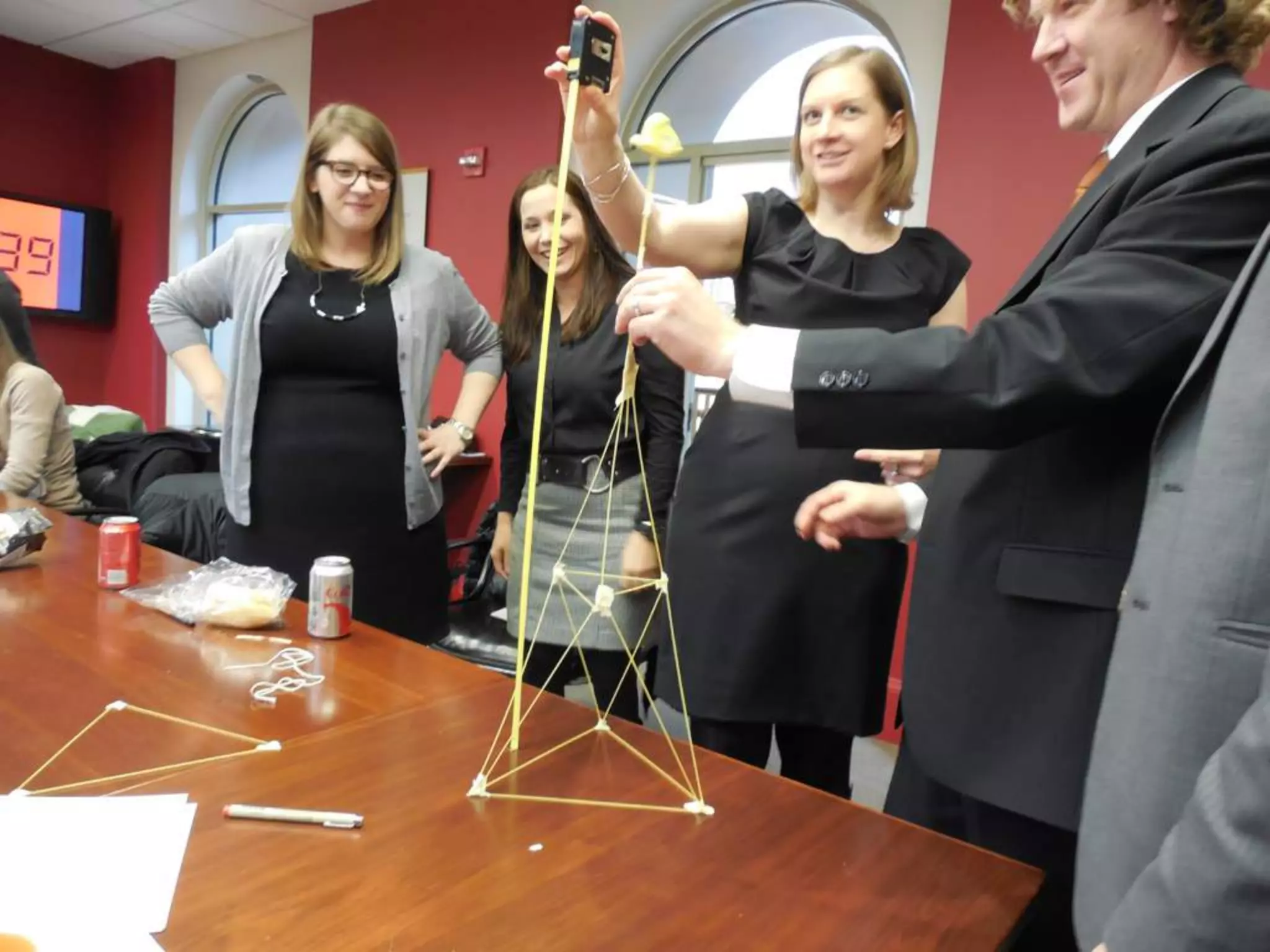
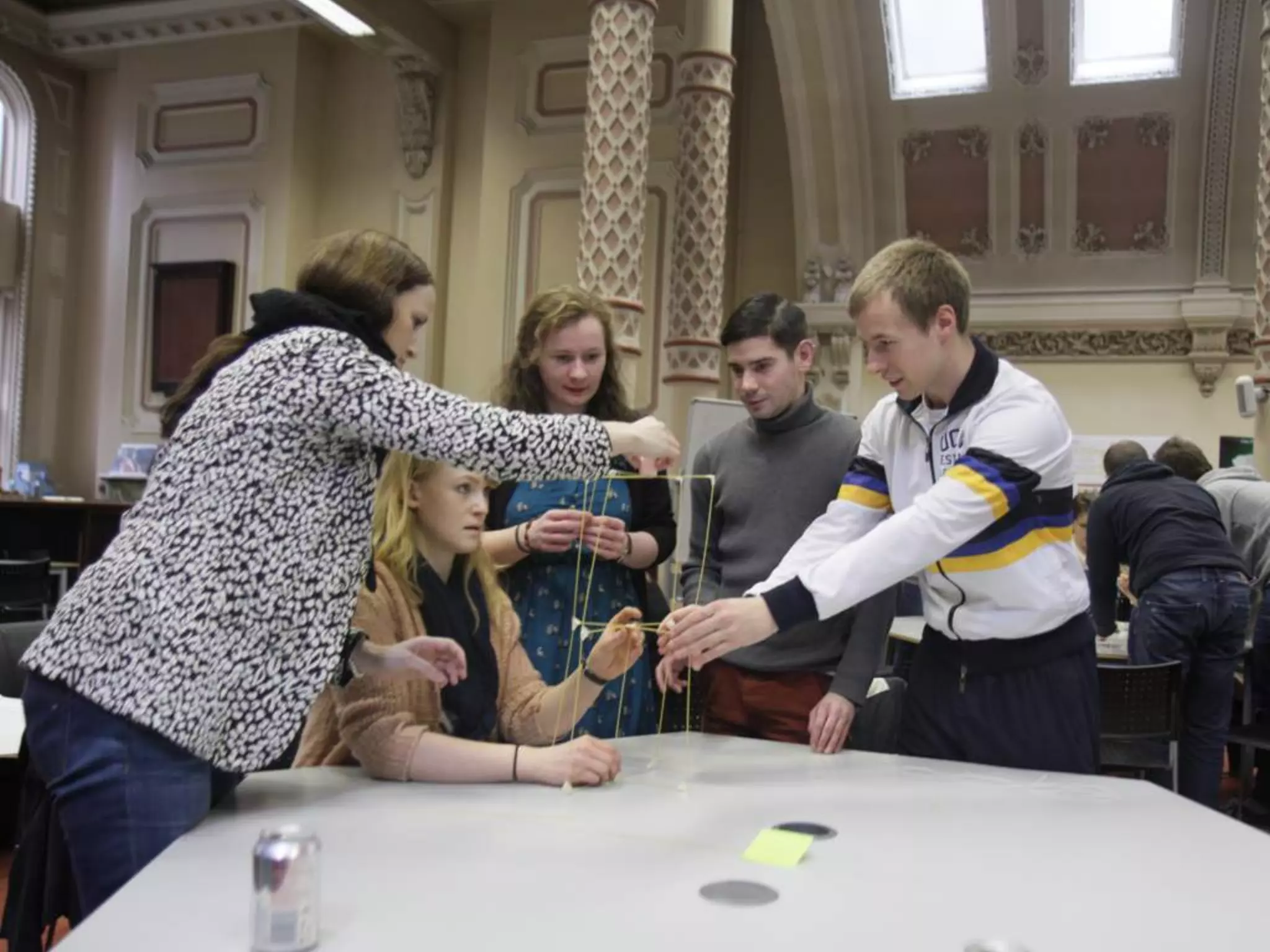
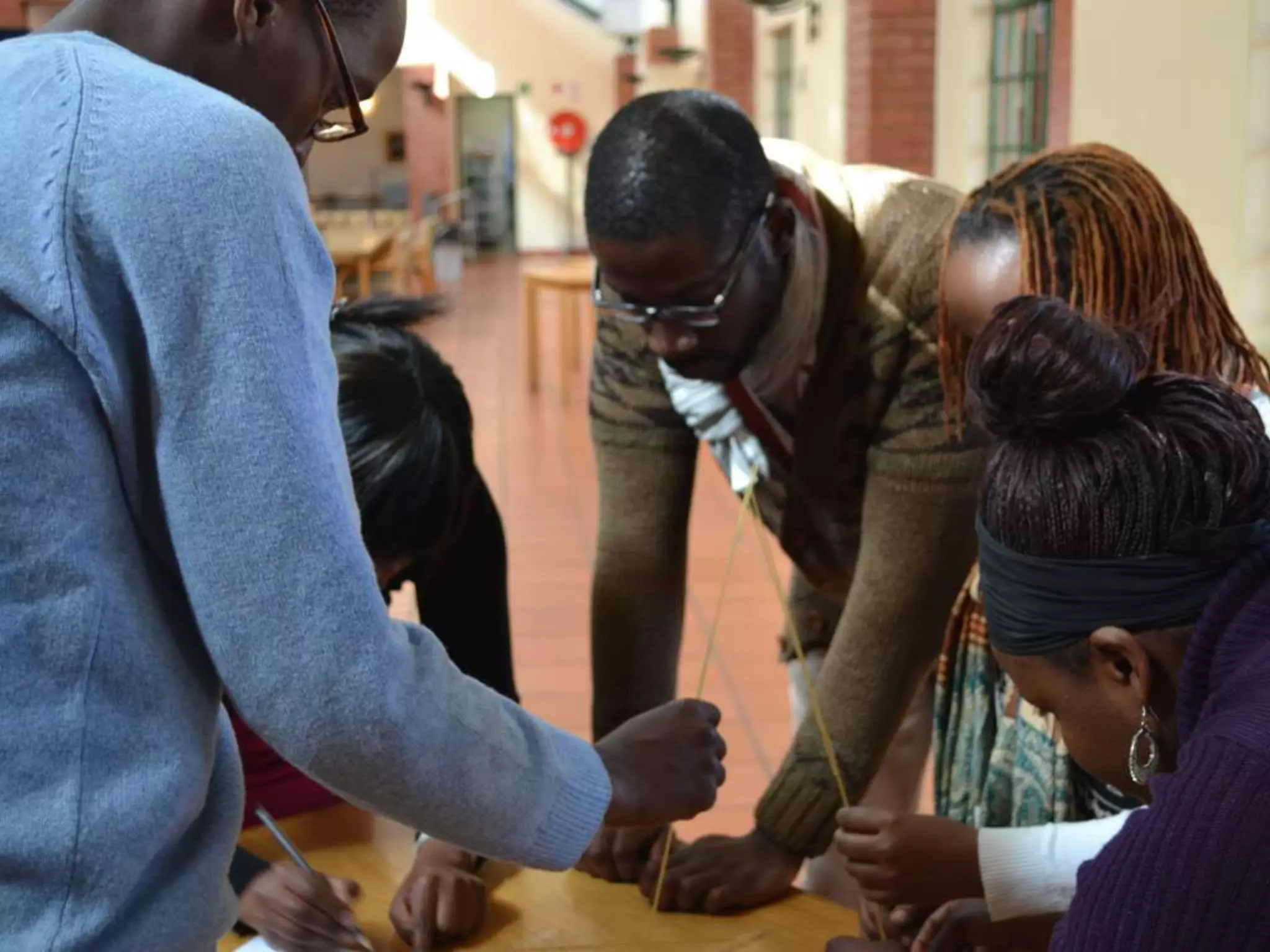
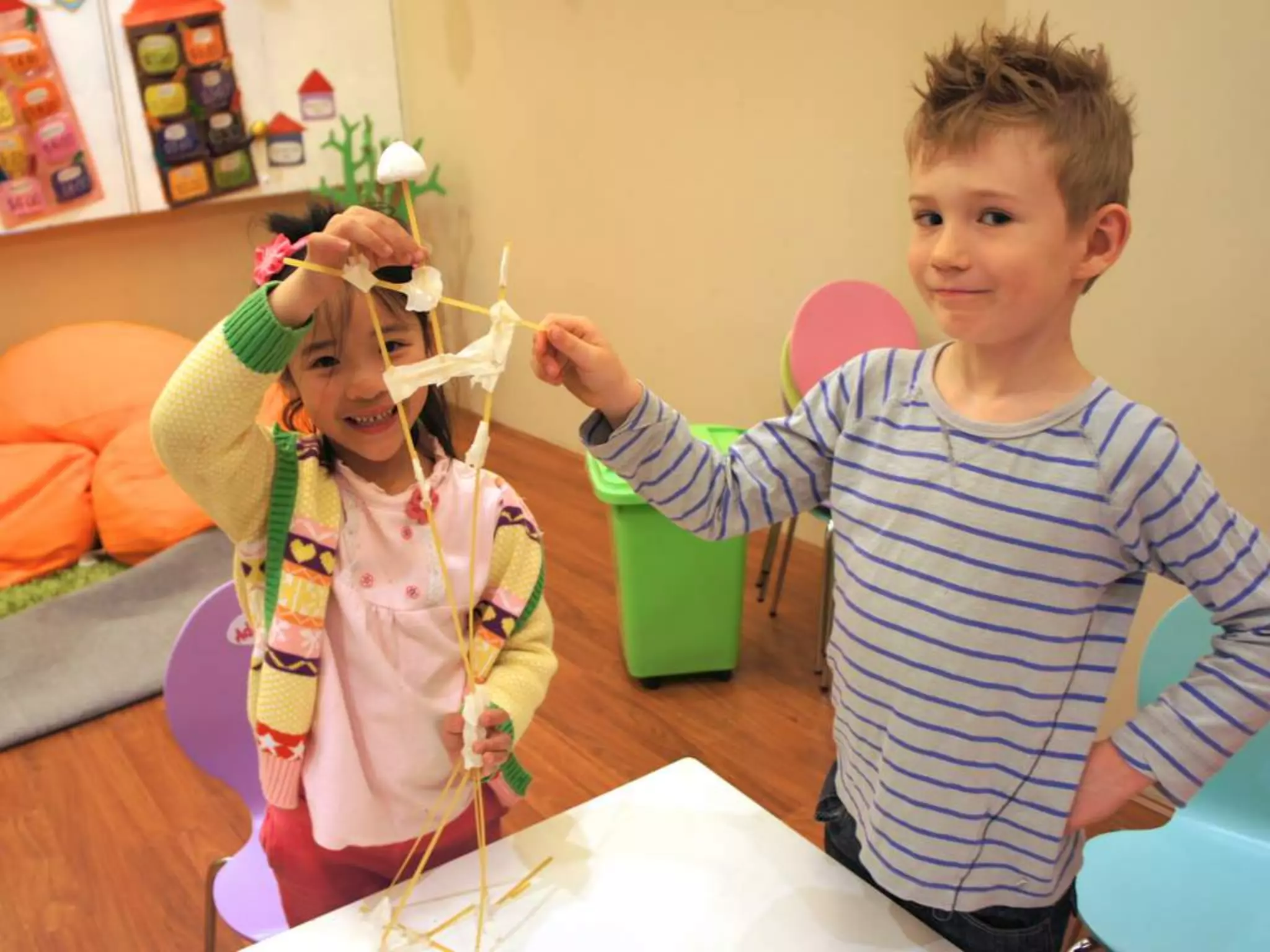
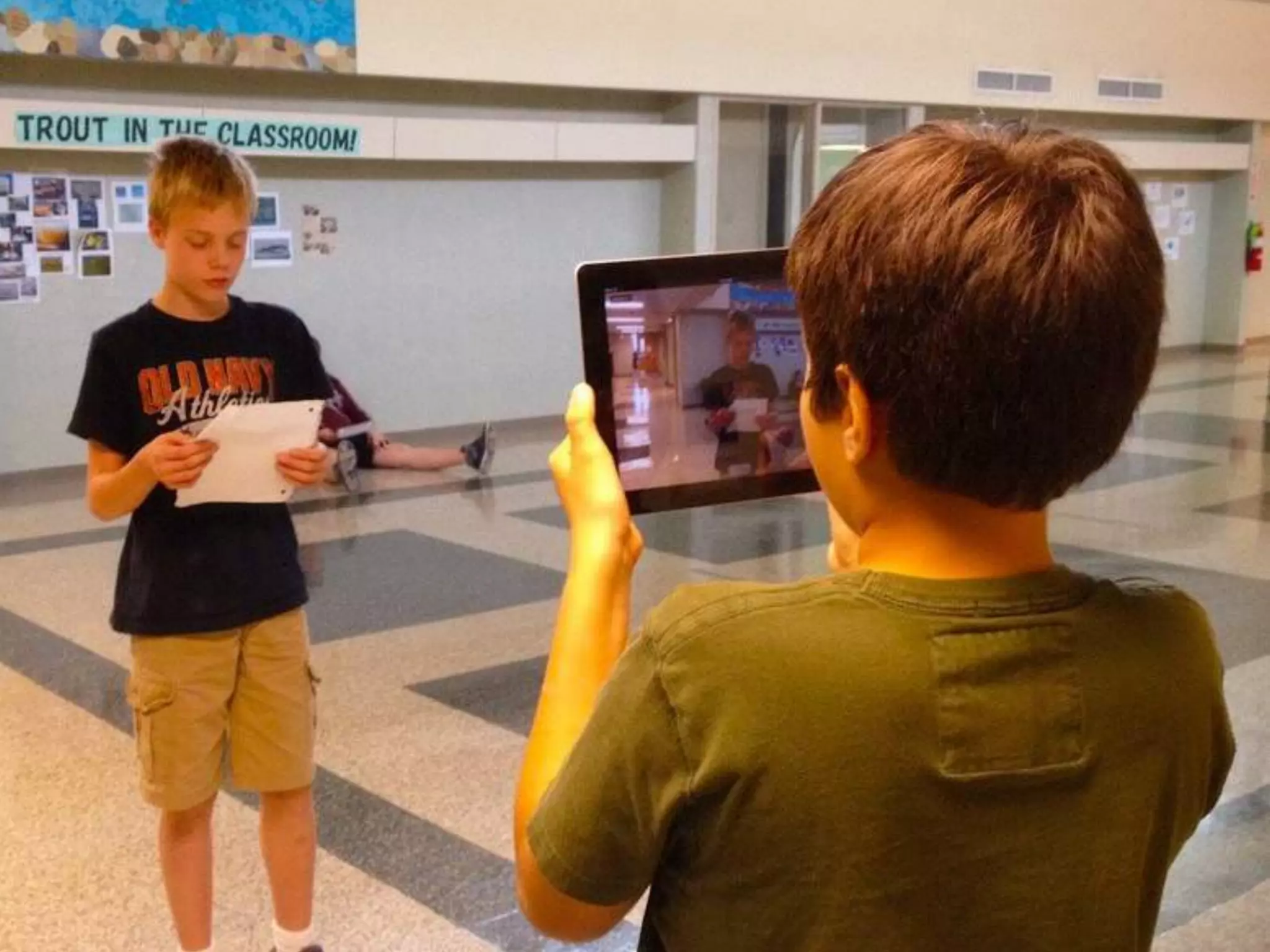
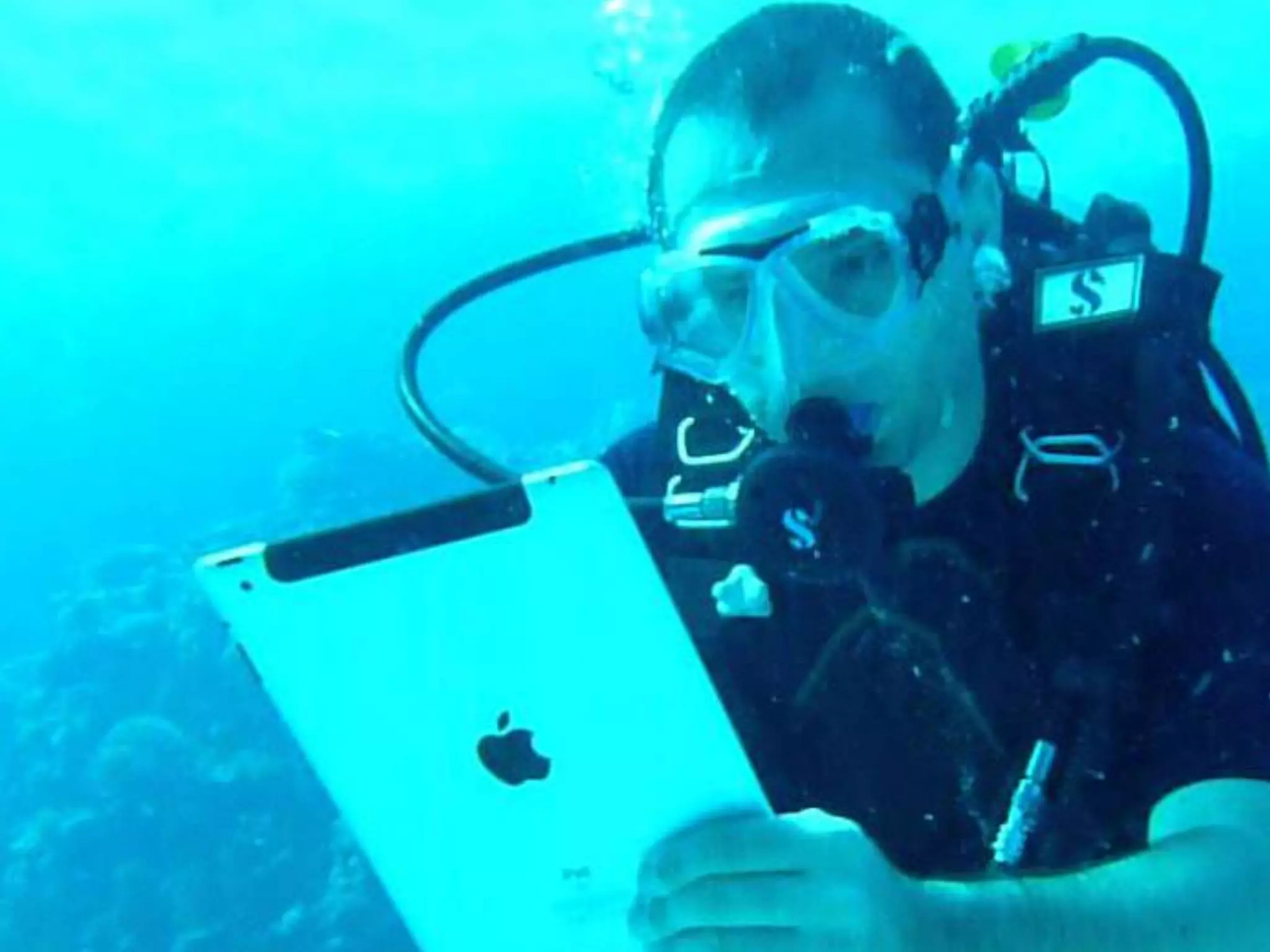
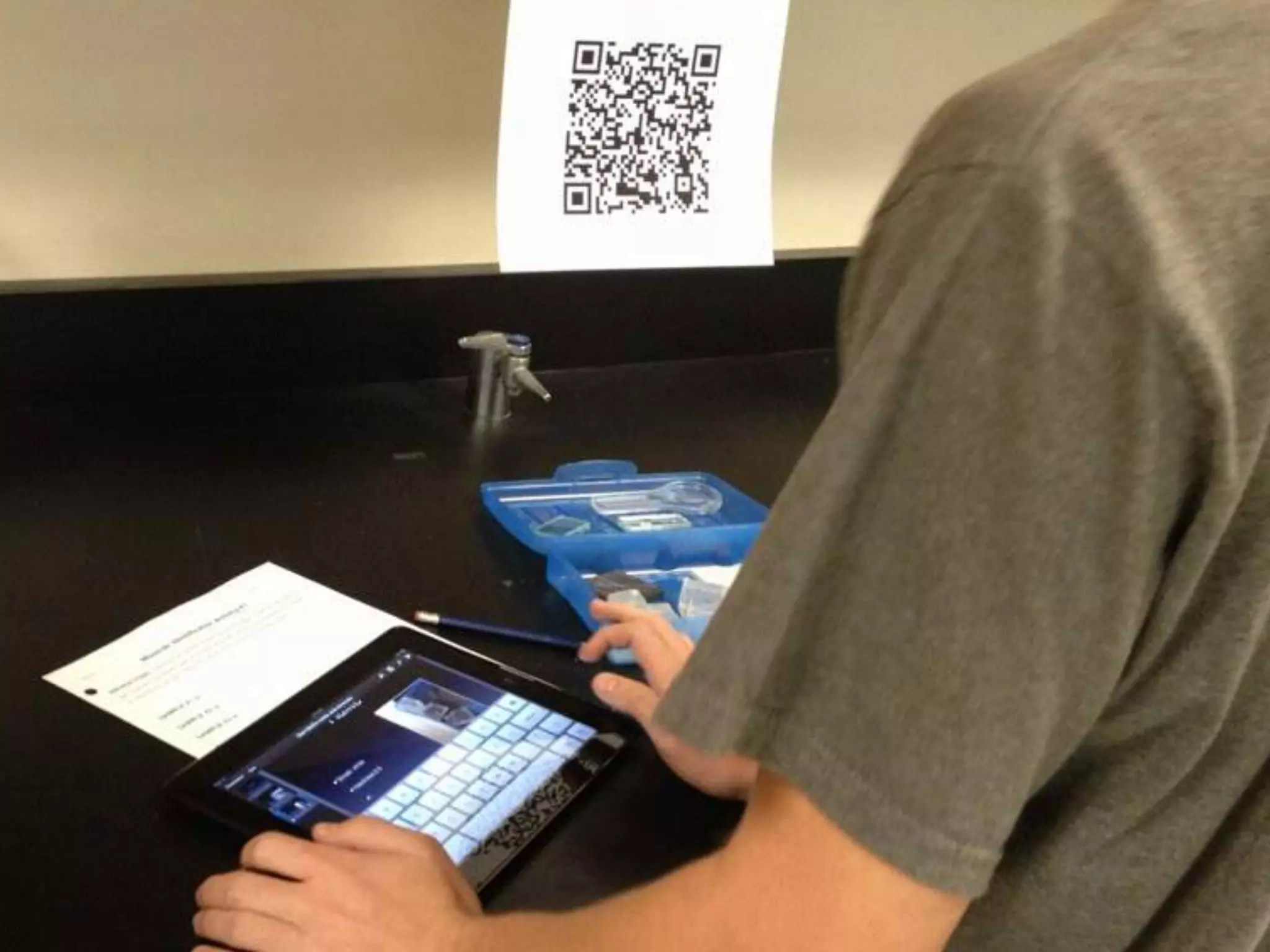
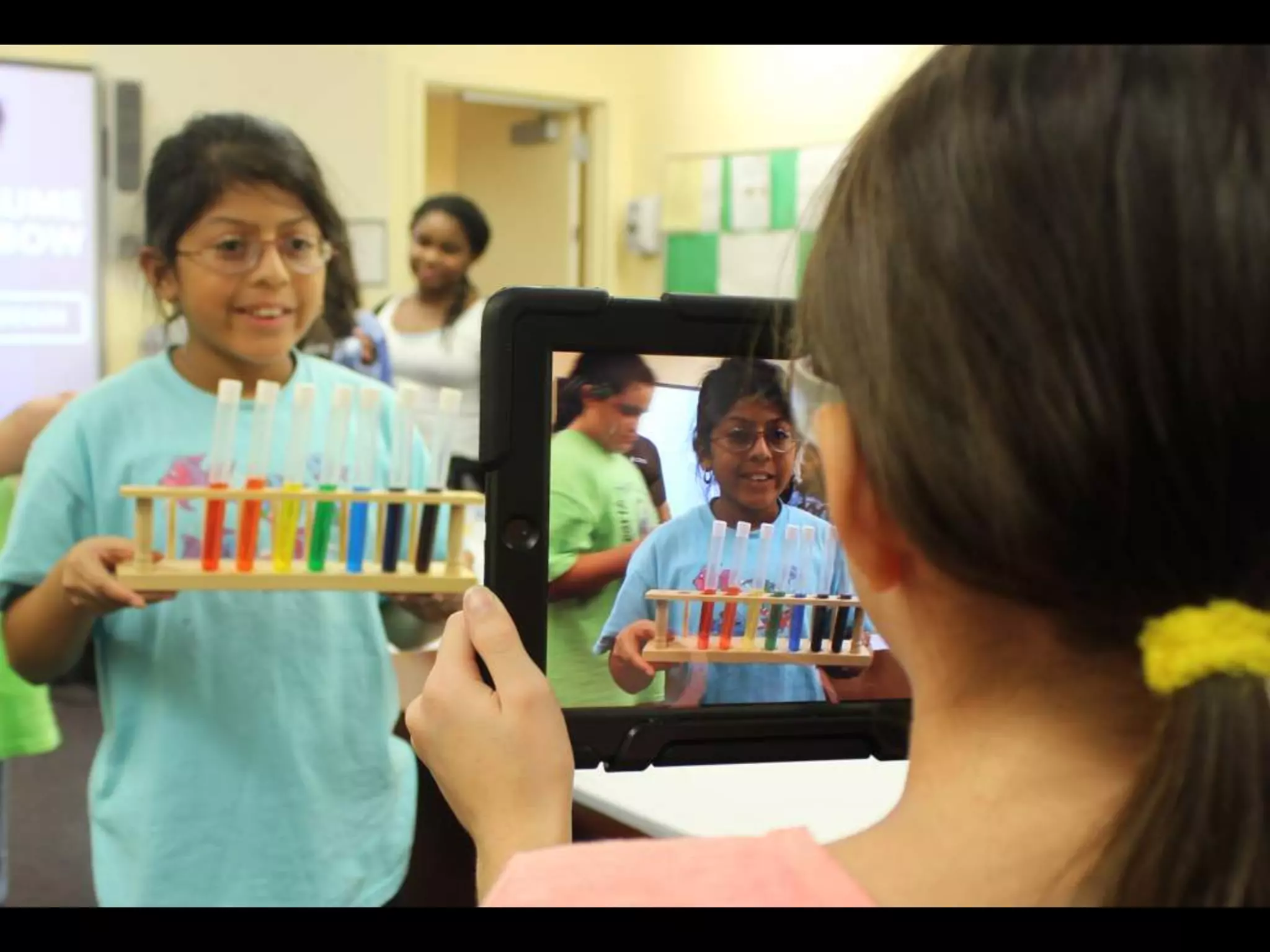
