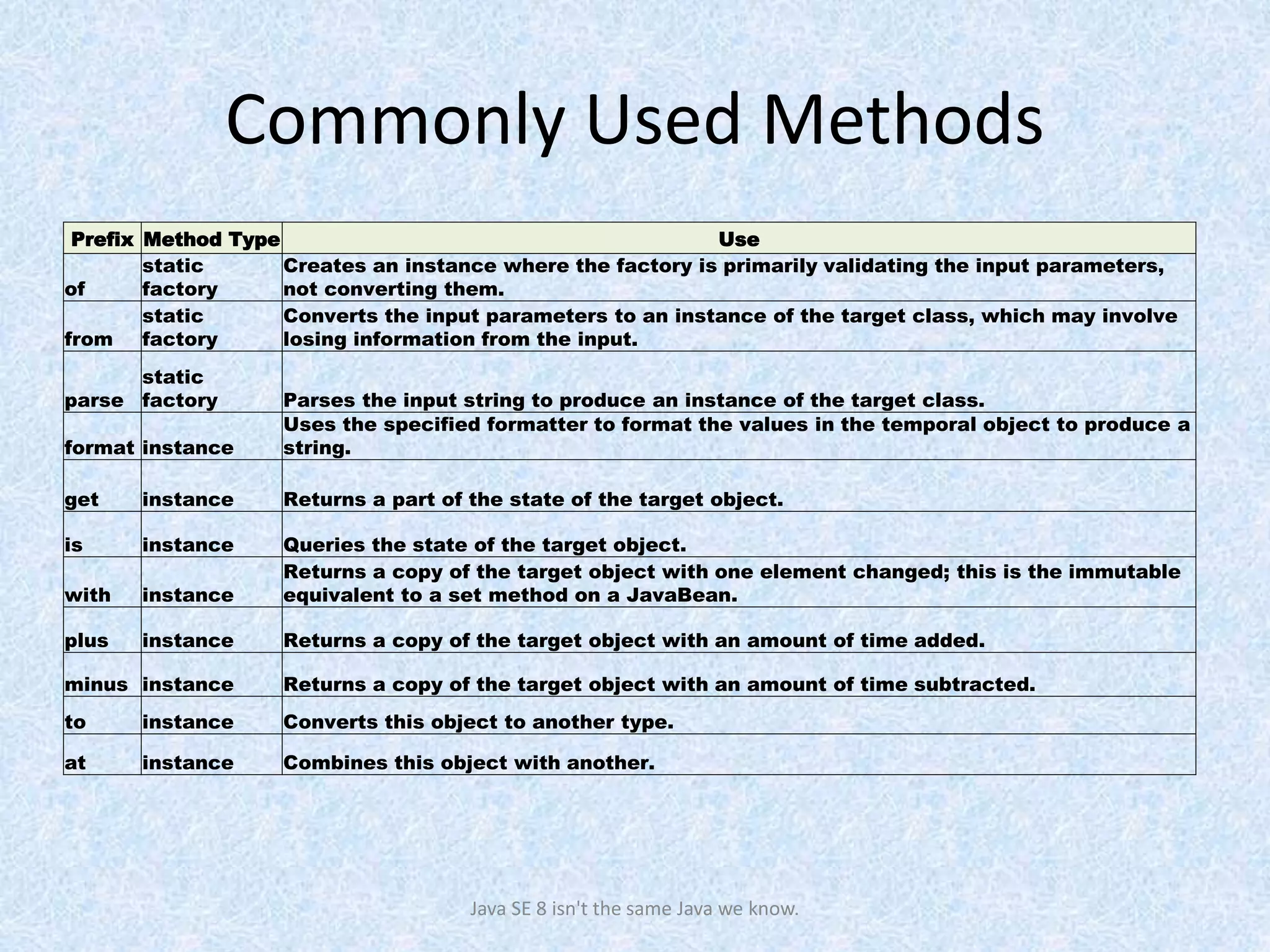
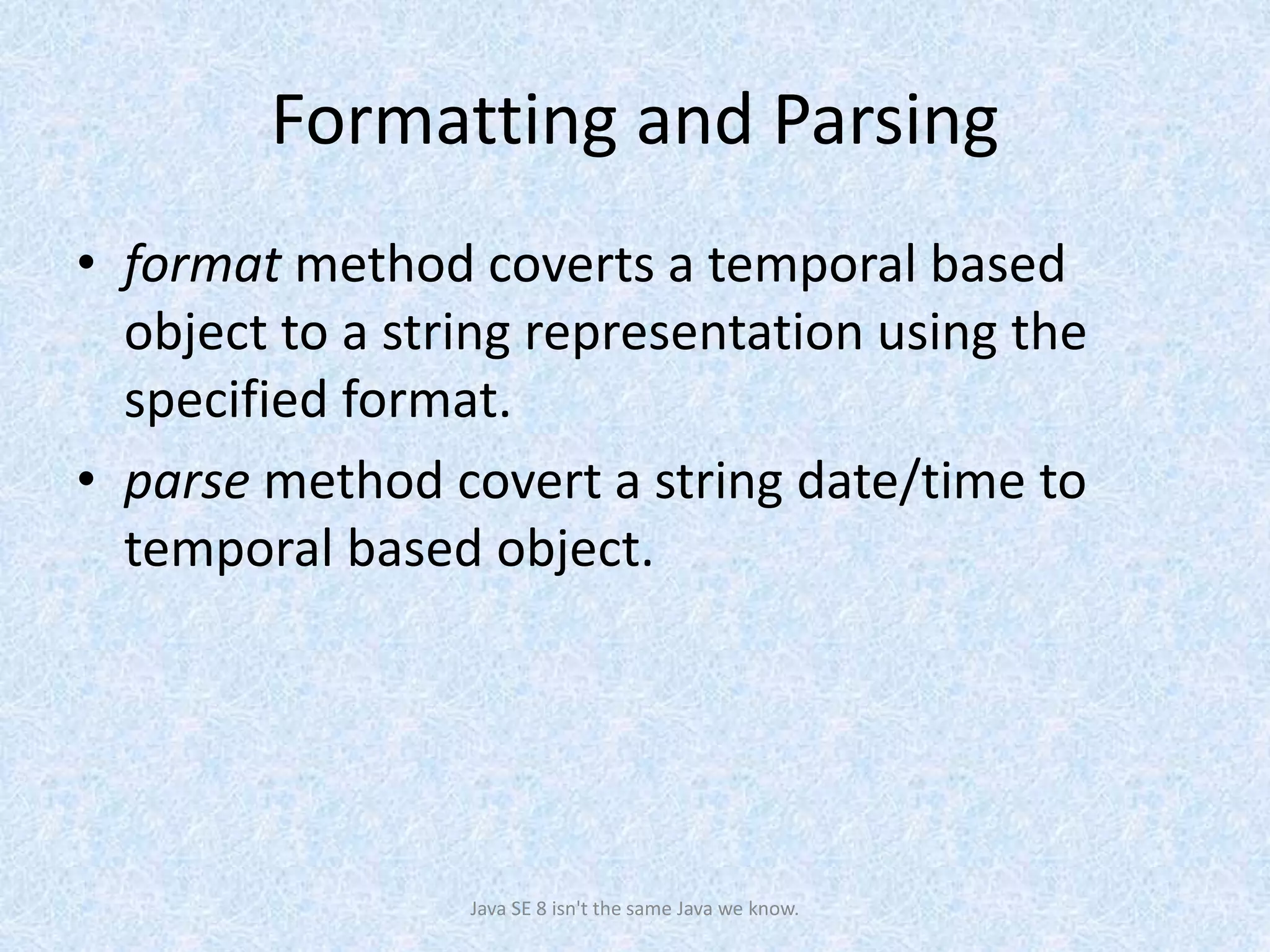
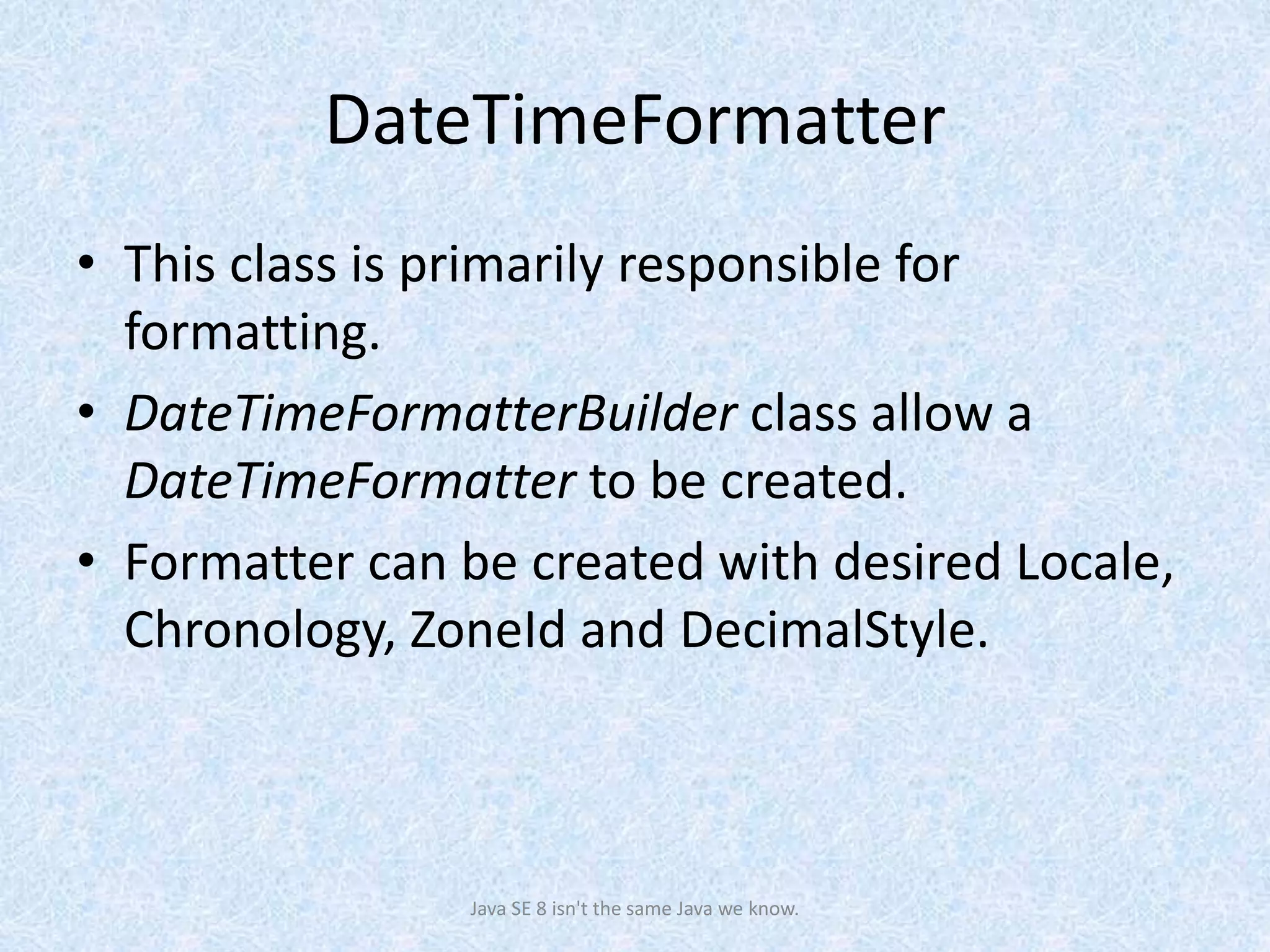
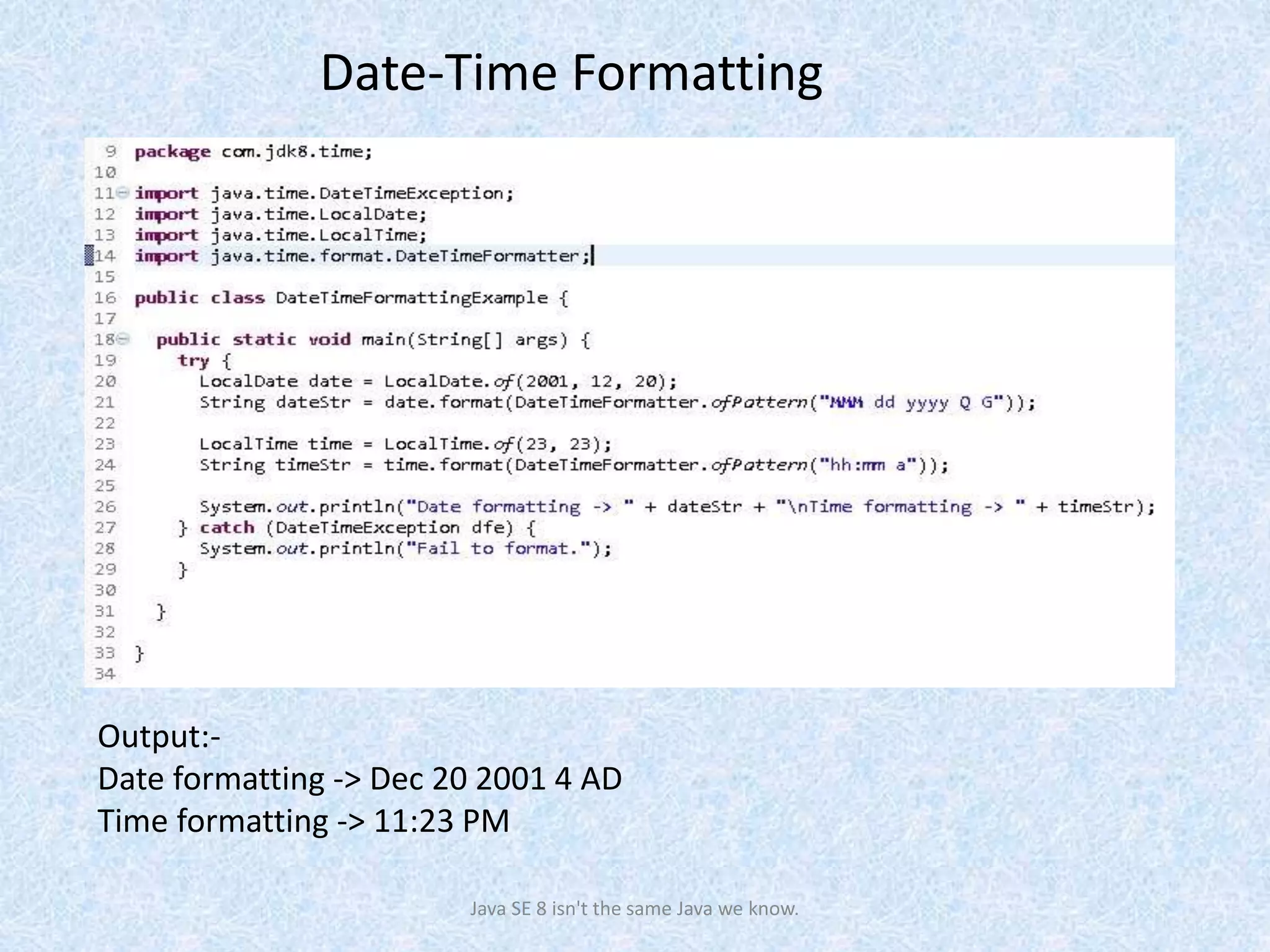
