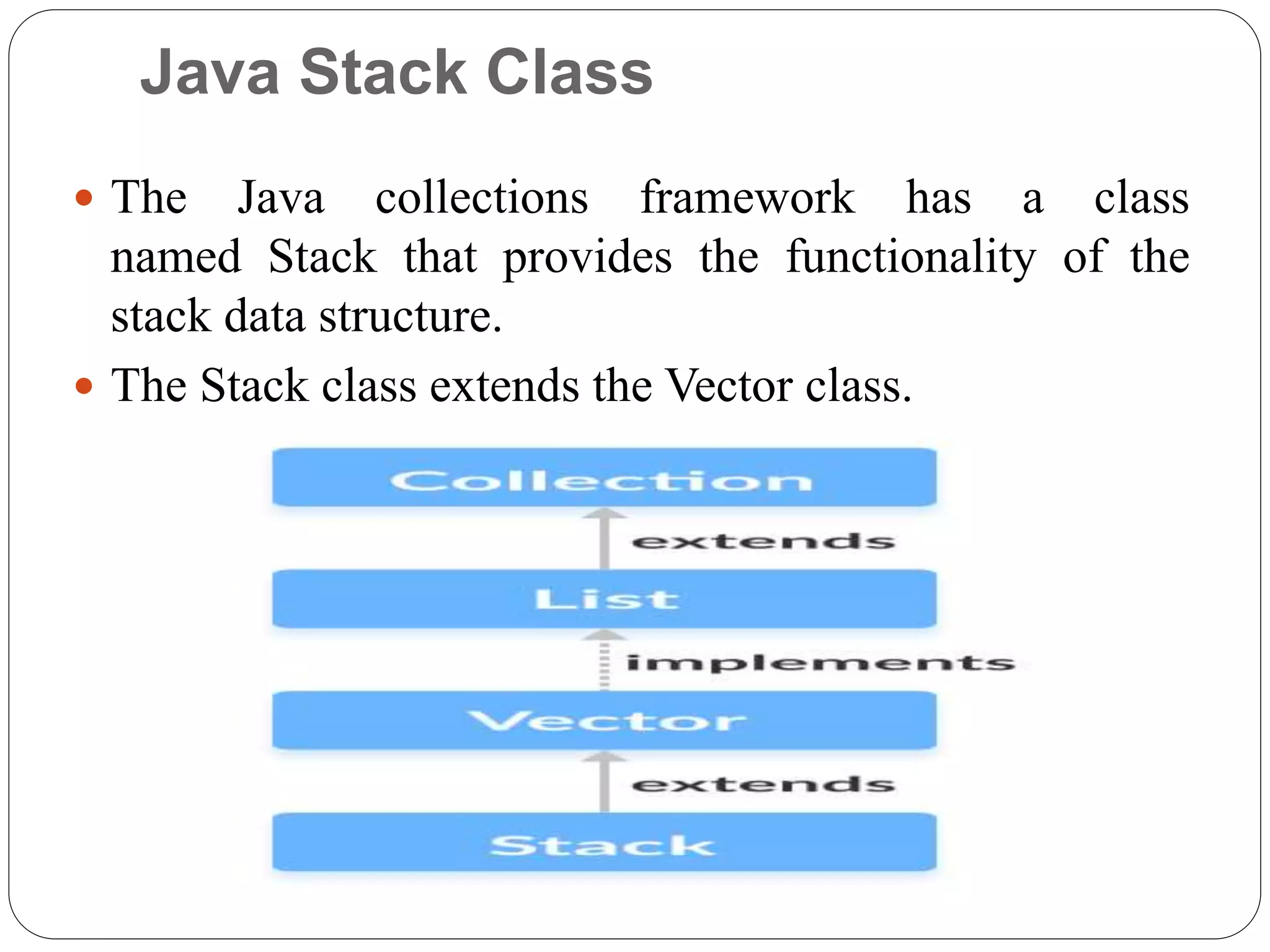
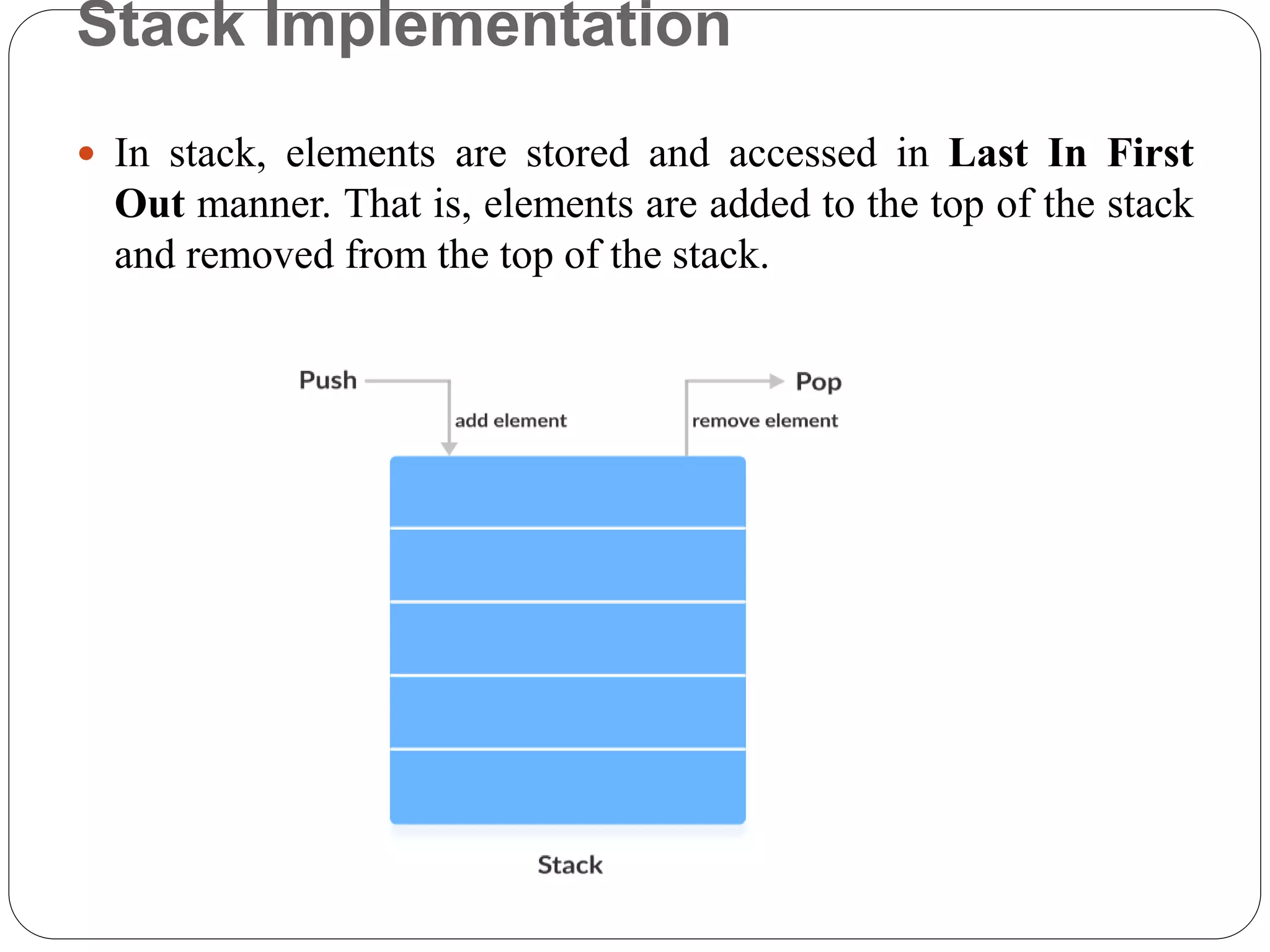
The Java Stack class implements a last-in, first-out (LIFO) data structure called a stack. It extends the Vector class and inherits its methods. Elements are added to the top of the stack using push() and removed from the top with pop(). The search() method returns the position of an element from the top, and empty() checks if the stack is empty. Common uses of stacks in Java include implementing undo/redo features and evaluating mathematical expressions.


