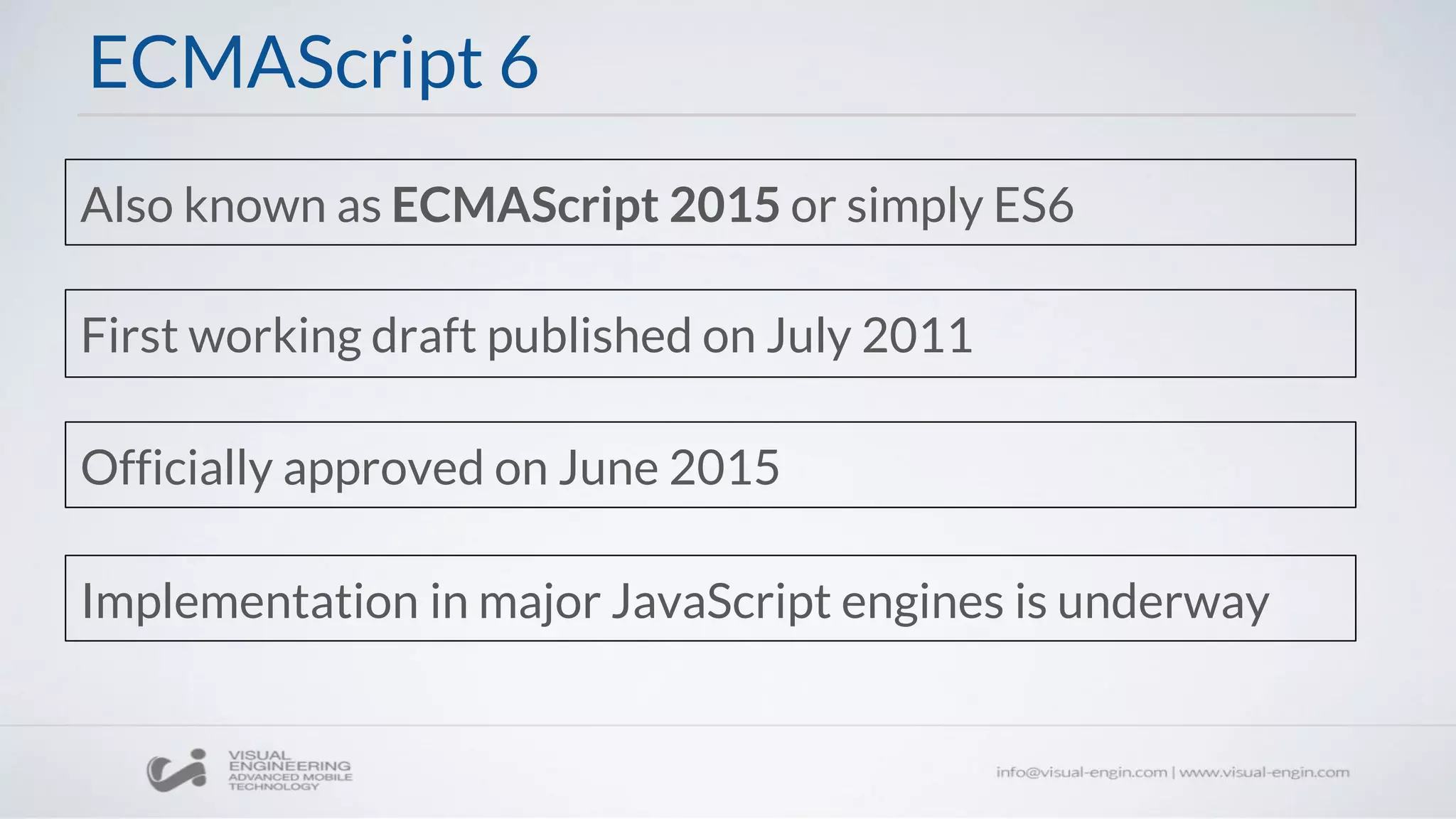
The document discusses the features and novelties of ECMAScript 6 (ES6), officially approved in June 2015, highlighting new syntax and capabilities such as default and rest parameters, arrow functions, classes, destructuring, and promises. It provides examples of how these features improve JavaScript programming by simplifying code and enhancing functionality. Additionally, the document covers various data structures introduced in ES6, including maps, sets, and typed arrays.





