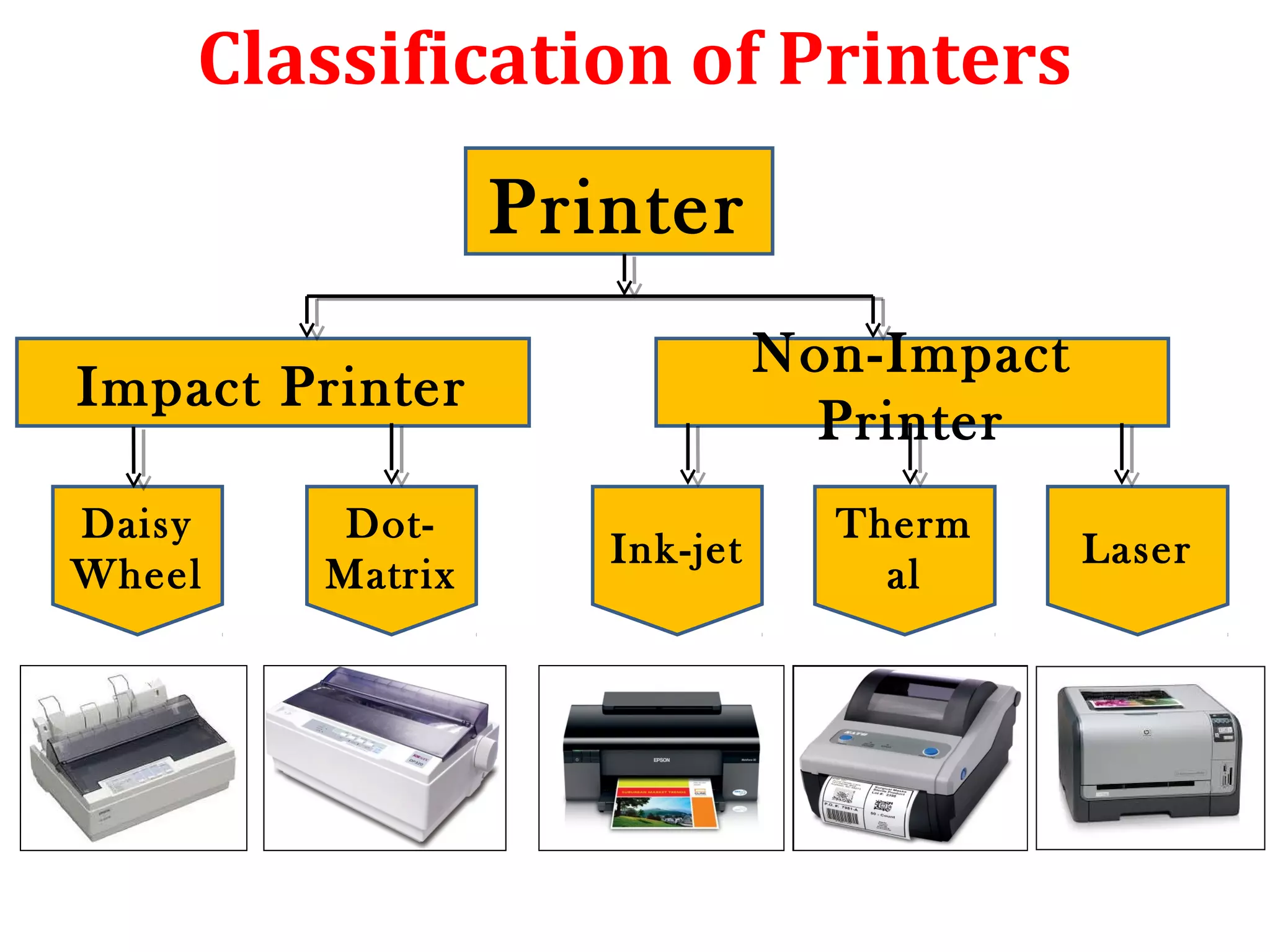
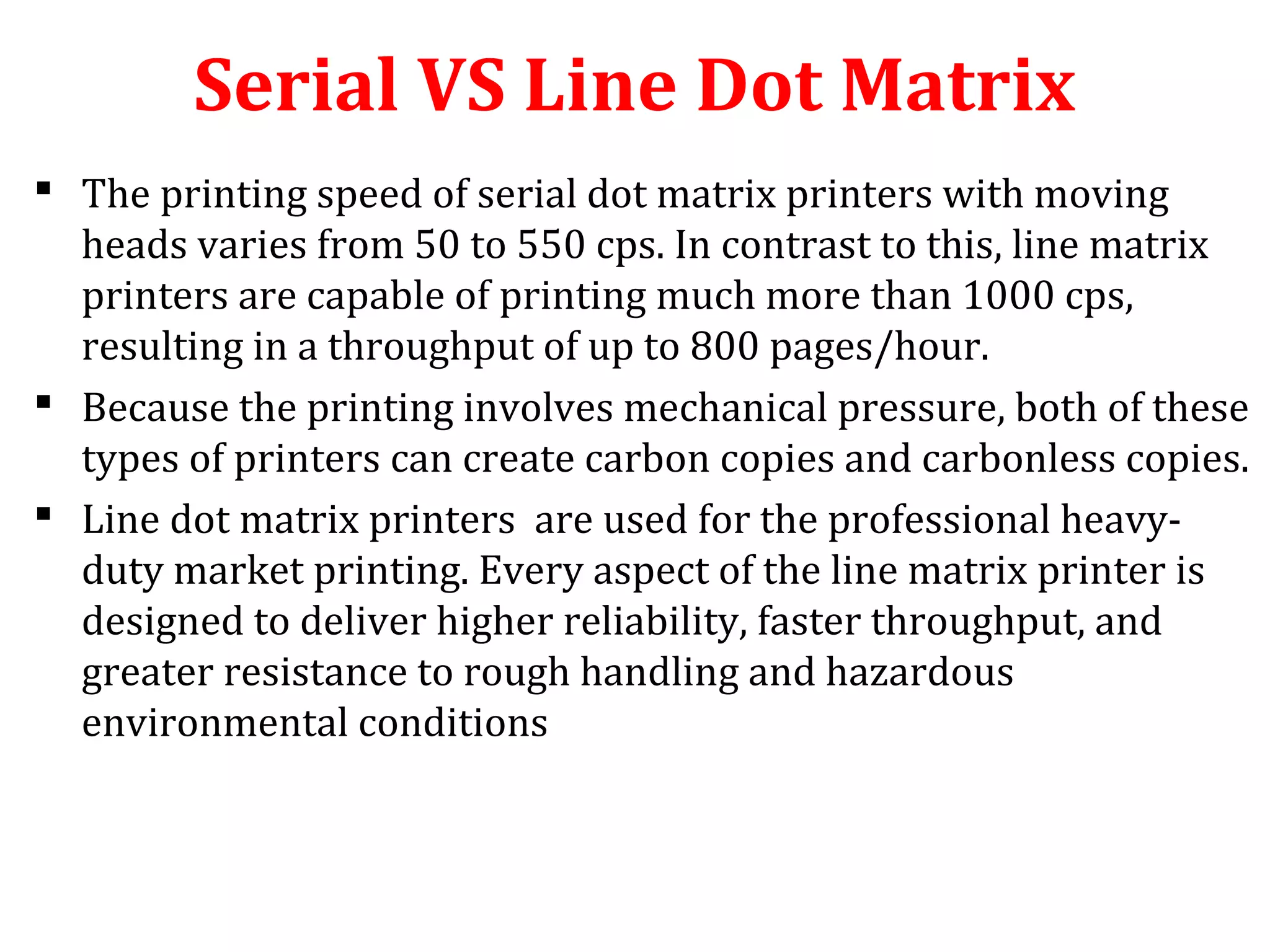
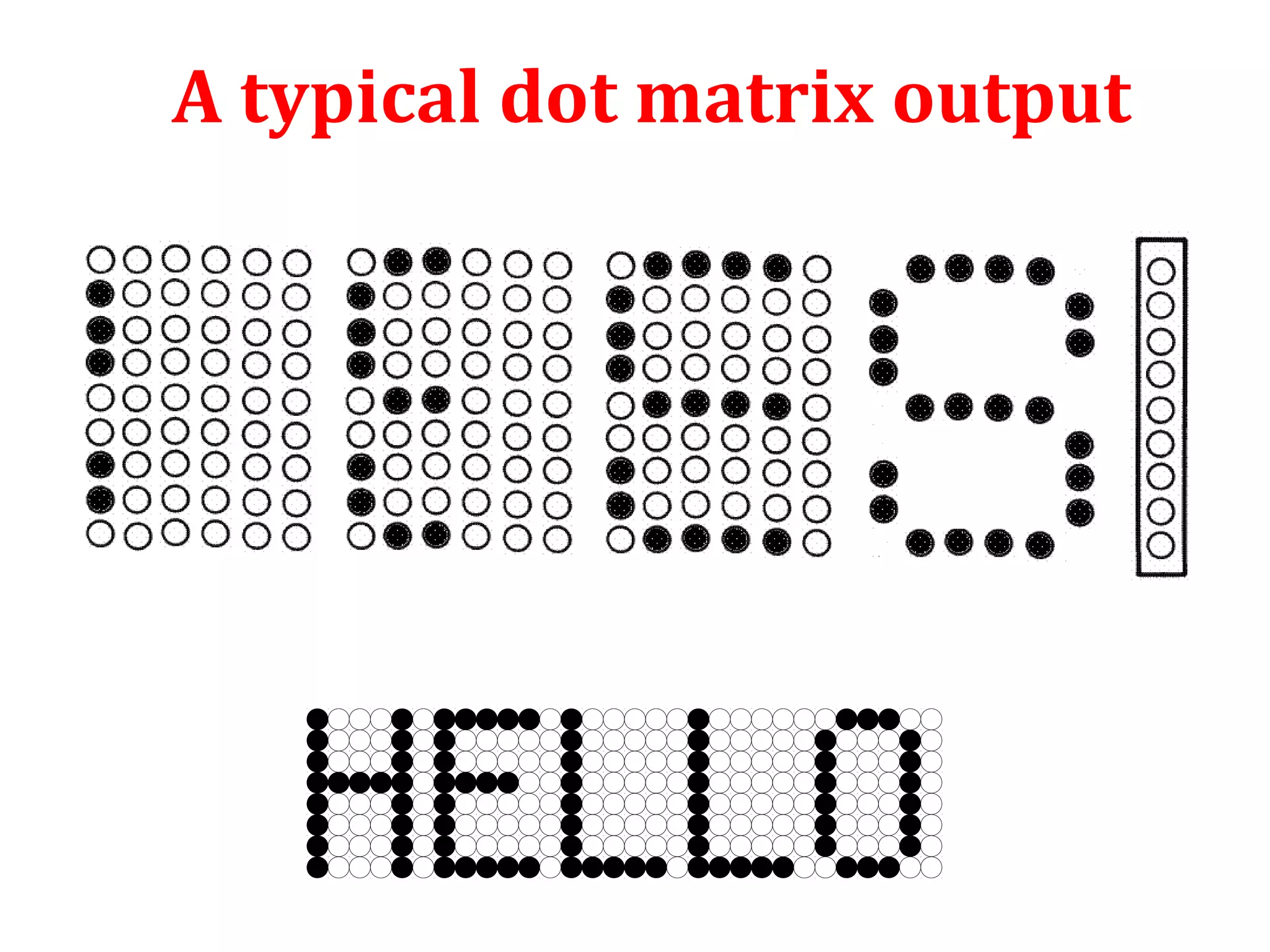
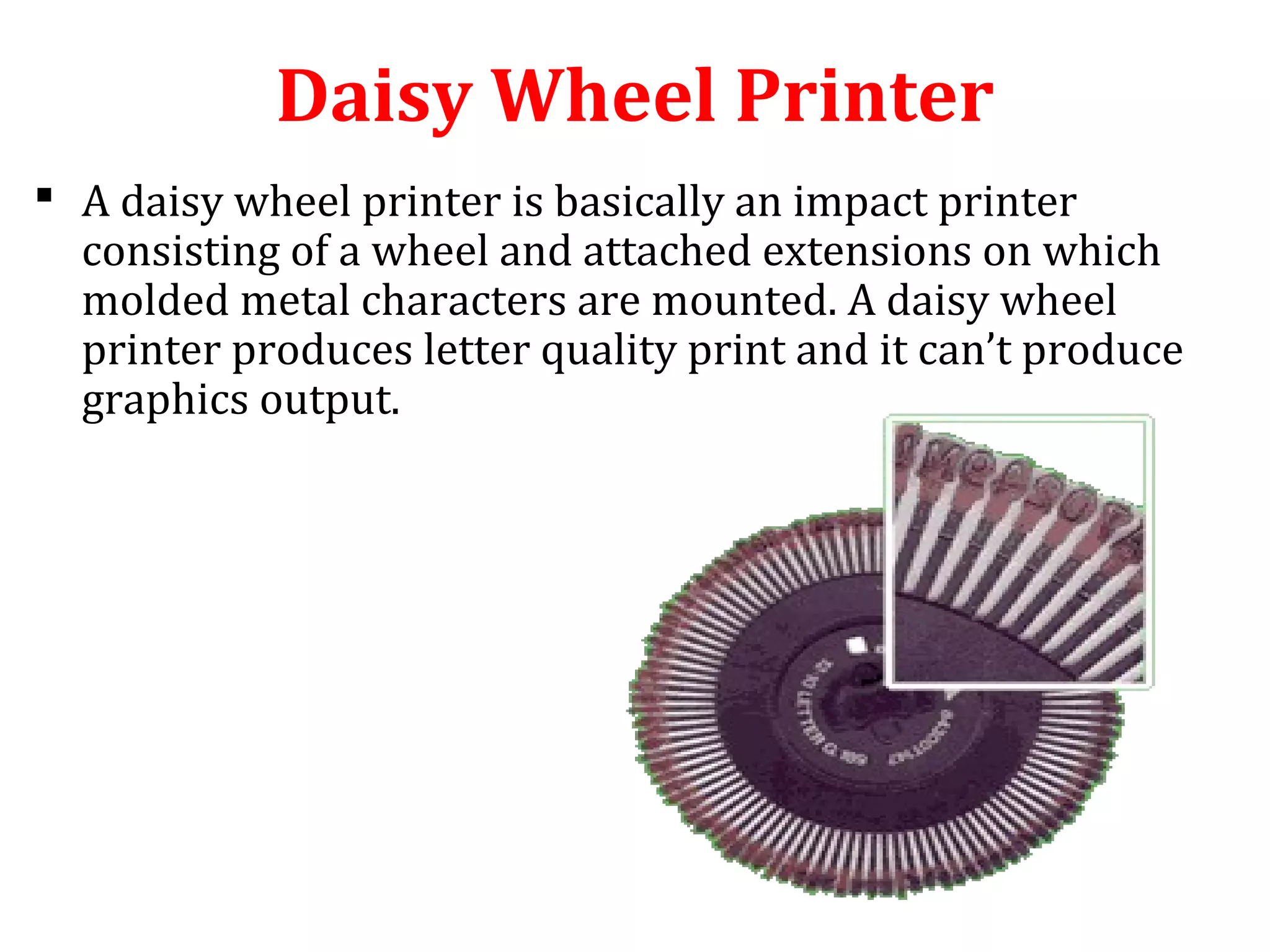
