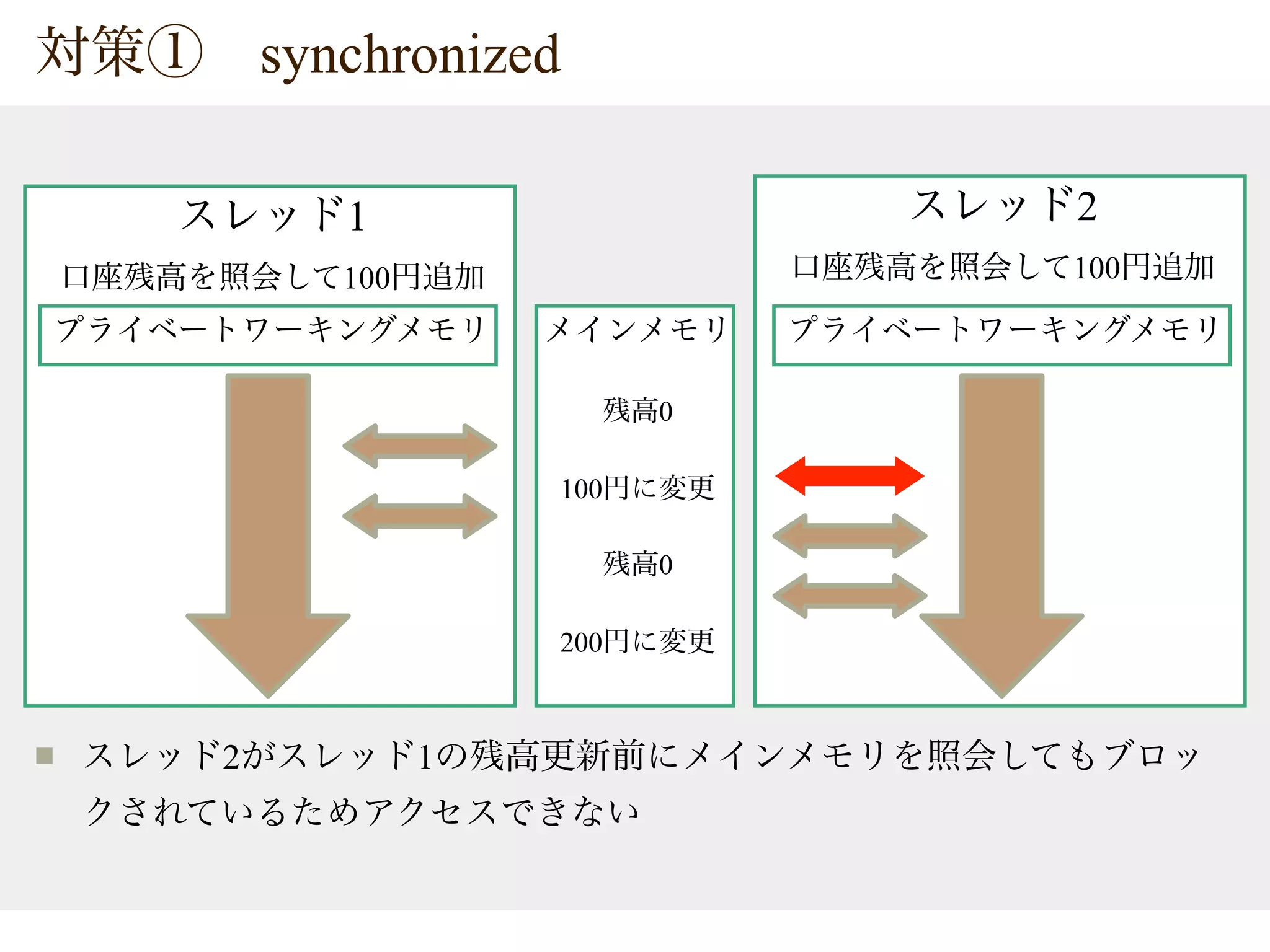
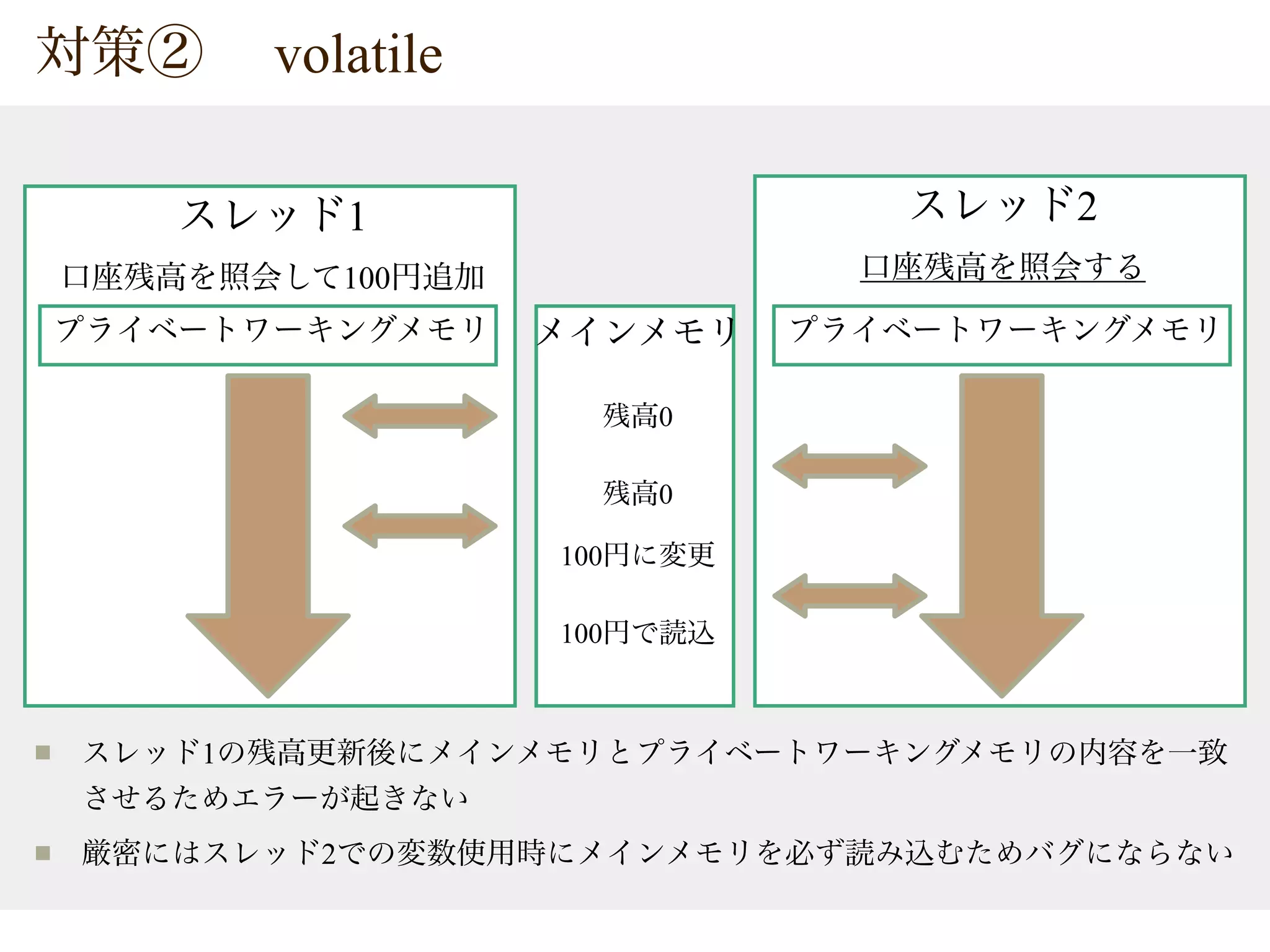
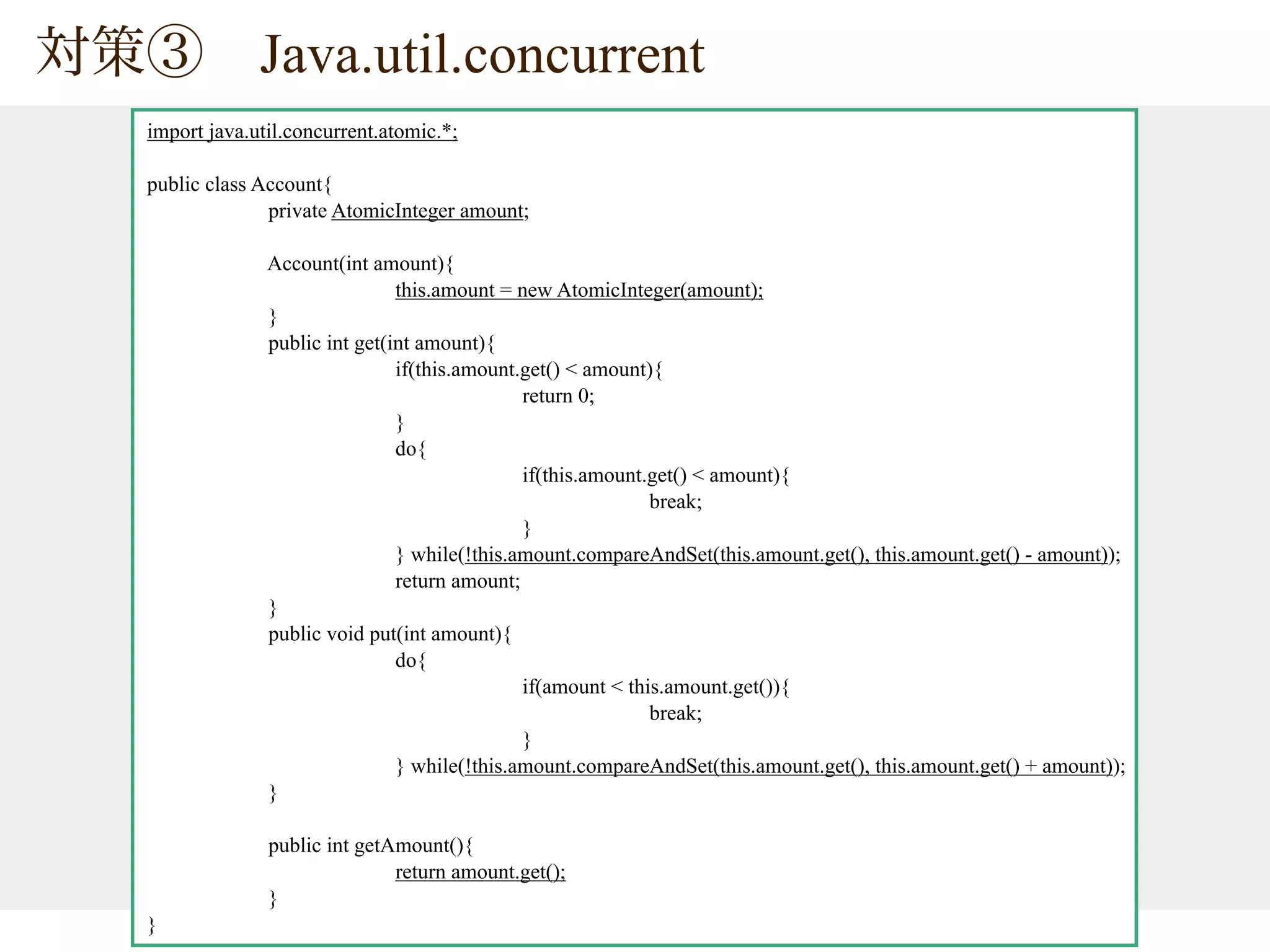
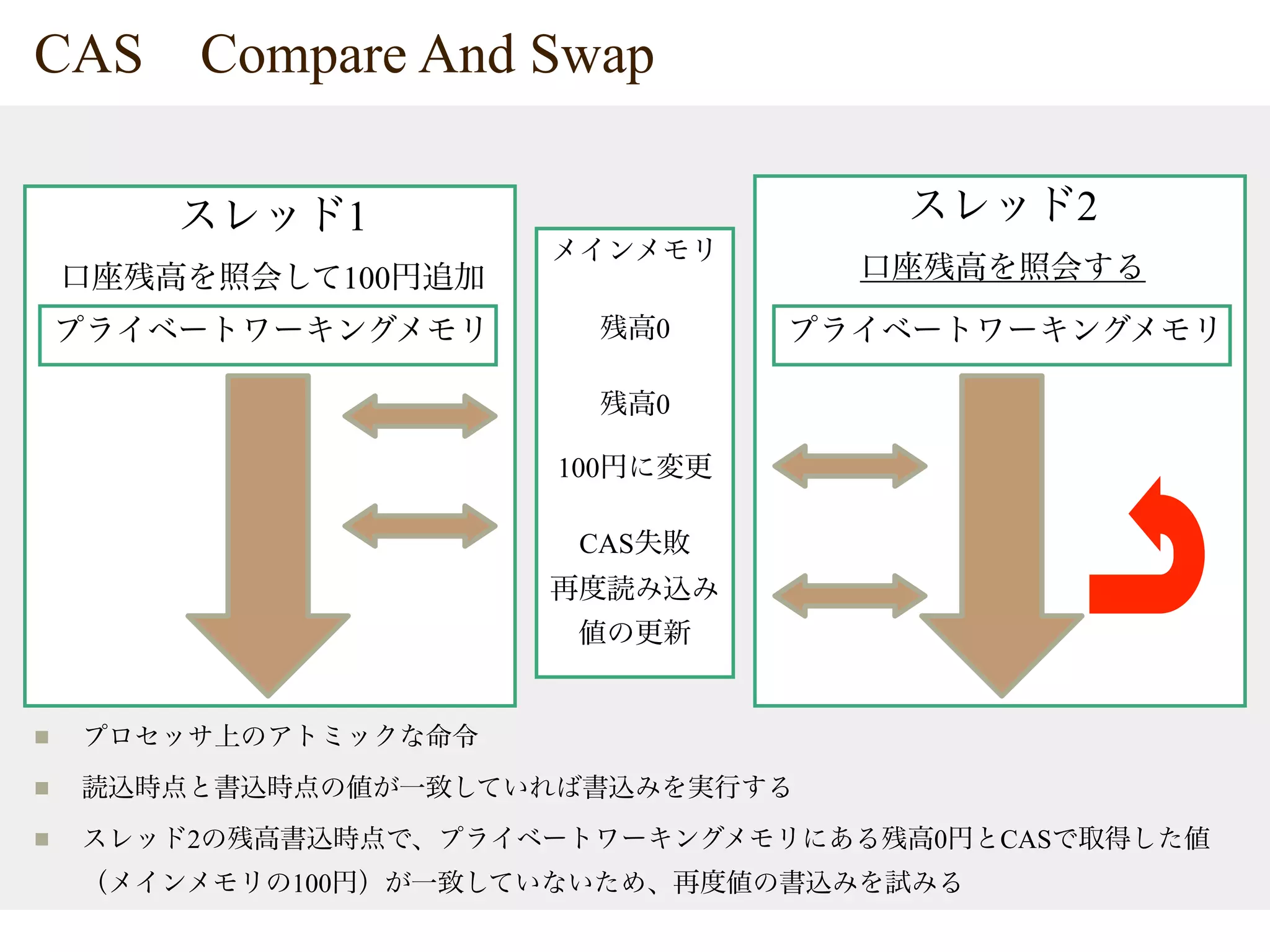
