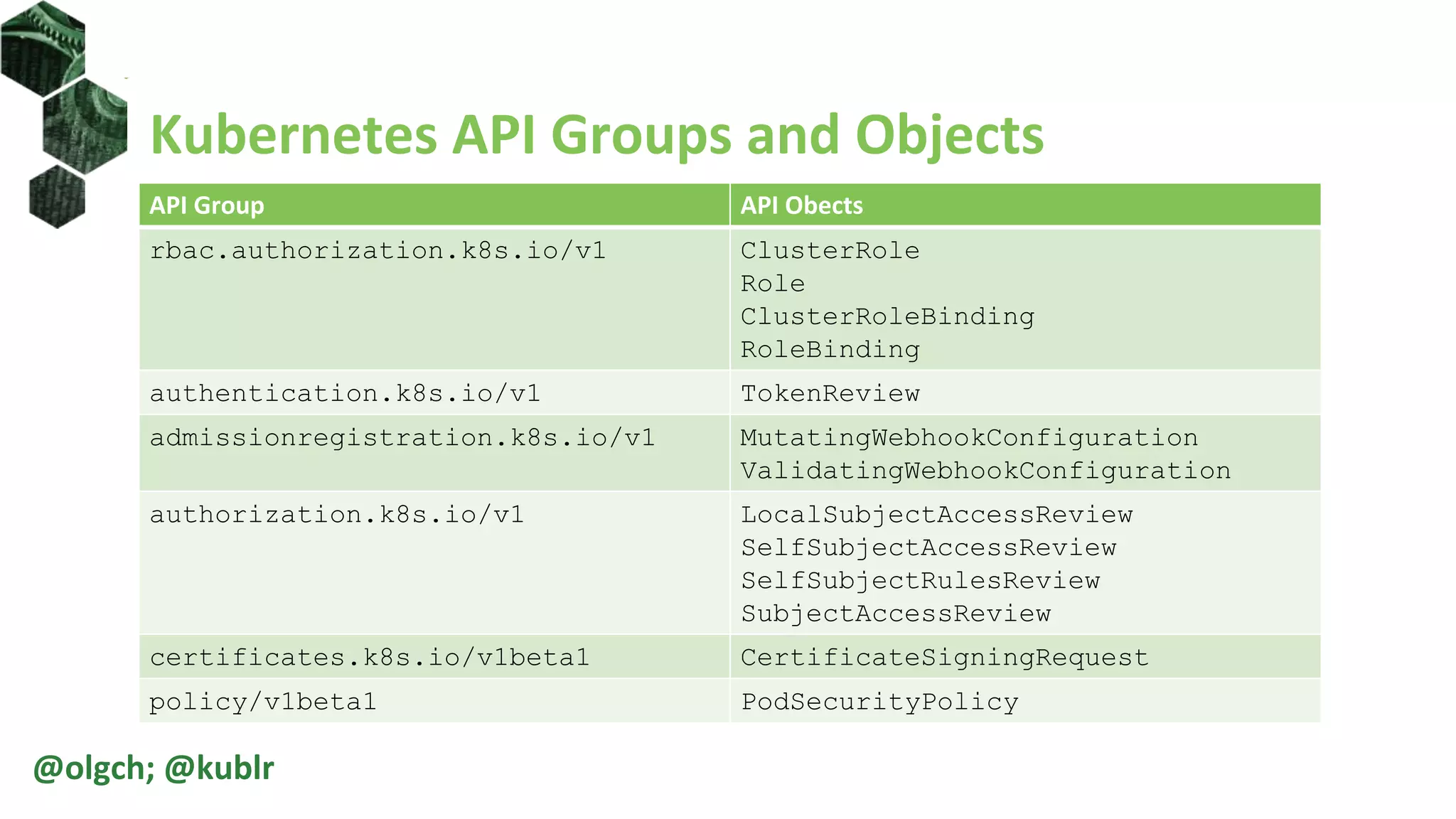
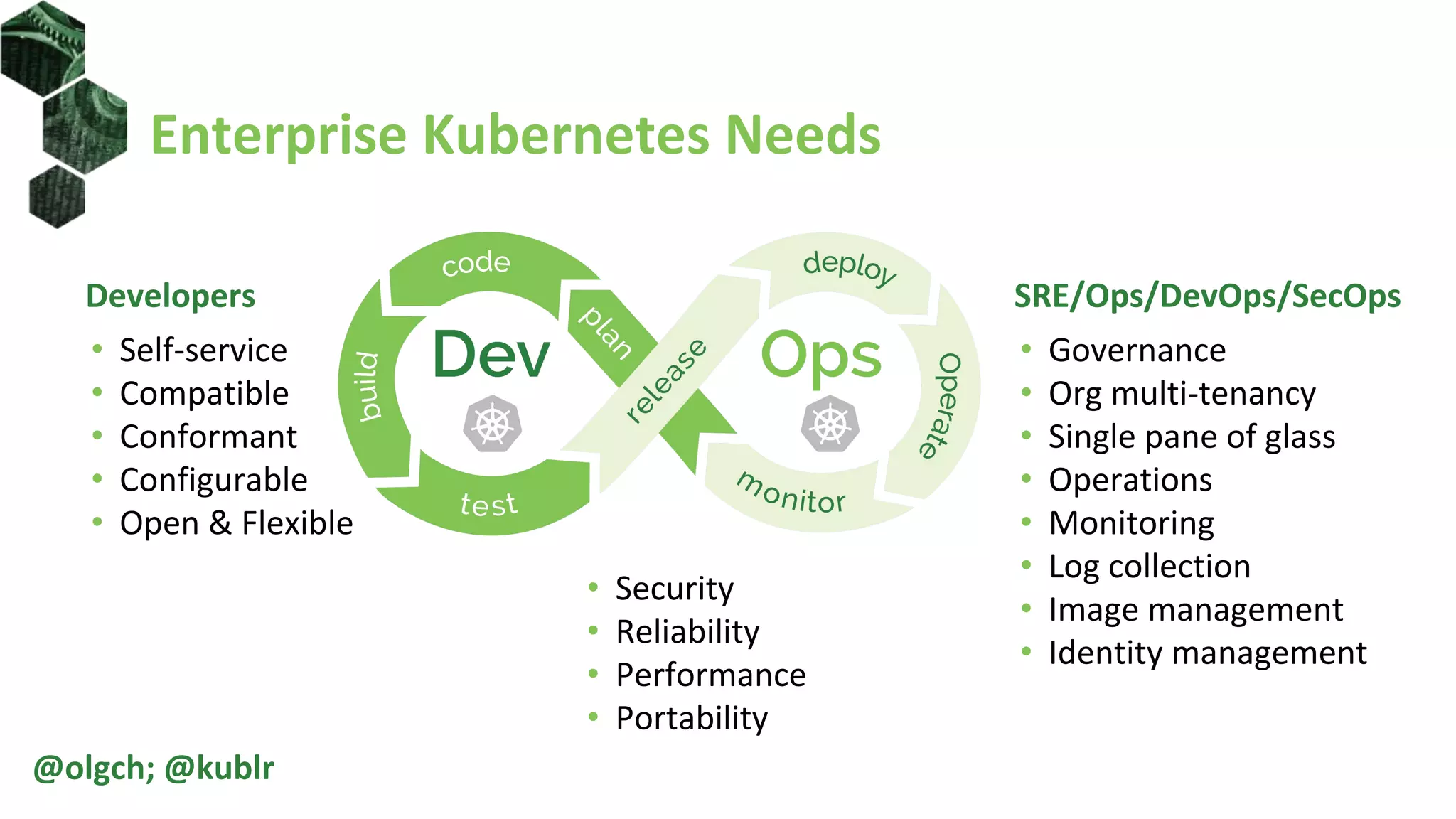
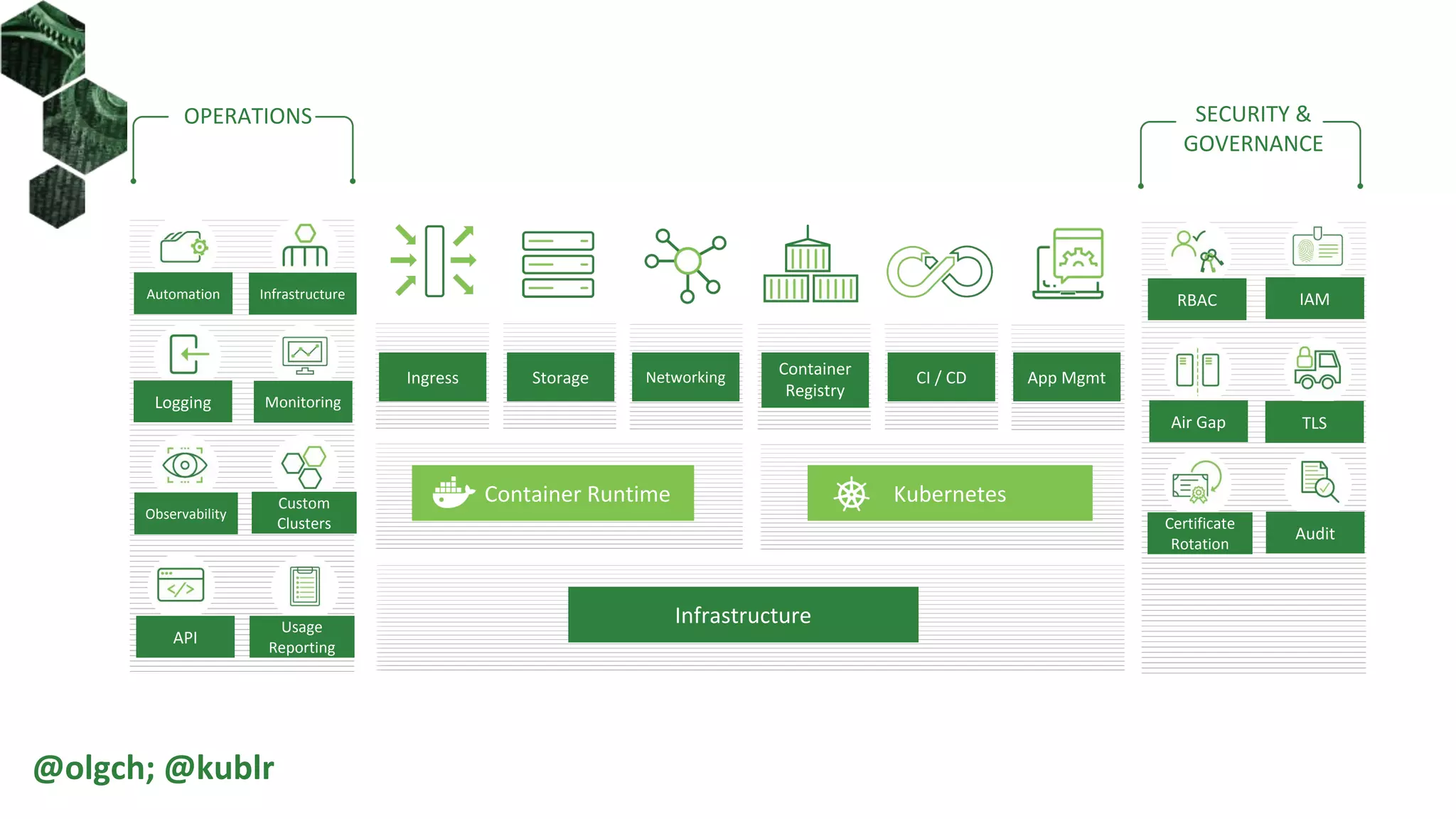
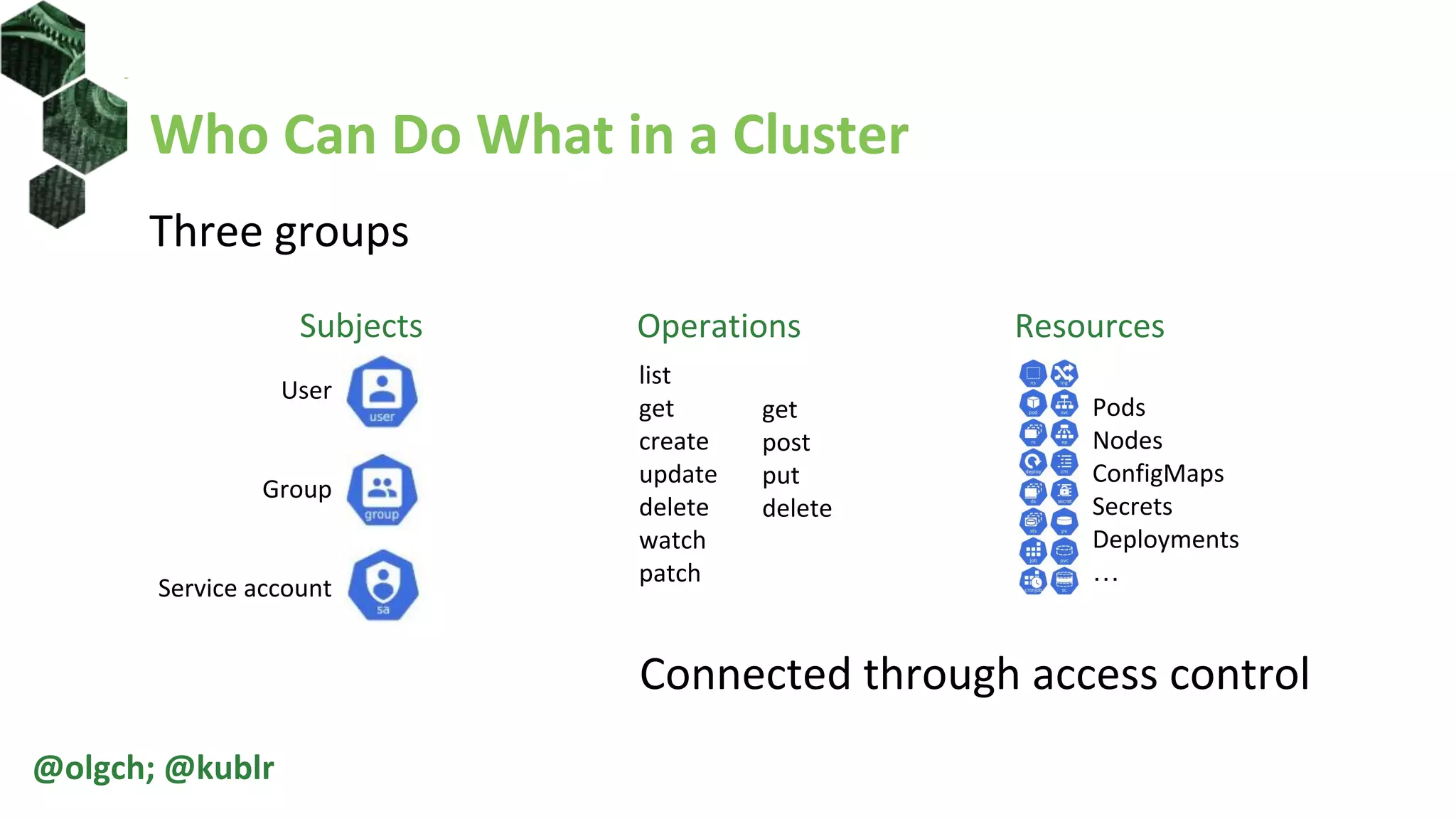
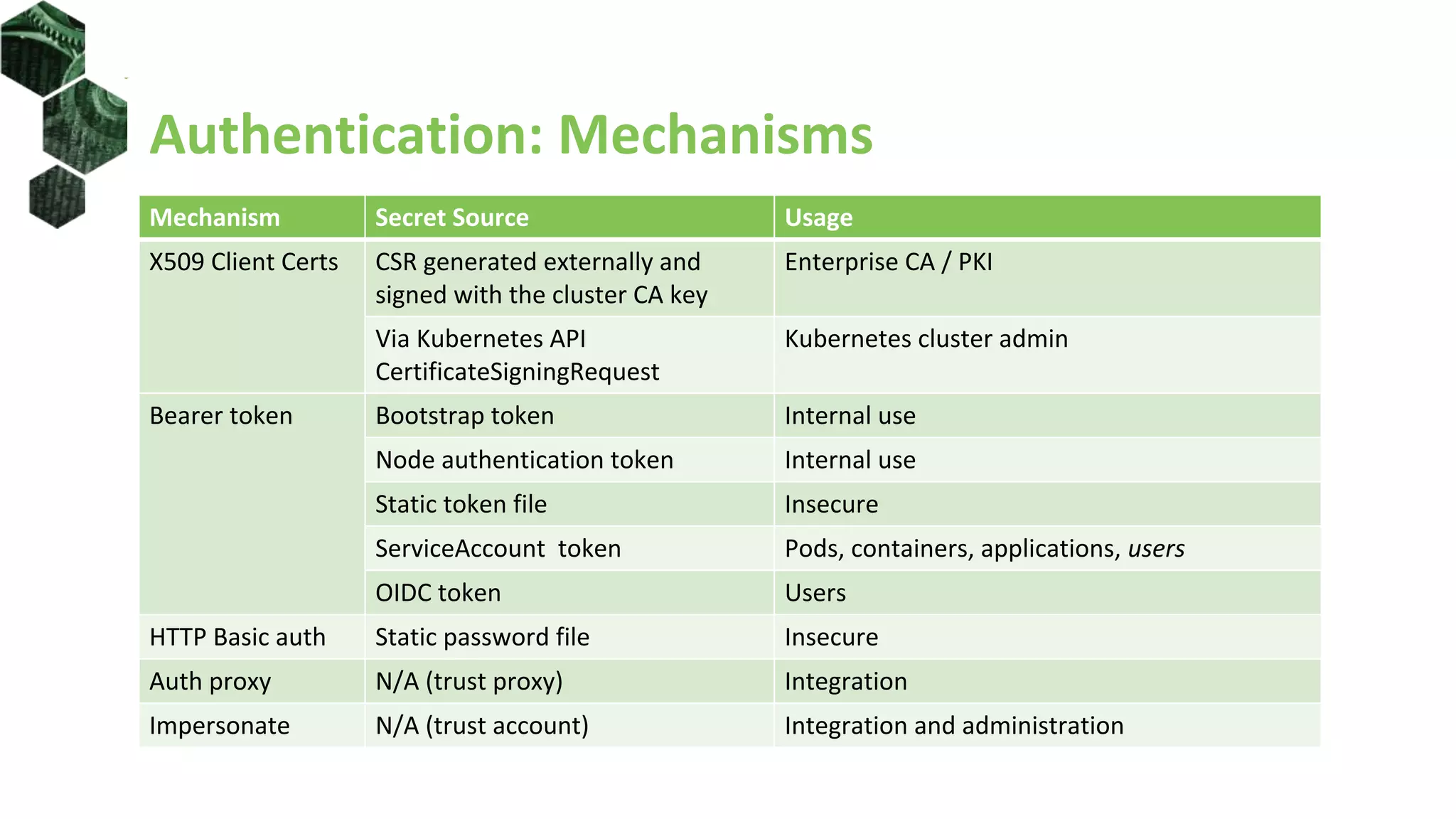
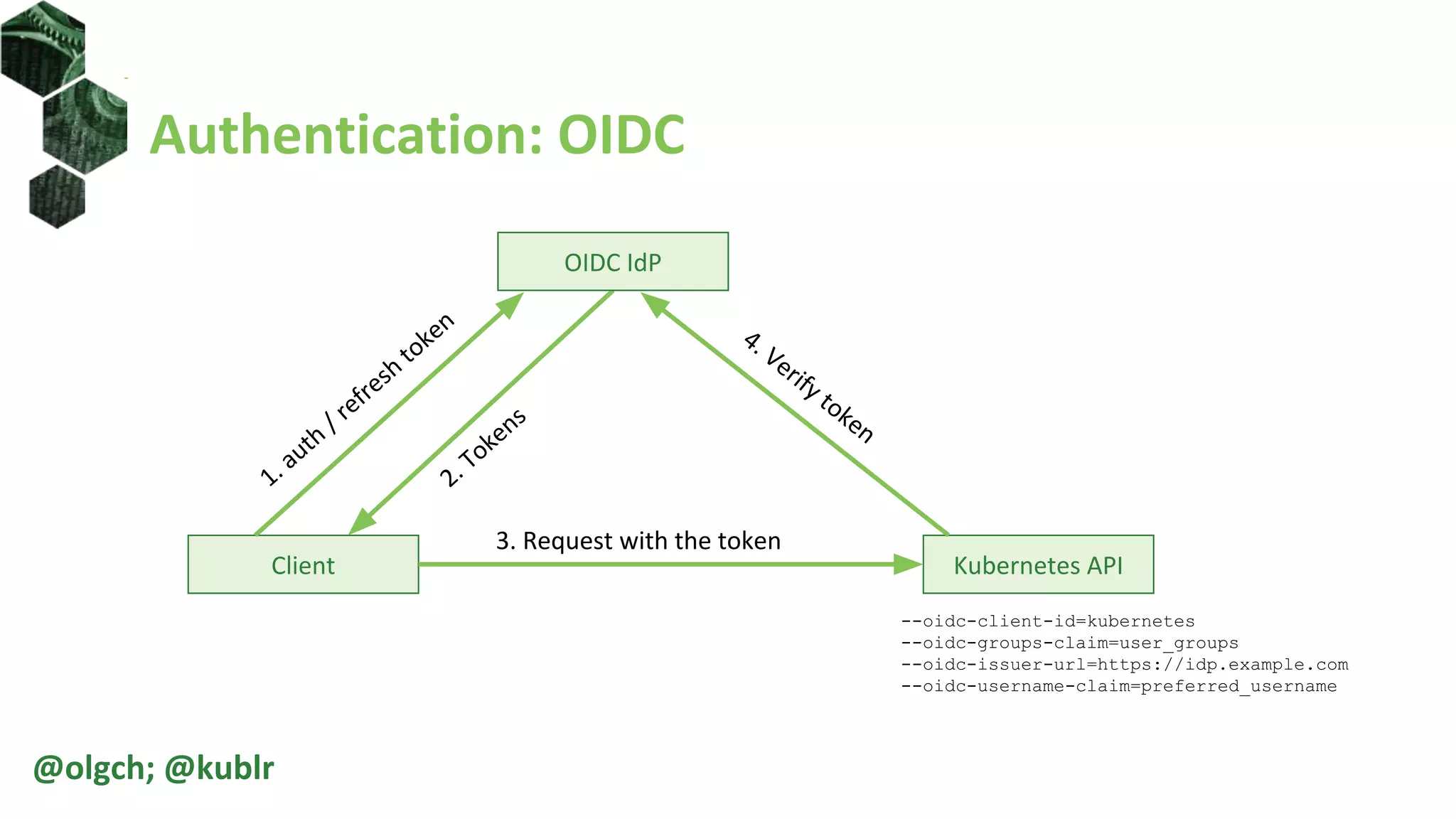
The document is a comprehensive introduction to Kubernetes Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) presented by Oleg Chunikhin. It covers key concepts in authentication and authorization mechanisms within Kubernetes, including users, groups, service accounts, roles, and cluster