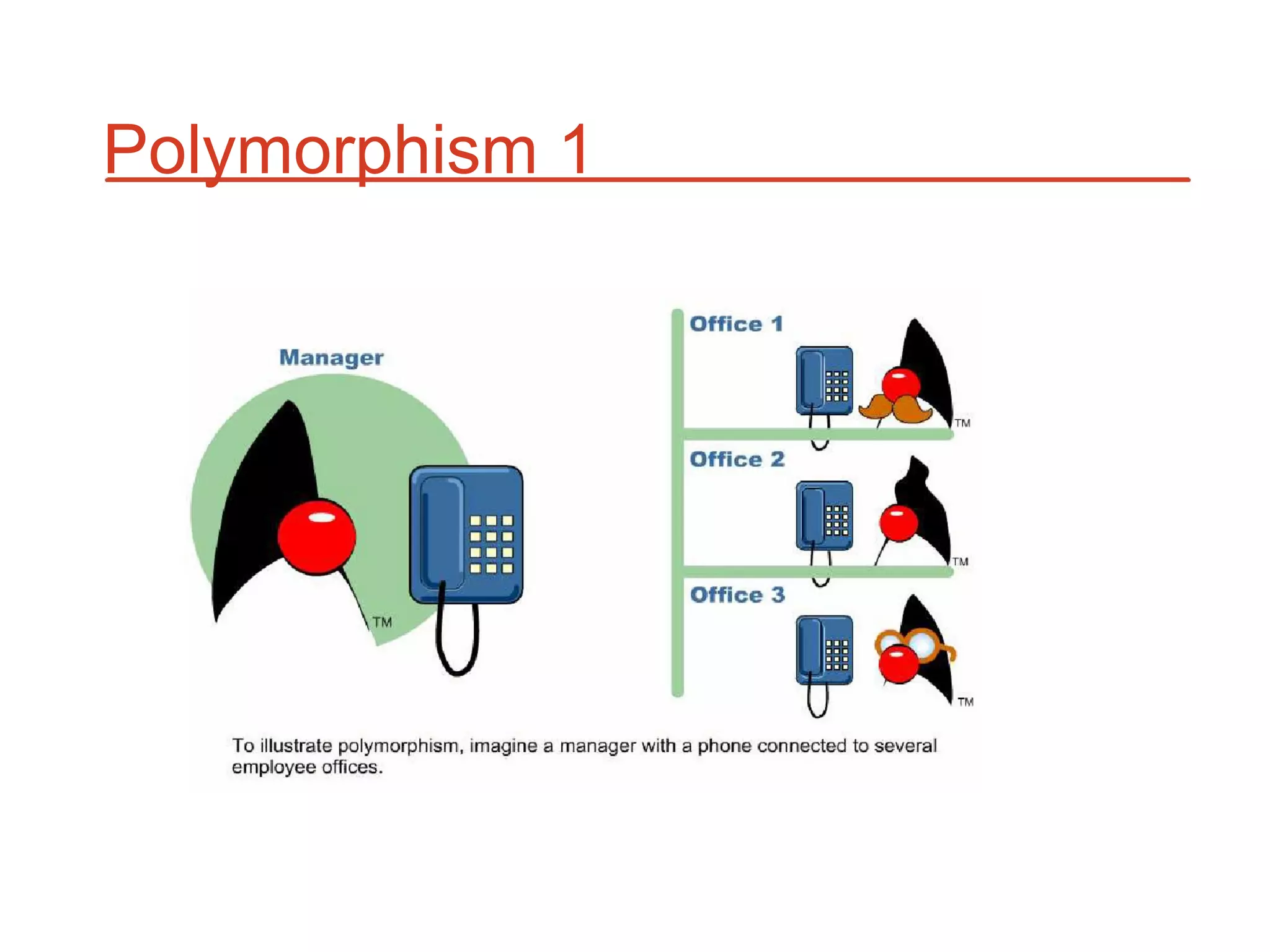
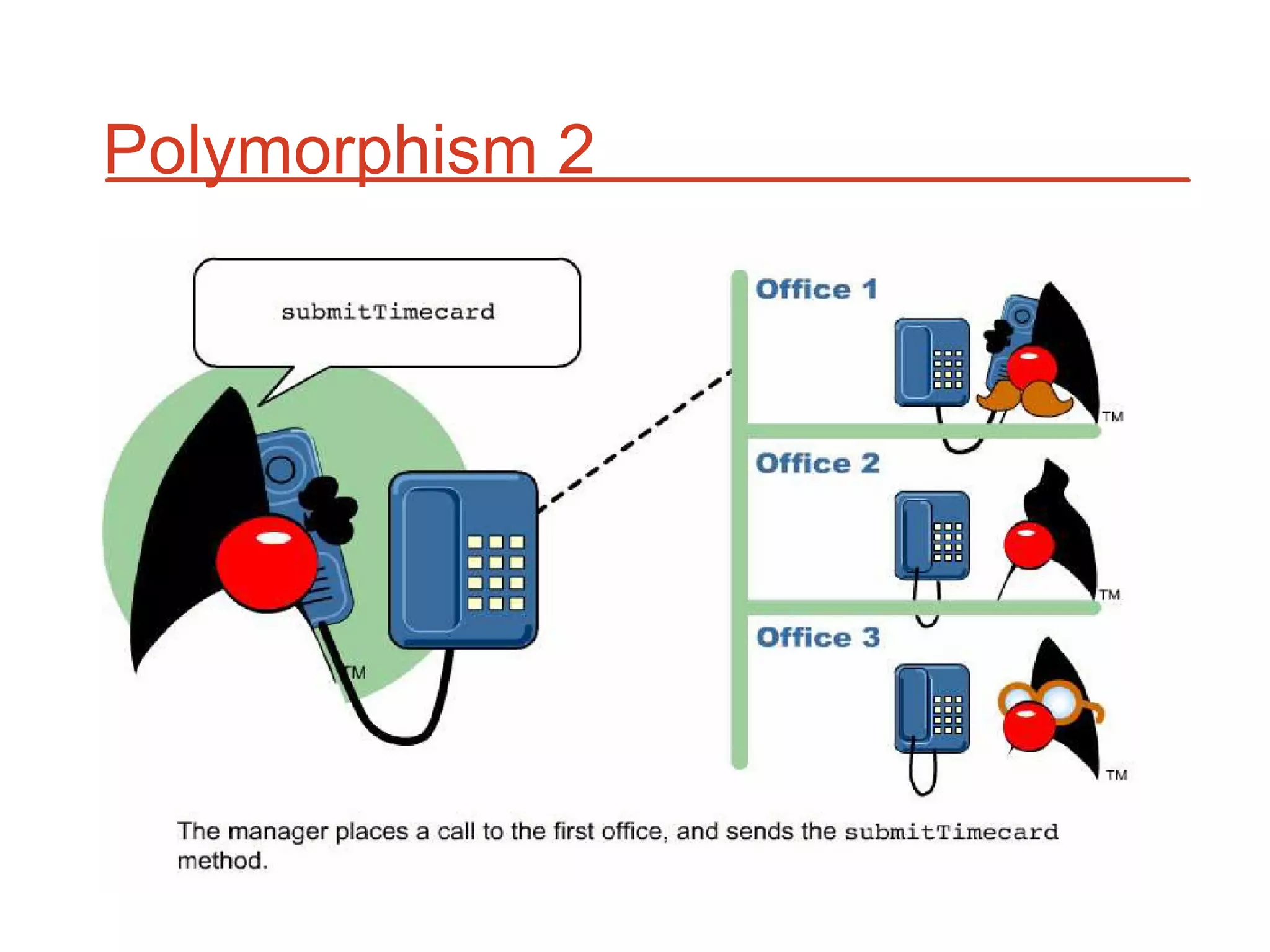
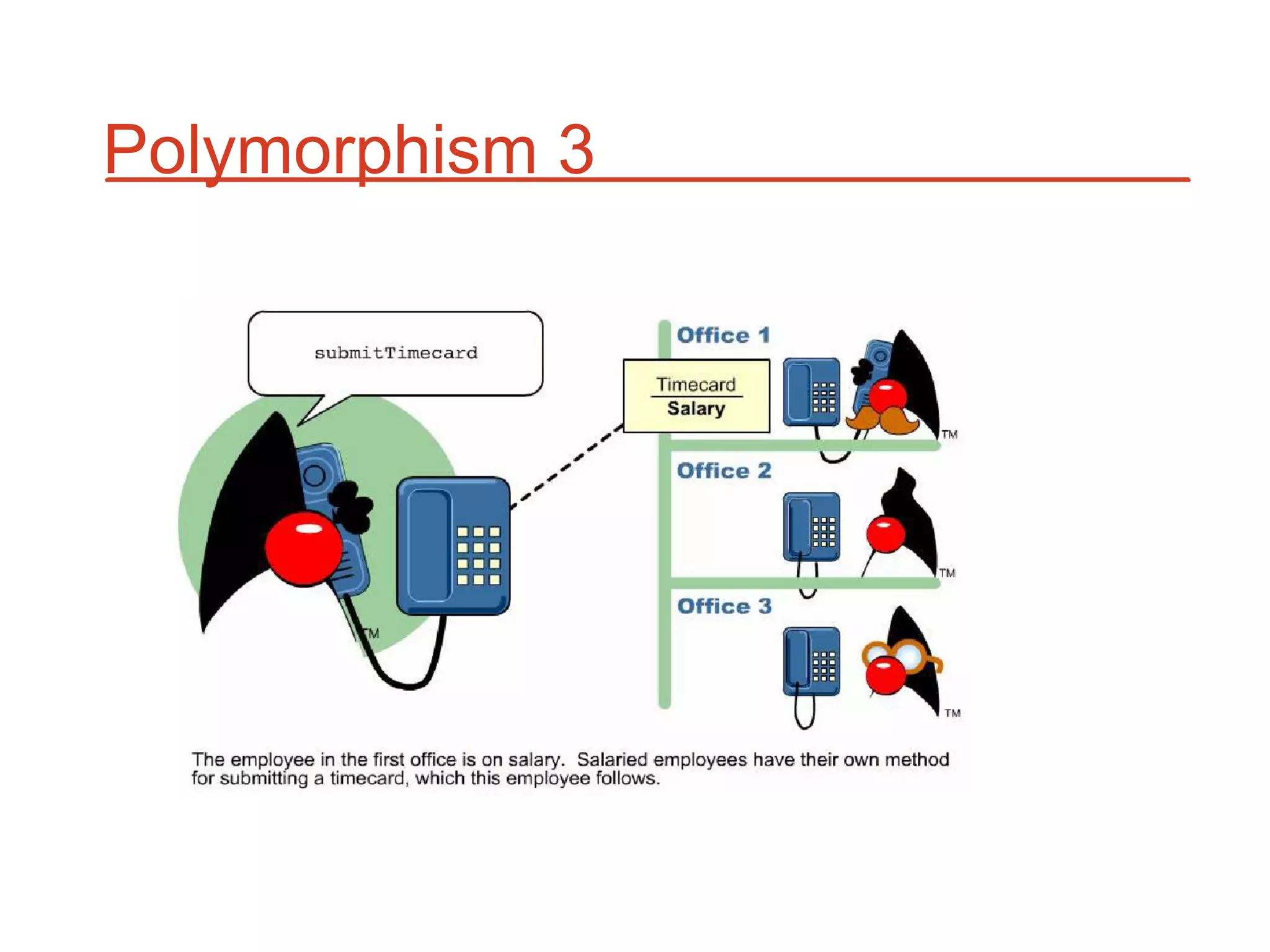