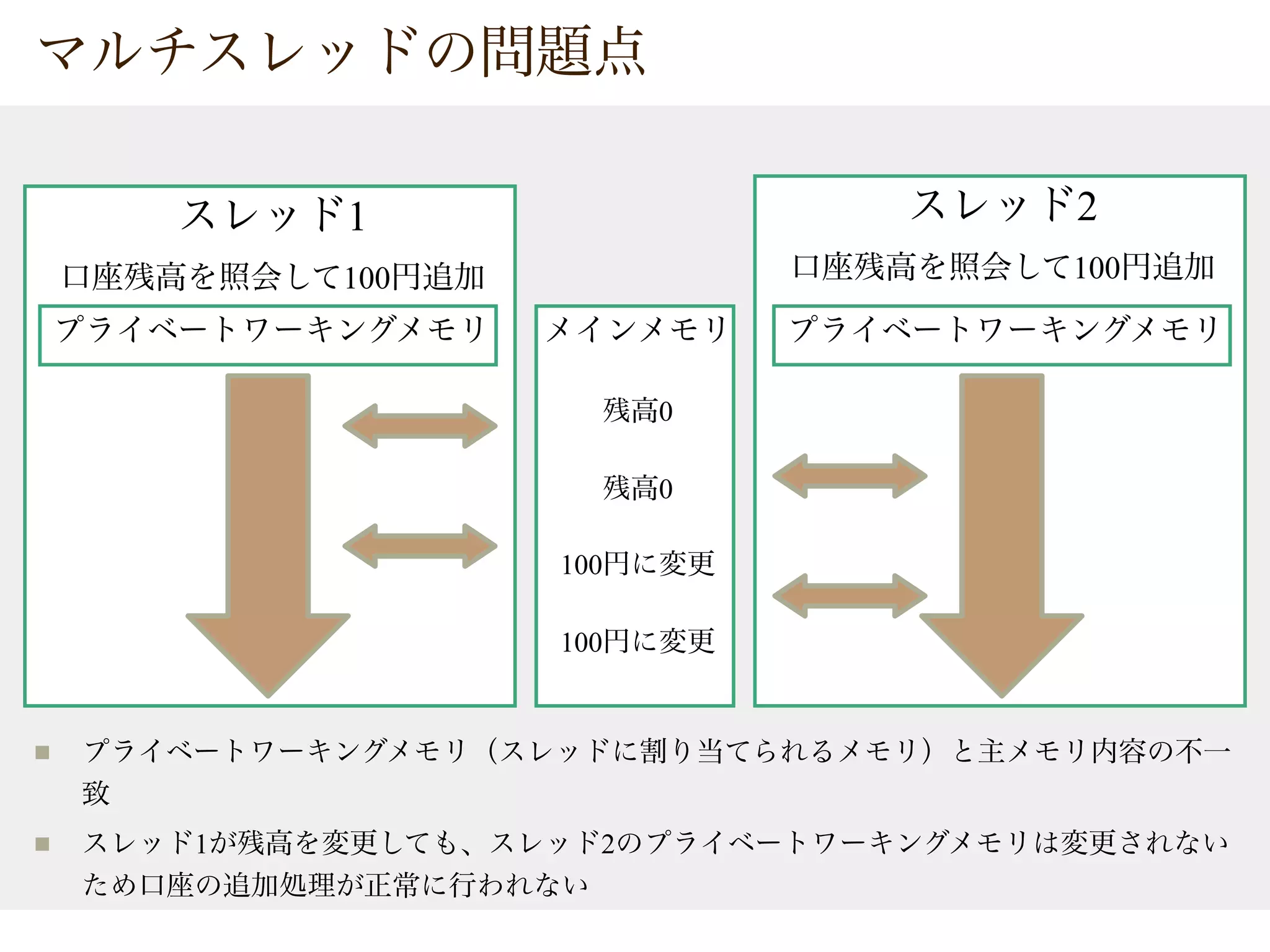
The document provides tips on Java concurrency. It discusses using synchronized, volatile and java.util.concurrent classes like AtomicInteger for thread-safe operations on shared resources like account balances. Synchronized uses locks for mutual exclusion but volatile only ensures visibility, so atomic classes use Compare-And-Swap (CAS) operations for thread-safe updates without blocking.