roles. Additionally, it discusses practical use cases and configurations for managing access control and security in enterprise Kubernetes environments.






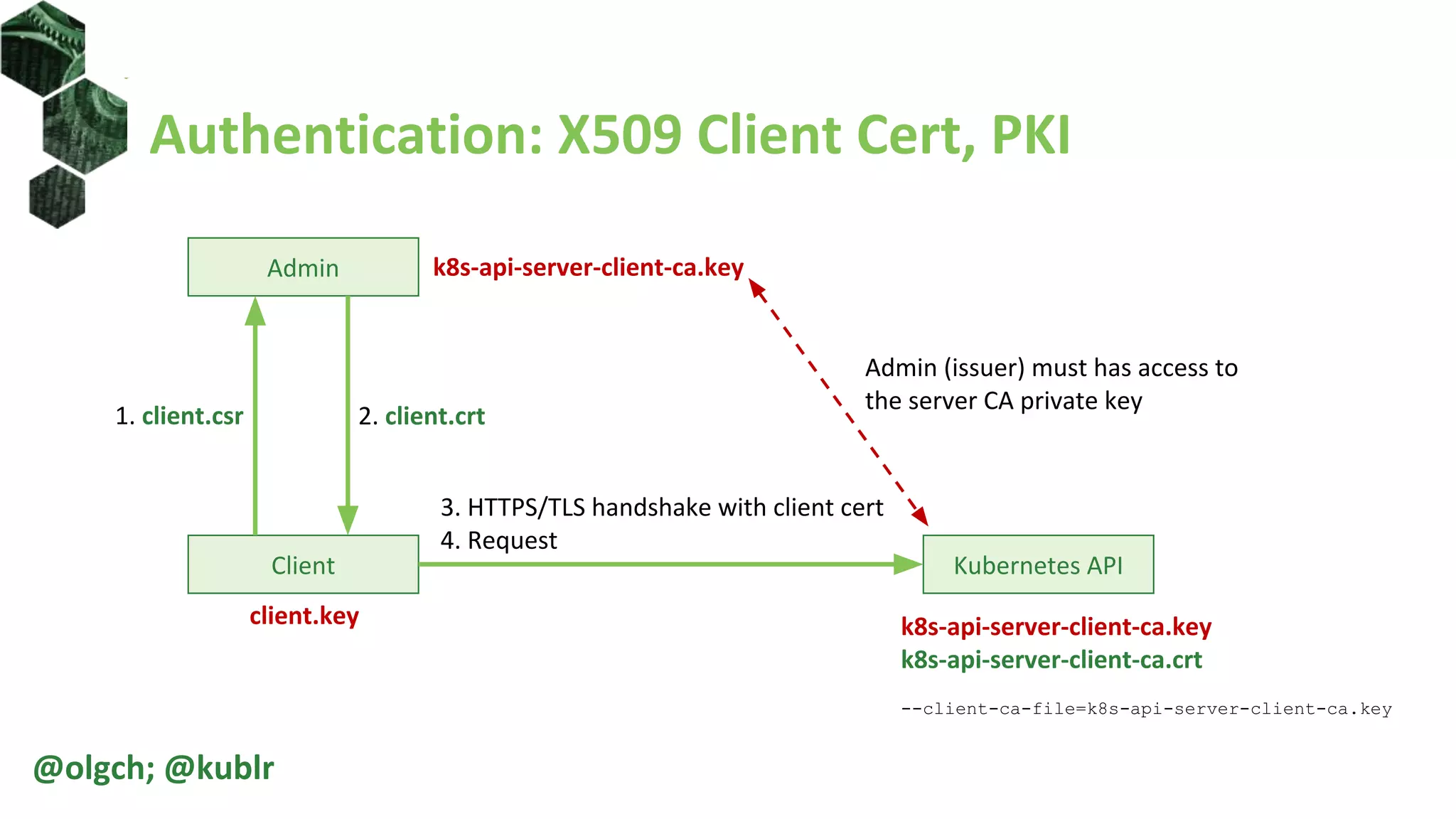


![Authentication: X509 Client Cert, K8S CSR
• User: generate user CSR
• Admin: use Kubernetes API server to sign the CSR
• User: use with kubectl via options or kubeconfig
openssl req -new -key user2.key -out user2.csr -subj "/CN=user2/O=group1/O=group2"
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: certificates.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CertificateSigningRequest