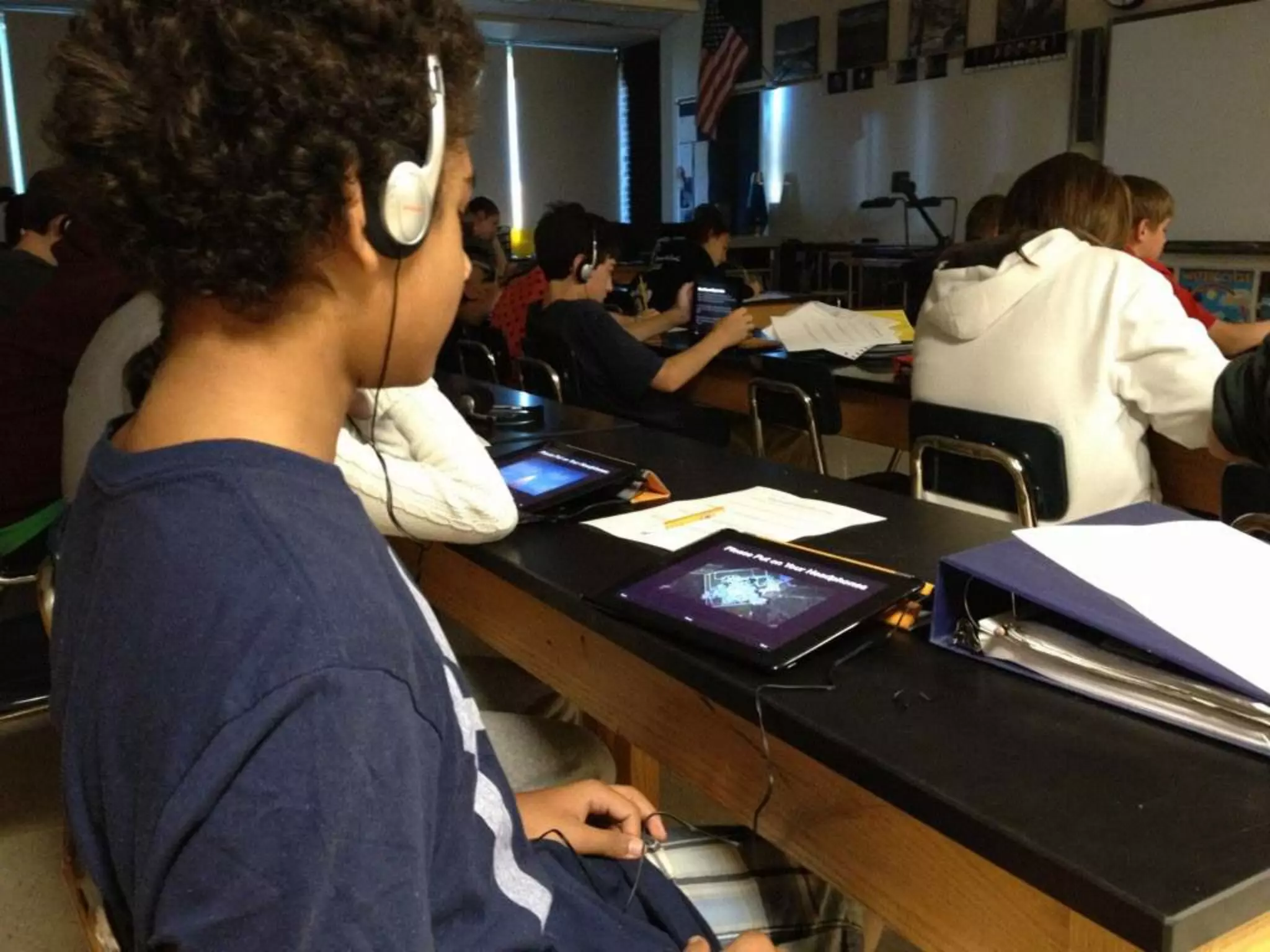
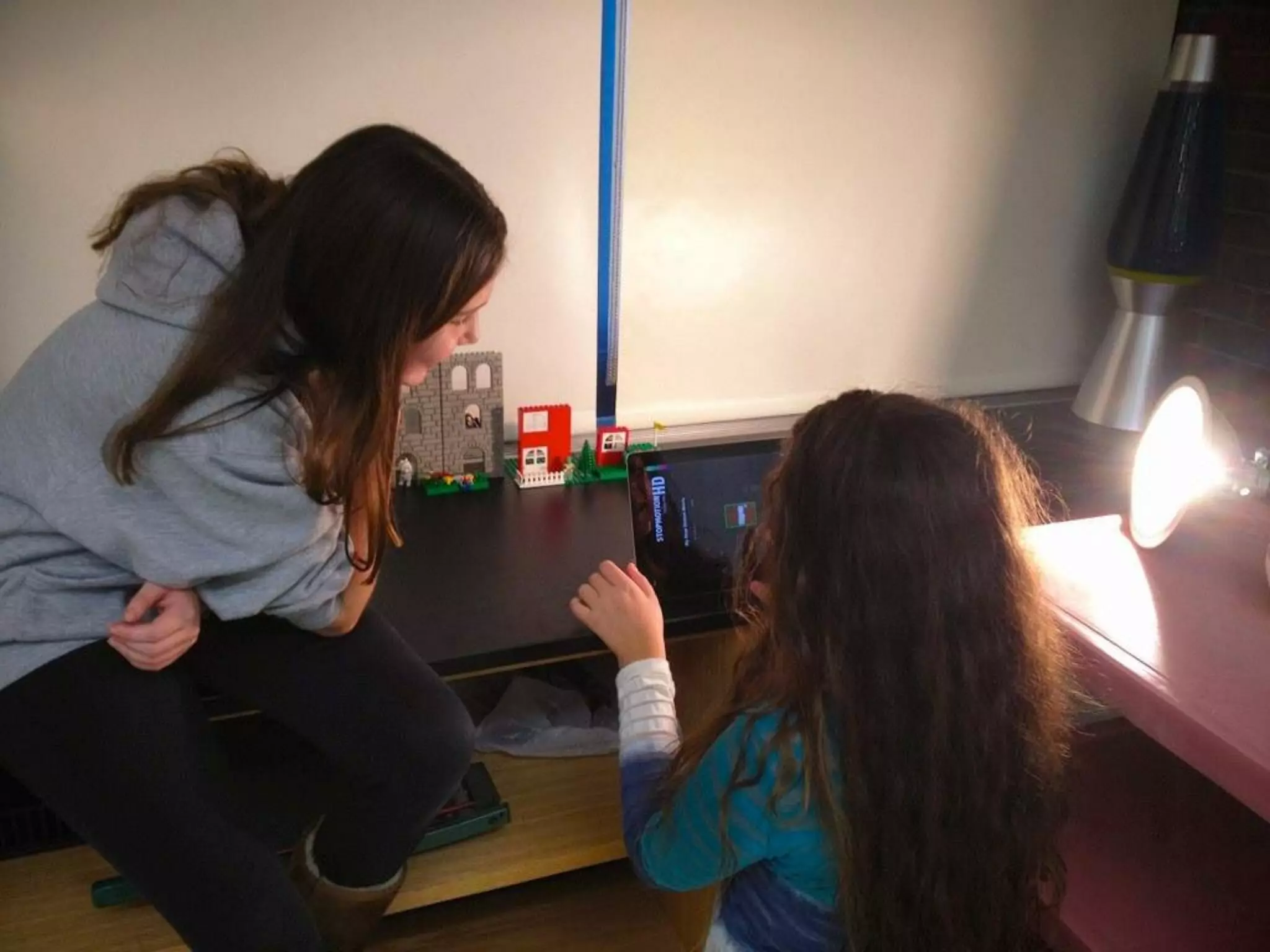
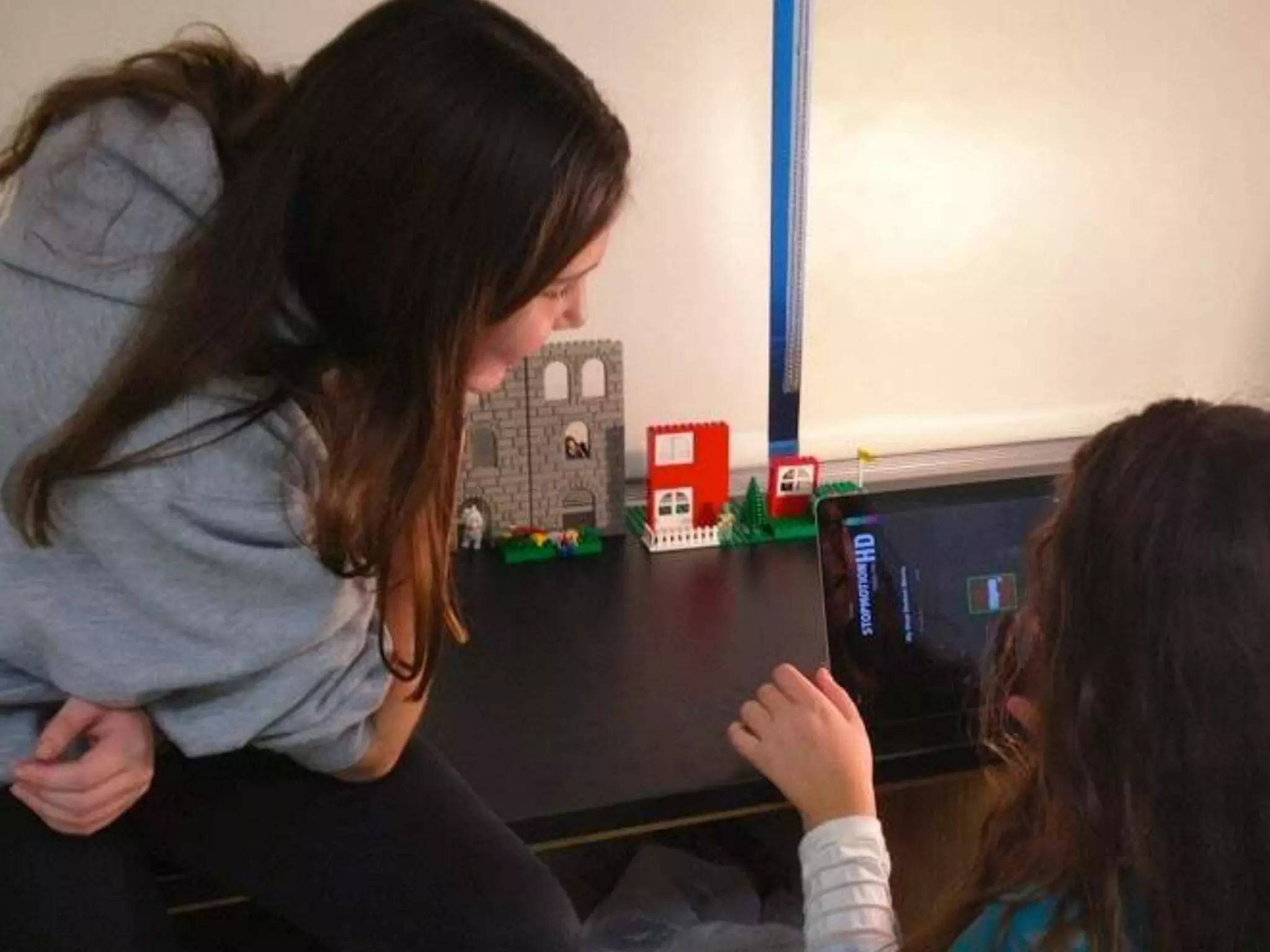
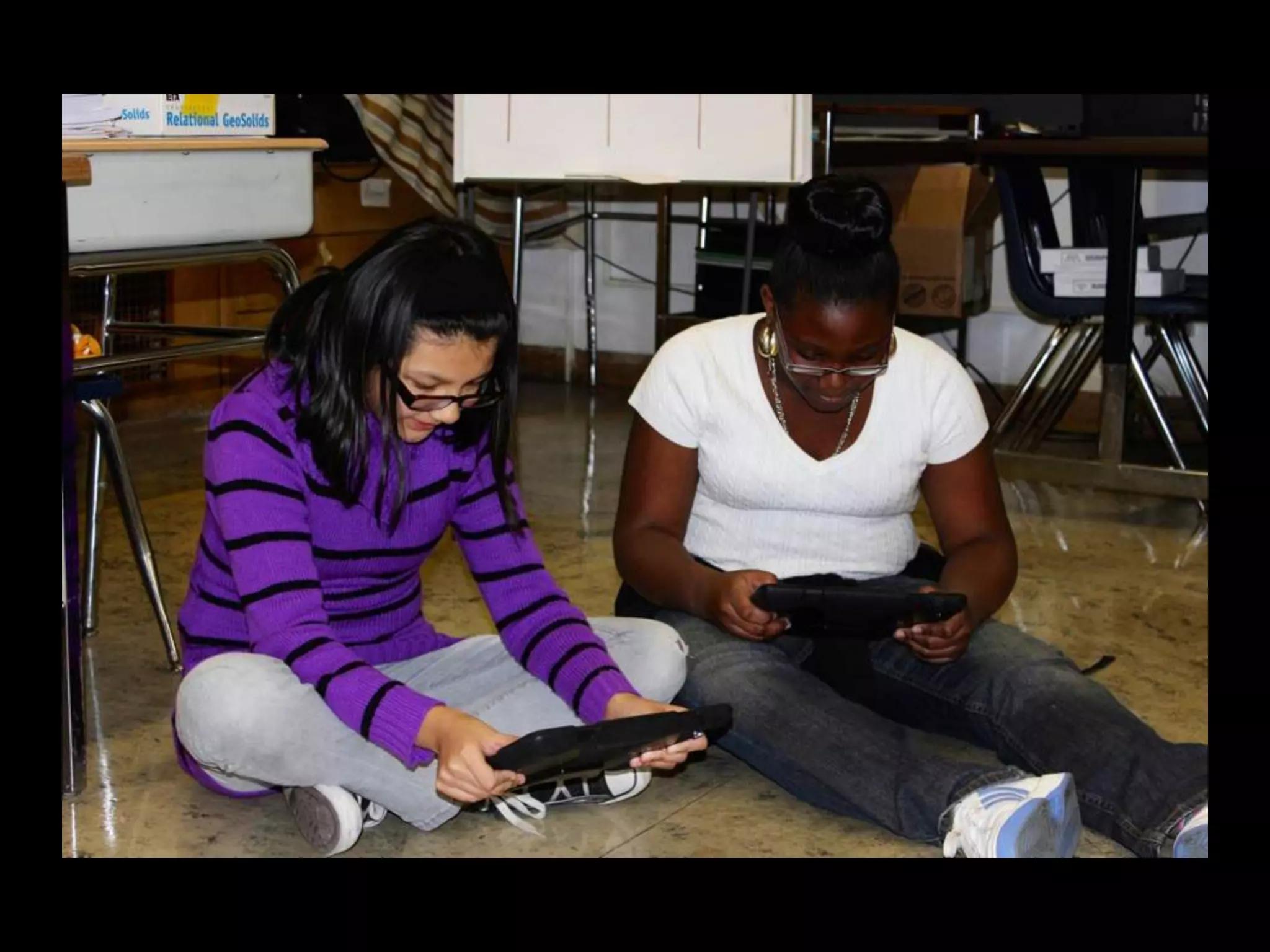
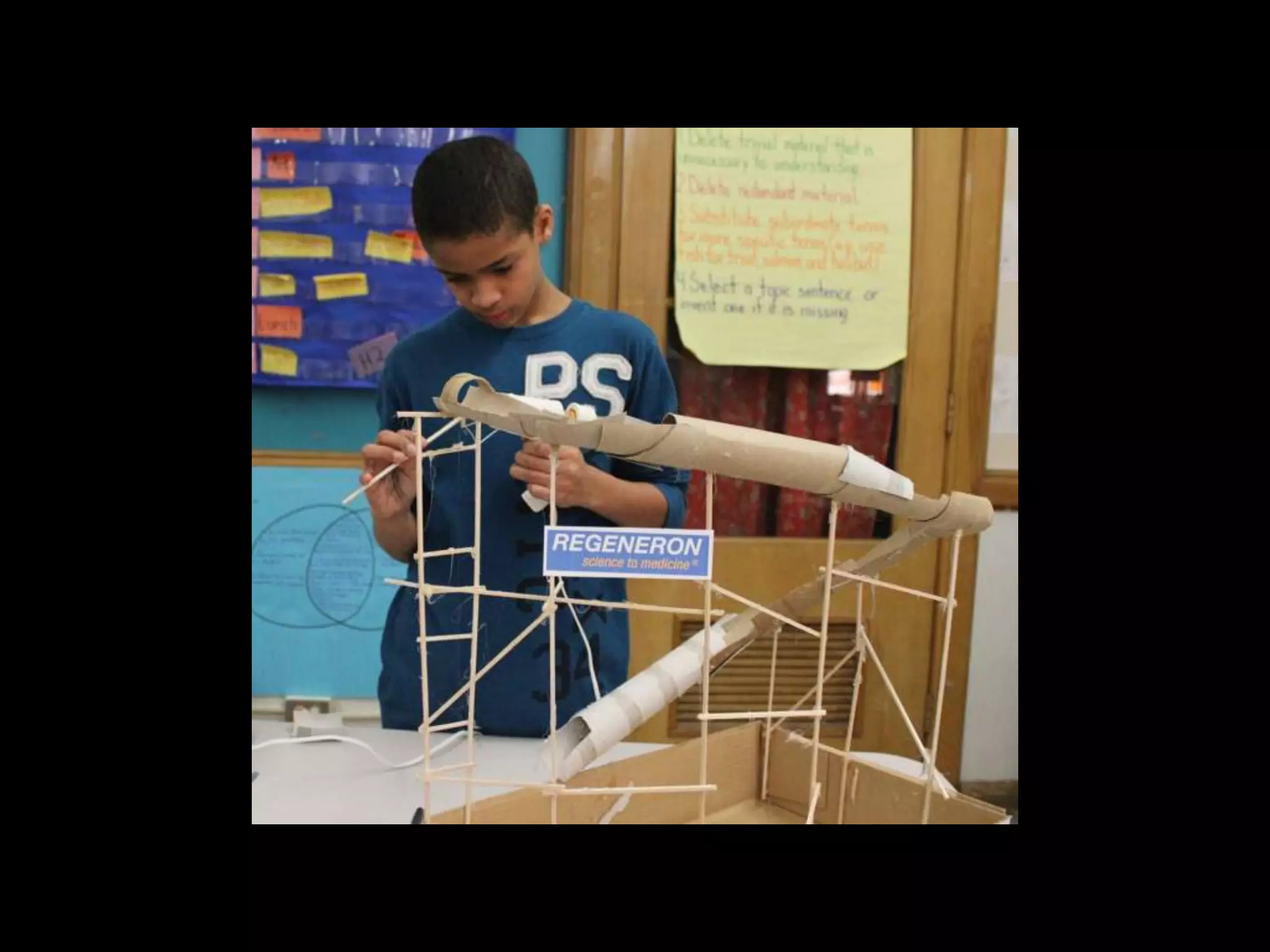
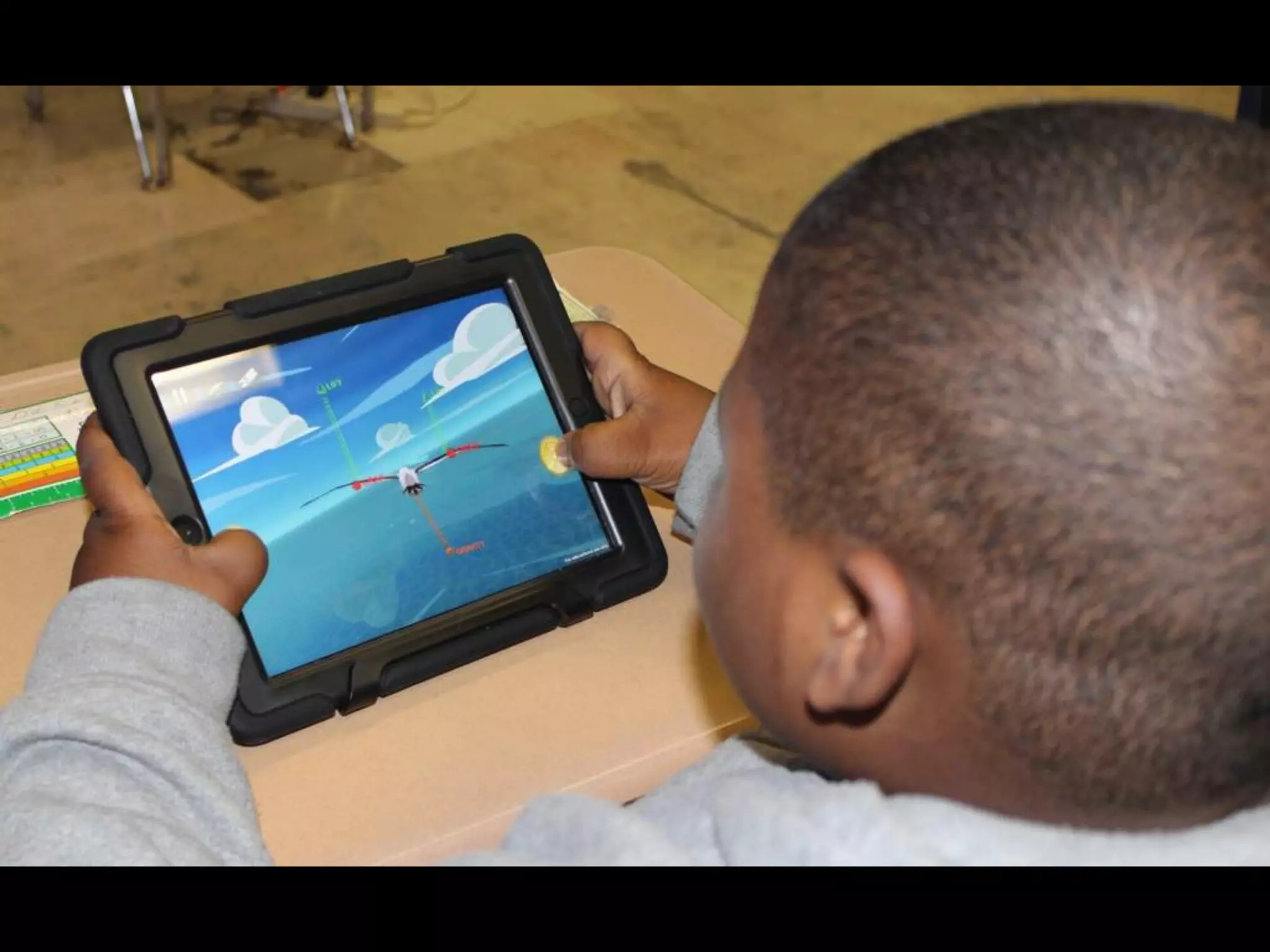
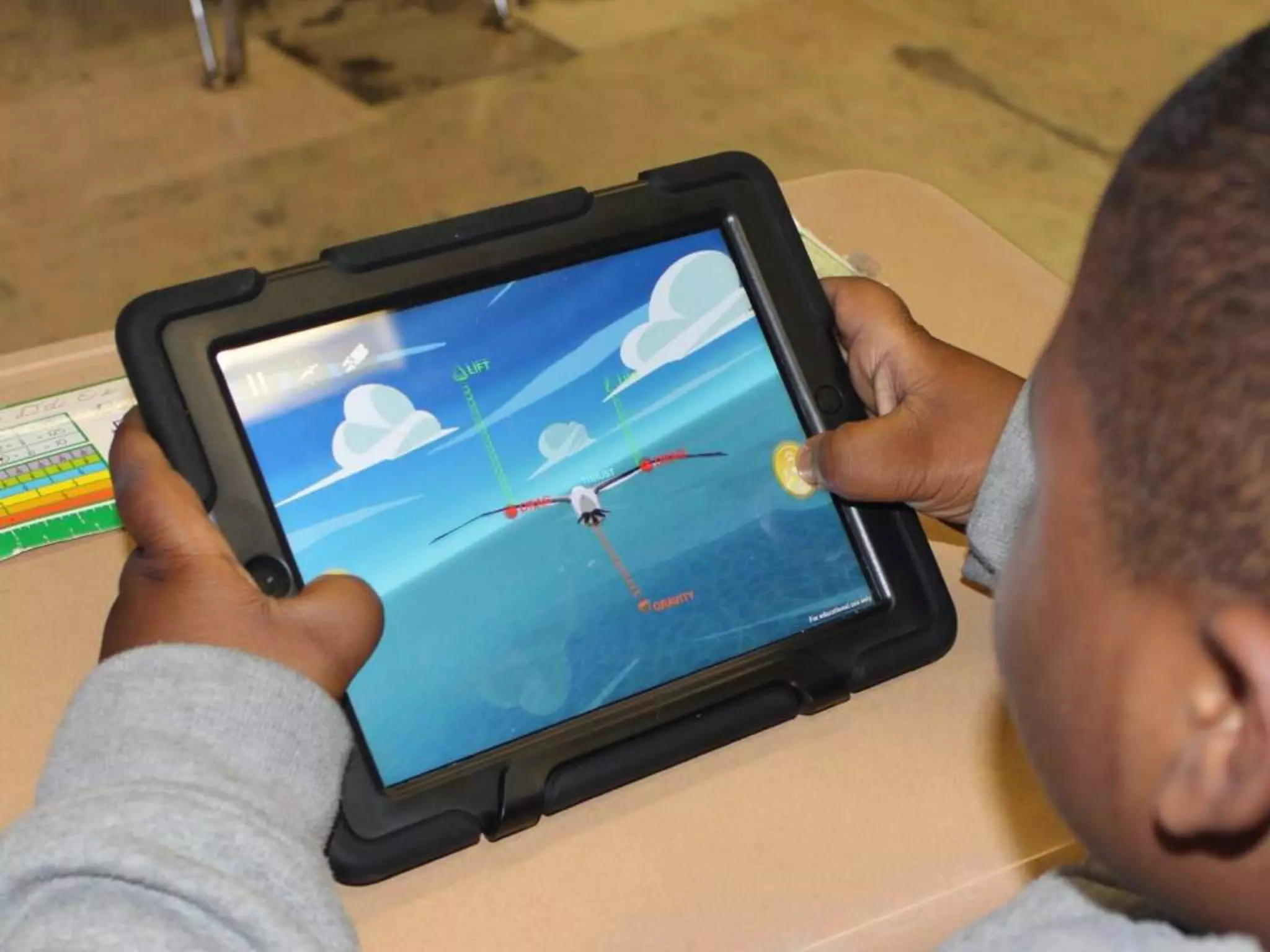
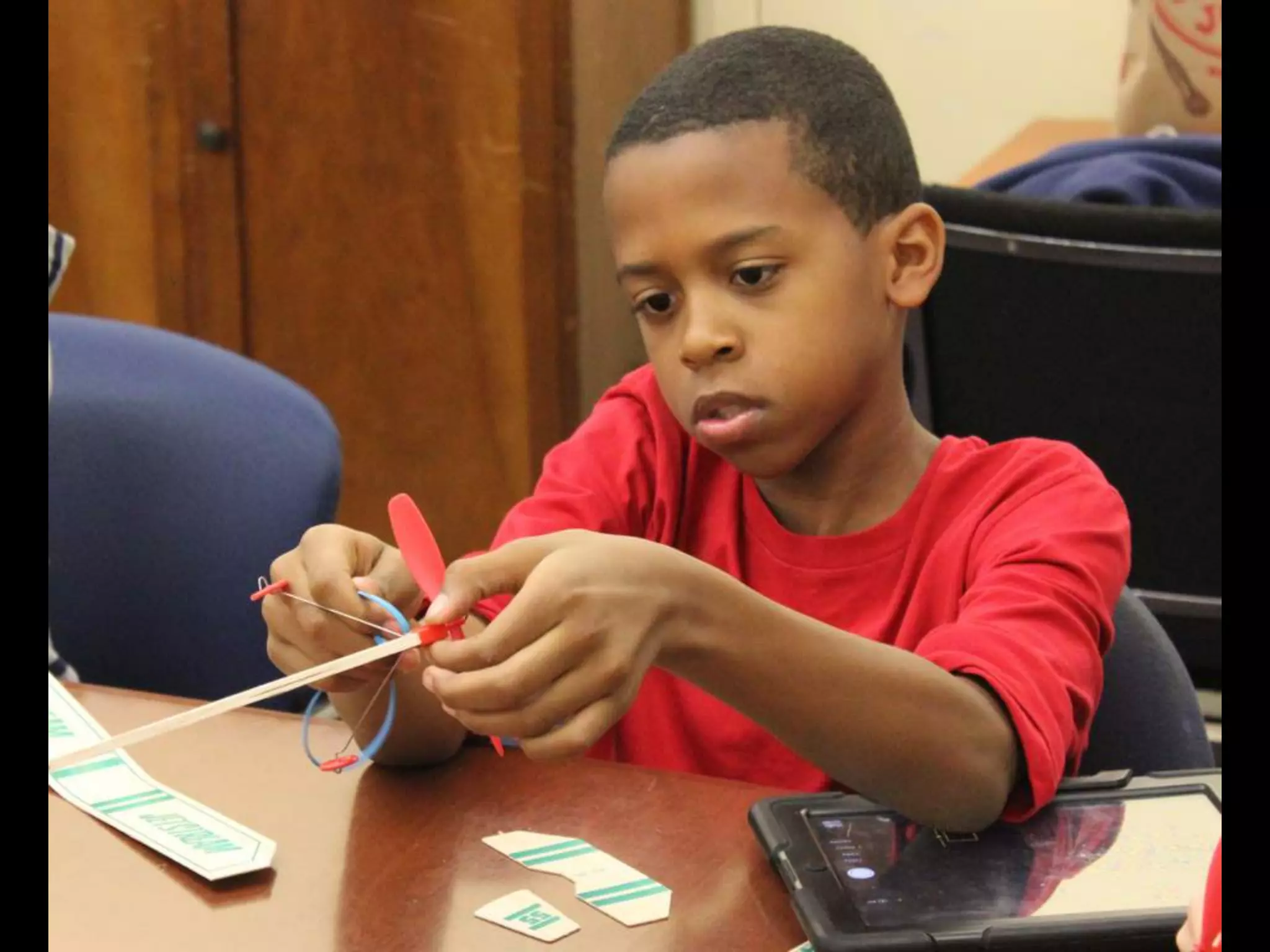
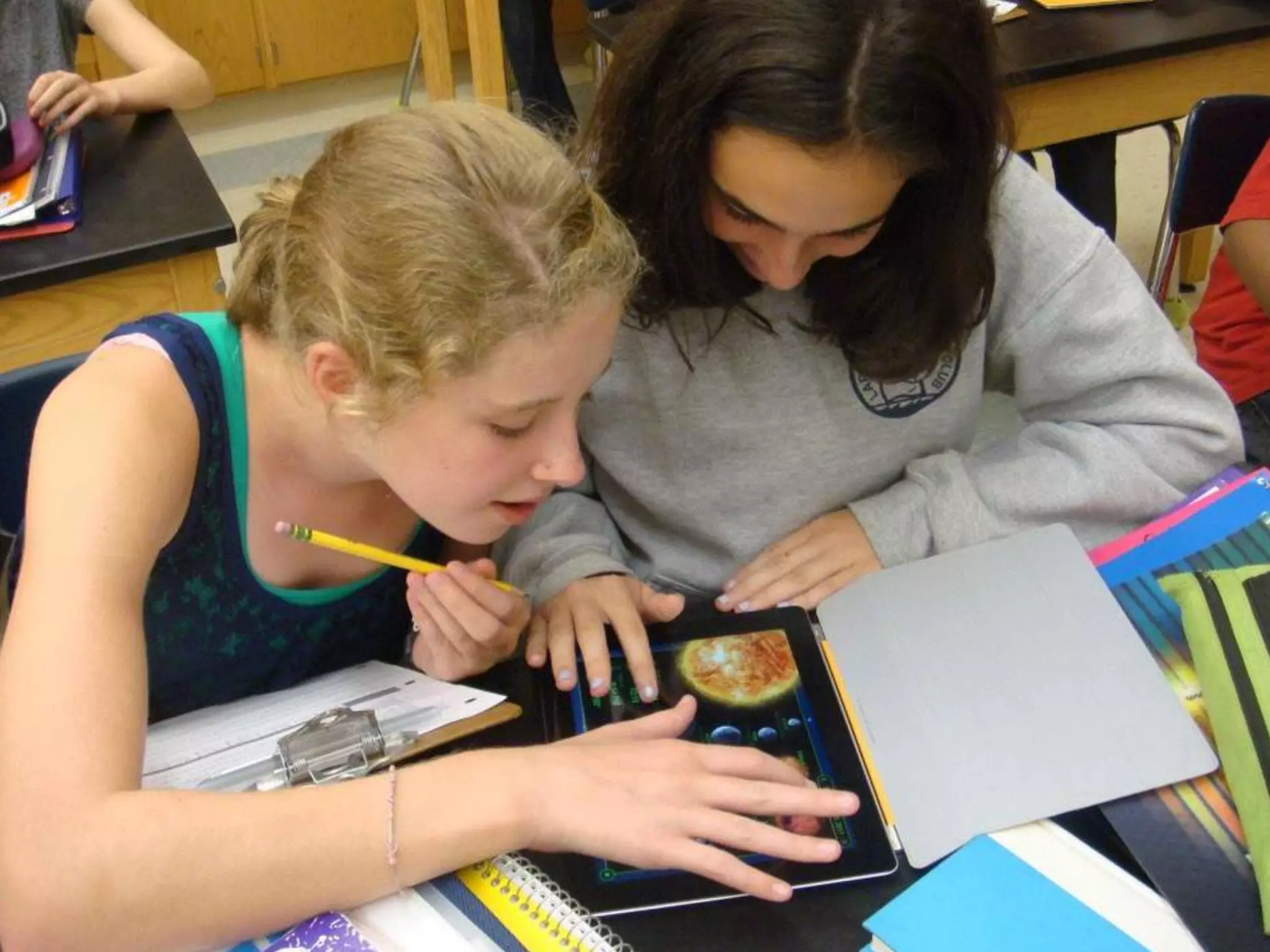
