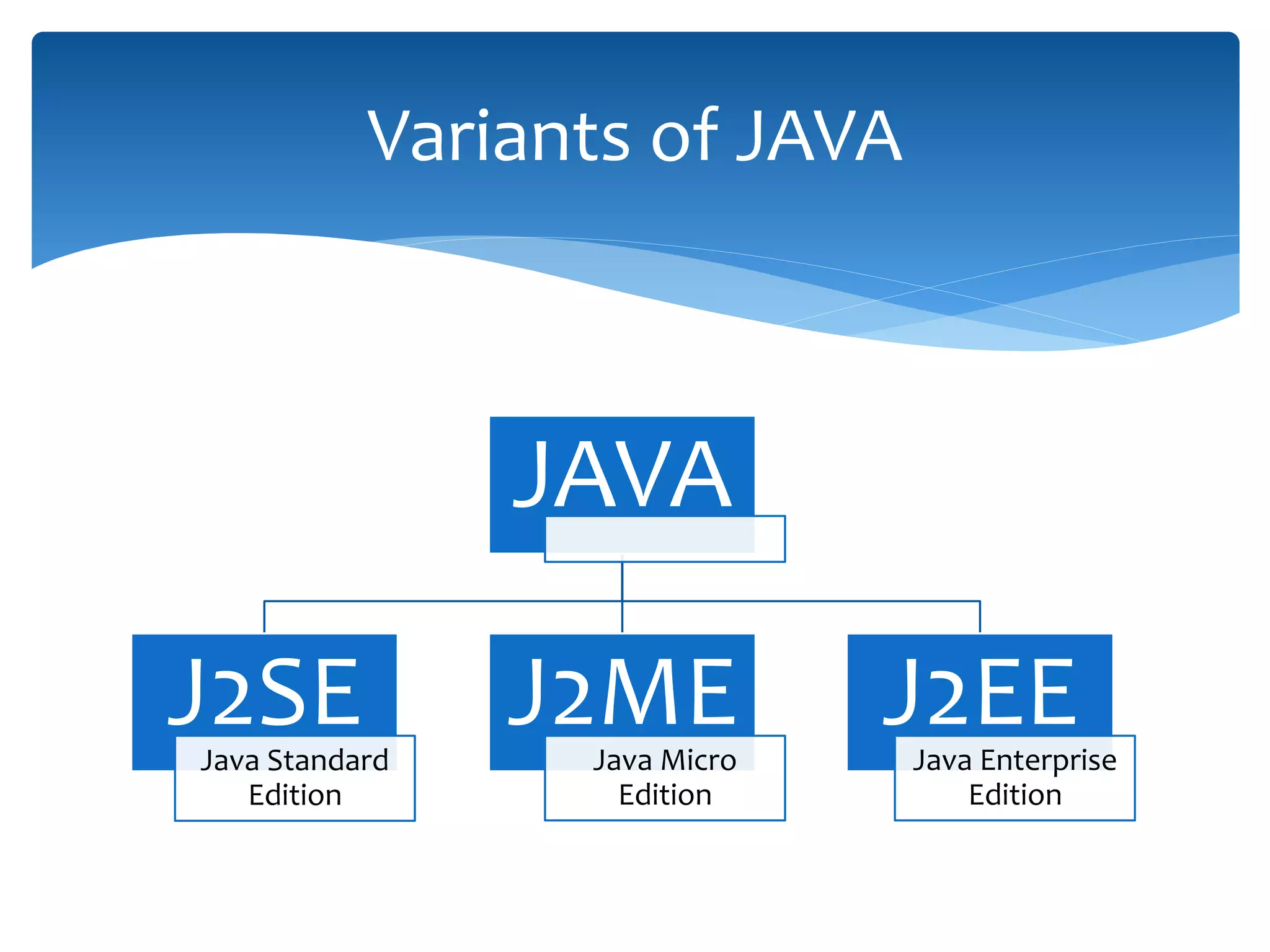
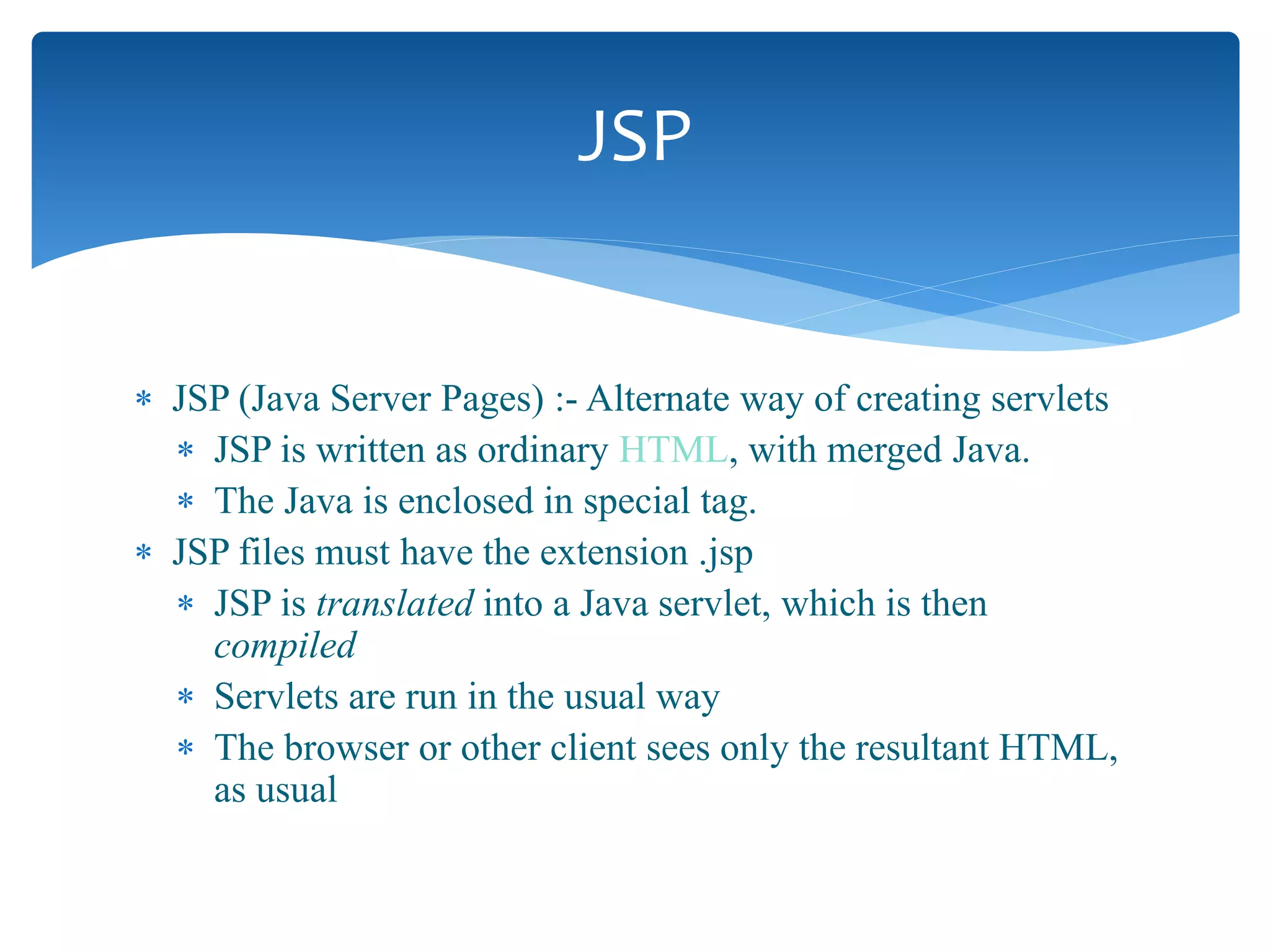
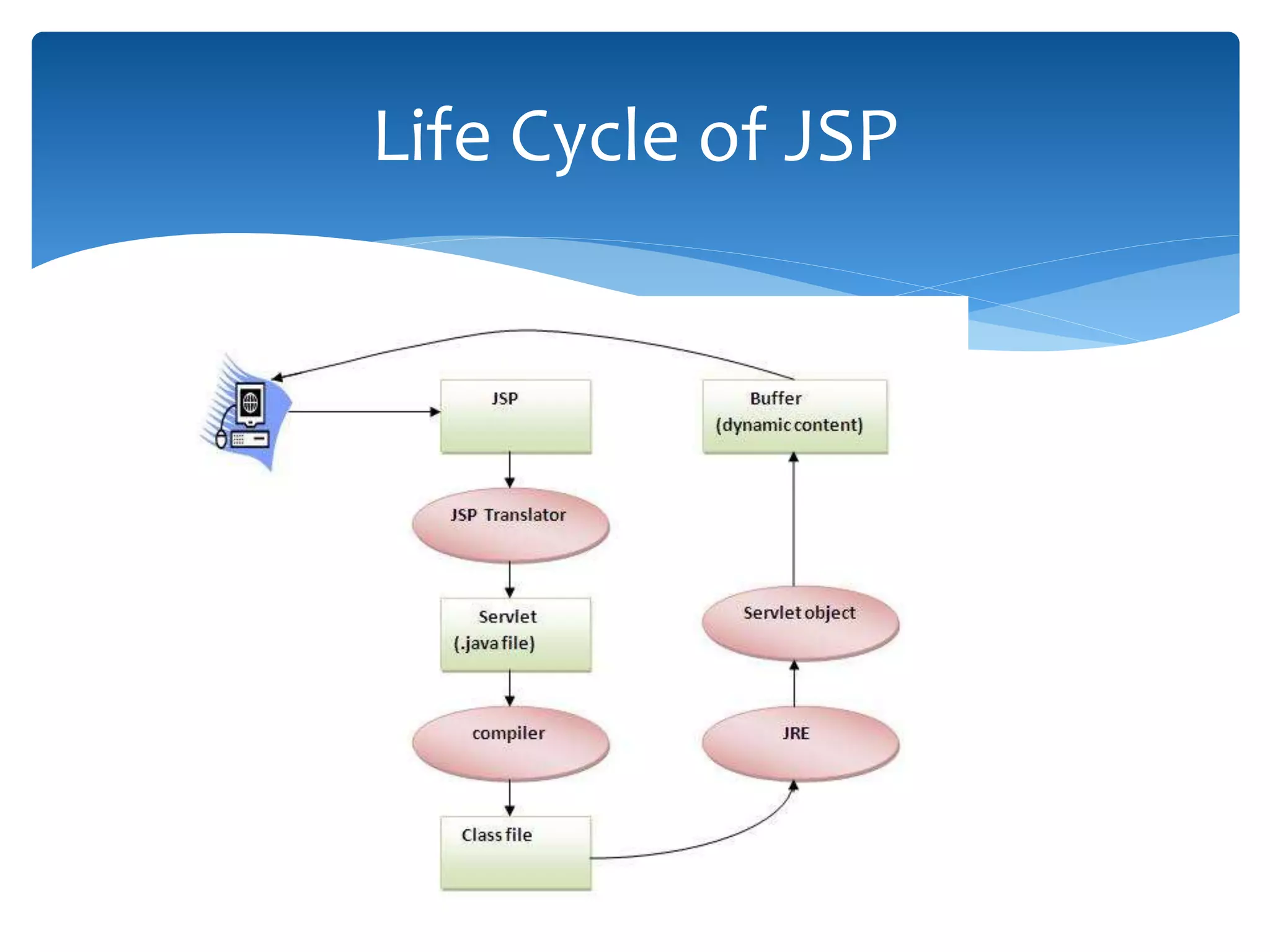
