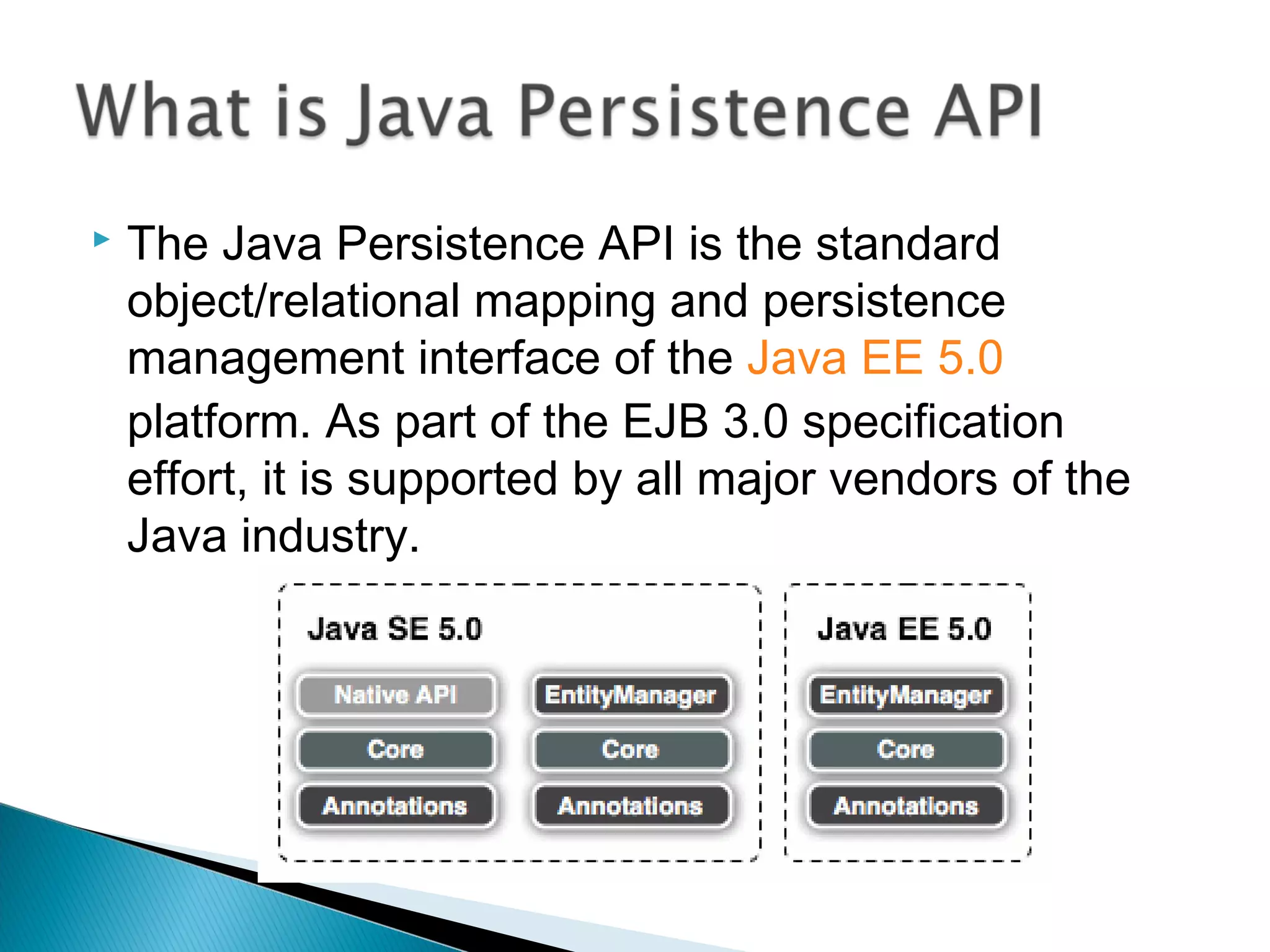
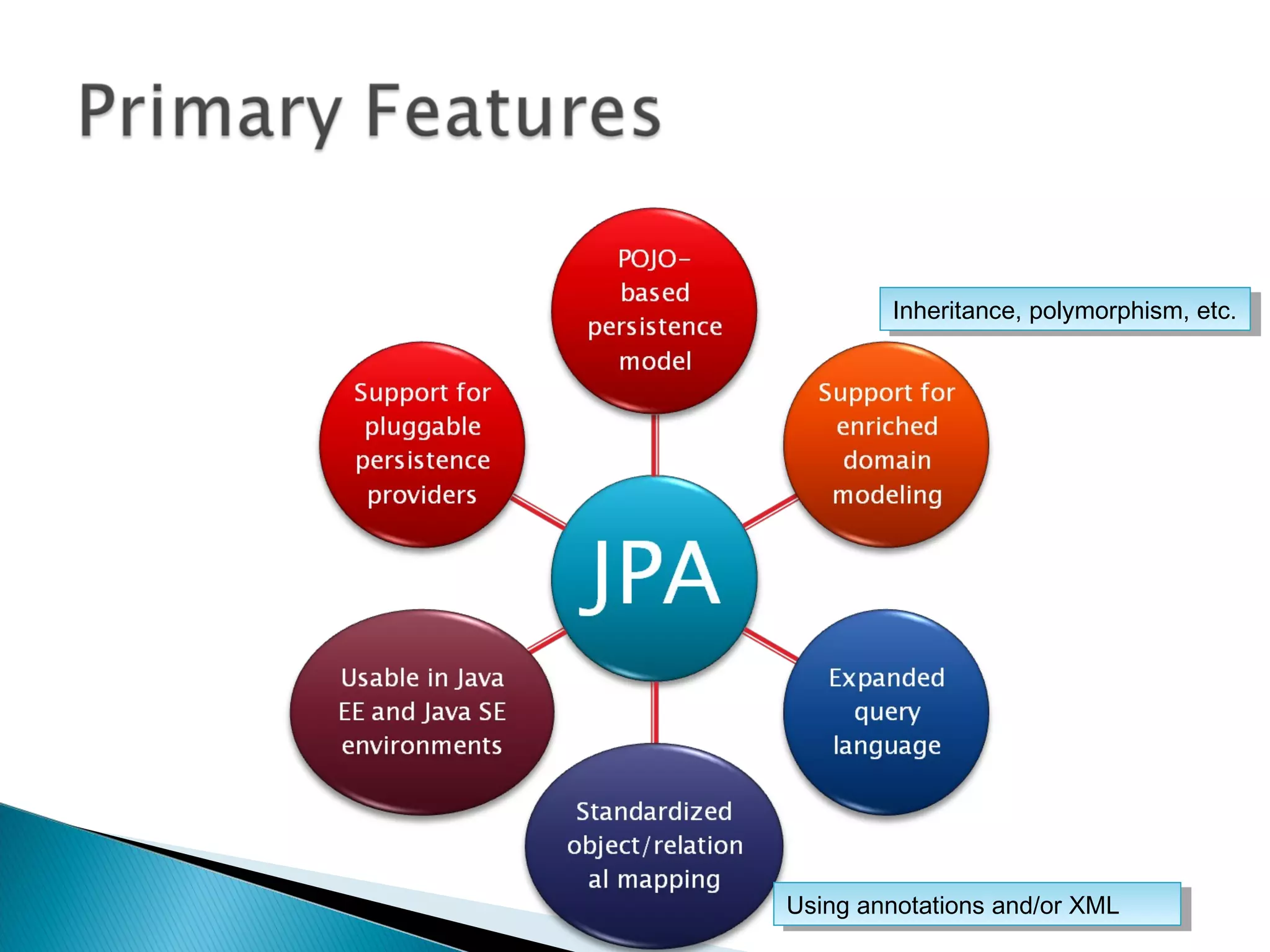
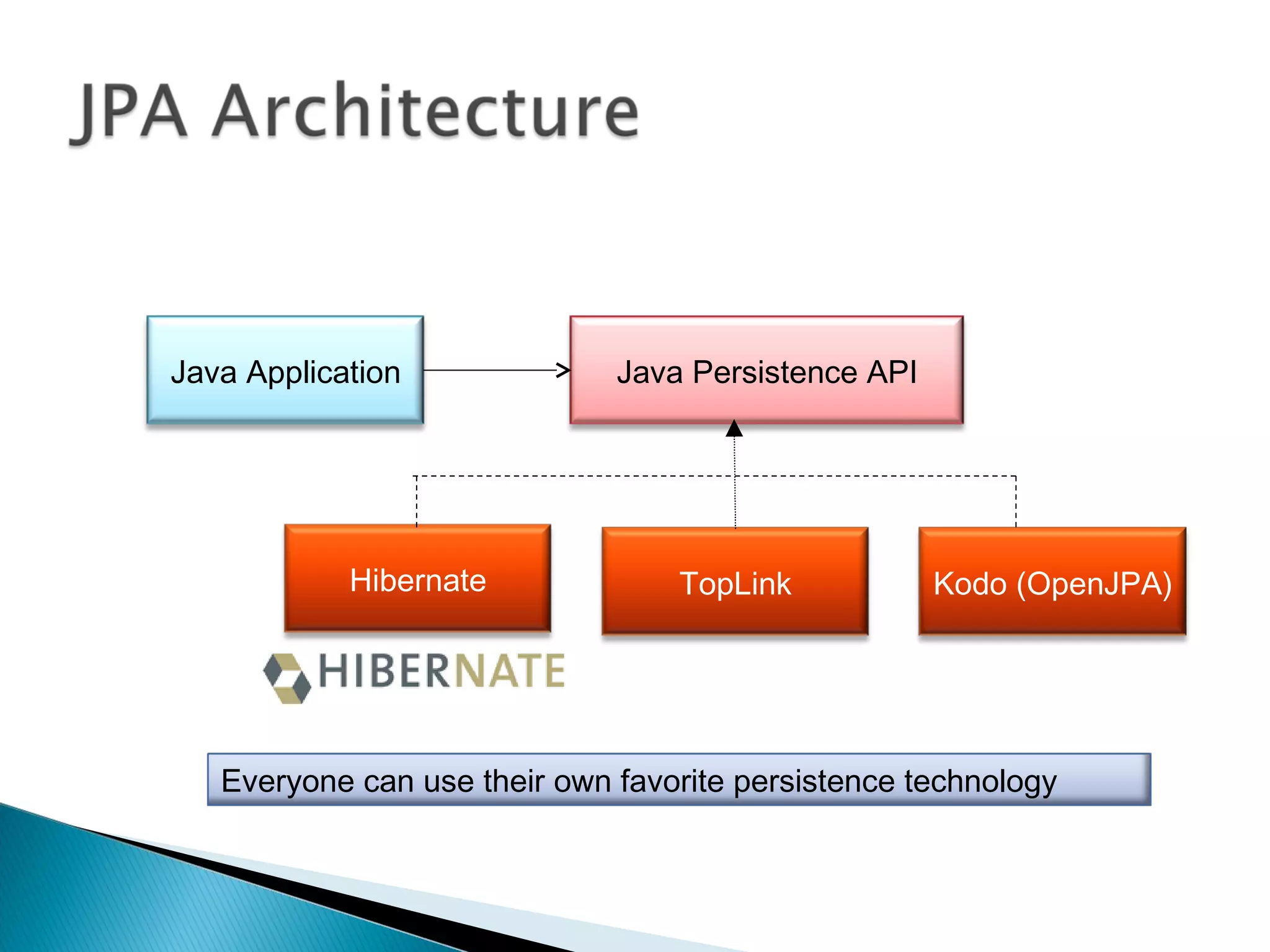
