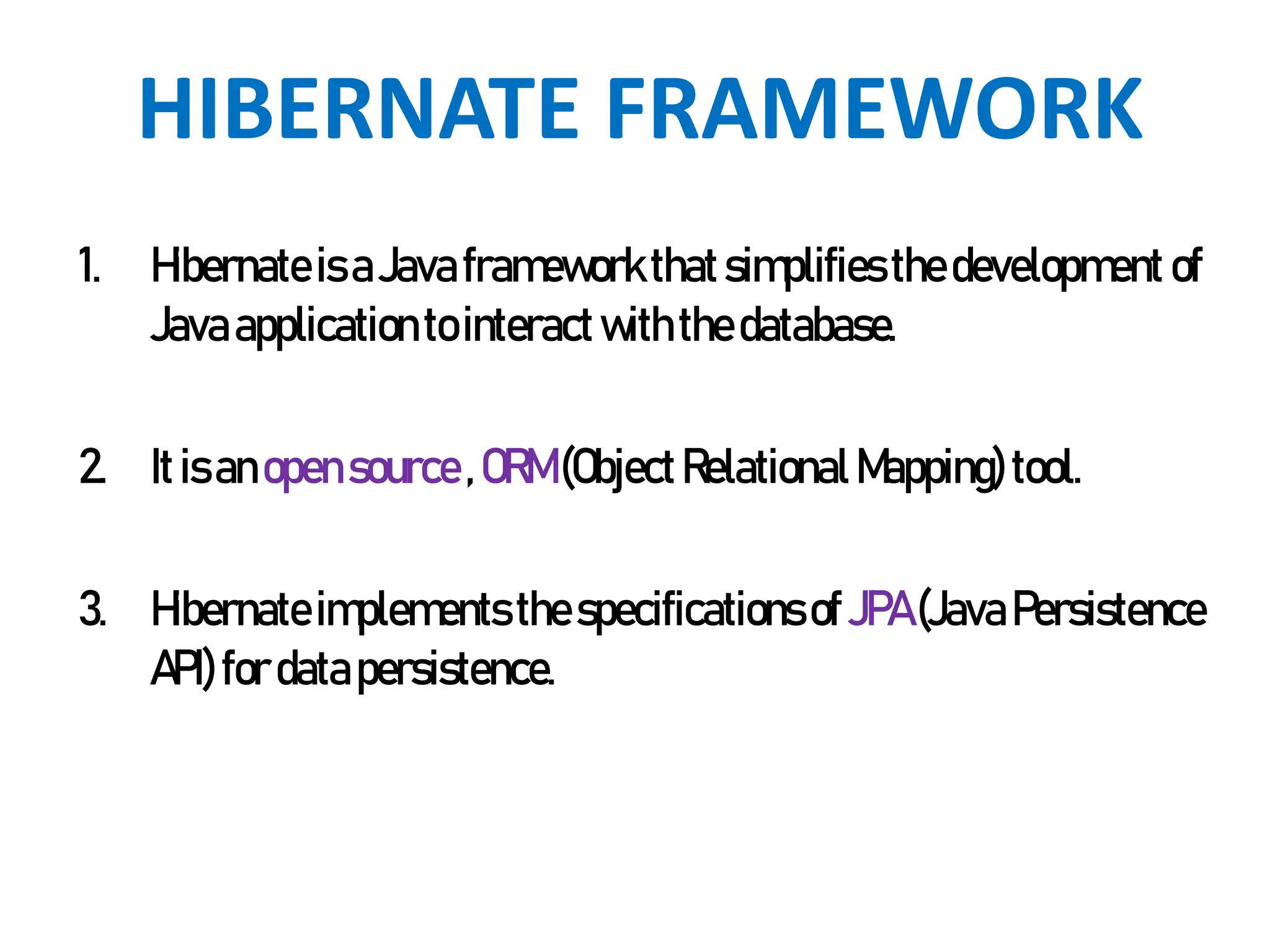
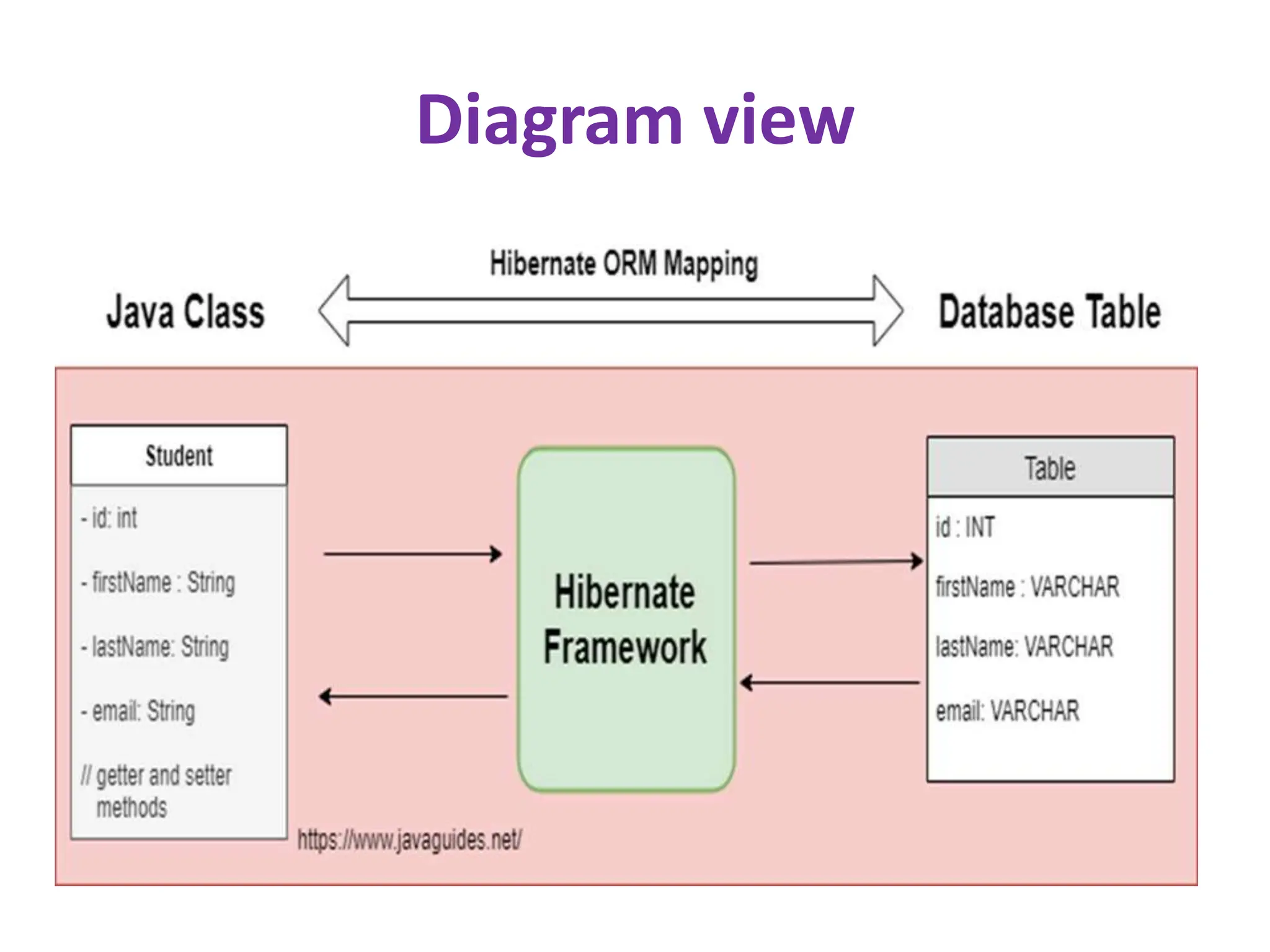
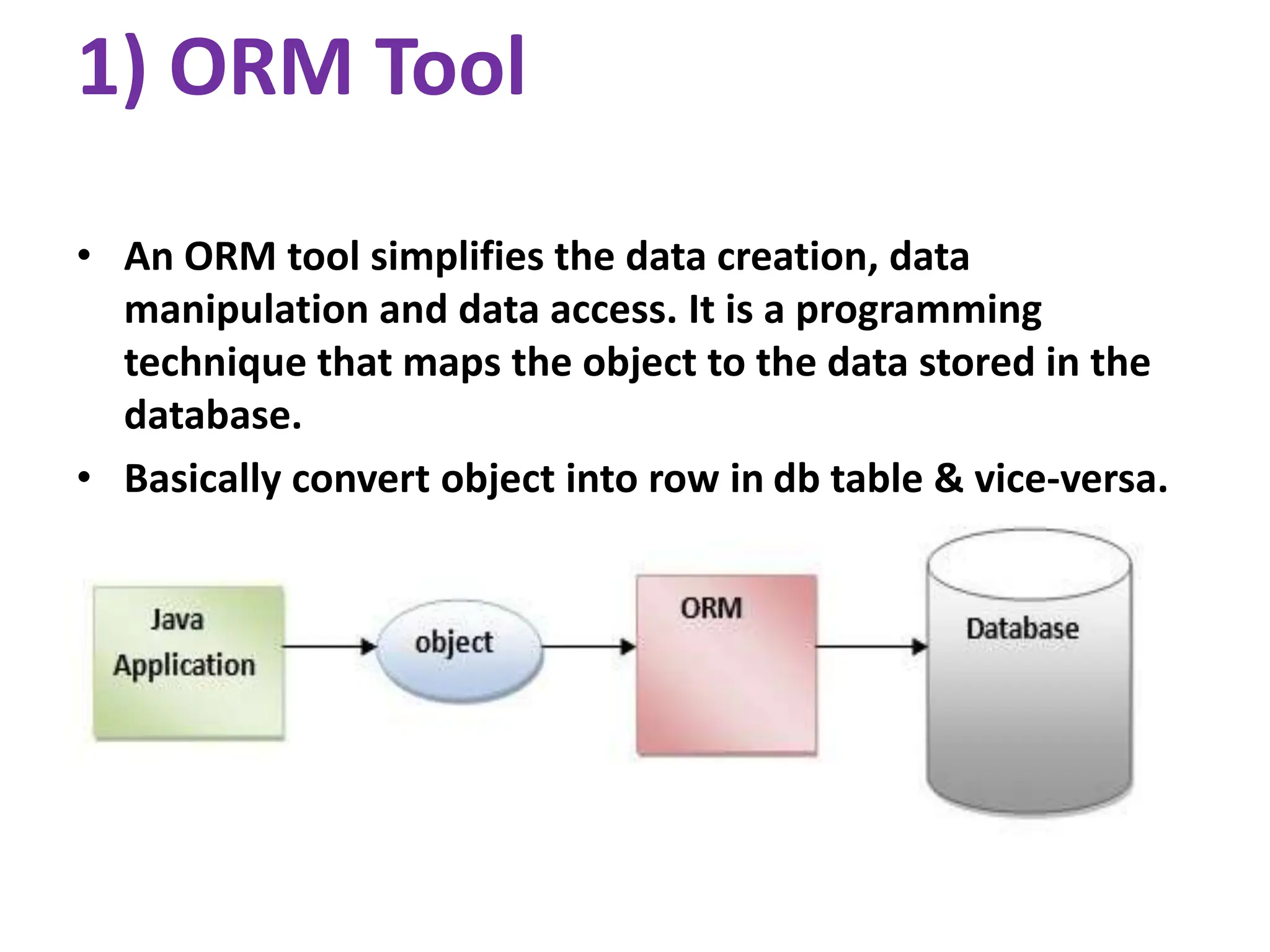