![push() Method
To add an element to the top of the stack, we use
the push() method. For example
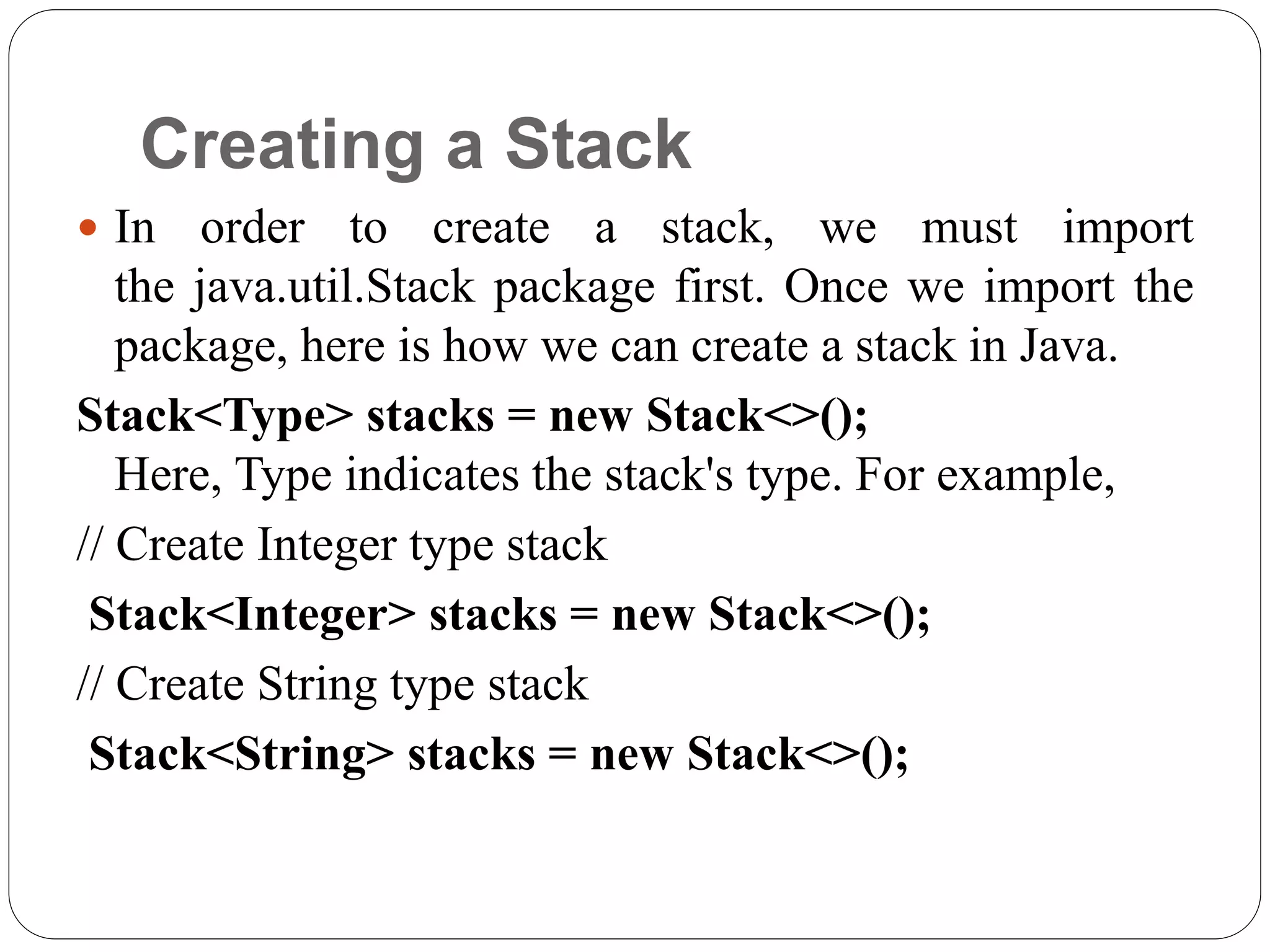
import java.util.Stack;
class Main { public static void main(String[] args)
{ Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastackdatastructure-220419064727/75/Java-Stack-Data-Structure-pptx-6-2048.jpg)
![pop() Method
import java.util.Stack;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + animals);
// Remove element stacks
String element = animals.pop();
System.out.println("Removed Element: " + element); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastackdatastructure-220419064727/75/Java-Stack-Data-Structure-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
![search() Method
to search an element in the stack, we use the search() method. It returns the position of the
element from the top of the stack. For example,
import java.util.Stack;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Search an elemen
t int position = animals.search("Horse");
System.out.println("Position of Horse: " + position); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastackdatastructure-220419064727/75/Java-Stack-Data-Structure-pptx-8-2048.jpg)
![empty() Method
To check whether a stack is empty or not, we use the empty() method.
For example,
import java.util.Stack;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Check if stack is empty
boolean result = animals.empty();
System.out.println("Is the stack empty? " + result); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javastackdatastructure-220419064727/75/Java-Stack-Data-Structure-pptx-9-2048.jpg)