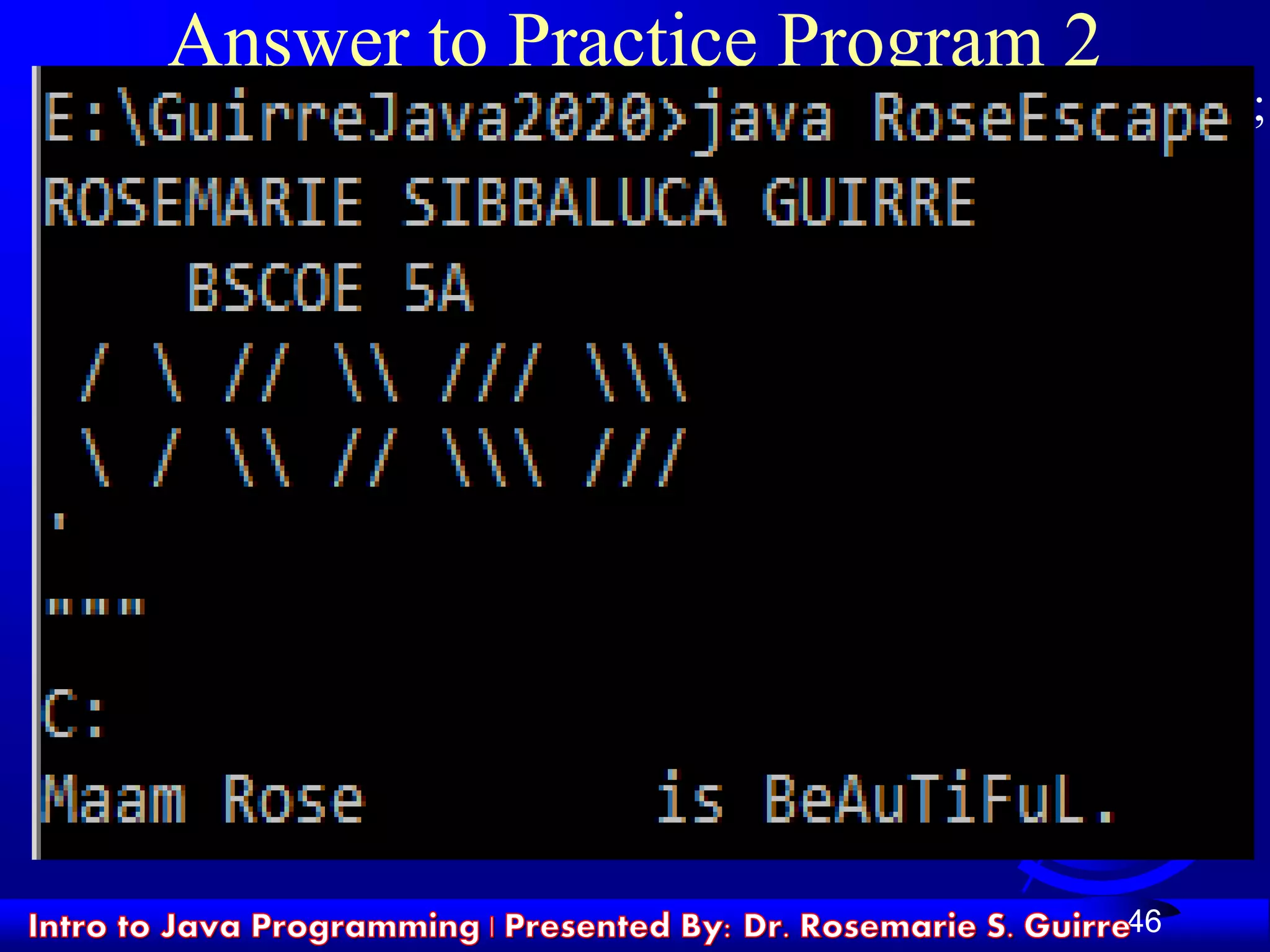
The document provides an introduction to Java programming. It discusses downloading and installing the Java Development Kit (JDK) to write and run Java programs. It then covers creating a simple "Hello World" Java program by defining a class with a main method that prints a message, and compiling and running the program. The document concludes by explaining some key Java concepts like classes, methods, and strings.