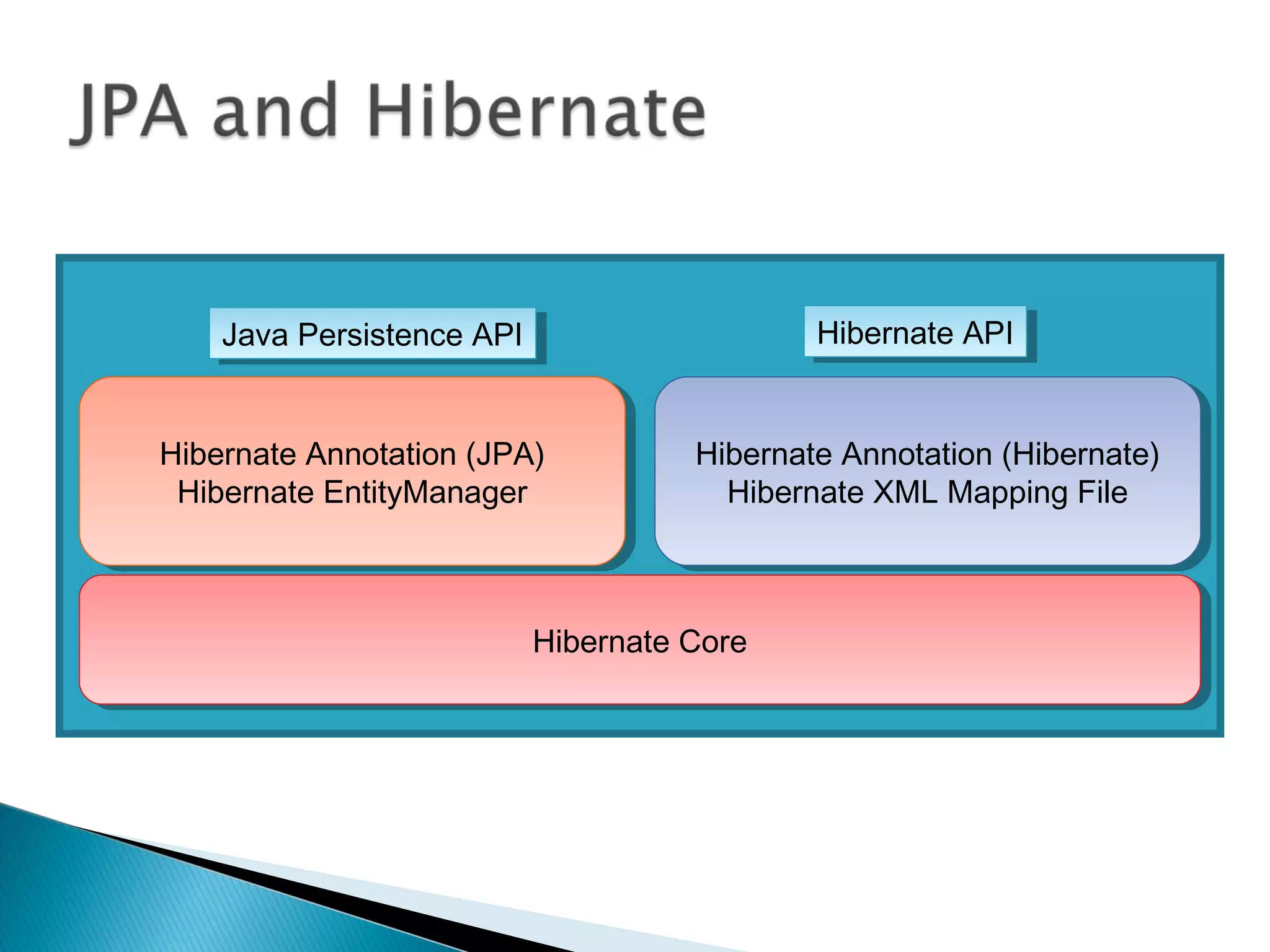
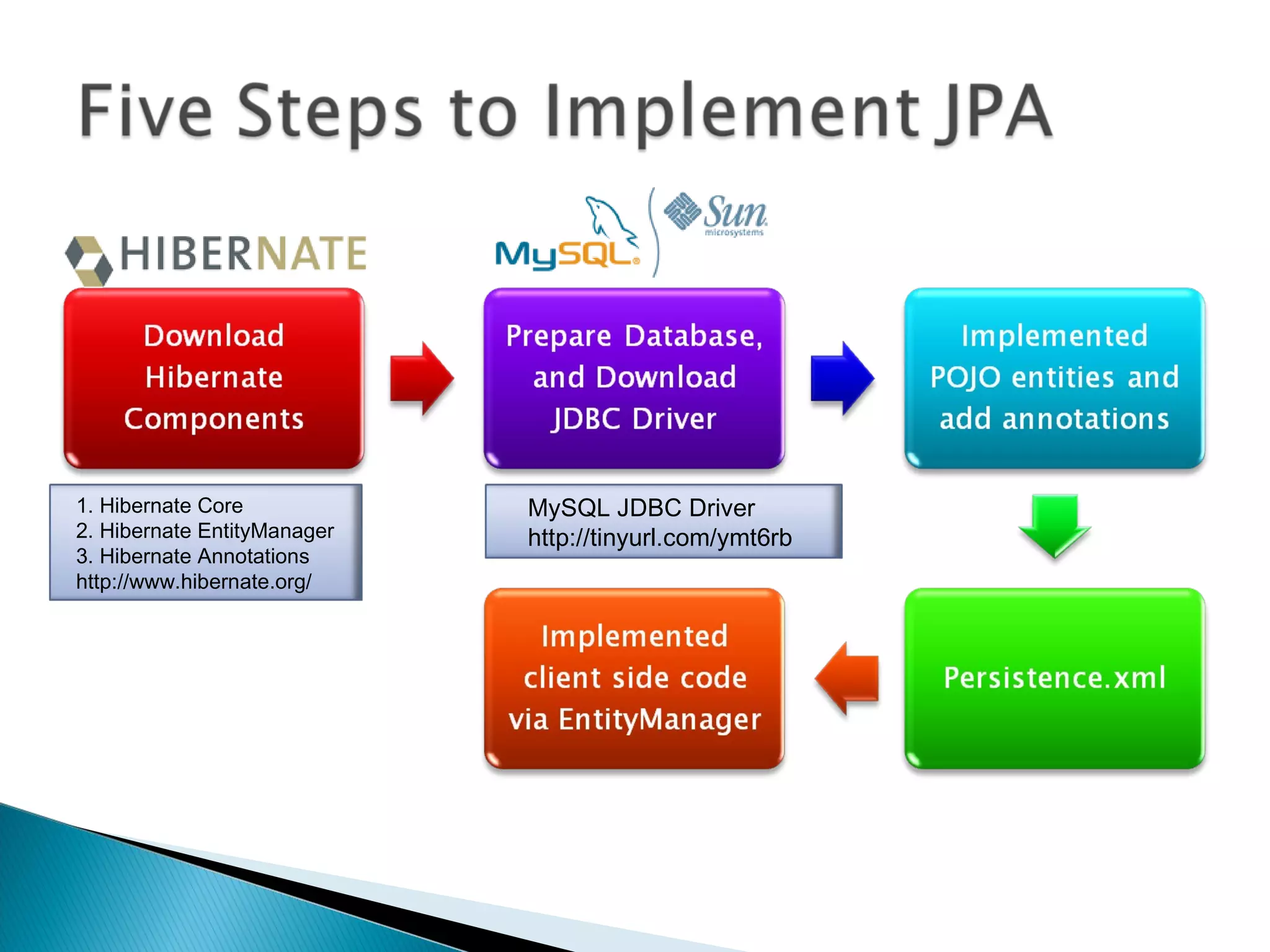
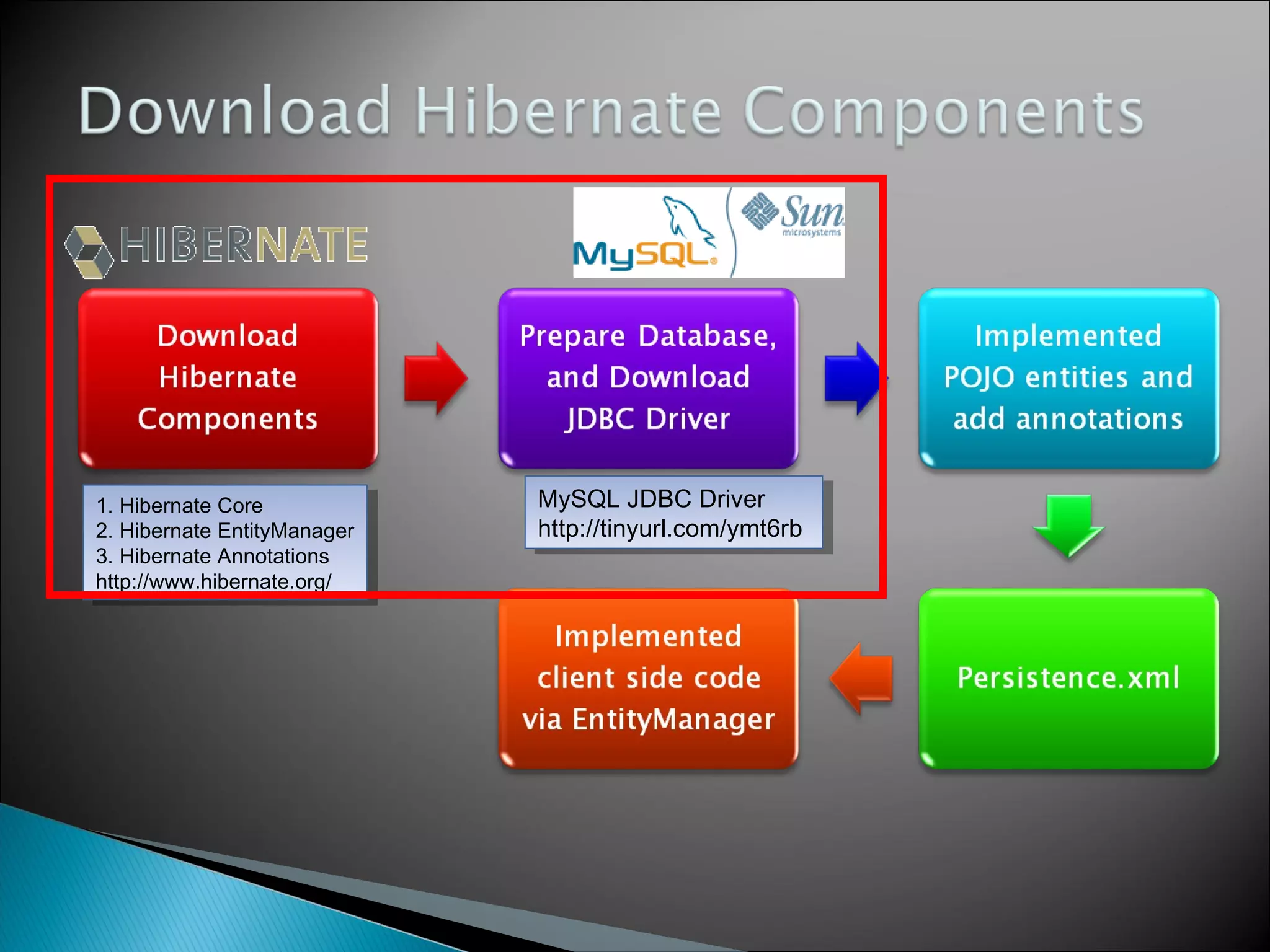
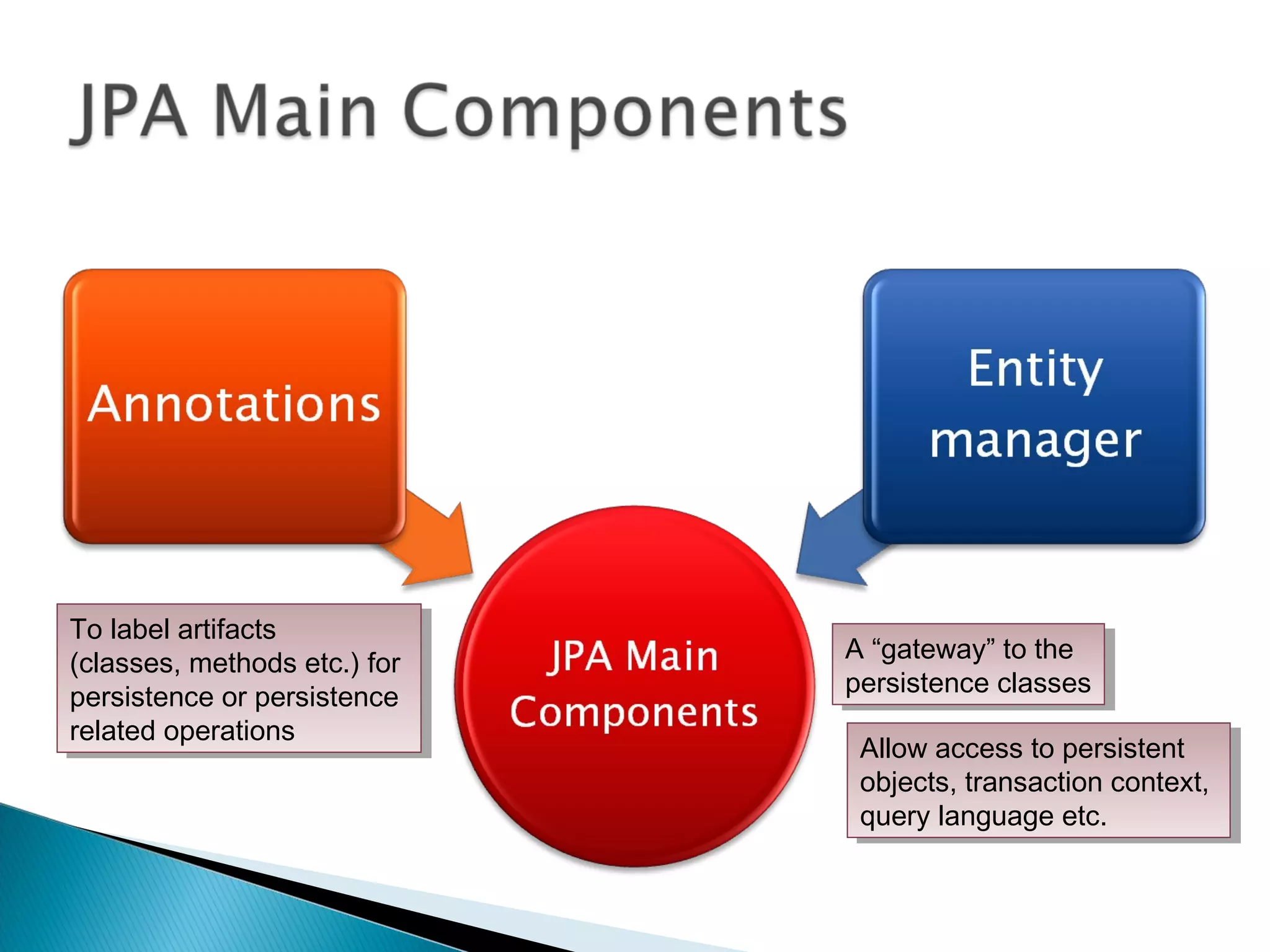