![Rest parameters
function f(x, ...y) {
console.log(x, y);
}
f(3, 'hello', true); // 3, ['hello', true]
f(3, 'hello', true, false); // 3, ['hello', true, false]
// ES 5
function logAllArguments() {
for (var i=0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
console.log(arguments[i]);
}
}
logAllArguments(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 1 2 3 4 5
// ES 6
function logAllArguments(...args) {
for (var i=0; i < args.length; i++) {
console.log(args[i]);
}
}
logAllArguments(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 1 2 3 4 5
Could replace usage of the ‘arguments’ variable...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-7-2048.jpg)
![Spread operator
function f(x, y, z) {
console.log(x + y + z);
}
f(...[1, 2, 3]); // 6
// ES 5
var numbers = [-1, 5, 11, 3];
Math.max.apply(Math, numbers); // 11
// ES 6
var numbers = [-1, 5, 11, 3];
Math.max(...numbers); // 11
var x = ['a', 'b'];
var y = ['c'];
var z = ['d', 'e'];
var arr = [...x, ...y, ...z]; // ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
Practical uses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-8-2048.jpg)
![for..of loops
var numbers = [2, 3, 4];
for (var value of numbers) {
console.log(value);
}
// 2, 3, 4
var letters = 'Homer';
for (var item of letters) {
console.log(item);
}
// 'H', 'o', 'm', 'e', 'r'
Do we really need another way of looping?
// Classic way
for (var i=0; i<numbers.length; i++) {
console.log(numbers[i]);
}
// ES 5
numbers.forEach(function(value) {
console.log(value);
});
// for..in
for (var i in numbers) {
console.log(numbers[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-9-2048.jpg)

![Destructuring
var homer = {
name: 'Homer',
surname: 'Simpson'
};
var { name, surname } = homer;
console.log(name); // 'Homer'
console.log(surname); // 'Simpson'
// ES 5
var foo = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
var one = foo[0];
var two = foo[1];
var three = foo[2];
// ES 6
var foo = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
var [one, two, three] = foo;
var foo = function() {
return [175, 75];
};
var [height, weight] = foo();
console.log(height); // 175
console.log(weight); // 75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-11-2048.jpg)

![let
var fns = [];
for (var i=0; i<4; i++) {
fns.push(function() {
console.log(i);
});
}
fns[0](); // 4
fns[1](); // 4
fns[2](); // 4
fns[3](); // 4
var fns = [];
for (let i=0; i<4; i++) {
fns.push(function() {
console.log(i);
});
}
fns[0](); // 0
fns[1](); // 1
fns[2](); // 2
fns[3](); // 3
Block scopedlet name = 'Homer';
In previous workshops...
