The document discusses object-oriented programming concepts in Java including classes, objects, methods, constructors, inheritance, and more. It includes examples of defining a Box class with attributes like width, height, and length, as well as methods to set dimensions and calculate volume. Constructors are demonstrated for initializing object attributes. Later sections cover topics like static members, method overloading, argument passing by value vs reference, and returning objects from methods.



![Class Box {
}
class BoxDemo1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
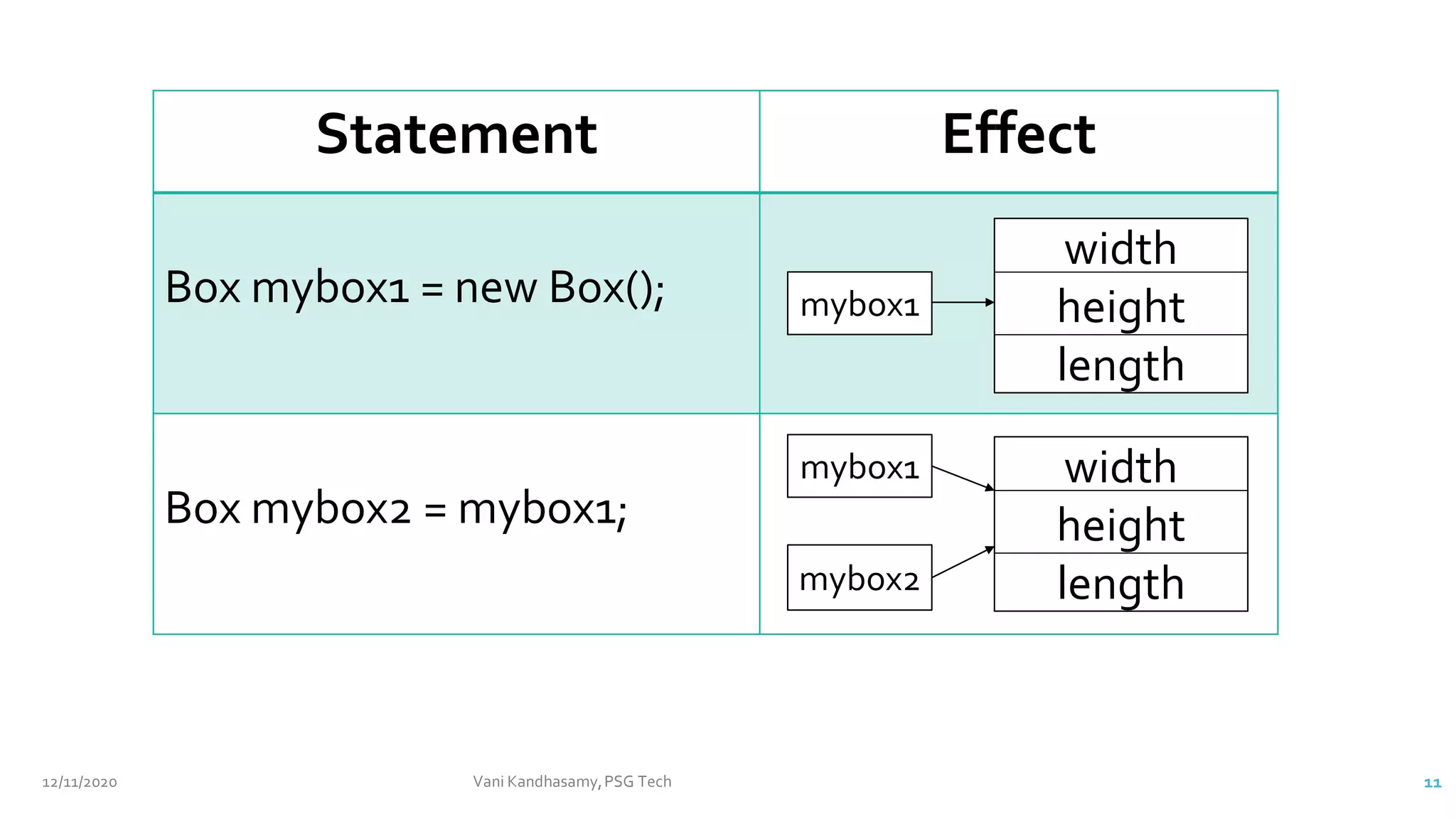
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box();
double vol;
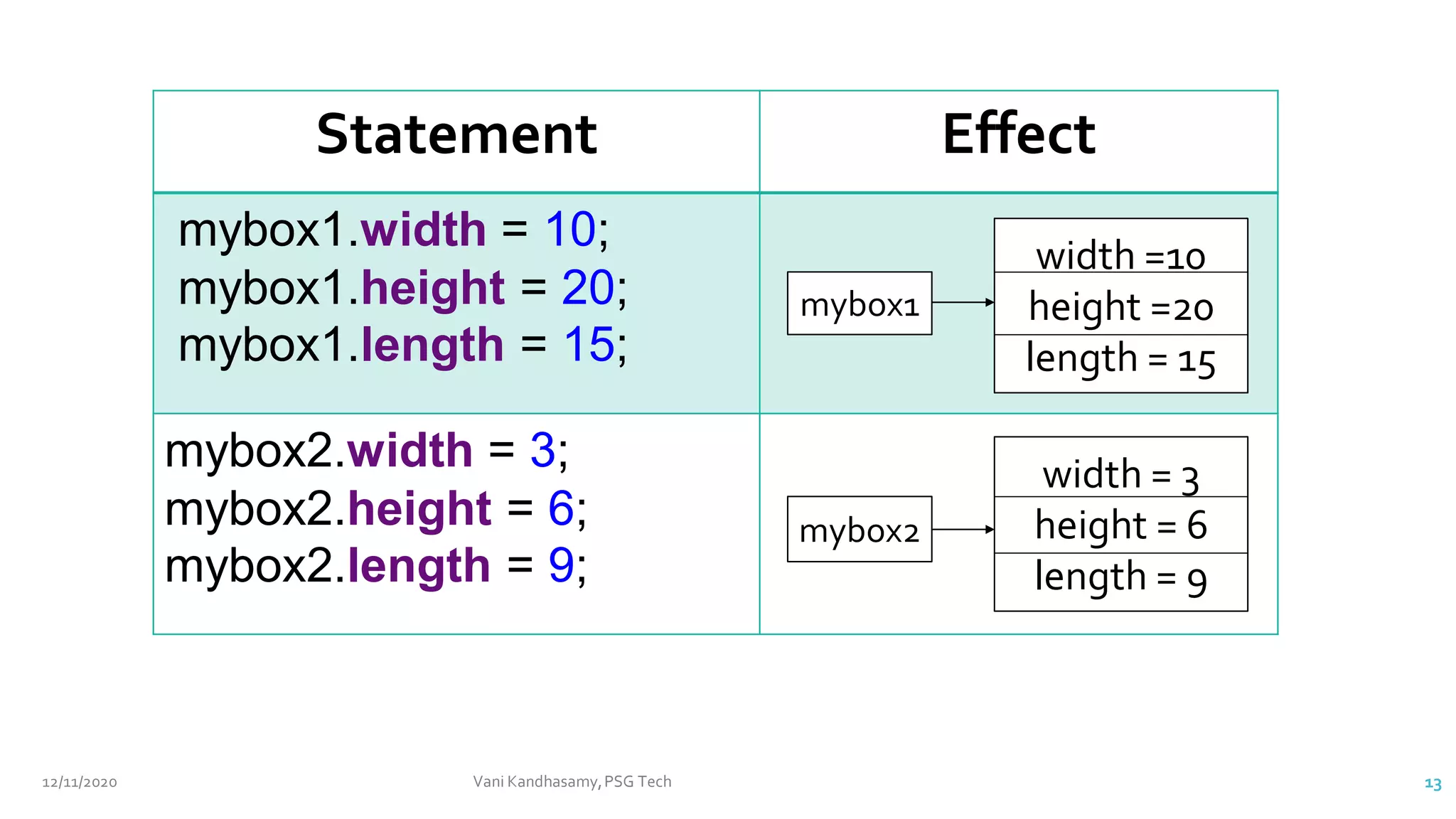
// assign values to mybox1's instance variables
mybox1.width = 10;
mybox1.height = 20;
mybox1.length = 15;
// assign values to mybox2's instance variables */
mybox2.width = 3;
mybox2.height = 6;
mybox2.length = 9;
// get volume of first box
vol = mybox1.volume();
System.out.println("Volume is " + vol);
// get volume of second box
vol = mybox2.volume();