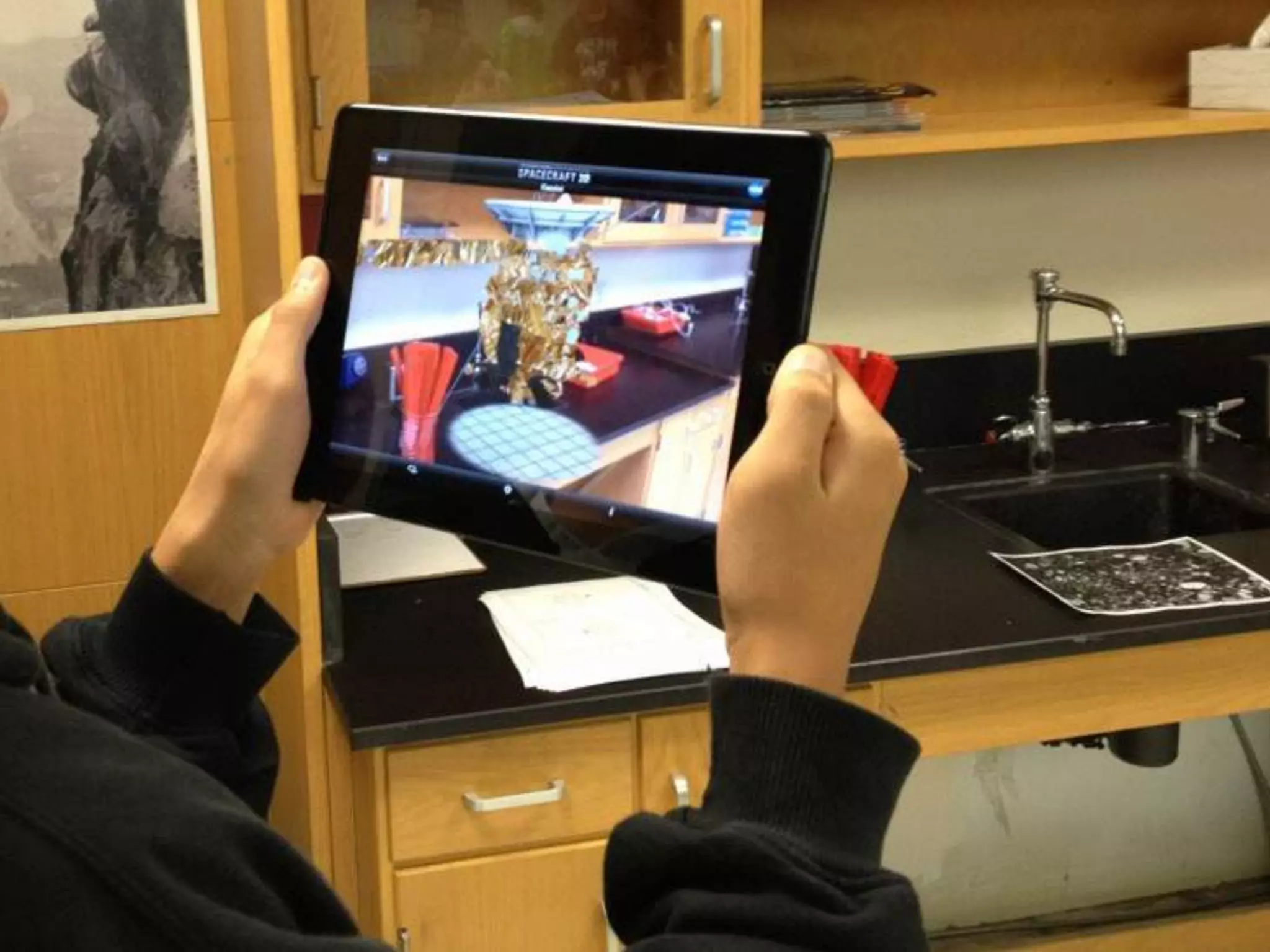
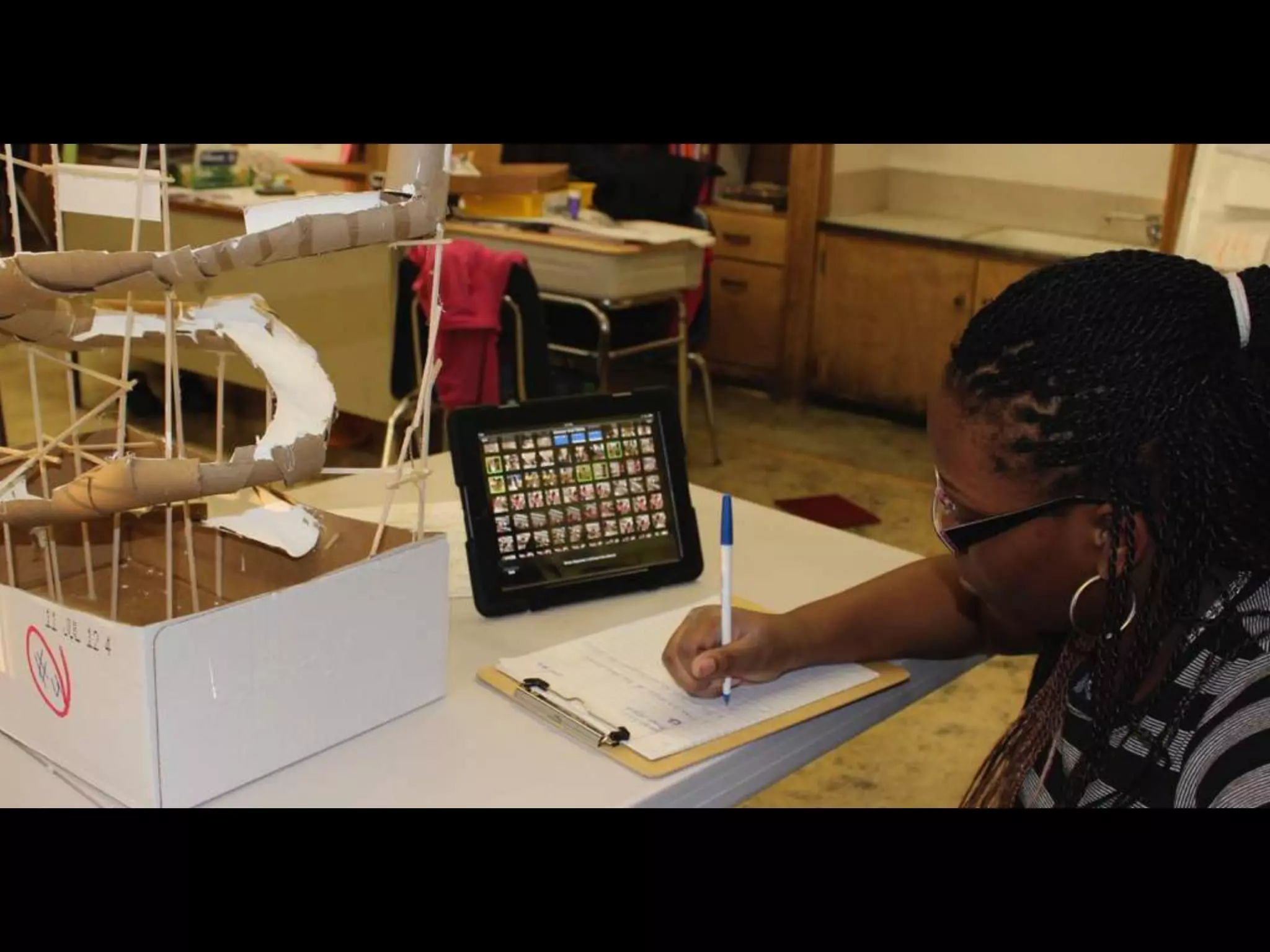
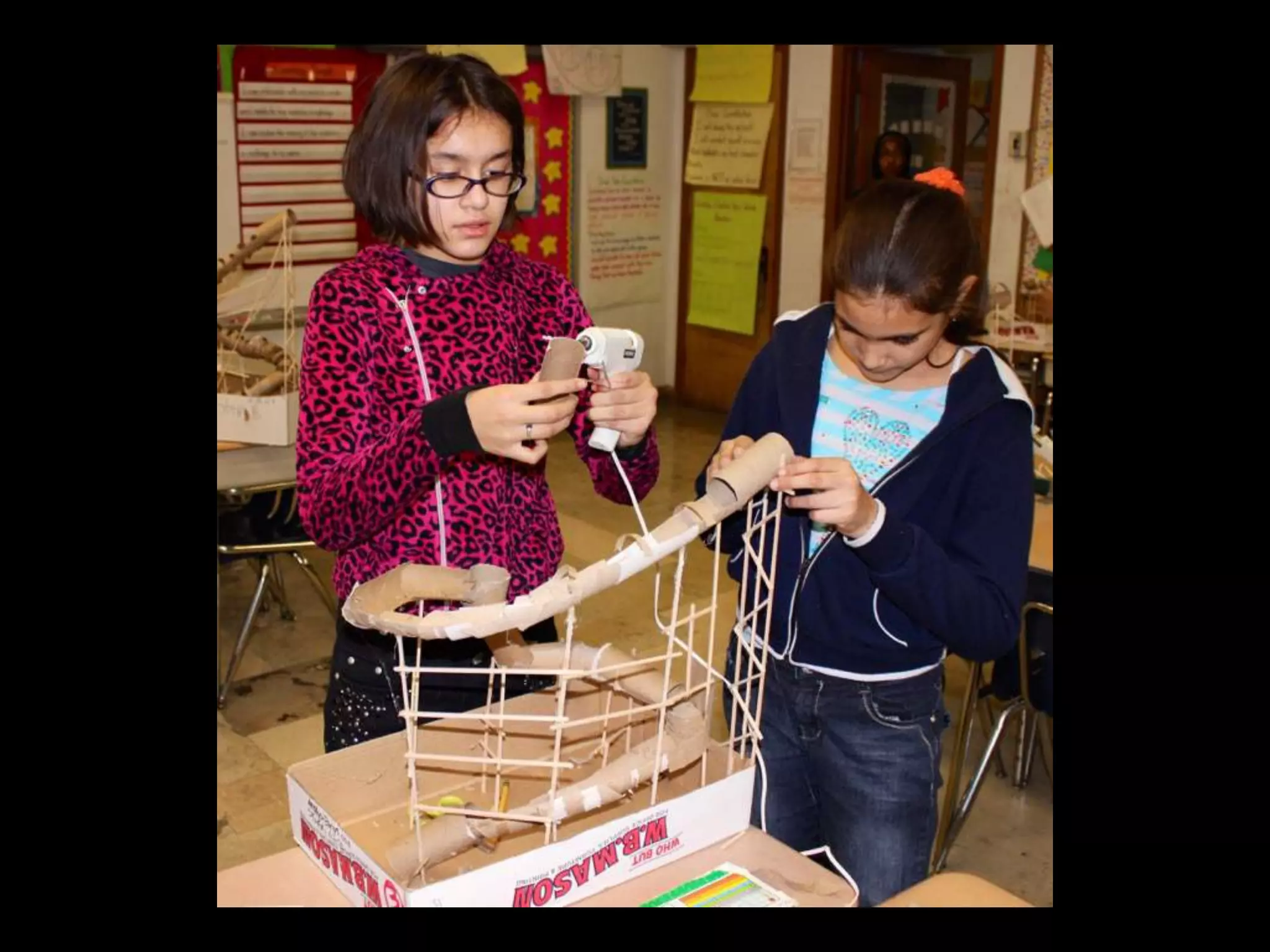
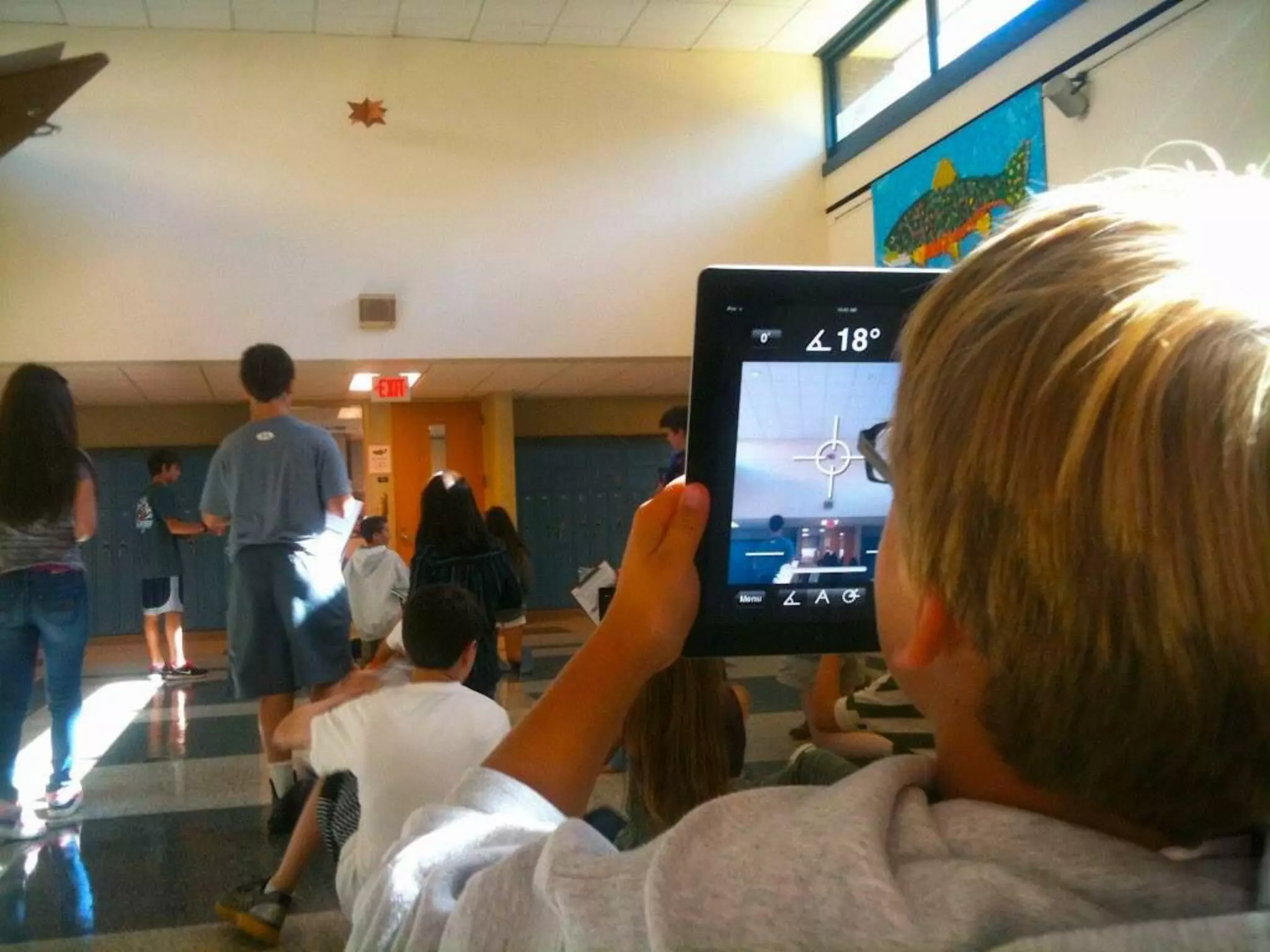
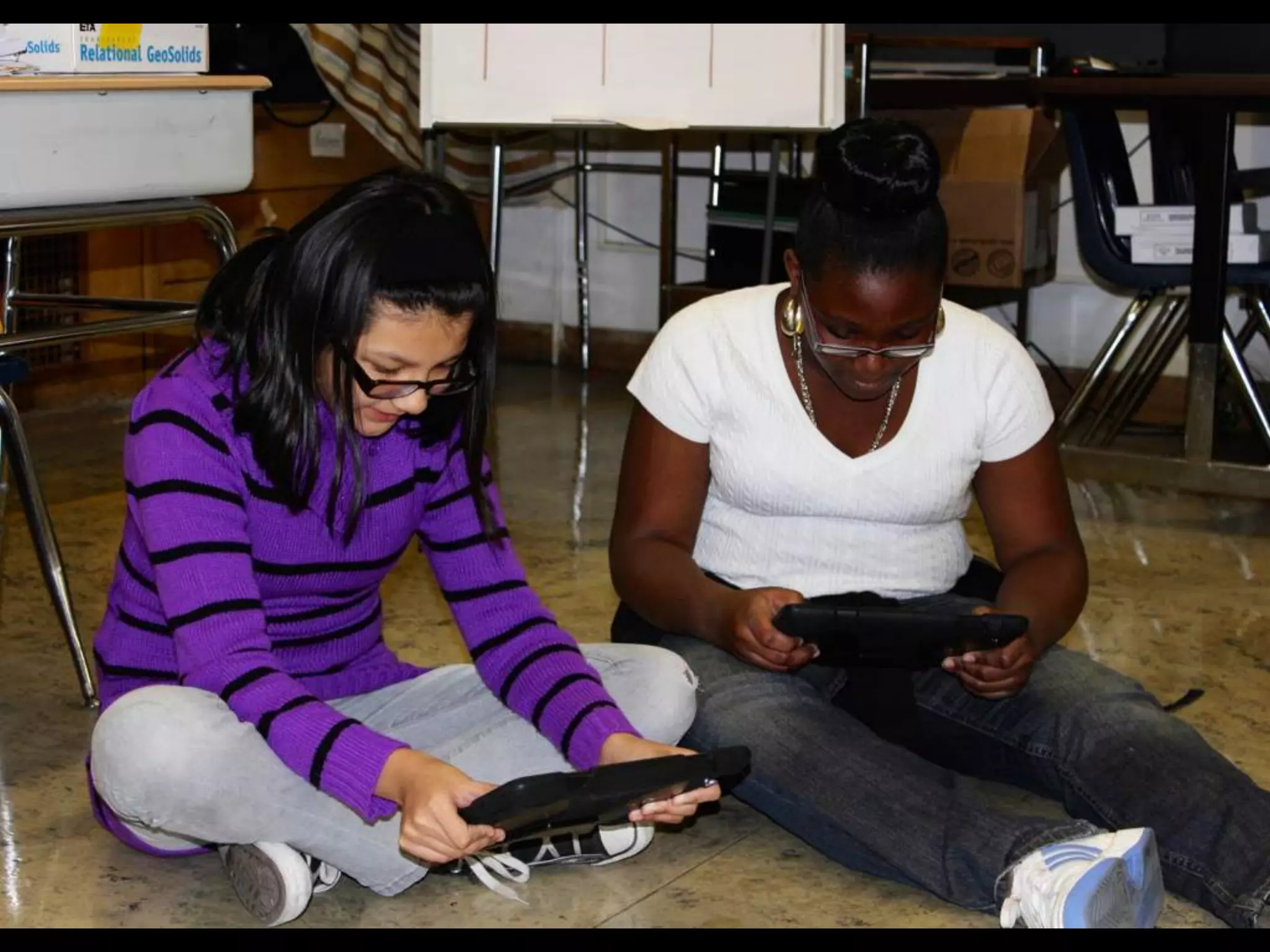
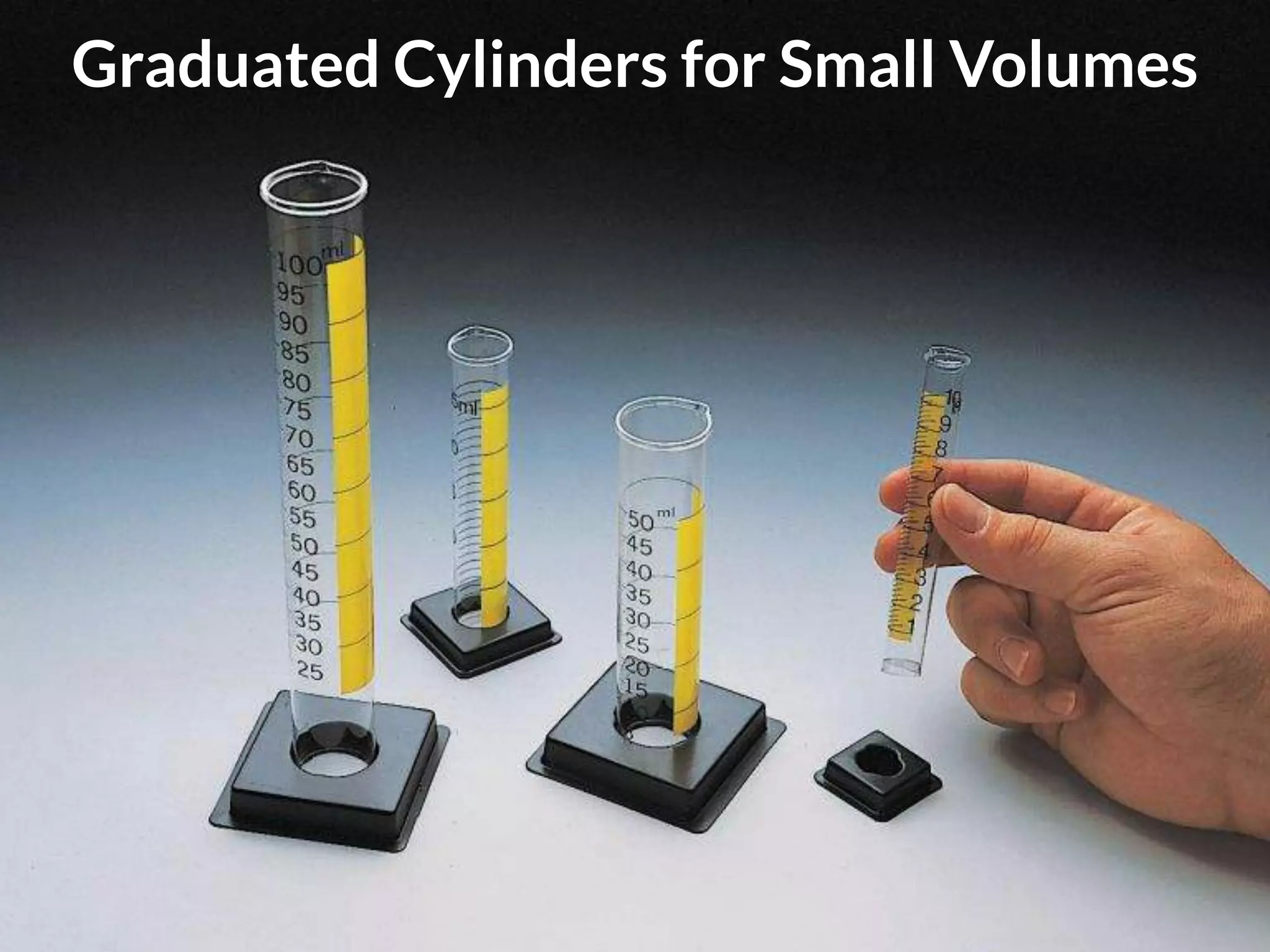
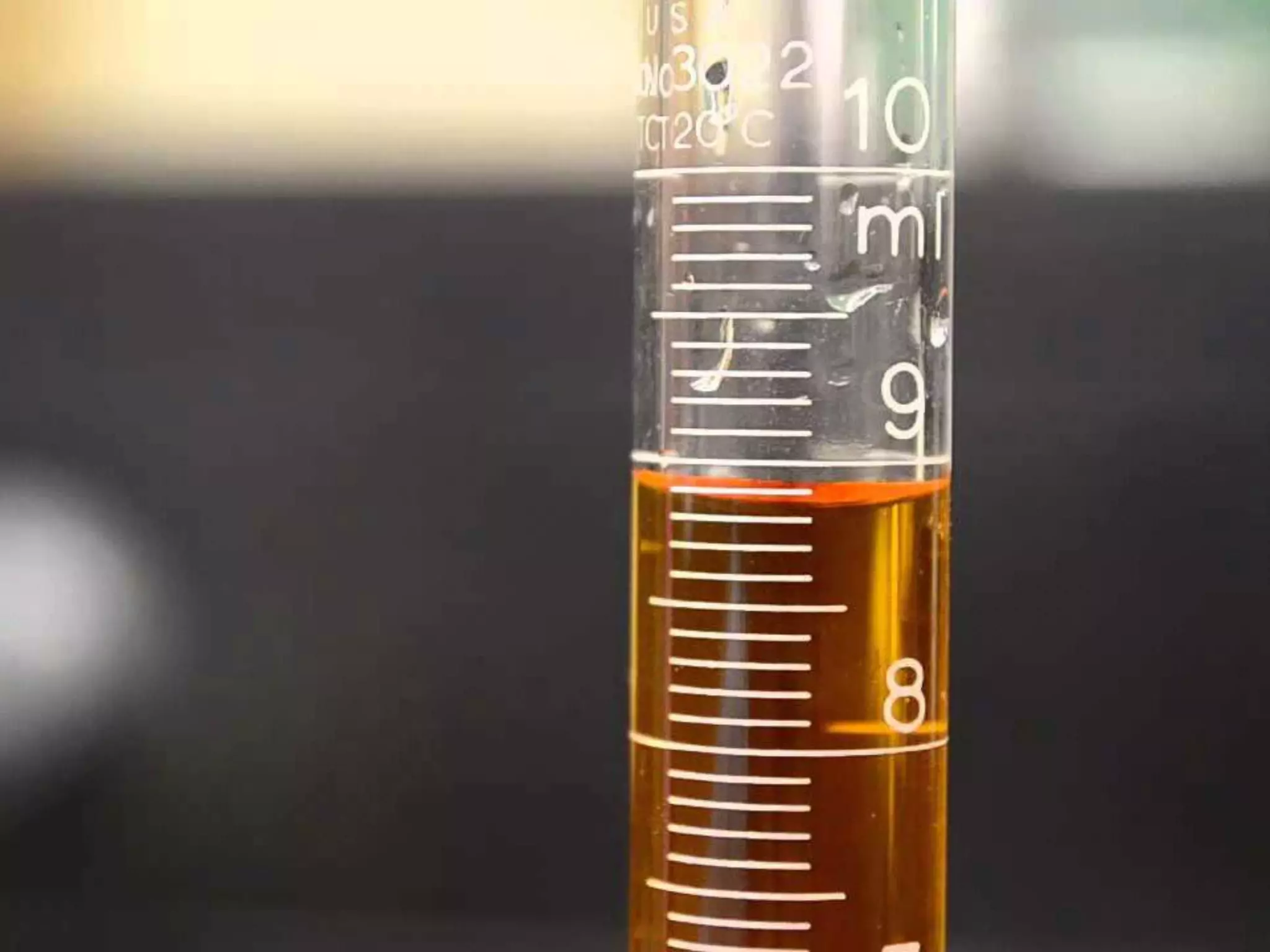
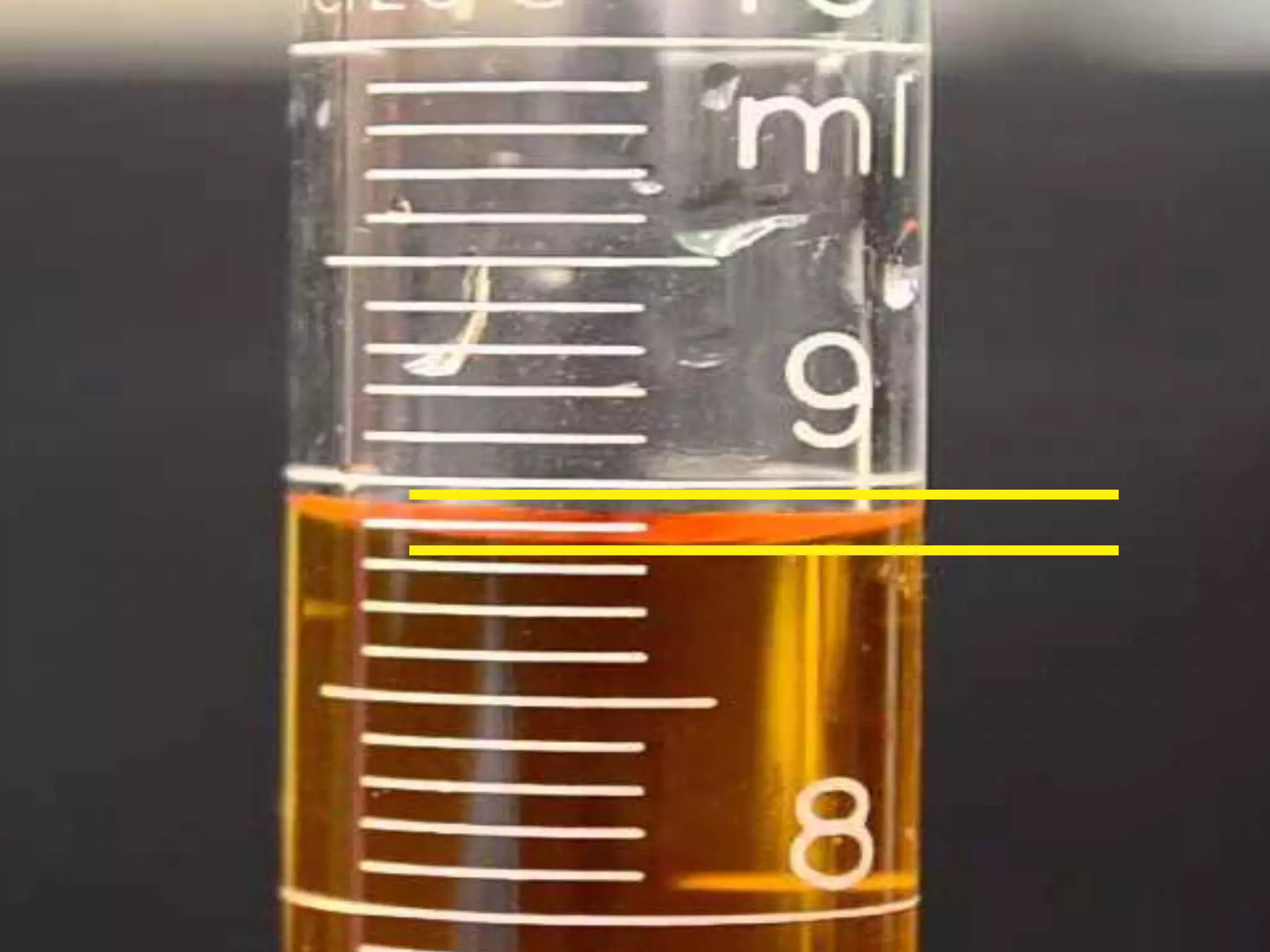