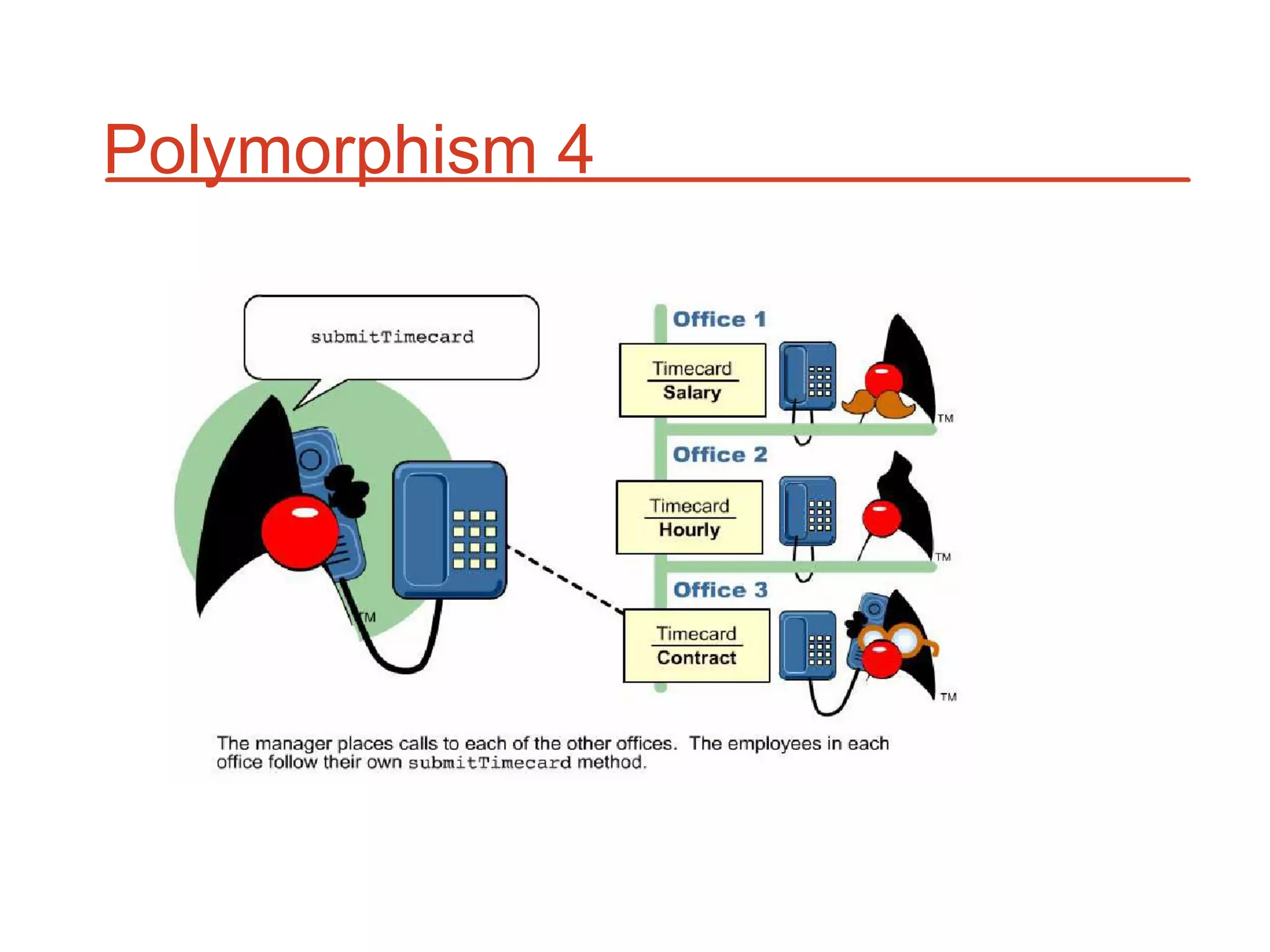
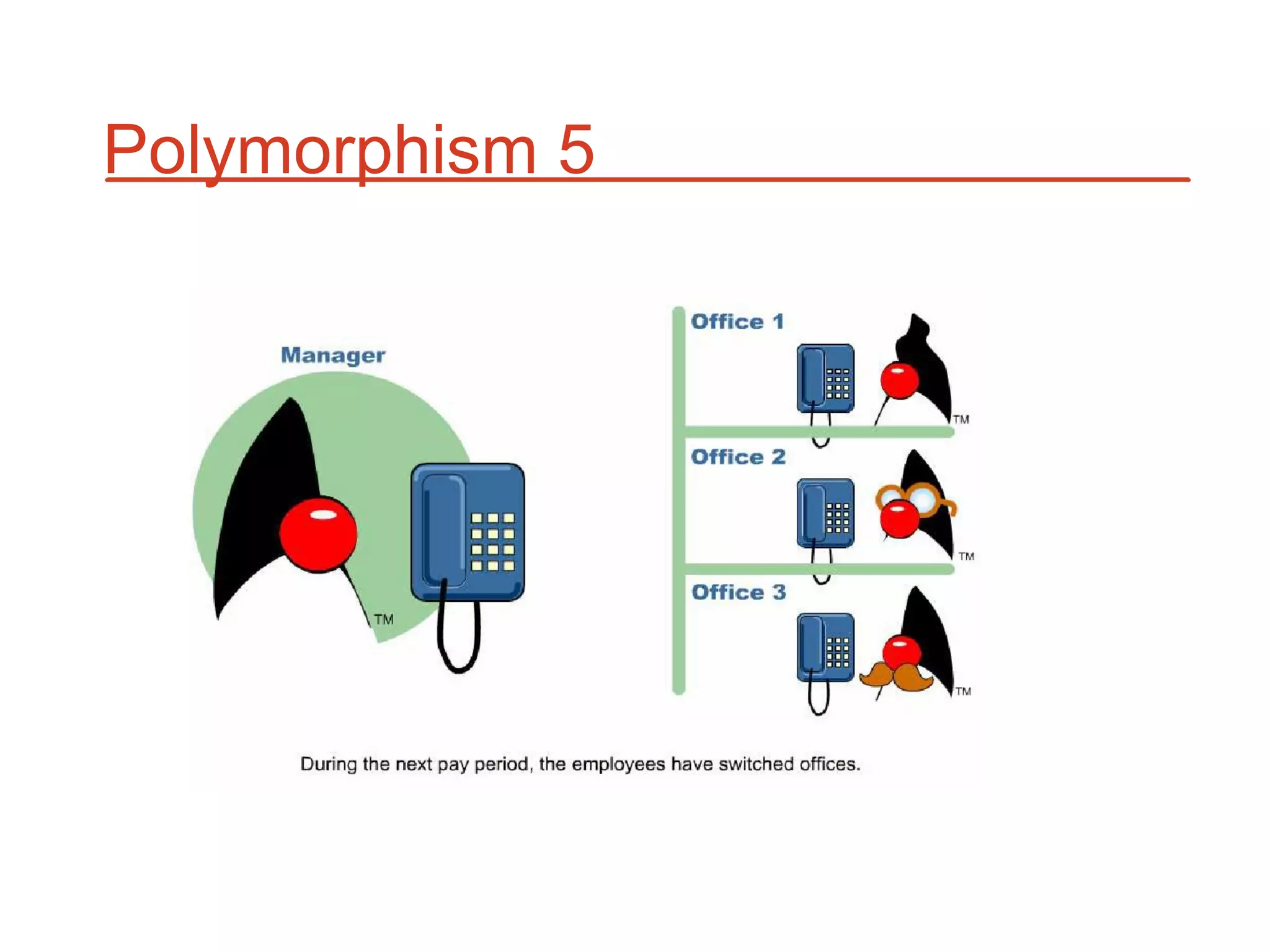
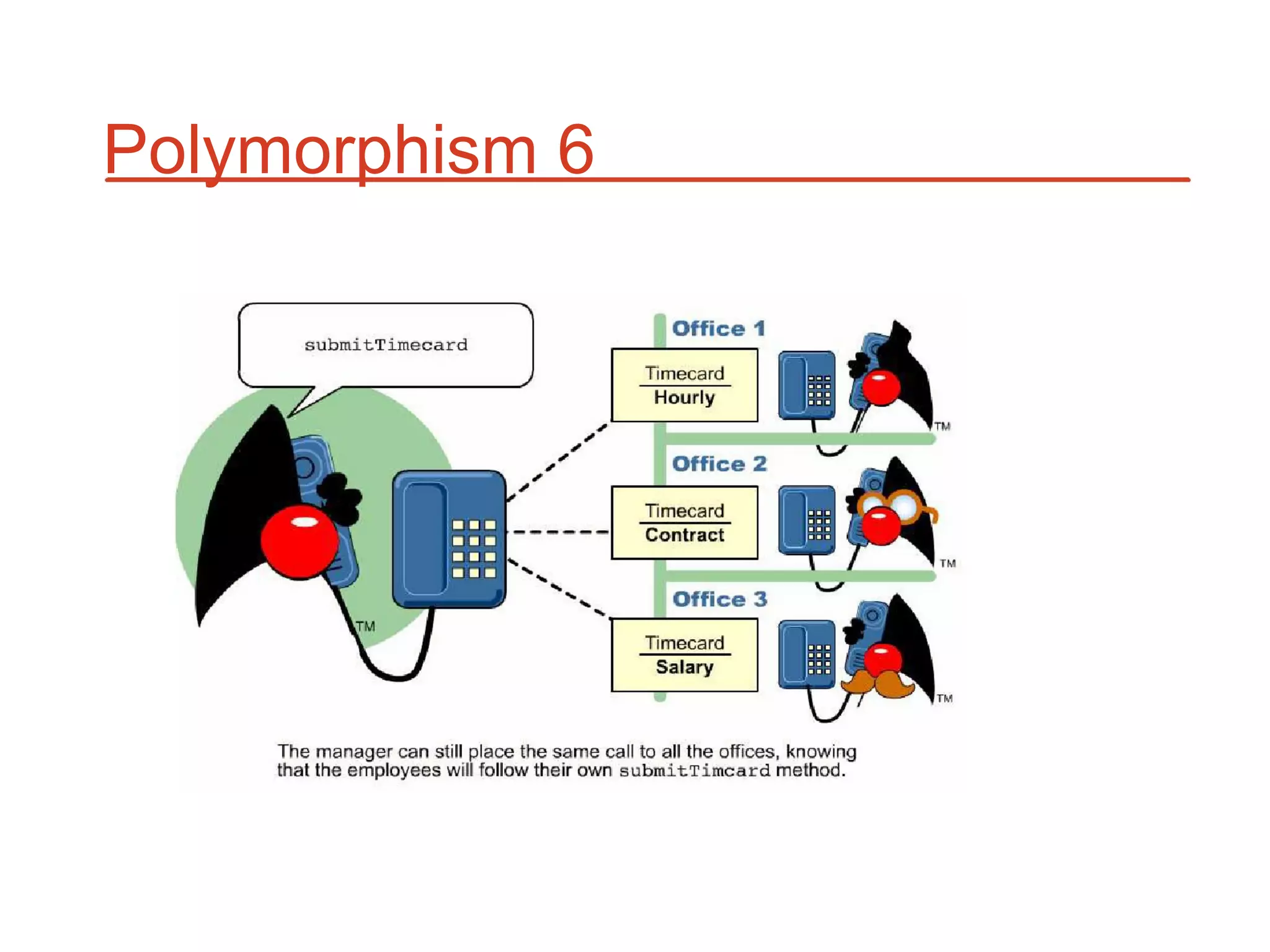
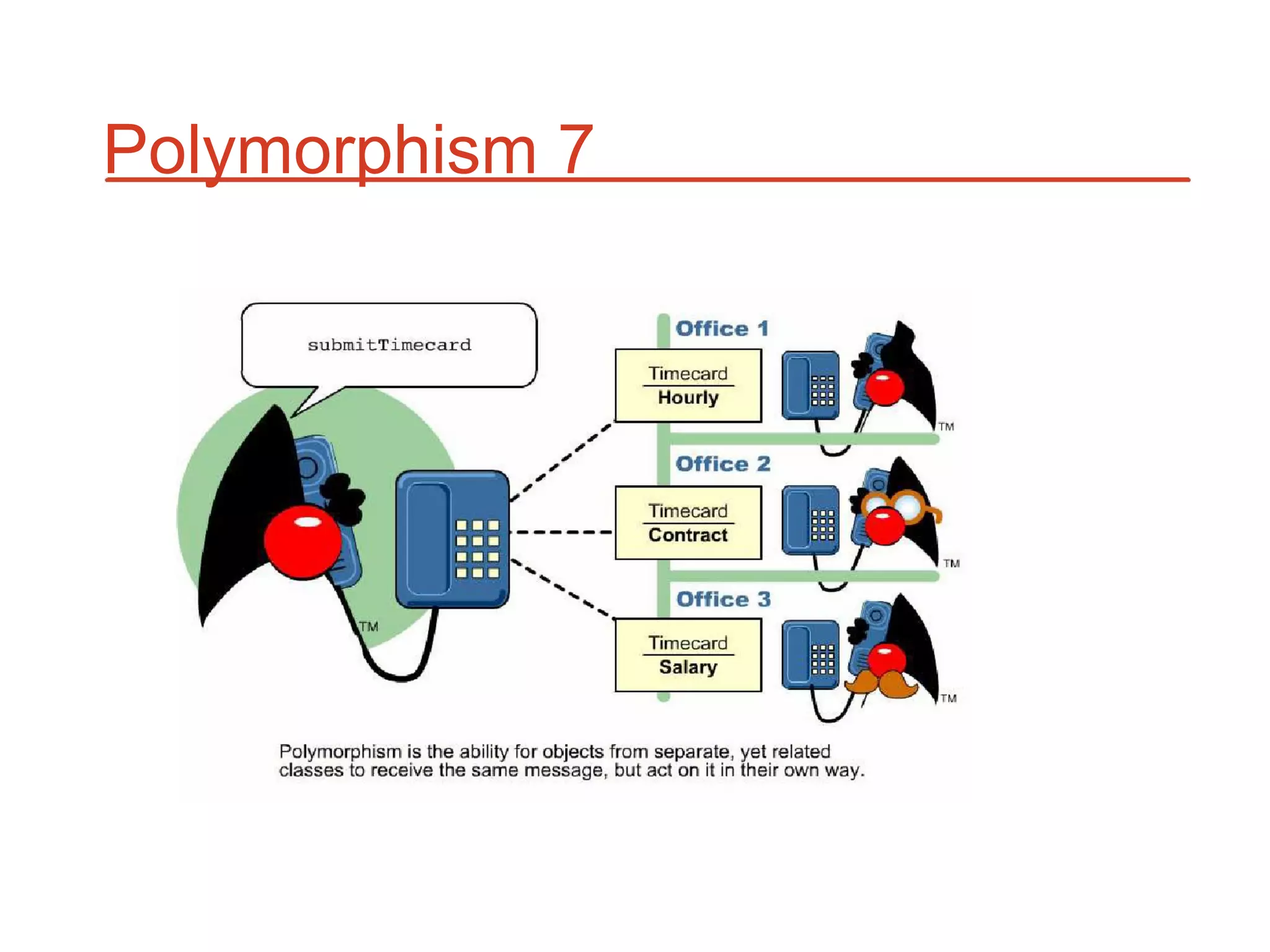
