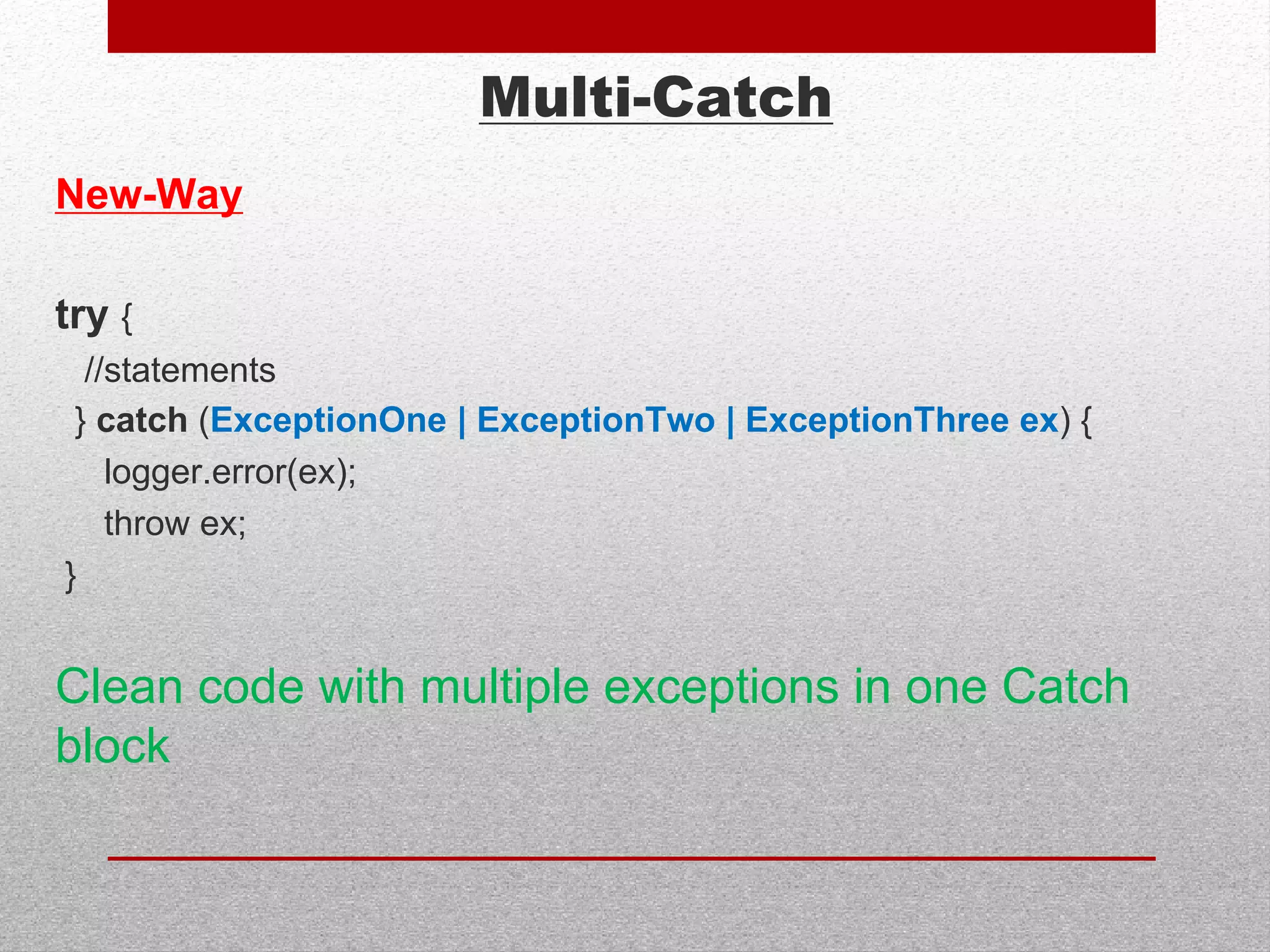
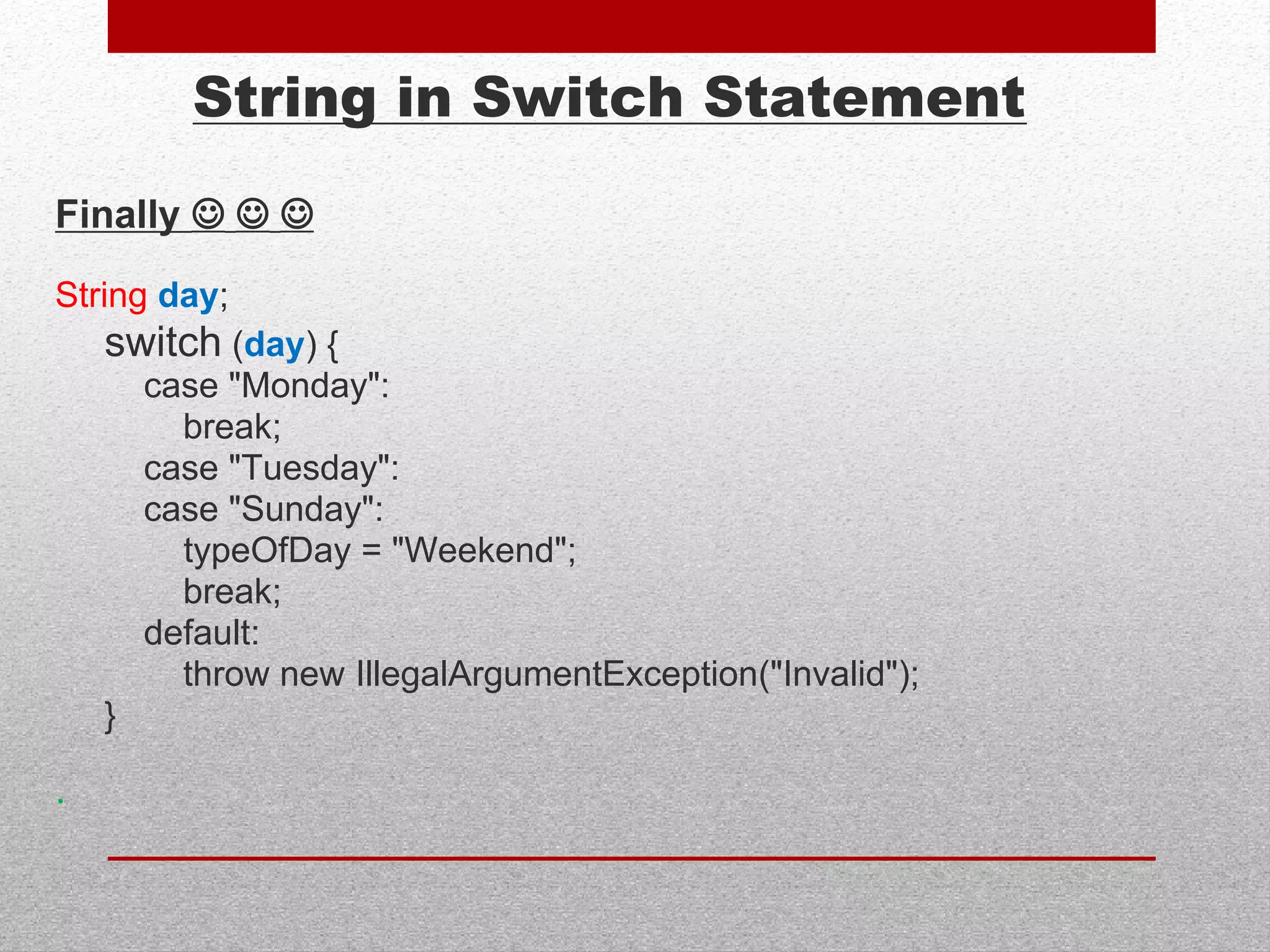
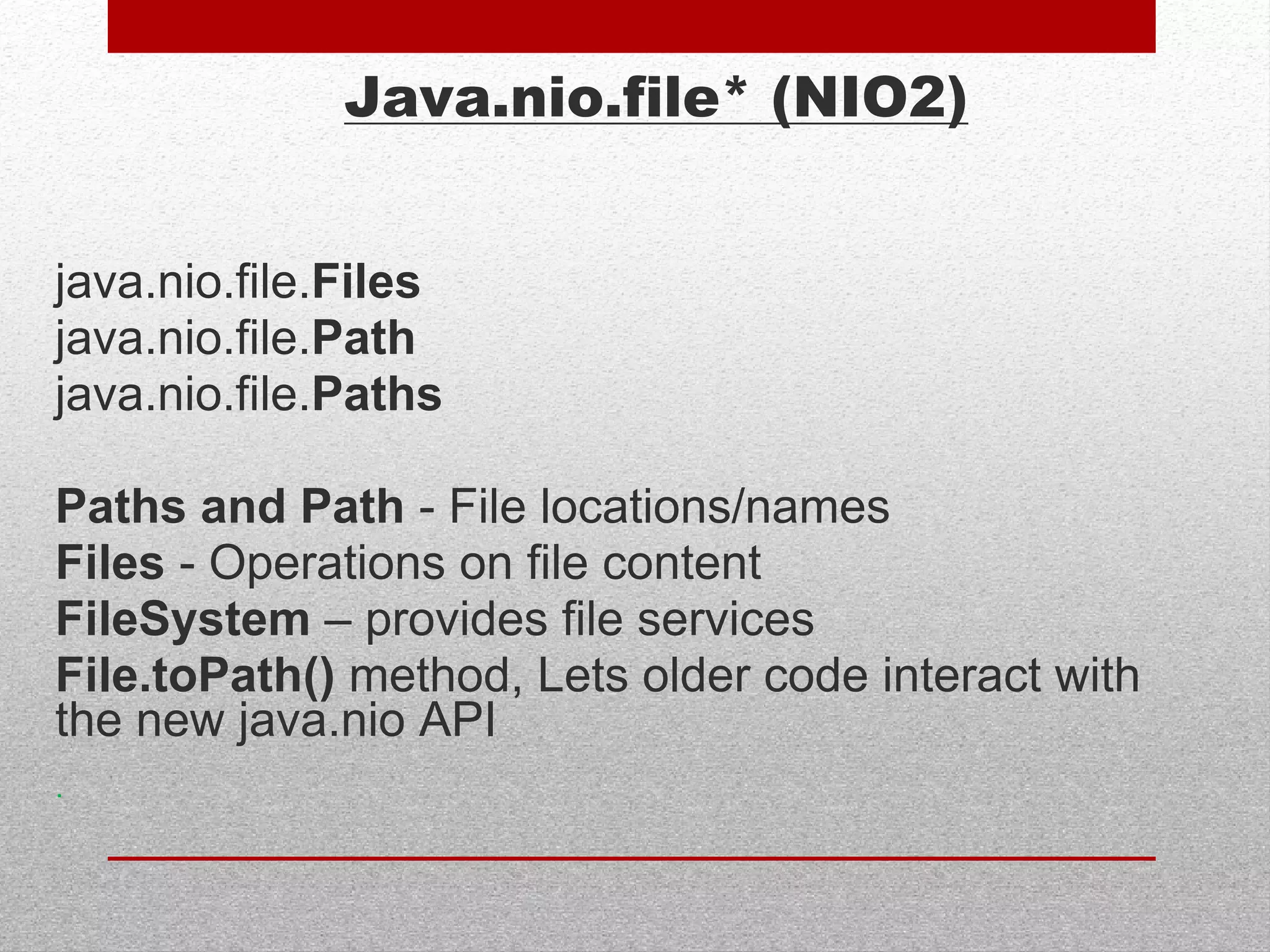