“var”... Are we going to see you ever again?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-13-2048.jpg)
![Arrow functions
// ES5
var sum = function(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// ES6
var sum = (a, b) => a + b;
function Person() {
this.age = 0;
setInterval(() => {
this.age++;
}, 1000);
}
function Person() {
var self = this;
self.age = 0;
setInterval(function() {
self.age++;
}, 1000);
}
// ES 5
var data = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
data.forEach(function(value) {
console.log(value)
});
// ES 6
var data = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
data.forEach(value => {
console.log(value);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-15-2048.jpg)
![Generators
function* genFunc() {
console.log('First');
yield; // (A)
console.log('Second'); // (B)
}
let genObj = genFunc();
genObj.next()
//First
{ value: undefined, done: false }
genObj.next()
//Second
{ value: undefined, done: true }
function* objectEntries(obj) {
let keys = Object.keys(obj);
for (let key of keys) {
yield [key, obj[key]];
}
}
let batman = { first: 'Bruce', last: 'Wayne' };
for (let [key,value] of objectEntries(batman)) {
console.log(`${key}: ${value}`);
}
// Output:
// first: Bruce
// last: Wayne](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-19-2048.jpg)
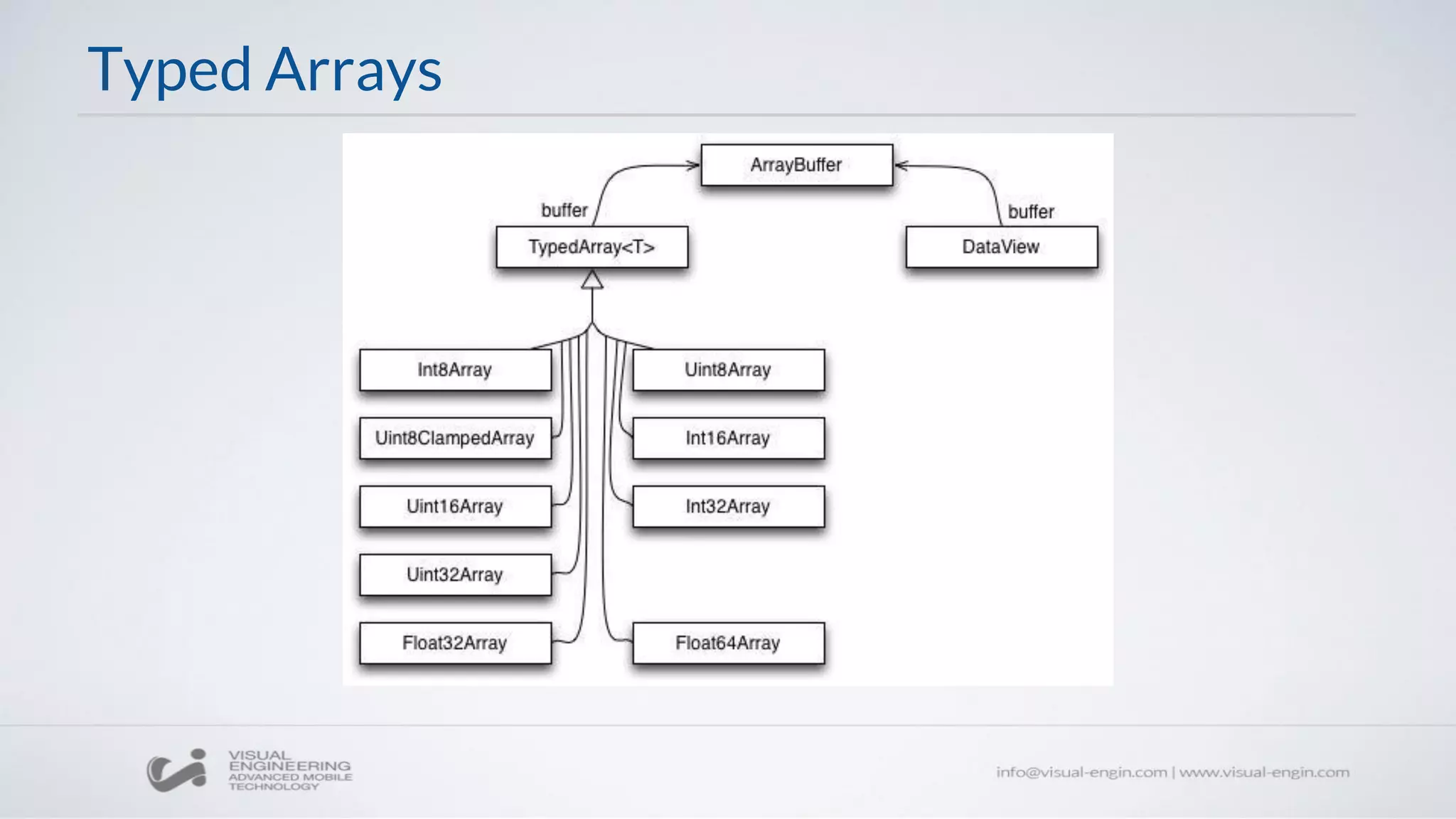
![Typed Arrays
let typedArray = new Uint8Array([0,1,2]);
console.log(typedArray.length); // 3
typedArray[0] = 5;
let normalArray = [...typedArray]; // [5,1,2]
// The elements are stored in typedArray.buffer.