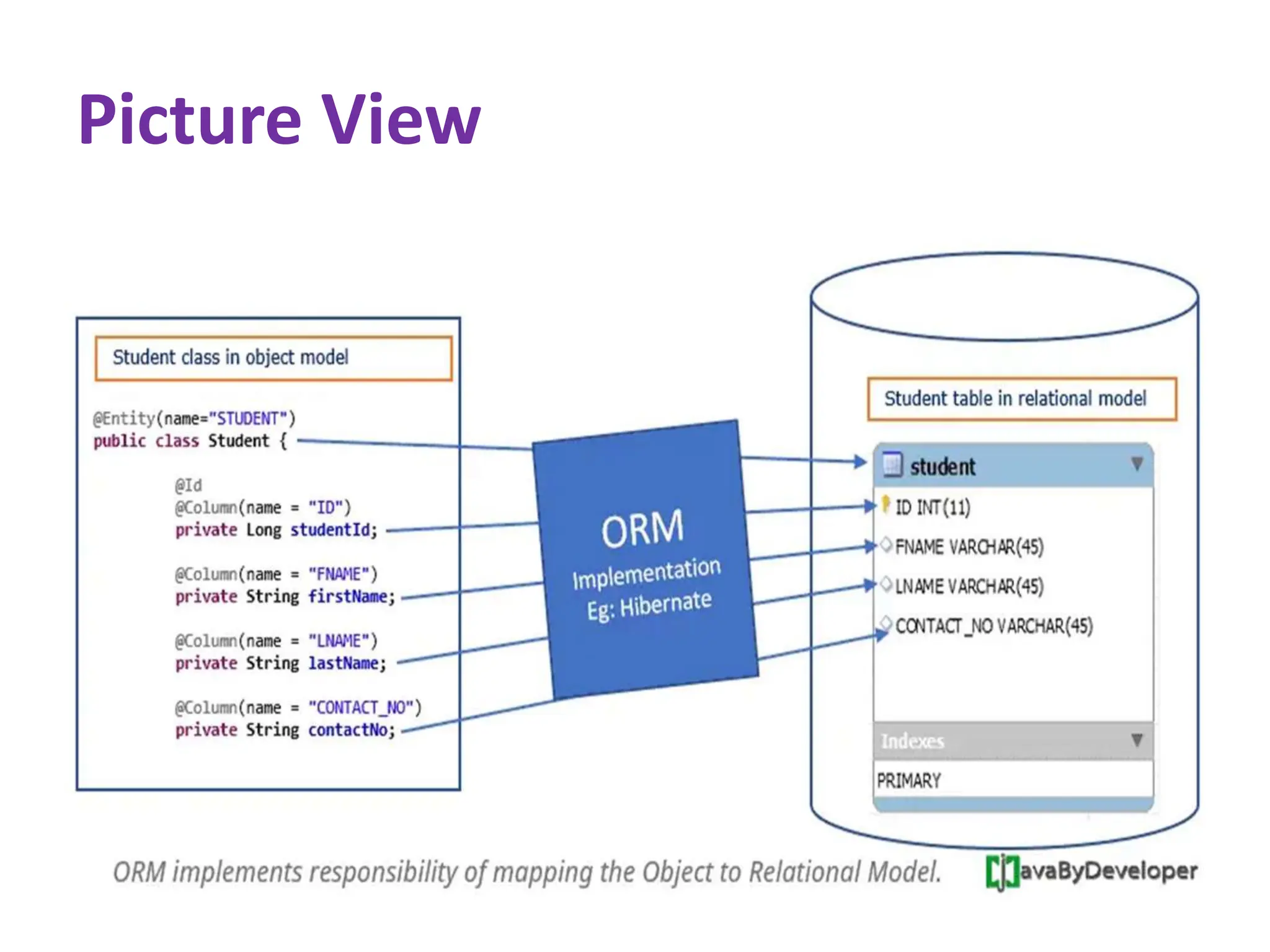
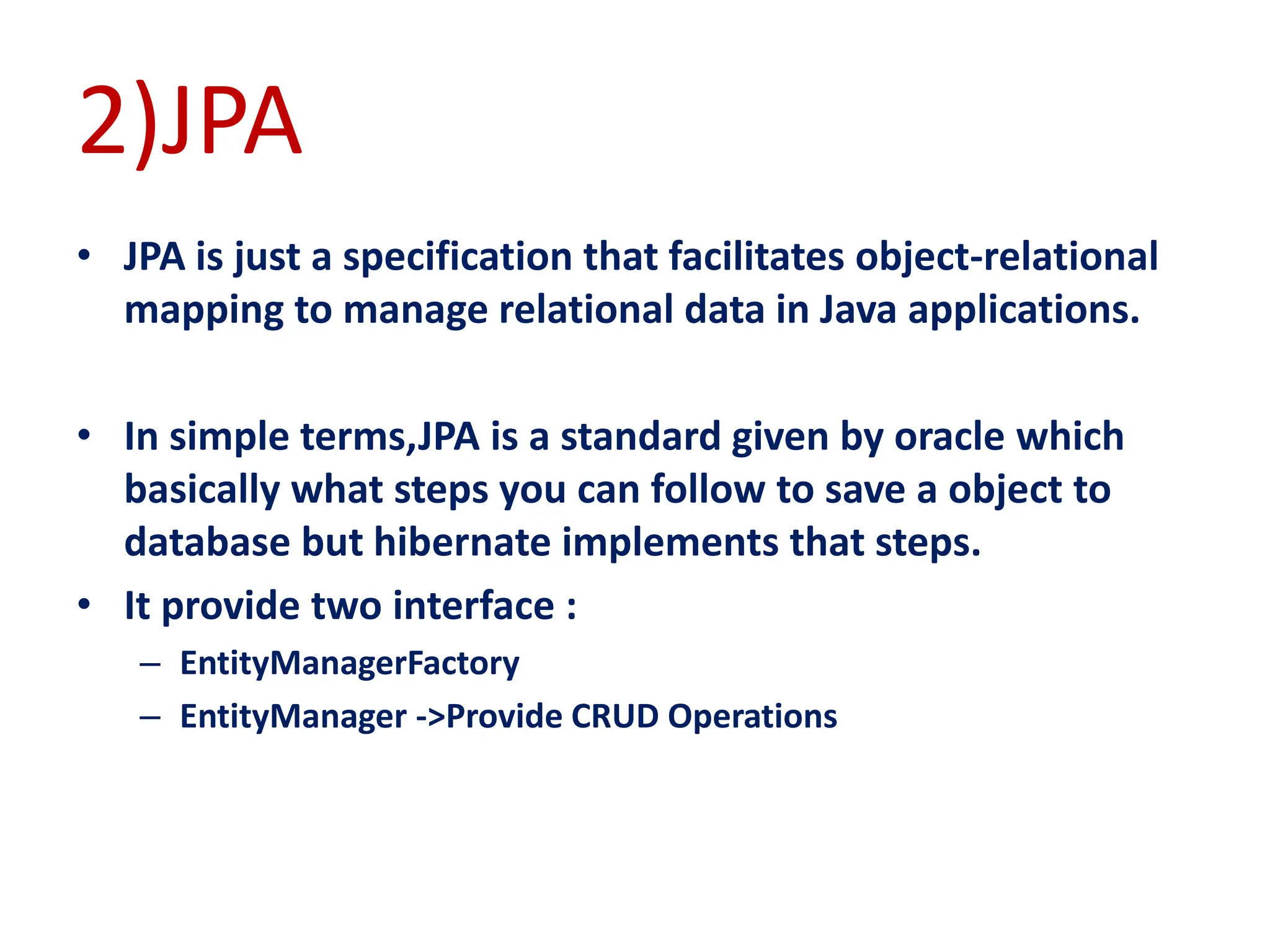
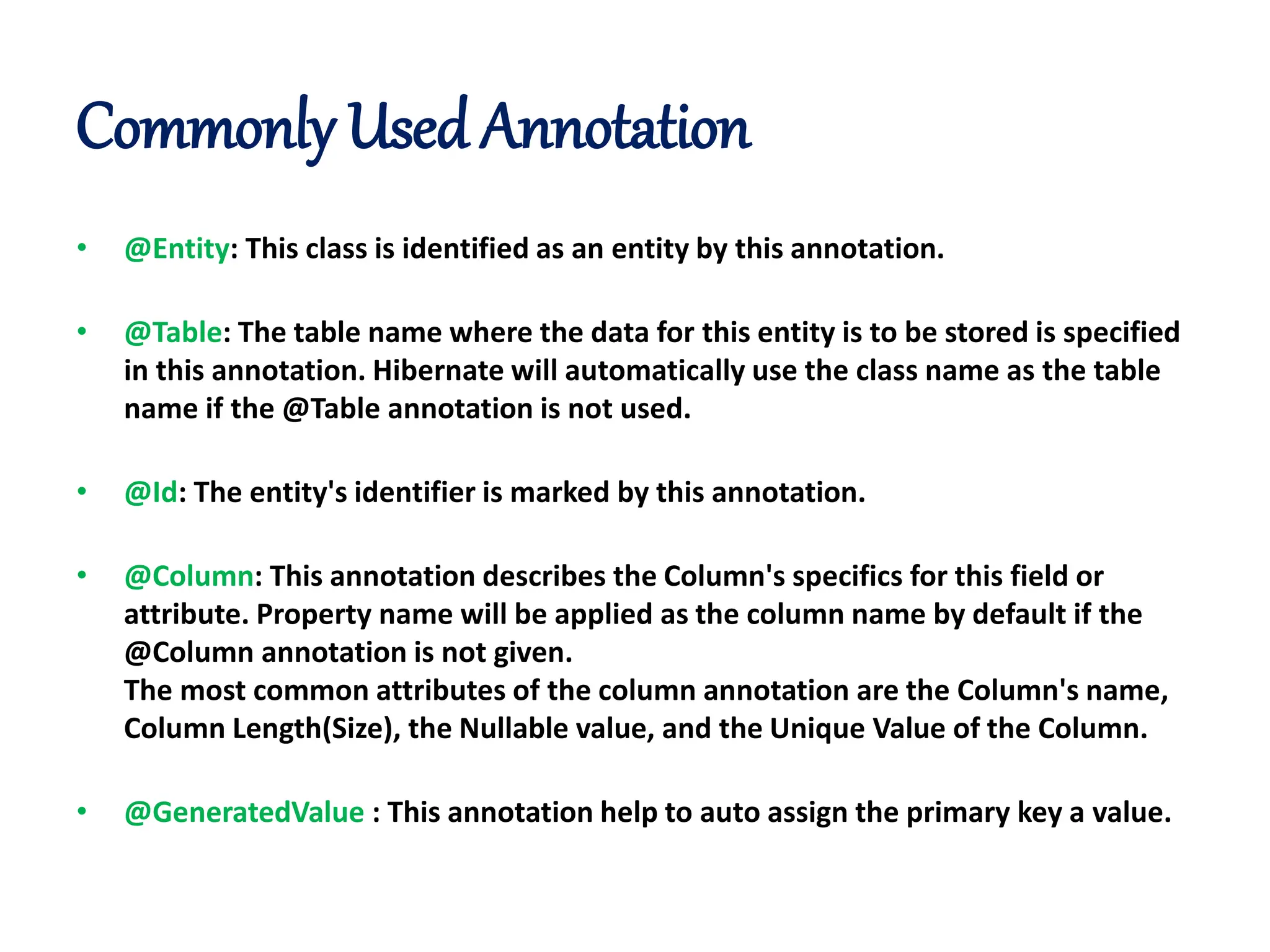
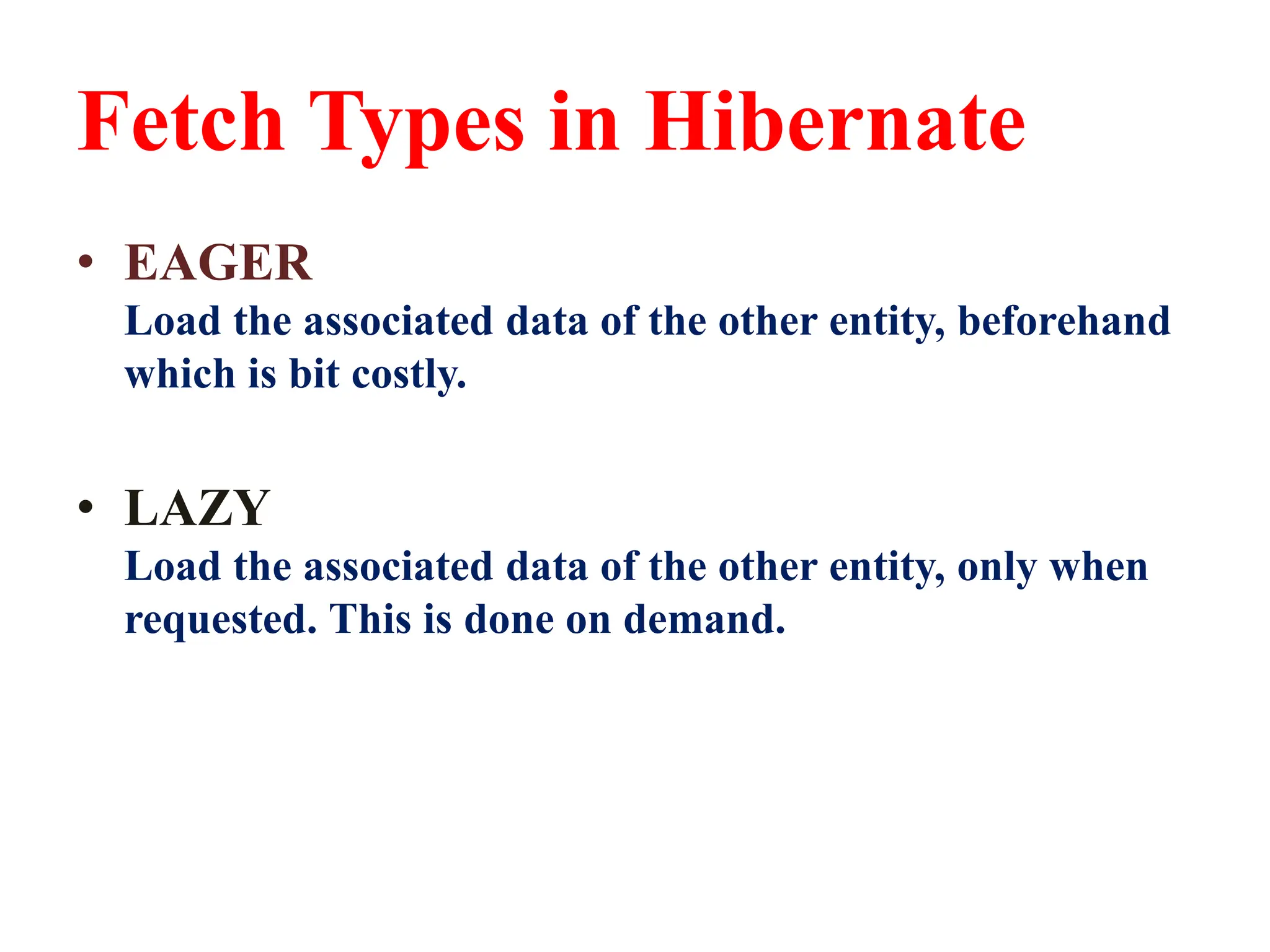