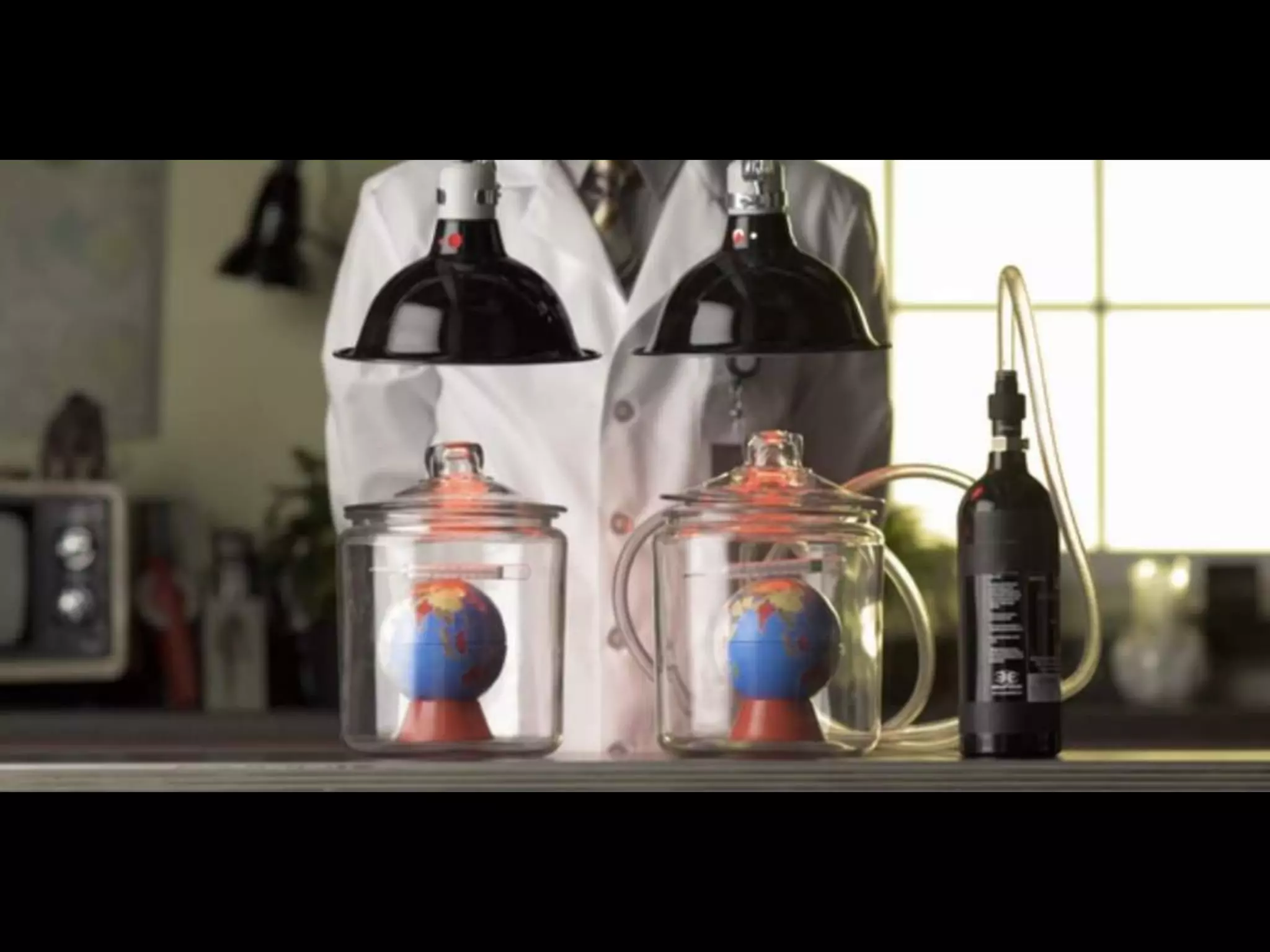
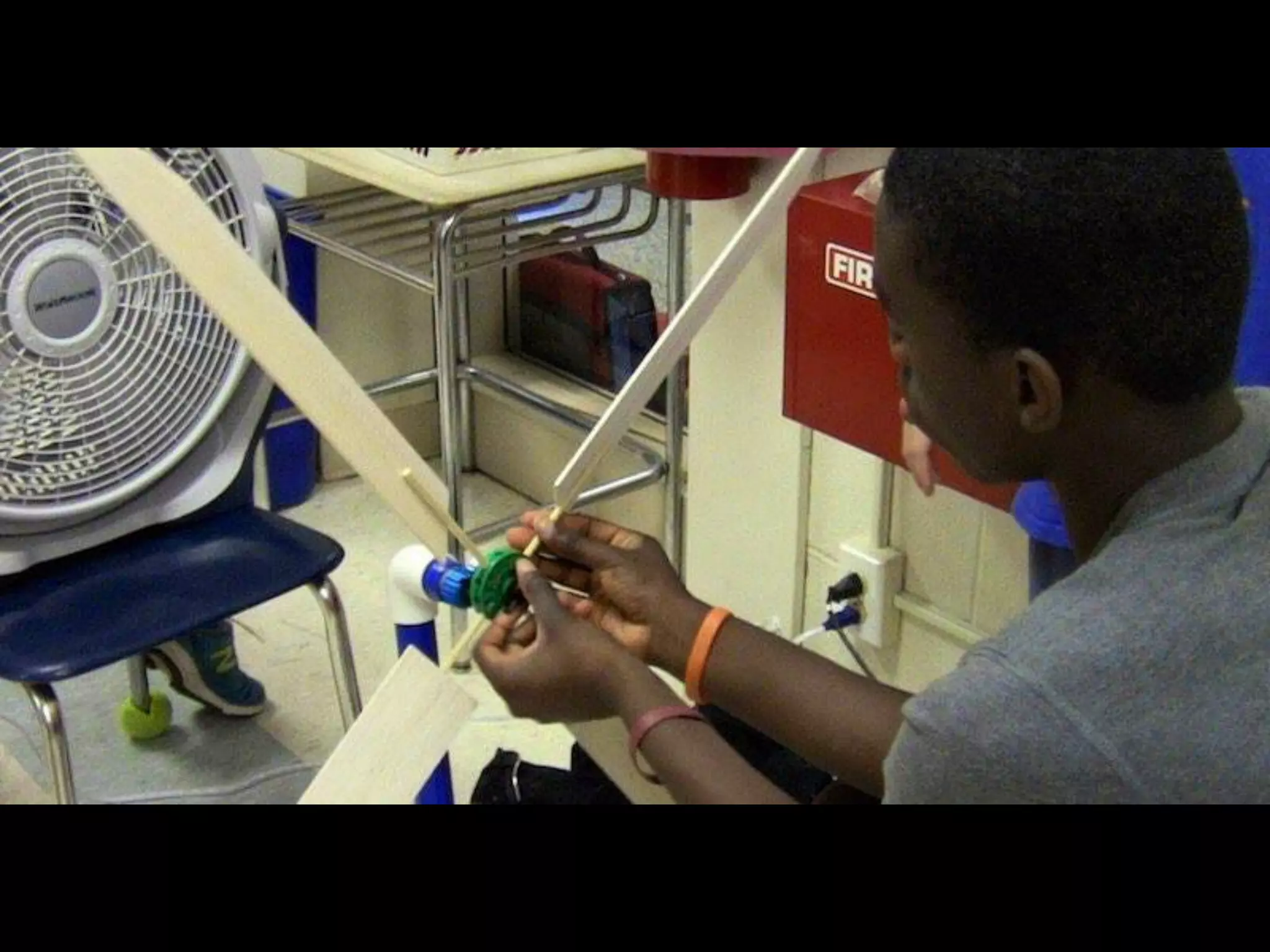
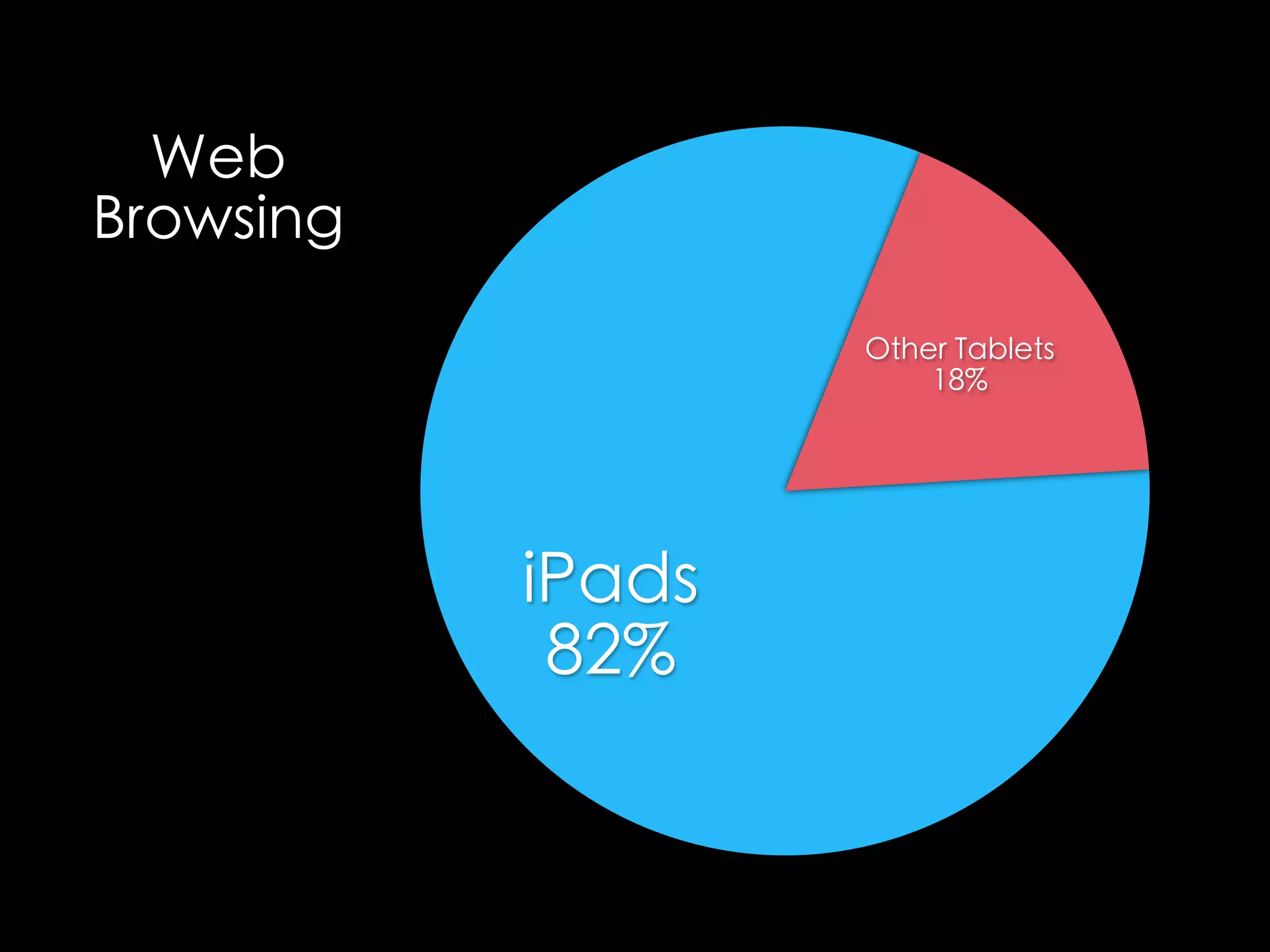
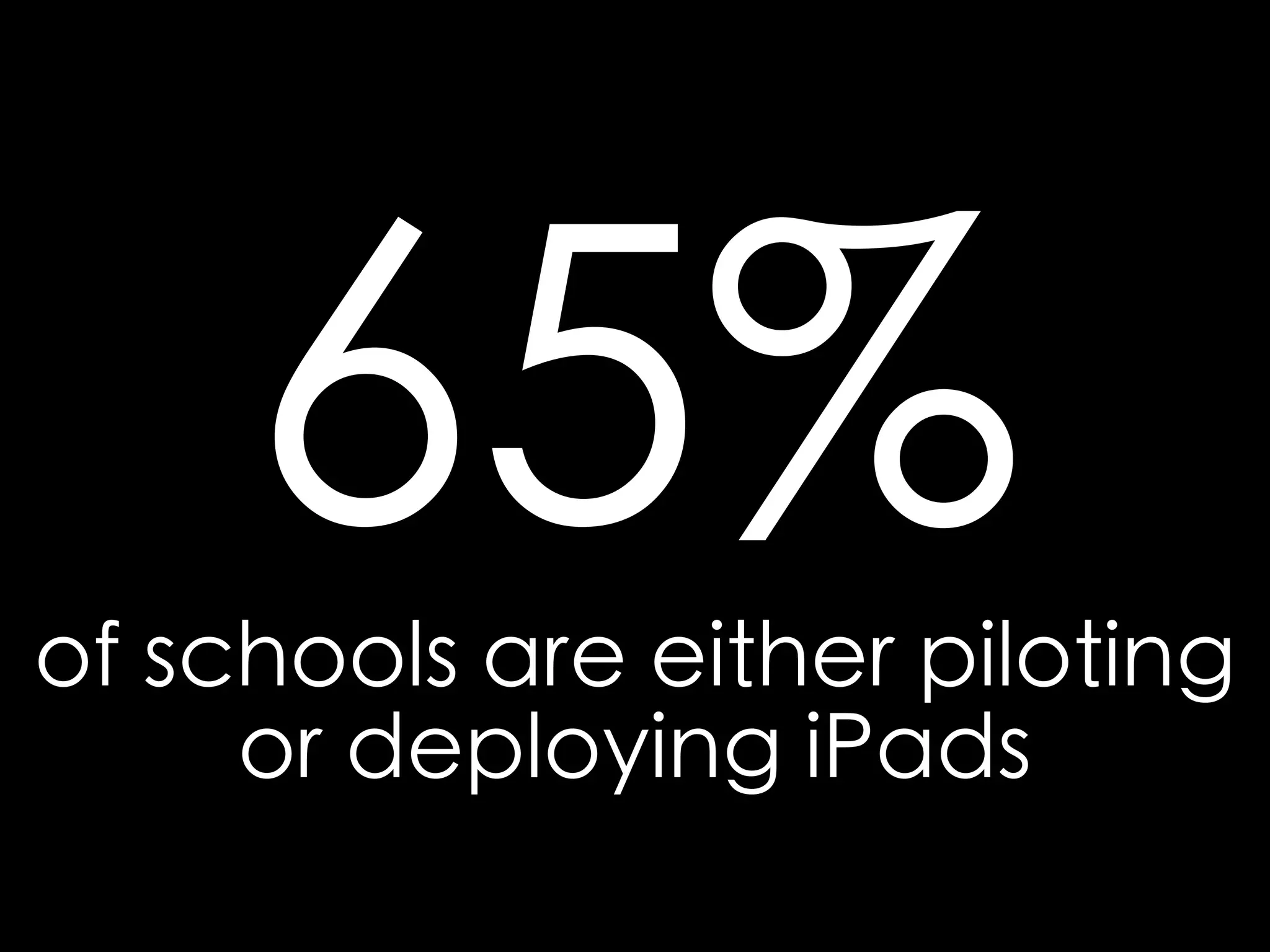
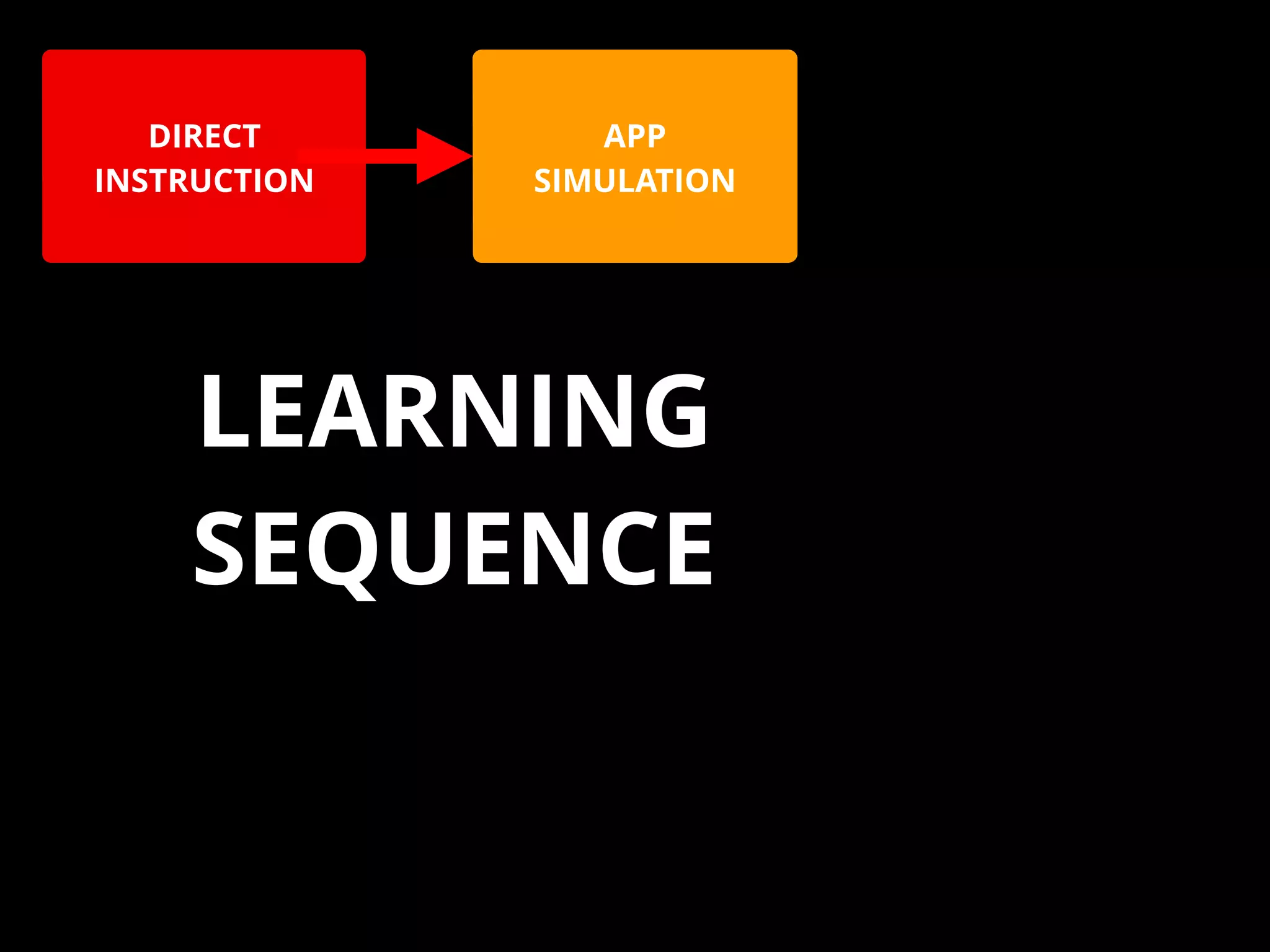
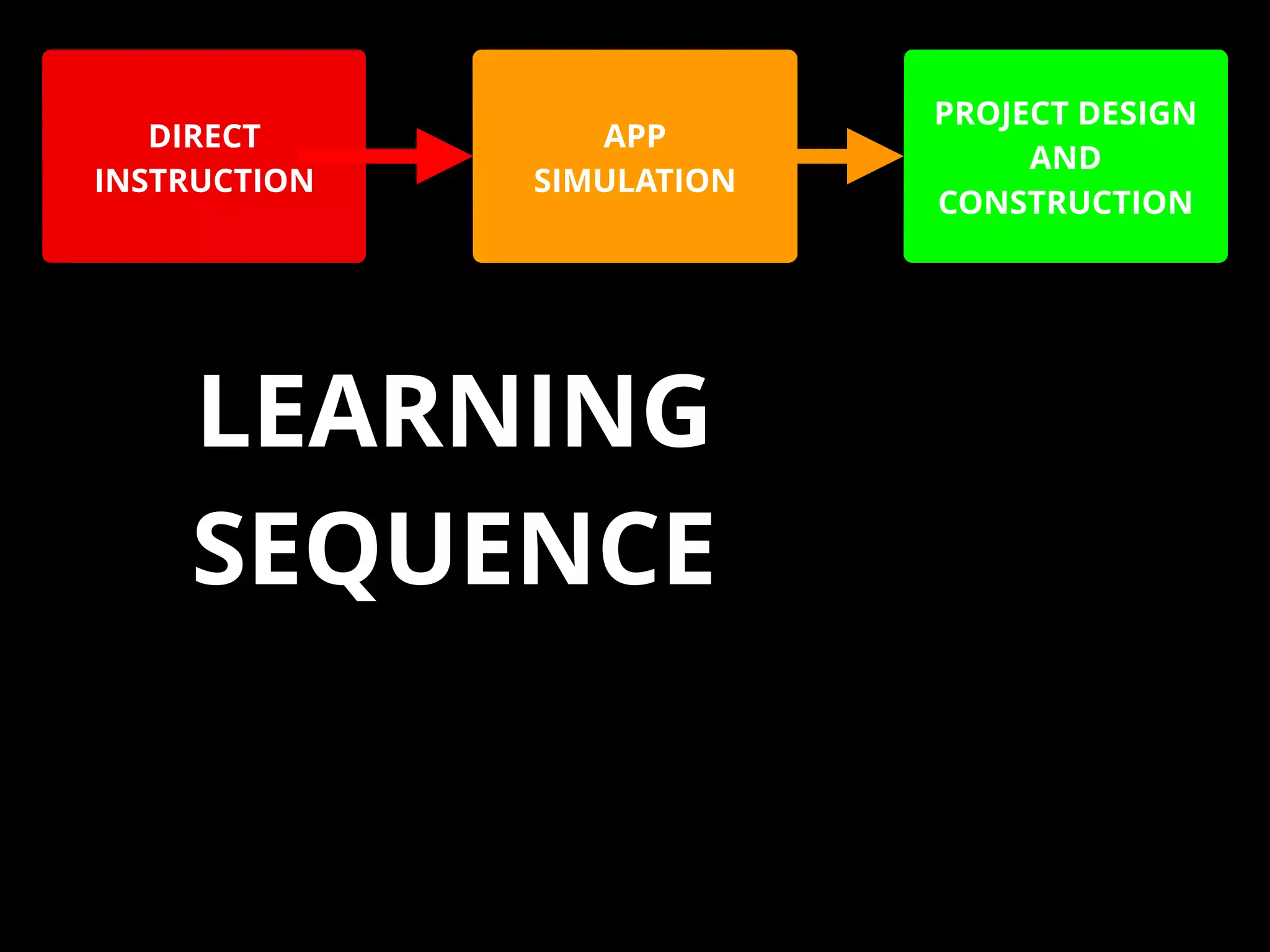
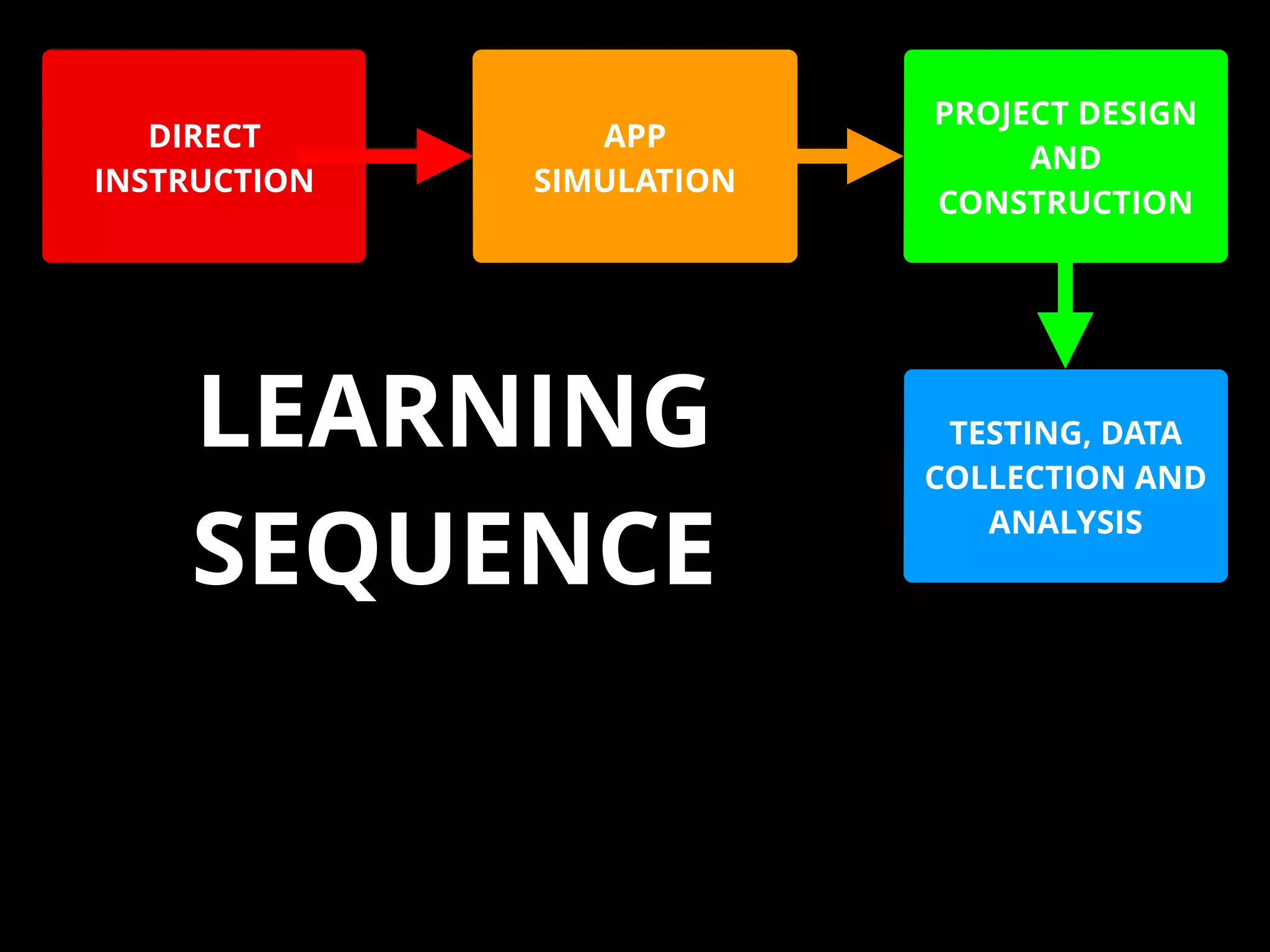
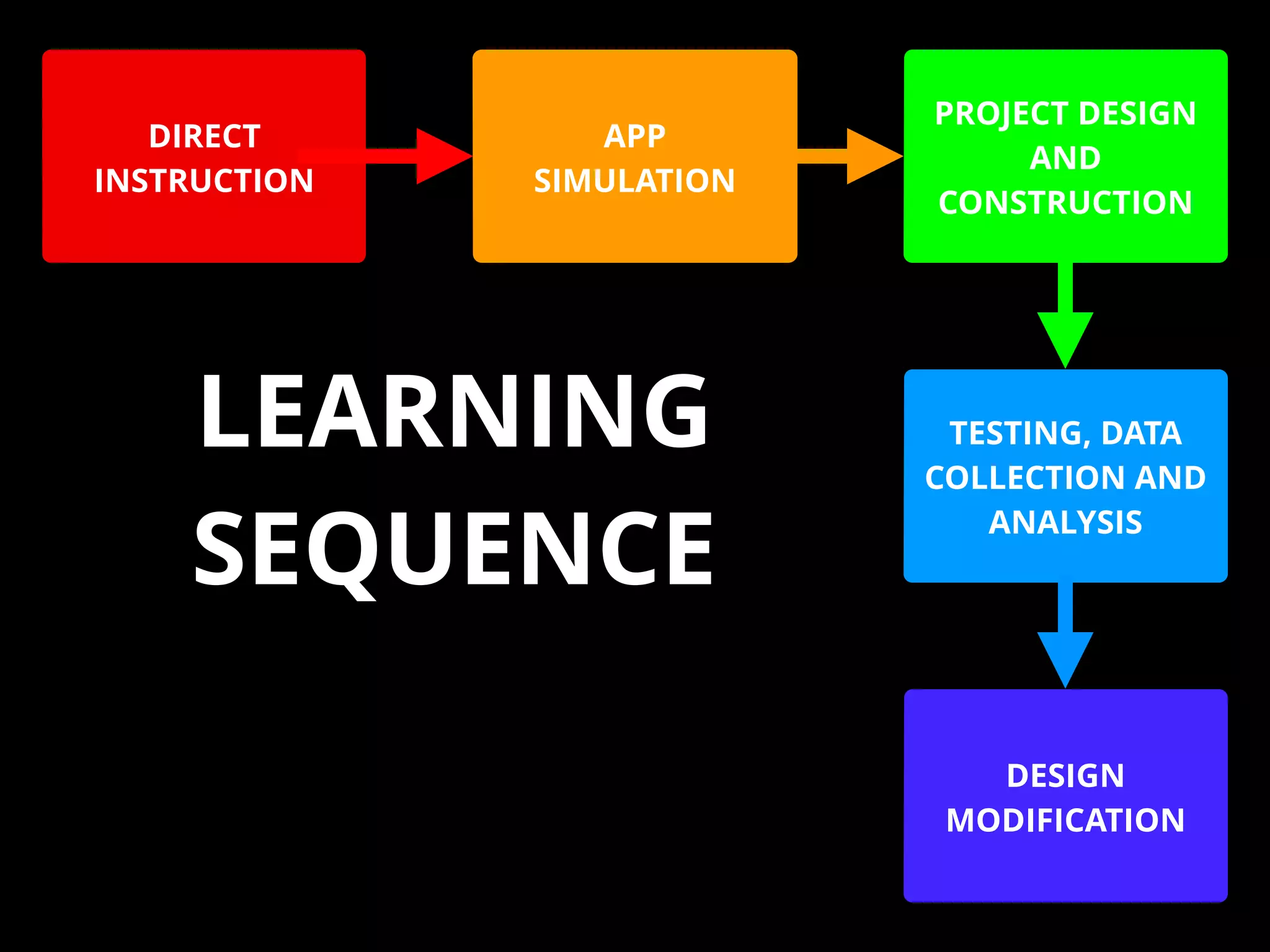
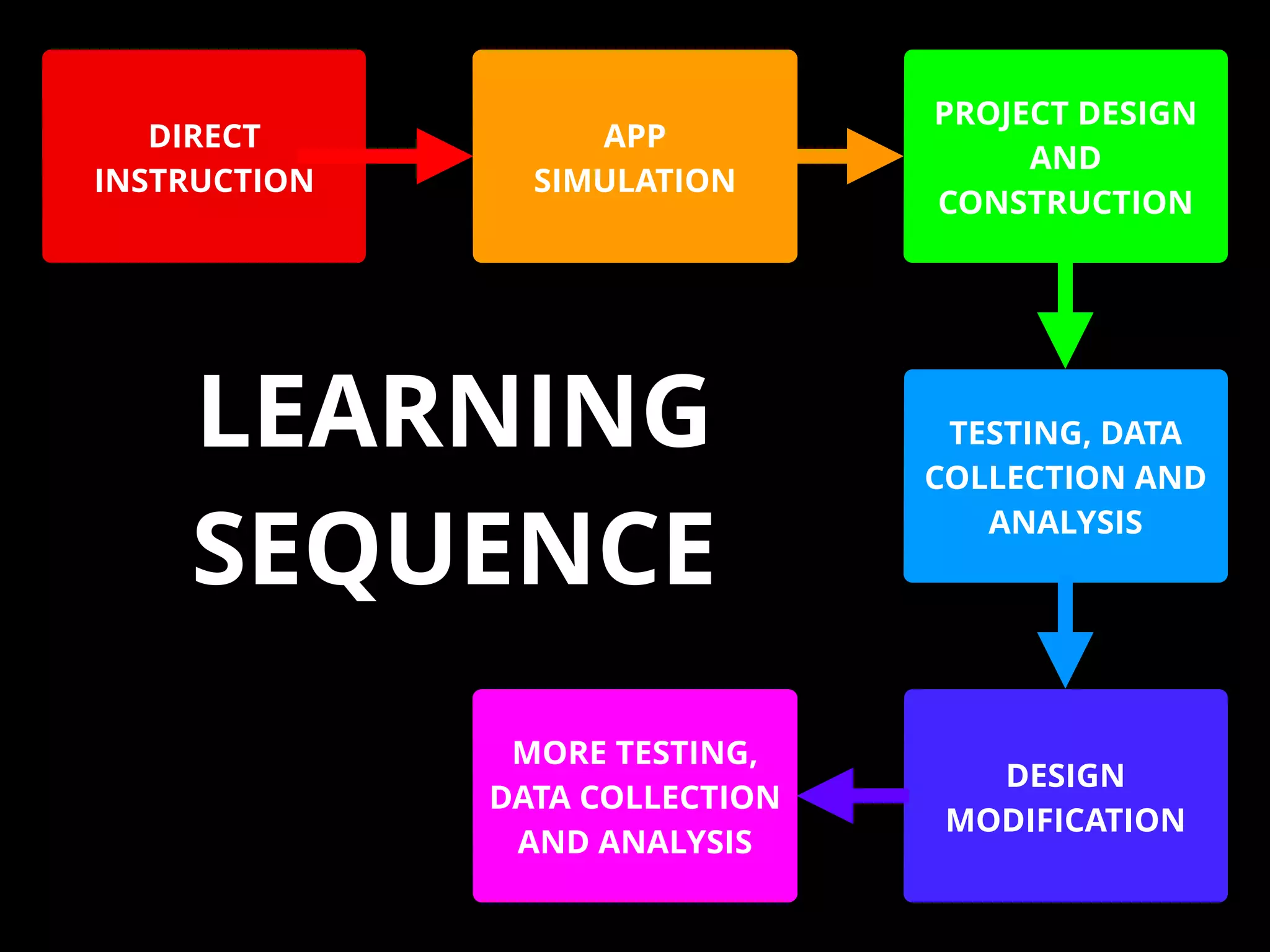
