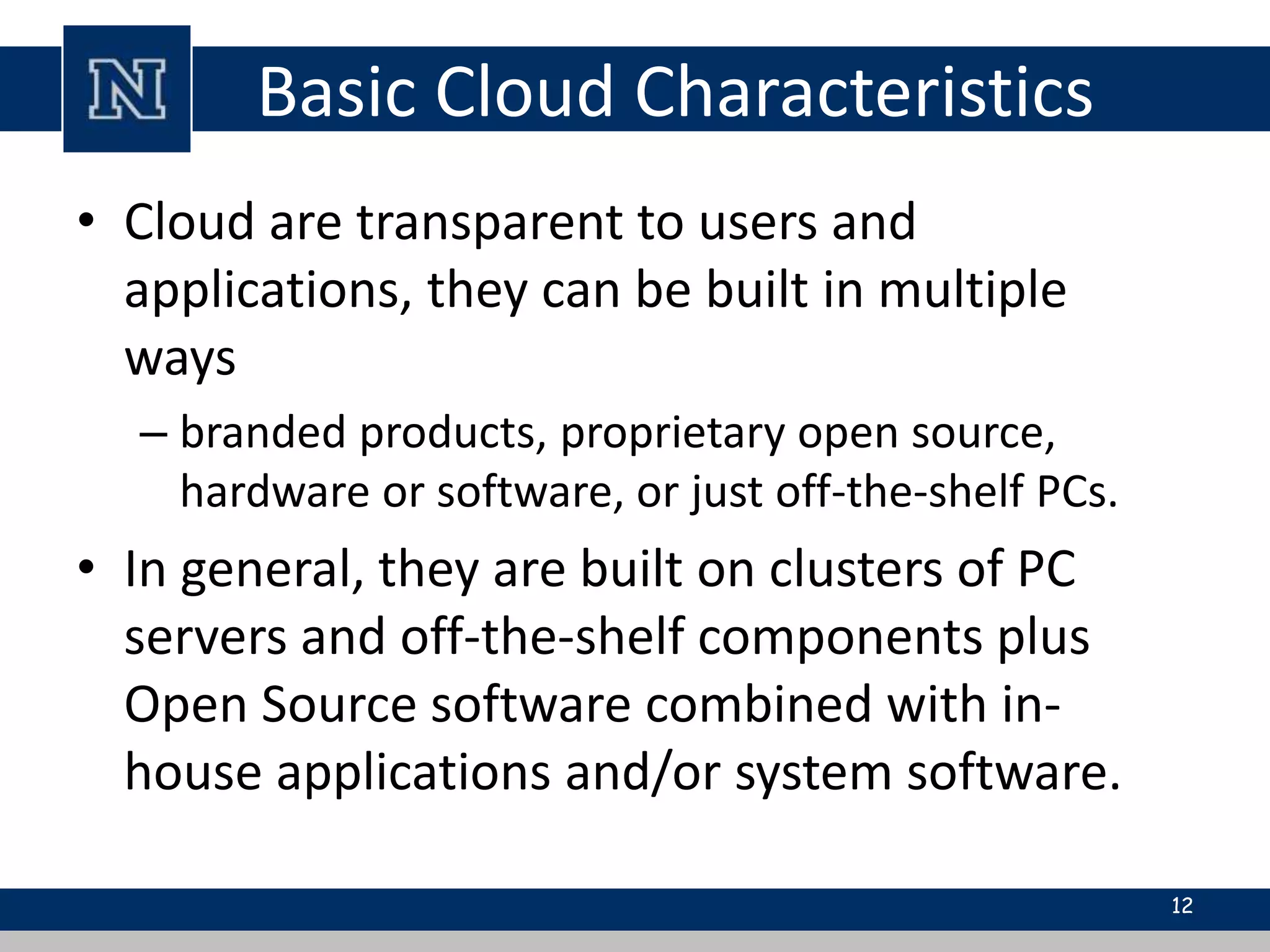
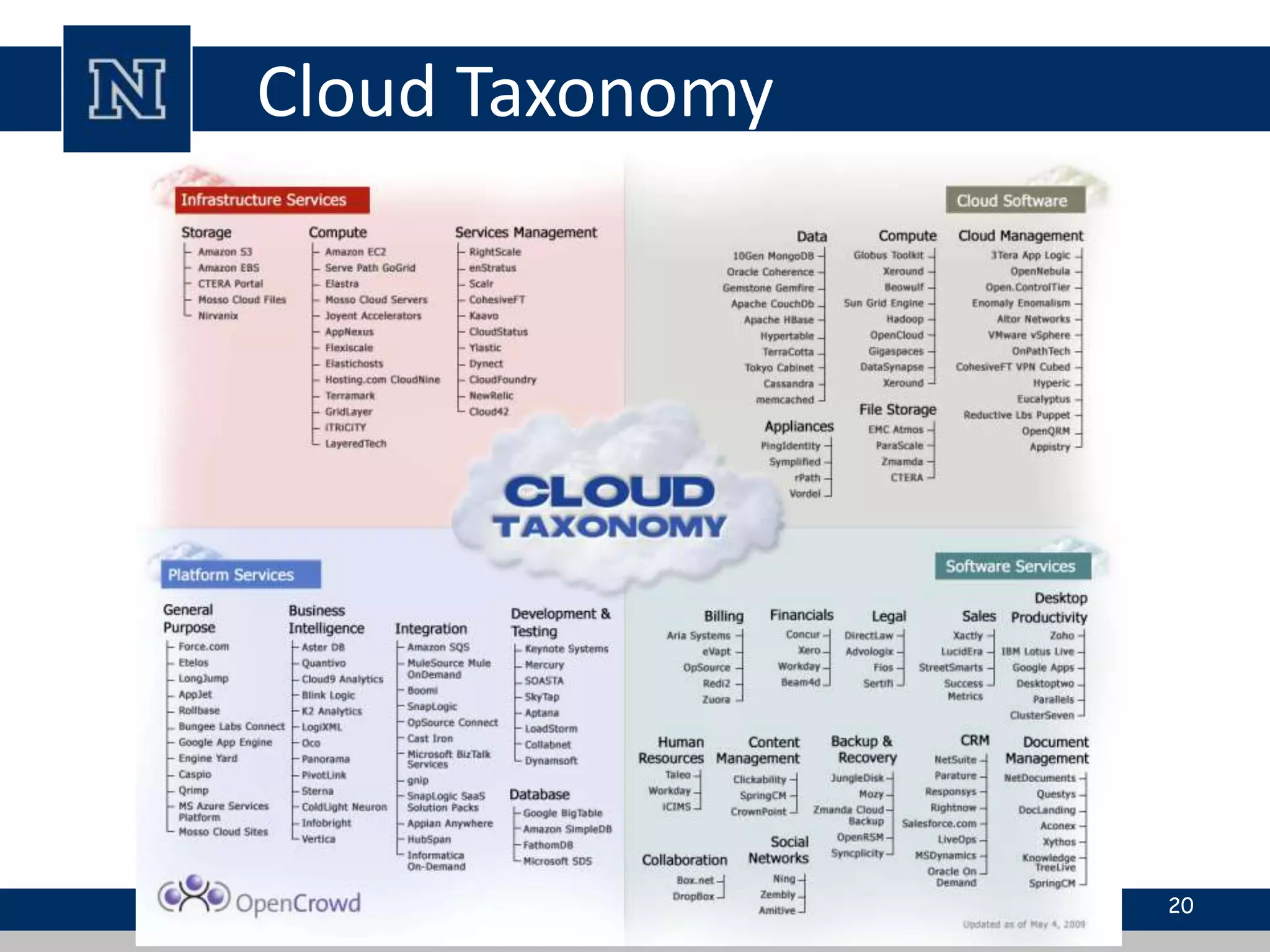
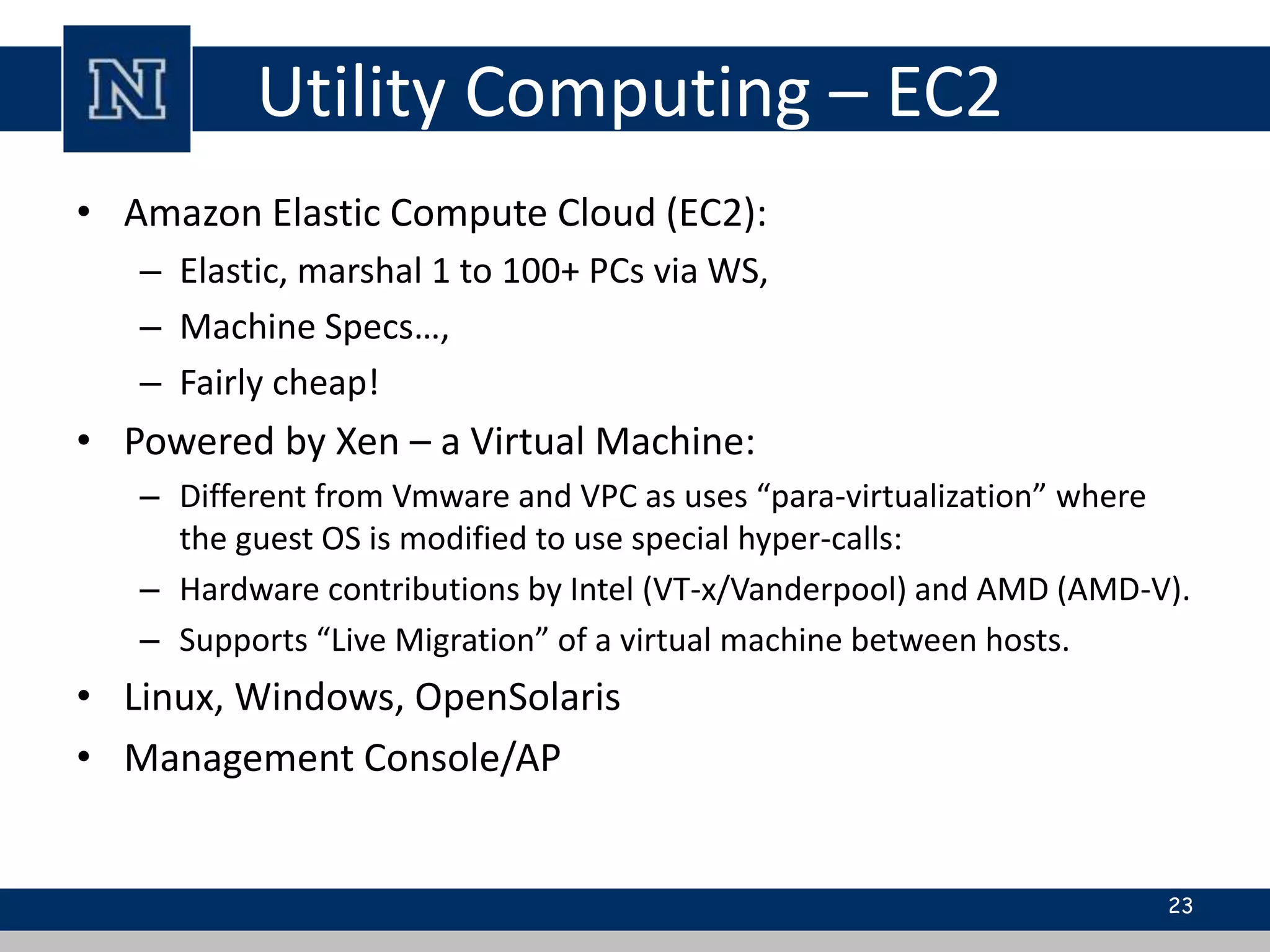
Cloud computing is a network-based computing model that provides scalable, on-demand services via the internet, allowing users to access shared resources without needing to understand the underlying infrastructure. Its key characteristics include elasticity, pay-per-use pricing, and broad accessibility, with service models classified into SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. While it offers significant advantages such as lower costs, improved performance, and unlimited storage, challenges include dependence on internet connectivity, potential security issues, and concerns over data control.