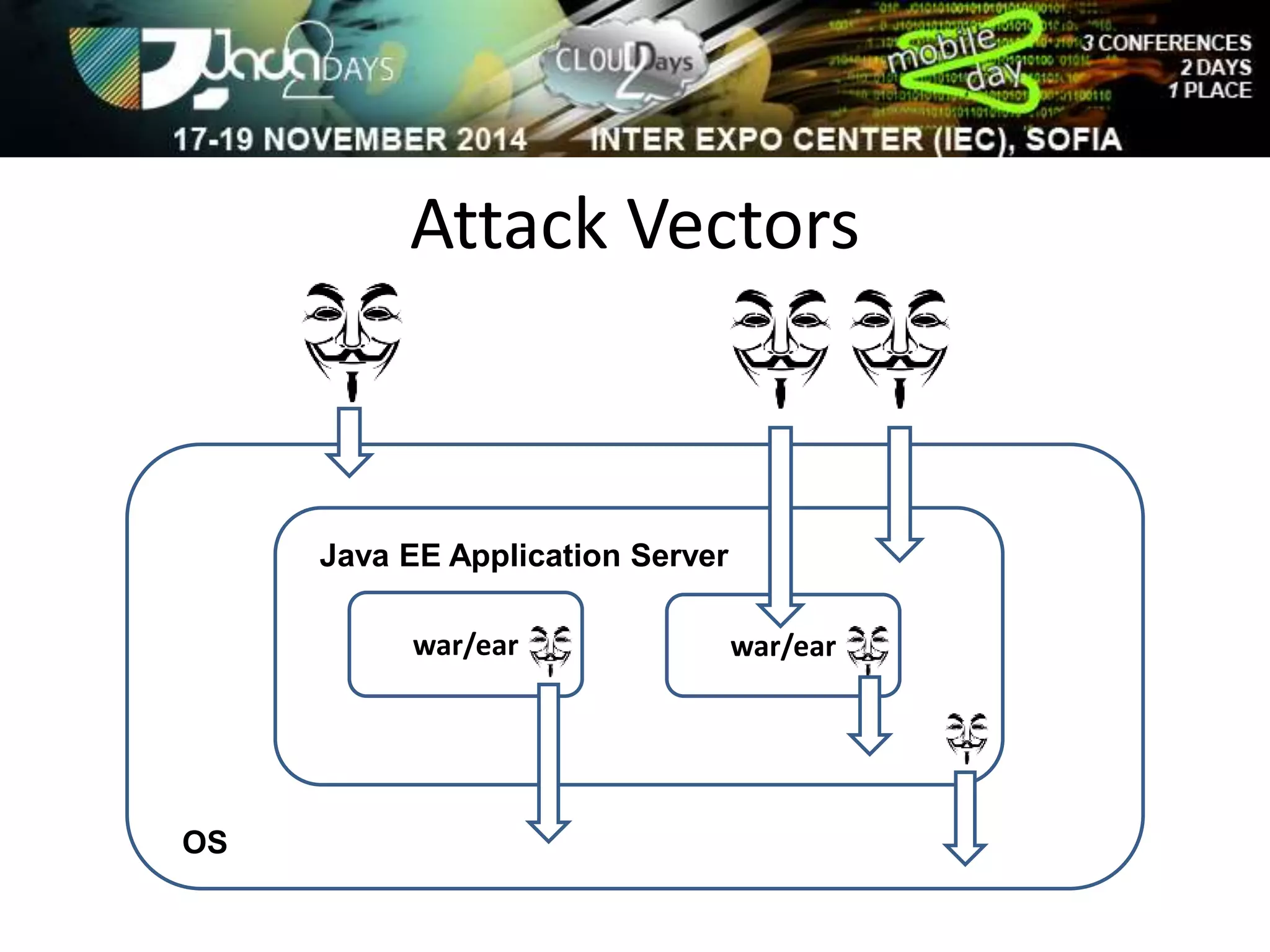
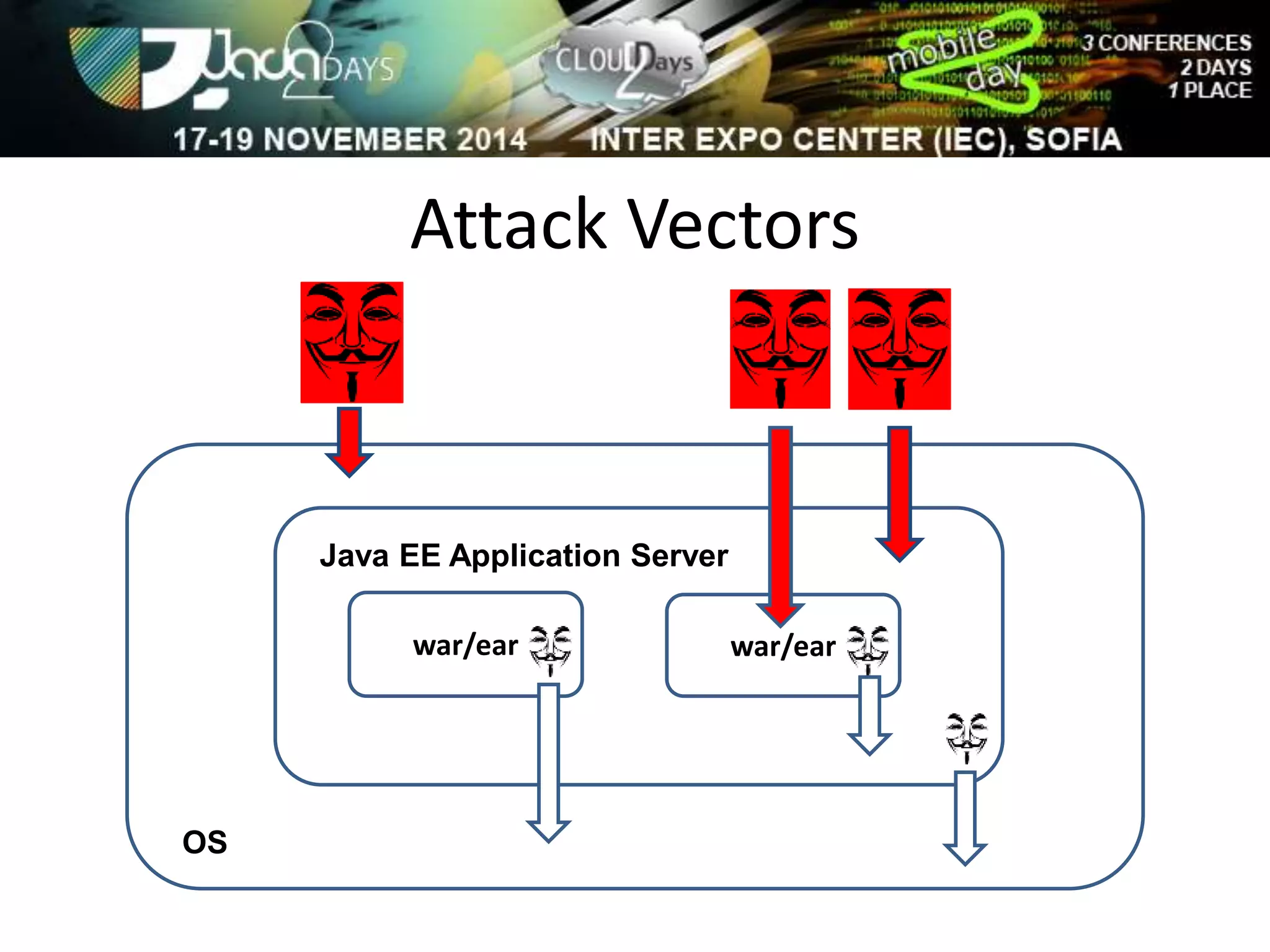
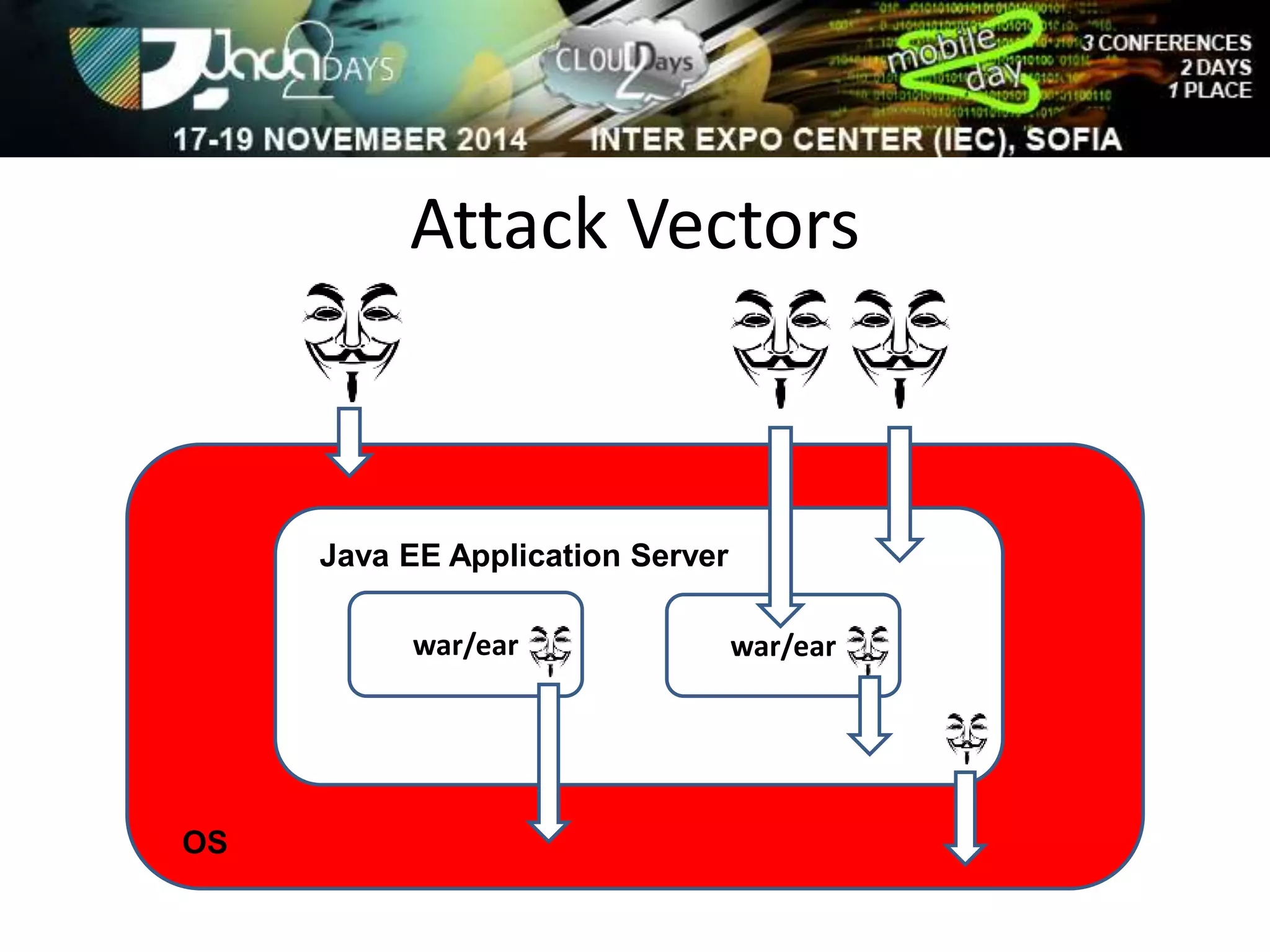