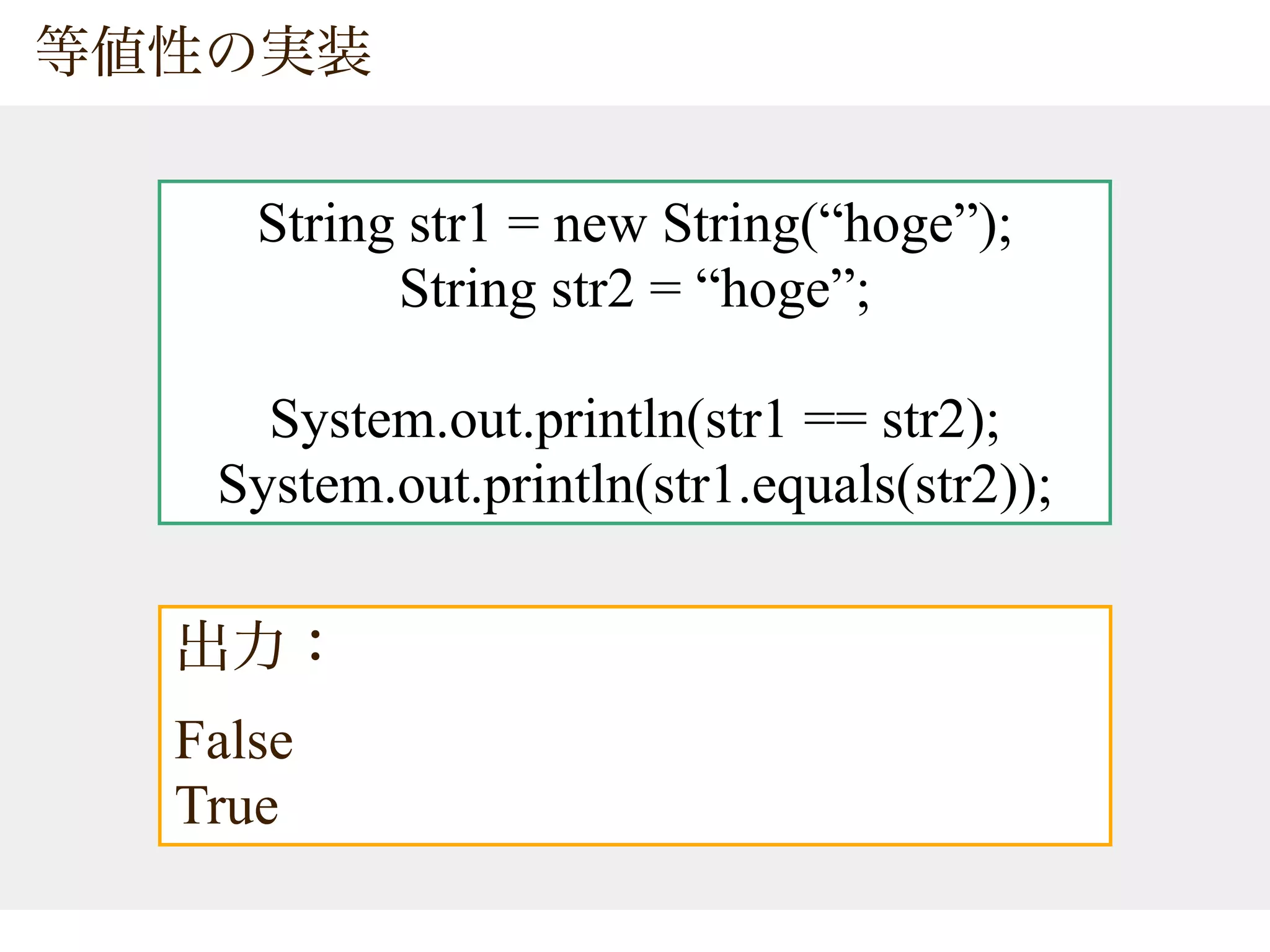
![== equals
char[] value
str1 str1 int length
boolean equals(Object obj)
char[] value
str2 str2 int length
boolean equals(Object obj)
str1 == str2 str1 str2
char[] value
str1.equals(str2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-5-2048.jpg)
![java.lang.String
public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence{
private final char value[];
private final int count;
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = count;
if (n == anotherString.count) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = offset;
int j = anotherString.offset;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i++] != v2[j++])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-6-2048.jpg)

![public abstract class Account{
private char[] custmorCode = new char[4];
Account(char[] custmorCode){
this.custmorCode = custmorCode;
}
public char[] getCustmorCode(){
return this.custmorCode;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object obj){
//
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-8-2048.jpg)
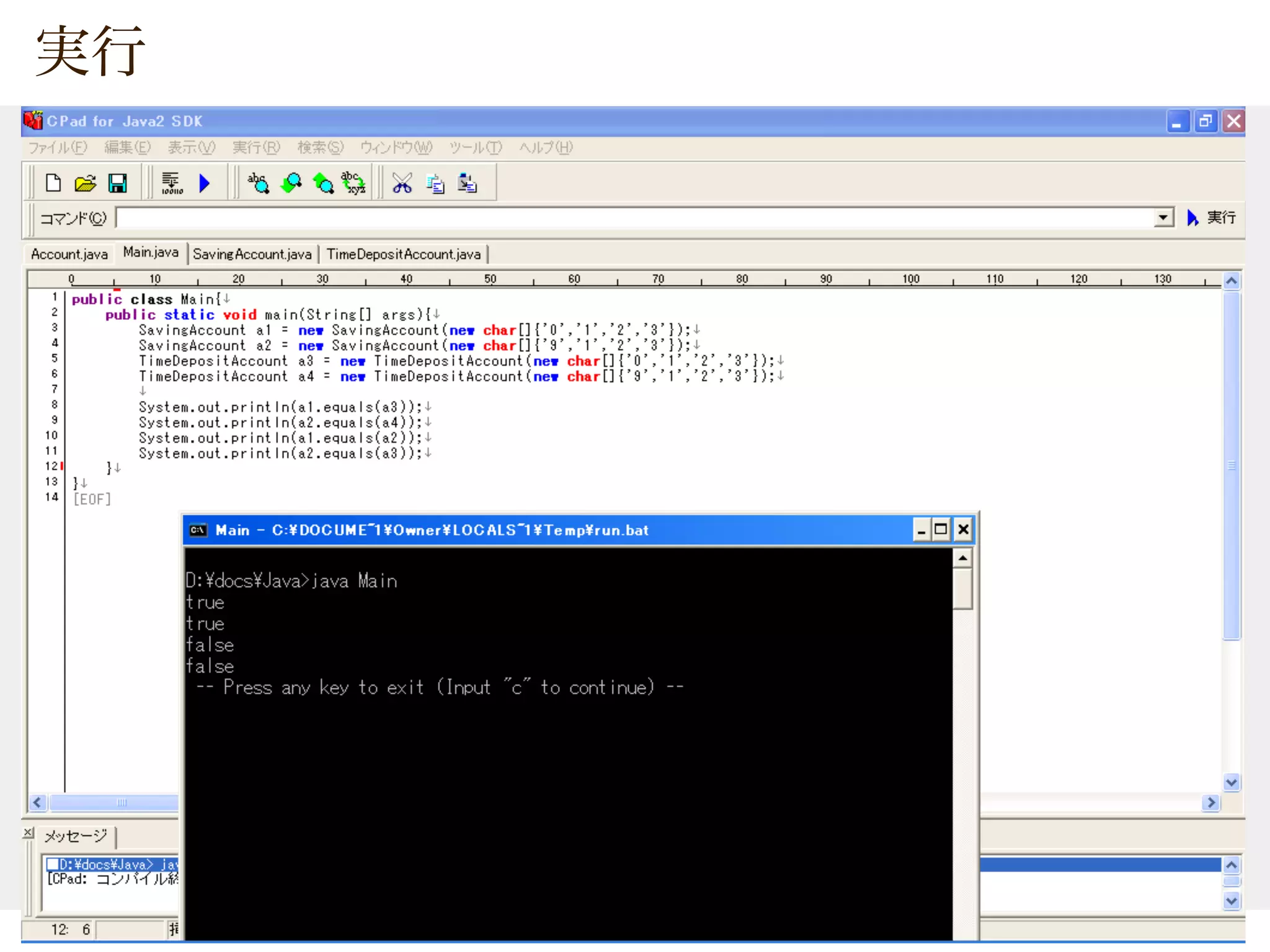
![SavingAccount a1 = new SavingAccount(new char[]{‘0’,’1’,’2’,’3’});