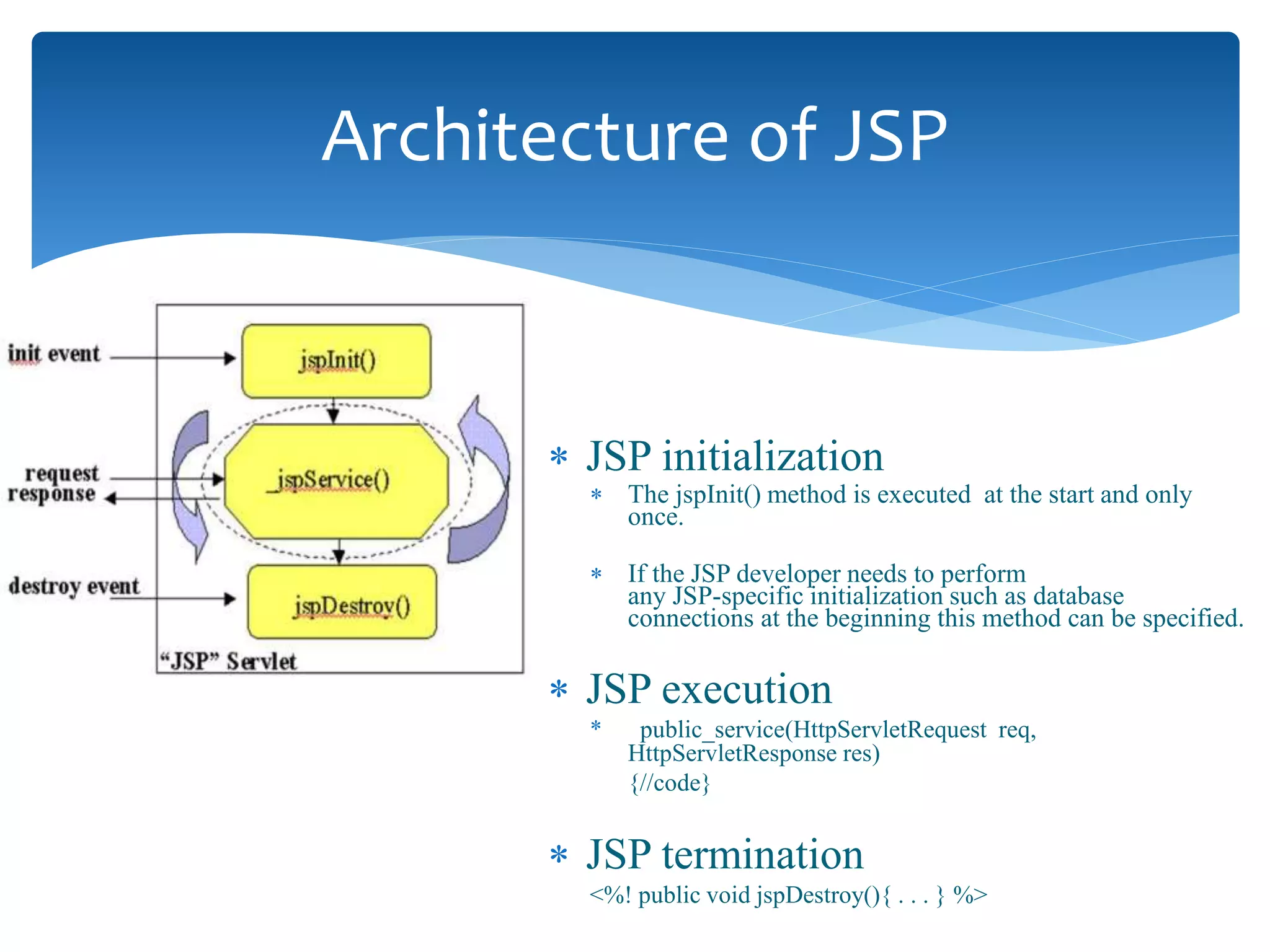
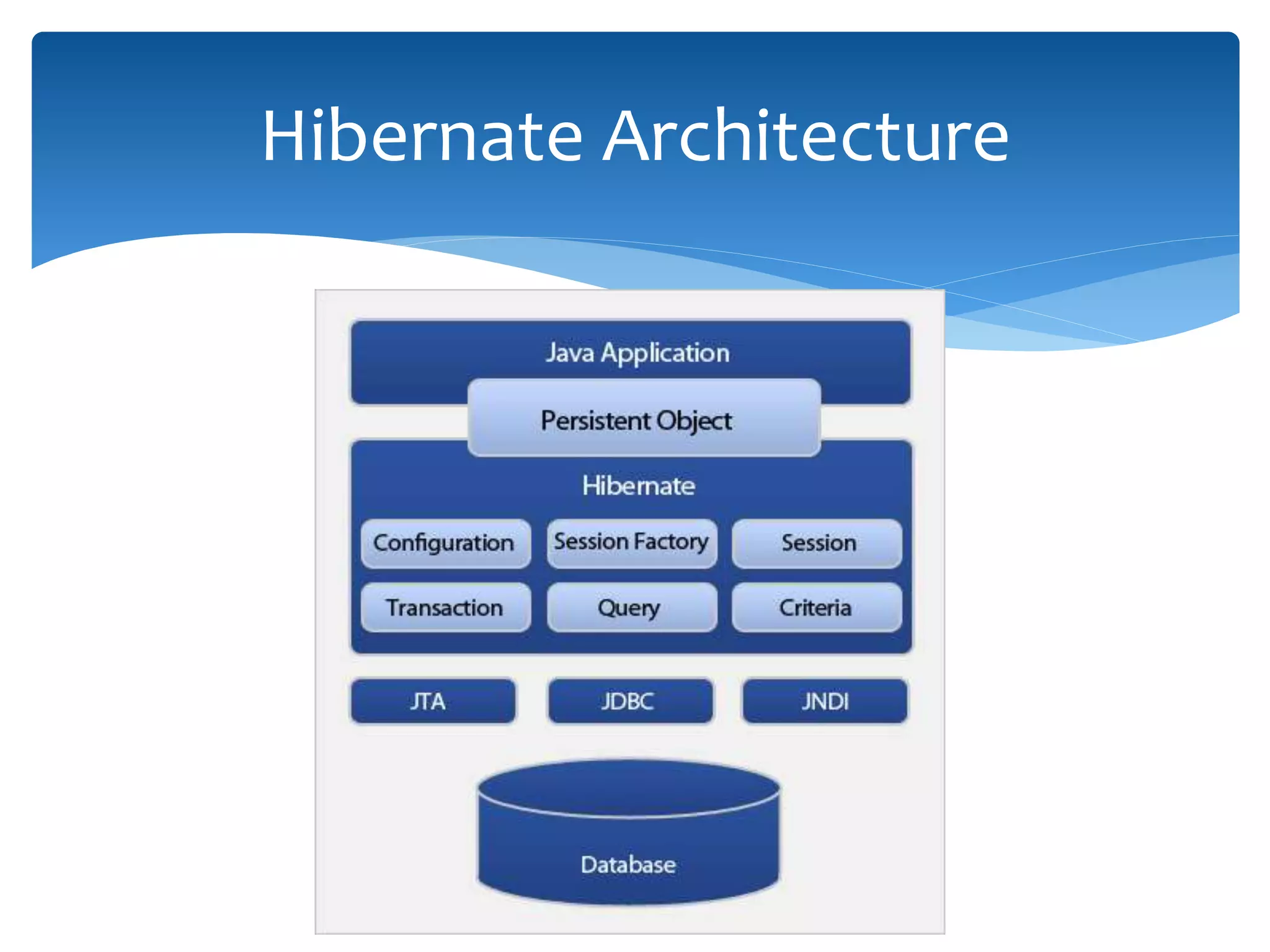
This document provides an overview of the J2EE Struts framework with Hibernate. It introduces Java and describes its major versions. It then discusses J2EE and its need for developing enterprise applications. Key J2EE components like servlets, JSP, Struts, and Hibernate are explained at a high level. Hibernate is presented as an object-relational mapping tool that simplifies data persistence compared to traditional JDBC. The document concludes with a thank you.