System.out.println("Volume is " + vol);
}
}
double width;
double length;
double height;
double volume() {
return width*length*height;
}
Objects
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-12-2048.jpg)
![class BoxDemo1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box();
double vol;
// assign values to mybox1's instance variables
mybox1.width = 10;
mybox1.height = 20;
mybox1.length = 15;
// assign values to mybox2's instance variables */
mybox2.width = 3;
mybox2.height = 6;
mybox2.length = 9;
// get volume of first box
vol = mybox1.volume();
System.out.println("Volume is " + vol);
// get volume of second box
vol = mybox2.volume();
System.out.println("Volume is " + vol);
}
}
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-14-2048.jpg)


![class Box {
// sets dimensions of box
void setDim(double w, double h, double l) {
width = w;
height = h;
length = l;
}
}
class BoxDemo2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box();
// initialize each box
mybox1.setDim(10, 20, 15);
mybox2.setDim(3, 6, 9);
}
}
Methods -
a fix for the
encapsulation violation
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-17-2048.jpg)
![class Box {
// sets dimensions of box
void setDim(double w, double h, double l) {
width = w;
height = h;
length = l;
}
}
class BoxDemo2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box();
// initialize each box
mybox1.setDim(10, 20, 15);
mybox2.setDim(3, 6, 9);
}
}
Automatic
Initialization:
Constructor
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-18-2048.jpg)
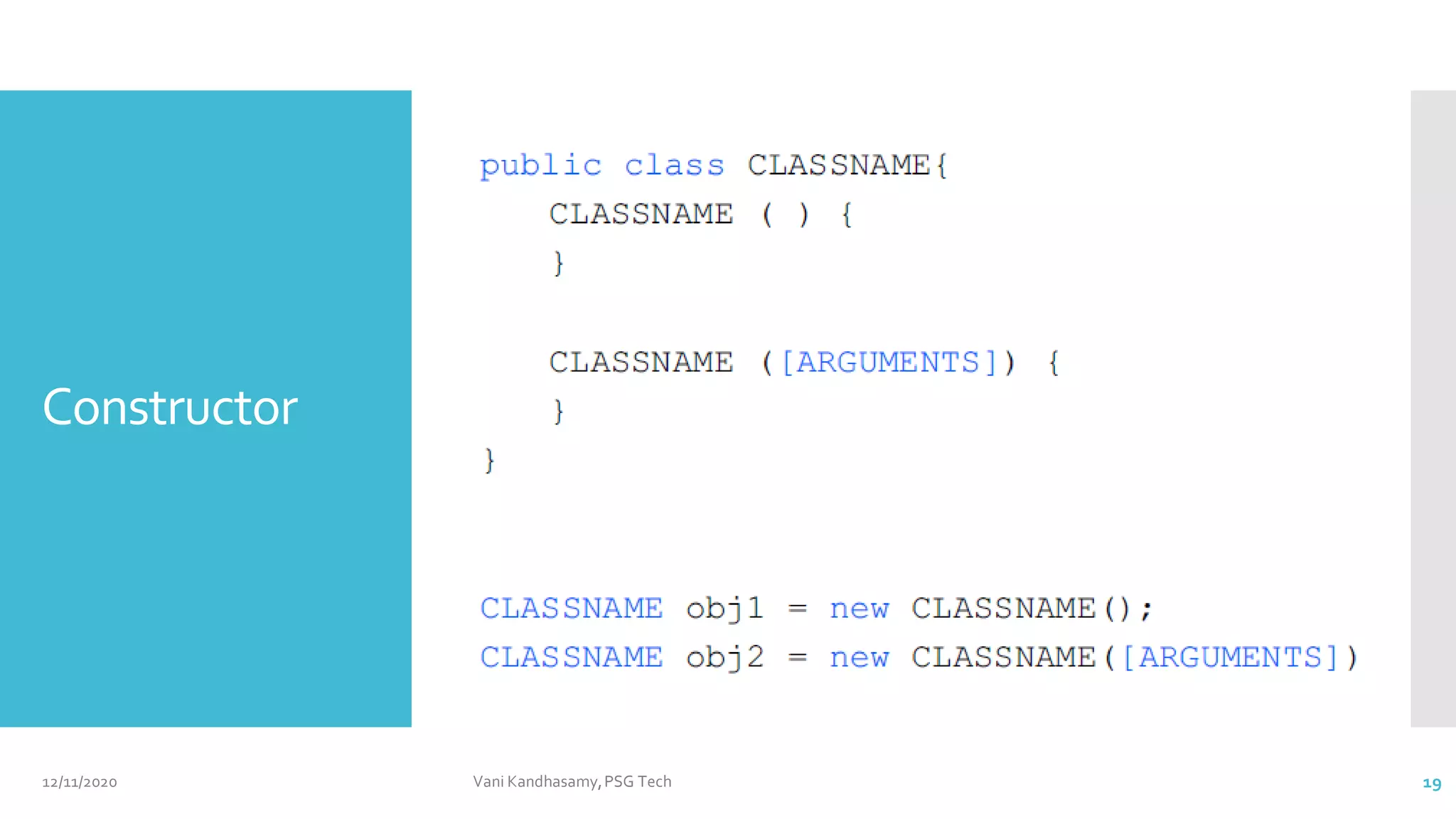
![class Box {
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box() {
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
width = 10;
height = 20;
length = 15;
}
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box(double w, double h, double l) {
width = w;
height = h;
length = l;
}
}
class BoxDemo6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare, allocate, and initialize Box objects
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box(3,6,9);
}
}
DefaultConstructor
Parameterized Constructor
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-20-2048.jpg)
![class Box {
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box() {
