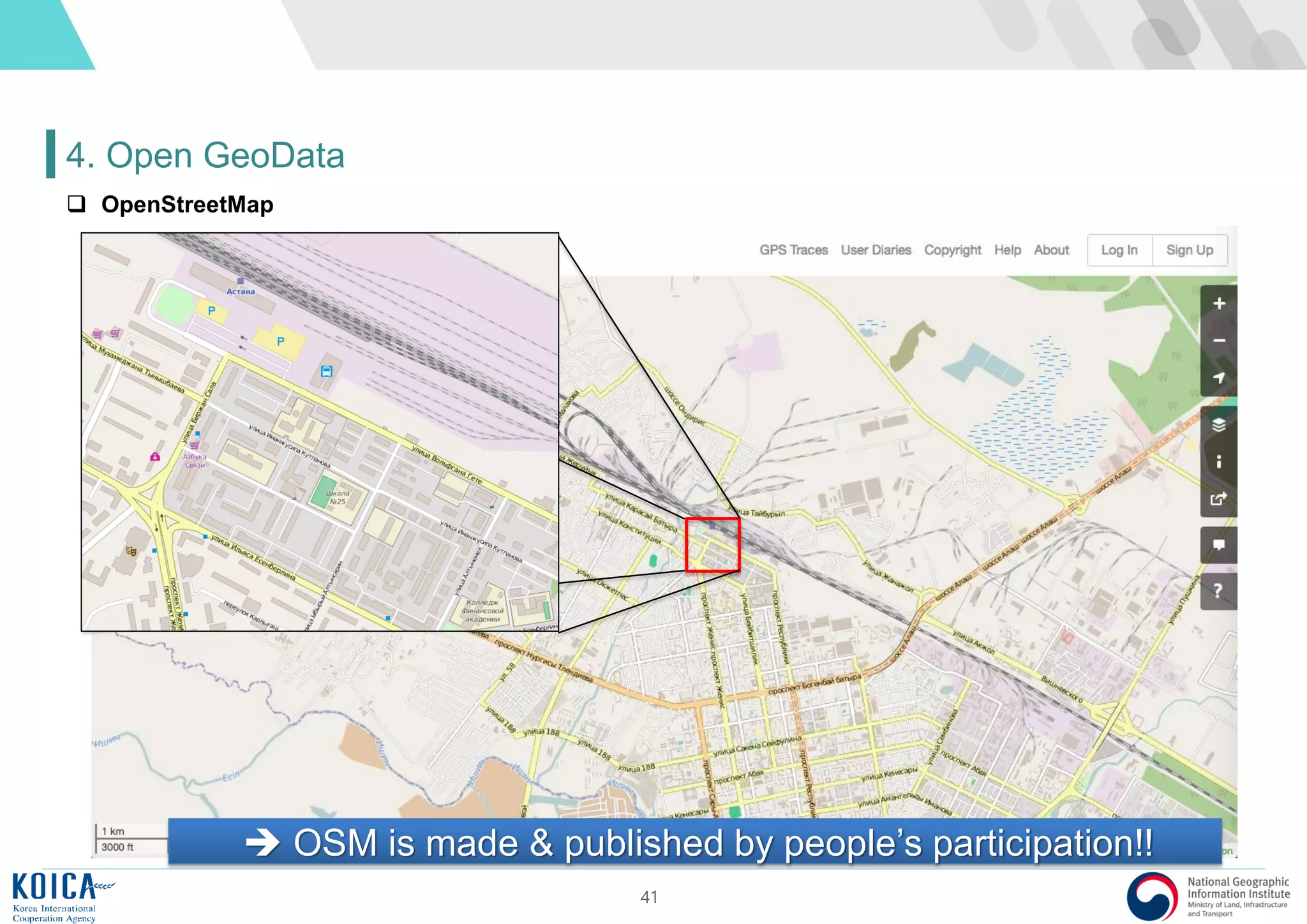
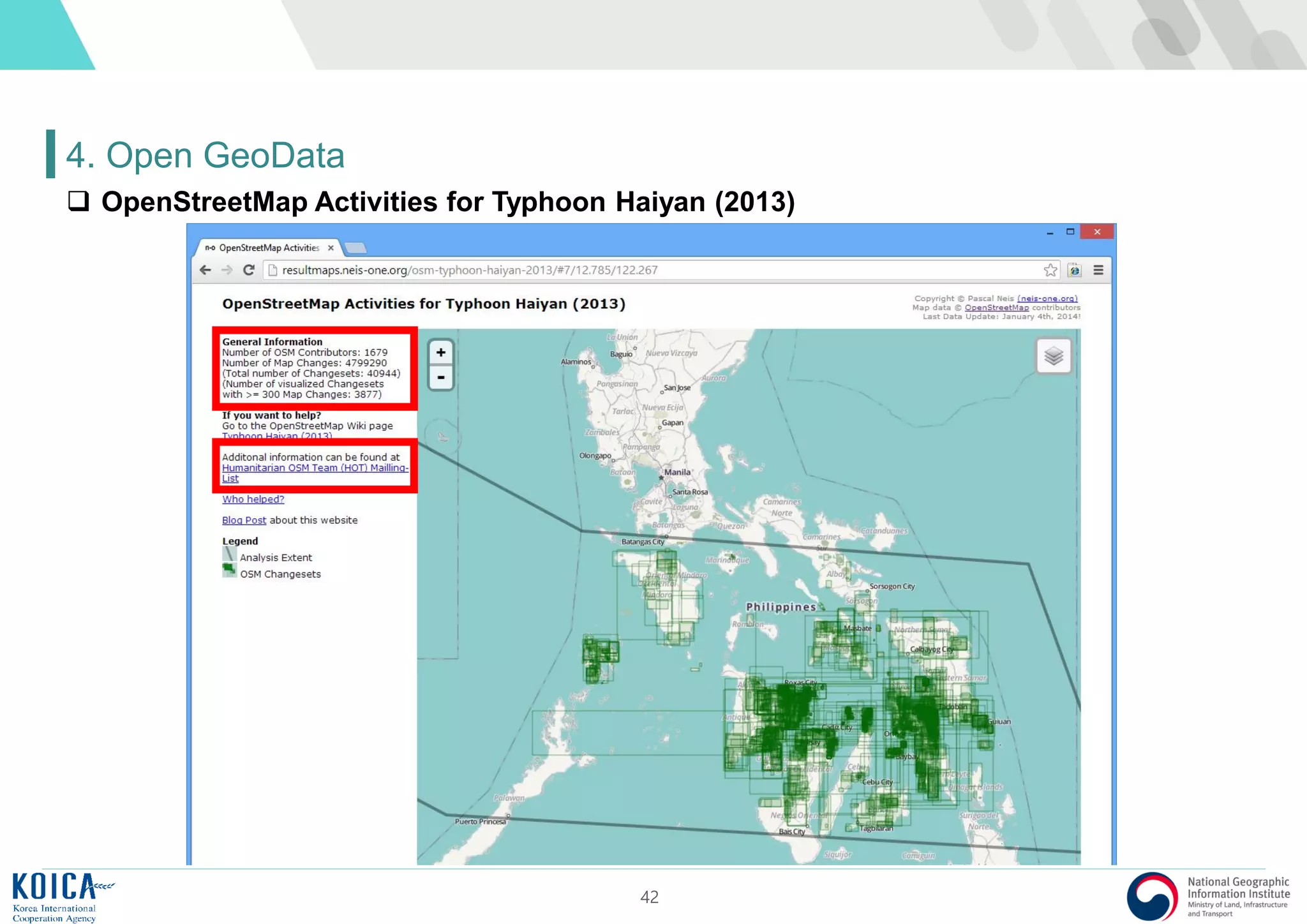
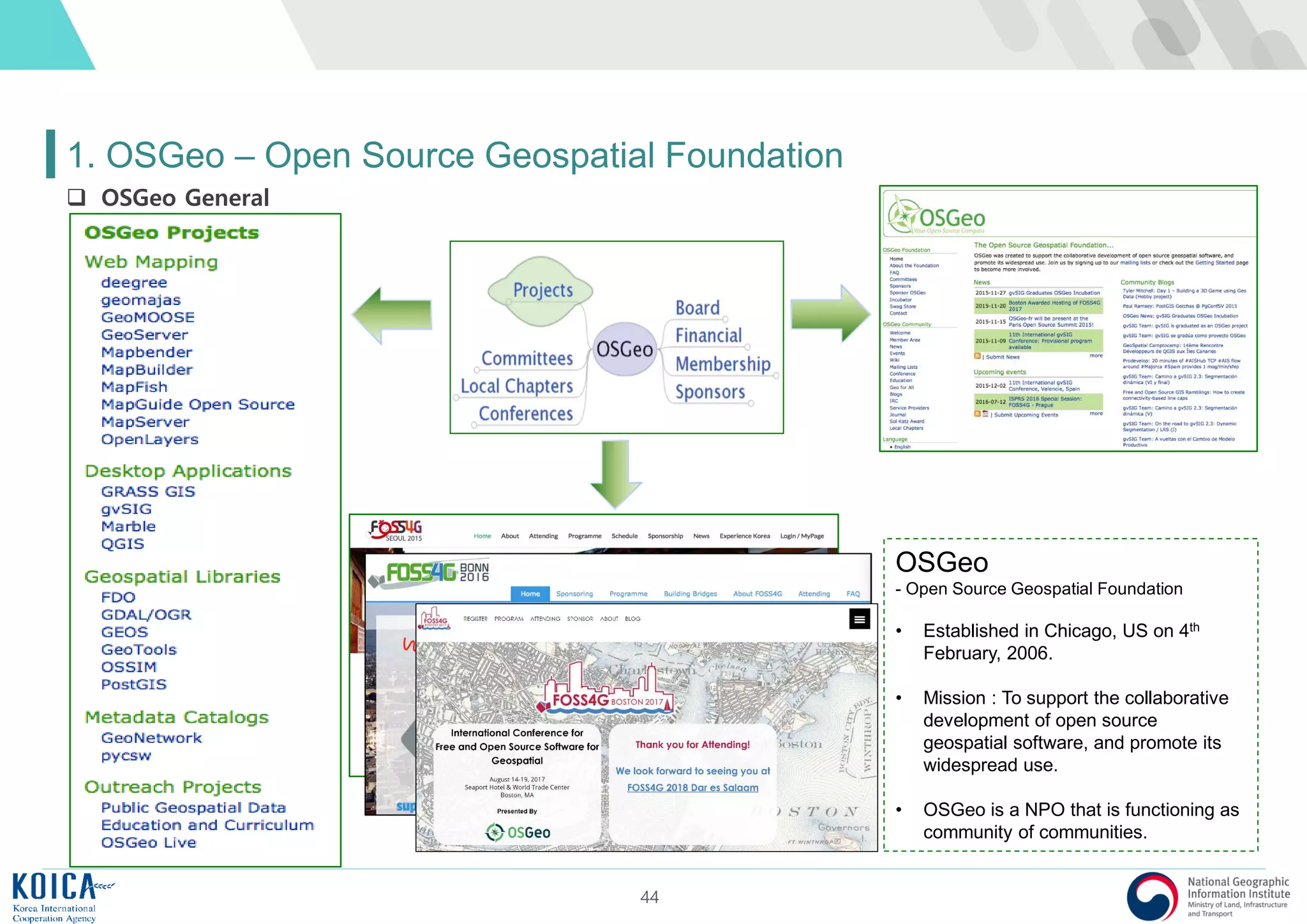
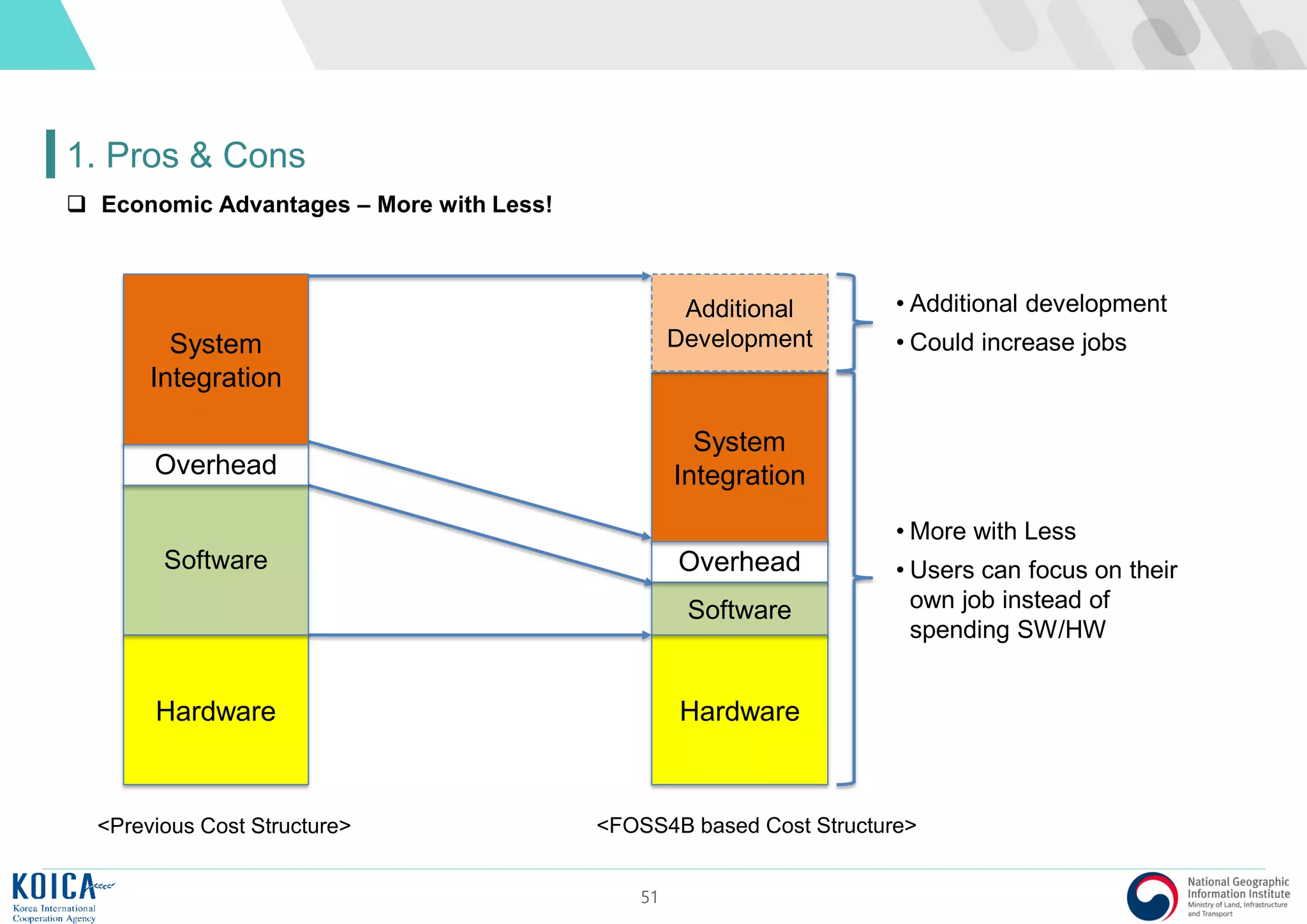