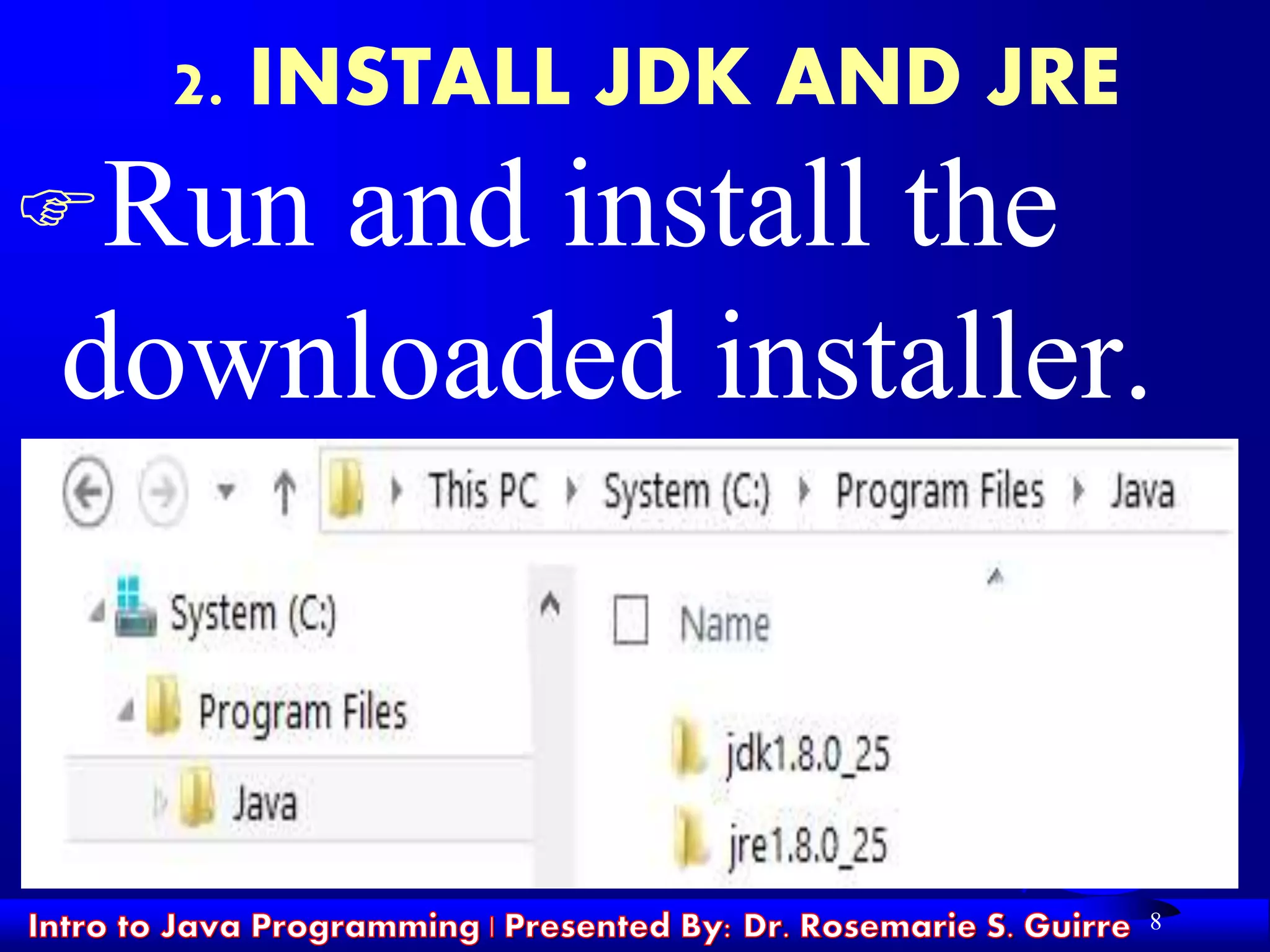
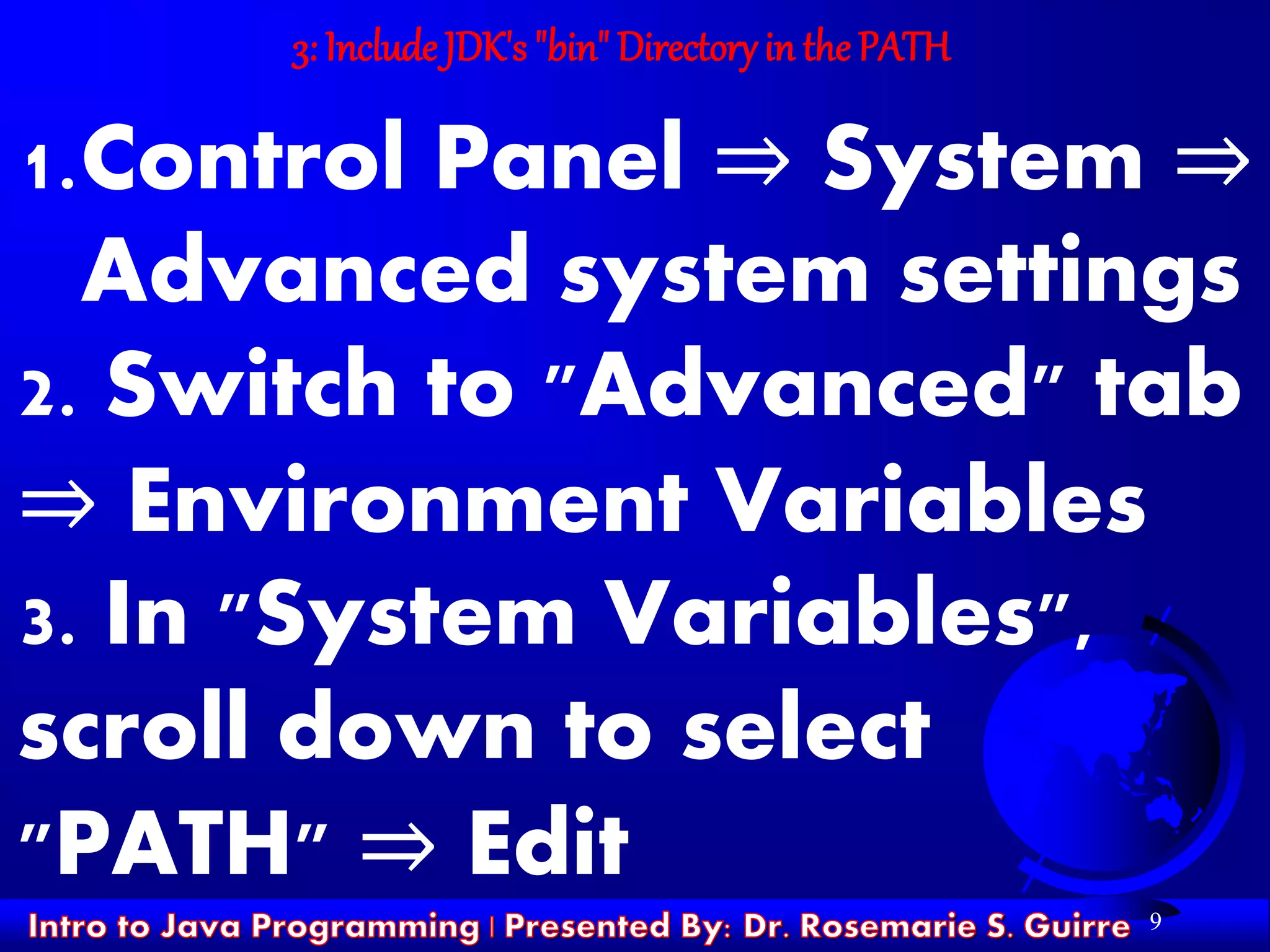

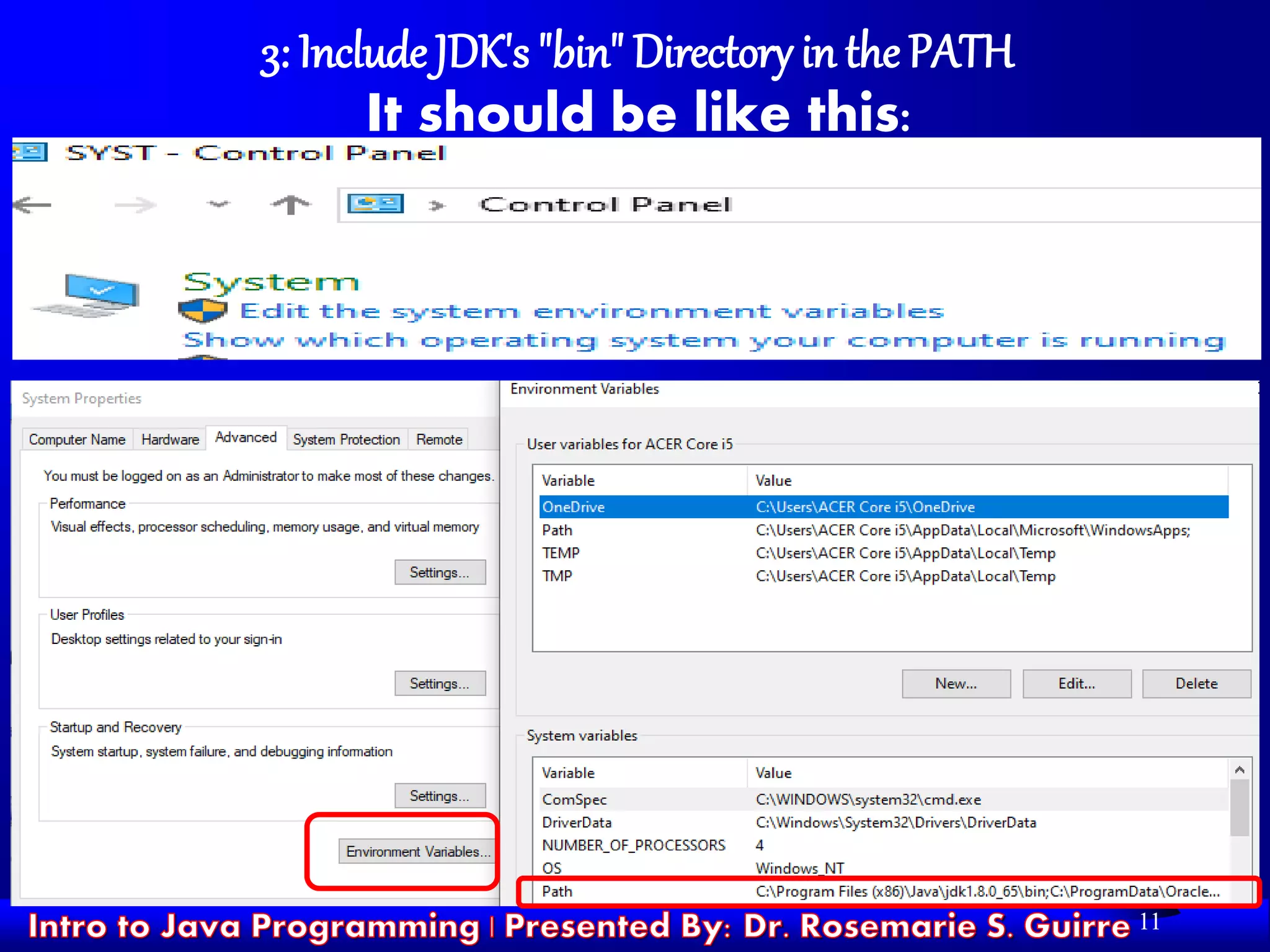



![17
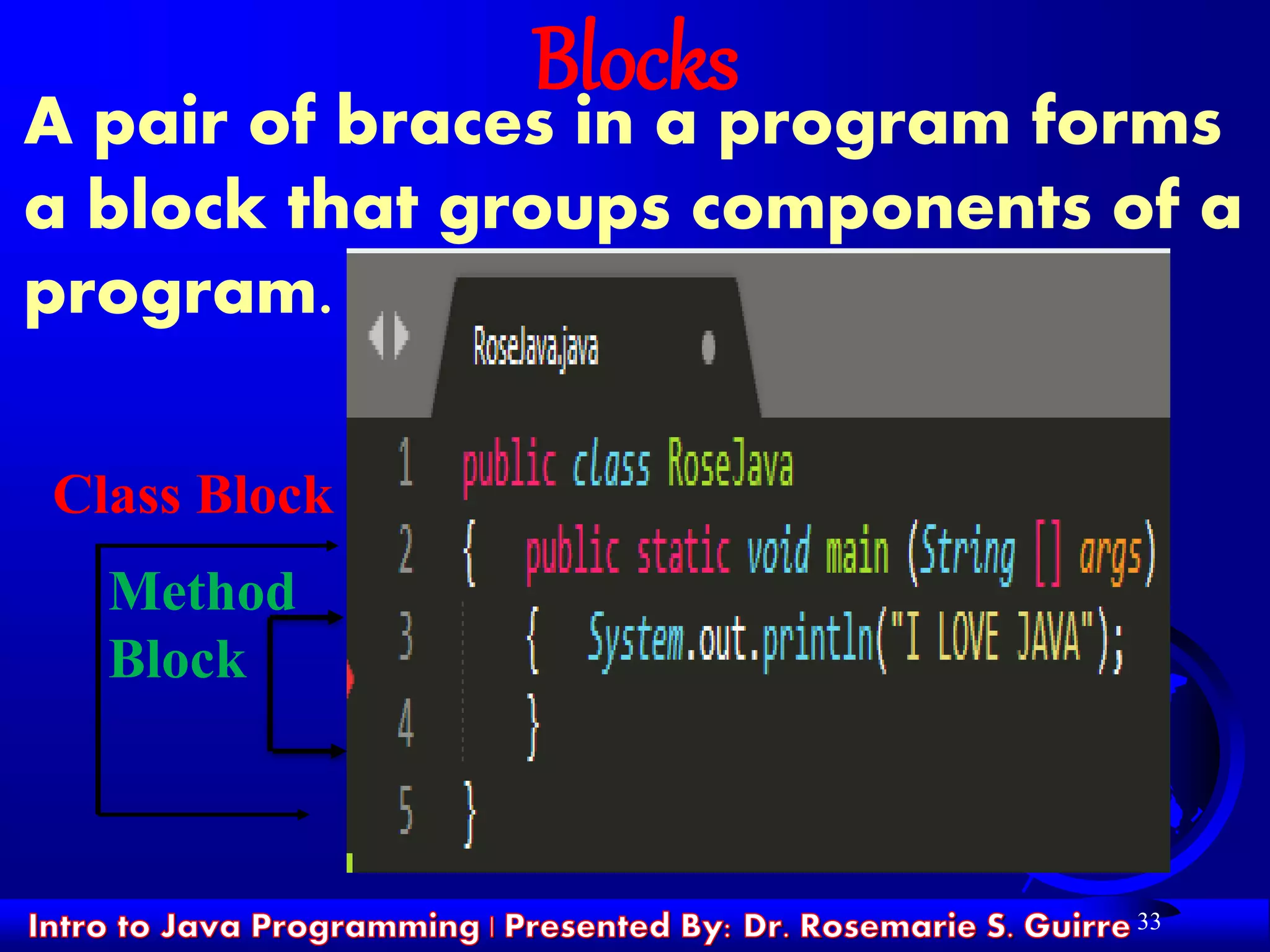
Structure of Java programs
public class <name>
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{ <statement(s)>;
}
}
Every executable Java program consists of a
class...
– that contains a method named main...
that contains the statements to be executed
The program with a class named RoseJava,
whose main method executes one statement
named System.out.println](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isoop223module1ch3-200123091241/75/Introduction-to-Java-Programming-17-2048.jpg)
![18
A Simple Java Program
public class RoseJava
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{ System.out.println(“I LOVE JAVA");
}
}
This would be in a text file named RoseJava.java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isoop223module1ch3-200123091241/75/Introduction-to-Java-Programming-18-2048.jpg)

















![37
main Method
The main method provides the
control of program flow. The Java
interpreter executes the application
by invoking the main method.
The main method looks like this:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Statements;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isoop223module1ch3-200123091241/75/Introduction-to-Java-Programming-37-2048.jpg)