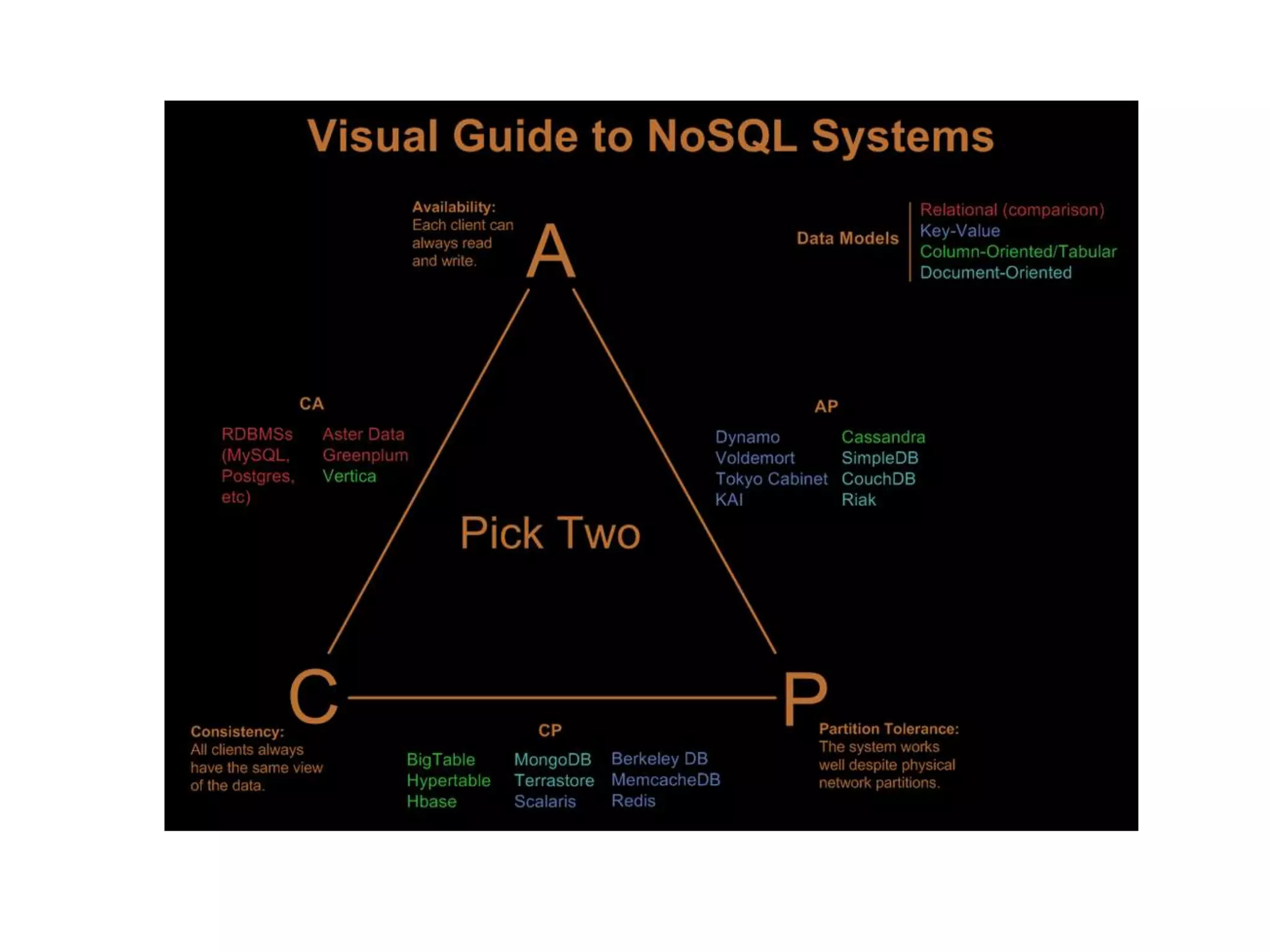
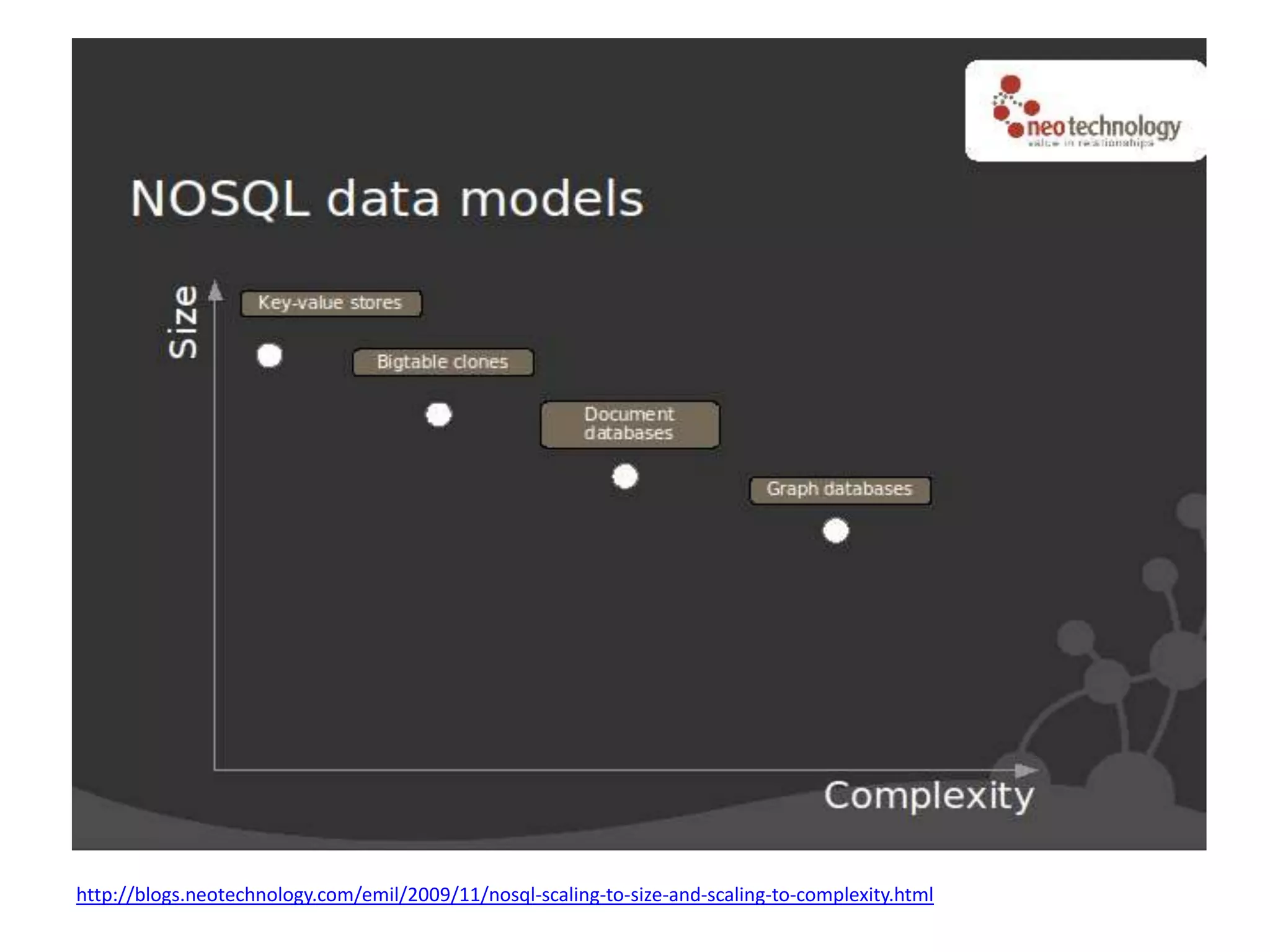
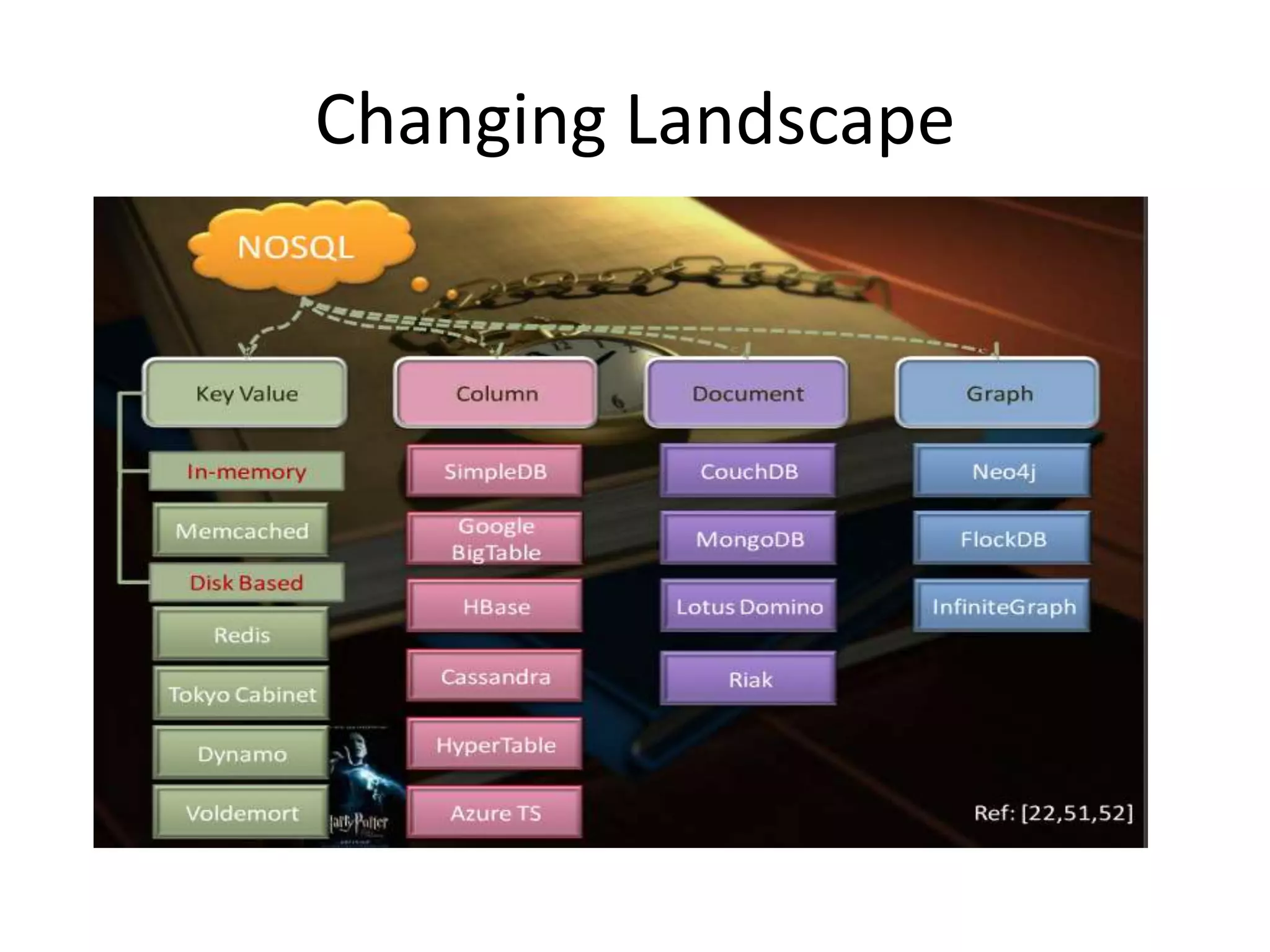
The document summarizes a meetup about NoSQL databases hosted by AWS in Sydney in 2012. It includes an agenda with presentations on Introduction to NoSQL and using EMR and DynamoDB. NoSQL is introduced as a class of databases that don't use SQL as the primary query language and are focused on scalability, availability and handling large volumes of data in real-time. Common NoSQL databases mentioned include DynamoDB, BigTable and document databases.