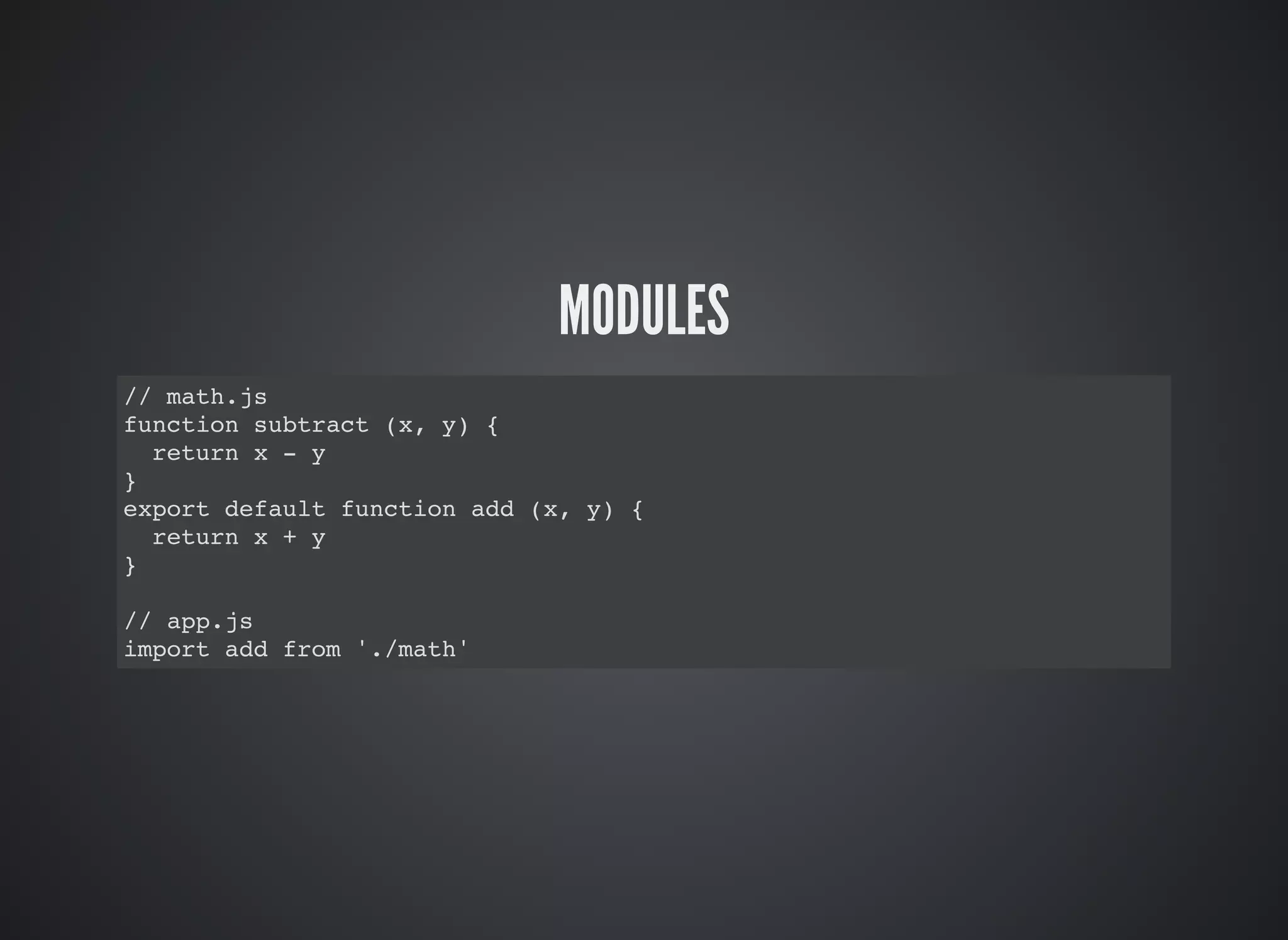
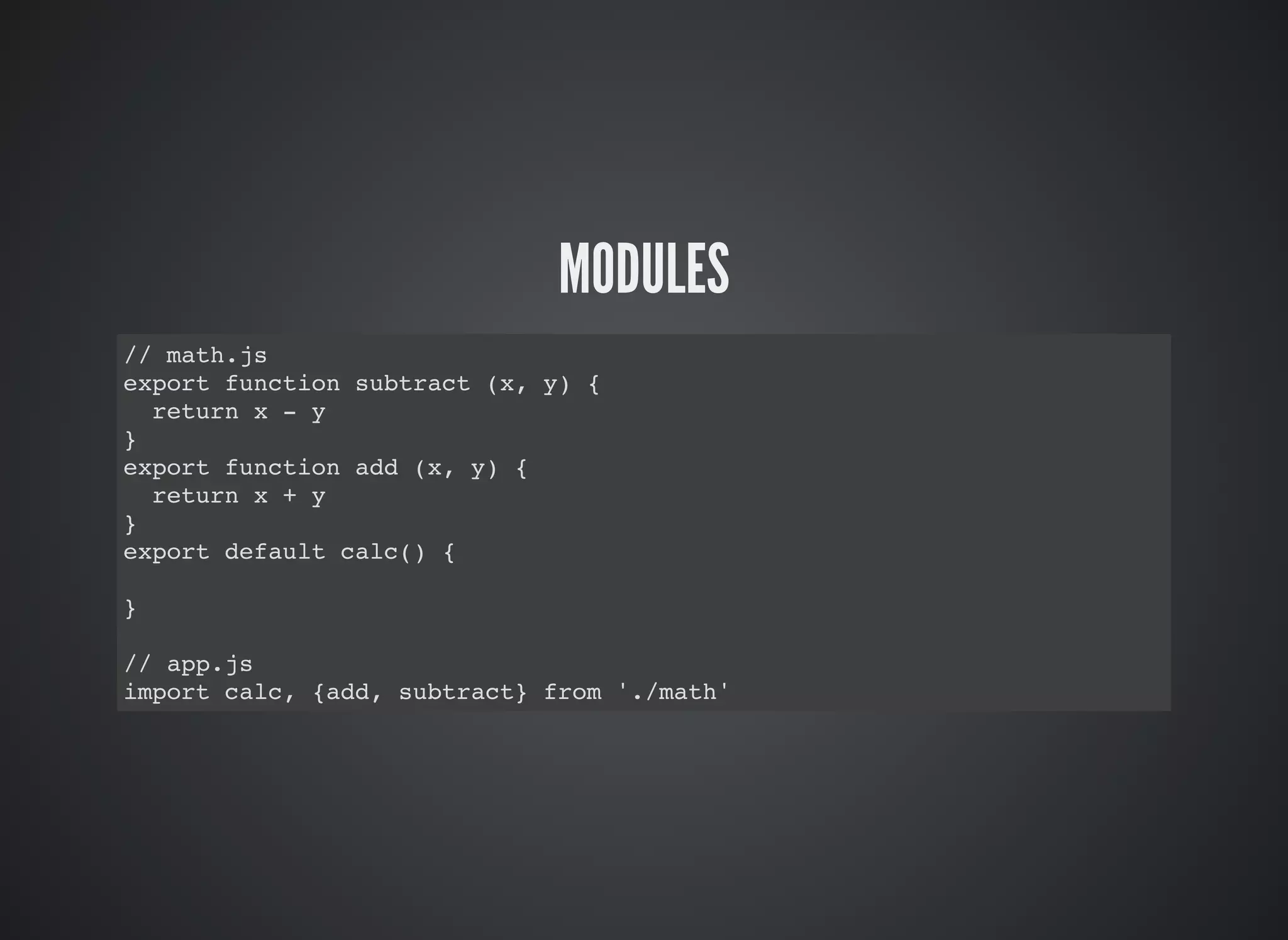
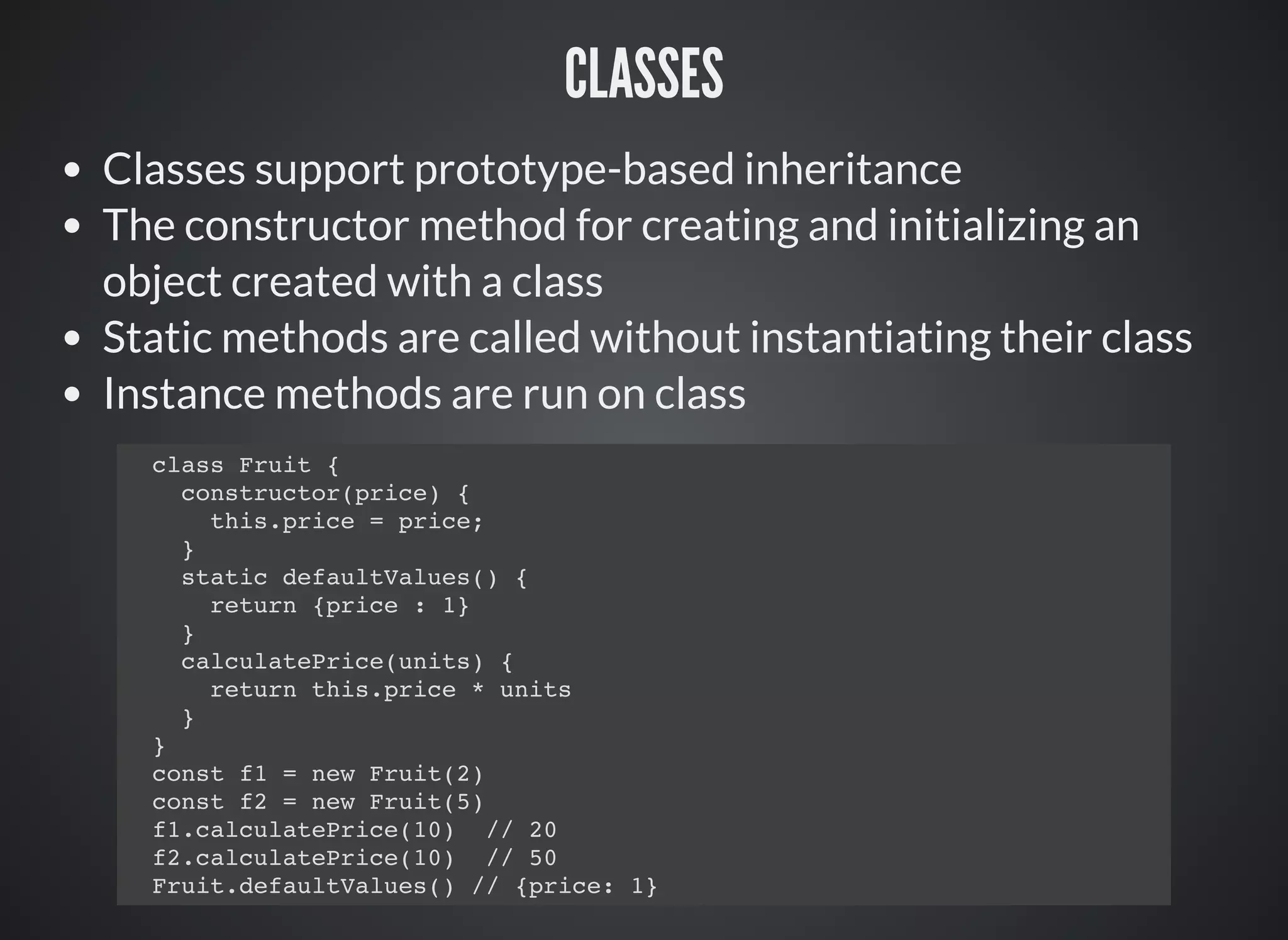
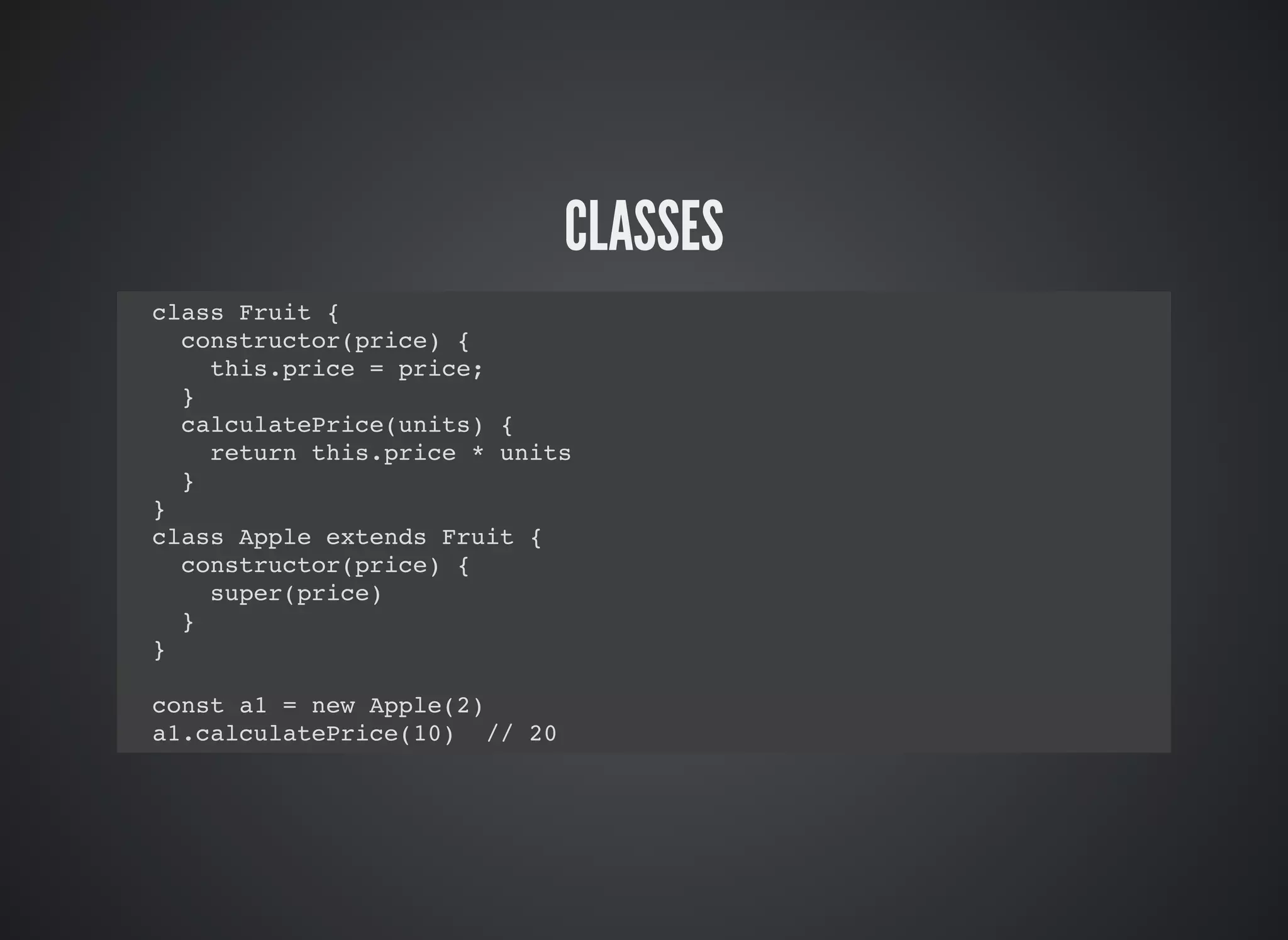
This document provides an introduction to ES2015 features, including: const and let for block scoping of variables, arrow functions for shorthand syntax, classes for object-oriented programming, template strings for string interpolation, destructuring for array and object patterns, default parameters, rest and spread operators, Sets, Maps, Promises, generators, and modules for code organization. Key ES2015 features