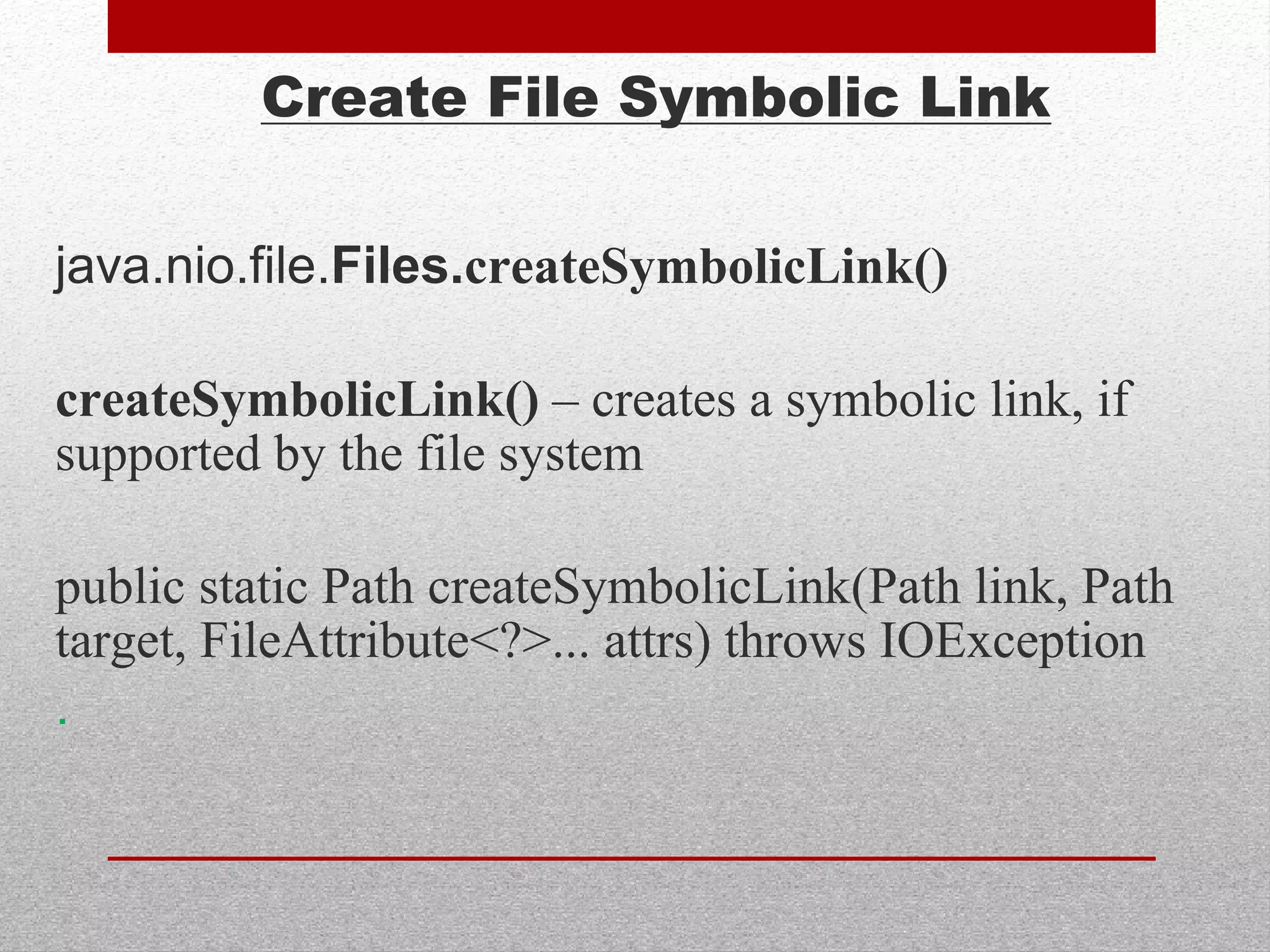
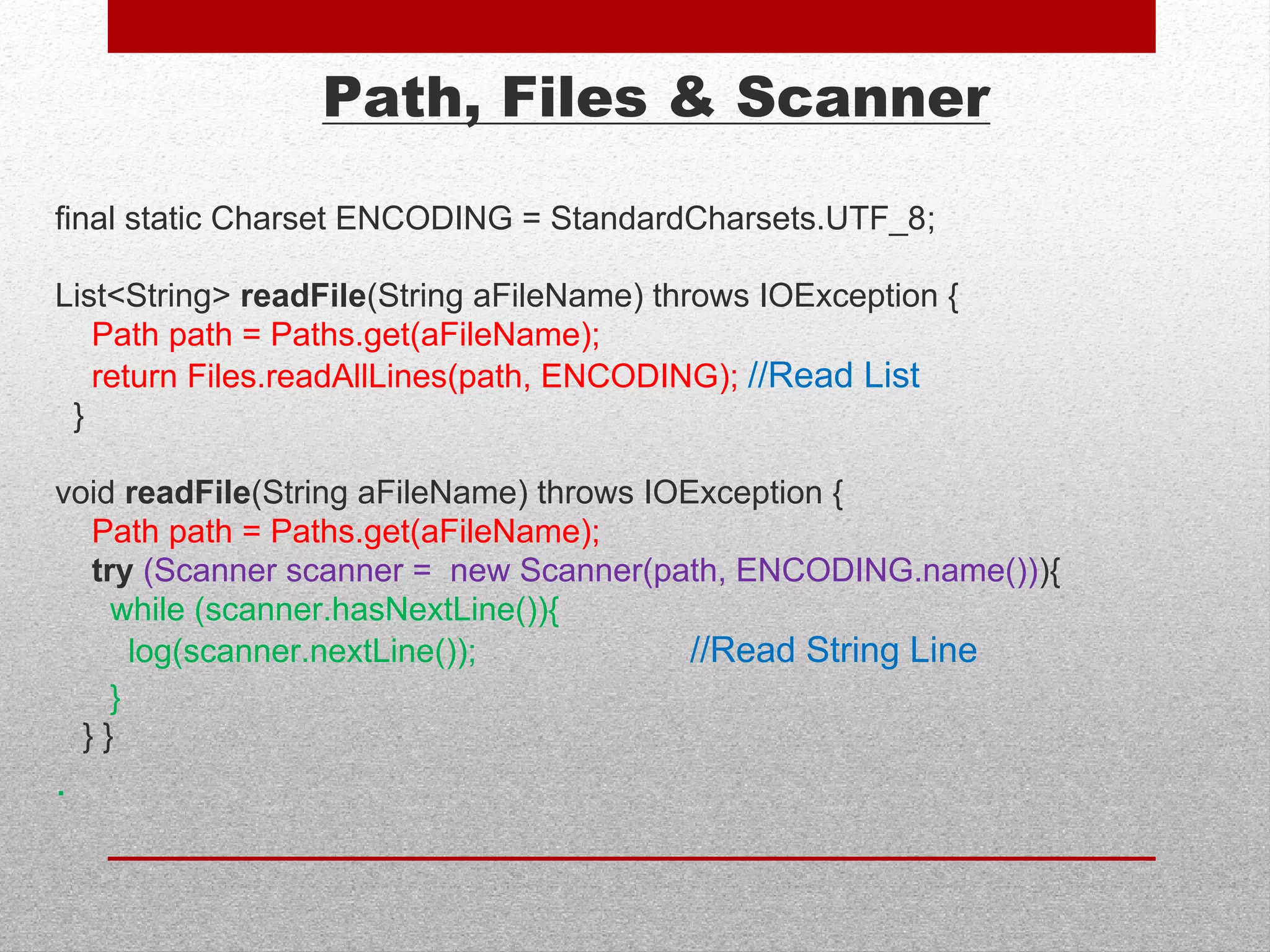
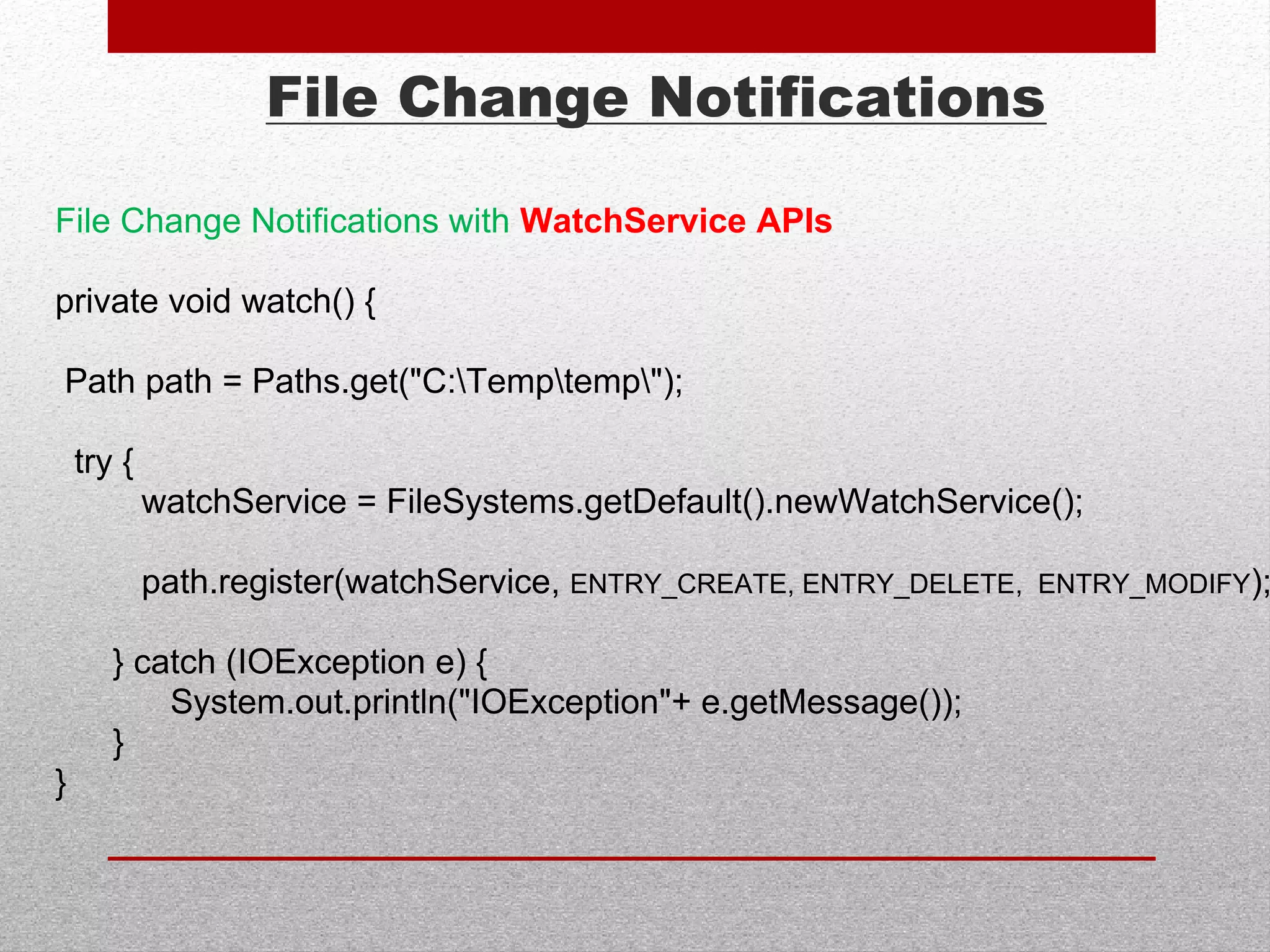
This document summarizes new features in Java 7, including underscores in numeric literals to improve readability, try-with-resource for automatic resource management, multi-catch exceptions, and various improvements to I/O, generics, and garbage collection. Key areas covered are numeric literals, collection initialization, try-with-resource blocks, multi-catch exceptions, final rethrow, strings in switch statements, generic instances, NIO2 file APIs, file change notifications, asynchronous I/O, URLClassLoader closing, JDBC row sets, varargs, the G1 garbage collector, and improved performance.