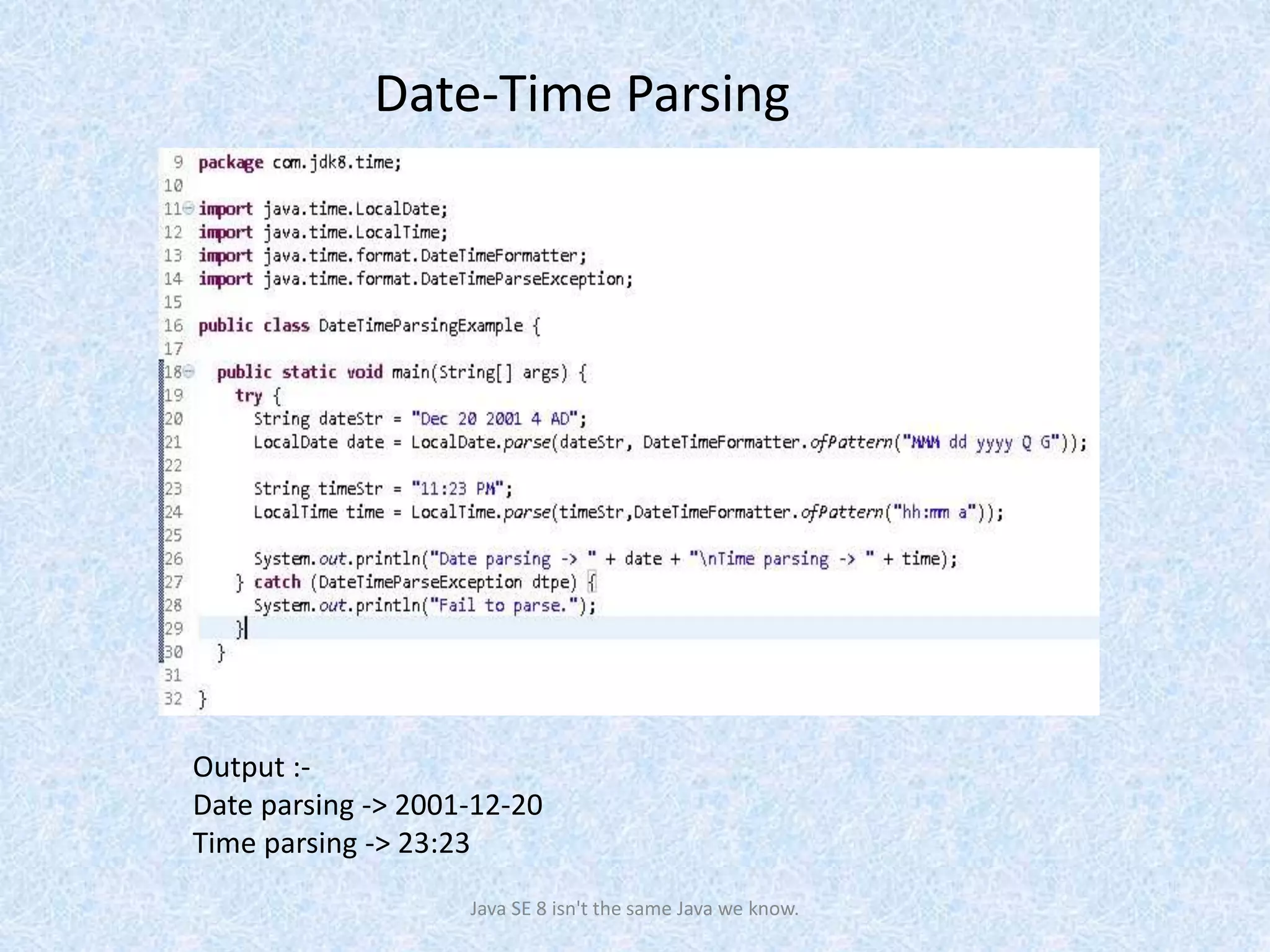
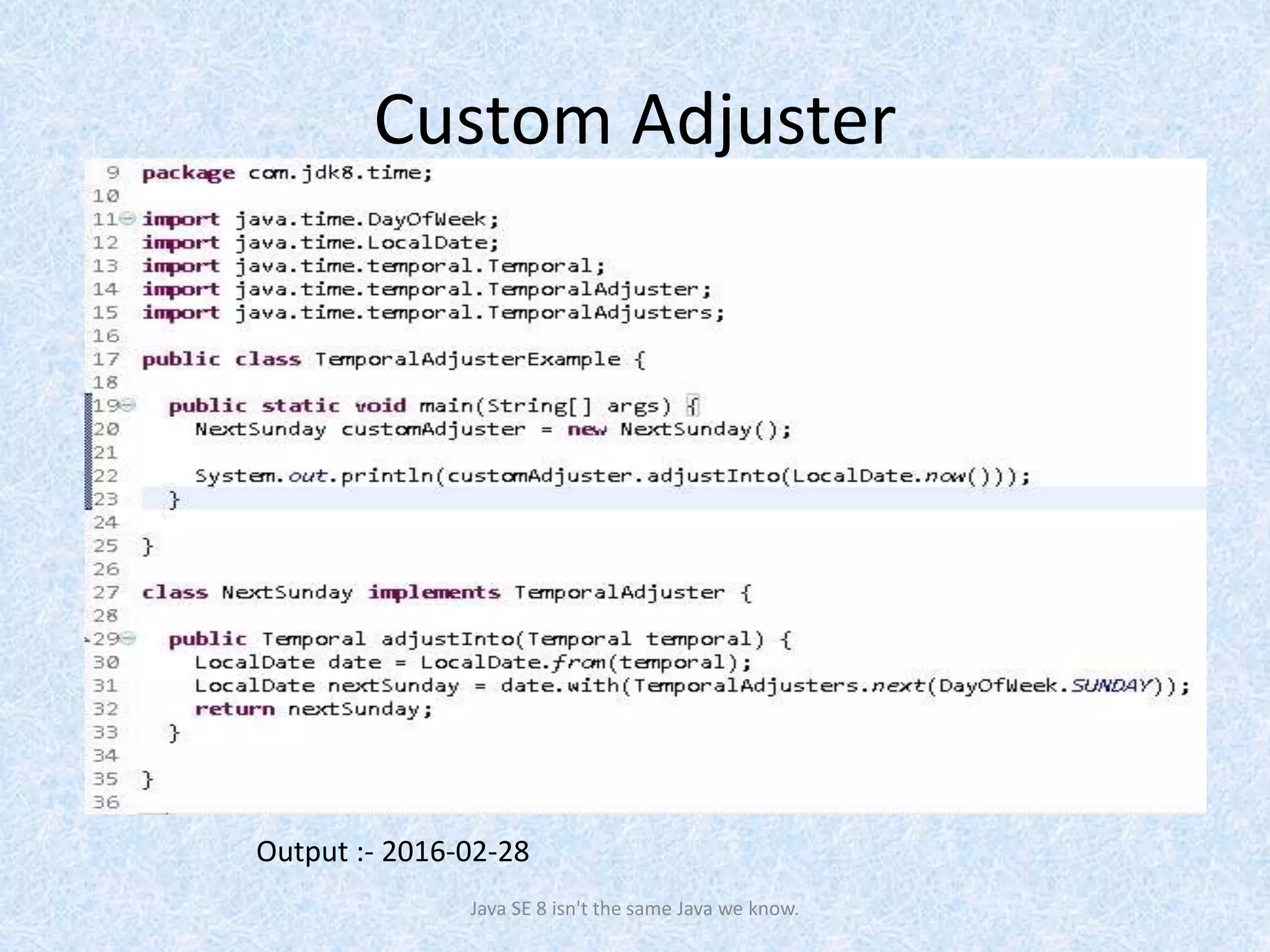
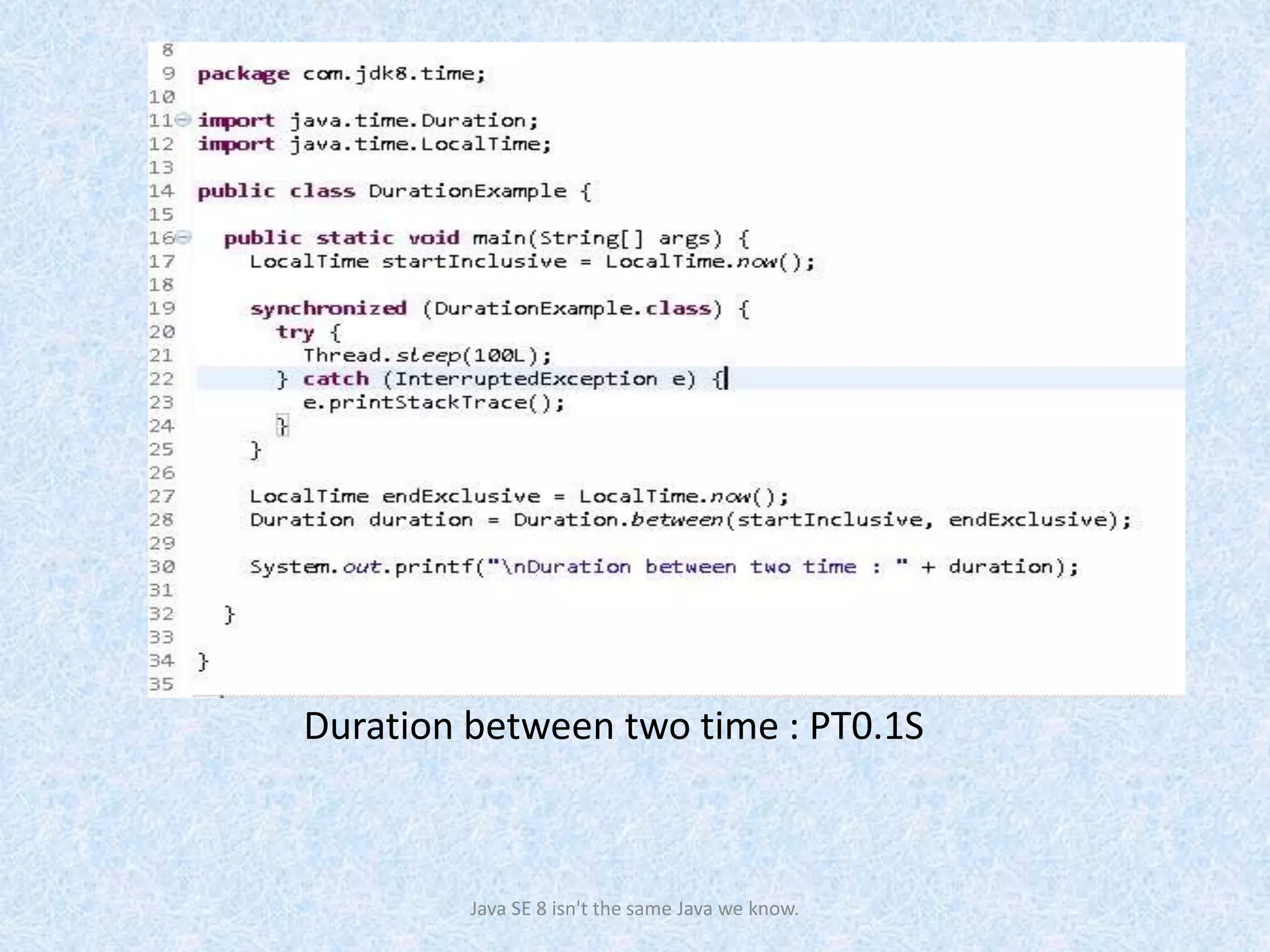
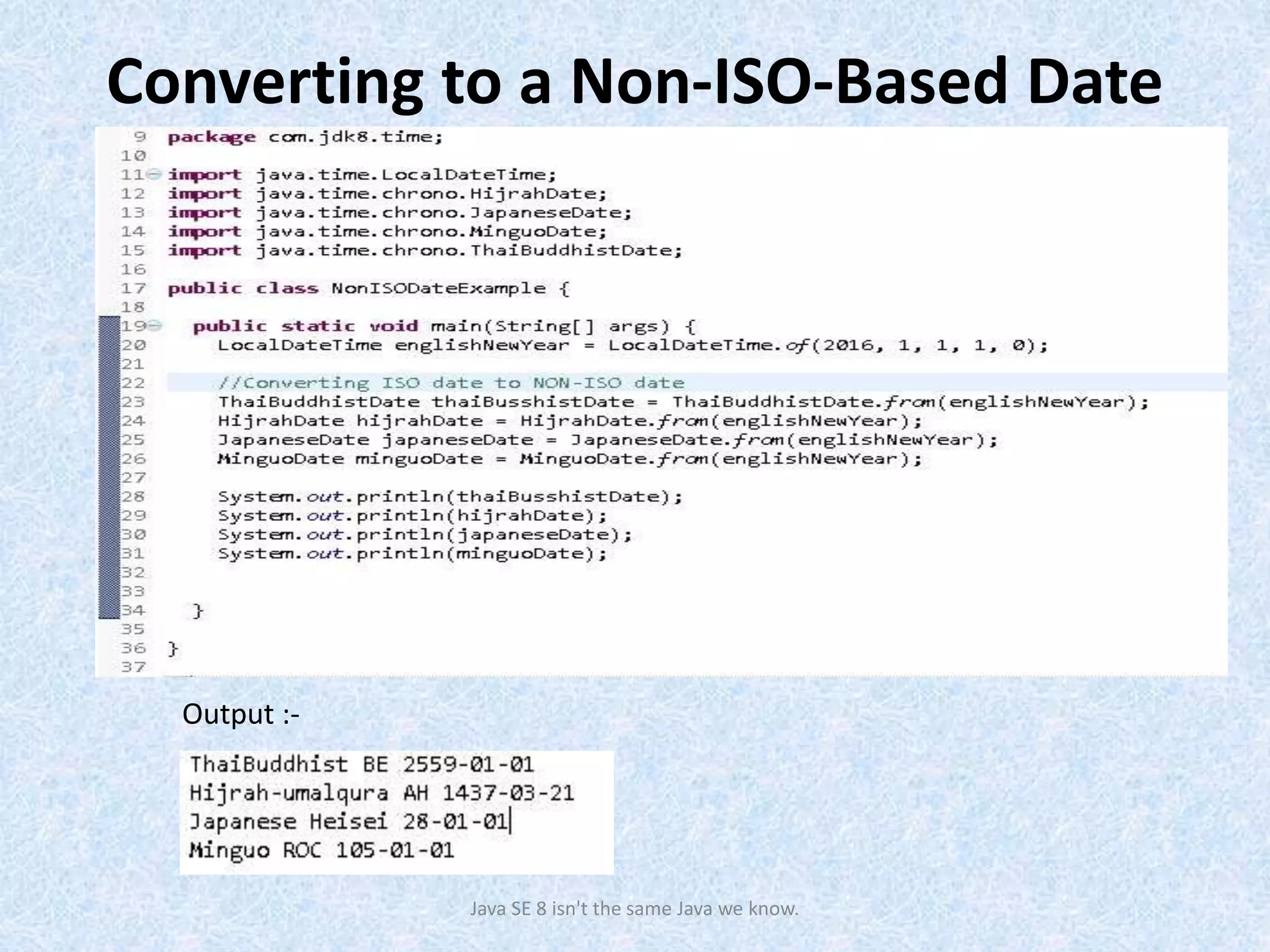
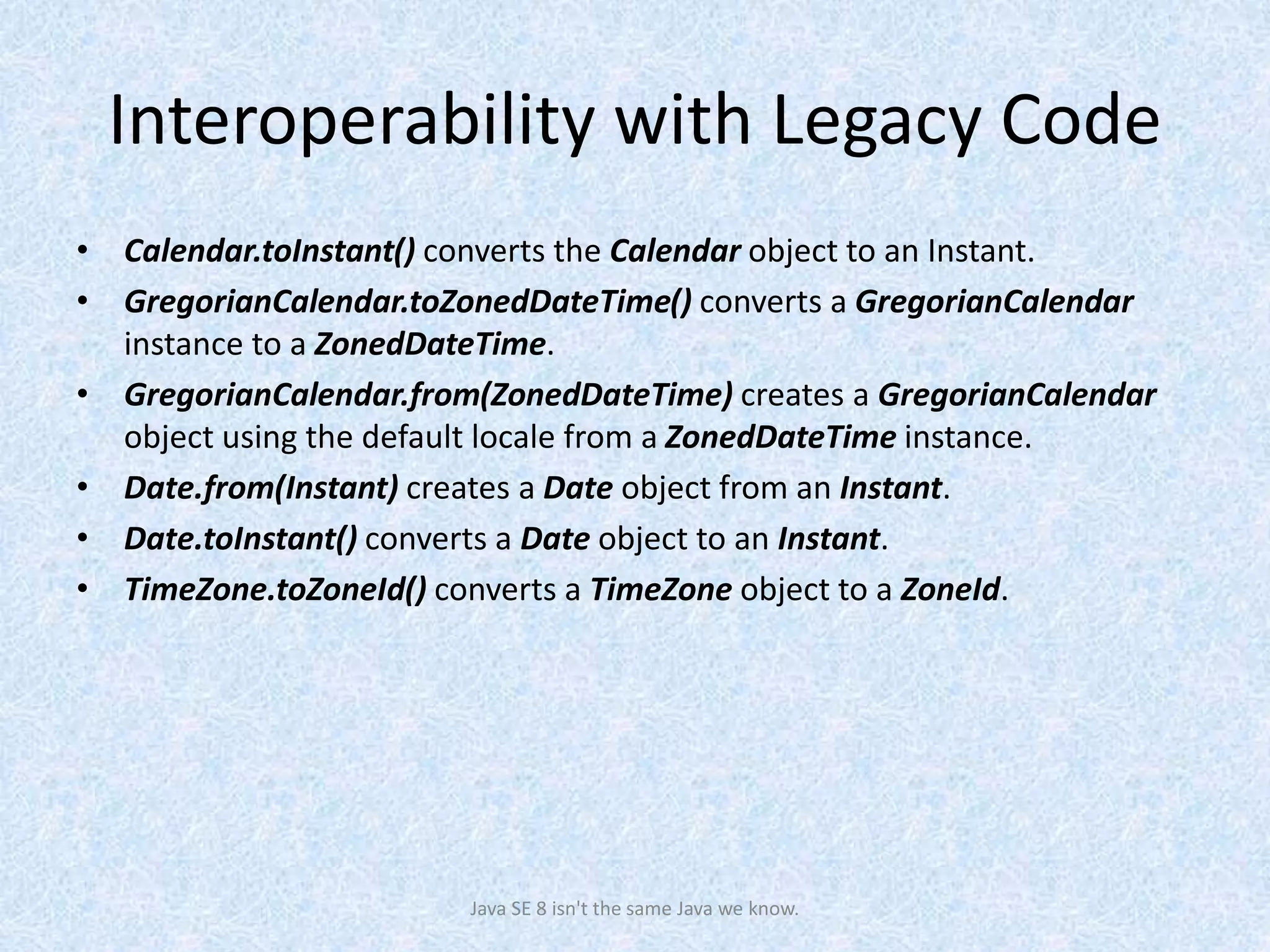