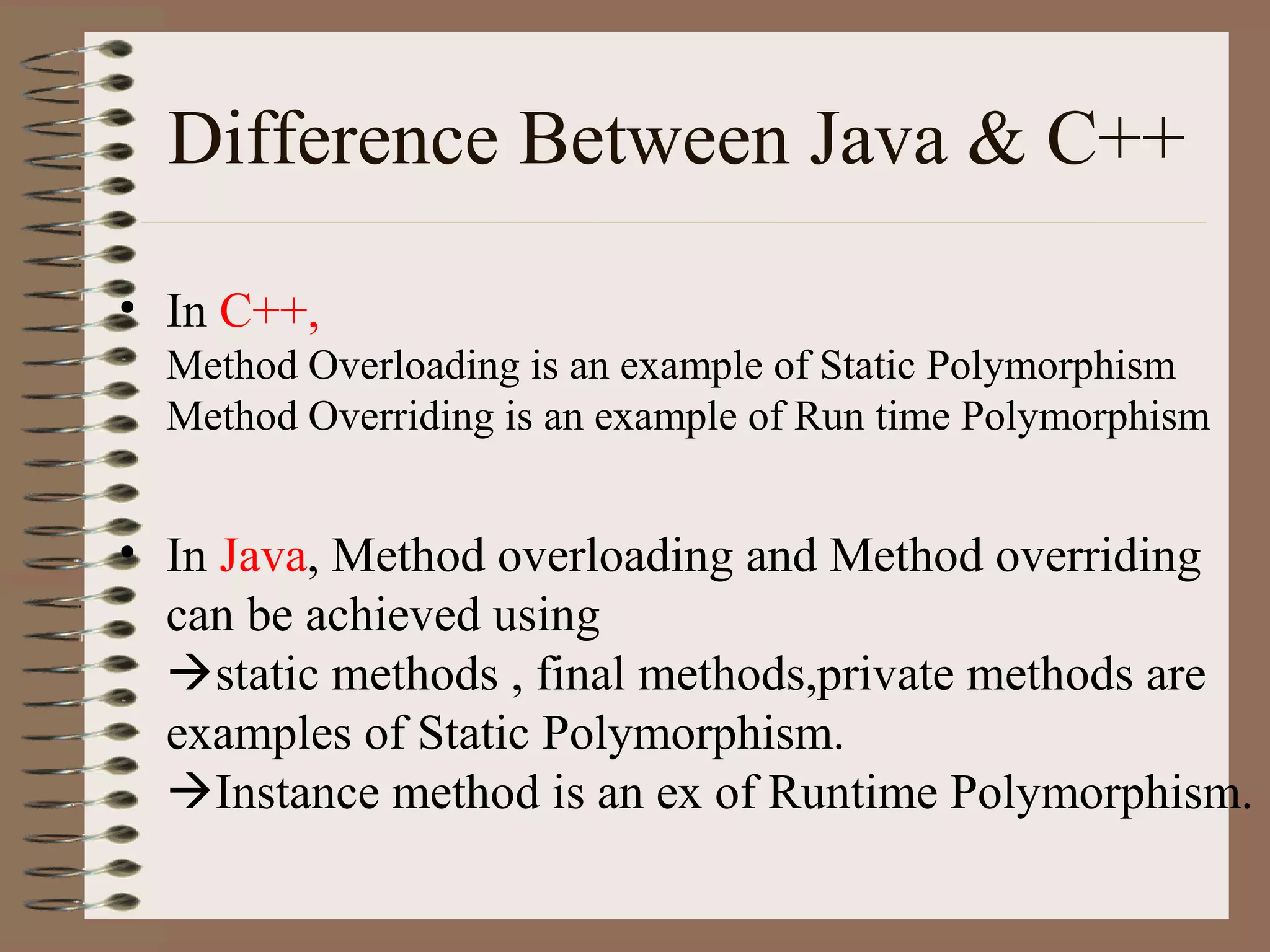
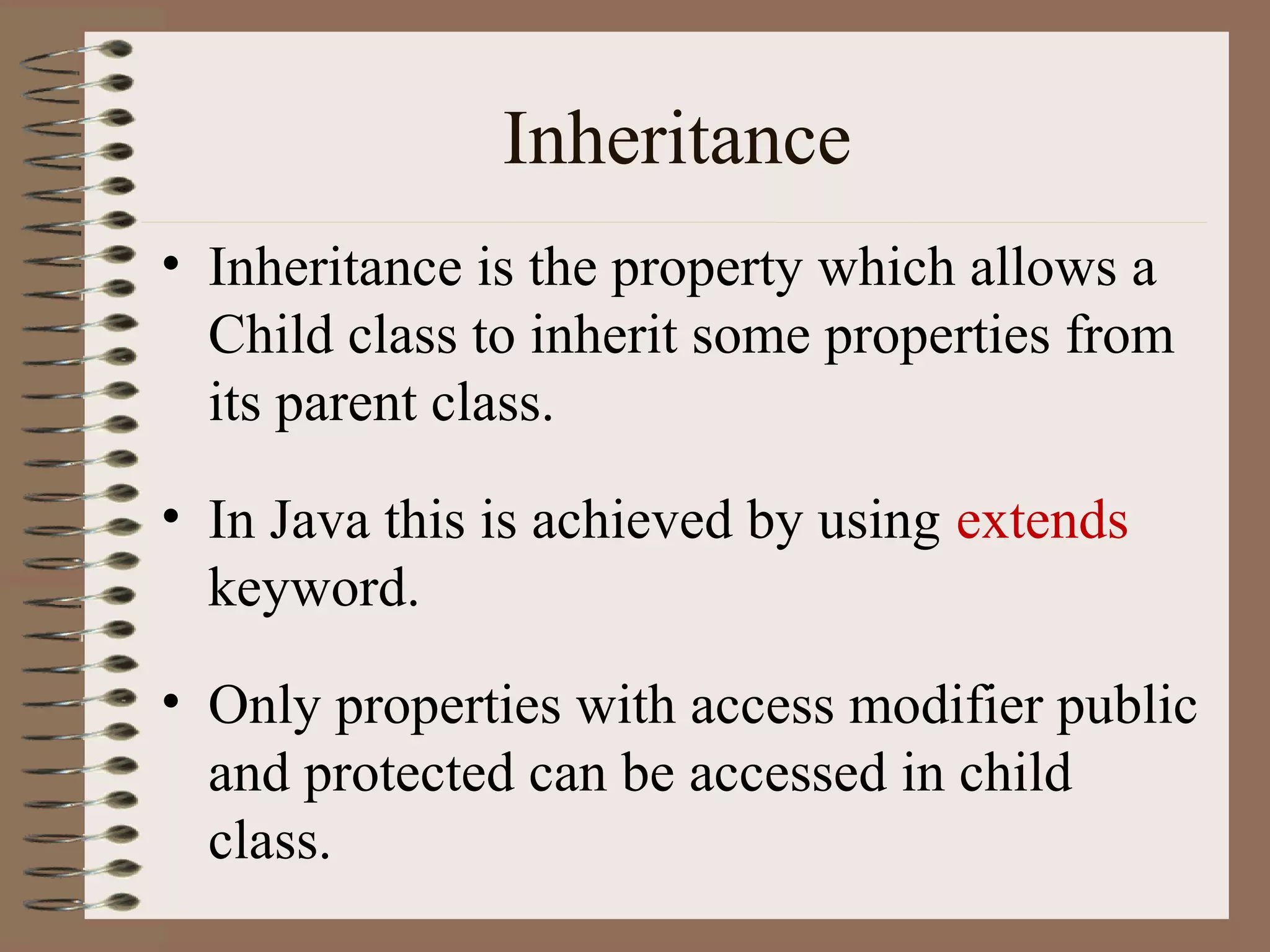
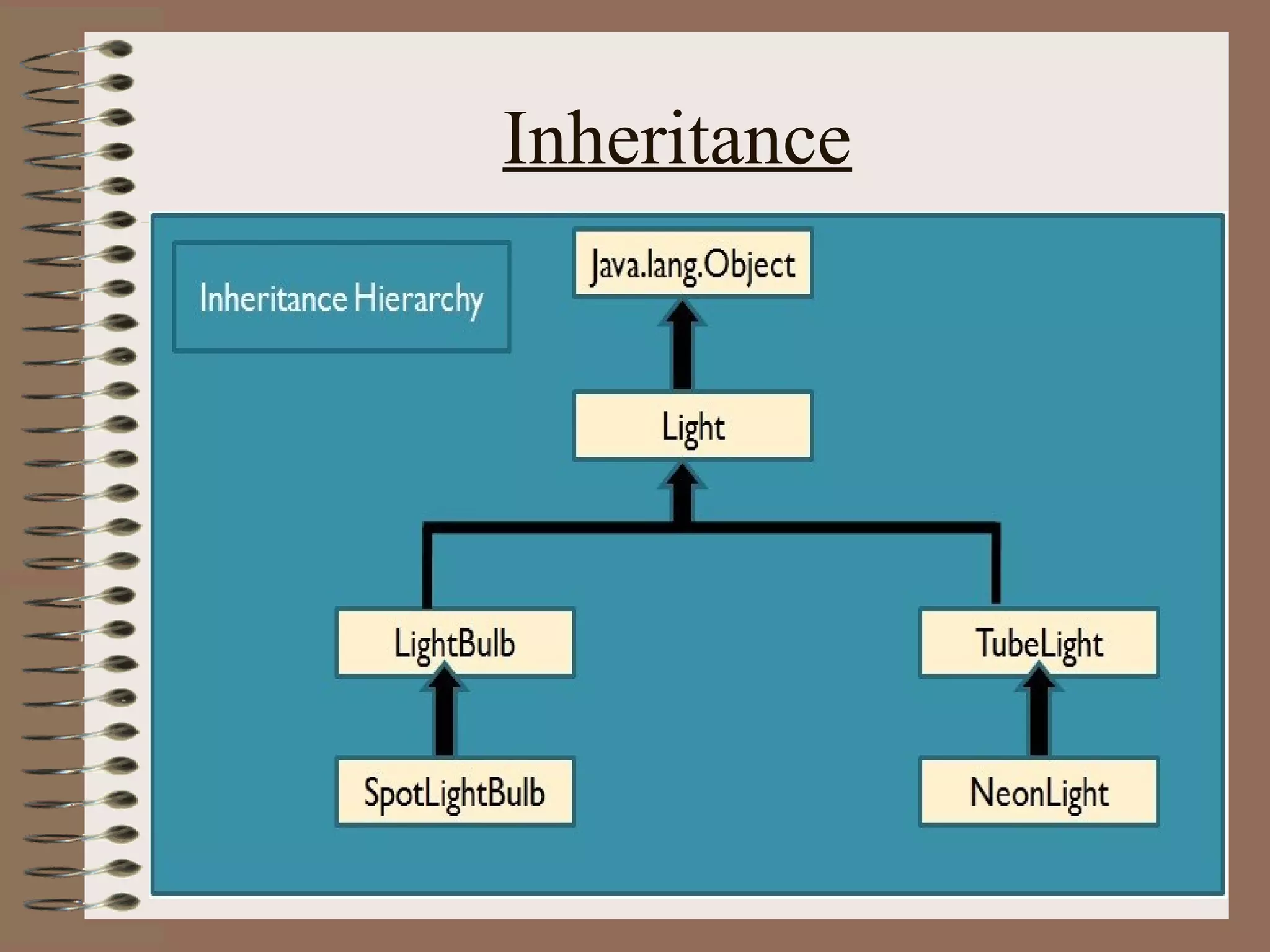