let dataView = new DataView(typedArray.buffer);
console.log(dataView.getUint8(0)); // 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-20-2048.jpg)
![Map
let map = new Map();
map.set('name','Bruce');
map.set('surname','Wayne');
map.size //2
map.get('name'); //Bruce
map.has('name'); //true
map.delete('name'); //true
map.clear();
map.size //0
let map = new Map([
[1, 'one'],
[2, 'two'],
[3, 'three'],
]);
for (let [key, value] of map) {
console.log(key, value);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-22-2048.jpg)
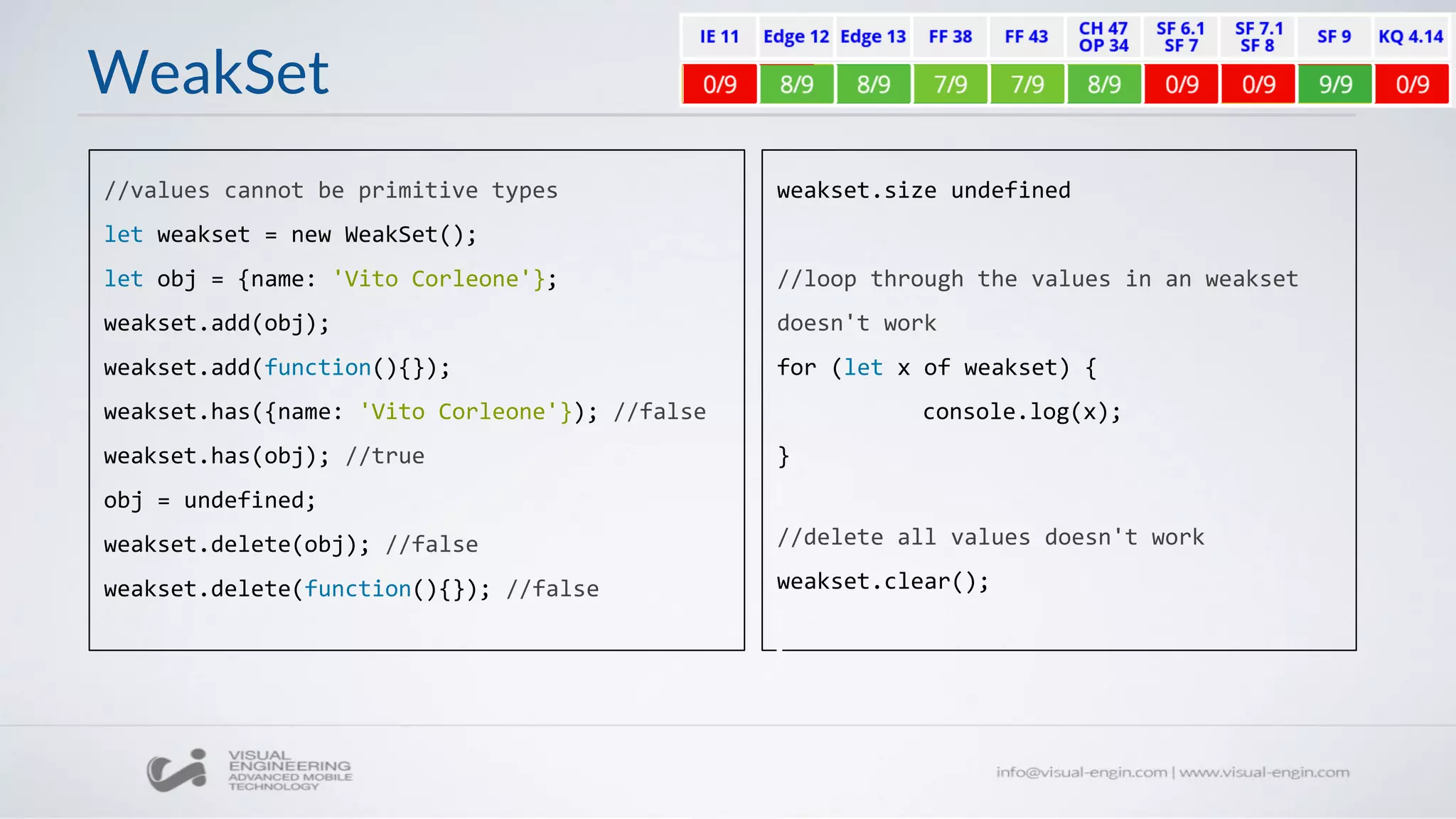
![Set
let set = new Set();
set.add('luke');
set.add('yoda');
set.size //2
set.has('luke'); //true
set.delete('luke'); //true
set.has('luke'); //false
set.size //1
set.clear();
set.size //0
let set = new Set(['luke', 'yoda', 'ben']);
set = new Set().add('luke').add('yoda').add('ben');
for (let x of set) {
console.log(x);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-24-2048.jpg)
![Proxy
let handler = {
get: function(target, name){
return name in target?