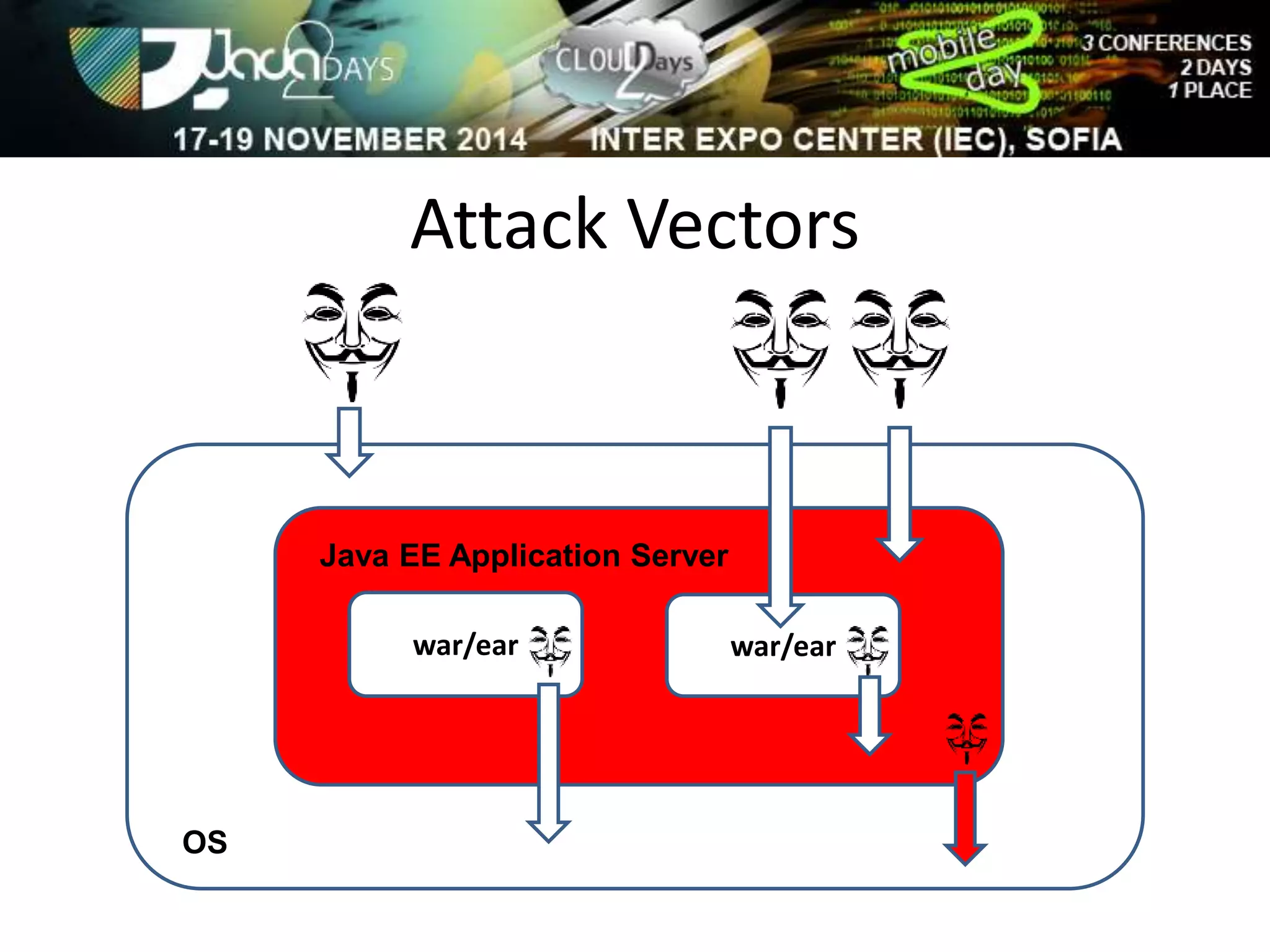
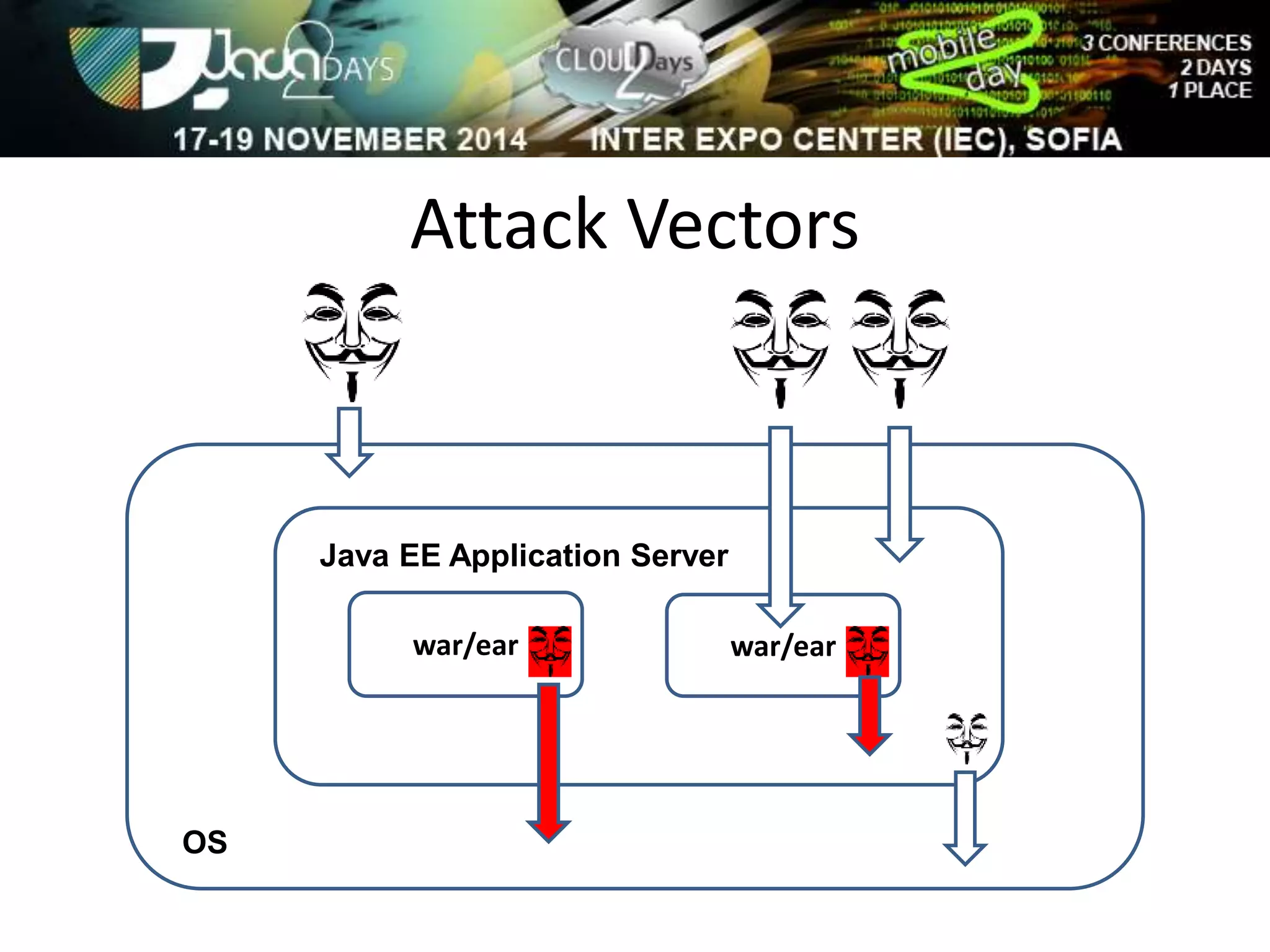