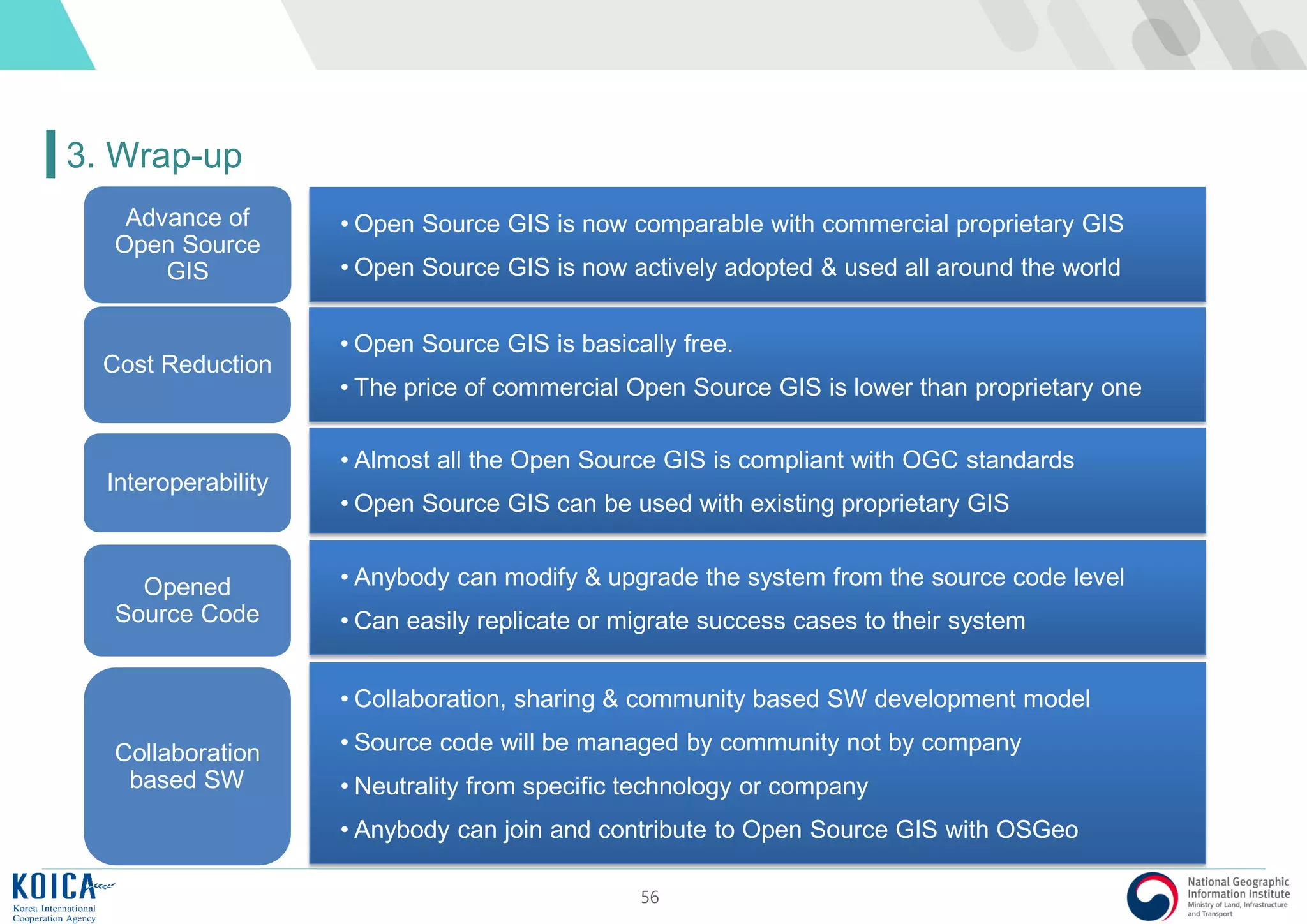
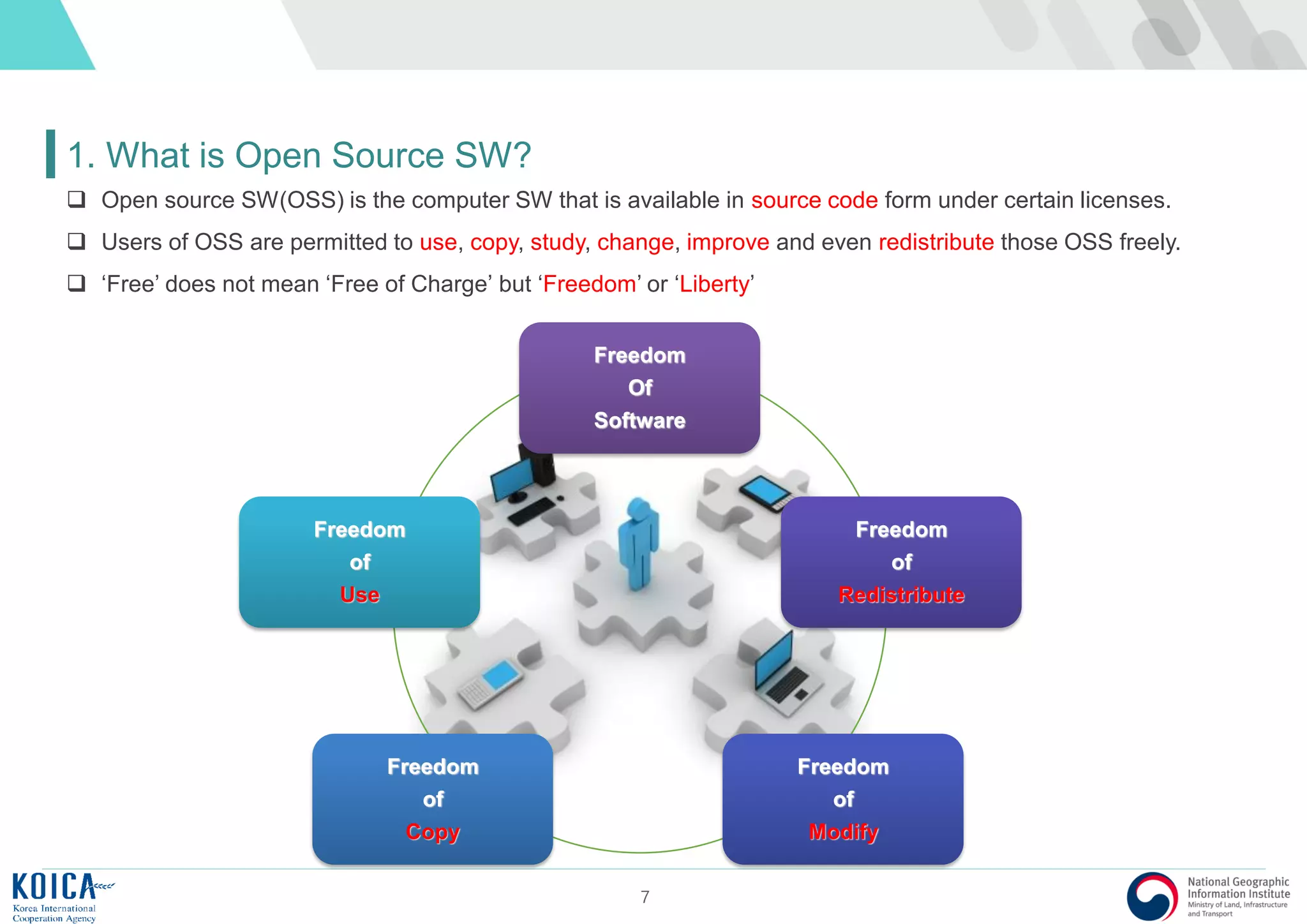
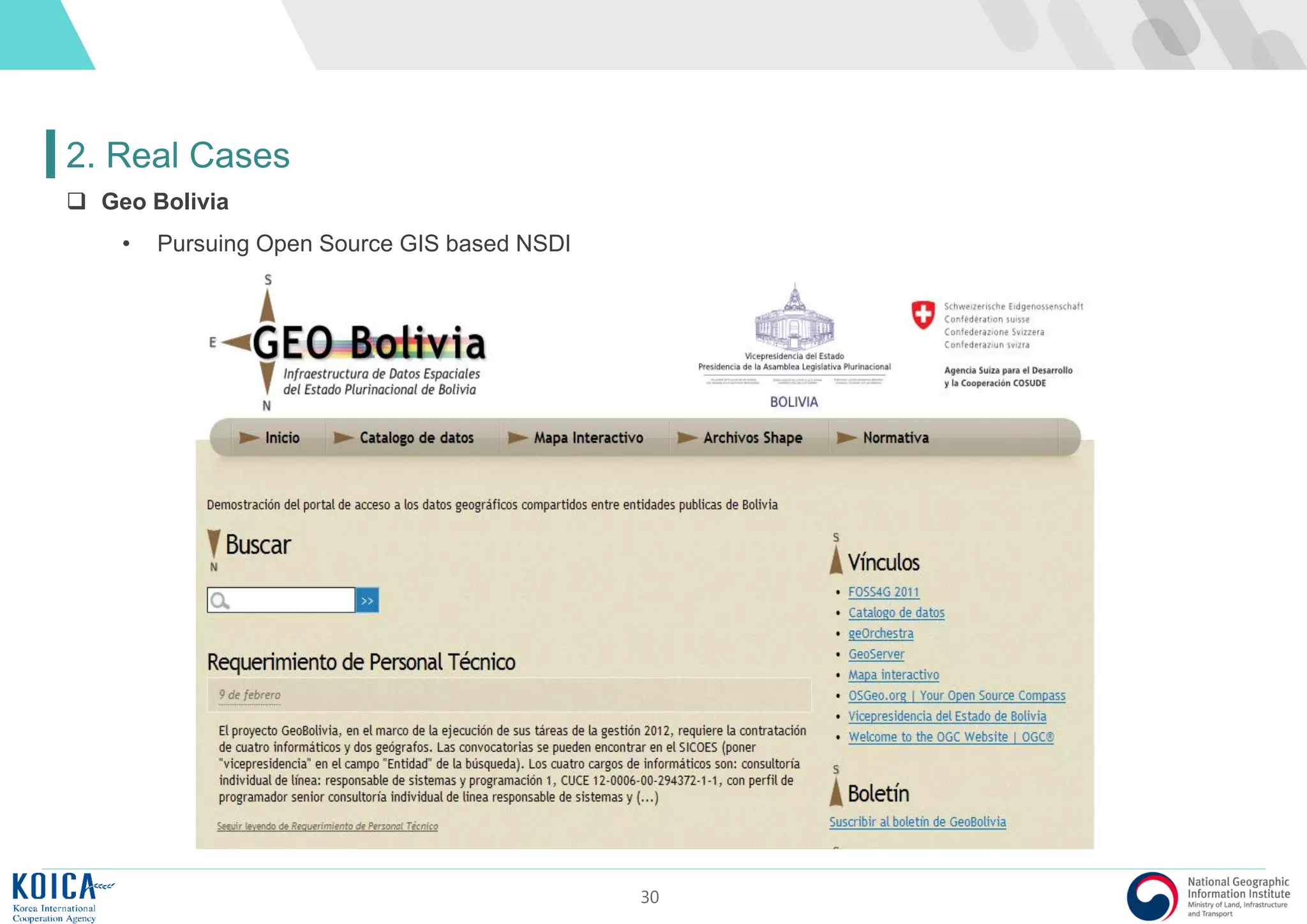
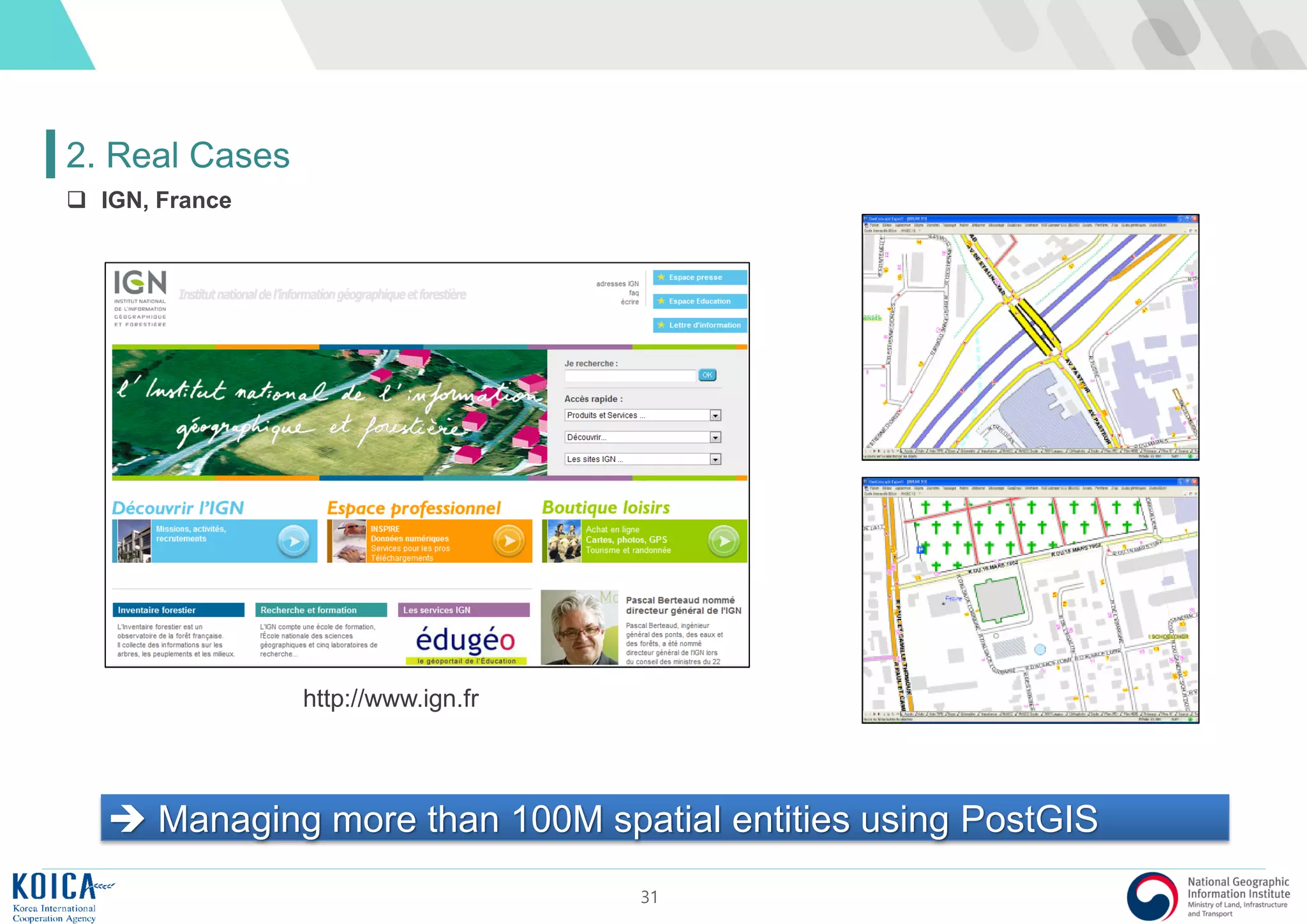