metadata:
name: user2
spec:
request: $(cat user2.csr | base64 | tr -d 'n')
usages: ['digital signature', 'key encipherment',
'client auth']
EOF
kubectl certificate approve user2
kubectl certificate deny user2
kubectl get csr user2 –o jsonpath='{.status.certificate}' |
base64 --decode > user2.crt
kubectl --client-key=user2.key --client-certificate=user2.crt get nodes
kubectl config set-credentials user2 --client-key user2.key --client-certificate user2.crt --embed-certs
kubectl config set-context user2 --cluster demo-rbac --user user2
@olgch; @kublr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontokubernetesrbac-200410213658/75/Introduction-to-Kubernetes-RBAC-16-2048.jpg)
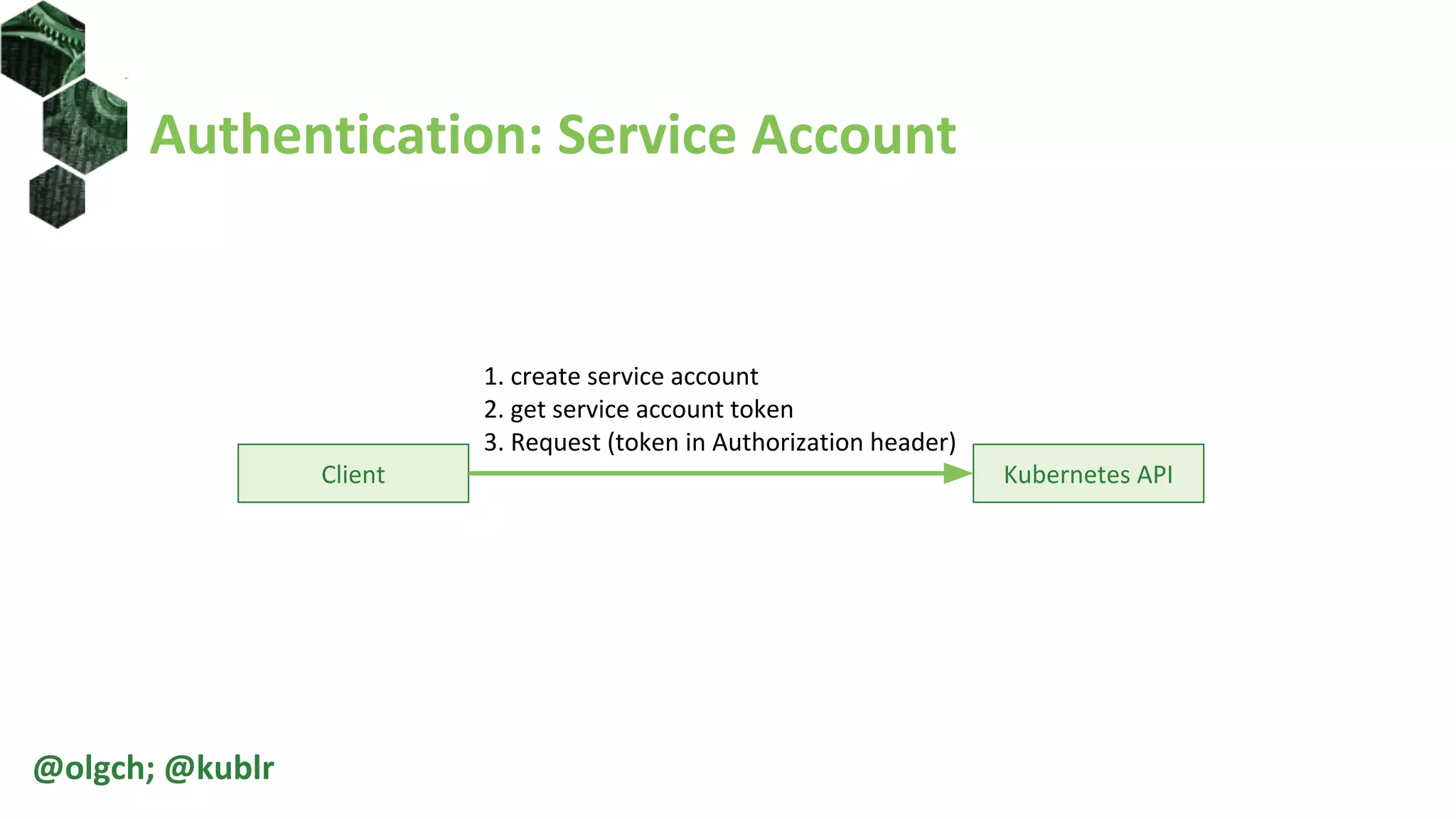
![Authentication: Service Account, Example
• Create service account
• Get service account token
• Send request
kubectl create serviceaccount sa1
kubectl "--token=${SA_TOKEN}" get nodes
kubectl config set-credentials sa1 "--token=${SA_TOKEN}"
kubectl config set-context sa1 --cluster demo-rbac --user sa1
kubectl get –o yaml sa sa1
