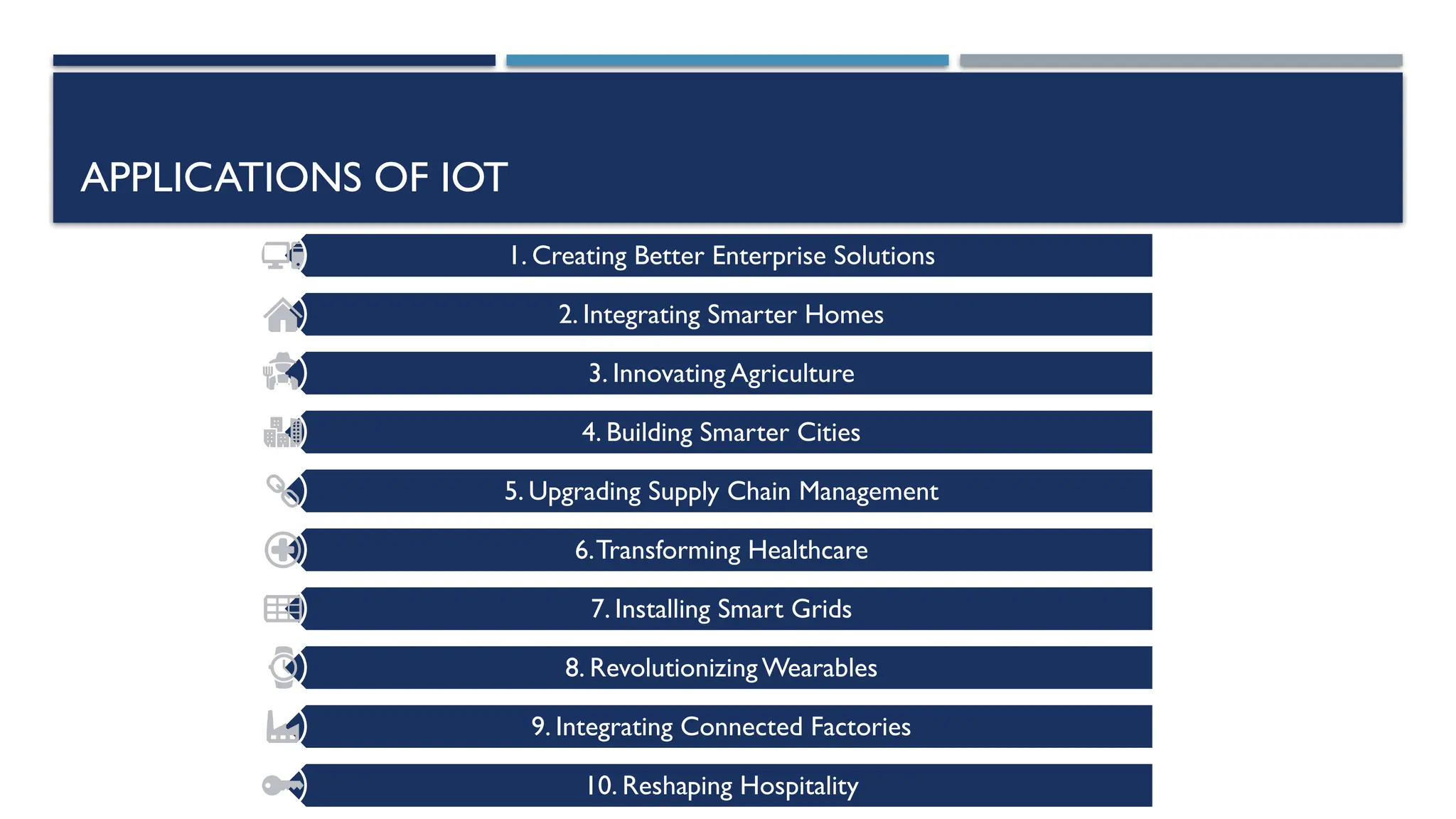
The Internet of Things (IoT) encompasses physical objects equipped with sensors and software that connect and exchange data over networks, enabling innovations in various industries such as healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing. Historically rooted in the late 1960s, IoT has evolved significantly, gaining mainstream recognition in recent years, driven by technological advancements and investments from major companies like Google and Apple. Future expectations include increased connectivity and intelligence in devices, leading to smarter homes, transportation systems, and energy management solutions.