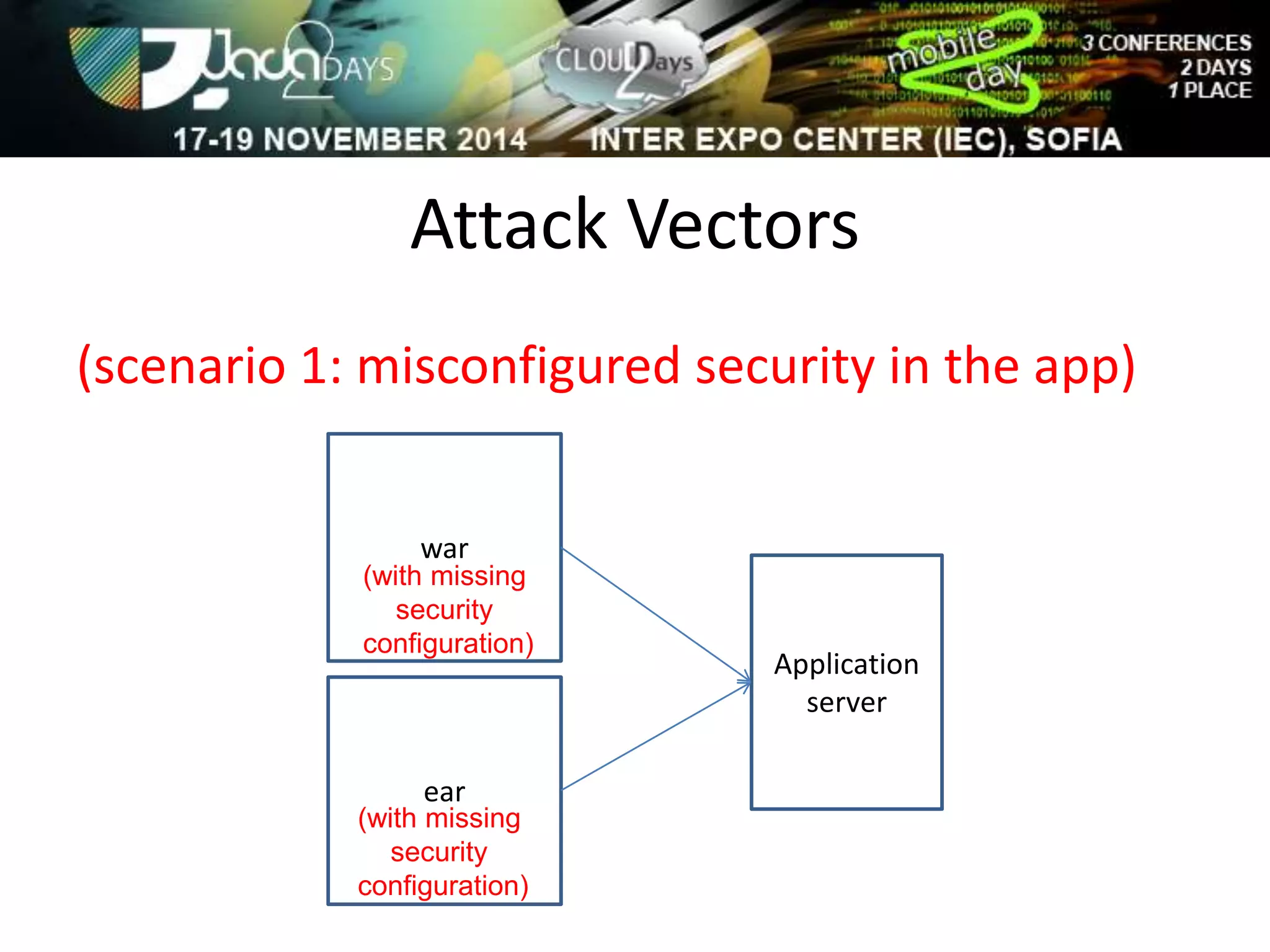
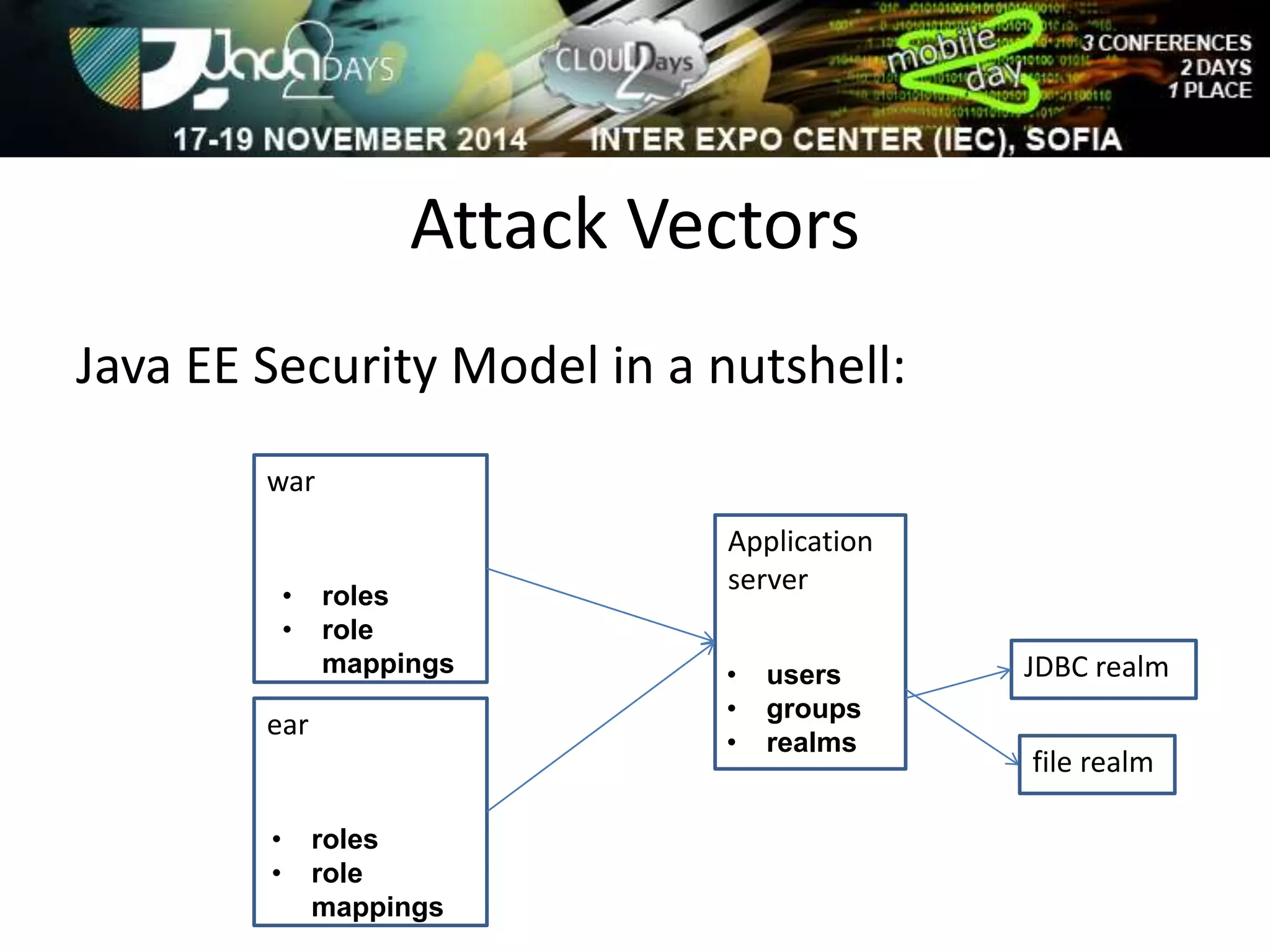
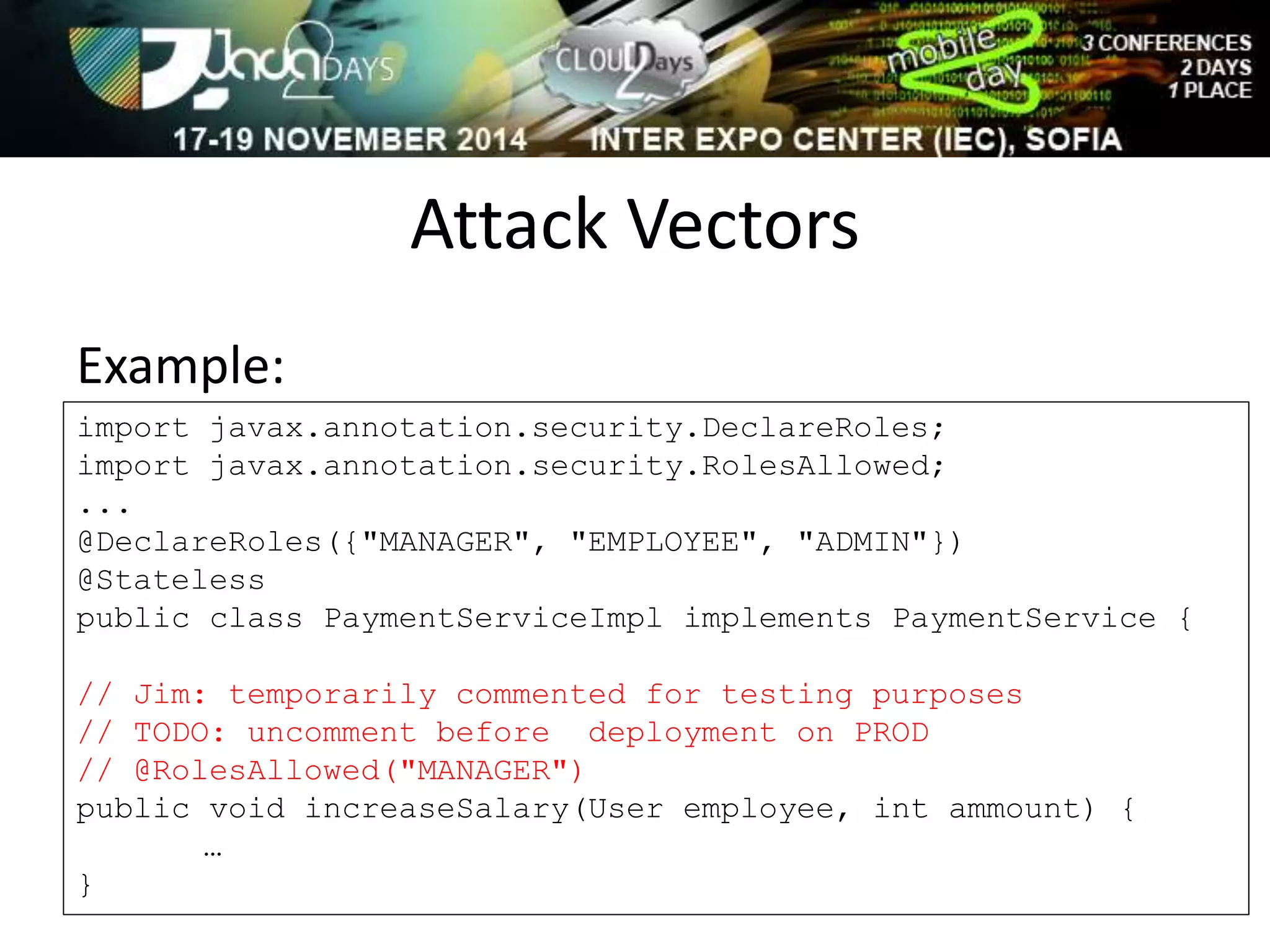
