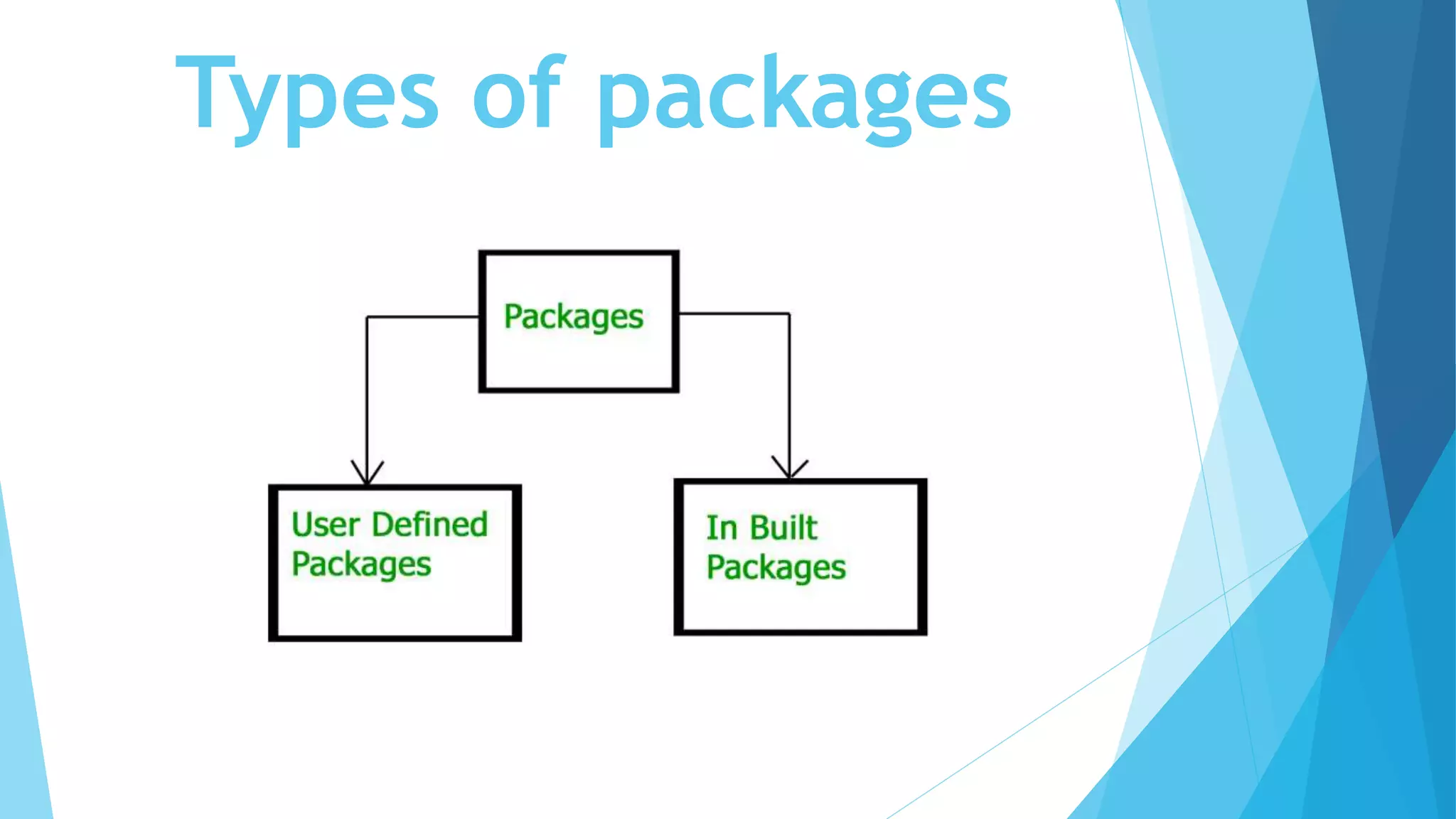
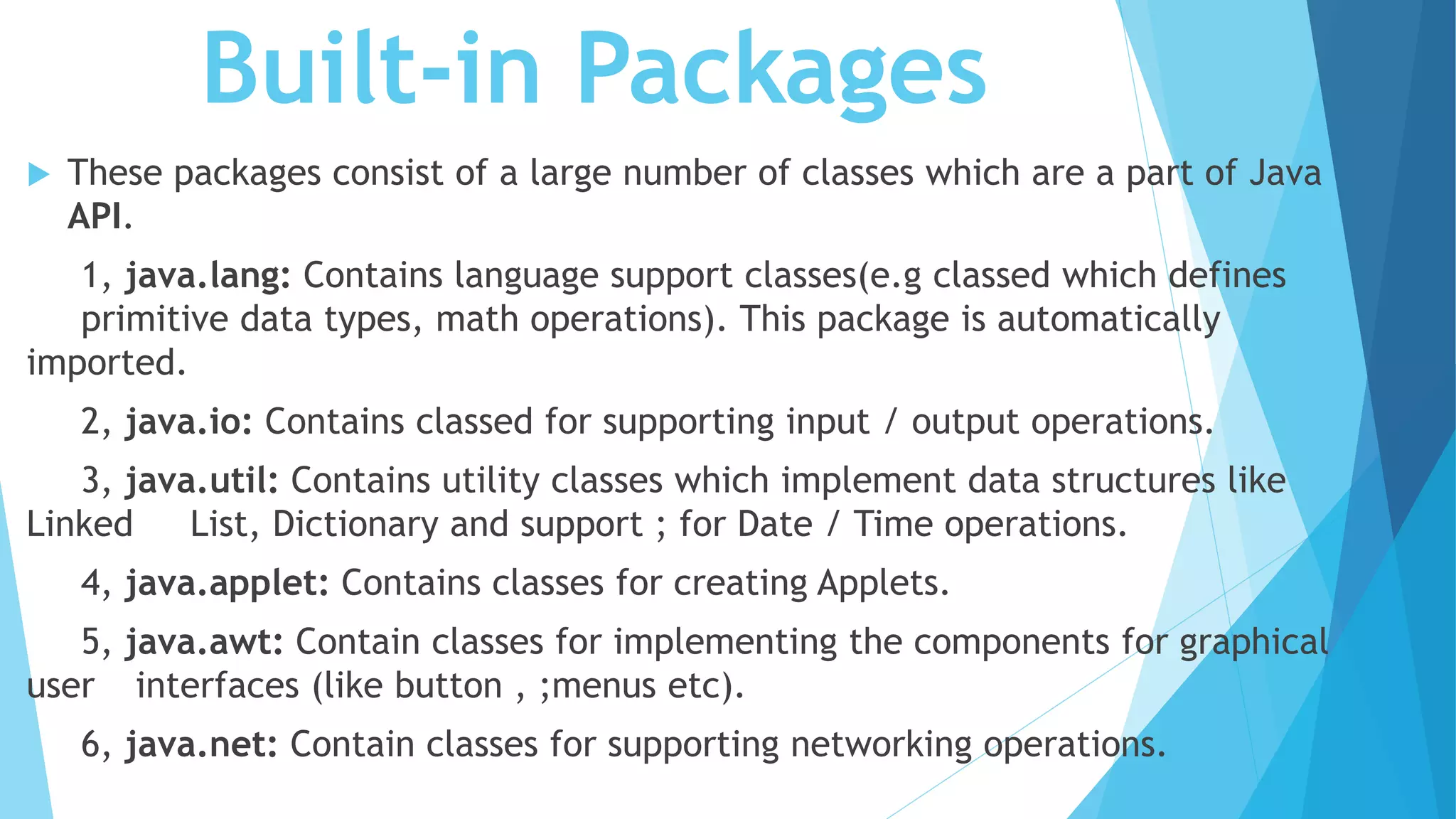
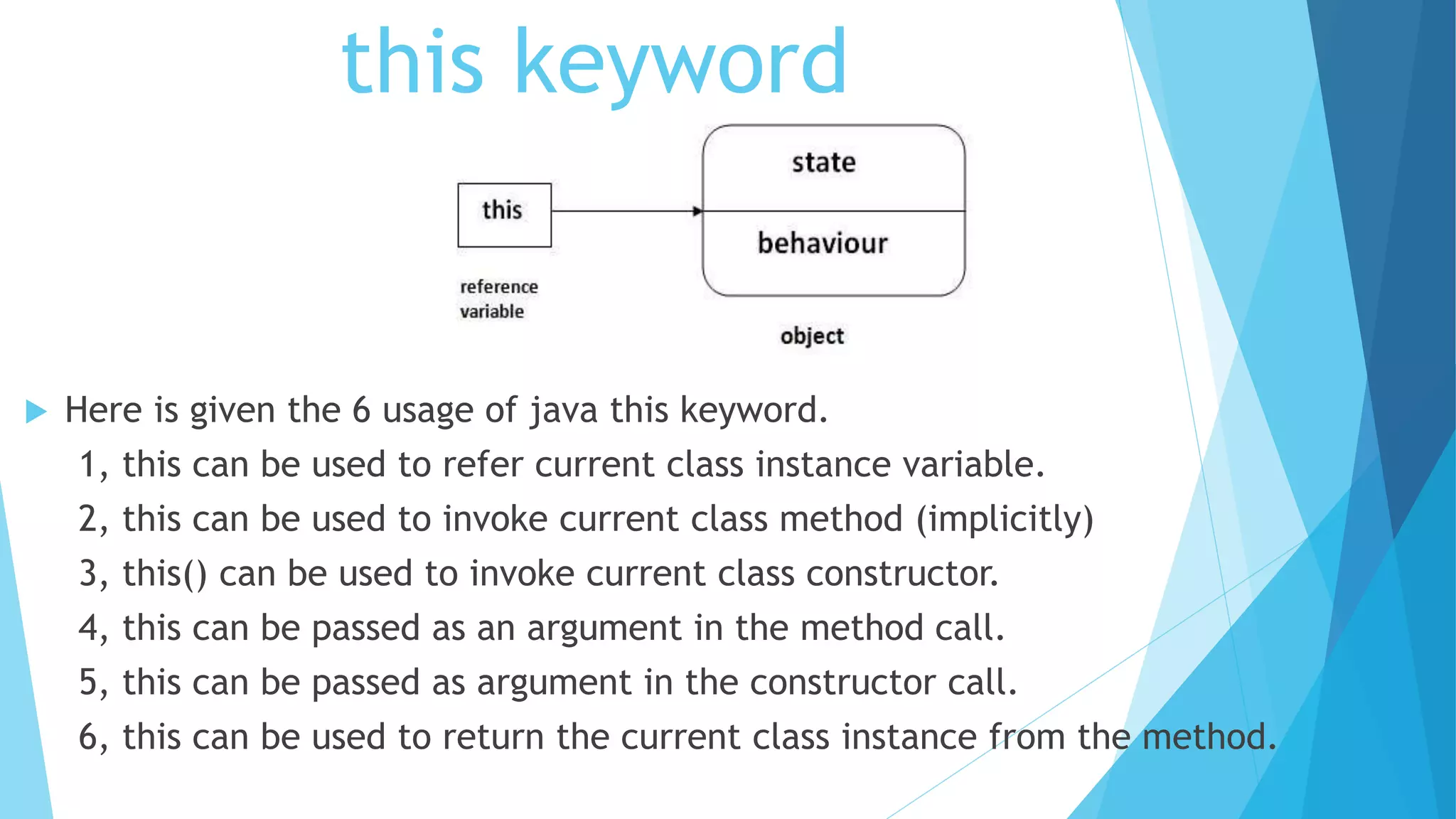
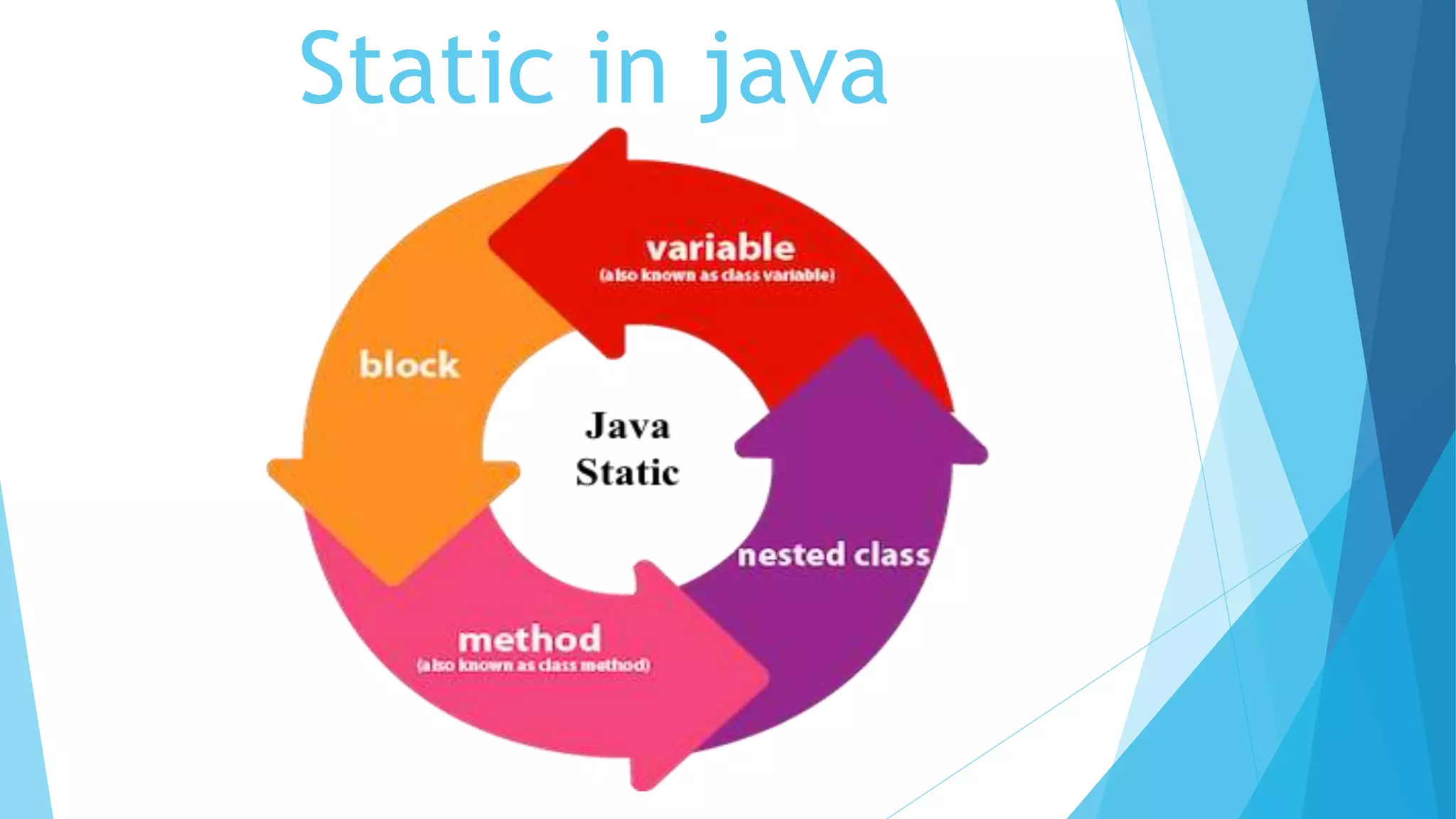
This document summarizes key concepts about packages, classes, and the static keyword in Java. It discusses how packages are used to organize classes and prevent naming conflicts. It also explains that the static keyword in Java is used for memory management and that static variables, methods, blocks, and nested classes belong to the class rather than object instances. The document provides examples of how to define packages and use the static keyword with variables, methods, and blocks in Java programs.





![ Now we can use the MyClass class in our program
import myPackage.MyClass;
public class PrintName {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Initializing the String variable with a value
String name = "GeeksforGeeks";
// Creating an instance of class MyClass in the package.
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
obj.getNames(name);
}
}
Note : MyClass.java must be saved inside the myPackage directory since it
is a part of the package.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesstaticthiskeywordinjava-190415025506/75/Packages-static-this-keyword-in-java-8-2048.jpg)

![Using Static Import
Static import is a feature introduced in Java programming language ( versions 5
and above ) that allows members ( fields and methods ) defined in a class as
public static to be used in Java code without specifying the class in which the
field is defined.
// Note static keyword after import.
import static java.lang.System.*;
class StaticImportDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// We don't need to use 'System.out' as imported using static.
out.println("GeeksforGeeks");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/packagesstaticthiskeywordinjava-190415025506/75/Packages-static-this-keyword-in-java-15-2048.jpg)
