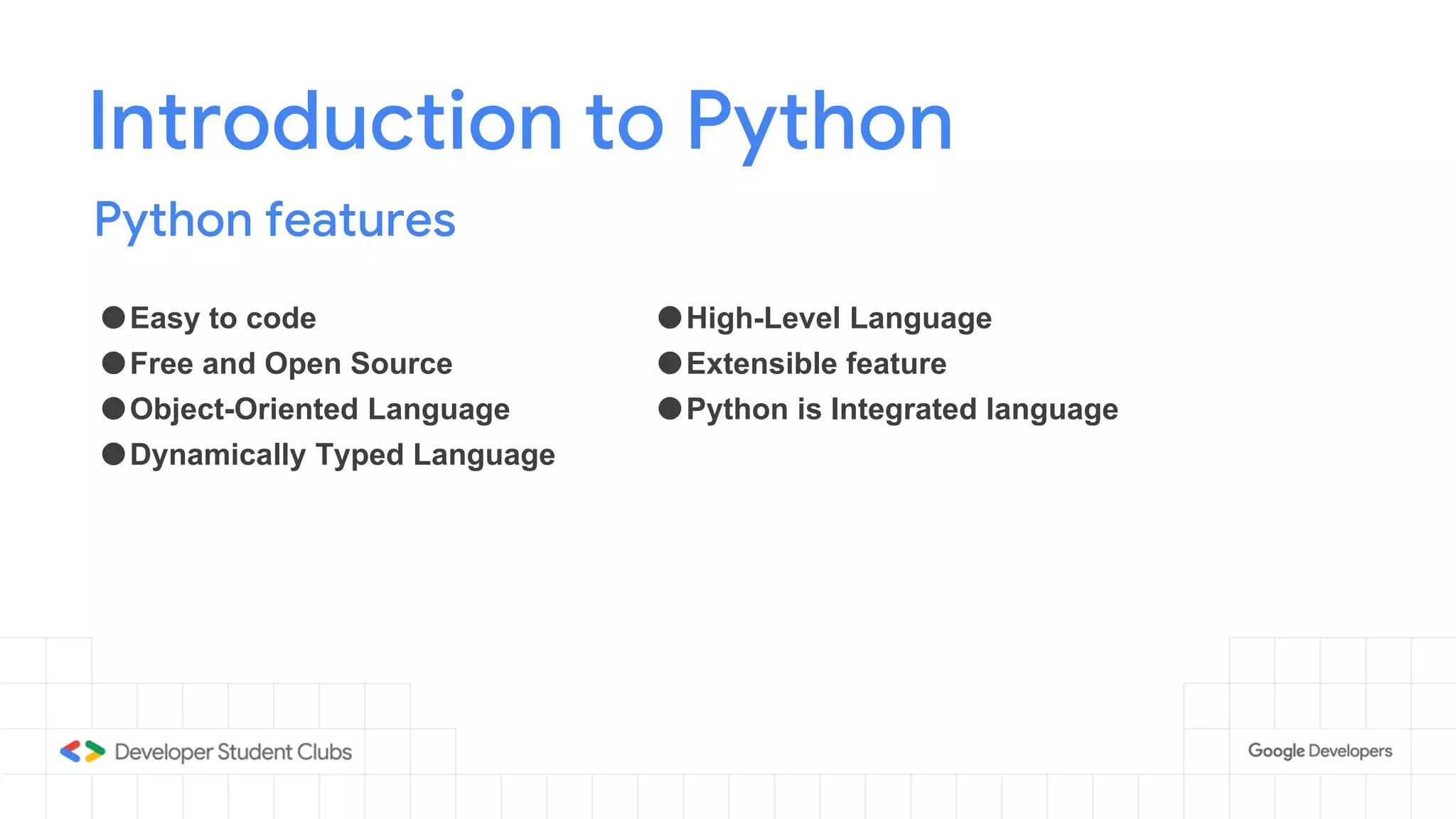
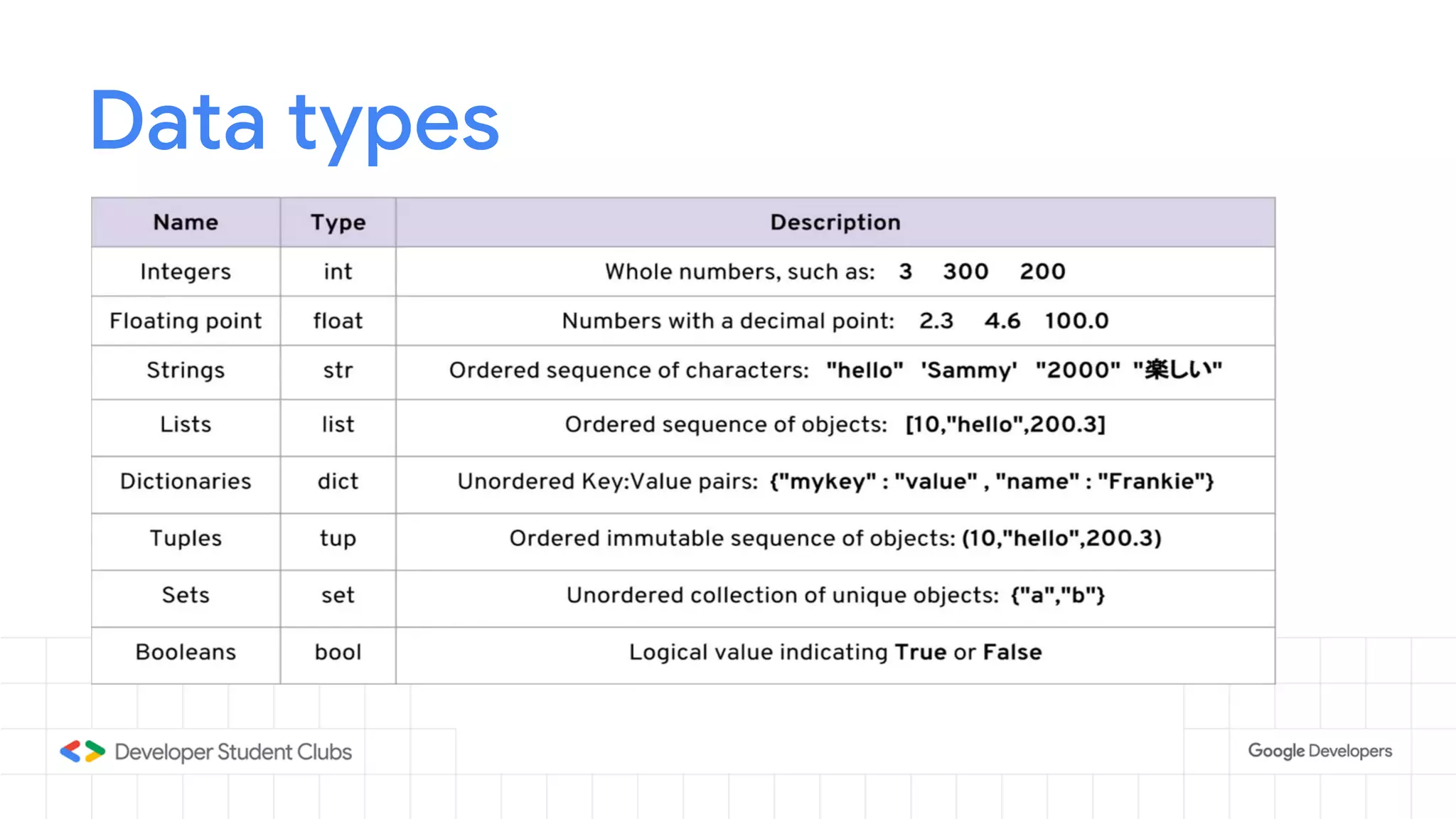
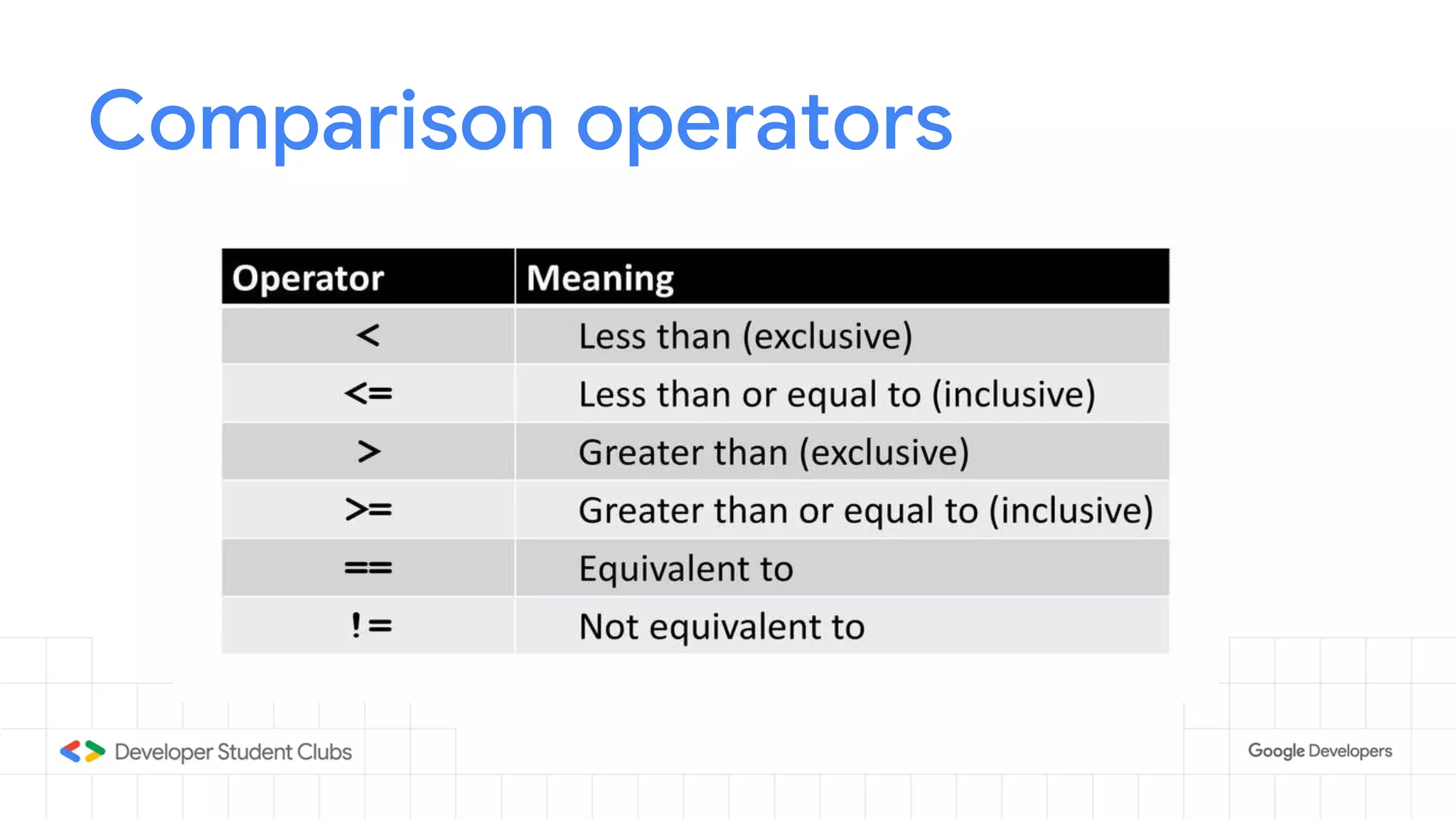