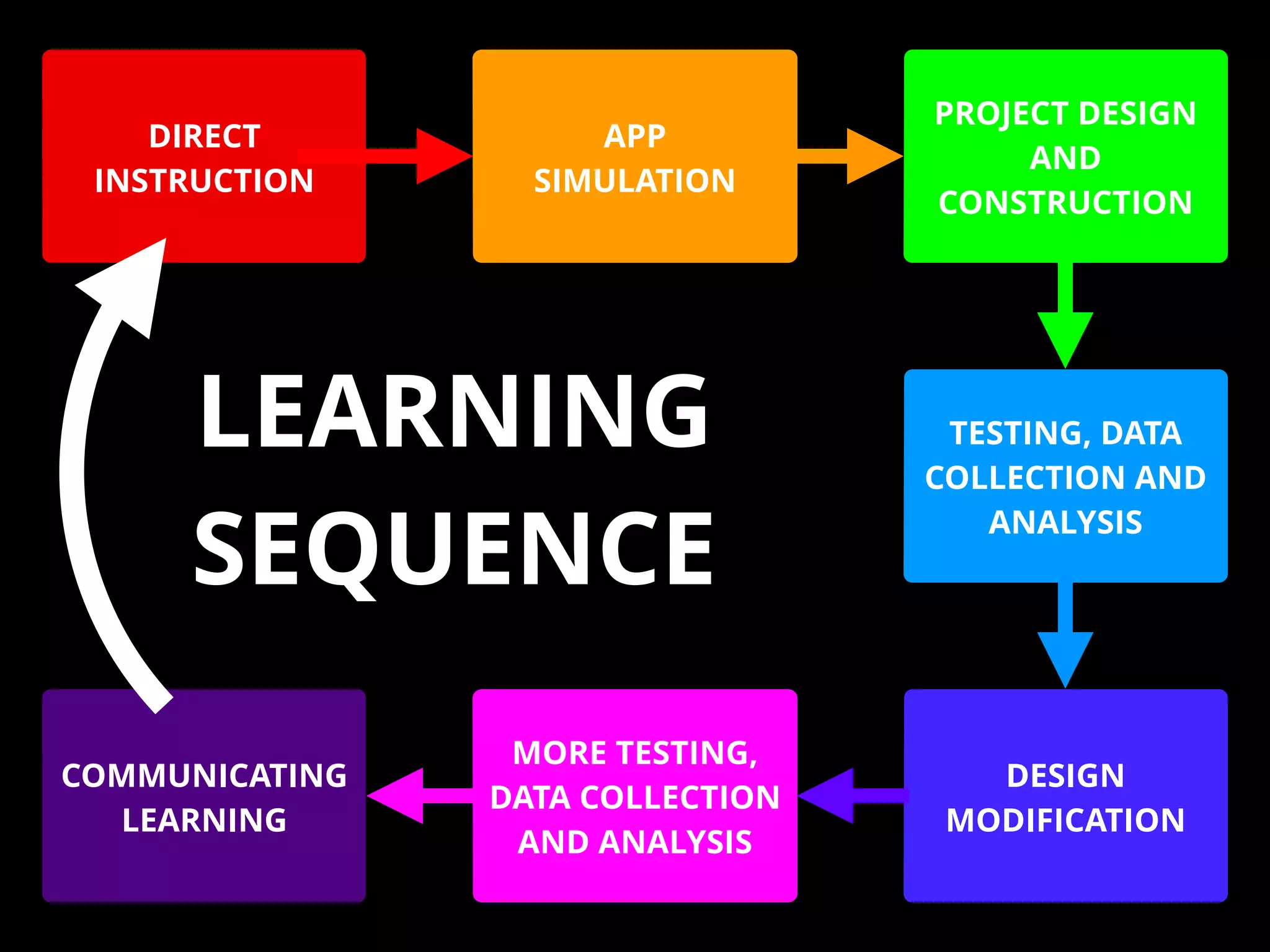
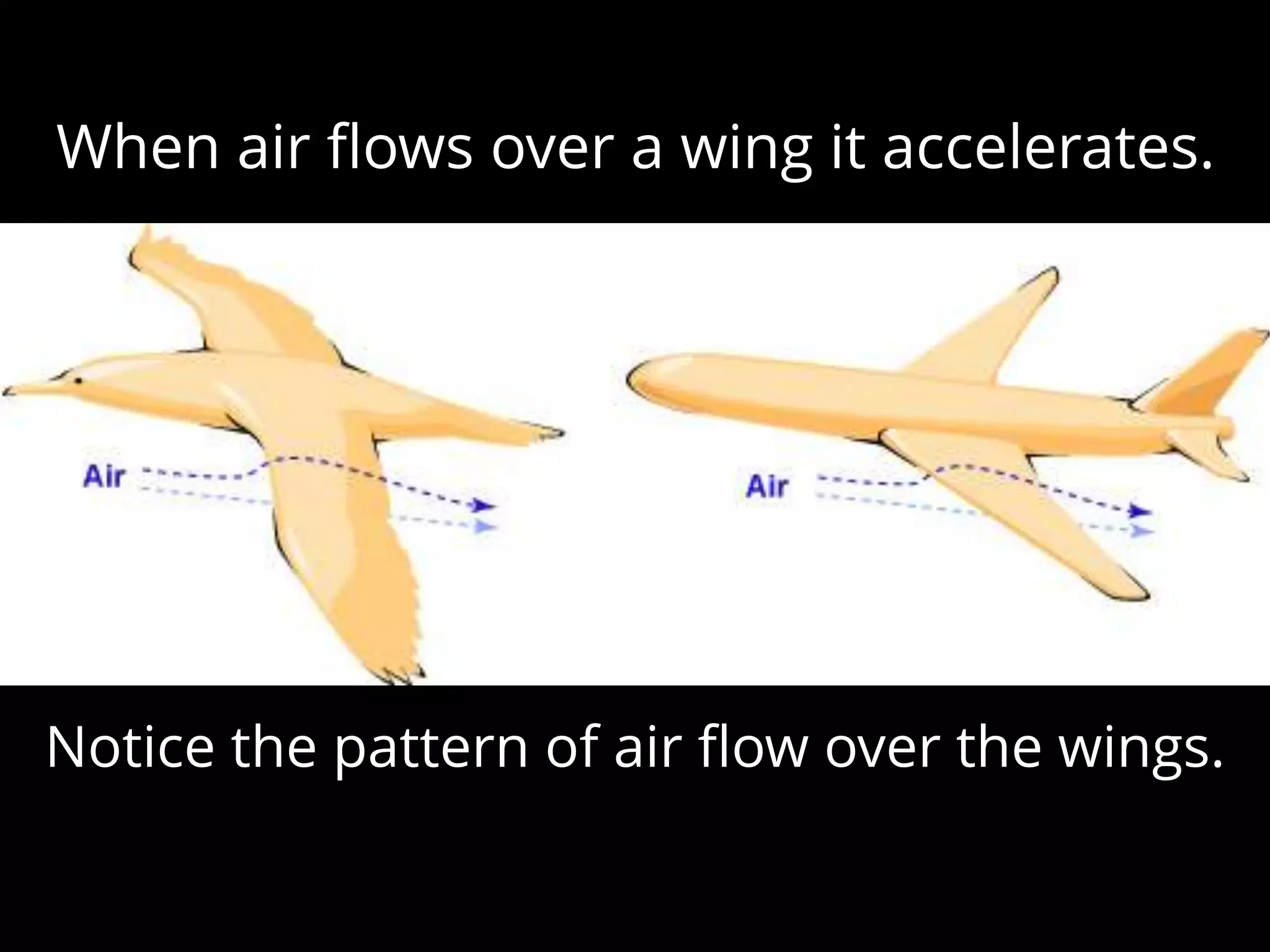
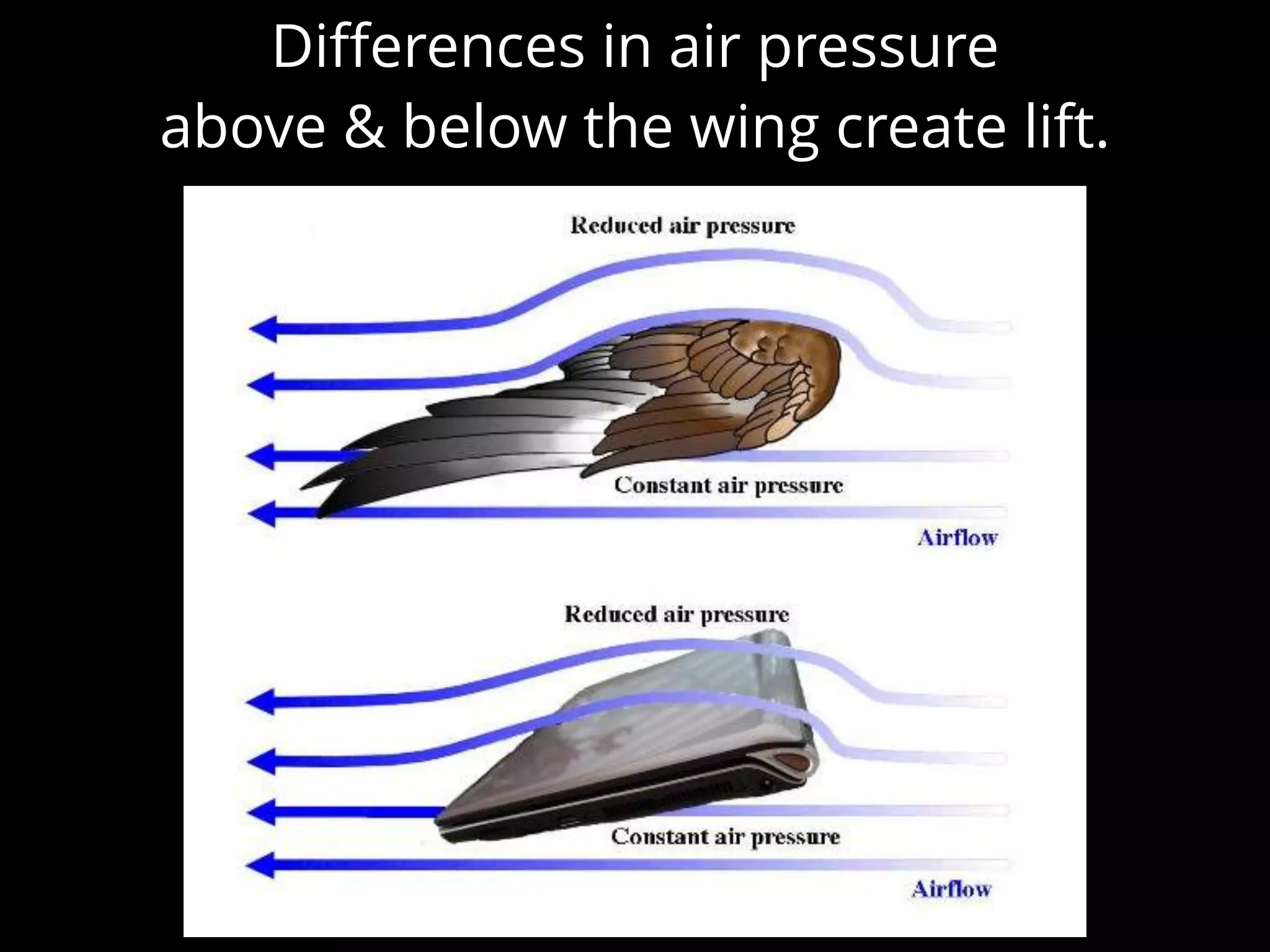
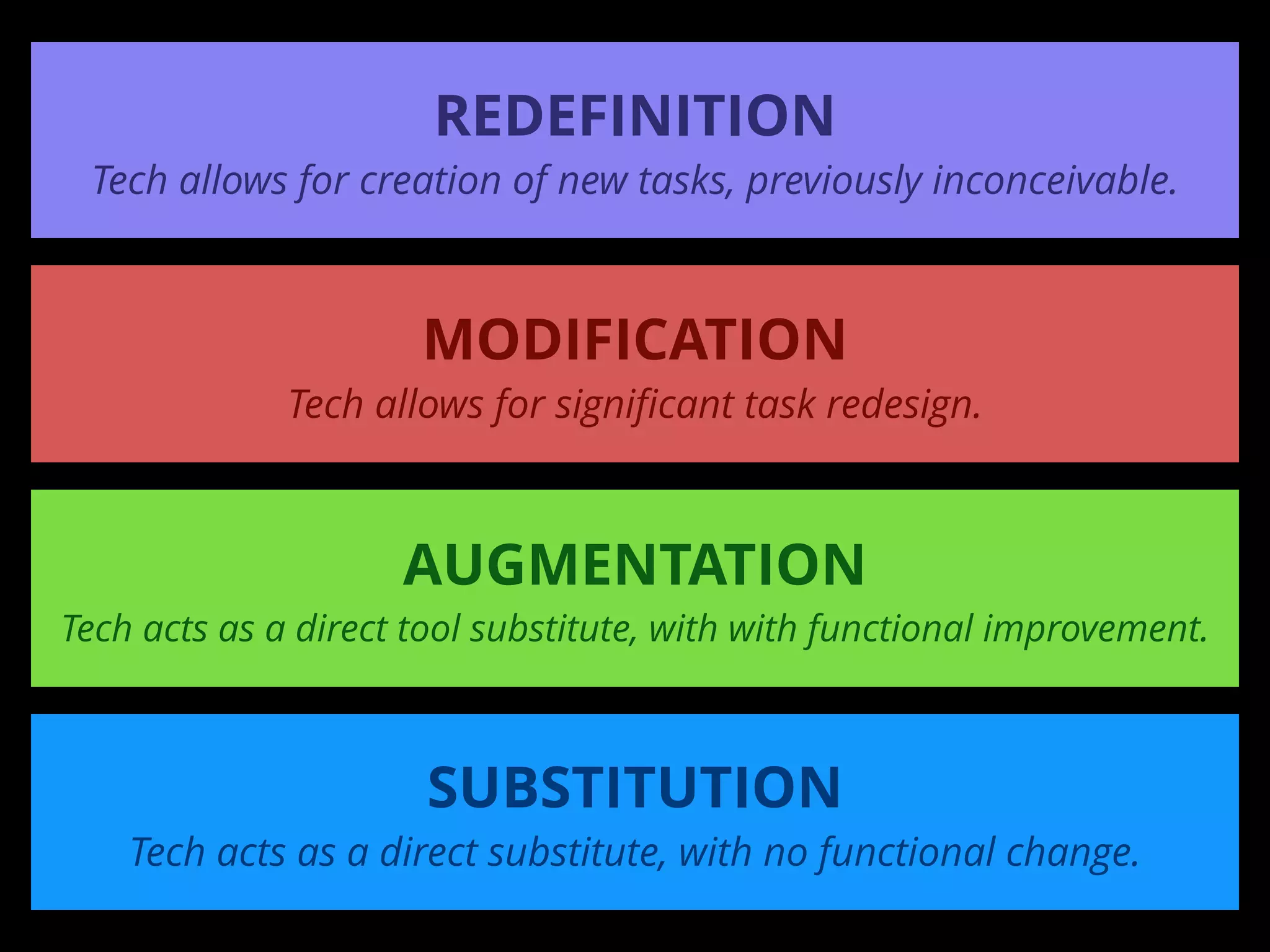
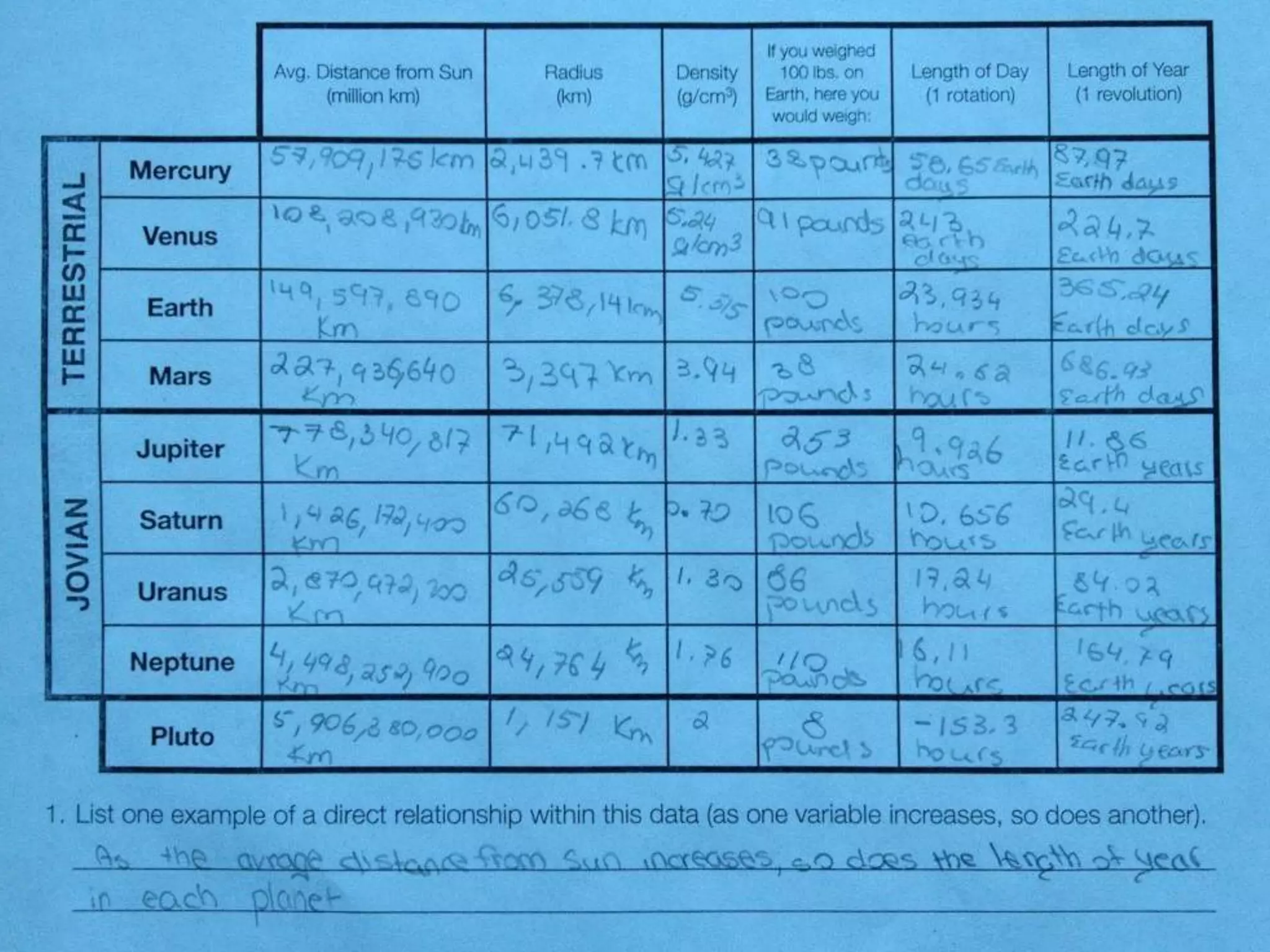
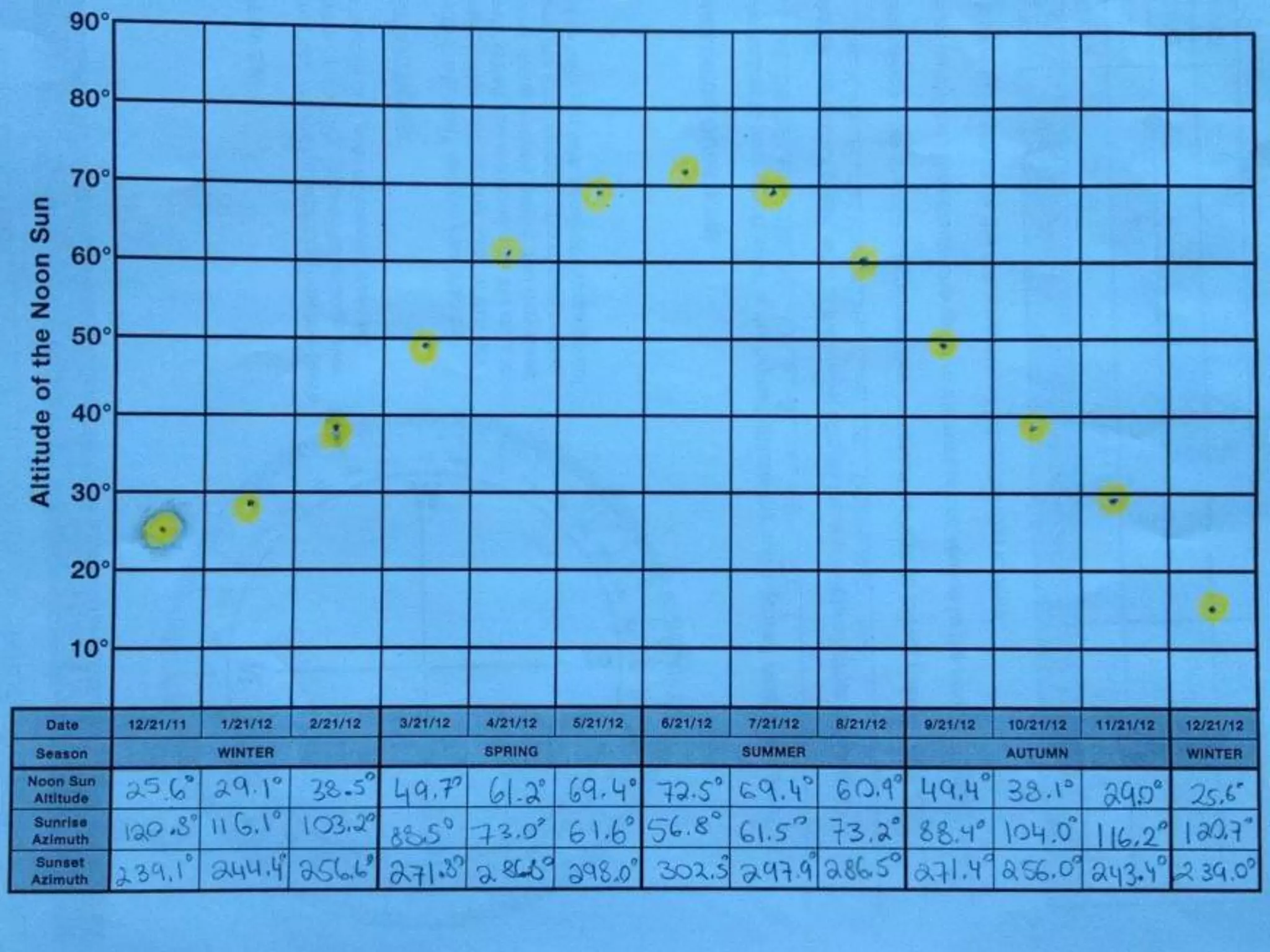
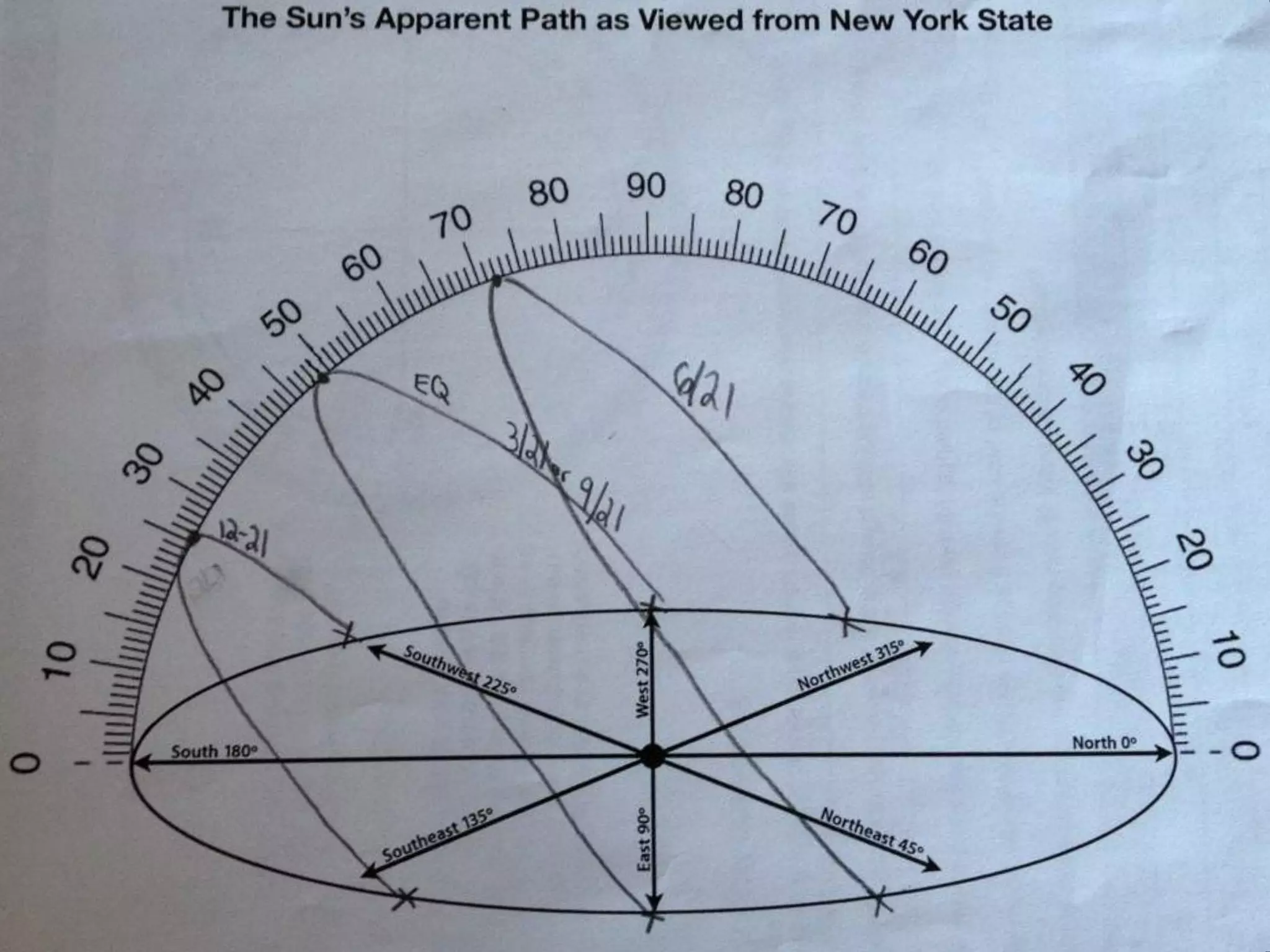
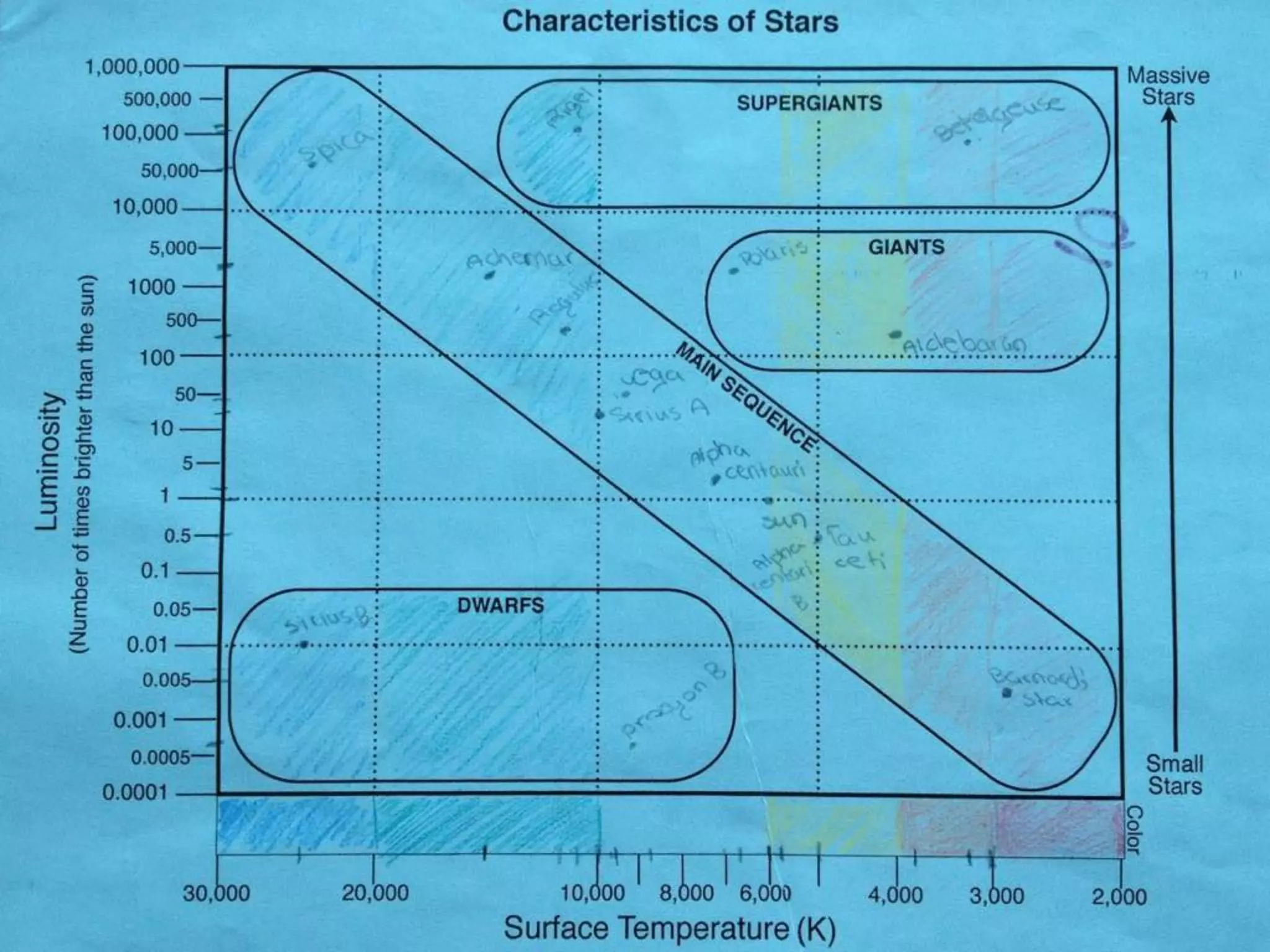
