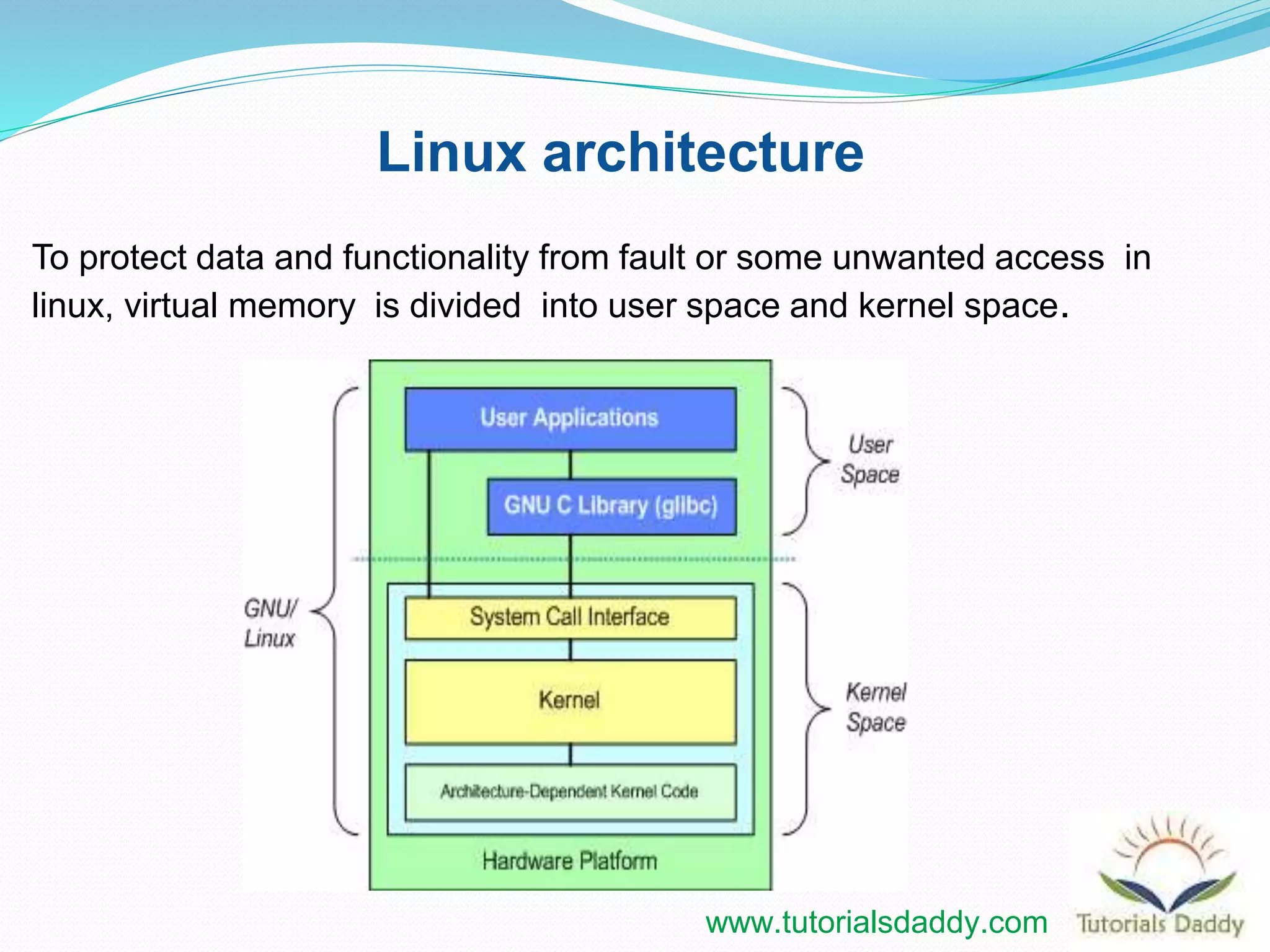
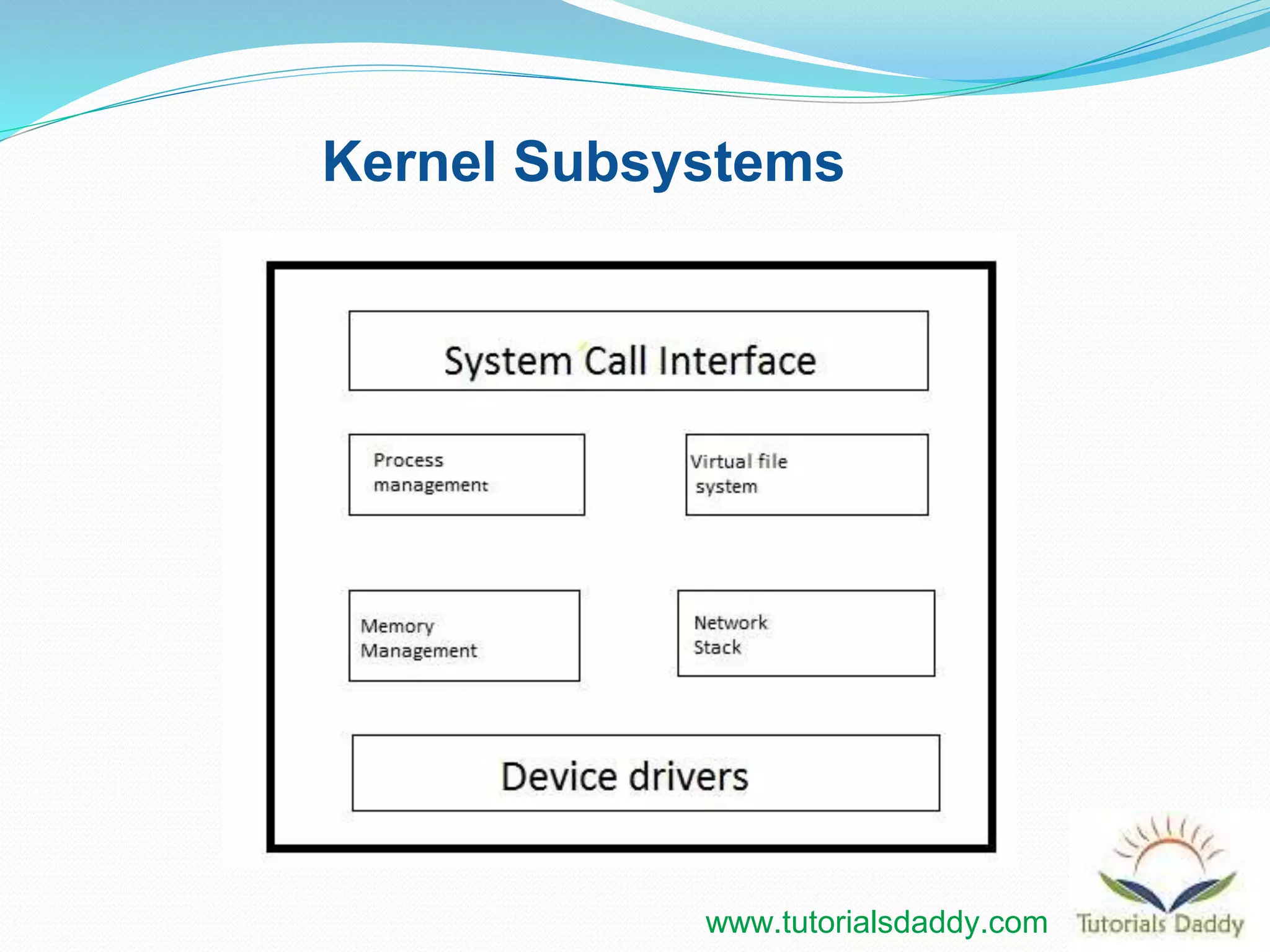
This document provides an introduction to the Linux kernel, including its main features and architecture. It discusses the kernel's portable, open source, multi-user nature and hierarchical file system. The document outlines the Linux versioning scheme and describes the kernel's main subsystems, including process management, memory management, the virtual file system, network stack, and system call interface. It explains how the kernel uses virtual memory to separate user space and privileged kernel space.