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
width = 10;
height = 20;
length = 15;
}
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box(double w, double h, double l) {
width = w;
height = h;
length = l;
}
}
class BoxDemo6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare, allocate, and initialize Box objects
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box(3,6,9);
}
}
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-21-2048.jpg)
![class Box {
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box() {
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
width = 10;
height = 20;
length = 15;
}
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box(double width, double height, double length) {
width = width;
height = height;
length = length;
}
}
class BoxDemo6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare, allocate, and initialize Box objects
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box(3,6,9);
}
}
Output:
3000
0
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-22-2048.jpg)
![class Box {
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box() {
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
width = 10;
height = 20;
length = 15;
}
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box(double width, double height, double length) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.length = length;
}
}
class BoxDemo6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare, allocate, and initialize Box objects
Box mybox1 = new Box();
Box mybox2 = new Box(3,6,9);
}
}
Keyword: this
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-23-2048.jpg)
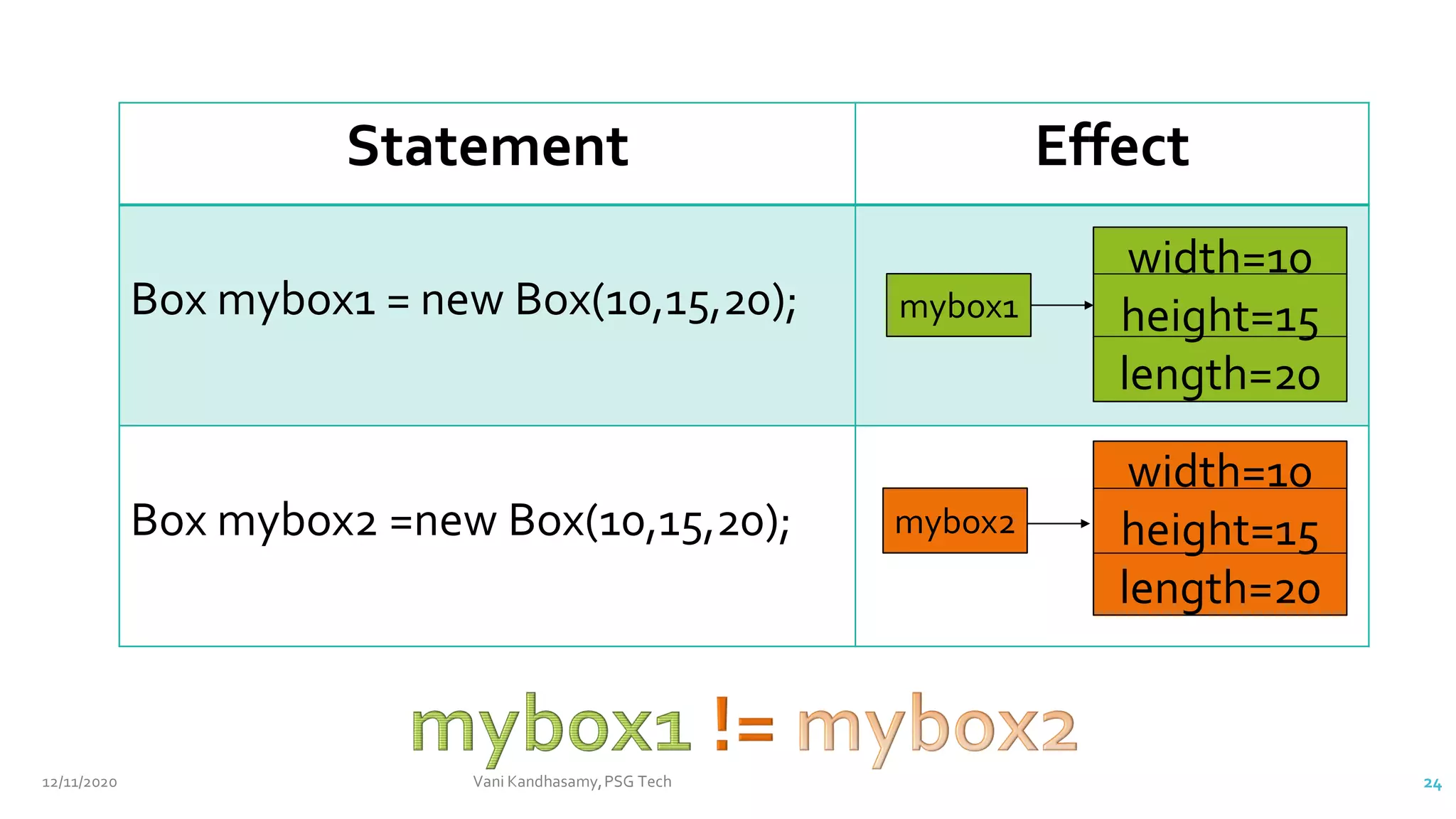
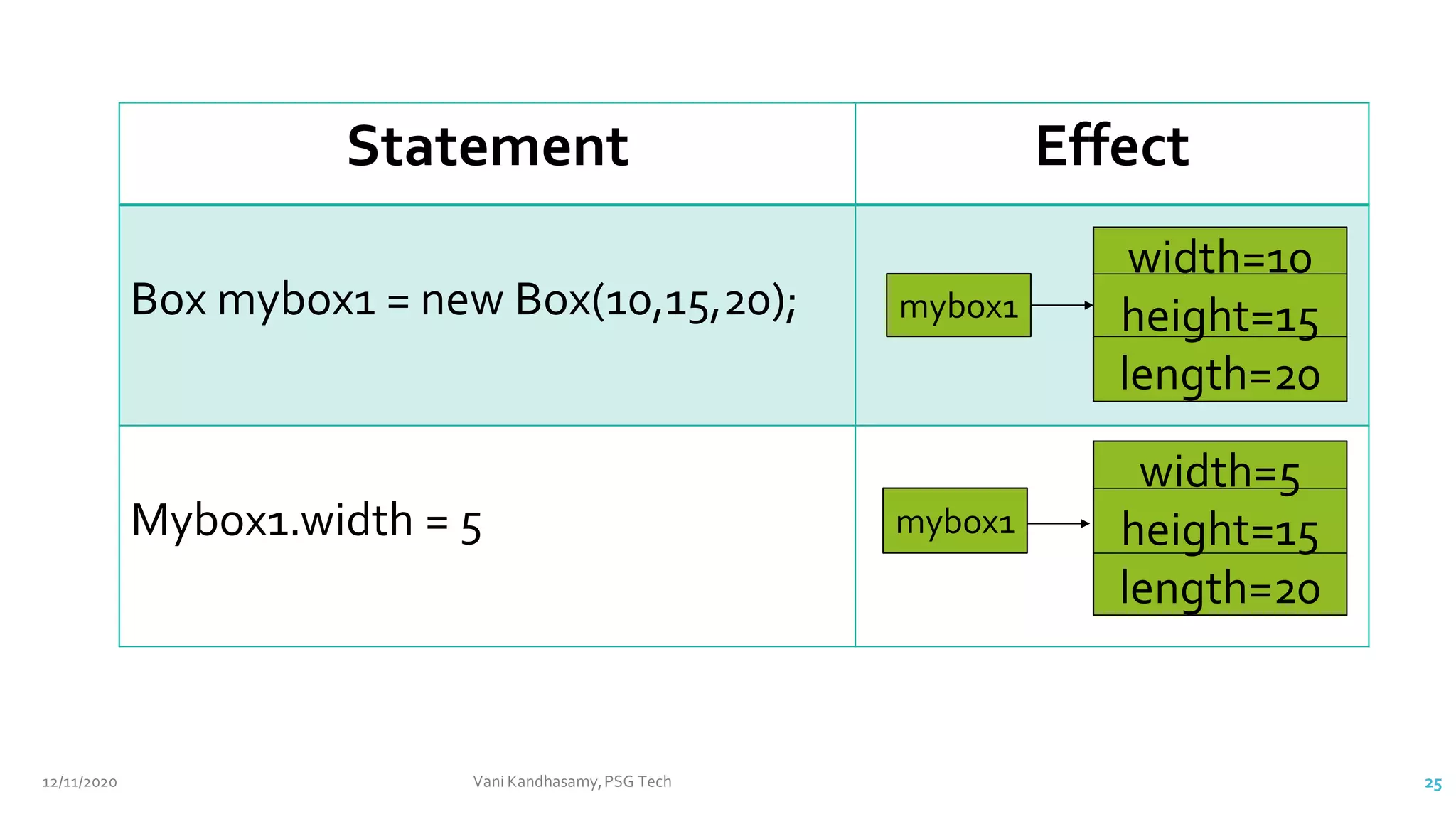
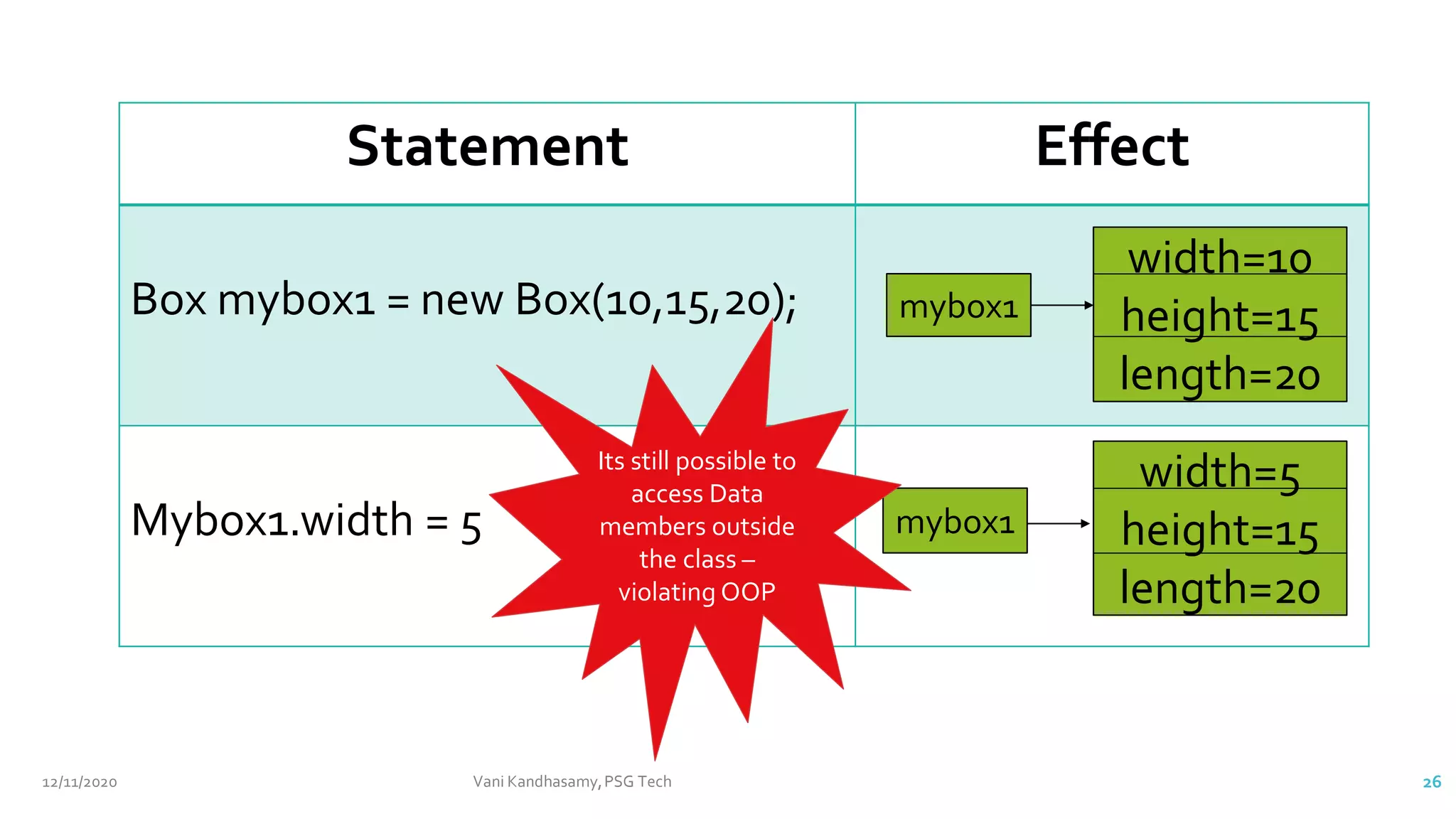
![class Box {
// This is the constructor for Box.
private double width;
private double height;
private double length;
// This is the constructor for Box.
Box(double width, double height, double length) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.length = length;
}
}
class BoxDemo6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare, allocate, and initialize Box objects
Box mybox2 = new Box(3,6,9);
mybox2.width = 10; // ERROR!!!