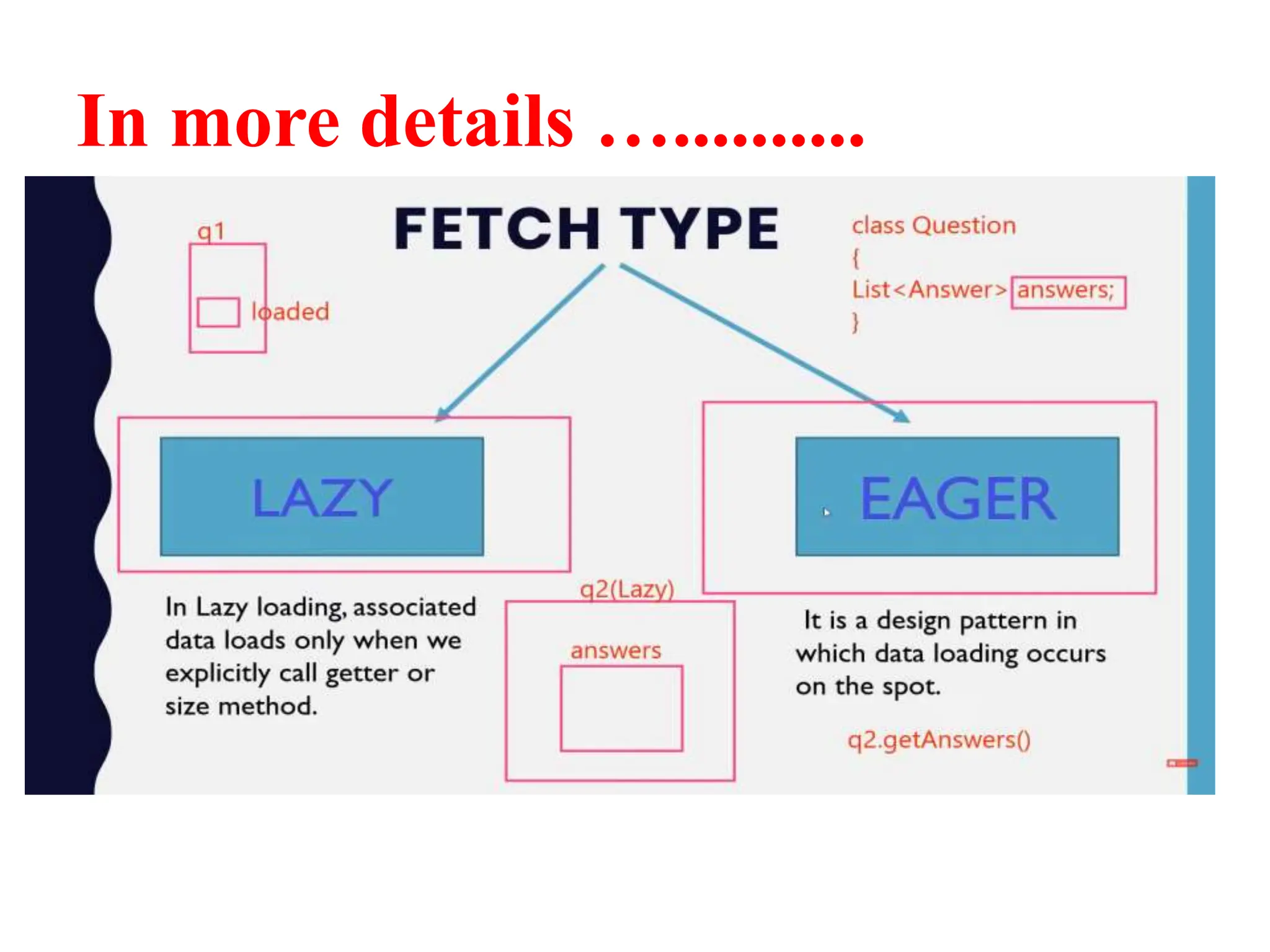
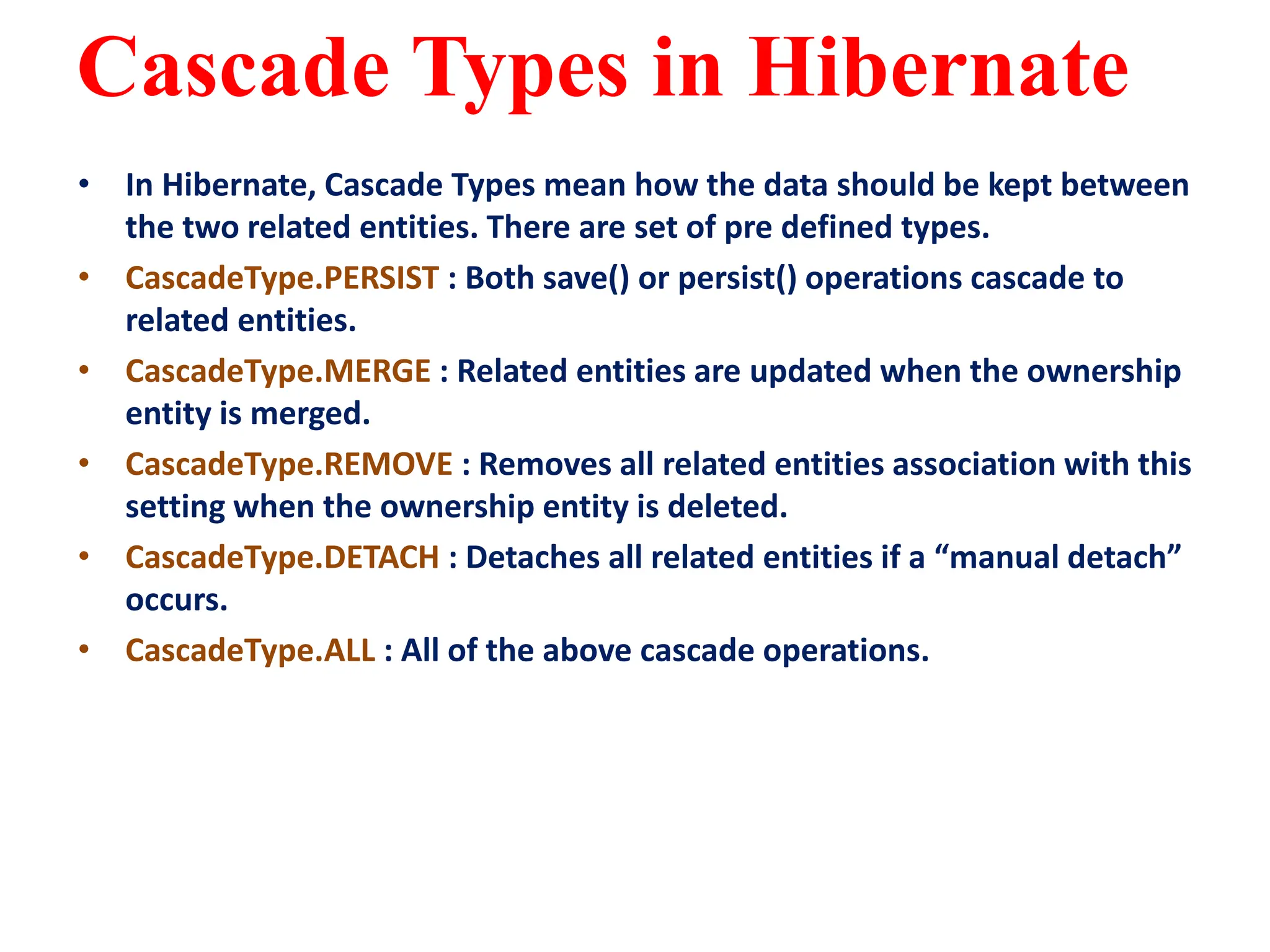
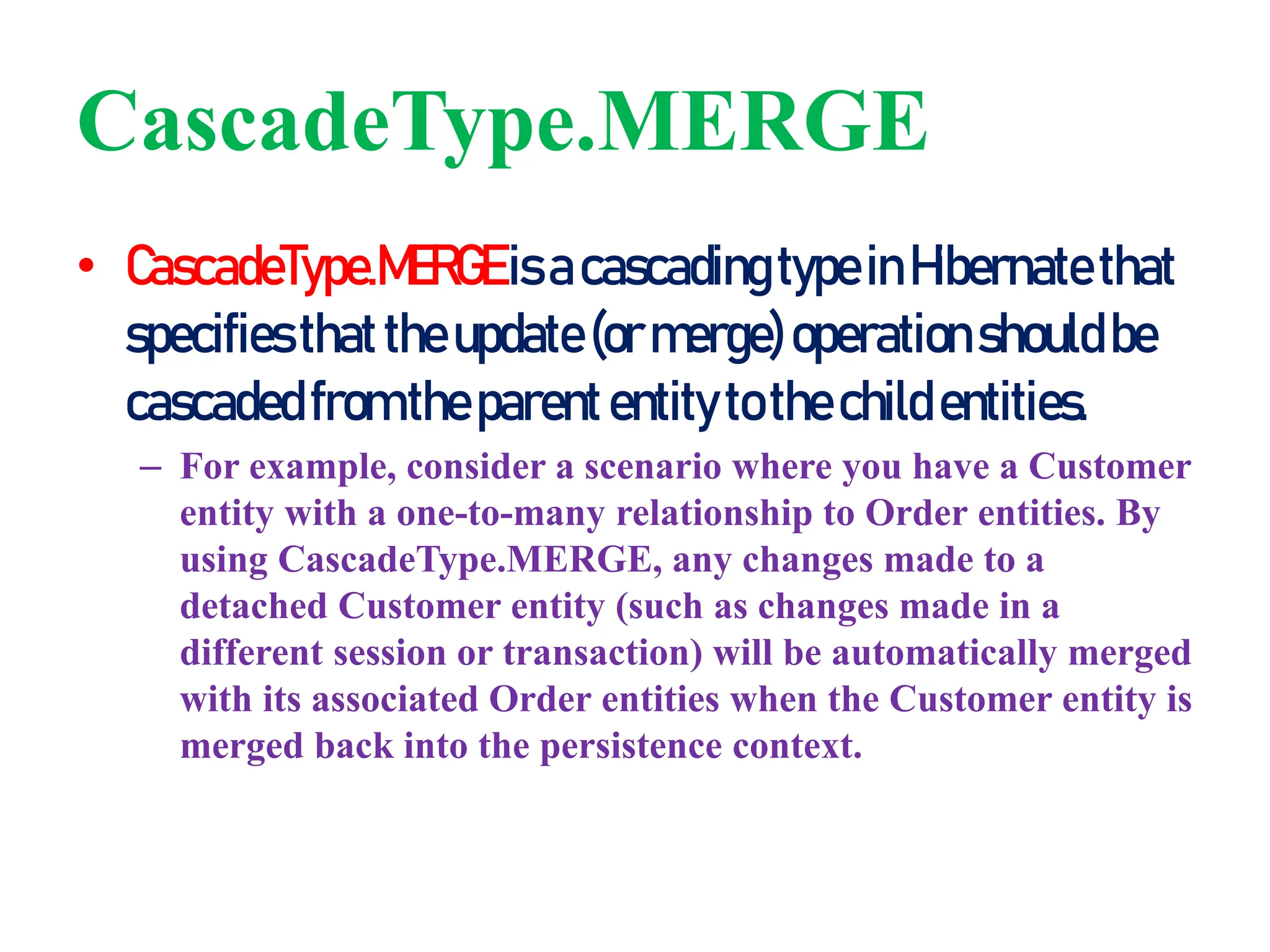