target[name] :
'not a jedi';
}
};
let proxy = new Proxy({}, handler);
proxy.a = 'ben';
proxy.b = 'yoda';
console.log(proxy.a, proxy.b); // ben, yoda
console.log(proxy.c); // not a jedi
let target = {}; // Start with an empty object
let handler = {}; // Don’t intercept anything
let {proxy, revoke} = Proxy.revocable(target,
handler);
proxy.foo = 123;
console.log(proxy.foo); // 123
revoke();
console.log(proxy.foo); // TypeError: Revoked](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-26-2048.jpg)



![String static methods
let name = 'Bob';
String.raw`Hin${name}!`;
// 'HinBob!', substitutions are processed.
String.raw`templateString`;
String.fromCodePoint(42); // "*"
String.fromCodePoint(65, 90); // "AZ"
String.fromCodePoint(0x404); // "u0404"
String.fromCodePoint('_'); // RangeError
String.fromCodePoint(num1[, ...[, numN]])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-33-2048.jpg)
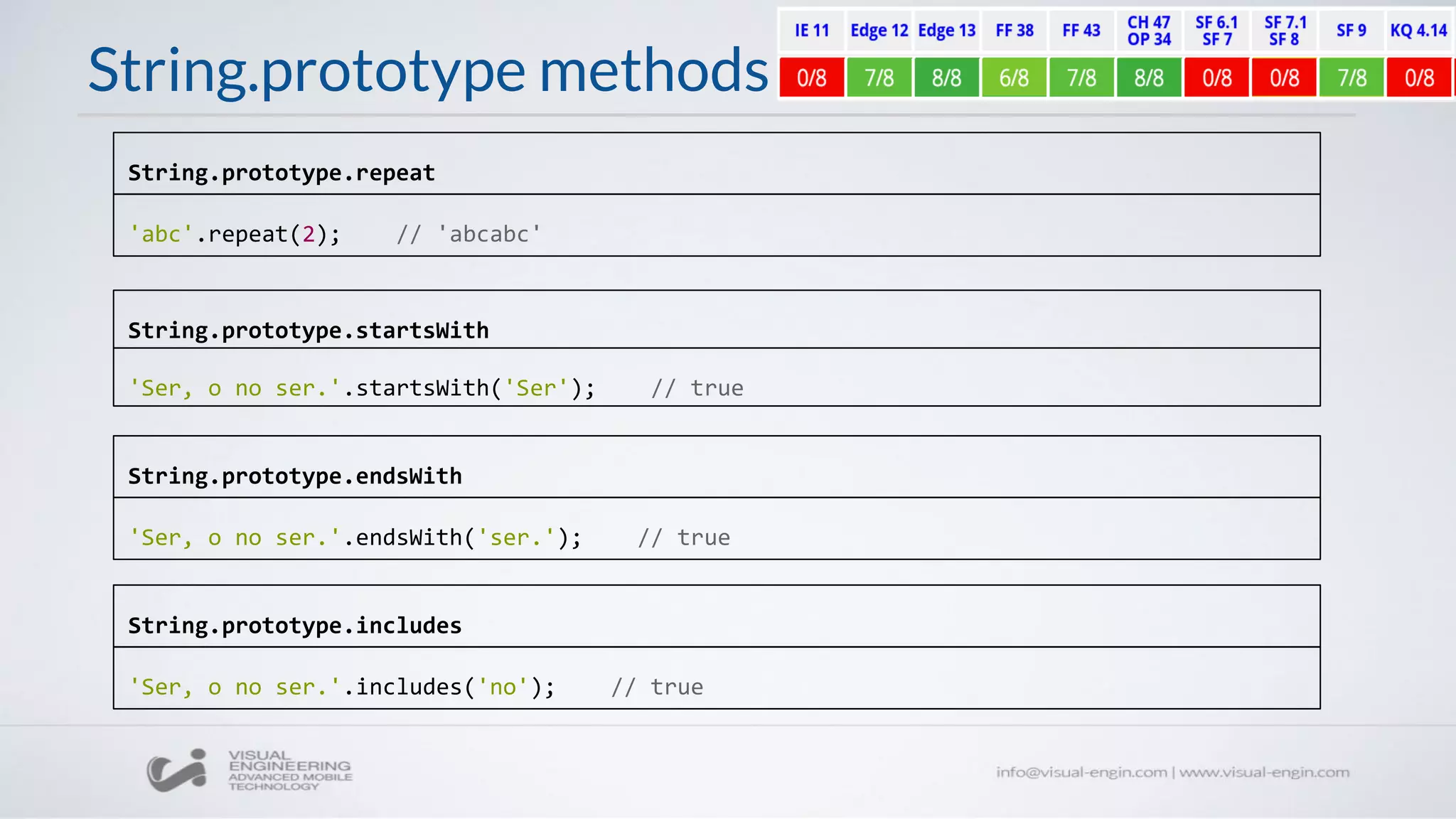
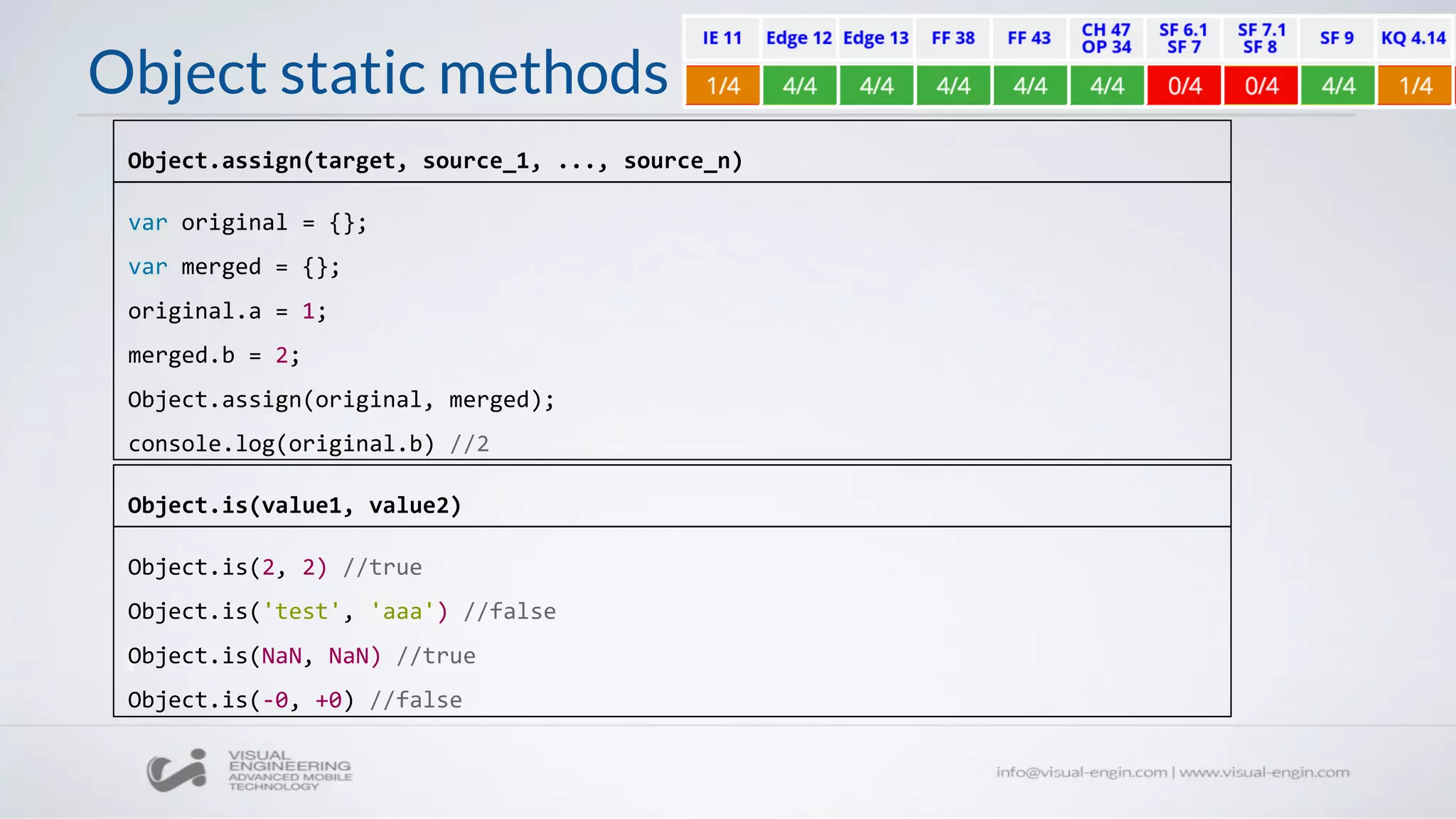