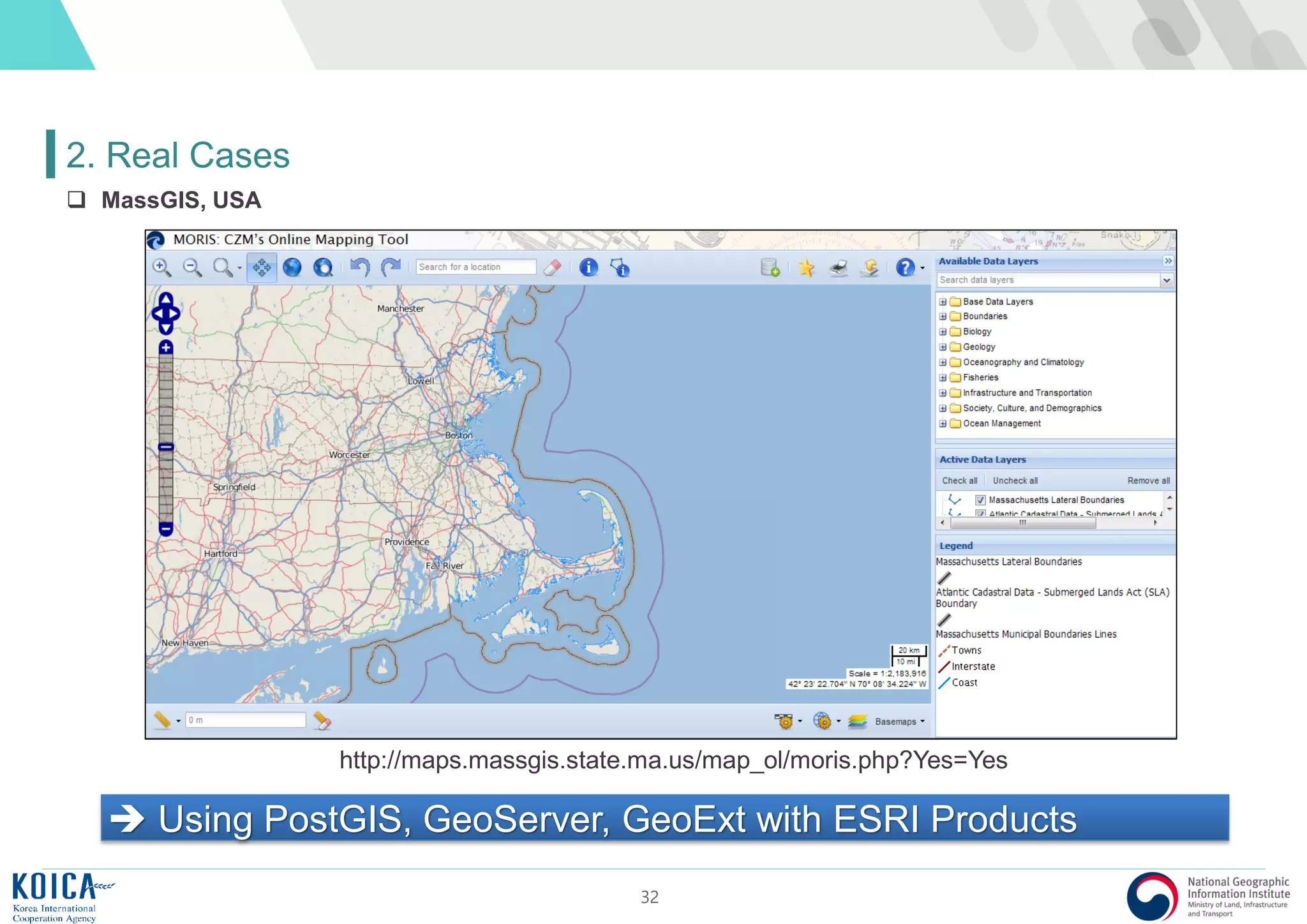
This document provides an overview of open source Geographic Information Systems (GIS), including