SavingAccount a2 = new SavingAccount(new char[]{‘9’,’1’,’2’,’3’});
TimeDepositAccount a3 = new TimeDepositAccount(new char[]{‘0’,’1’,’2’,’3’});
TimeDepositAccount a4 = new TimeDepositAccount(new char[]{‘9’,’1’,’2’,’3’});
System.out.println(a1.equals(a3));
System.out.println(a2.equals(a4));
System.out.println(a1.equals(a2));
System.out.println(a2.equals(a3));
True
True
False
False](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-9-2048.jpg)

![public abstract class Account{
//
@Override public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj instanceof Account){
//if(getClass() == obj.getClass()){
char[] compareCode = ((Account)obj).getCustmorCode();
if(custmorCode.length != compareCode.length){
return false;
}
for(int i = 0; i<custmorCode.length; i++){
if(custmorCode[i] != compareCode[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-11-2048.jpg)
![equals
java.lang.Object String
char[] value
equals Instanceof
getClass equals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-13-2048.jpg)




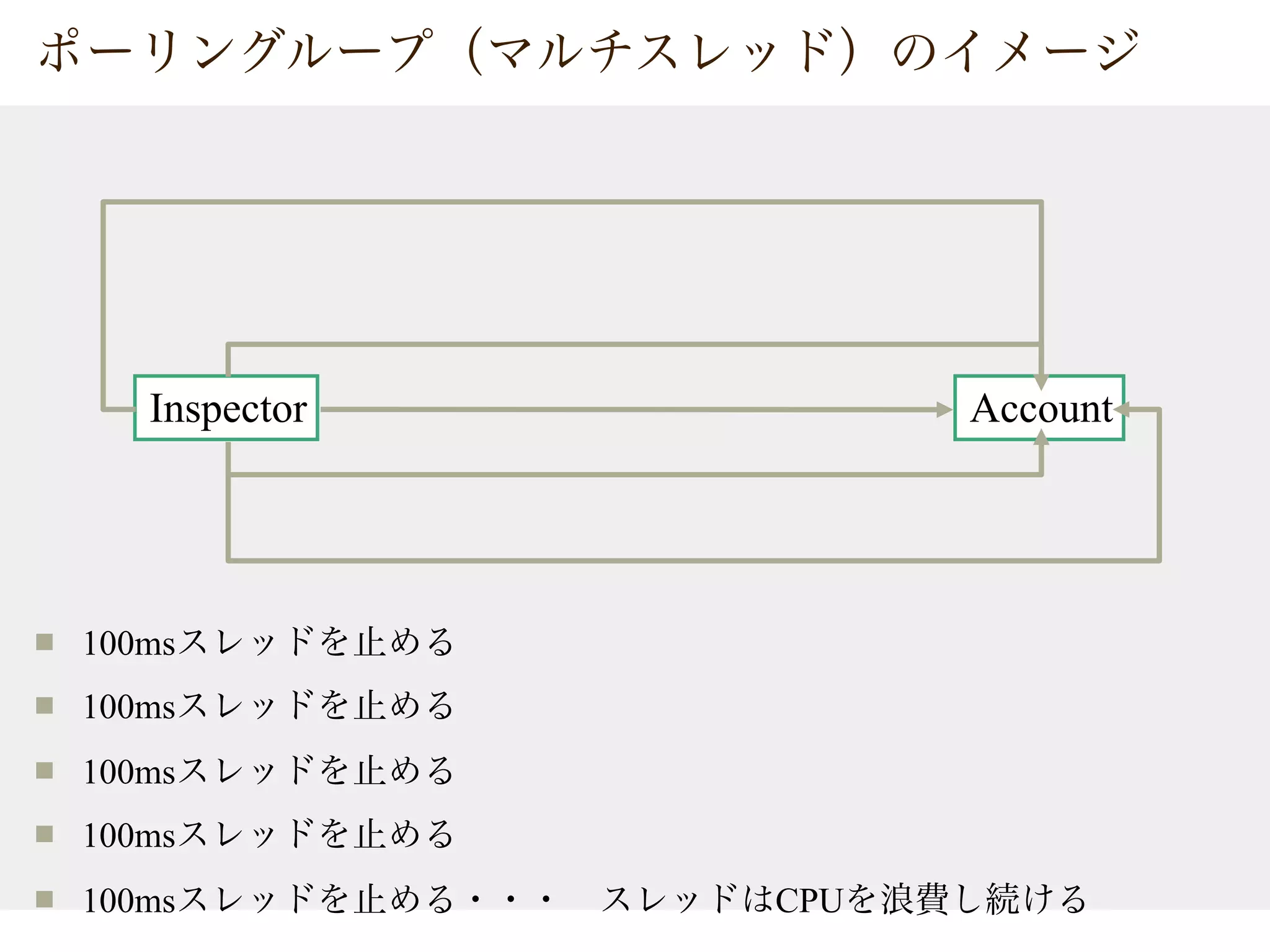

![public class Account{
private byte[] lock = new byte[0];
private ArrayList<Inspector> targets = new ArrayList<Inspector>();
