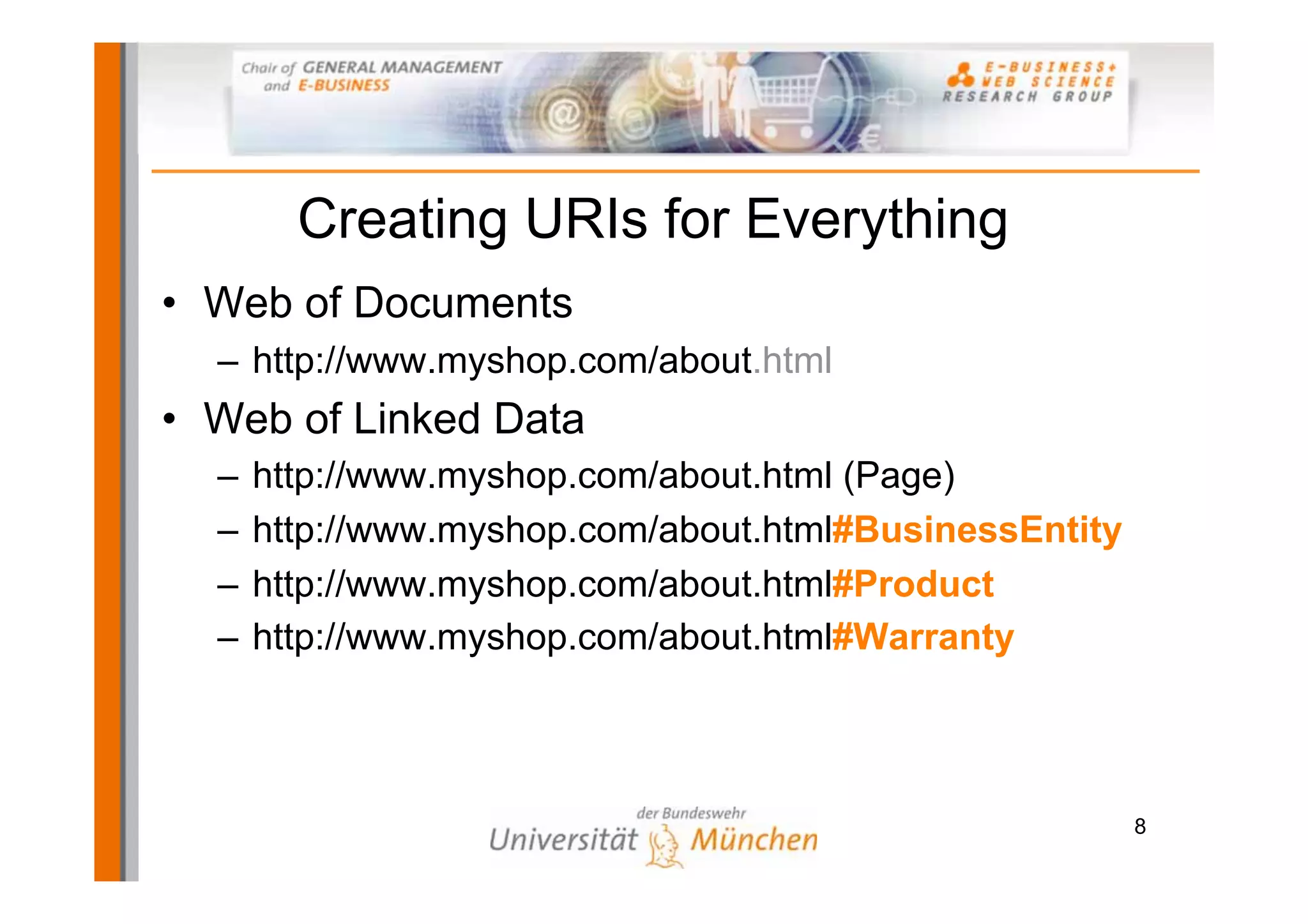
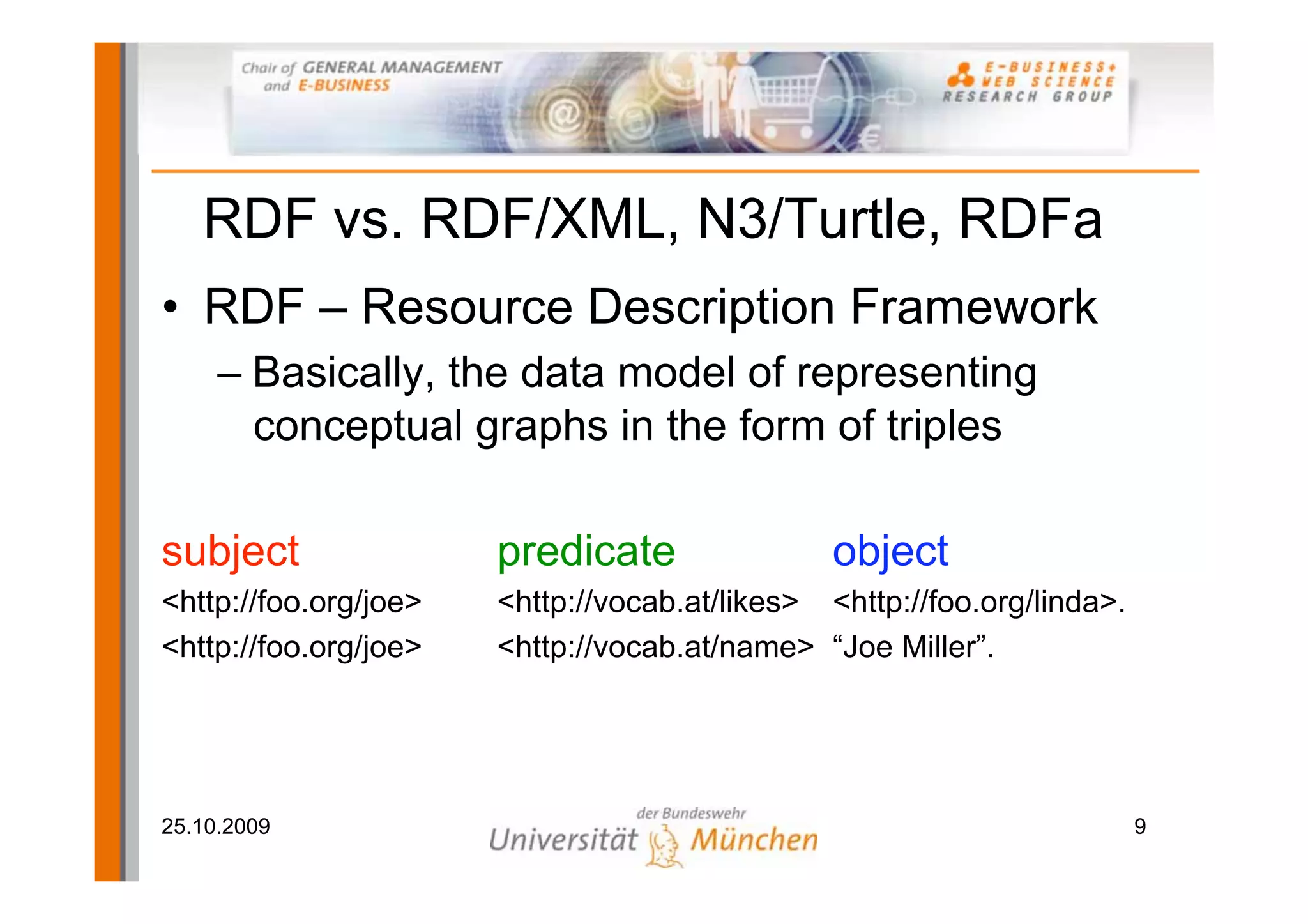
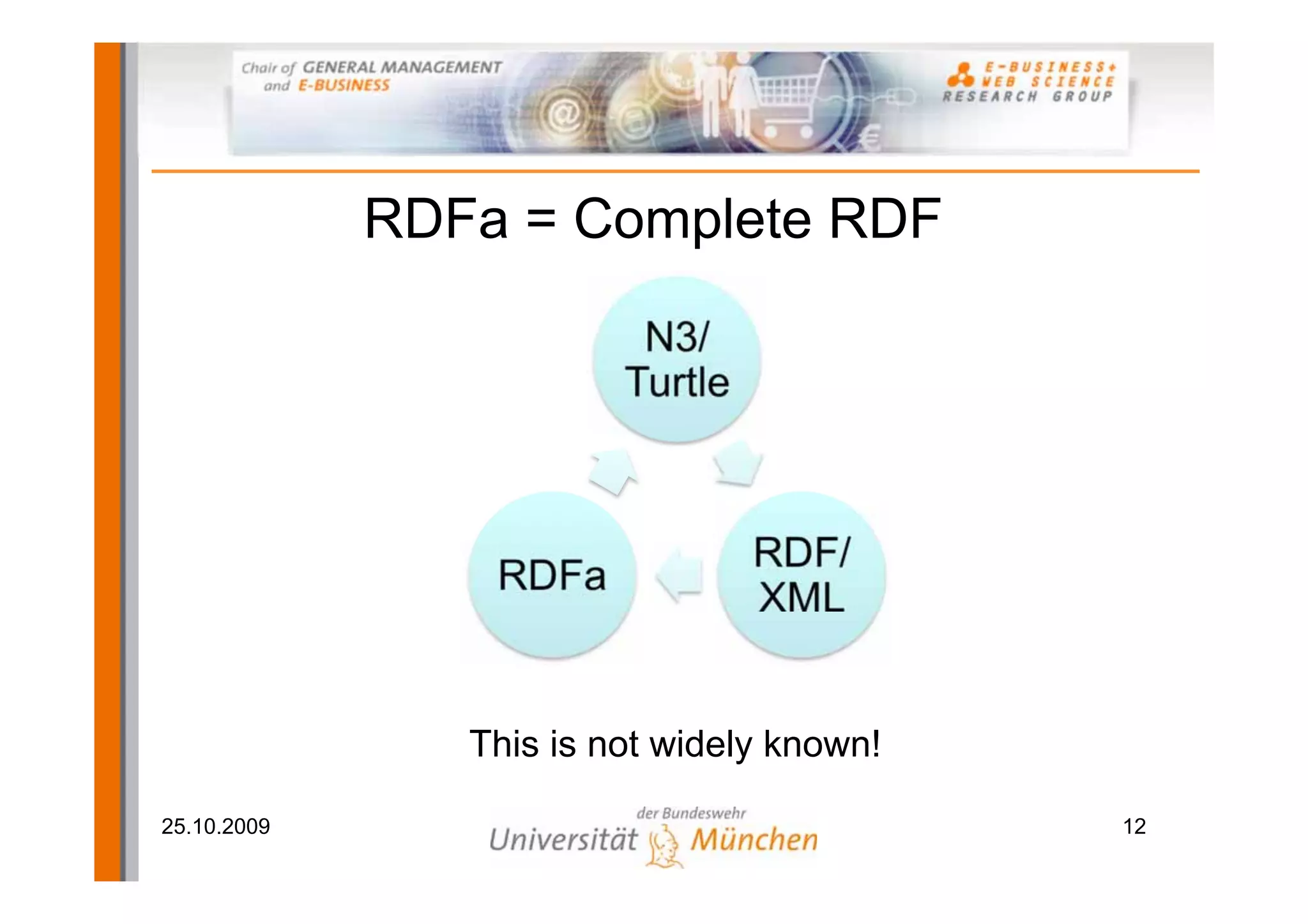
