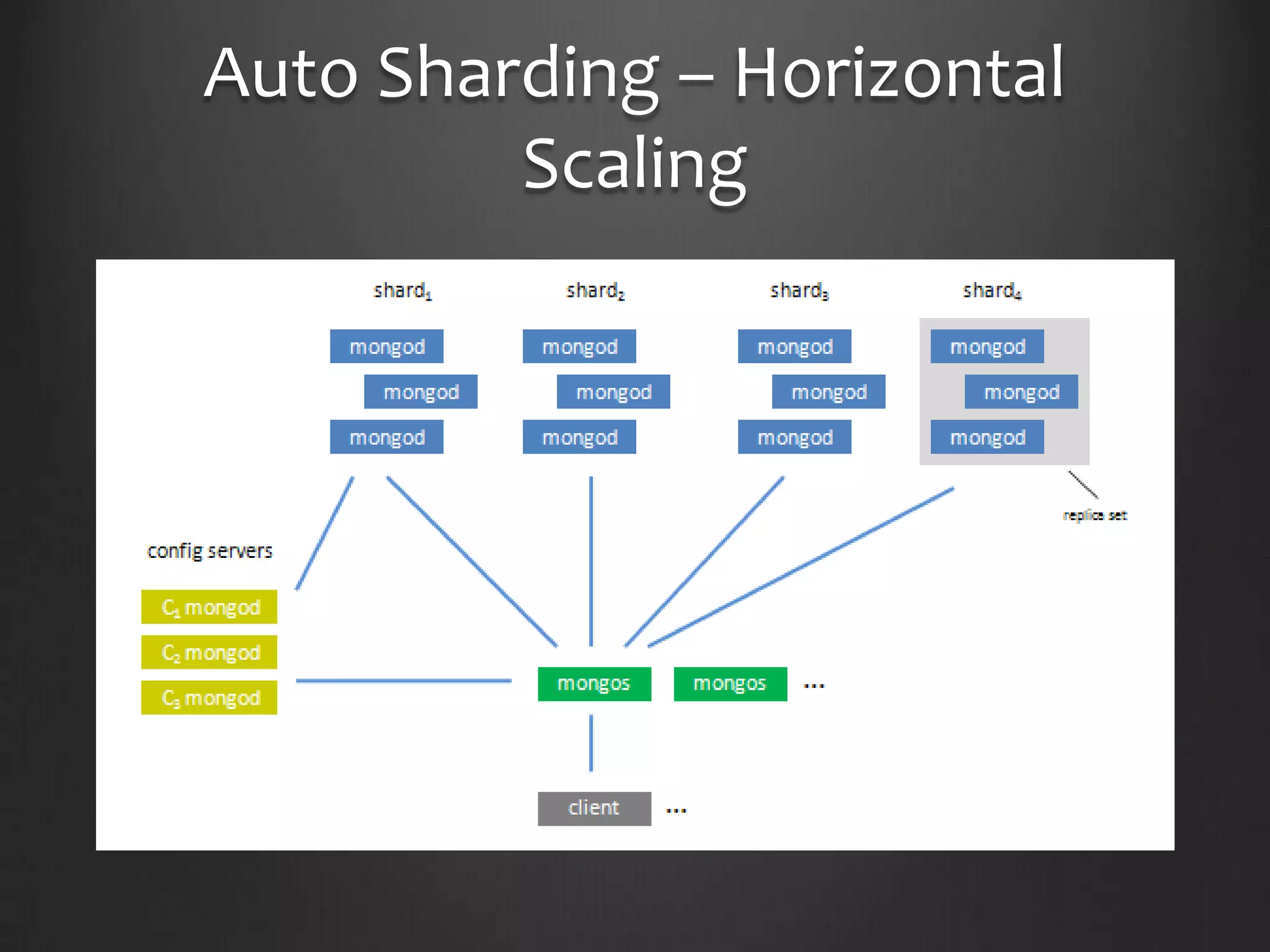
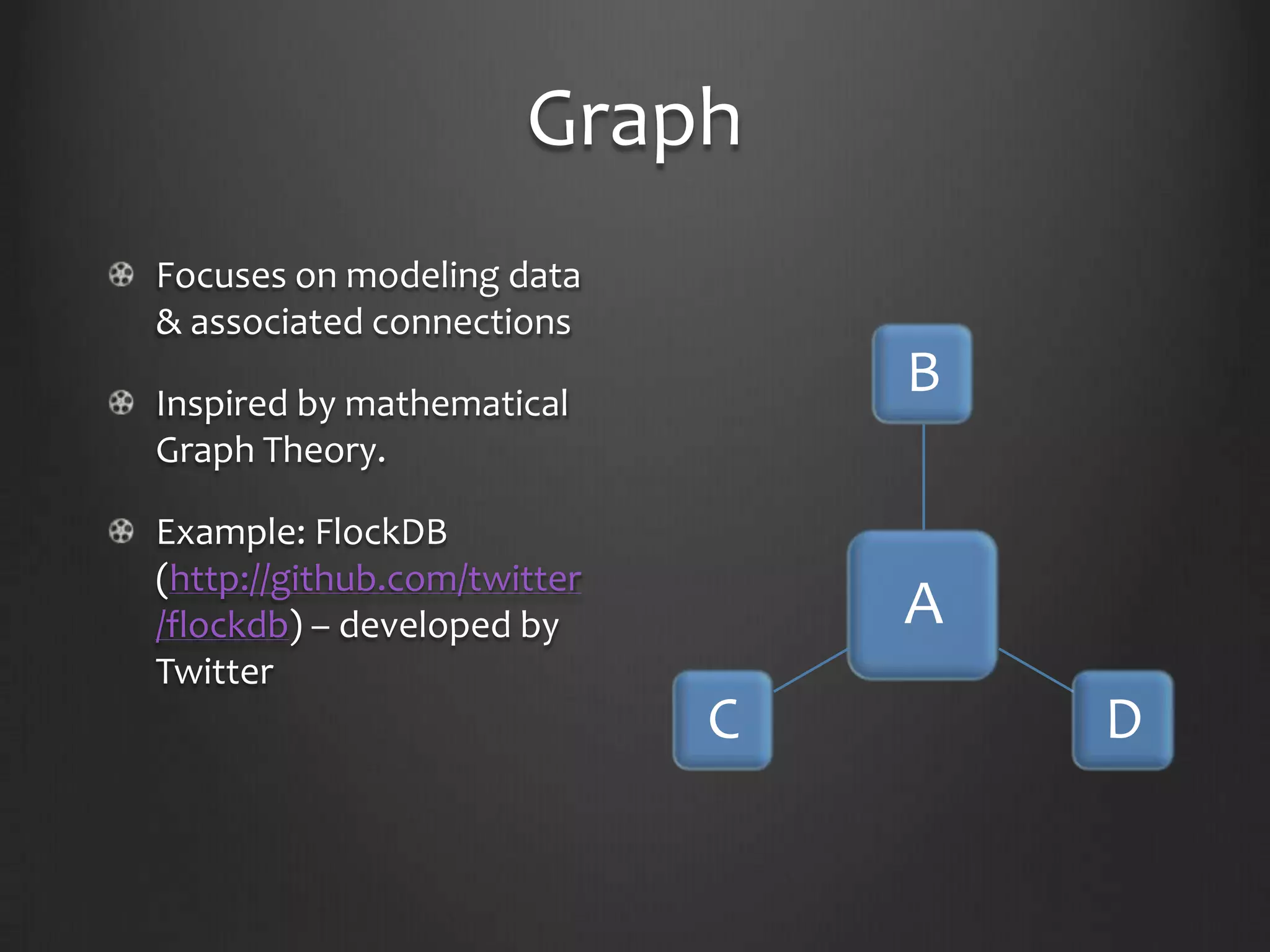
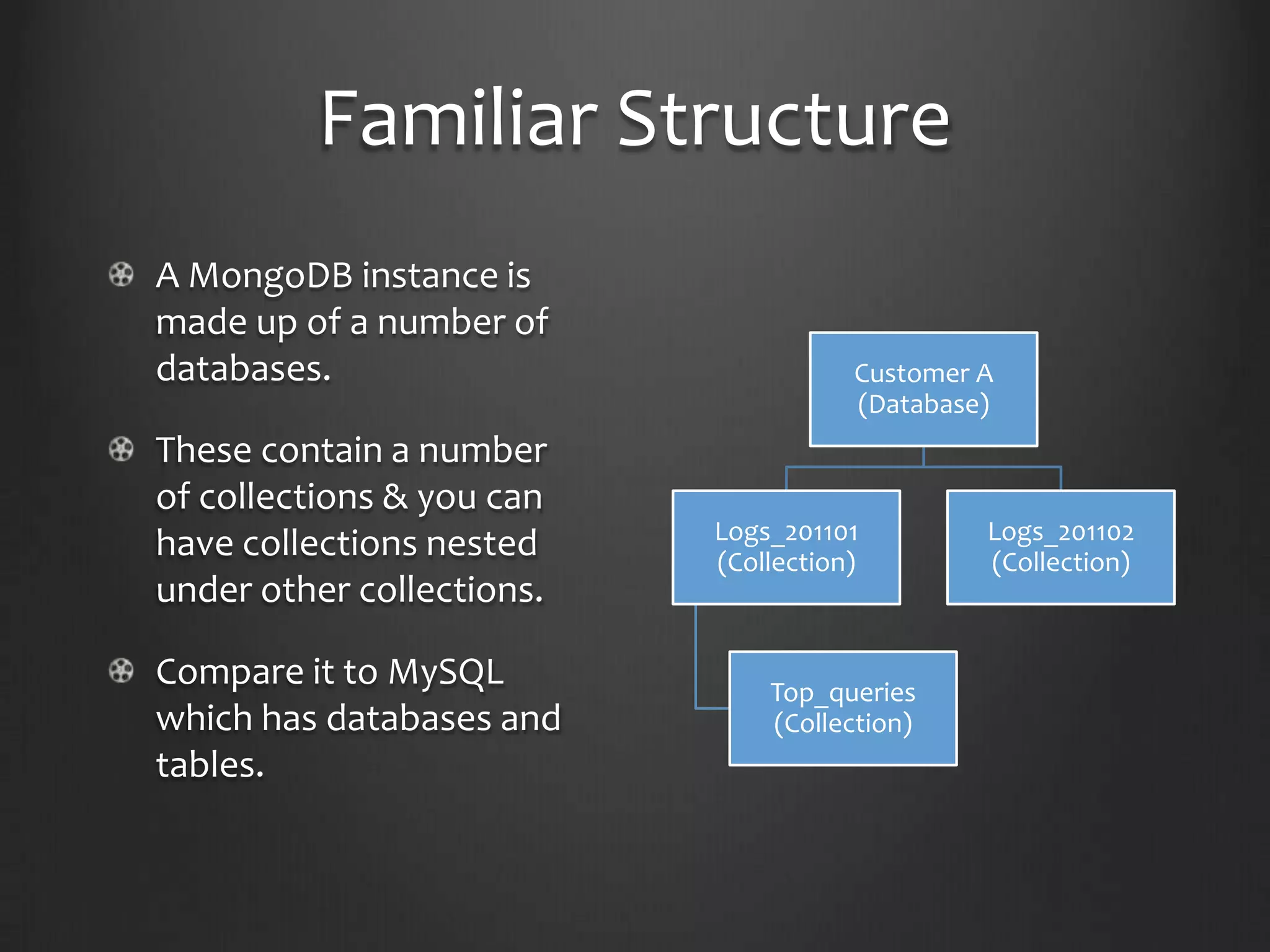
This document provides an introduction to NoSQL and MongoDB. It discusses that NoSQL is a non-relational database management system that avoids joins and is easy to scale. It then summarizes the different flavors of NoSQL including key-value stores, graphs, BigTable, and document stores. The remainder of the document focuses on MongoDB, describing its structure, how to perform inserts and searches, features like map-reduce and replication. It concludes by encouraging the reader to try MongoDB themselves.








![Inserts – As Easy As Pieuse cookbook;db.recipes.save({ “name”: “Cherry Pie”, “ingredients”: [“cherries”, “pie”], “cooking_time”: 30});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtonosqlandmongodb-110708014925-phpapp01/75/An-Introduction-To-NoSQL-MongoDB-11-2048.jpg)




![Reduce FunctionTakes the results from the map function, does something (normally combine the results) and produces output in key/value pairsreduce = function(key, values) {var count = 0;values.forEach(function(v) { count += v[‘count’]; } return {count: count;}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtonosqlandmongodb-110708014925-phpapp01/75/An-Introduction-To-NoSQL-MongoDB-16-2048.jpg)