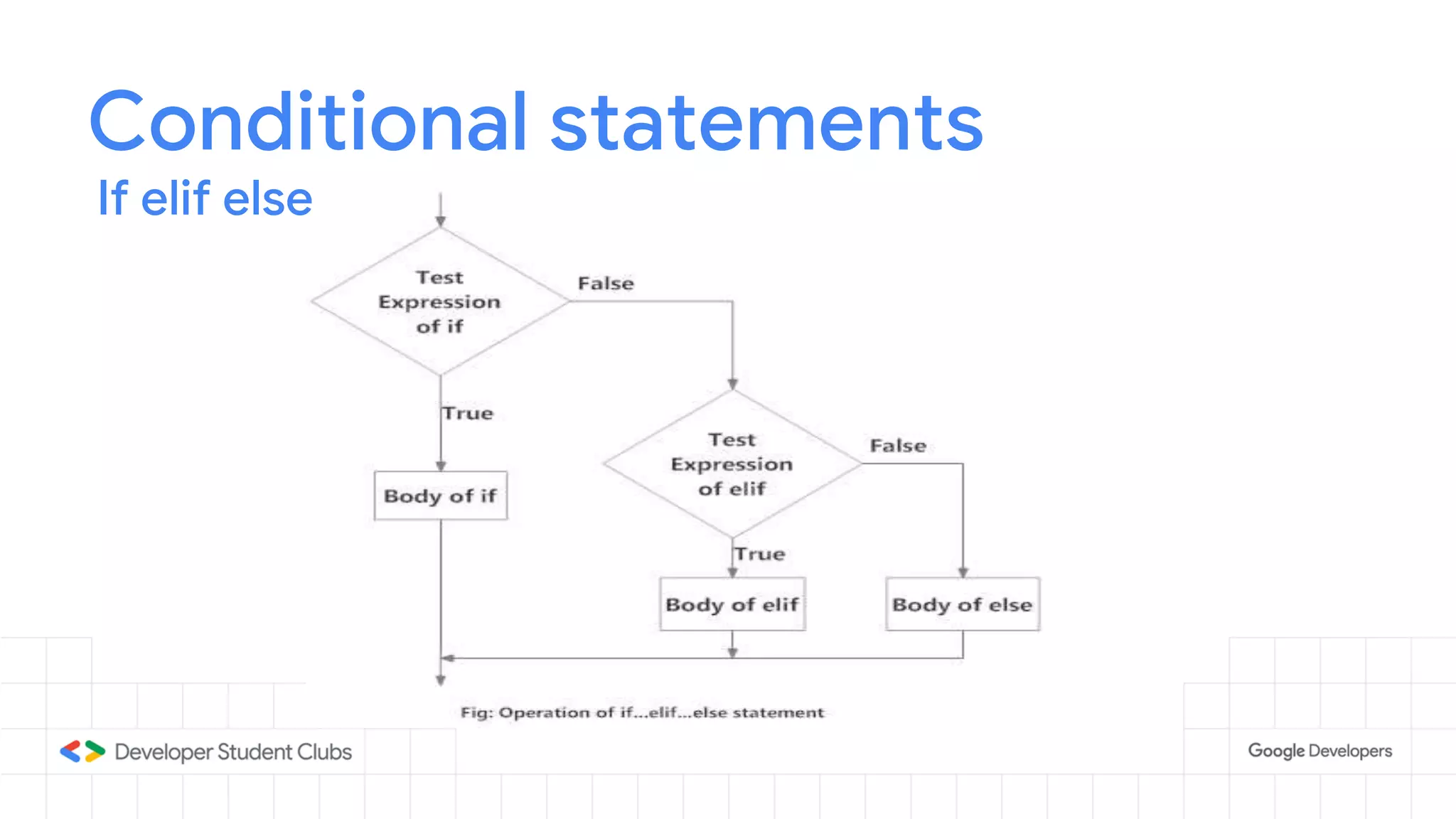
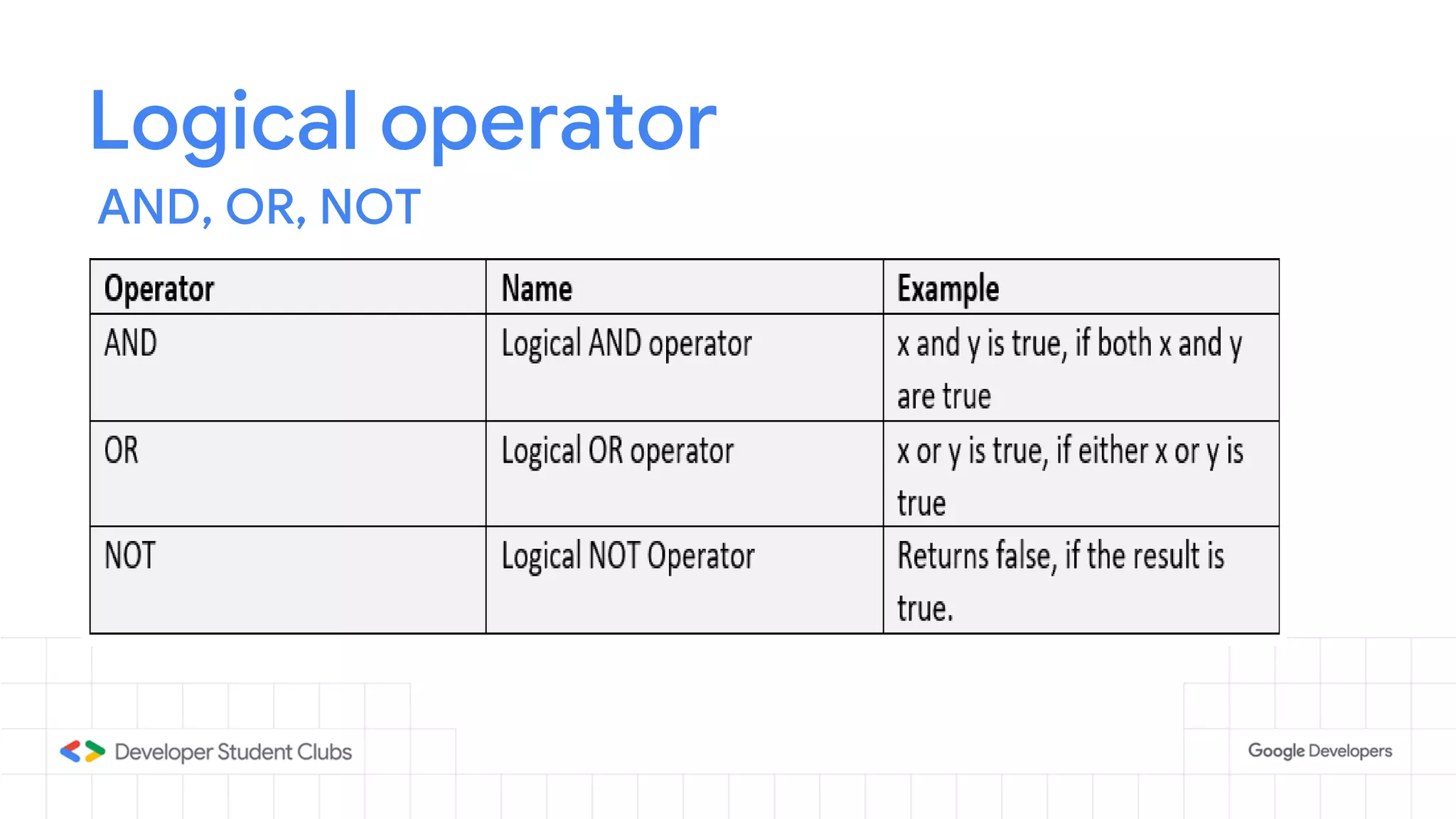
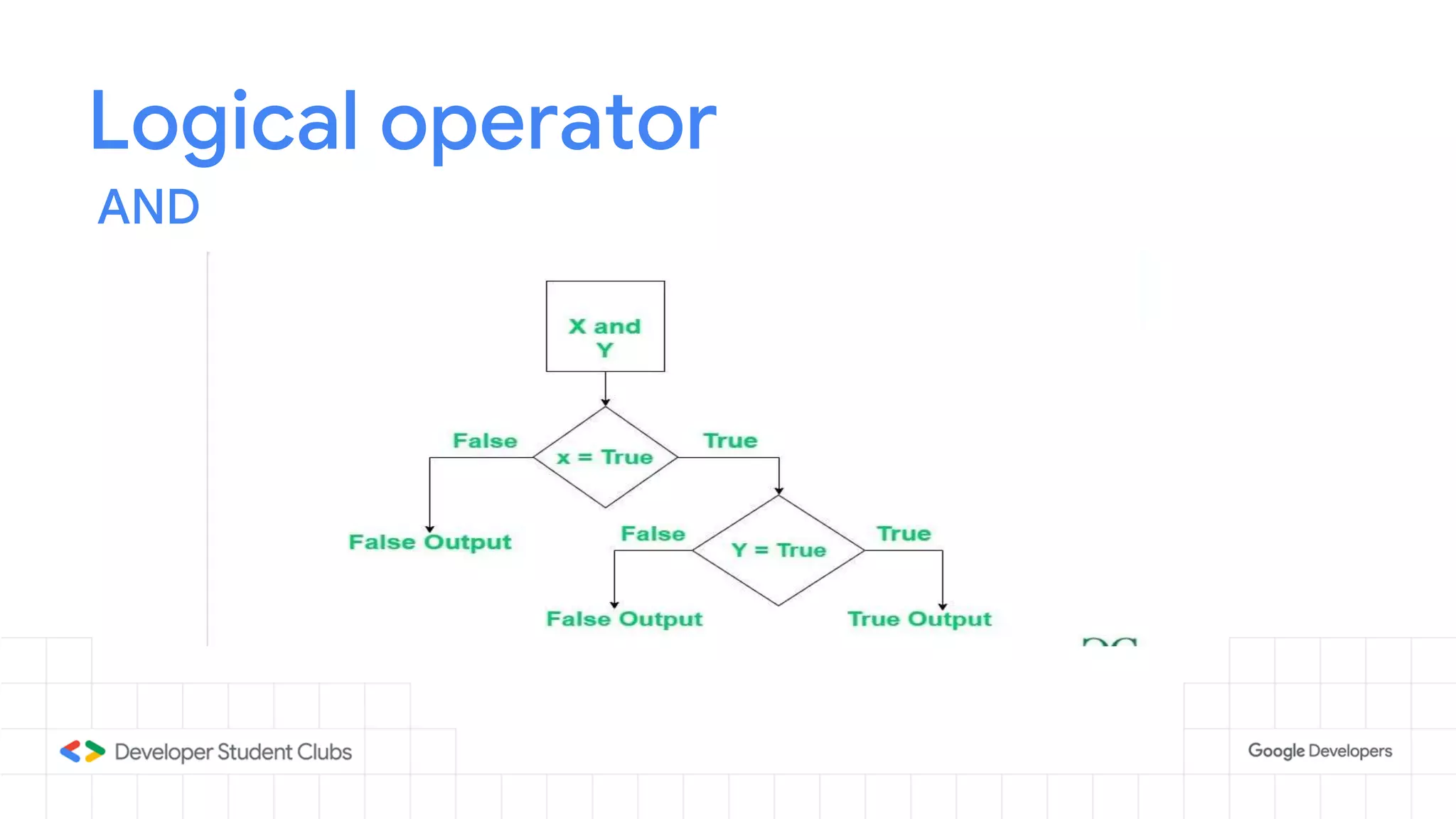