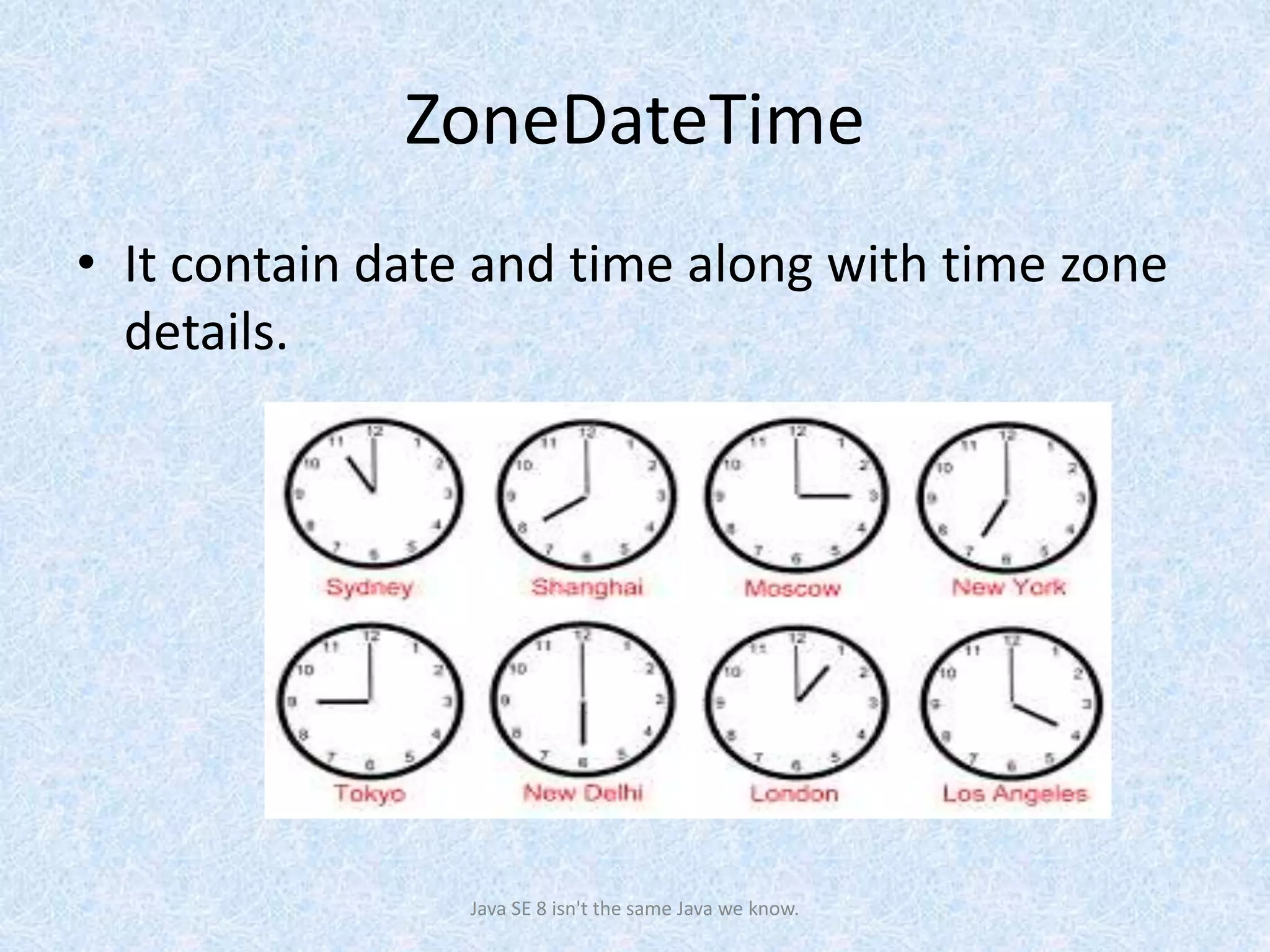
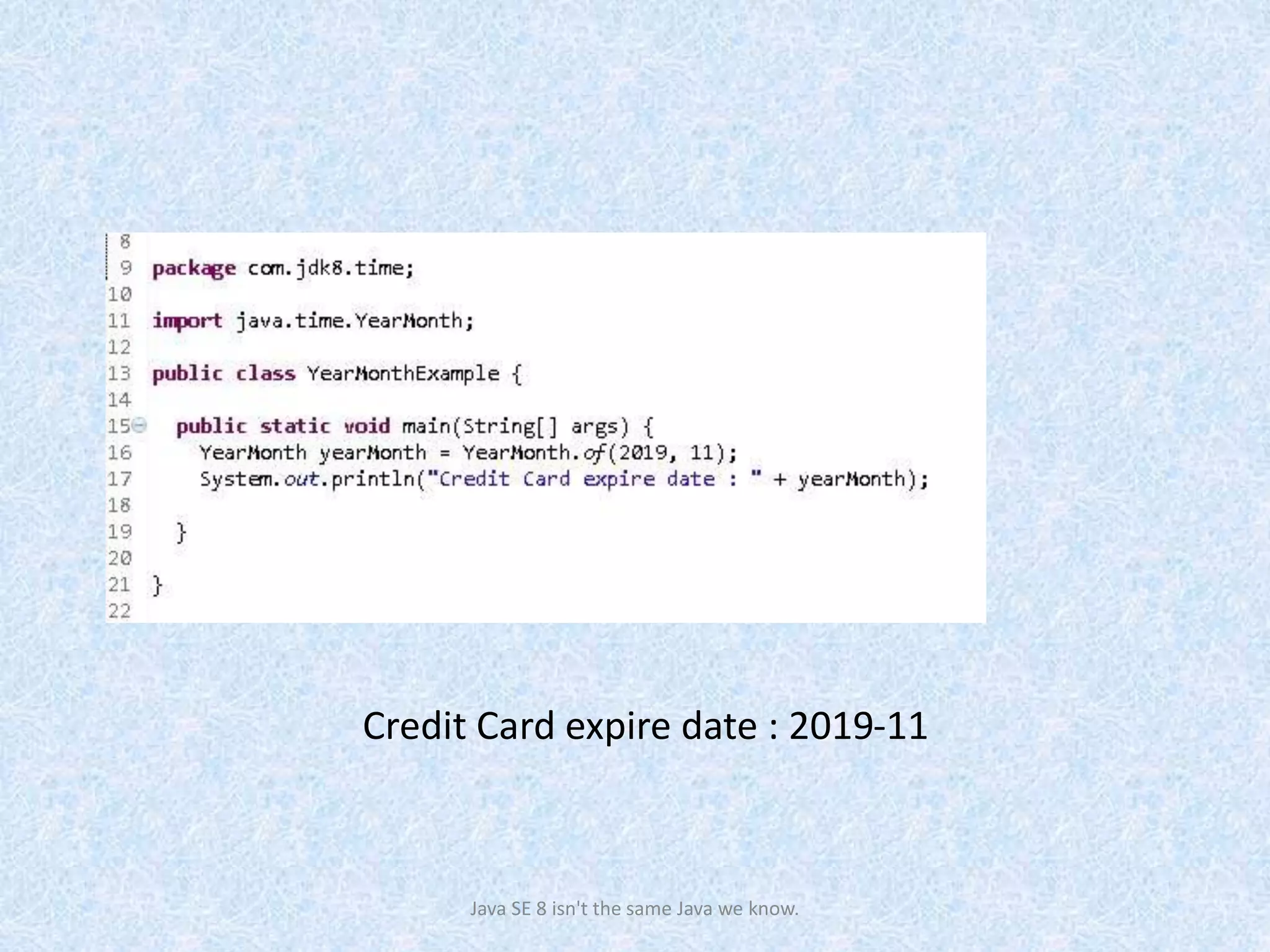
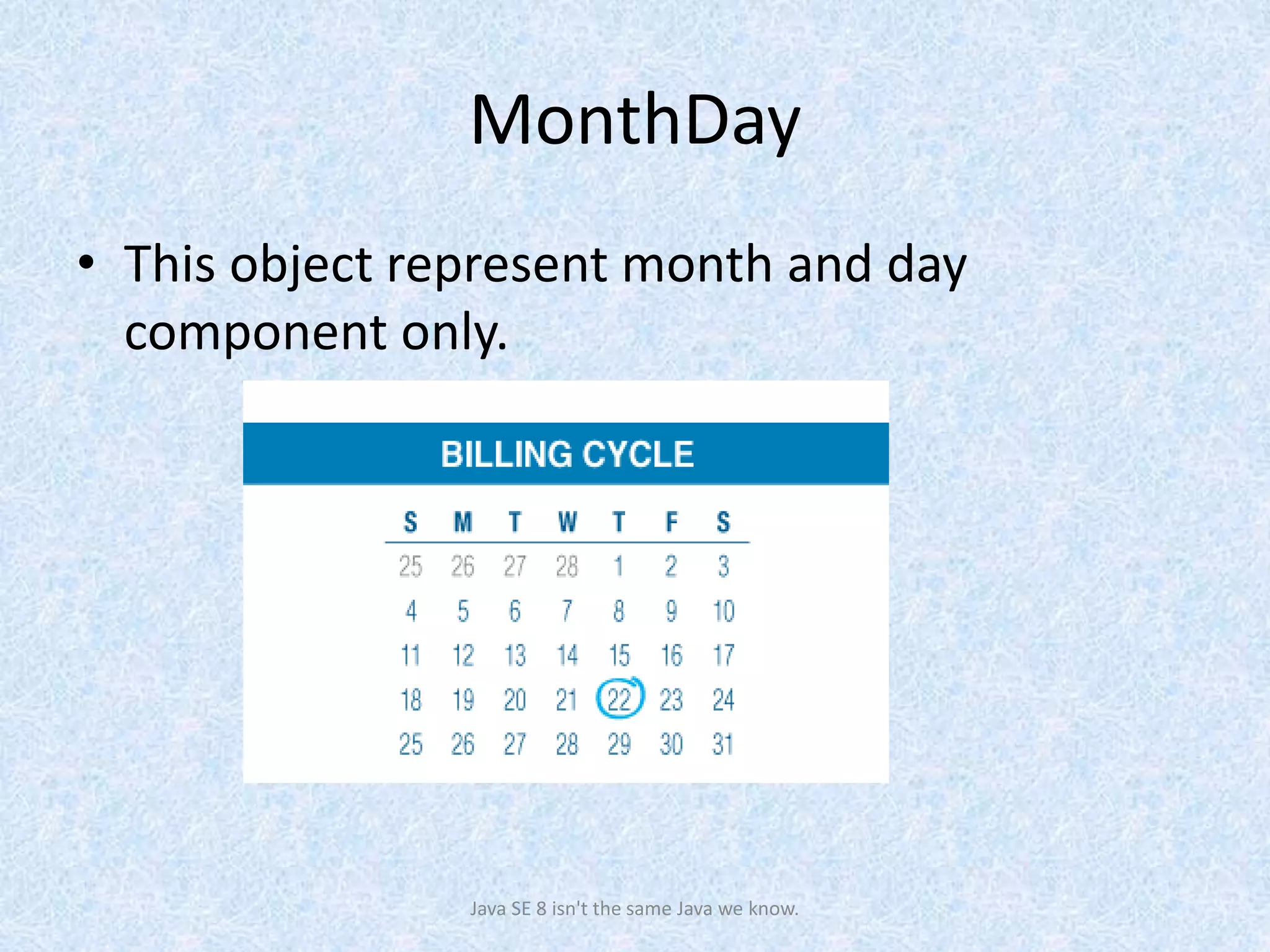
The document discusses the new date and time