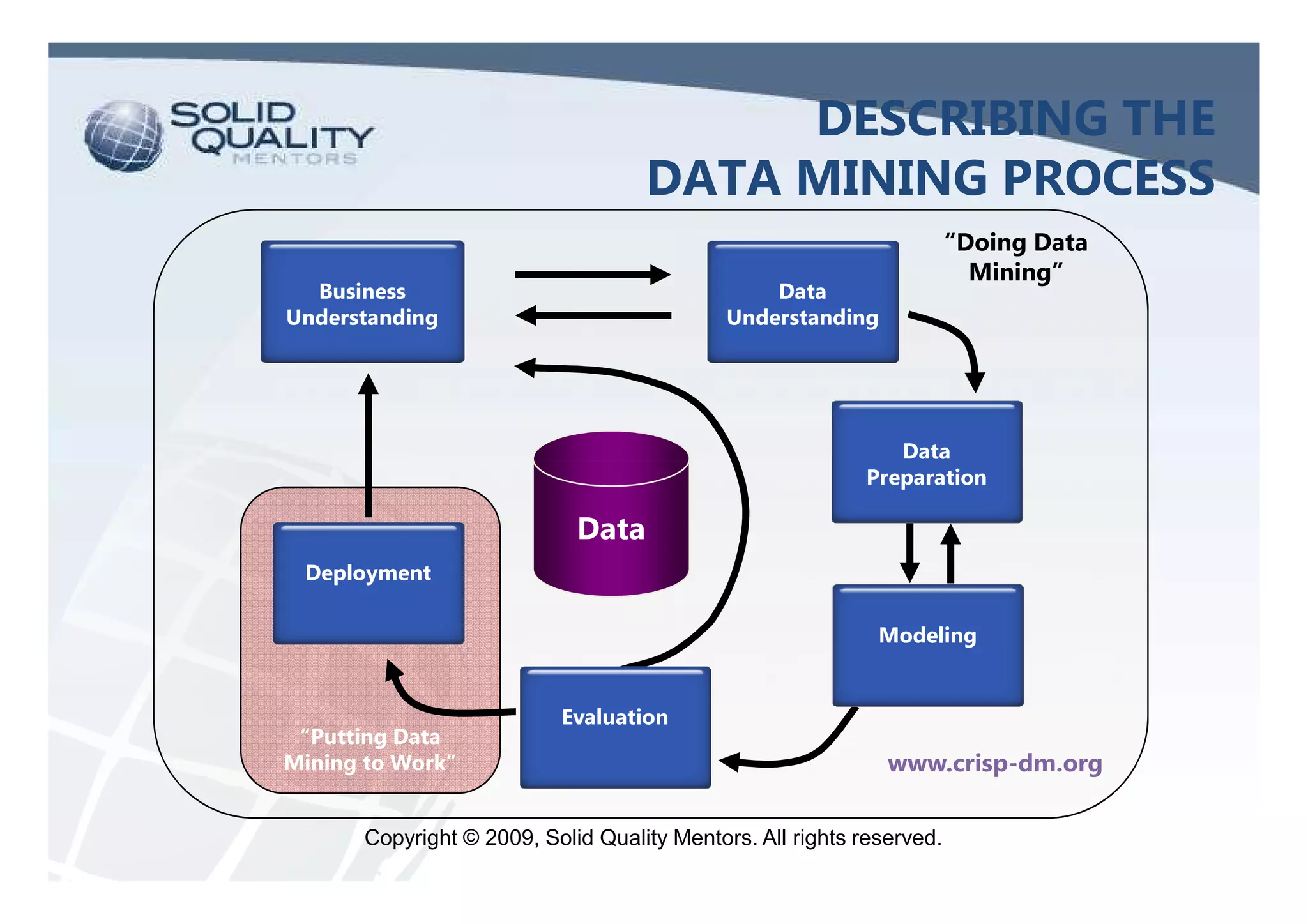
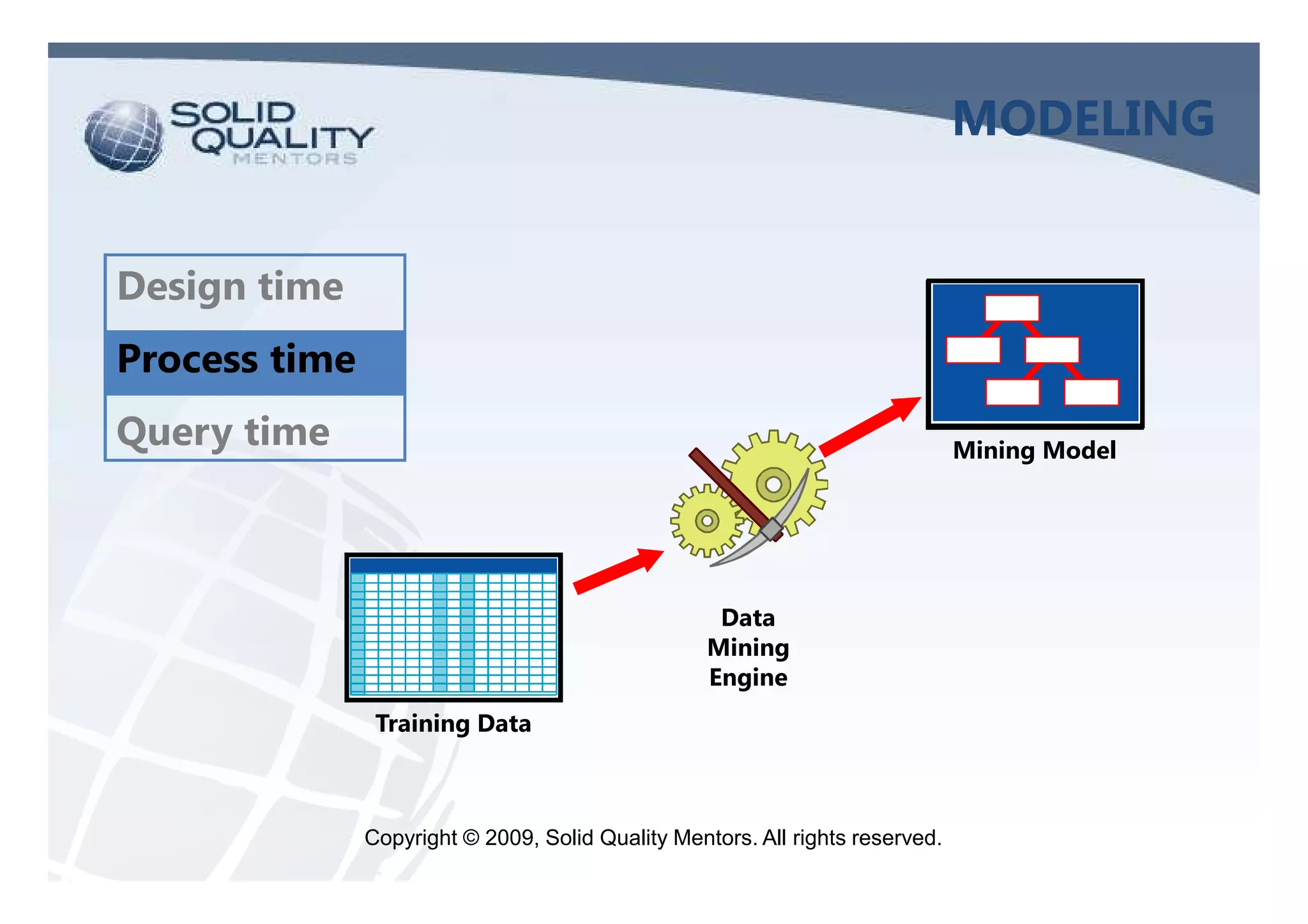
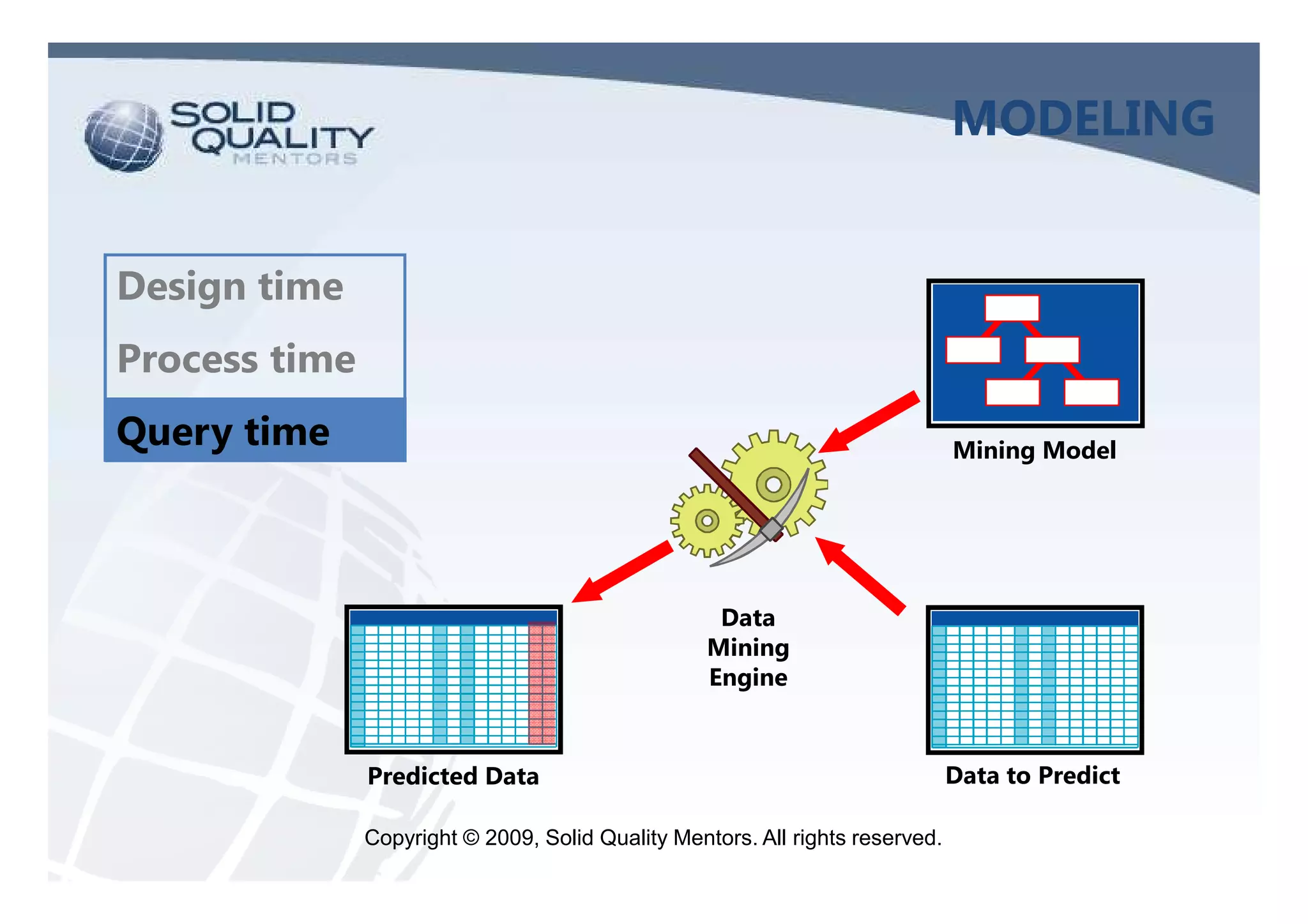