SA_SECRET="$(kubectl get sa sa1 -o jsonpath='{.secrets[0].name}')"
kubectl get -o yaml secret "${SA_SECRET}"
SA_TOKEN="$(kubectl get secret "${SA_SECRET}" -o jsonpath='{.data.token}' | base64 -d)"
@olgch; @kublr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontokubernetesrbac-200410213658/75/Introduction-to-Kubernetes-RBAC-18-2048.jpg)







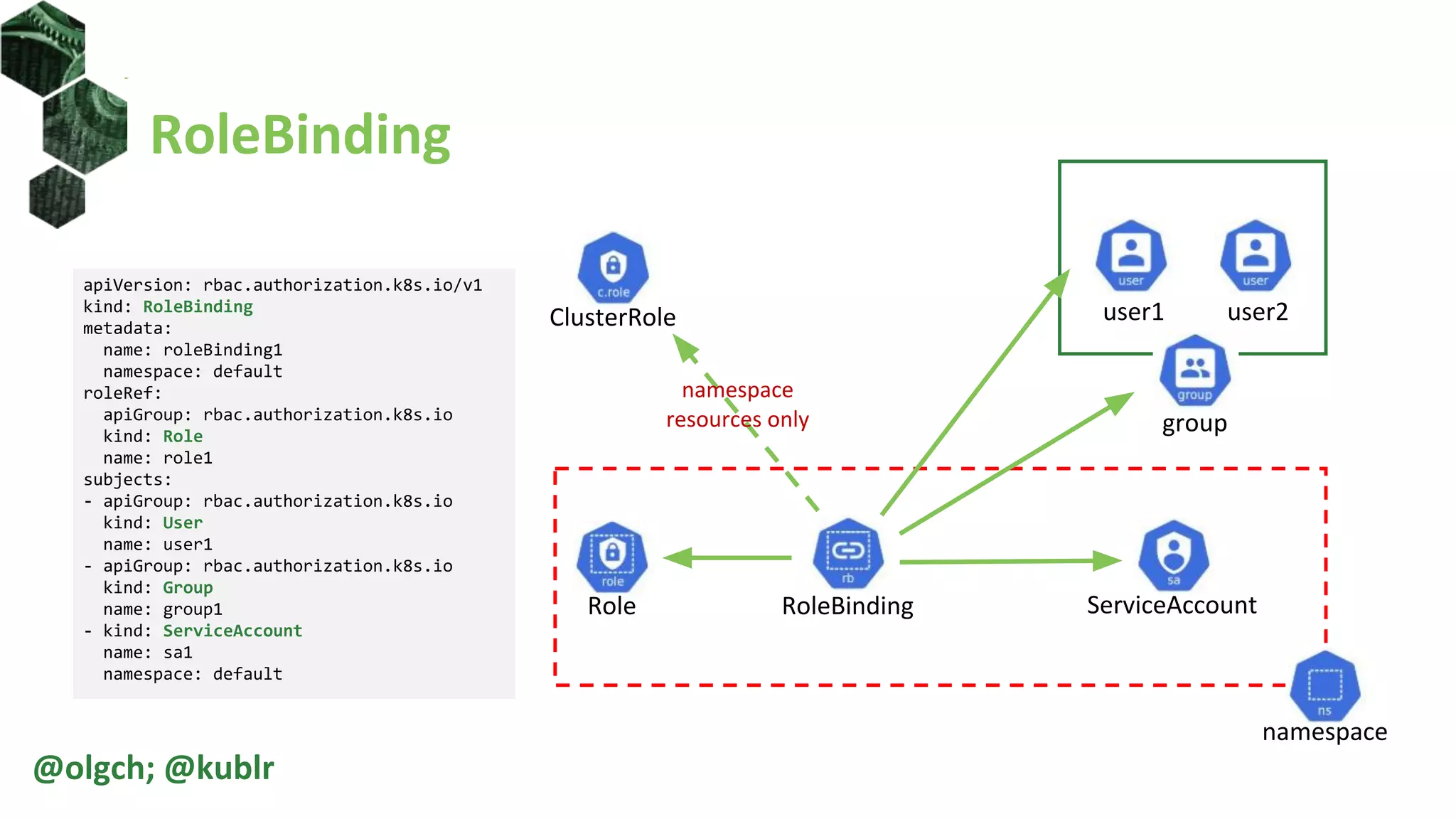
![Roles and ClusterRoles
• Roles and ClusterRoles define a set of
allowed actions on resources
• Role is namespaced
• Cannot include non-namespaces