API introduced in Java 8 (JSR-310). It provides examples of using the new classes like LocalDate, LocalTime, LocalDateTime to represent date, time, and date-time. These classes are immutable and thread-safe. The API also supports different calendar systems and time zones. Methods are demonstrated for getting the current date/time, modifying dates, checking for leap years, formatting and parsing dates from strings.








![What is epoch ?
• In the fields of chronology and periodization,
an epoch is an instant in time chosen as the
origin of a particular era. The "epoch" then
serves as a reference point from which time is
measured.
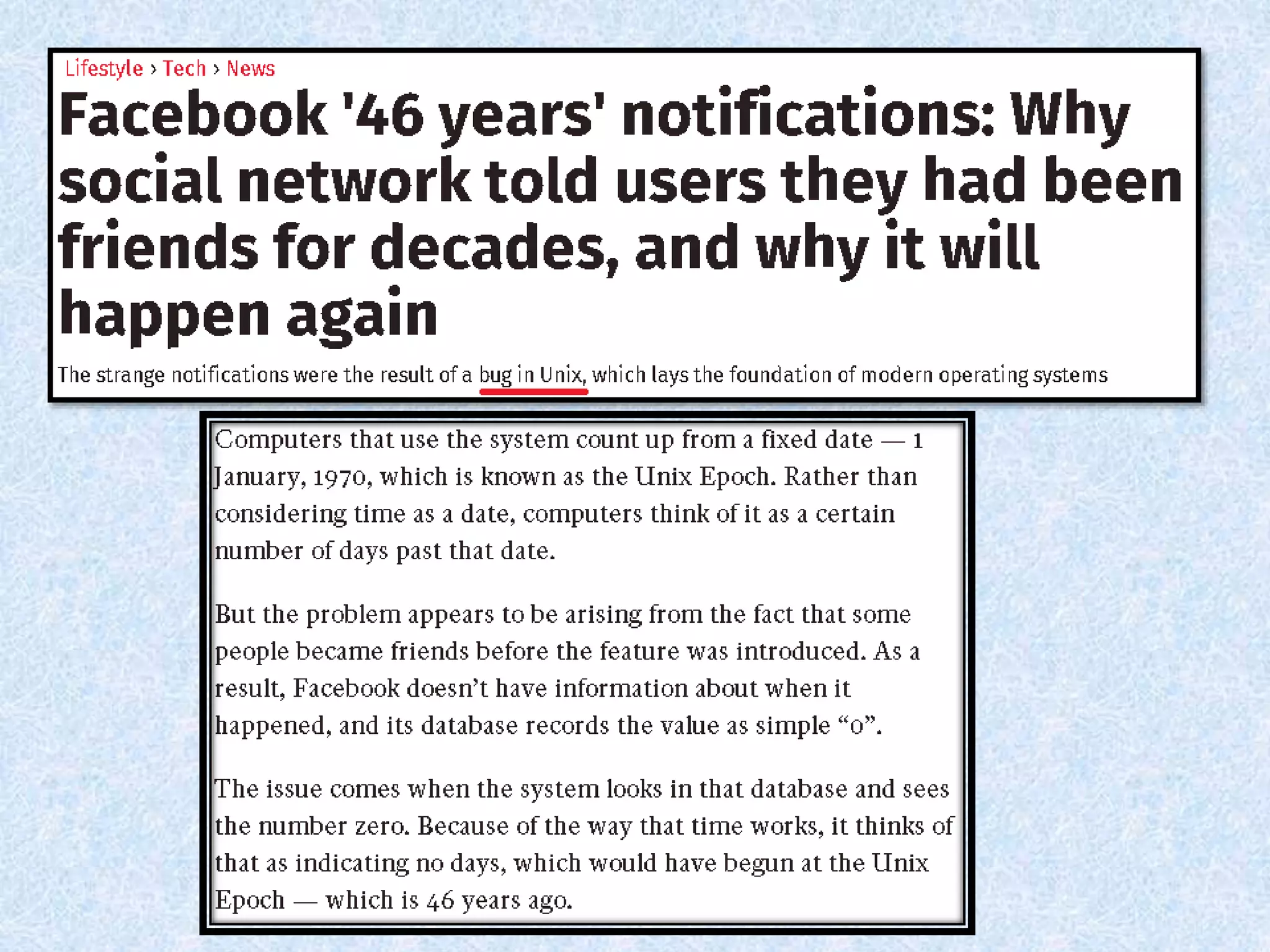
• For us it is Unix Time [Epoch Time].