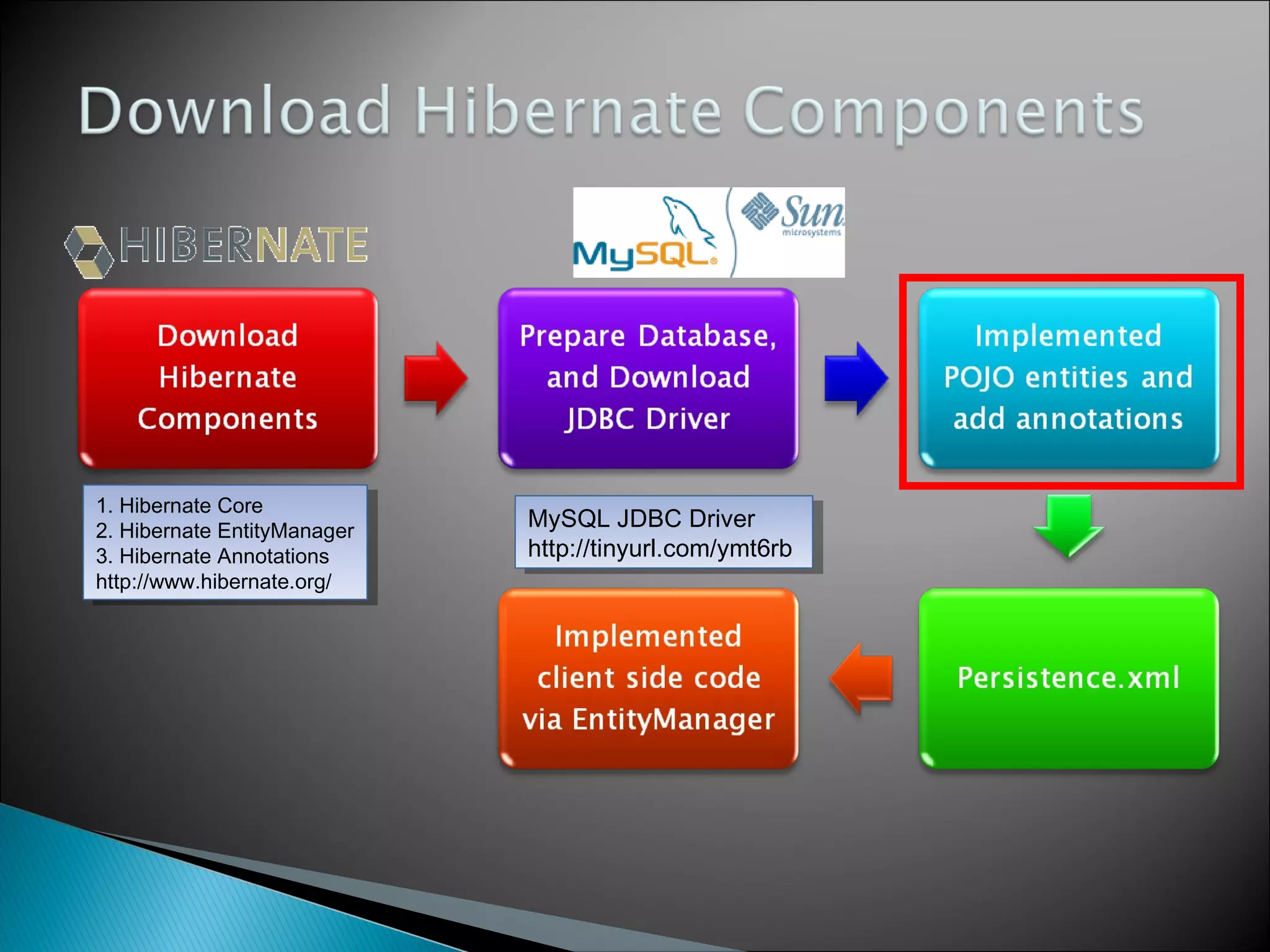
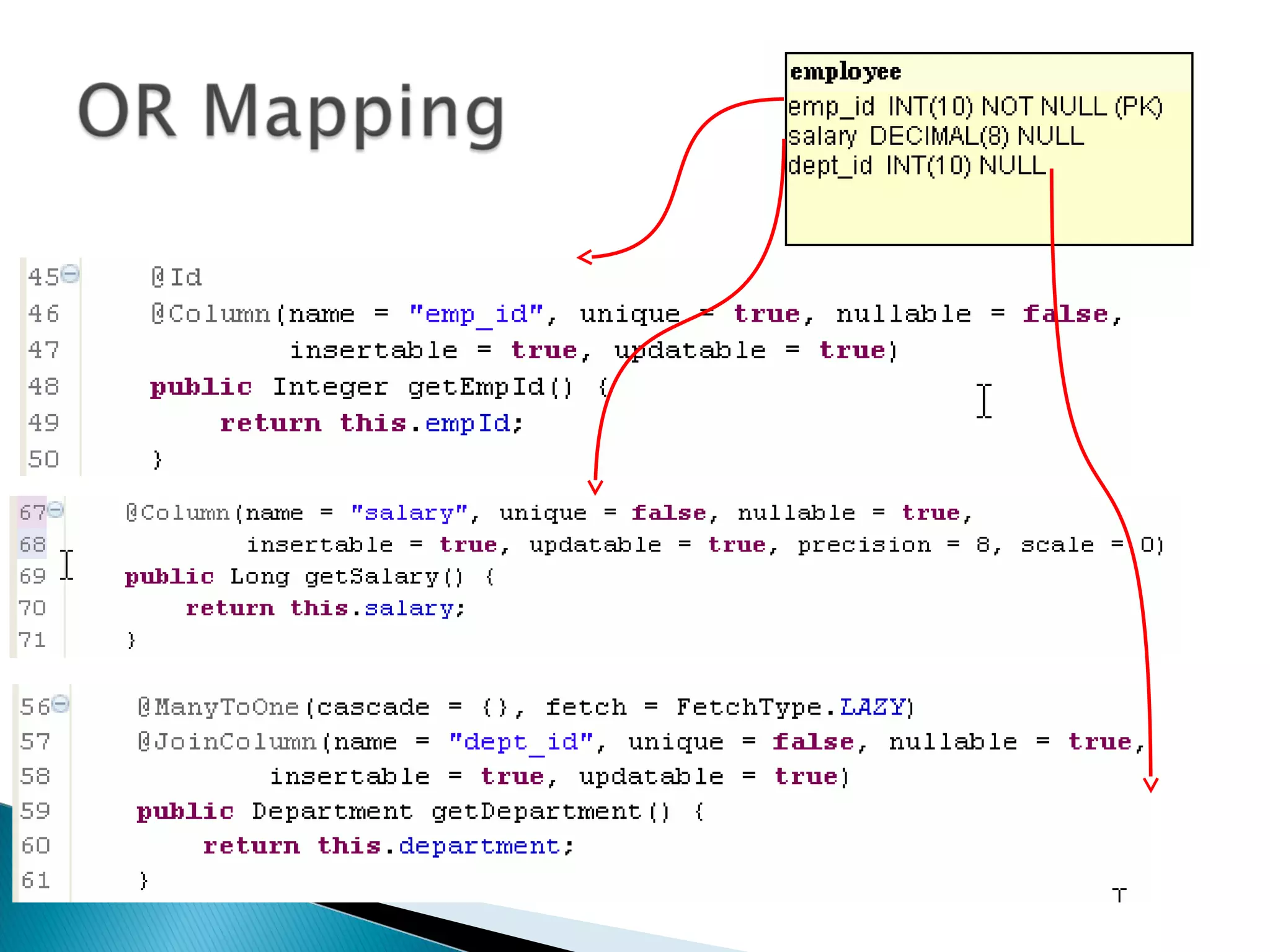
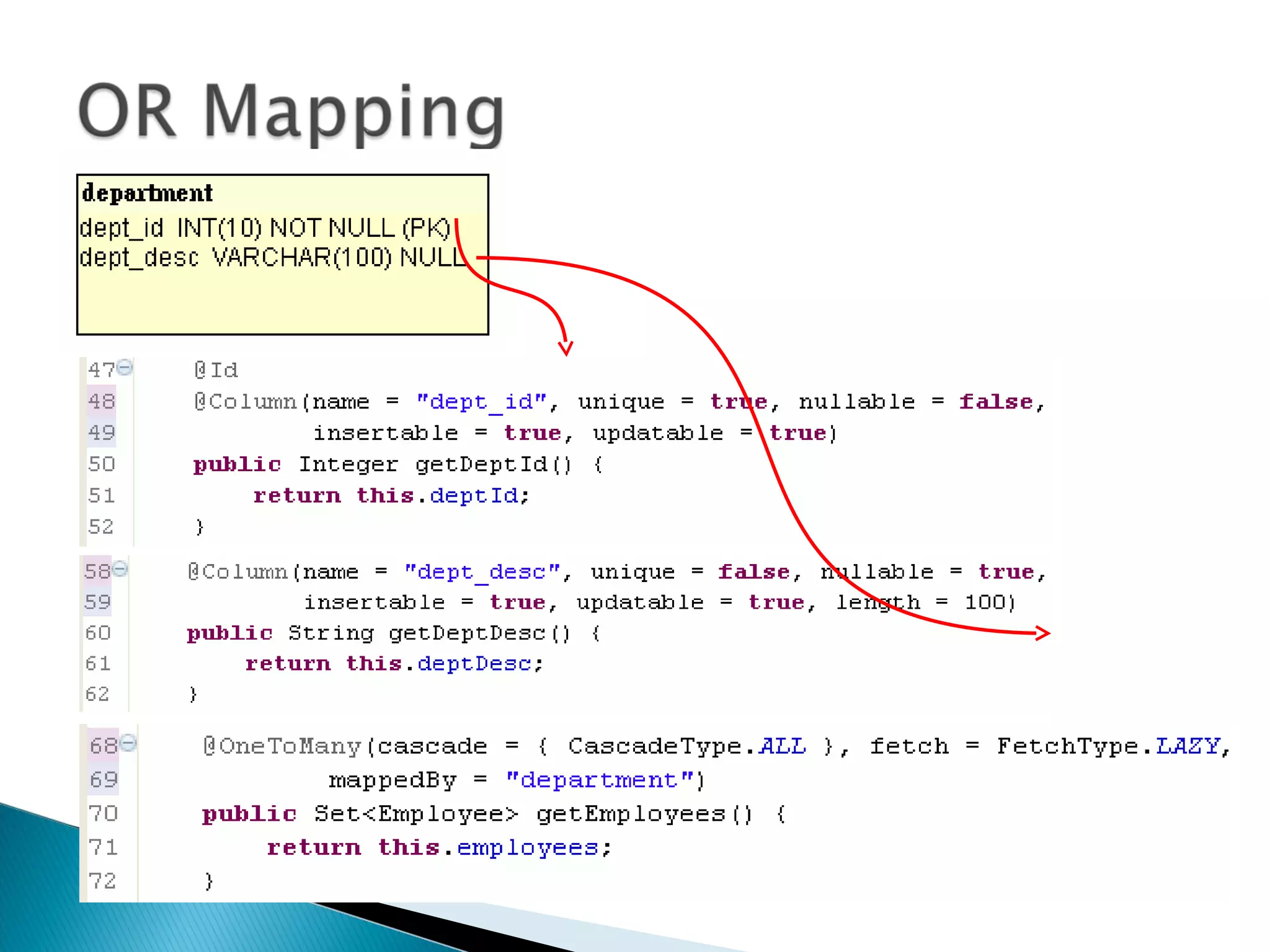