definitions, benefits, and implementation examples. It highlights the increasing adoption of open source GIS by various organizations and governments, emphasizing cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and community collaboration. The document also discusses the role of the Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo) in promoting open source GIS initiatives worldwide.











![39
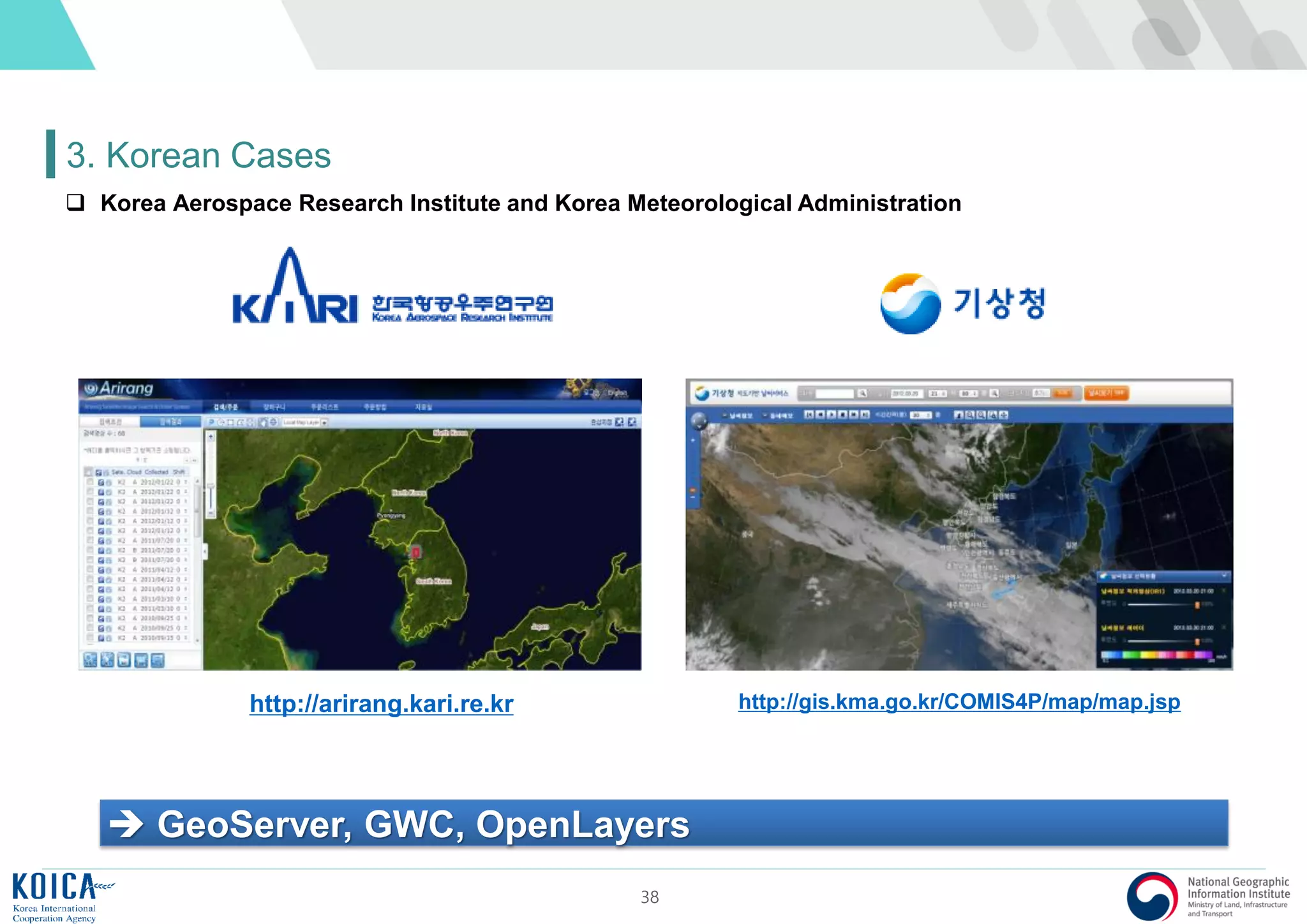
3. Korean Cases