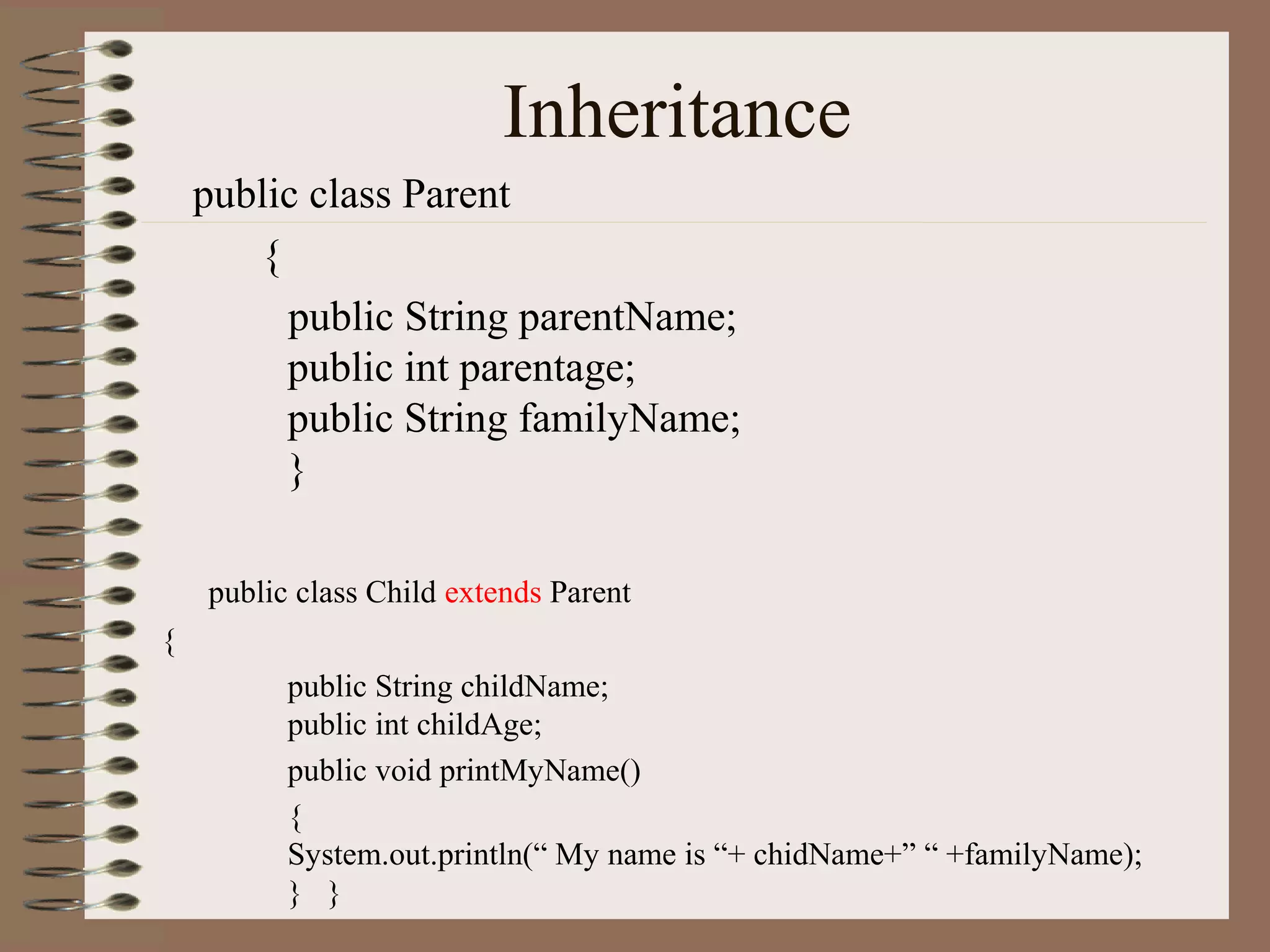
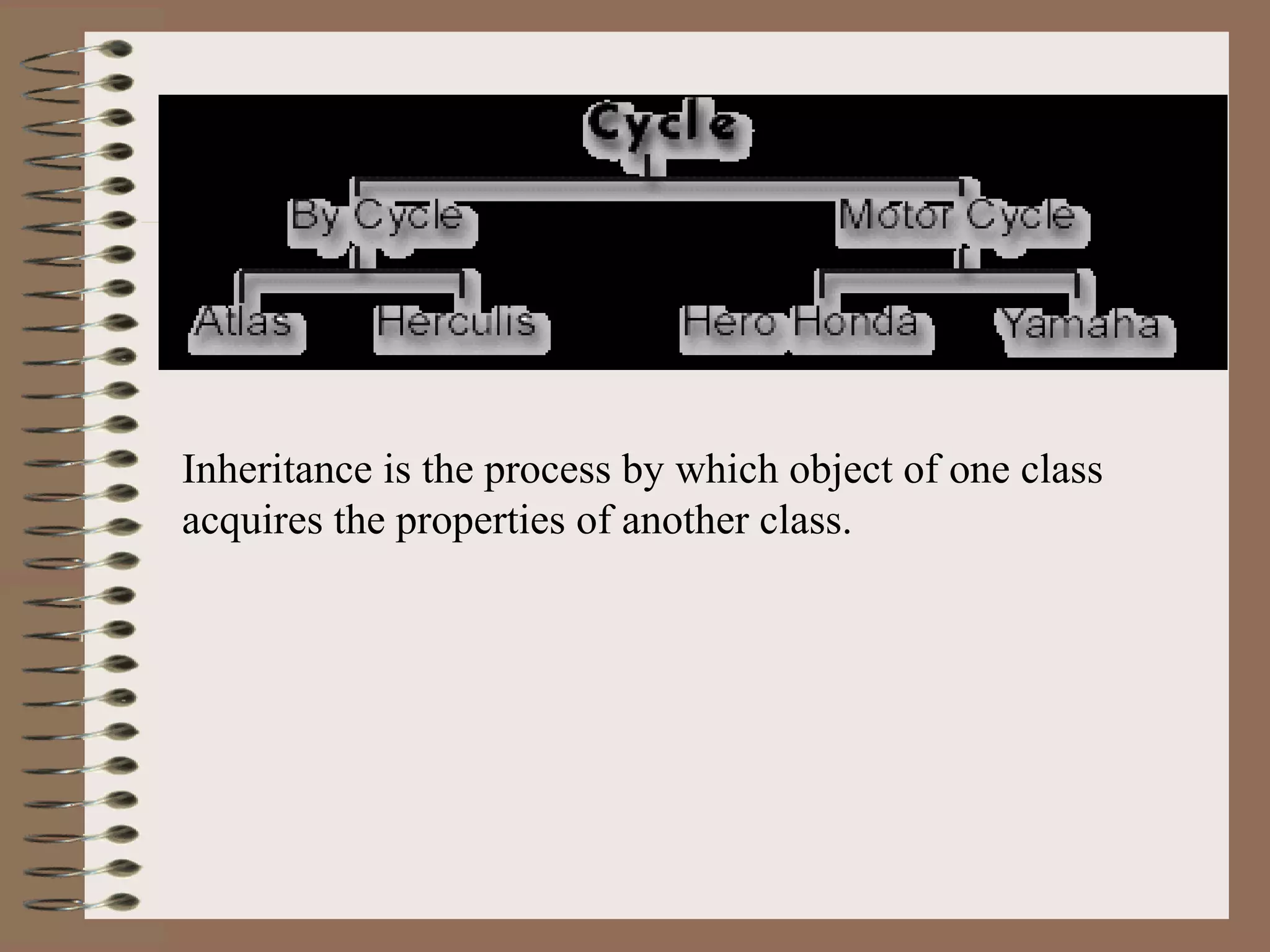
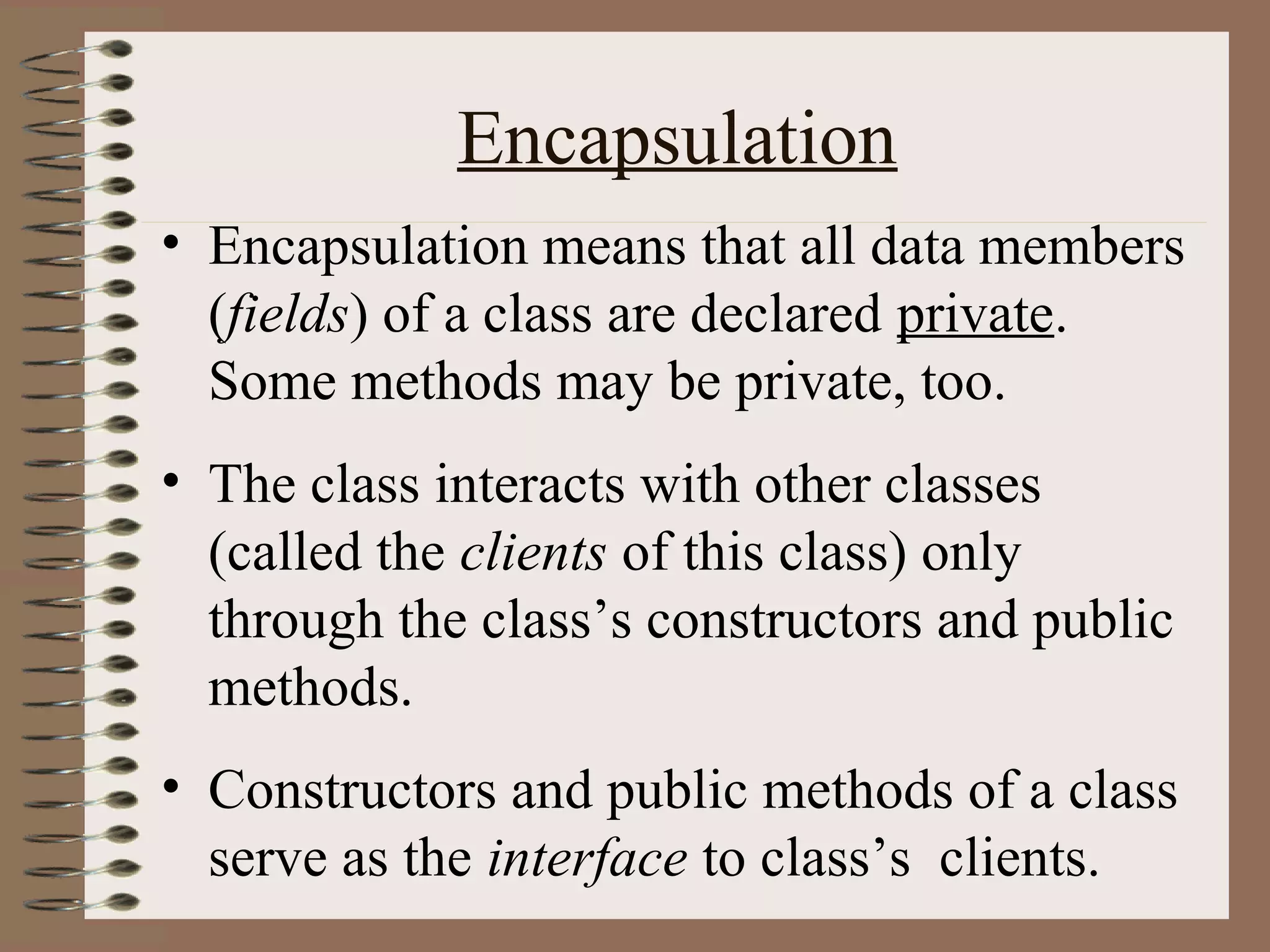