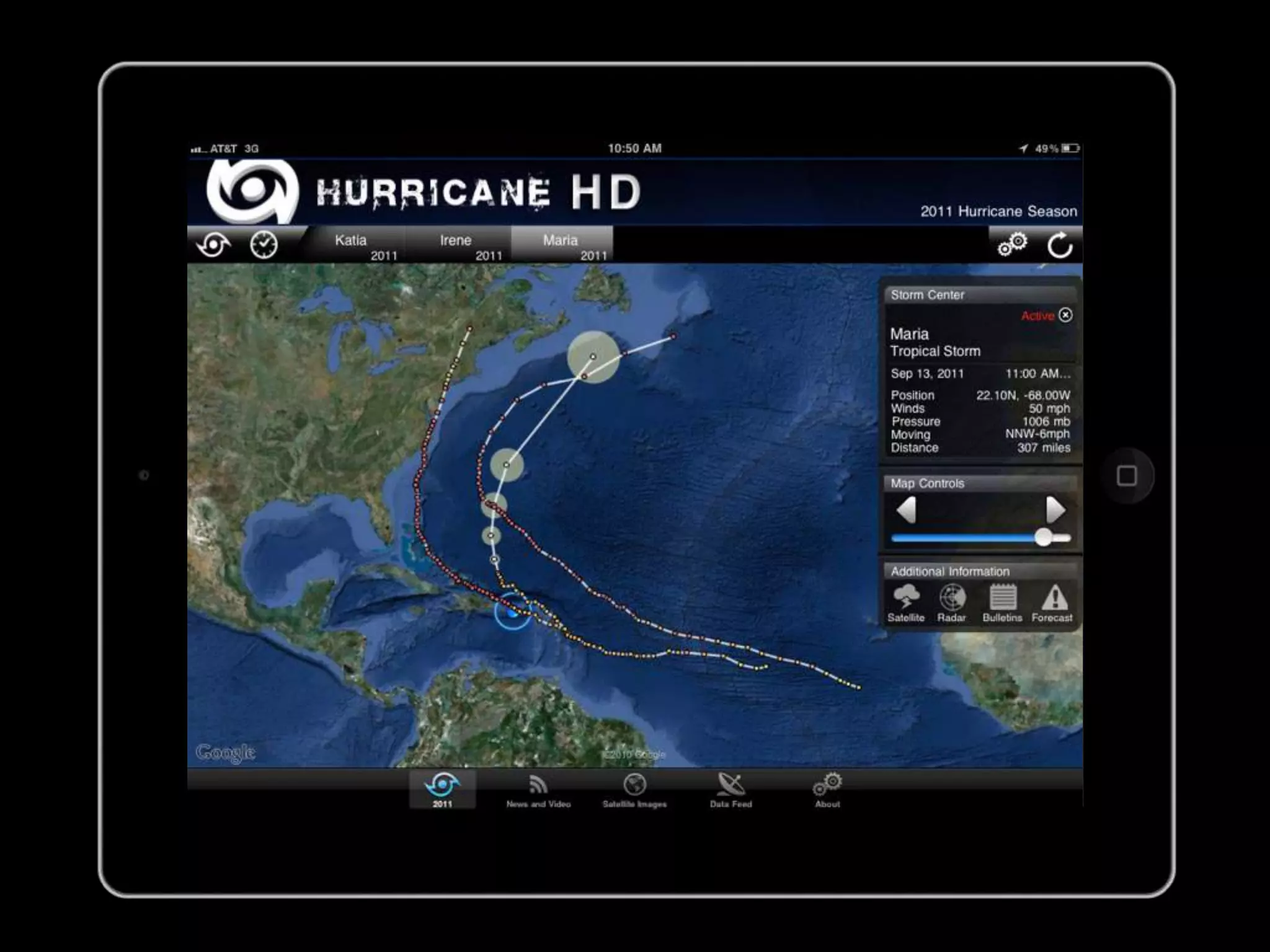
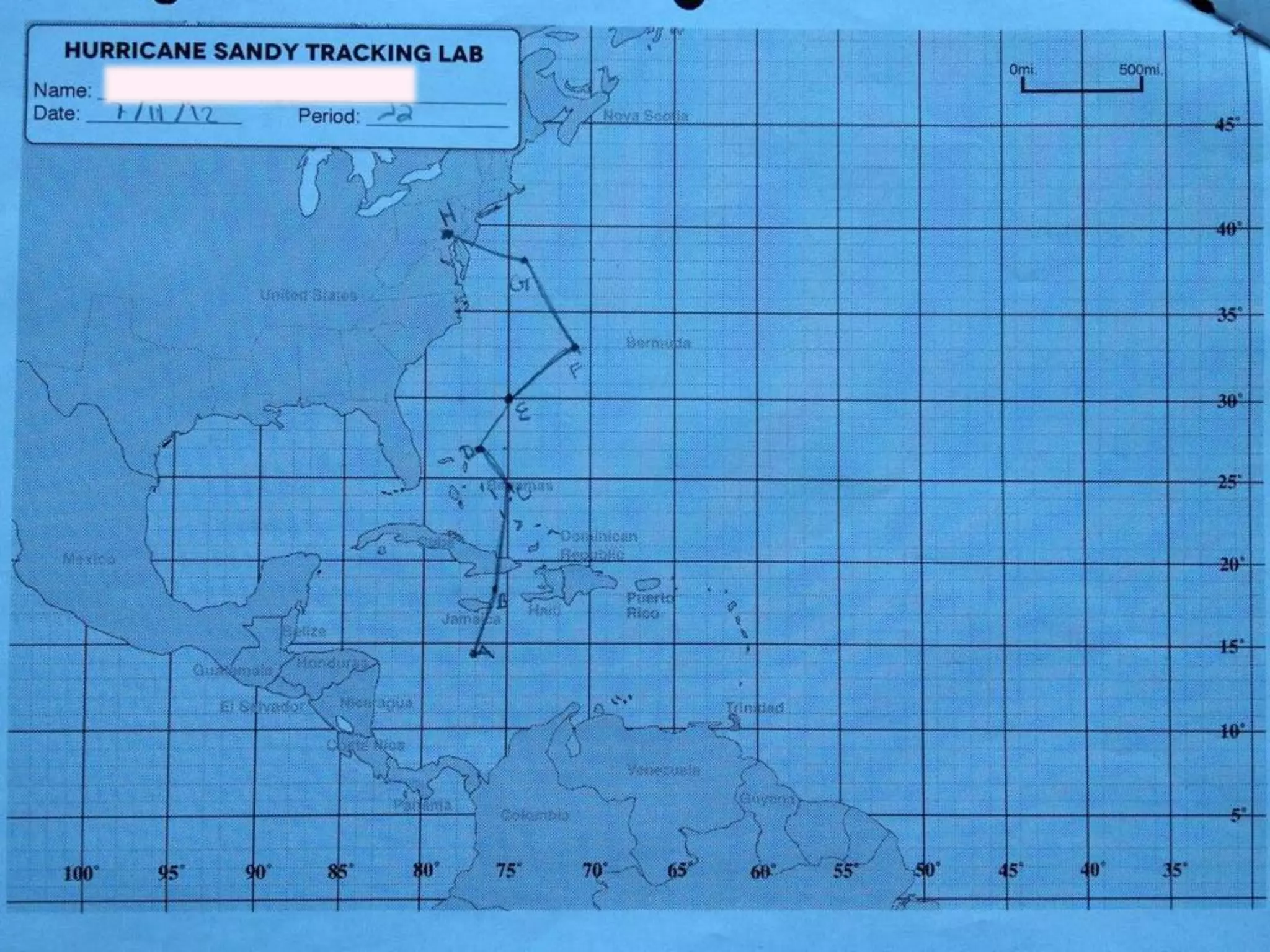
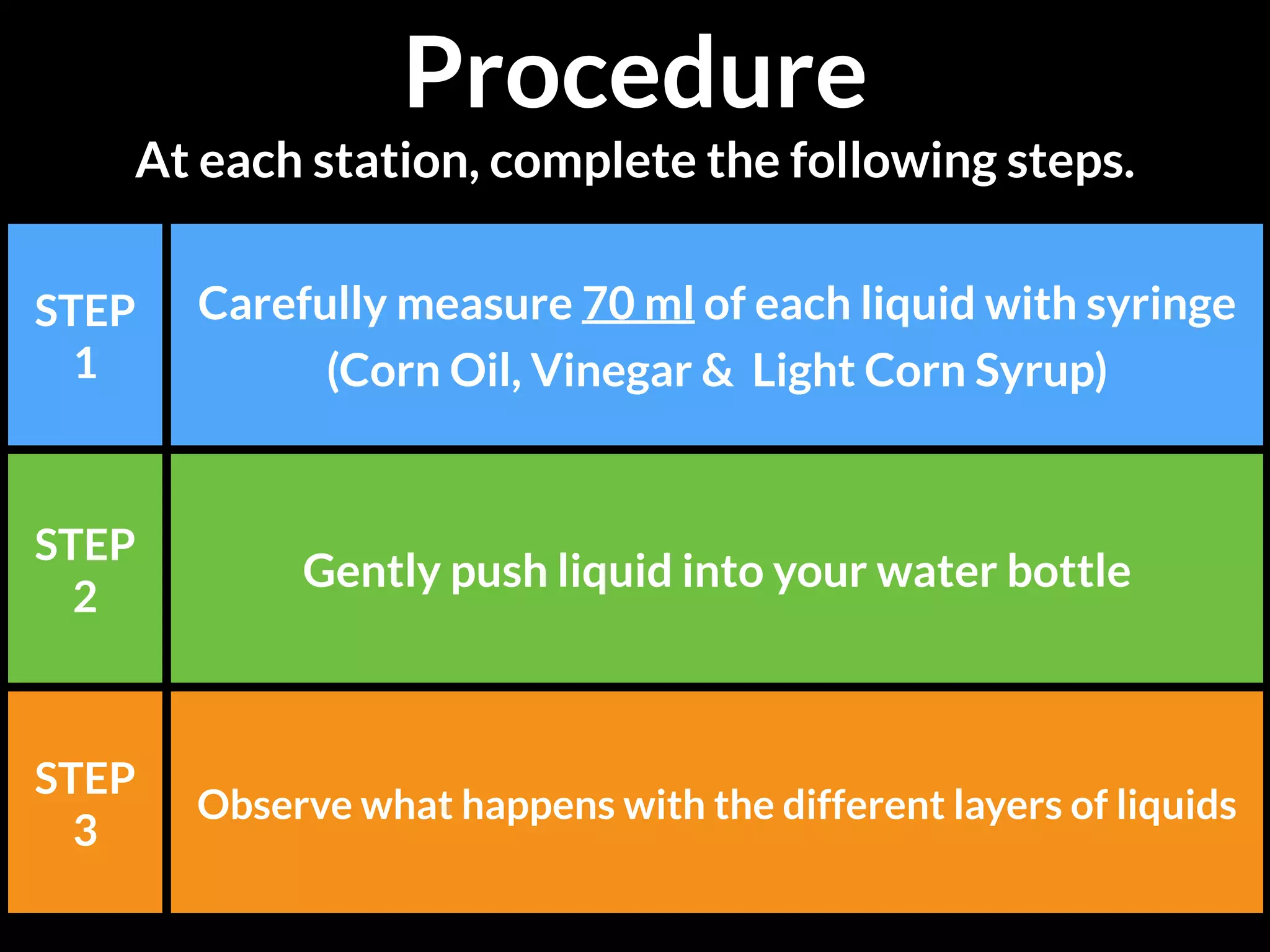
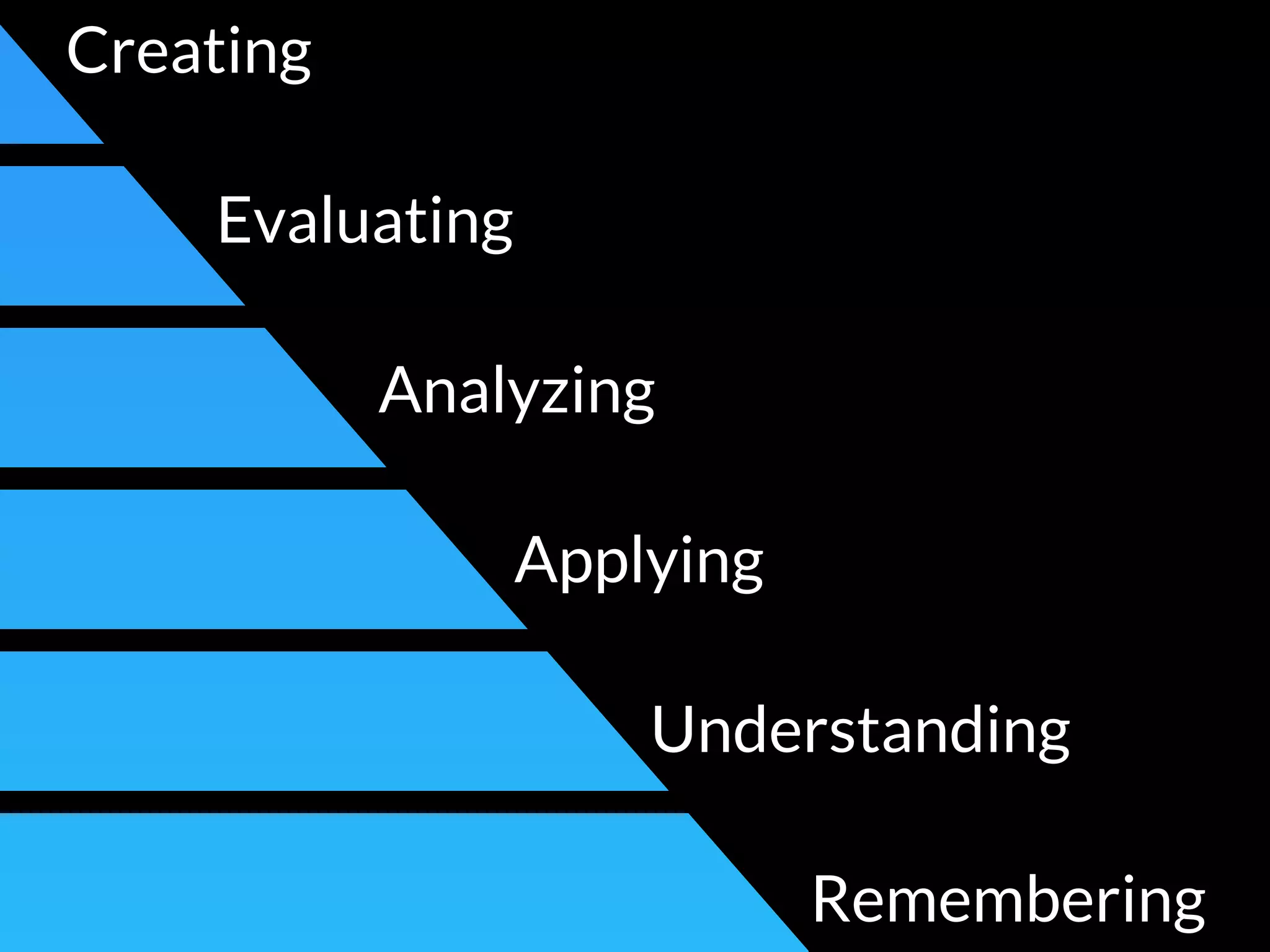
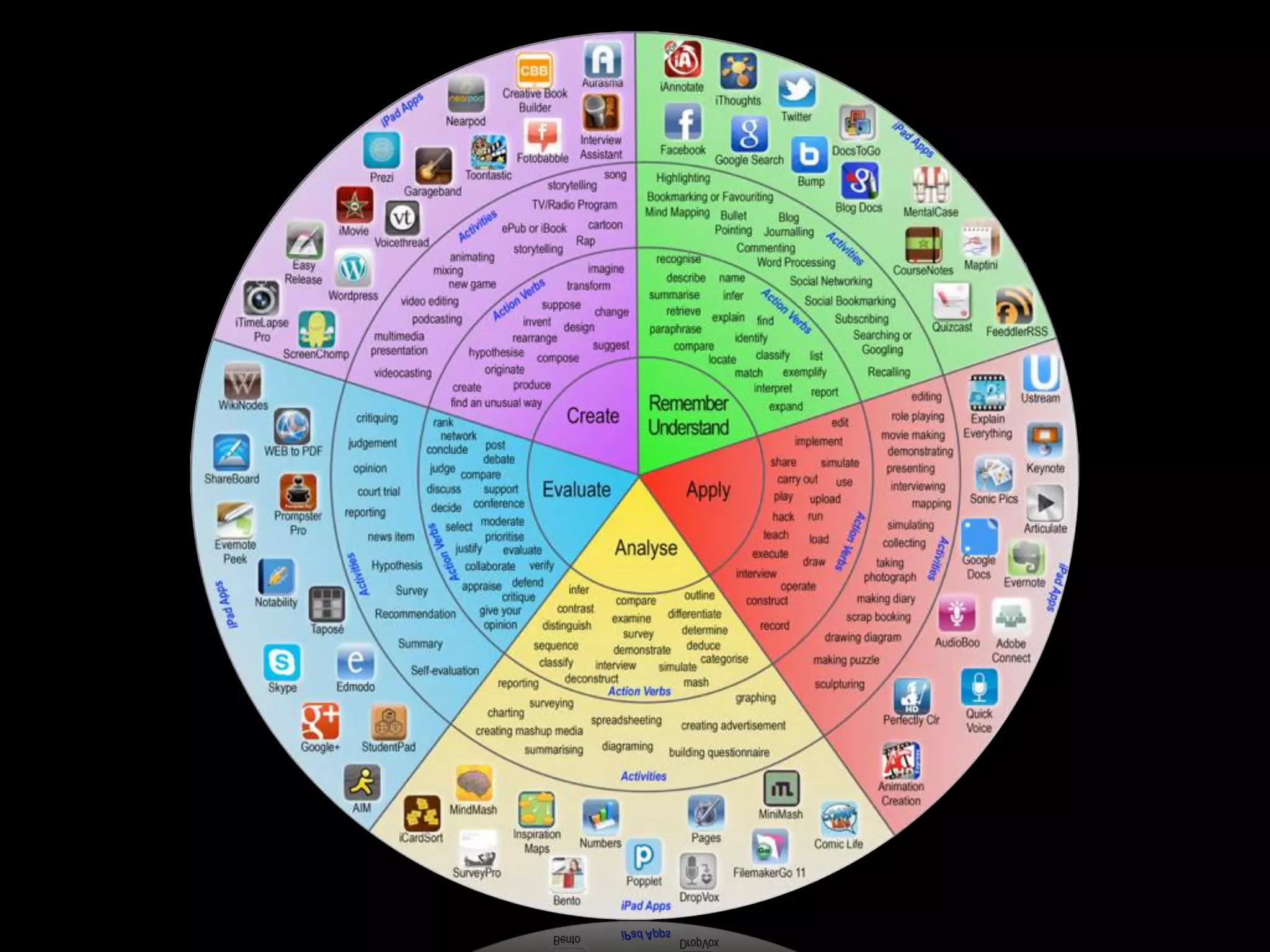
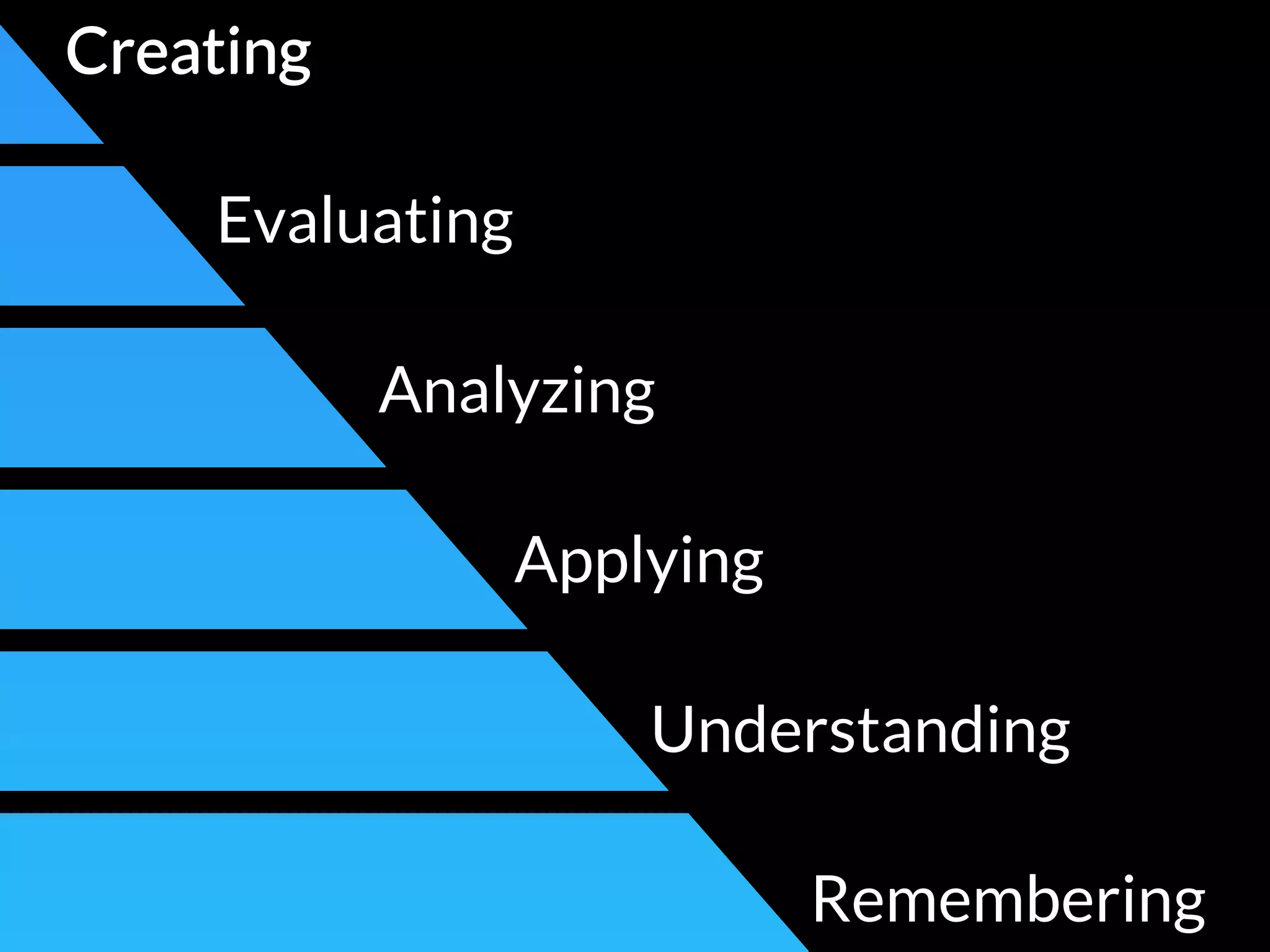
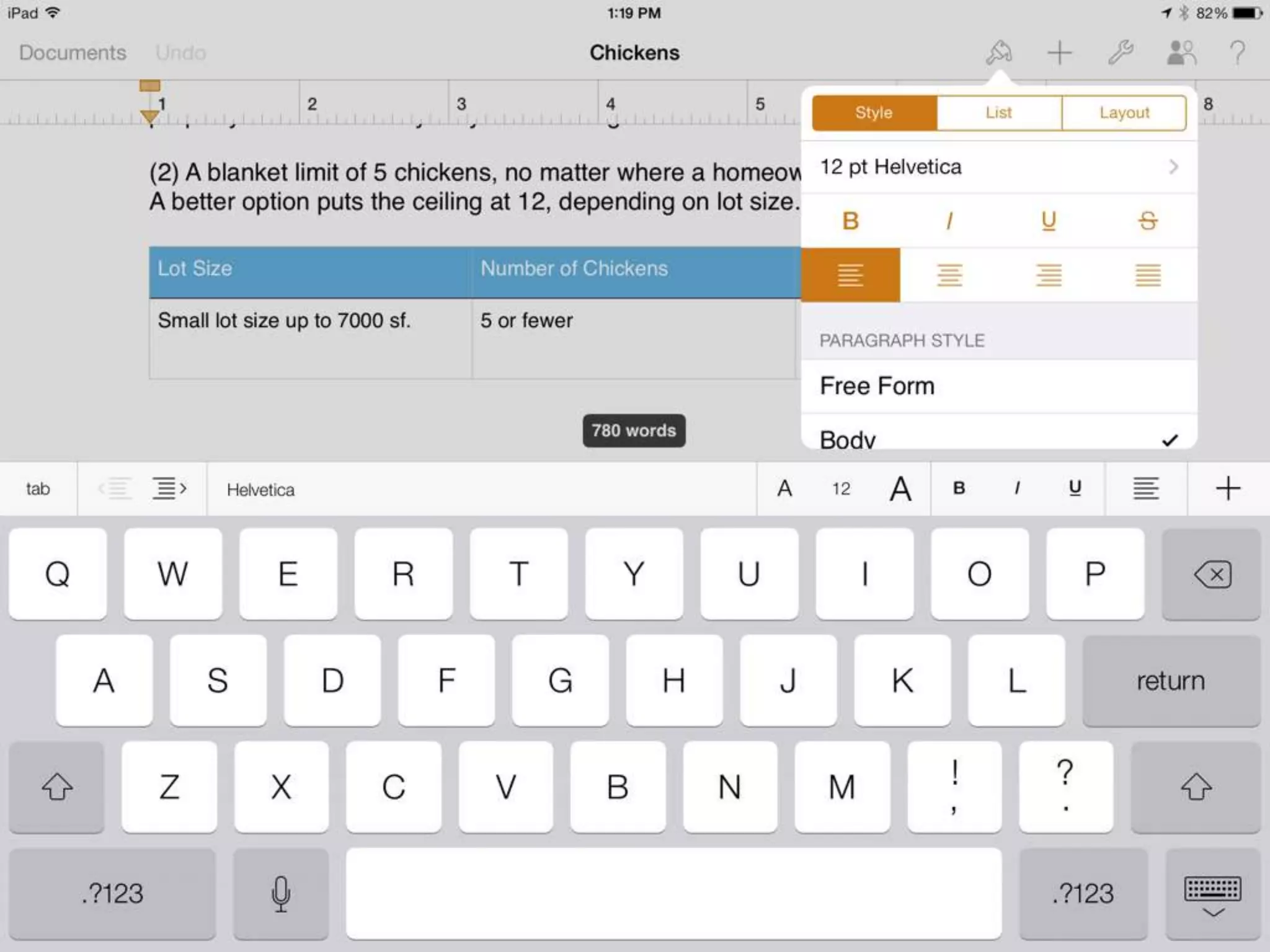
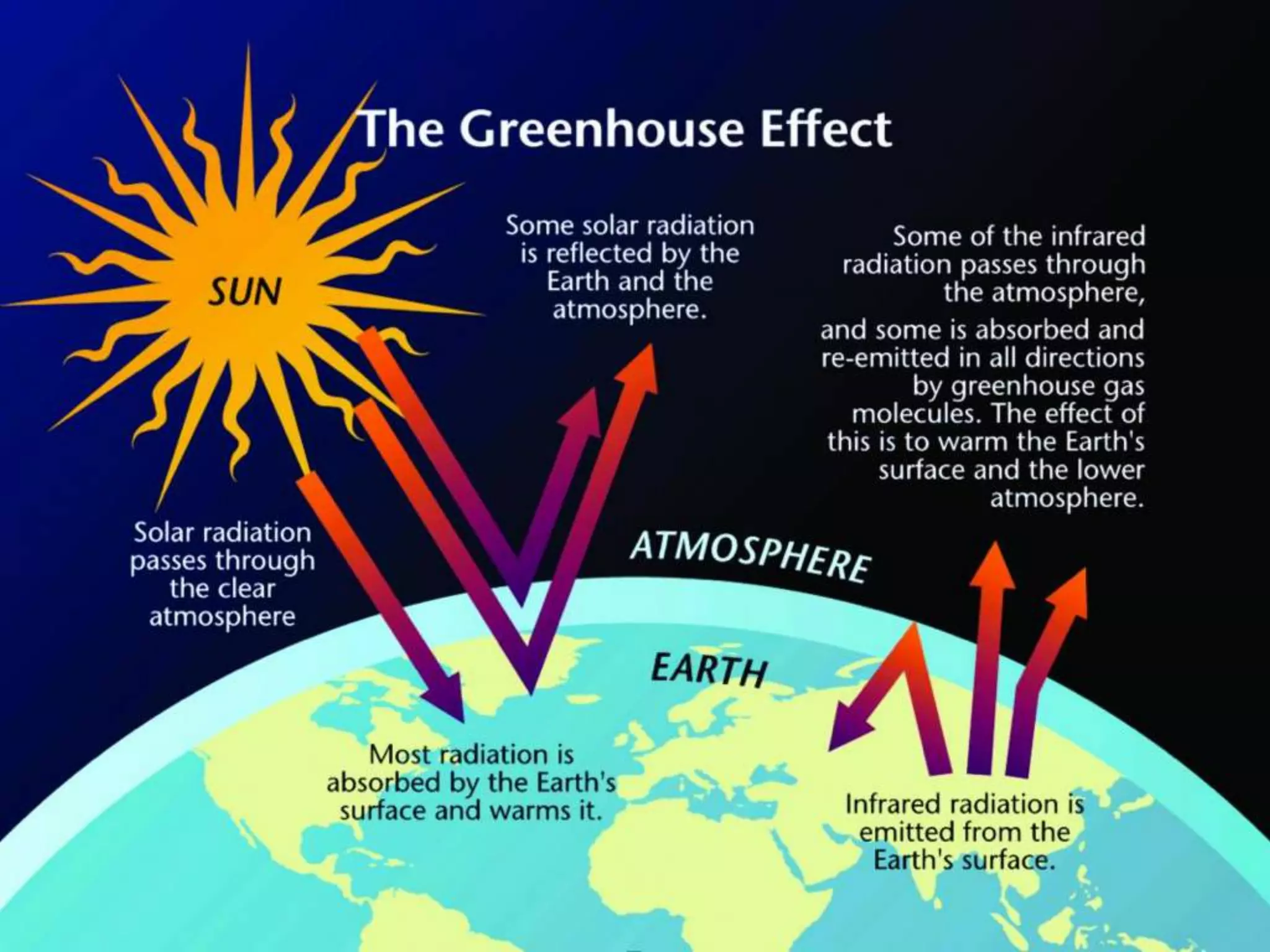