}
}
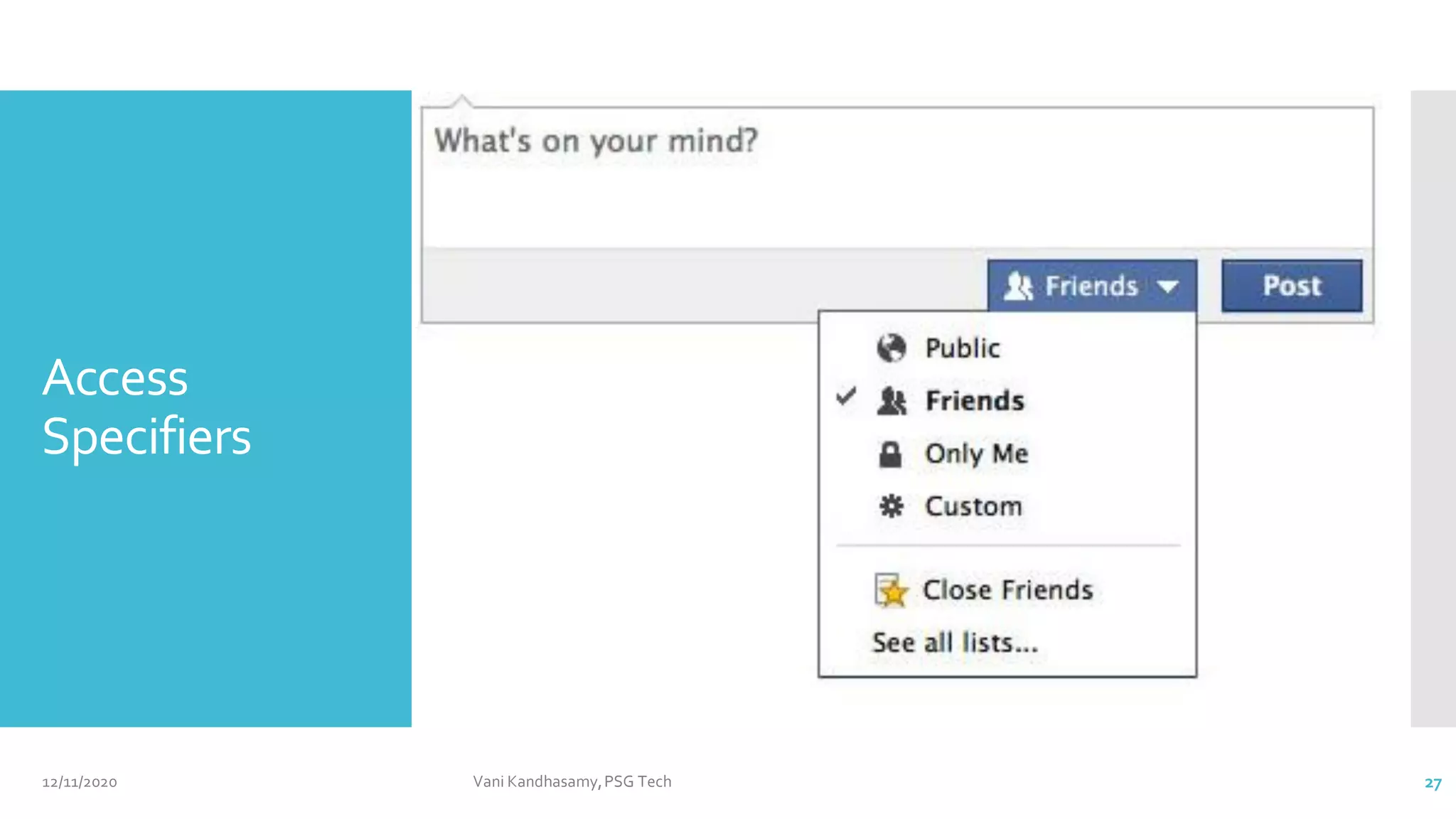
Access Specifiers -
a fix for the abstraction
violation
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-28-2048.jpg)
![Static
members
public class UseStatic {
static int a = 3;
static int b;
static void meth(int x) {
b = a * 4;
System.out.println("x = " + x);
System.out.println("a = " + a);
System.out.println("b = " + b);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
meth(42);
}
}
a, b - StaticVariables
meth - Static Method
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-29-2048.jpg)
![class StaticDemo {
static int a = 42;
static int b = 99;
static void callme() {
System.out.println("a = " + a);
}
}
class StaticByName {
public static void main(String args[]) {
StaticDemo.callme();
System.out.println("b = " + StaticDemo.b);
}
}
Class name is used to
access static methods
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-30-2048.jpg)
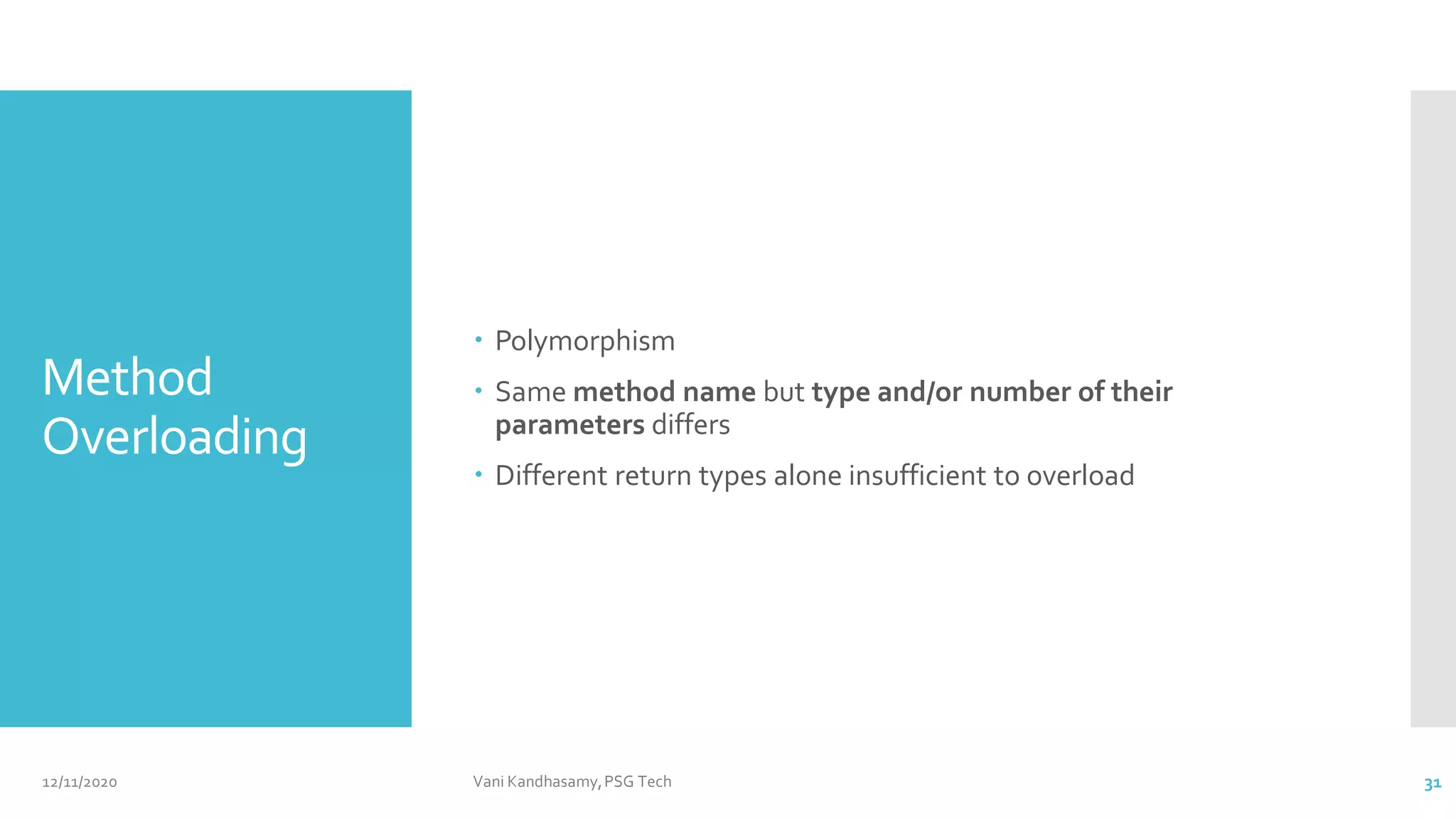
![class OverloadDemo {
void test() {
System.out.println("No parameters");
}
// Overload test for one integer parameter.
void test(int a) {
System.out.println("a: " + a);
}
// Overload test for two integer parameters.
void test(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("a and b: " + a + " " + b);
}
// overload test for a double parameter
double test(double a) {
System.out.println("double a: " + a);
return a*a;
}
}
class Overload {
public static void main(String args[]) {
OverloadDemo ob = new OverloadDemo();
double result;
// call all versions of test()
ob.test();
ob.test(10);
ob.test(10, 20);
result = ob.test(123.25);