Java SE 8 isn't the same Java we know.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdk8datetime-160216173930/75/Java-8-Date-Time-API-11-2048.jpg)
![What is Unix time ?
• Unix time (also known as POSIX time or Epoch
time) is a system for describing instants in
time, defined as the number of seconds that
have elapsed since 00:00:00 Coordinated
Universal Time (UTC), Thursday, 1 January
1970,[1][note 1] not counting leap seconds.
Java SE 8 isn't the same Java we know.
1st Jan 1970 Midnight Current UTC time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdk8datetime-160216173930/75/Java-8-Date-Time-API-12-2048.jpg)


![Overview of java.time package
• java.time - the base package containing the value
objects
• java.time.chrono -provides access to different calendar
systems [like Thai Buddhist ]
• java.time.format - allows date and time to be
formatted and parsed
• java.time.temporal - the low level framework and
extended features
• java.time.zone - support classes for time-zones
Java SE 8 isn't the same Java we know.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdk8datetime-160216173930/75/Java-8-Date-Time-API-16-2048.jpg)
























![• Get an Instant from clock object =>2016-01-26T13:06:35.776Z
• Create an Instant from the reference of clock object =>2016-
01-26T13:06:35.792Z
• Create an LocalDateTime from the reference of clock object
=>2016-01-26T18:36:35.792
• Create an ZonedDateTime from the reference of clock object
=>2016-01-26T18:36:35.792+05:30[Asia/Calcutta]
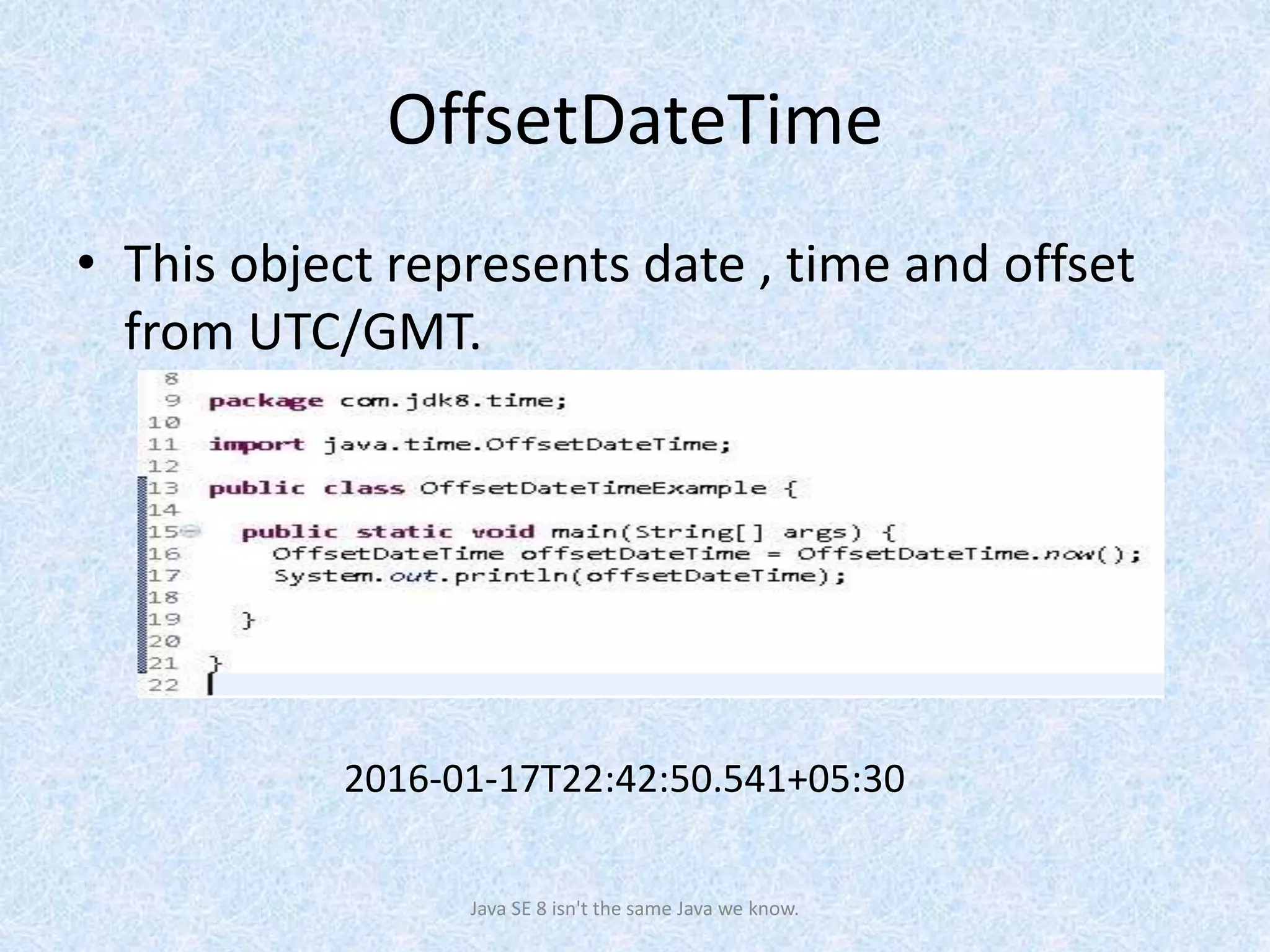
• Create an OffsetDateTime from the reference of clock object
=>2016-01-26T18:36:35.792+05:30
Java SE 8 isn't the same Java we know.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdk8datetime-160216173930/75/Java-8-Date-Time-API-46-2048.jpg)