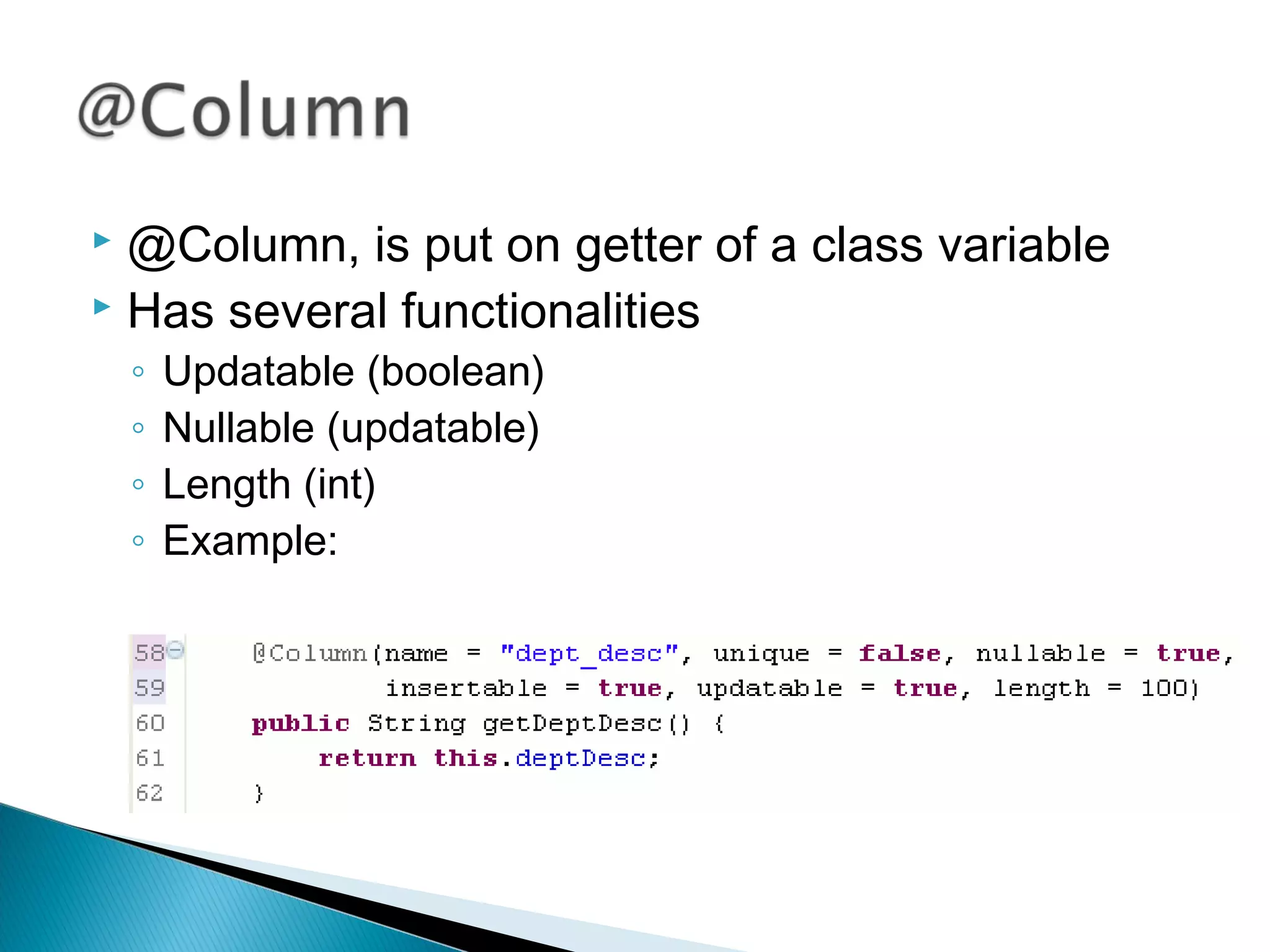
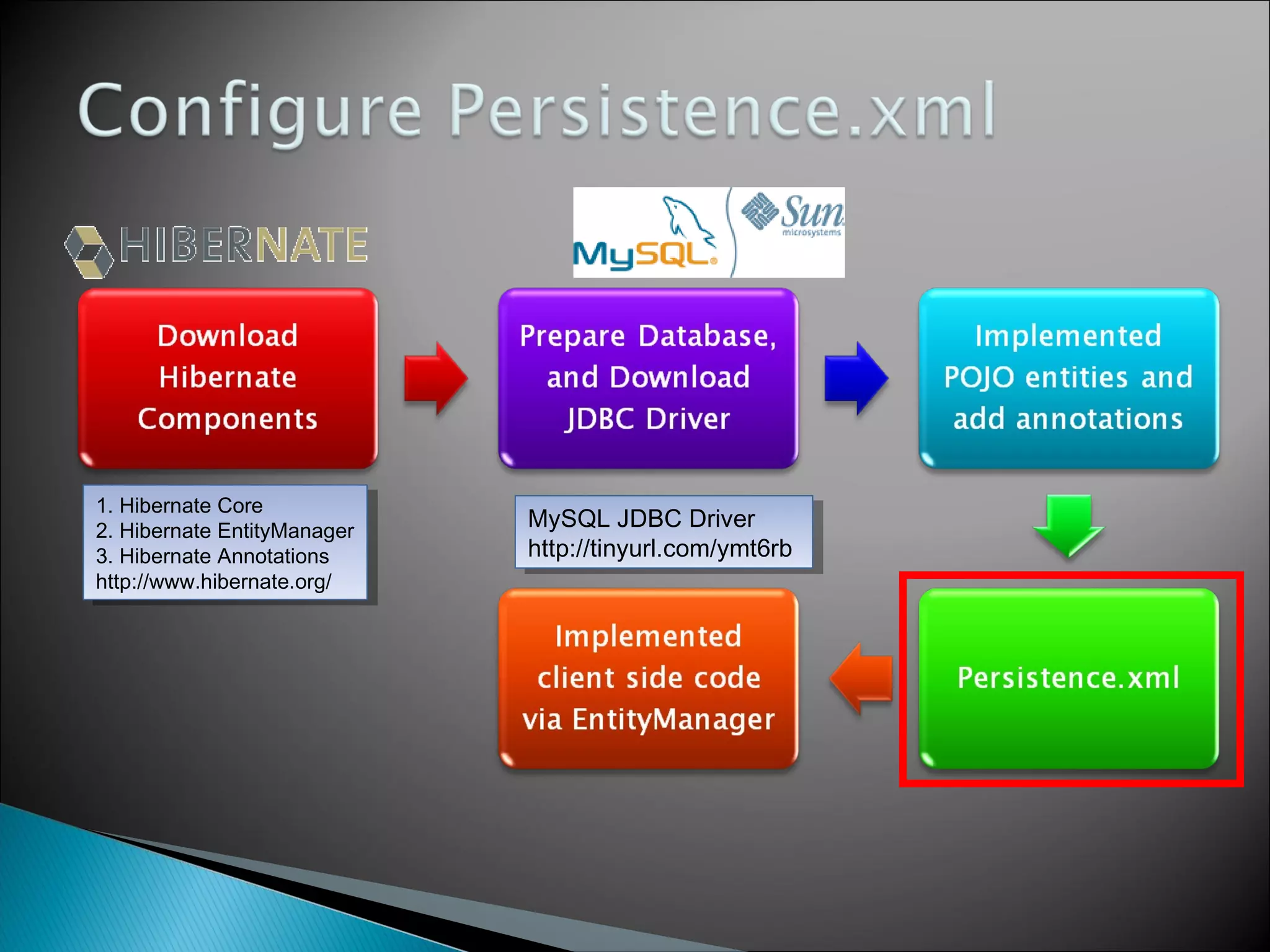
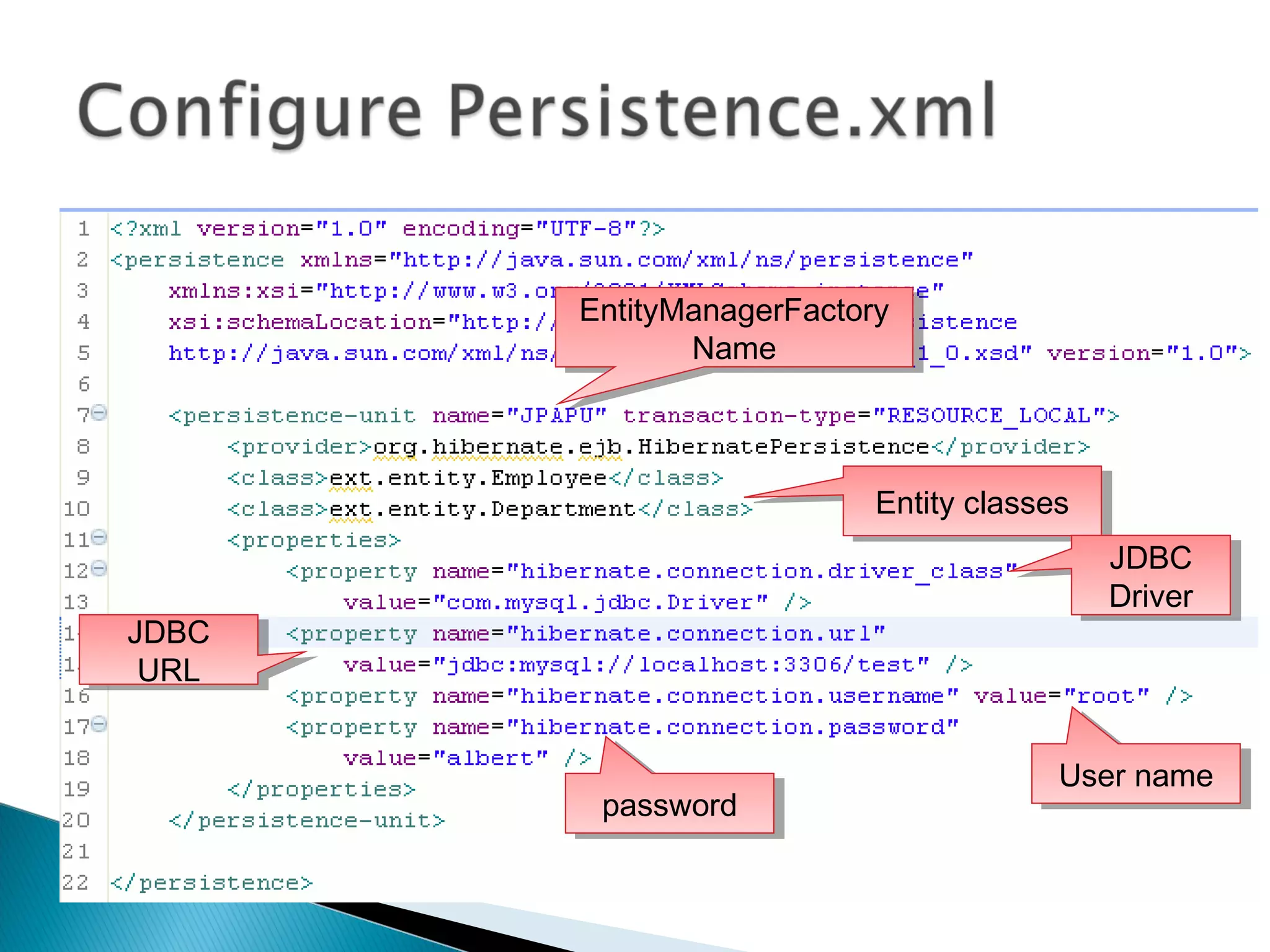
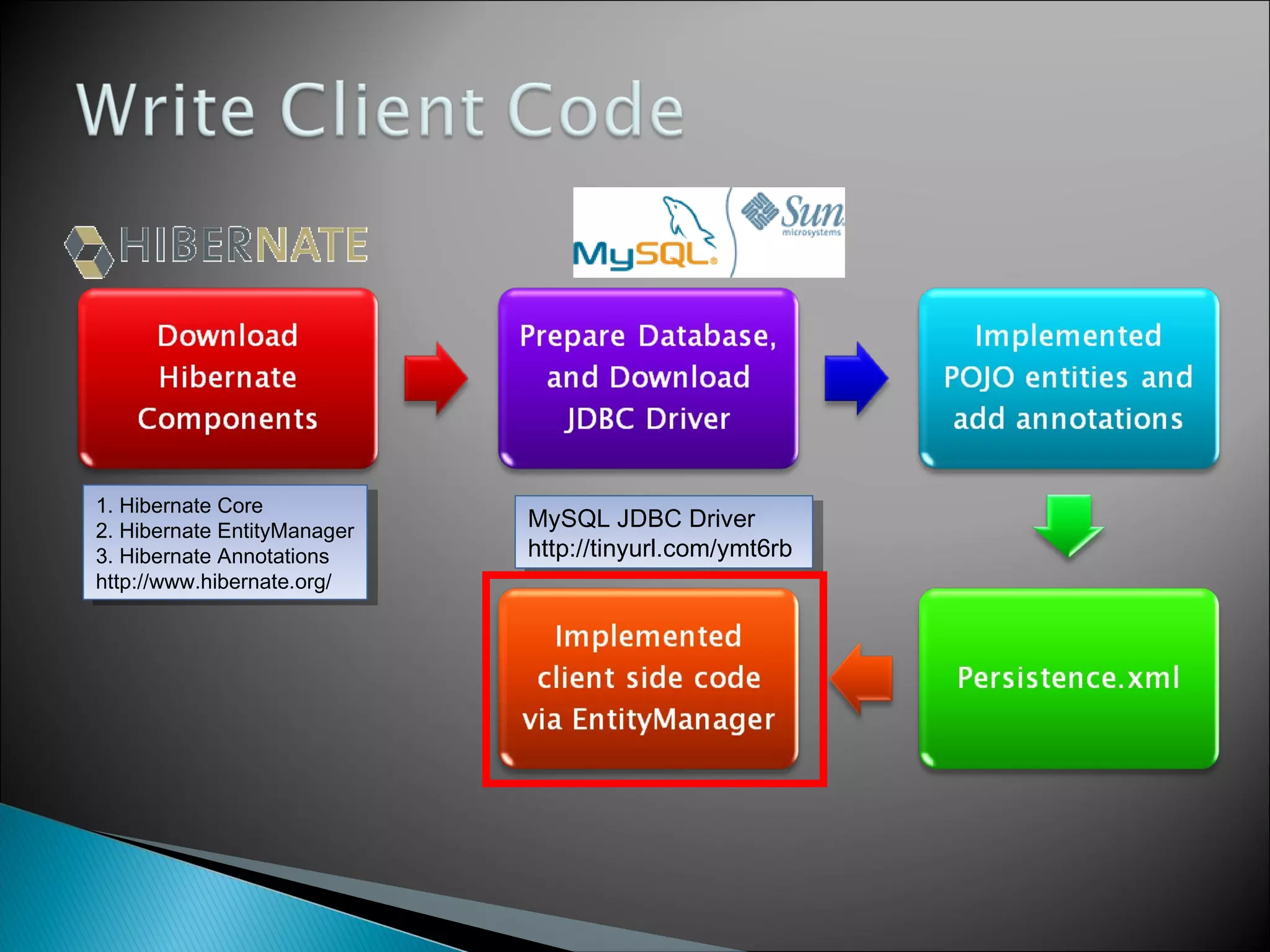