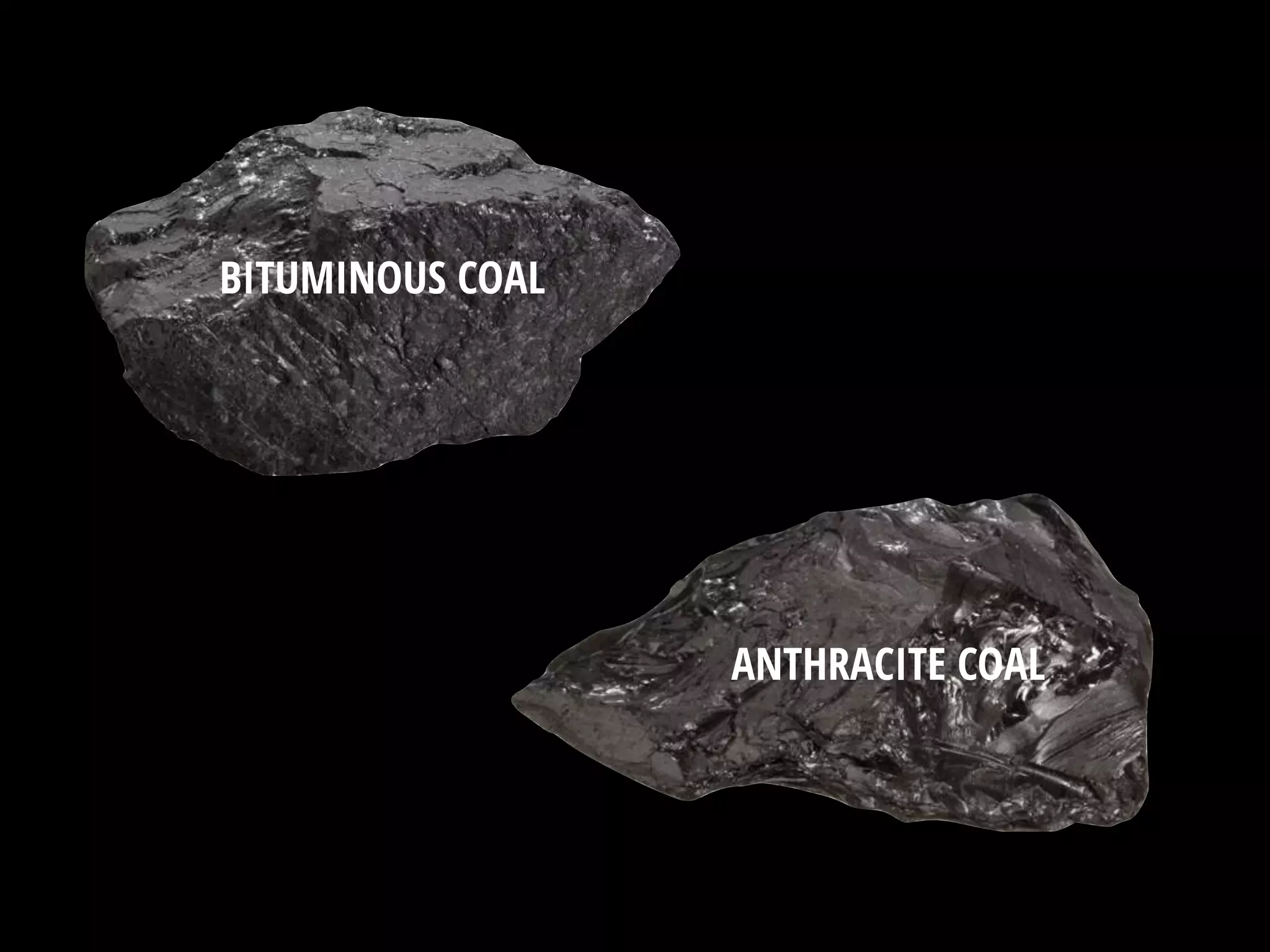
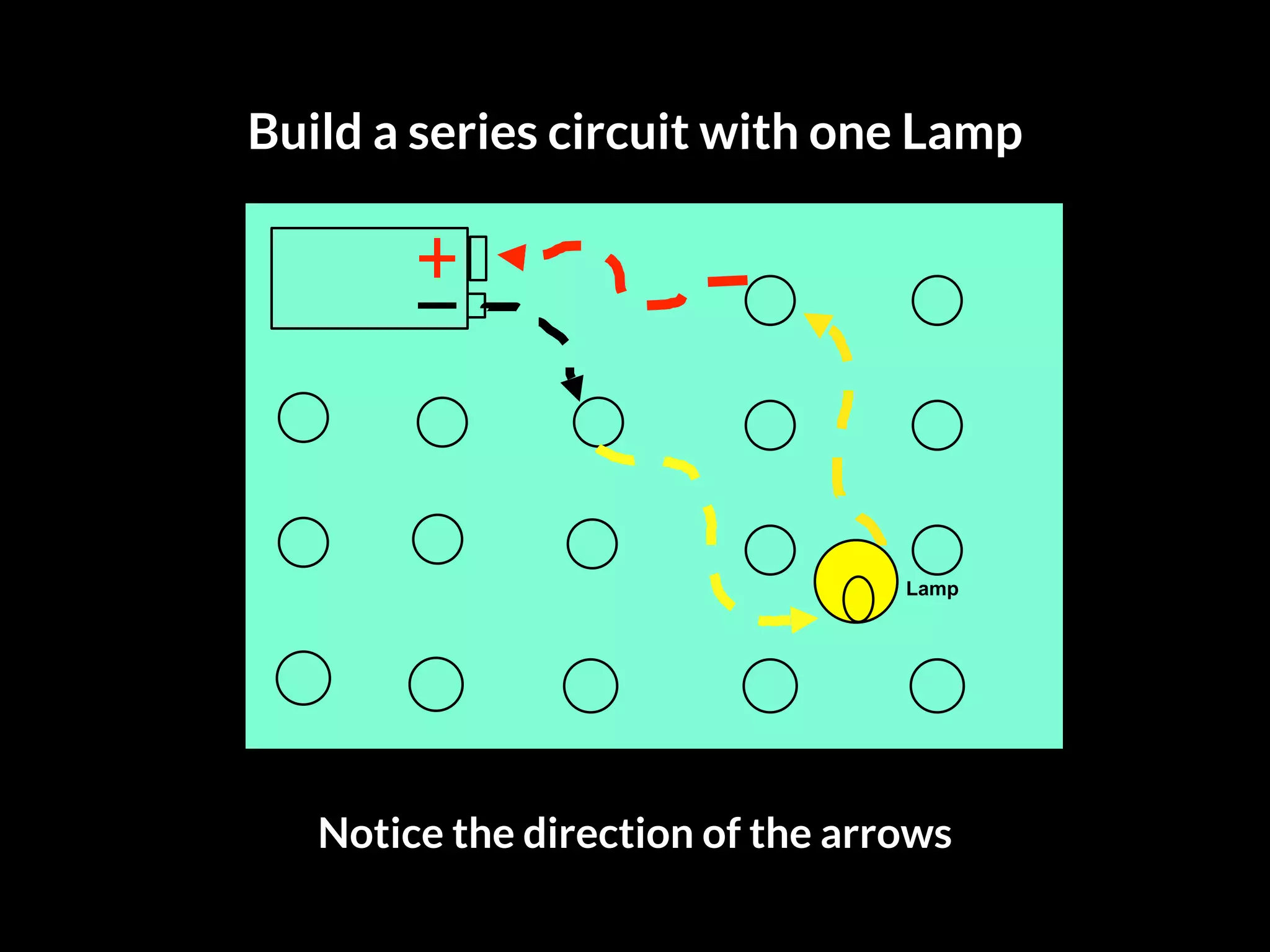
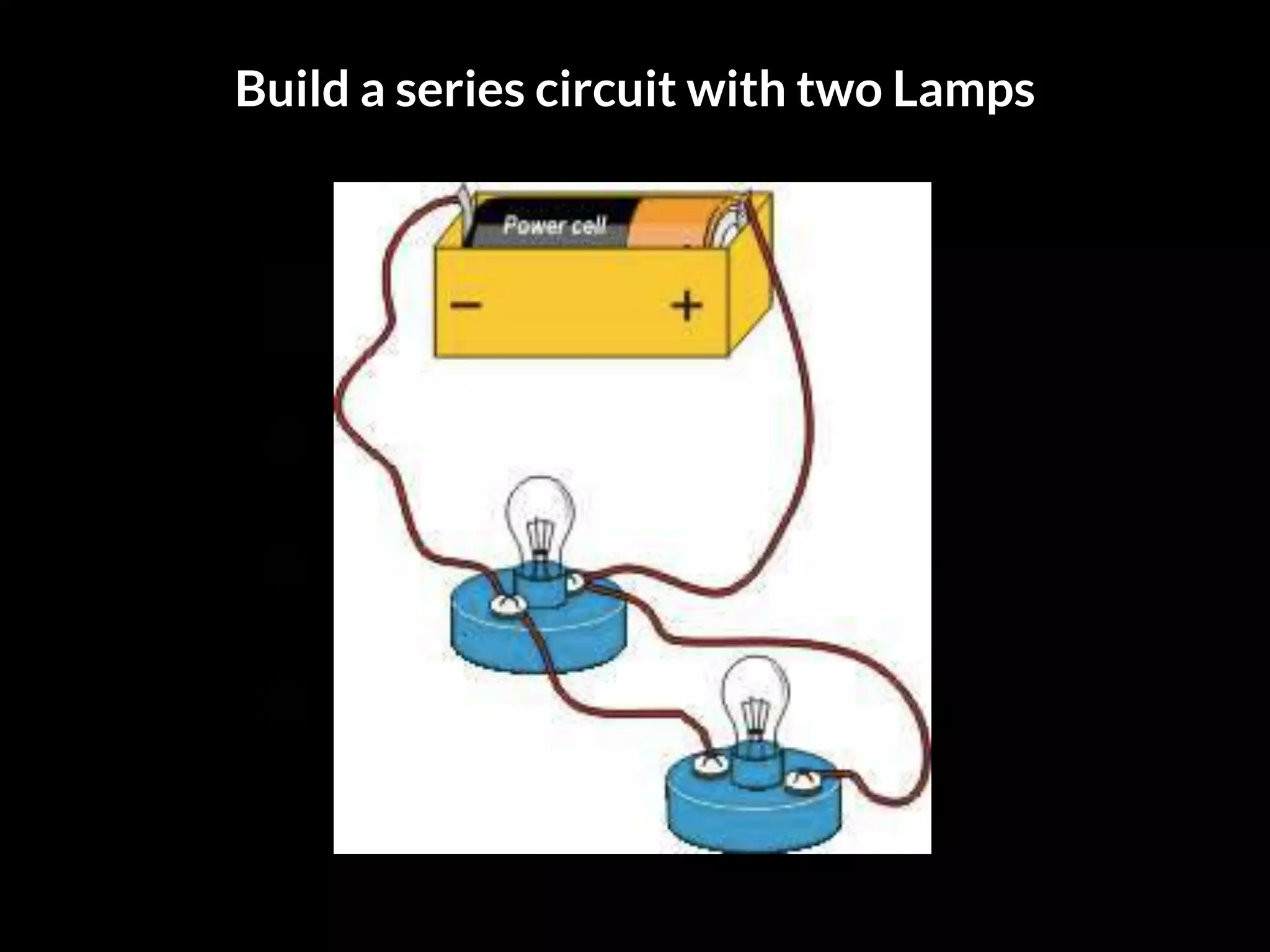
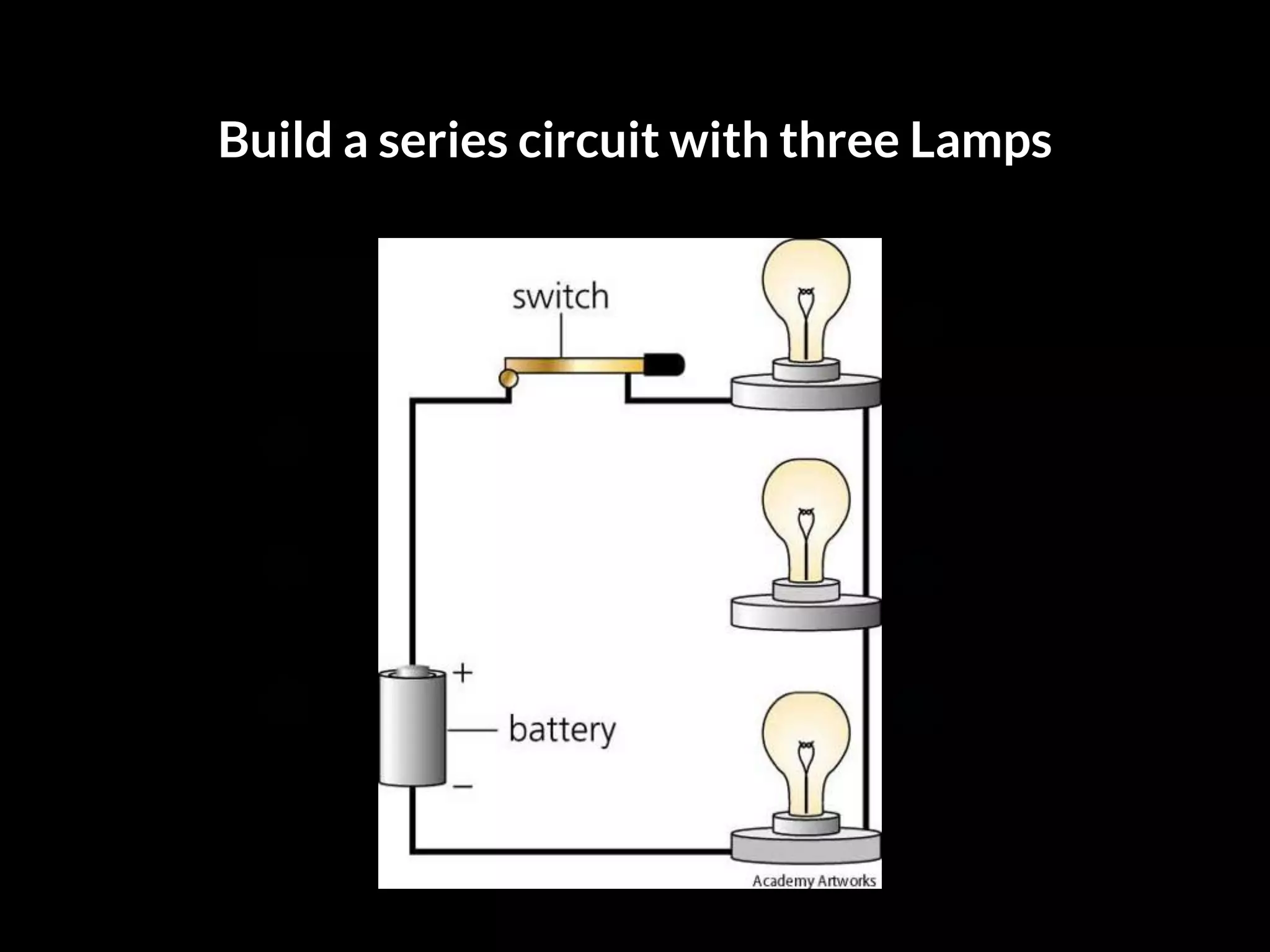
The document discusses integrating iPads into science classrooms. It describes activities like taking photos with iPads during a marshmallow building challenge. Teachers are introduced who have experience with classroom and 1:1 iPad integration. The benefits of 1:1 computing and using iPads specifically are discussed, including the large number of available apps, the ability to create and consume content, and their intuitive interface. Project-based learning sequences using iPads are presented, covering areas like aerodynamics and density.