allow for more concise code through features like arrow functions, classes, template strings, and let/const variables.







![DESTRUCTURING
Array destructuring
const [a, ,c] = [1,2,3];
a === 1;
c === 3;
Object destructuring
const values = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}
const {a, c} = values
a === 1;
c === 3;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-es2015-160823100127/75/Introduction-to-ES2015-12-2048.jpg)

![REST OPERATOR
const f(x, ...y) {
// x === 1
// y === [2, 3, 4]
}
f(1, 2, 3, 4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-es2015-160823100127/75/Introduction-to-ES2015-14-2048.jpg)
![SPREED OPERATOR
function f(x, y, z) {
// x === 1
// y === 2
// z === 3
}
f(...[1,2,3])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-es2015-160823100127/75/Introduction-to-ES2015-15-2048.jpg)
![SET
let mySet = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
mySet.add(6)
mySet.add(5)
mySet.has(5) // true
mySet.size // 6
mySet.delete(5)
for(let i of mySet.values()) {
console.log(i)
}
mySet.forEach(function (item) {
console.log(item)
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-es2015-160823100127/75/Introduction-to-ES2015-16-2048.jpg)
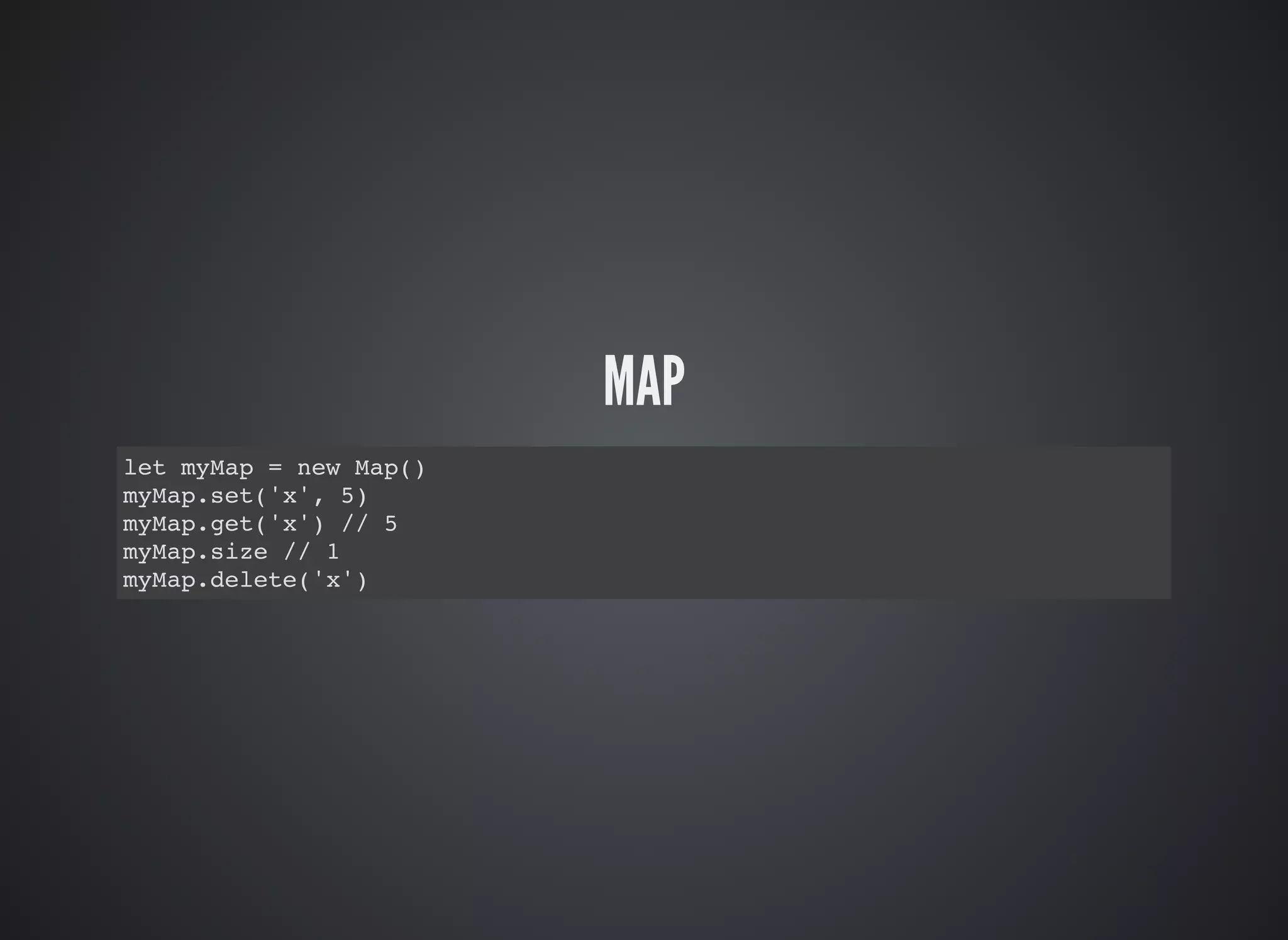
![MAP ITERATIONS
let myMap = new Map([['x', 1], ['y', 2], ['z', 3]])
for (let key of myMap.keys()) {
console.log(key)
}
for (let key of myMap.values()) {
console.log(key)
}
for (let [key, value] of myMap.entries()) {
console.log(key, value)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-es2015-160823100127/75/Introduction-to-ES2015-18-2048.jpg)


![GENERATORS
function* fibonacci() {
let pre = 0, cur = 1;
while (true) {
[pre, cur] = [cur, pre + cur];
yield cur
}
}
const fib = fibonacci()
console.log(fib.next()) // {value: 1, done: false}
console.log(fib.next().value) // 2
console.log(fib.next().value) // 3
console.log(fib.next().value) // 5
console.log(fib.next().value) // 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-es2015-160823100127/75/Introduction-to-ES2015-21-2048.jpg)
![GENERATORS
function* fibonacci() {
let pre = 0, cur = 1;
while (true) {
[pre, cur] = [cur, pre + cur];
yield cur
}
}
for (let n of fibonacci()) {
console.log(n)
if (n > 100) {
break
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-es2015-160823100127/75/Introduction-to-ES2015-22-2048.jpg)