System.out.println("Result of ob.test(123.25): " + result);
}
}
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-32-2048.jpg)
![class OverloadDemo {
void test() {
System.out.println("No parameters");
}
// Overload test for two integer parameters.
void test(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("a and b: " + a + " " + b);
}
// overload test for a double parameter
double test(double a) {
System.out.println("double a: " + a);
return a*a;
}
}
class Overload {
public static void main(String args[]) {
OverloadDemo ob = new OverloadDemo();
double result;
int a = 88;
// call all versions of test()
ob.test();
ob.test(a);
ob.test(10, 20);
result = ob.test(123.25);
System.out.println("Result of ob.test(123.25): " + result);
}
}
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-33-2048.jpg)
![class OverloadDemo {
void test() {
System.out.println("No parameters");
}
// Overload test for two integer parameters.
void test(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("a and b: " + a + " " + b);
}
// overload test for a double parameter
double test(double a) {
System.out.println("double a: " + a);
return a*a;
}
}
class Overload {
public static void main(String args[]) {
OverloadDemo ob = new OverloadDemo();
double result;
int a = 88;
// call all versions of test()
ob.test();
ob.test(a);
ob.test(10, 20);
result = ob.test(123.25);
System.out.println("Result of ob.test(123.25): " + result);
}
}
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-34-2048.jpg)
![Constructor
Overloading
class Box {
// This is the constructor for cube.