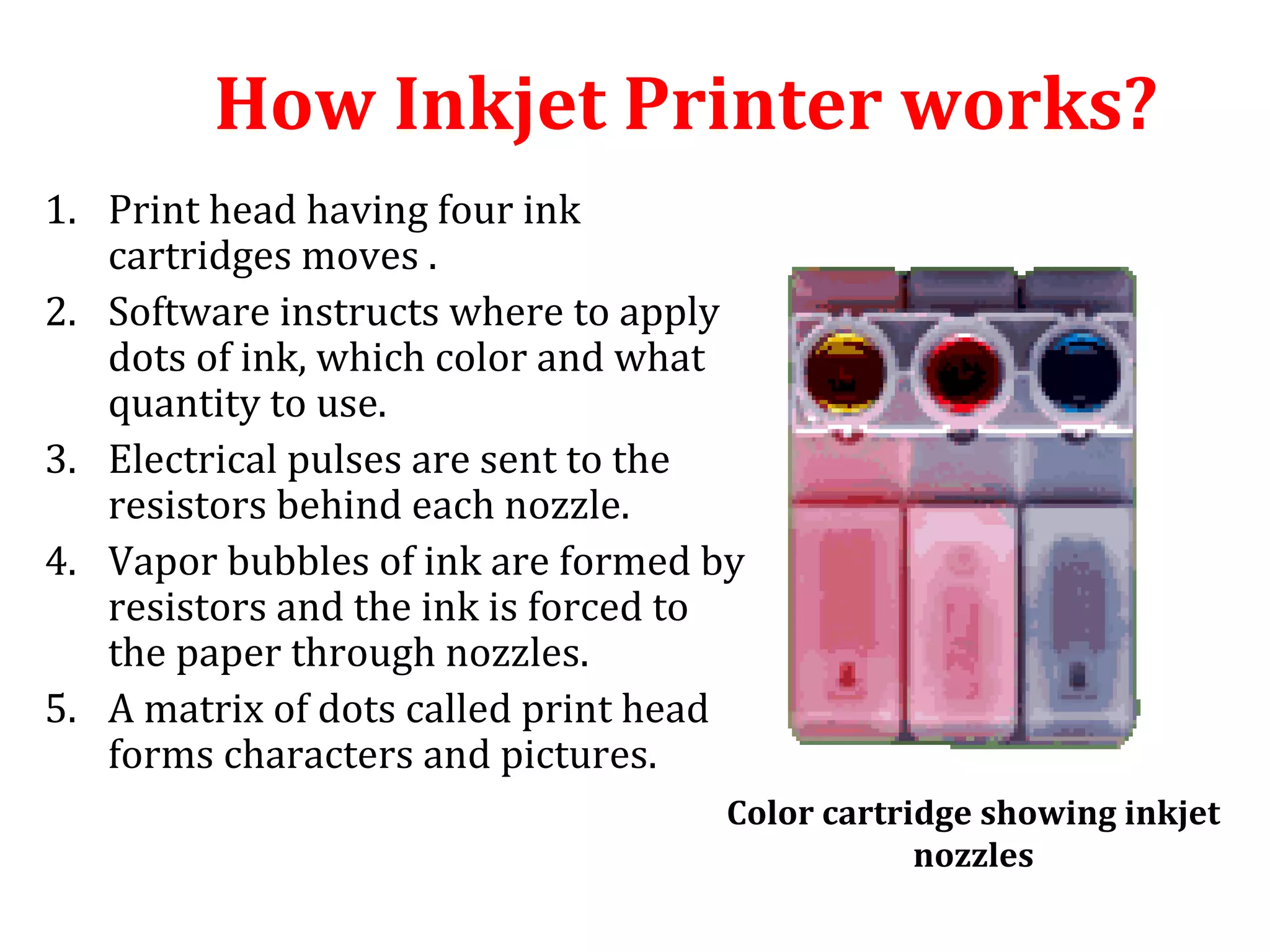
The document provides an introduction to computer printers, detailing their classification into impact and non-impact types, and explaining the functionality of various printer technologies including dot matrix, daisy wheel, inkjet, and laser printers. It discusses the differences between impact and non-impact printers, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and highlights factors affecting print quality, as well as considerations for purchasing a printer. Additionally, it covers printer interfaces and the concept of virtual printers.