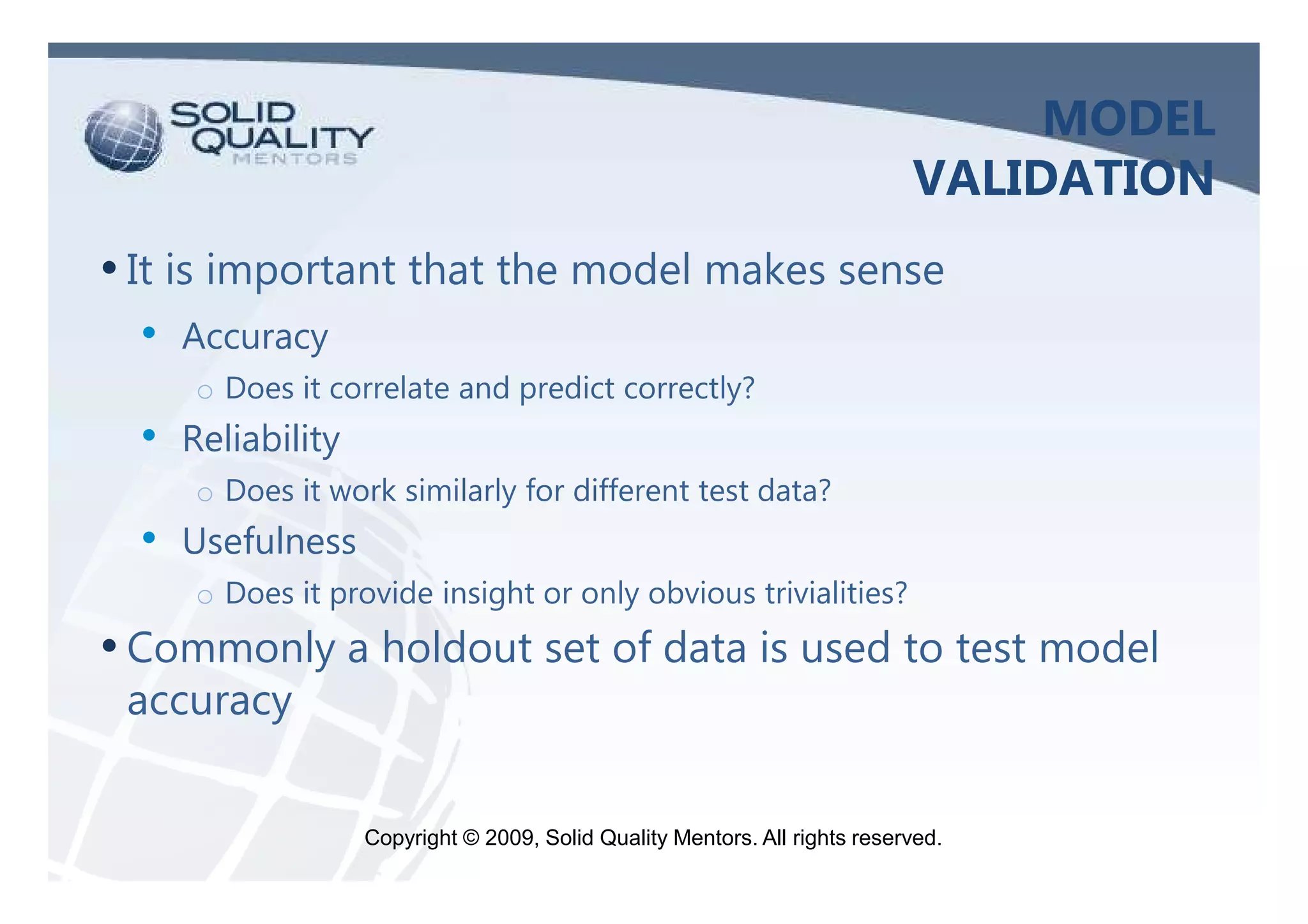
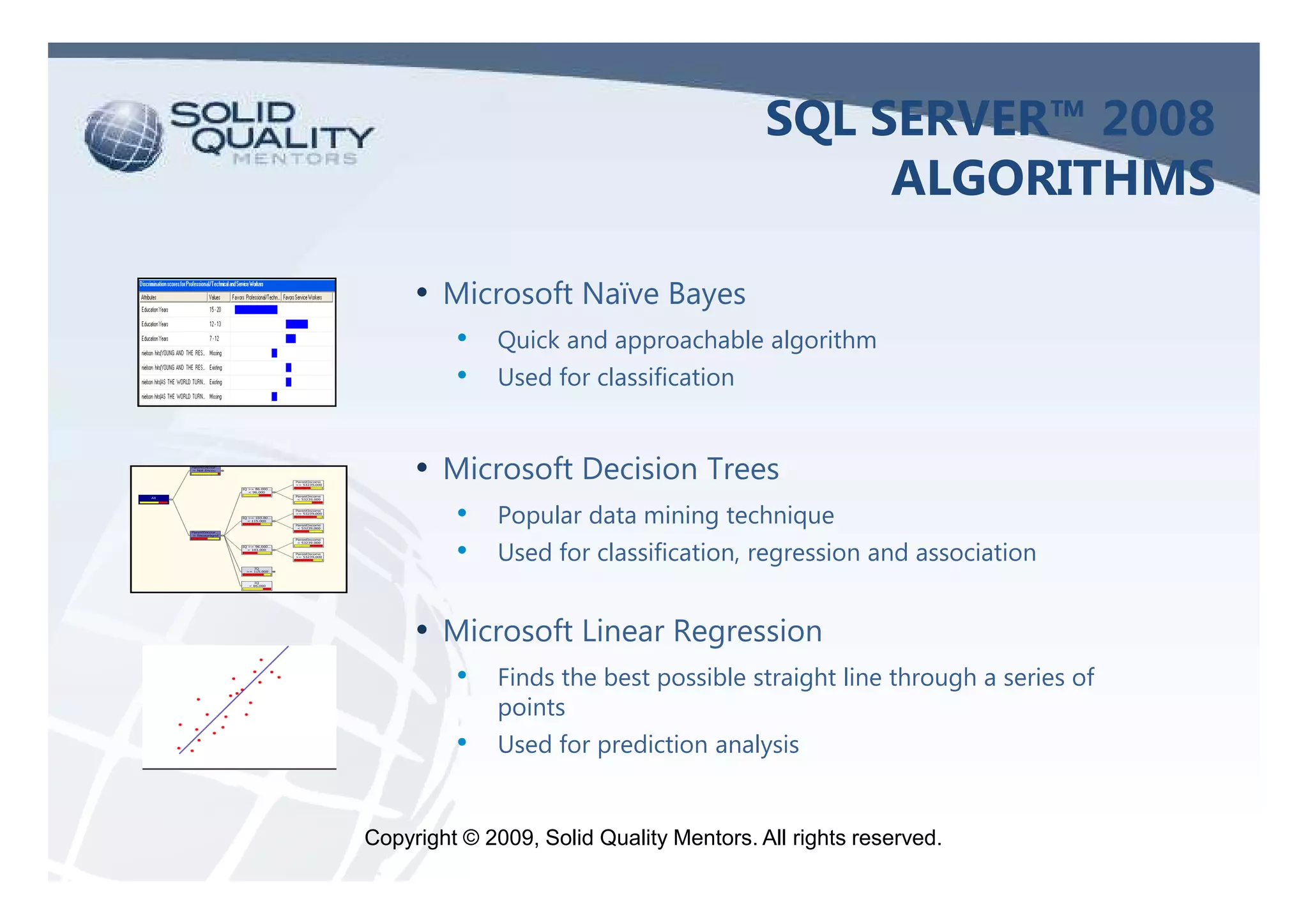