Box(double side) {
width = height = length = side;
}
// This constructor is used when all dimensions specified
Box(double w, double h, double l) {
width = w;
height = h;
length = l;
}
}
class BoxDemo6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare, allocate, and initialize Box objects
Box mycube1 = new Box(4);
Box mybox2 = new Box(3,6,9);
}
}
Differs only by
#parameters
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-35-2048.jpg)
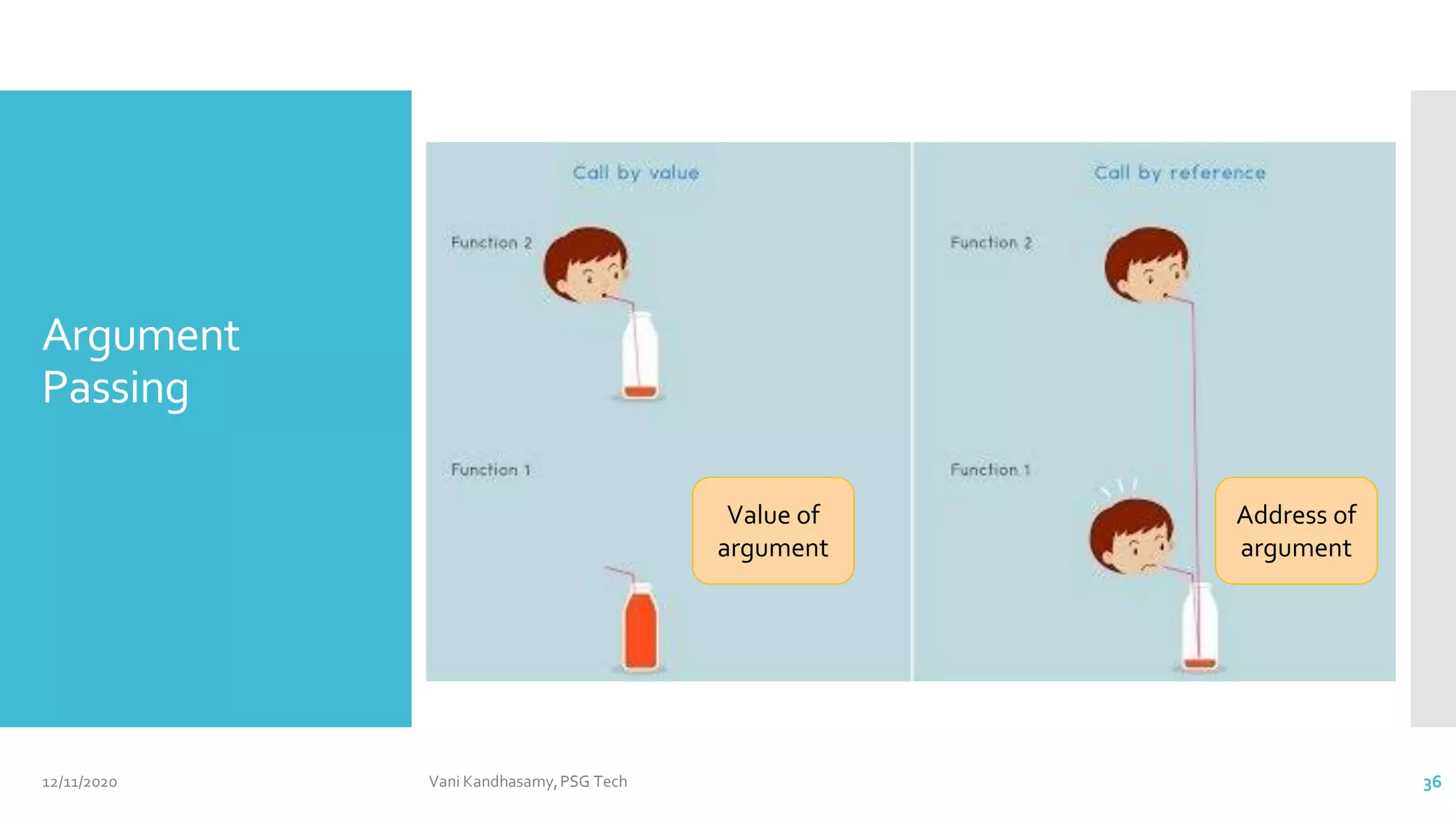
![class Test {
void meth(int a, int b) {
a *= 2;
b /= 2;
}
}
class CallByValue {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Test ob = new Test();
int a = 15, b = 20;
System.out.println("a and b before call: " +
a + " " + b);
ob.meth(a, b);
System.out.println("a and b after call: " +
a + " " + b);
}
}
class Test {
int a, b;
Test(int i, int j) {
a = i;
b = j;
}
// pass an object
void meth(Test o) {
o.a *= 2;
o.b /= 2;
}
}
class CallByRef {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Test ob = new Test(15, 20);
System.out.println("ob.a and ob.b before call: " +
ob.a + " " + ob.b);
ob.meth(ob);
System.out.println("ob.a and ob.b after call: " +
ob.a + " " + ob.b);
}
}
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-37-2048.jpg)
![Constructor +
Object
class Box {
// This is the constructor for cube.
Box(double side) {
width = height = length = side;
}
// This constructor is used when all dimensions specified
Box(Box ob) {
width = ob.width;
height = ob.height;
length = ob.length;
}
}
class BoxDemo6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare, allocate, and initialize Box objects
Box mycube1 = new Box(4);
Box mycube2 = new Box(mycube1);
}
}
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-38-2048.jpg)
![Returning
Objects
class Test {
int a;
Test(int i) {
a = i;
}
Test incrByTen() {
Test temp = new Test(a+10);
return temp;
}
}
class RetOb {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Test ob1 = new Test(2);
Test ob2;
ob2 = ob1.incrByTen();
System.out.println("ob1.a: " + ob1.a);
System.out.println("ob2.a: " + ob2.a);
ob2 = ob2.incrByTen();
System.out.println("ob2.a after second increase: "
+ ob2.a);
}
}
Returning Objects
12/11/2020 Vani Kandhasamy,PSG Tech 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2b-210512071605/75/Java-Basics-Part2-39-2048.jpg)