resources or non-resource URLs
@olgch; @kublr
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: role1
rules:
- apiGroups: ['*']
resources: ['nodes', 'pods', 'pods/log']
verbs: ['get', 'list']
- apiGroups: ['*']
resources: ['configmaps']
resourceNames: ['my-configmap']
verbs: ['get', 'list']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontokubernetesrbac-200410213658/75/Introduction-to-Kubernetes-RBAC-30-2048.jpg)
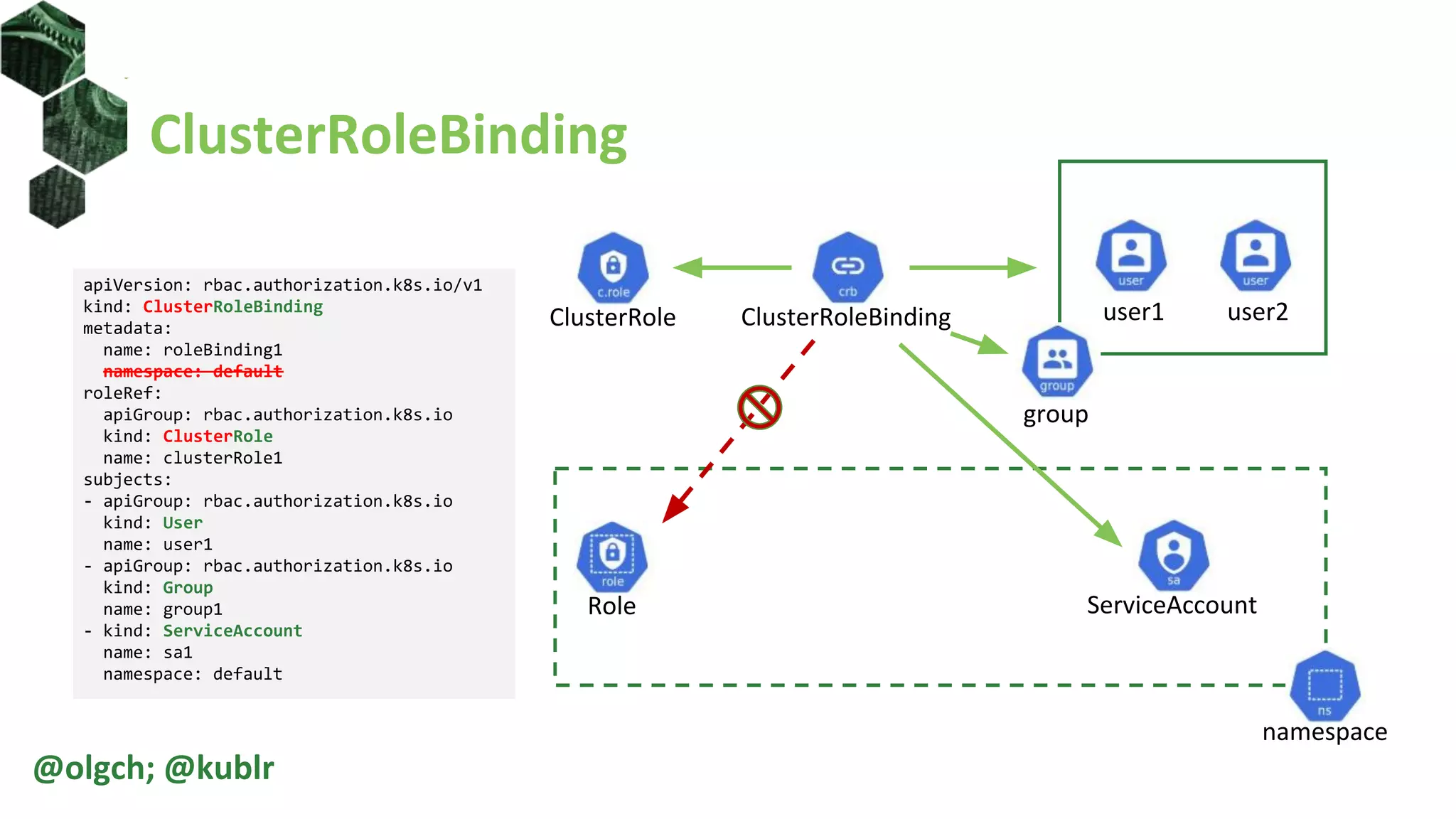
![ClusterRoles
• ClusterRole is not namespaced
• non-namespaced resources access
• non-resource URLs access
@olgch; @kublr
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
namespace: default
name: clusterRole1
rules:
- apiGroups: ['*']
resources: ['nodes', ‘pods']
verbs: ['get', 'list']
- nonResourceURLs: ['/api', '/healthz*']
verbs: ['get', 'head']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontokubernetesrbac-200410213658/75/Introduction-to-Kubernetes-RBAC-31-2048.jpg)
![Aggregated ClusterRoles
Aggregated ClusterRole combines rules from other cluster roles
@olgch; @kublr
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: aggregatedClusterRole1
aggregationRule:
clusterRoleSelectors:
- matchLabels:
label1: value1
# The control plane automatically fills in the rules
rules: []
Aggregated
ClusterRole
clusterRole1
aggregationRule:
clusterRoleSelectors:
- matchLabels:
label1: value1
metadata:
labels:
label1: value1
clusterRole1
metadata:
labels:
label1: value1
label2: value2
clusterRole1
metadata:
labels:
label2: value2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontokubernetesrbac-200410213658/75/Introduction-to-Kubernetes-RBAC-32-2048.jpg)