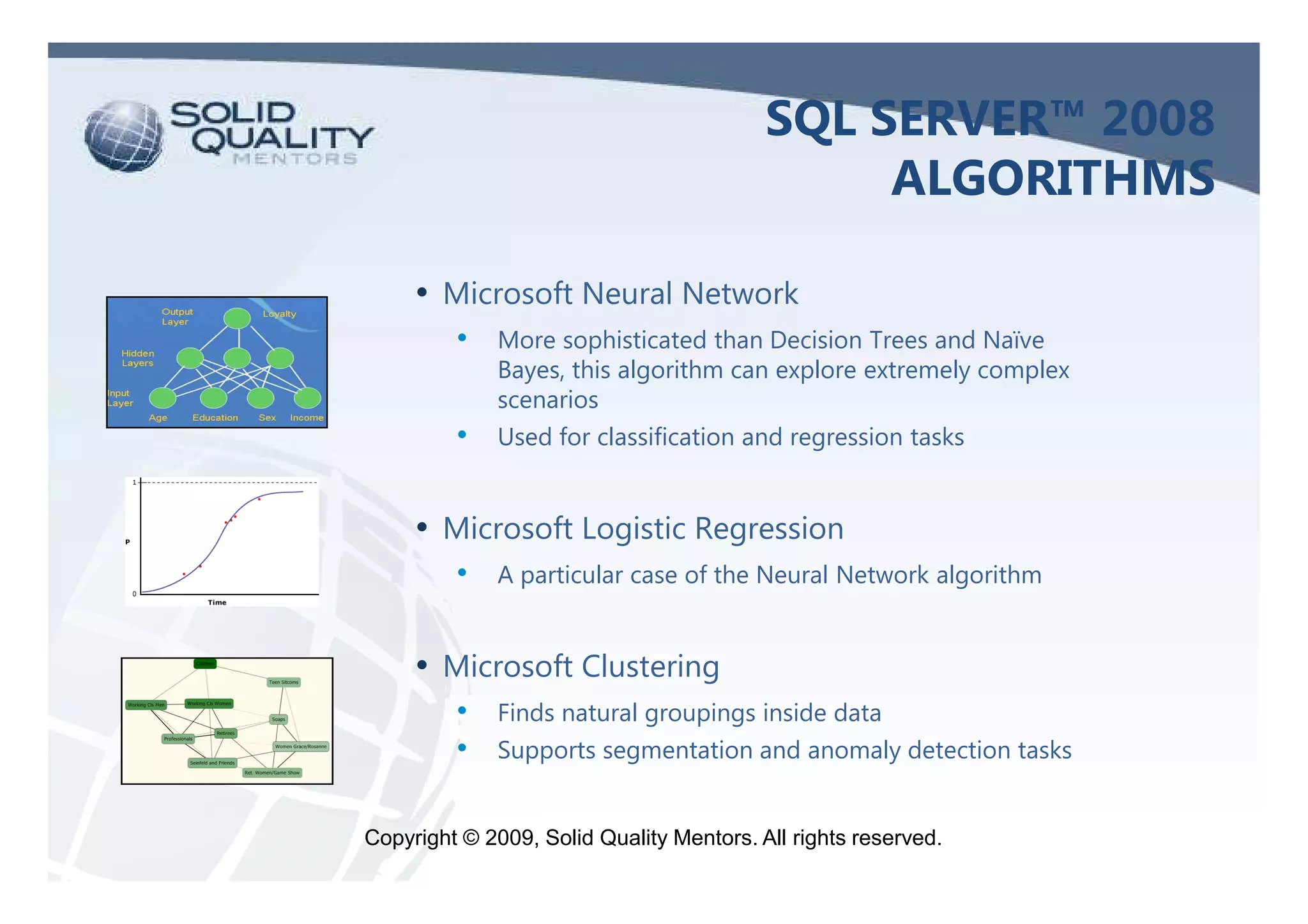
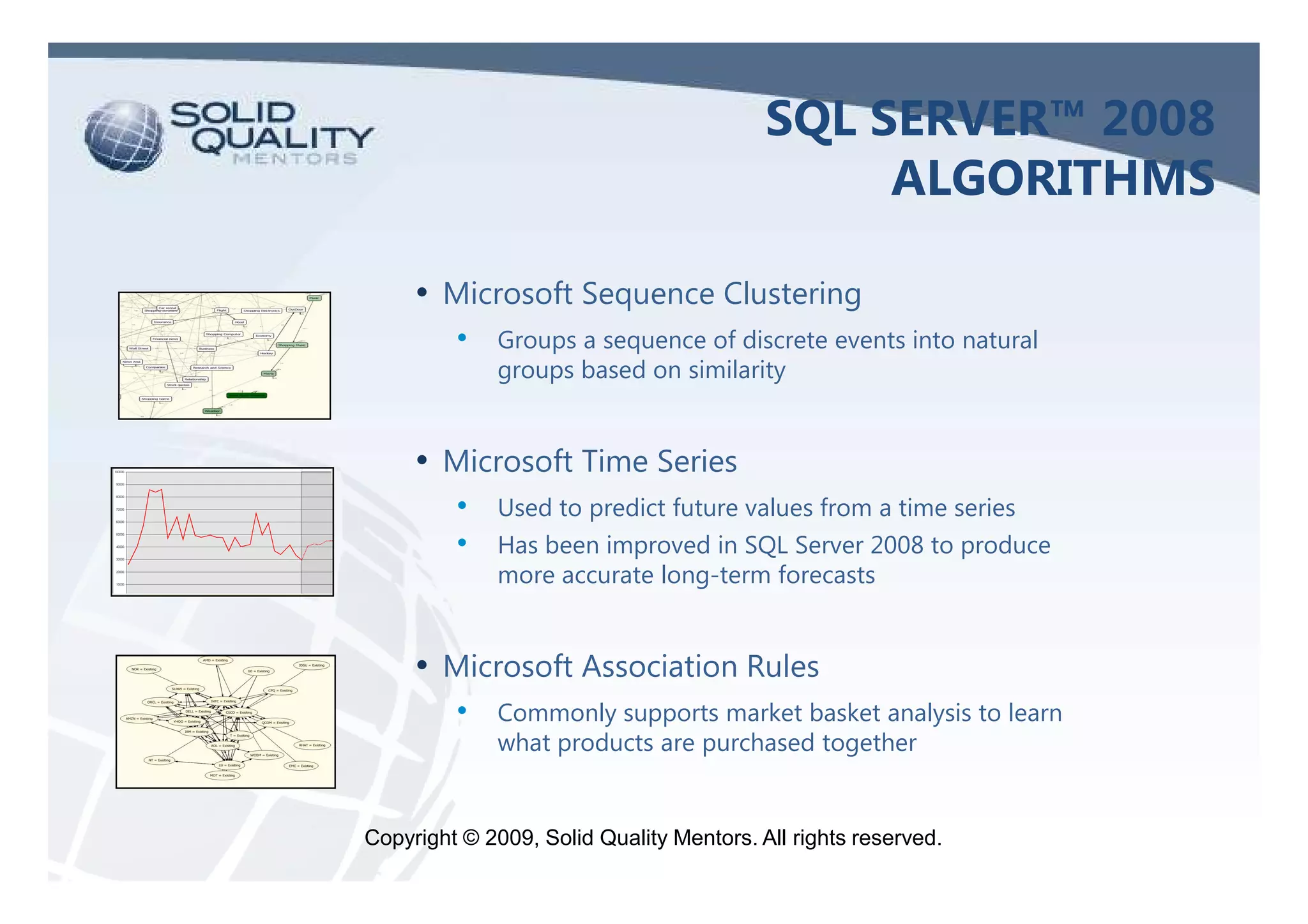
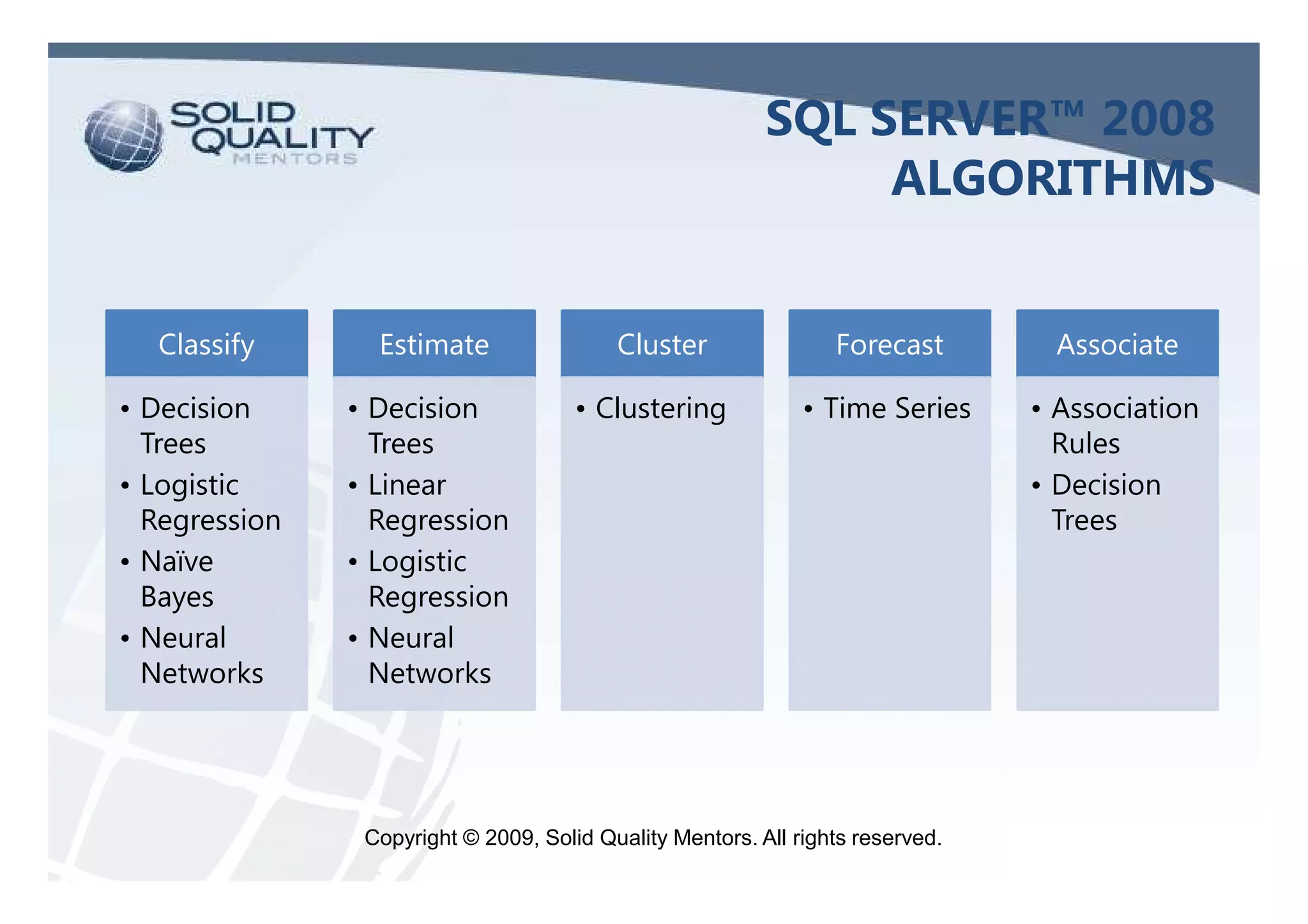
The document provides an overview of SQL Server 2005 and 2008 data mining, introducing the data mining process and its relevance in business intelligence solutions. It details the various algorithms available in SQL Server 2008 for data classification, regression, clustering, and association, emphasizing the importance of data preparation and model validation. Additionally, it discusses data mining visualization and demonstrates practical applications, including customer analysis and market basket analysis.