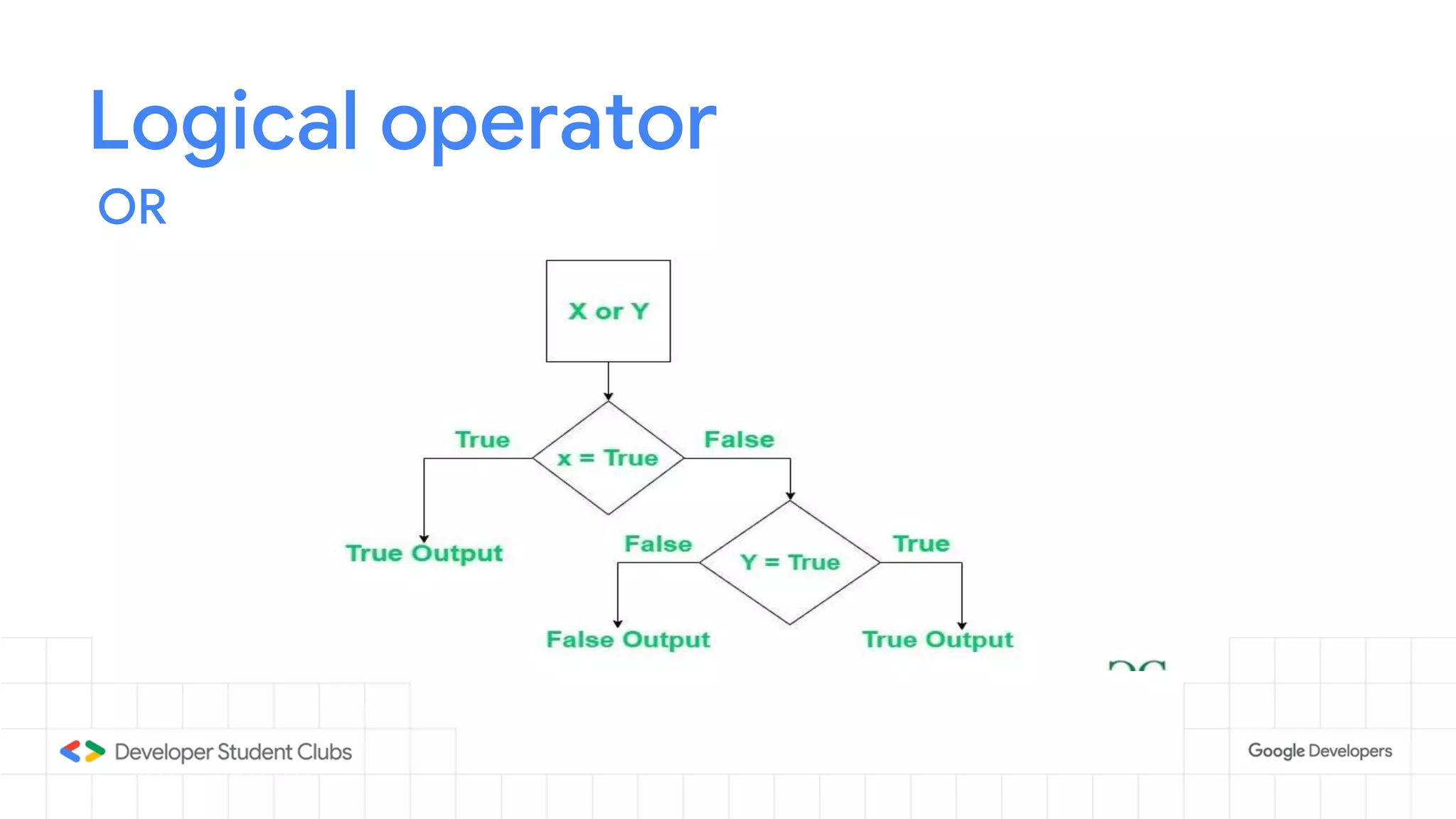
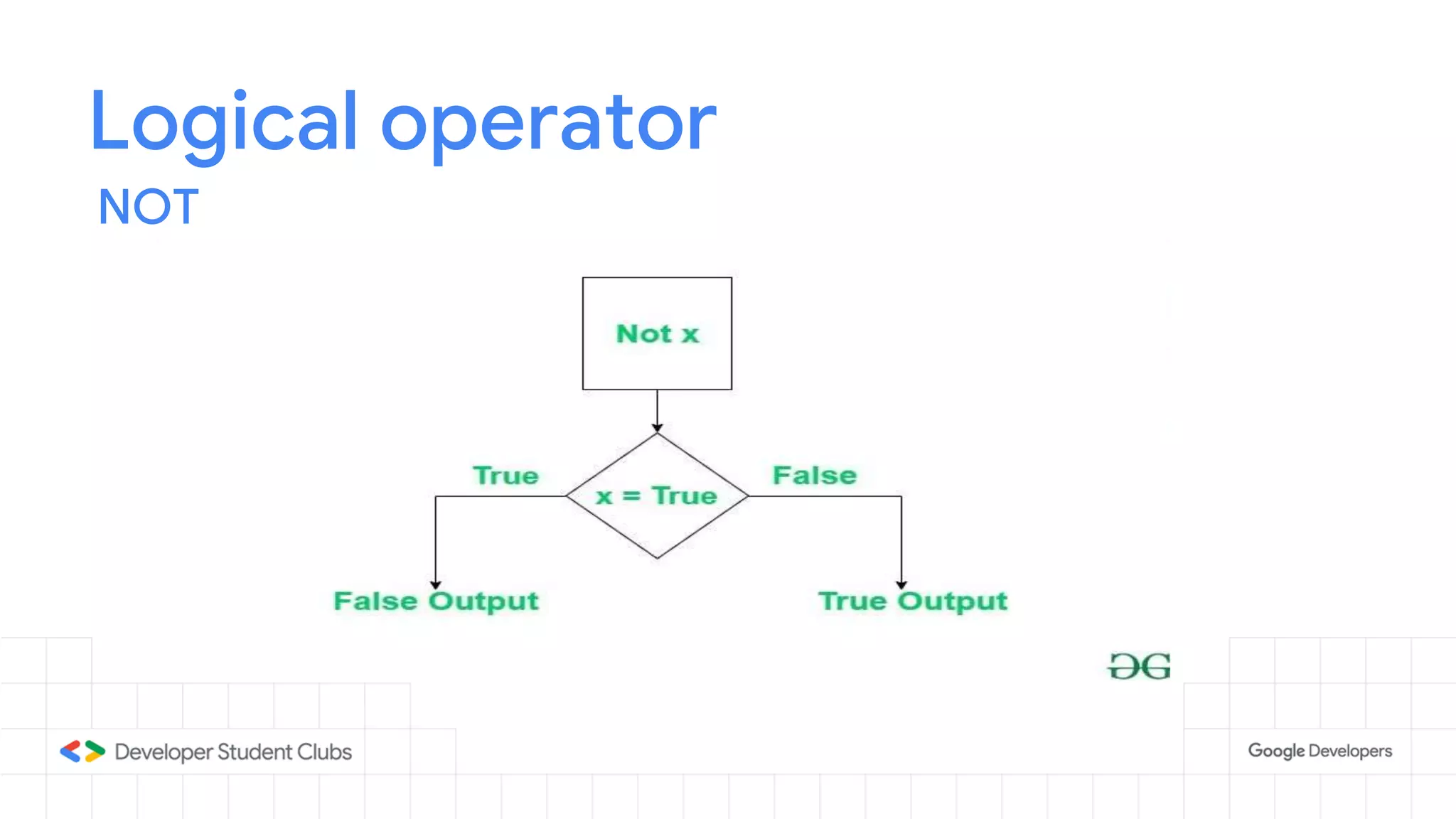
This document provides an introduction to the Python programming language. It discusses that Python was created in 1991 and is known for being easy to read and write. Key features of Python include being open source, object-oriented, and high-level. Popular applications of Python include web development, machine learning, data science, and desktop applications. Common Python IDEs and software written in Python are also listed. The document then covers basic Python programming concepts like variables, data types, operators, control flow statements, functions, and loops.