![Array static methods
// Array-like primitive types to Array
Array.from([1, 2, 3]);
//[1, 2, 3]
// Any iterable object...
// Set
var s = new Set(["foo", window]);
Array.from(s);
// ["foo", window]
Array.from(arrayLike[, mapFn[, thisArg]])
// Map
var m = new Map([[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 8]]);
Array.from(m);
// [[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 8]]
// String
Array.from("foo");
// ["f", "o", "o"]
// Using an arrow function as the map
function to manipulate the elements
Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x);
// [2, 4, 6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-35-2048.jpg)
![Array static methods
Array.of(1); // [1]
Array.of(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
Array.of(undefined); // [undefined]
//The difference between Array.of() and the Array constructor is in the handling of
//integer arguments: Array.of(42) creates an array with a single element, 42, whereas
//Array(42) creates an array with 42 elements, each of which is undefined.
Array.of(element0[, element1[, ...[, elementN]]])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-36-2048.jpg)
![Array.prototype methods
Array.from([ 'a', 'b' ].keys()); //[ 0, 1 ]
Array.prototype.keys()
Array.from([ 'a', 'b' ].values()); //[ 'a', 'b' ]
Array.prototype.values()
Array.from([ 'a', 'b' ].entries()); //[ [ 0, 'a' ], [ 1, 'b' ] ]
for (let [index, elem] of ['a', 'b'].entries()) {
console.log(index, elem);
}
Array.prototype.entries()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-37-2048.jpg)
![Array.prototype methods
[6, -5, 8].find(x => x < 0); //-5
Array.prototype.find(predicate, thisArg?)
[6, -5, 8].findIndex(x => x < 0); //1
Array.prototype.findIndex(predicate, thisArg?)
['a', 'b', 'c'].fill(7); //[ 7, 7, 7 ]
['a', 'b', 'c'].fill(7, 1, 2); //[ 'a', 7, 'c' ]
Array.prototype.fill(value, start?, end?)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmascript6-160426085138/75/Workshop-10-ECMAScript-6-38-2048.jpg)