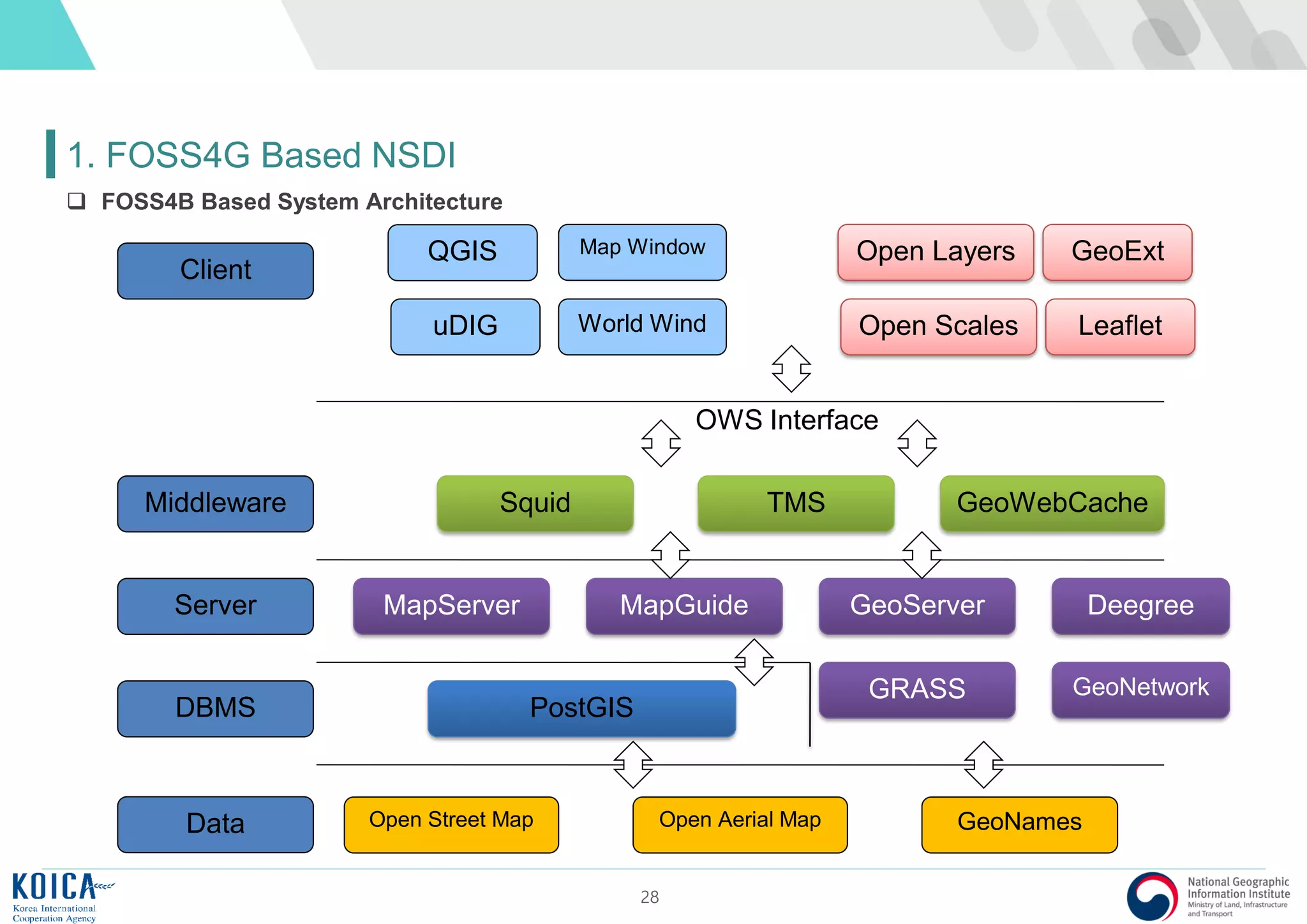
GeoServer, GWC, Squid, OpenLayers
[Smart Phone] [FOSS4B based Transport Information Service System Architecture]
National Transport Information Center](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofoss4g-170918223020/75/Introduction-to-Open-Source-GIS-39-2048.jpg)