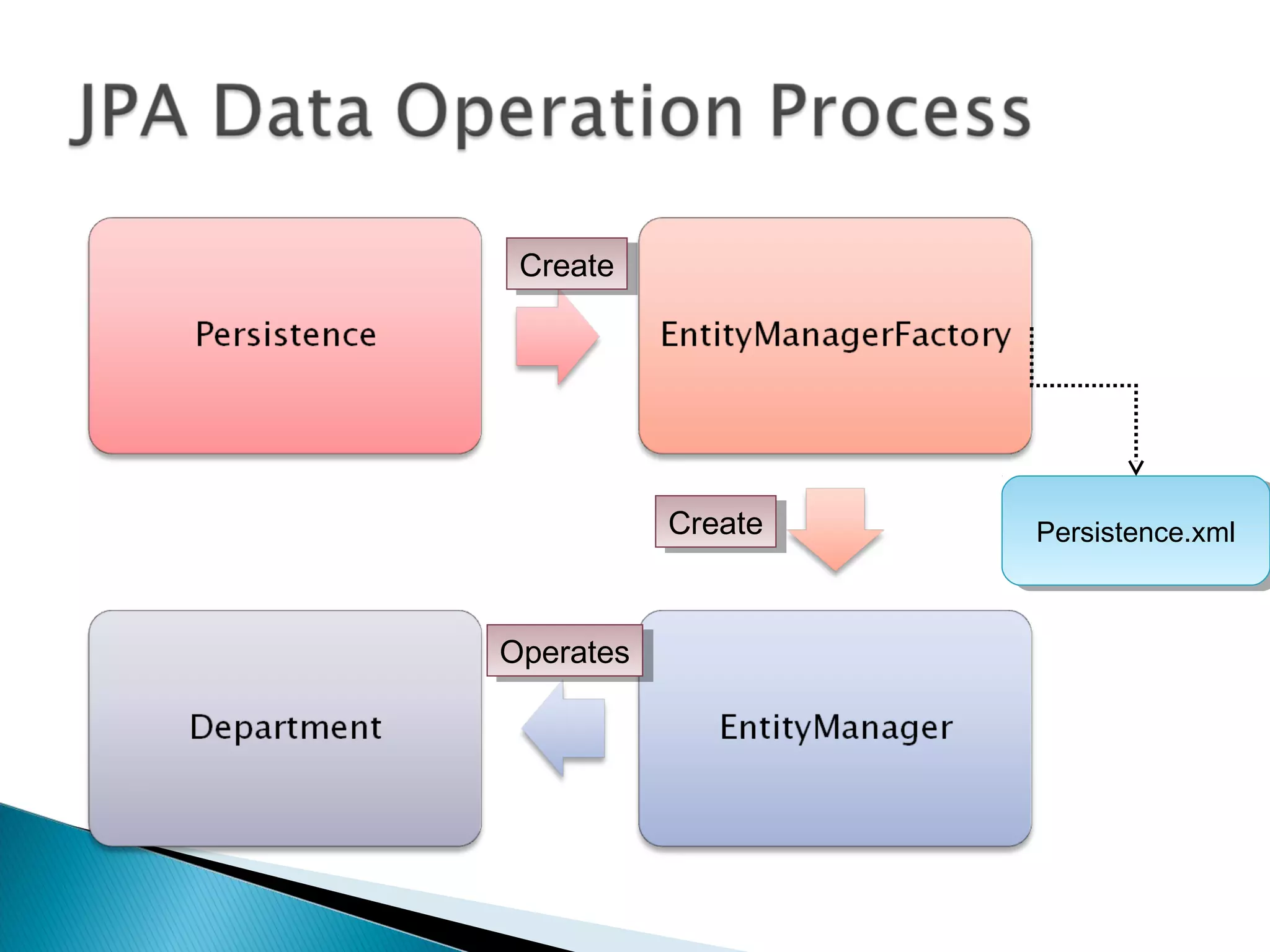
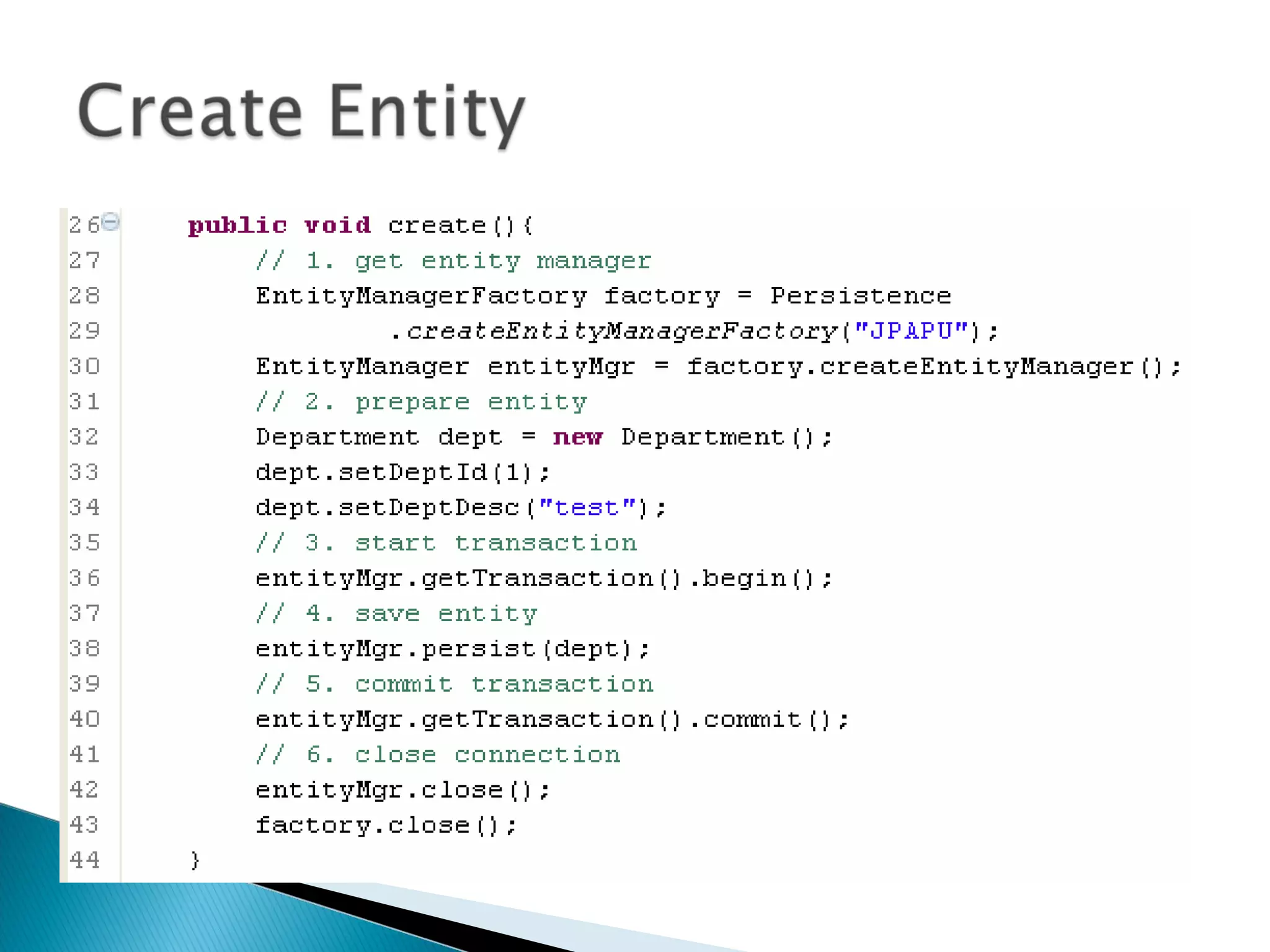
The document discusses Java Persistence API (JPA) and Hibernate. It describes JPA as the standard for object/relational mapping and persistence management. It outlines five steps to implement JPA using Hibernate: download components, prepare the database, implement POJO entities with annotations, configure persistence.xml, and write client code using EntityManager. Hibernate provides the core functionality and additional annotations and tools to implement JPA standards.