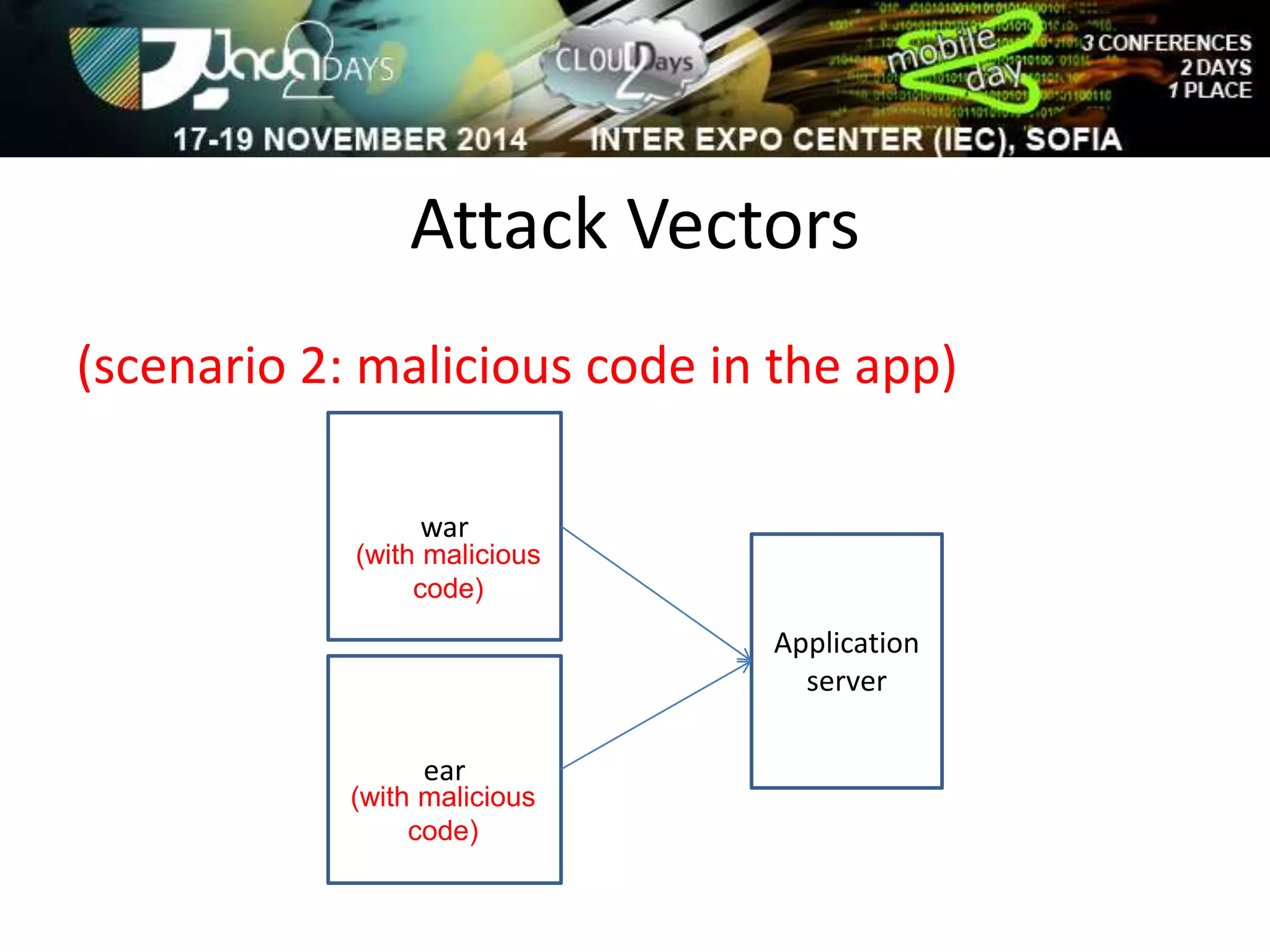
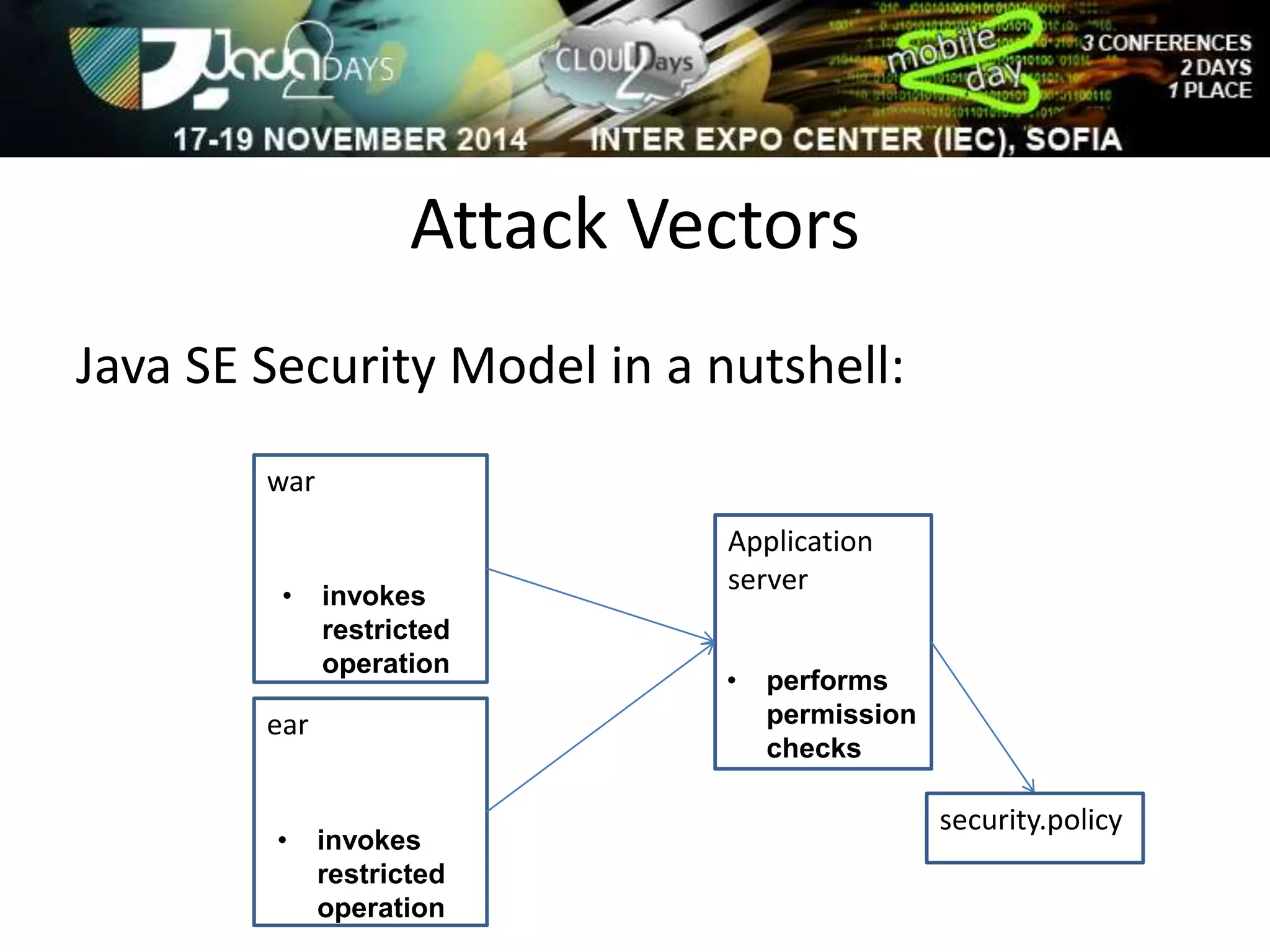
The document discusses attacking Java EE application servers by exploring various attack vectors and strategies. It outlines how attacks could originate externally, from within the application server itself, or from deployed applications. It then discusses tools that can be used to exploit vulnerabilities and recommends secure coding practices like applying patches, implementing proper security configurations, and performing testing to harden applications and servers against attacks.