public int get(int amount){
synchronized(lock){
if(this.amount < amount){
return 0;
}
for(Inspector i : targets){
i.inspect();
}
this.amount = this.amount - amount;
return amount;
}
}
public void addInspector(Inspector insp){
this.targets.add(insp);
}
addInspector
Inspector](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-20-2048.jpg)


![String
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
String className = "RefrectionTest";
RefrectionTest rt = null;
try{
rt = (RefrectionTest)Class
.forName(className).newInstance();
} catch(Exception e) {
}
rt.dosth();
}
}
public class RefrectionTest{
public void dosth(){
System.out.println("Do Something");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-23-2048.jpg)
![String
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
String className = "RefrectionTest";
RefrectionTest rt = null;
try{
rt = (RefrectionTest)Class.forName(className).newInstance();
} catch(Exception e) {
}
String methodName = "dosth";
Method method = null;
try{
method = (Method)Class.forName(className)
.getMethod(methodName,null);
} catch(Exception e) {
}
method.invoke(Class.forName(className).newInstance(),null);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-24-2048.jpg)

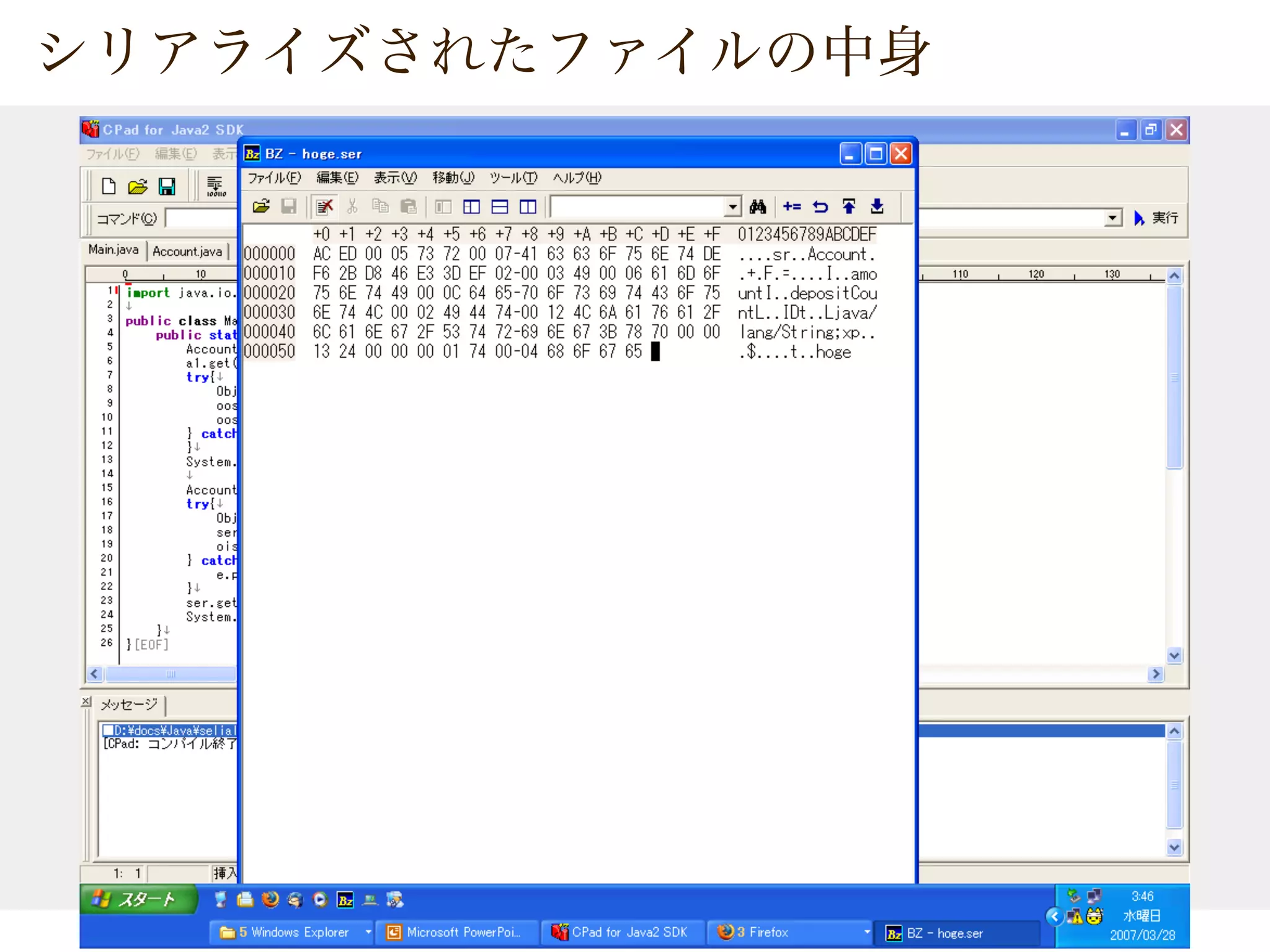
![import java.io.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Account a1 = new Account("hoge",5000);
a1.get(100);
try{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("hoge.ser"));
oos.writeObject(a1);
oos.close();
} catch(Exception e) {}
System.out.println(a1);
Account ser = null;
try{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("hoge.ser"));
ser = (Account)ois.readObject();
ois.close();
} catch(Exception e) {}
ser.get(100);
System.out.println(ser);
}
}
public class Account implements Serializable{ // }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-26-2048.jpg)

![synchronized
public class Account{
private int amount;
private byte[] lock = new byte[0];
Account(int amount){
this.amount = amount;
}
public int get(int amount){
synchronized(lock){
this.amount = this.amount - amount;
return amount;
}
}
public void put(int amount){
synchronized(lock){
this.amount = this.amount + amount;
}
}
}
Synchonized:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20070329-javatips-100718081714-phpapp02/75/20070329-Java-Programing-Tips-30-2048.jpg)