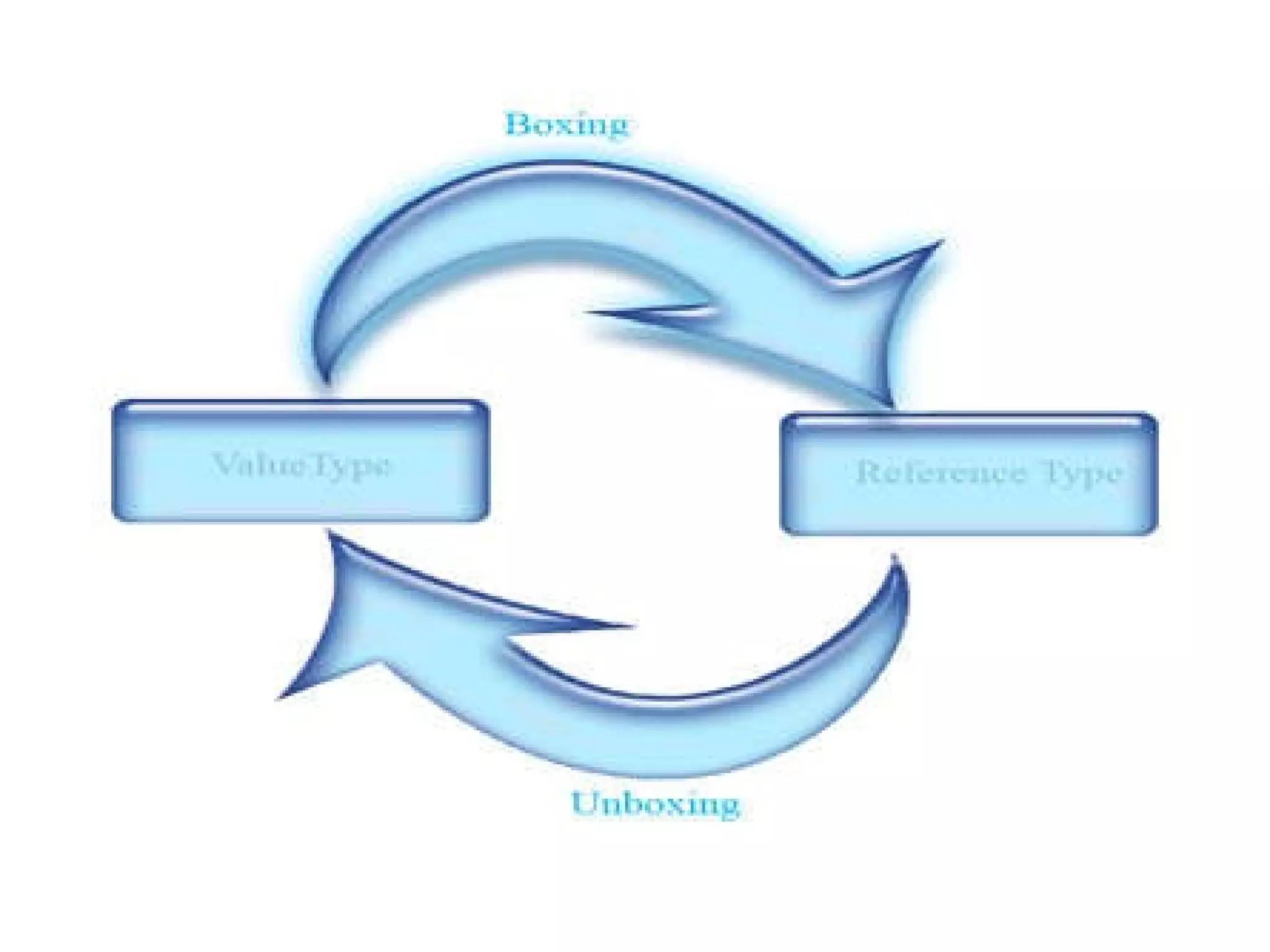
The document discusses different system types and interfaces in .NET, including common data types like value types and reference types. It also covers various collection types for storing multiple objects like arrays, lists, stacks and queues. The document explains generics and interfaces that define standard behaviors for classes to ensure type safety when working with different data types.