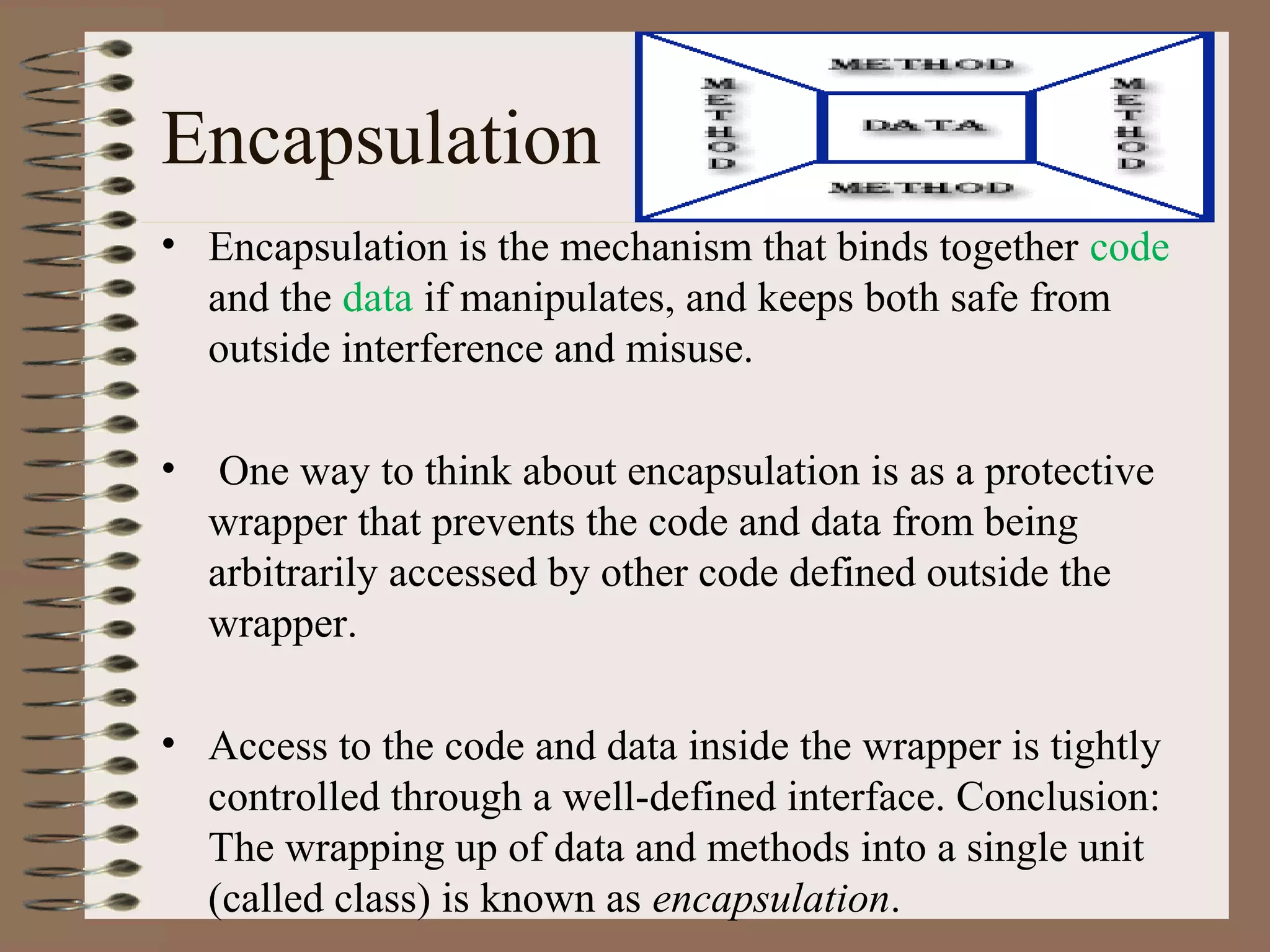
The document outlines key concepts of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java, including principles such as encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. It details the differences between Java and C++ in terms of static and runtime polymorphism, and describes the benefits of Java's design, including security, portability, and robustness. The document also emphasizes Java's capabilities for multithreading, dynamic loading, and its suitability for distributed environments.