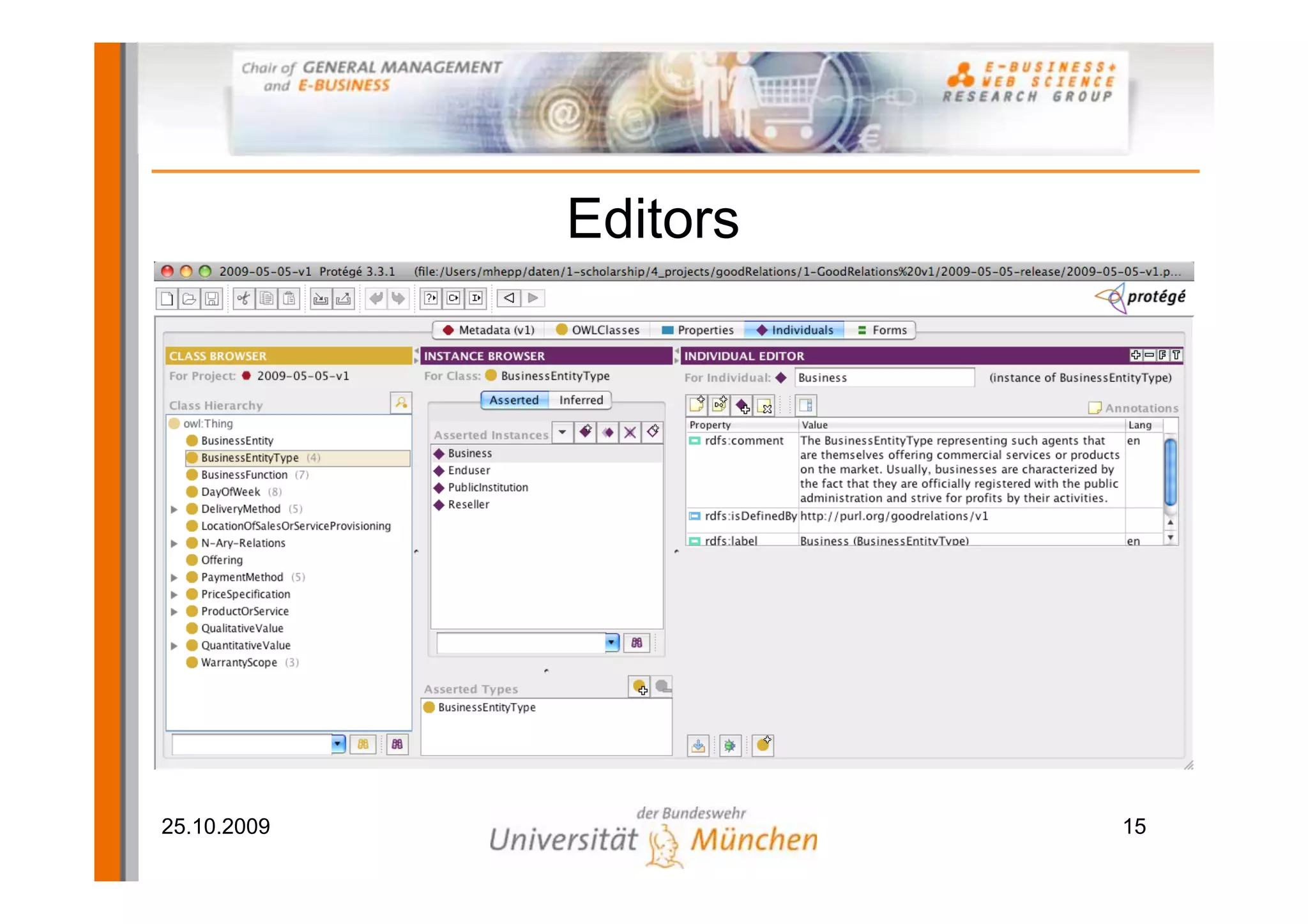
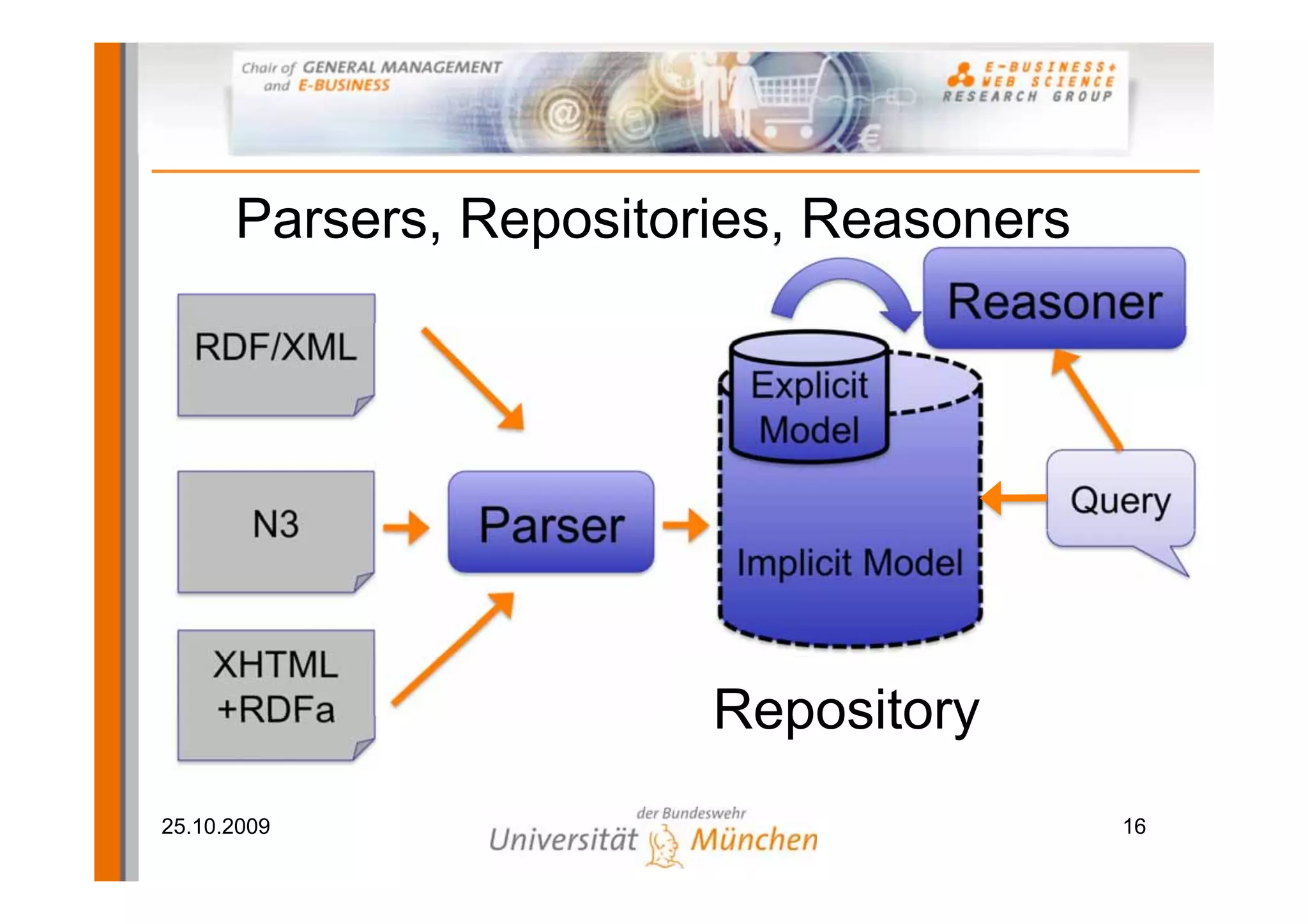
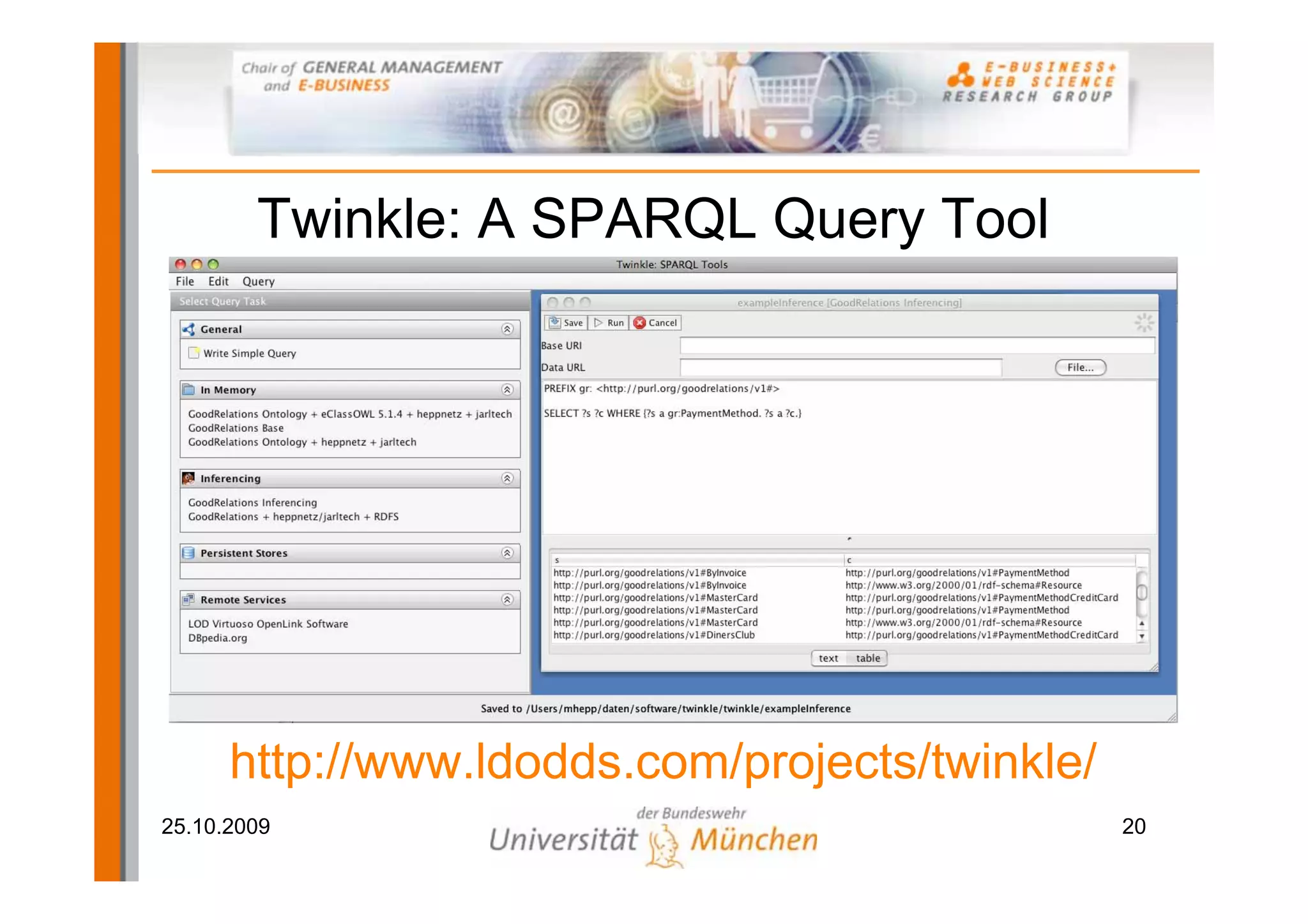
The document outlines a tutorial on the GoodRelations ontology, RDFa, and Yahoo! SearchMonkey for e-commerce, held at the Westfields Conference Center. It includes an overview of prerequisites, sessions on semantic web technology, hands-on exercises for annotating a web shop, and discussions on publishing and querying semantic data. The tutorial aims to equip participants with practical knowledge and skills to leverage the web of data in their e-commerce applications.