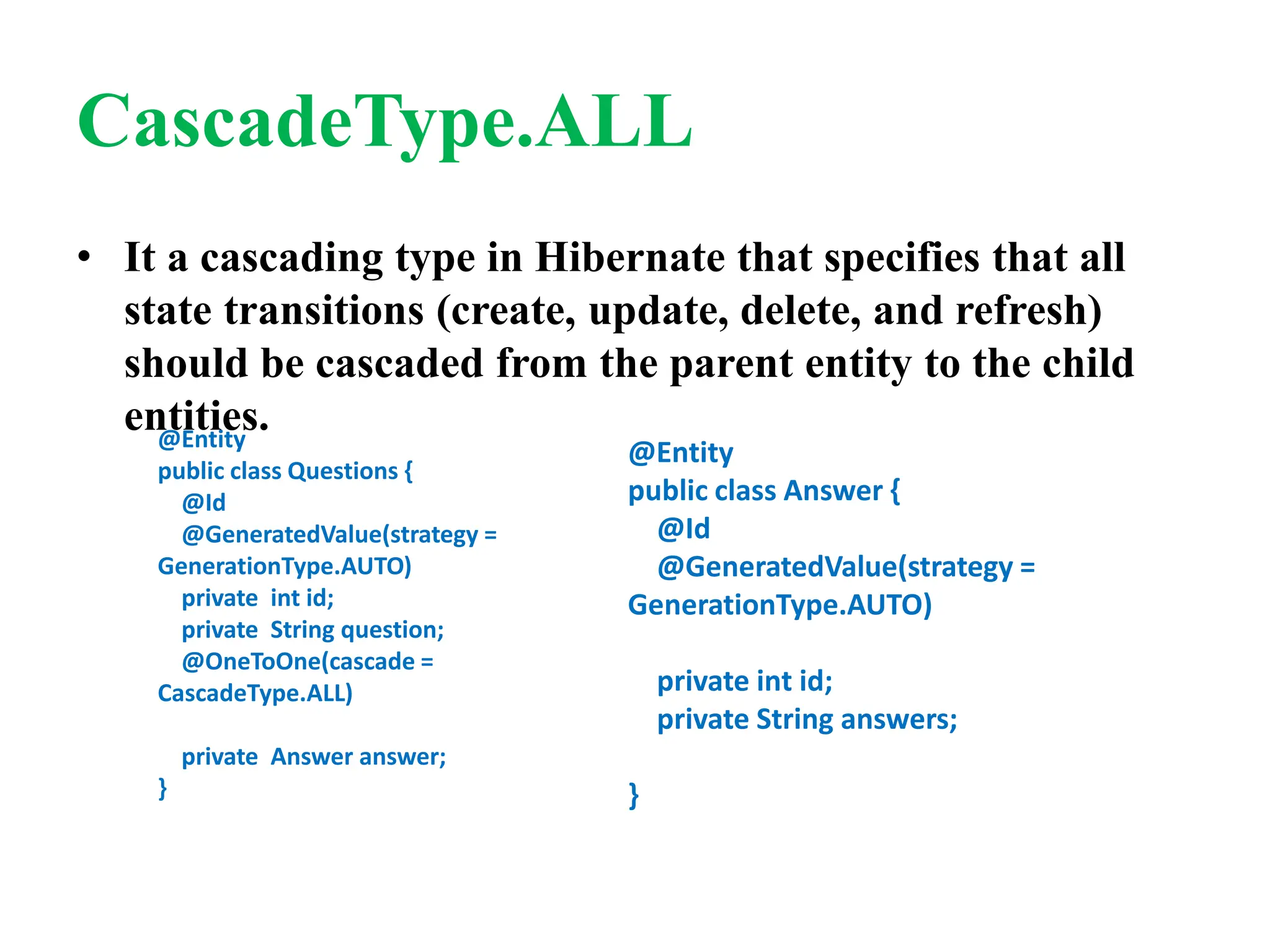
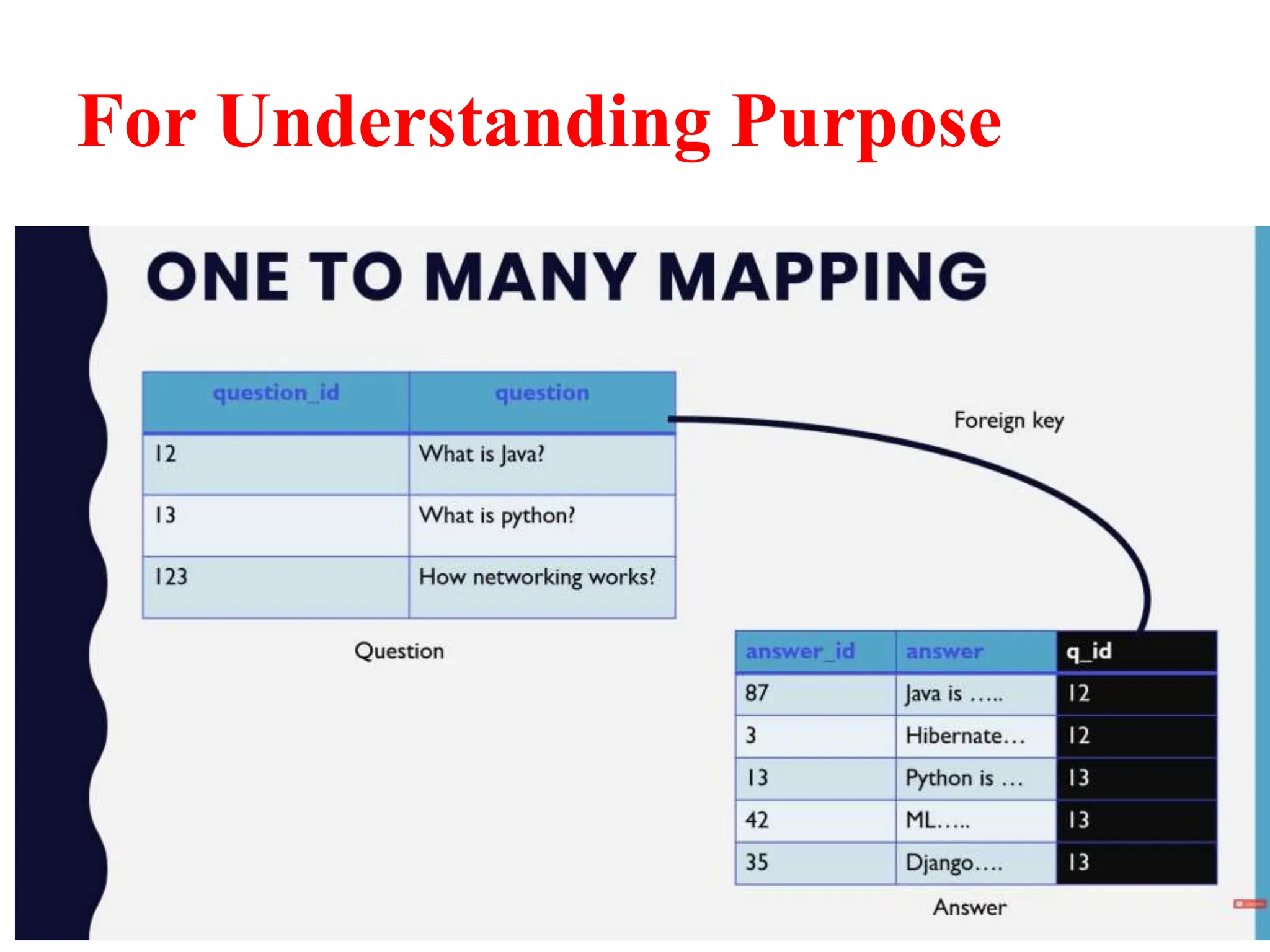
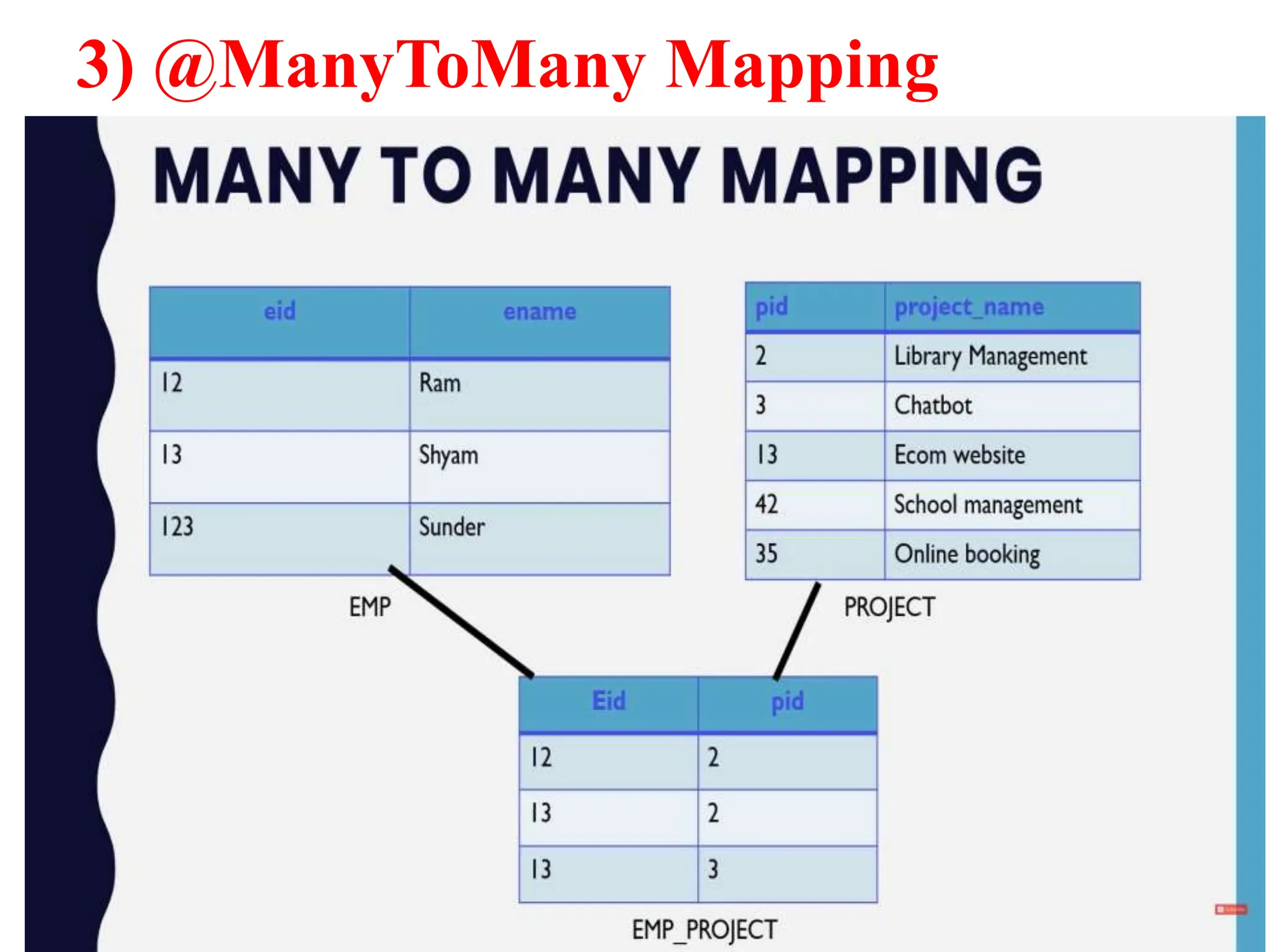
Hibernate is a Java framework that simplifies database interactions through Object-Relational Mapping (ORM), enabling easier data persistence and manipulation. It implements the Java Persistence API (JPA) and supports various annotations for entity management, such as @Entity and @Table, as well as cascading operations for related entities. The document also discusses mapping relationships like one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many, and emphasizes the importance of configurations for effective data handling within Spring Boot applications.