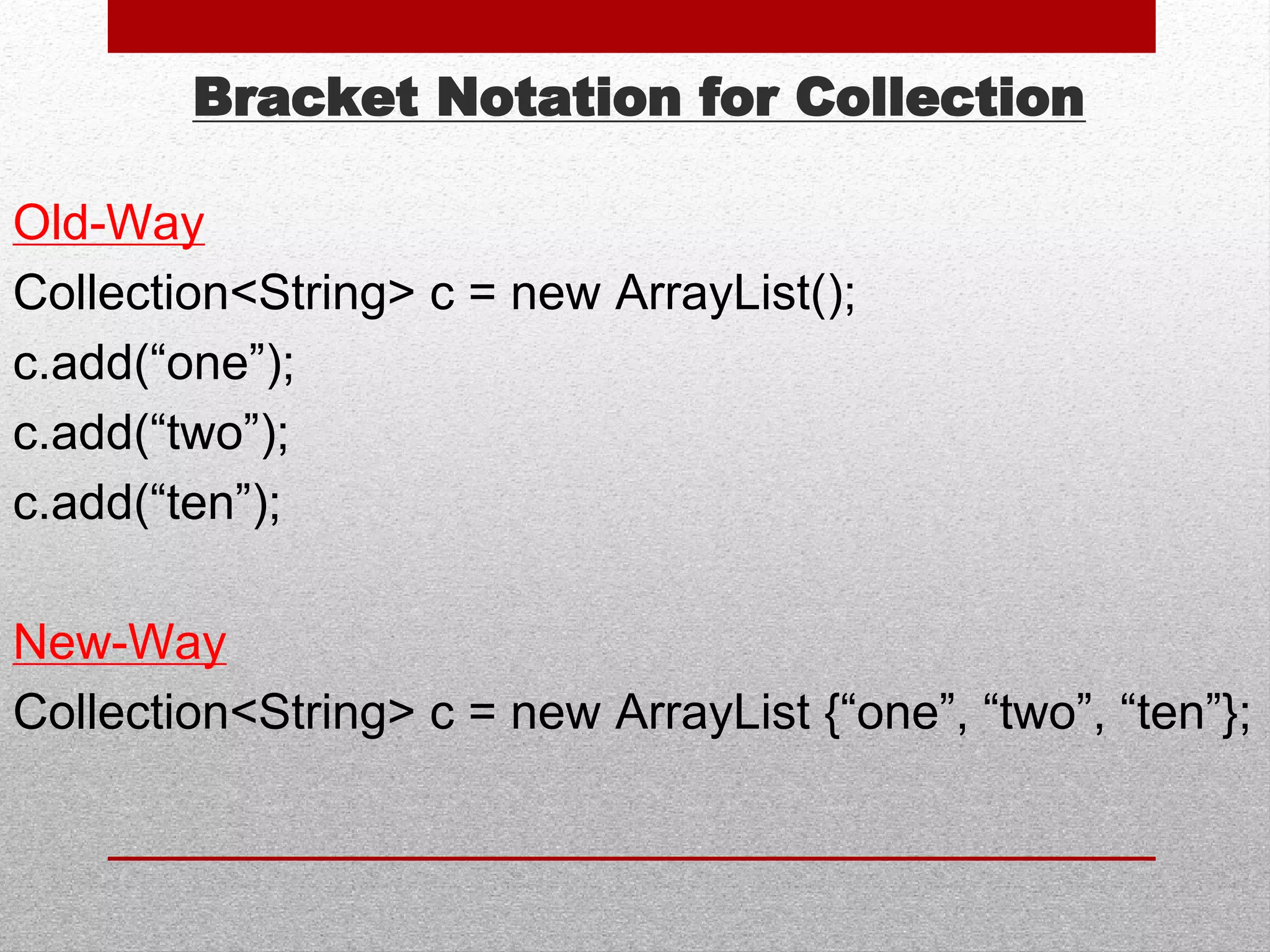








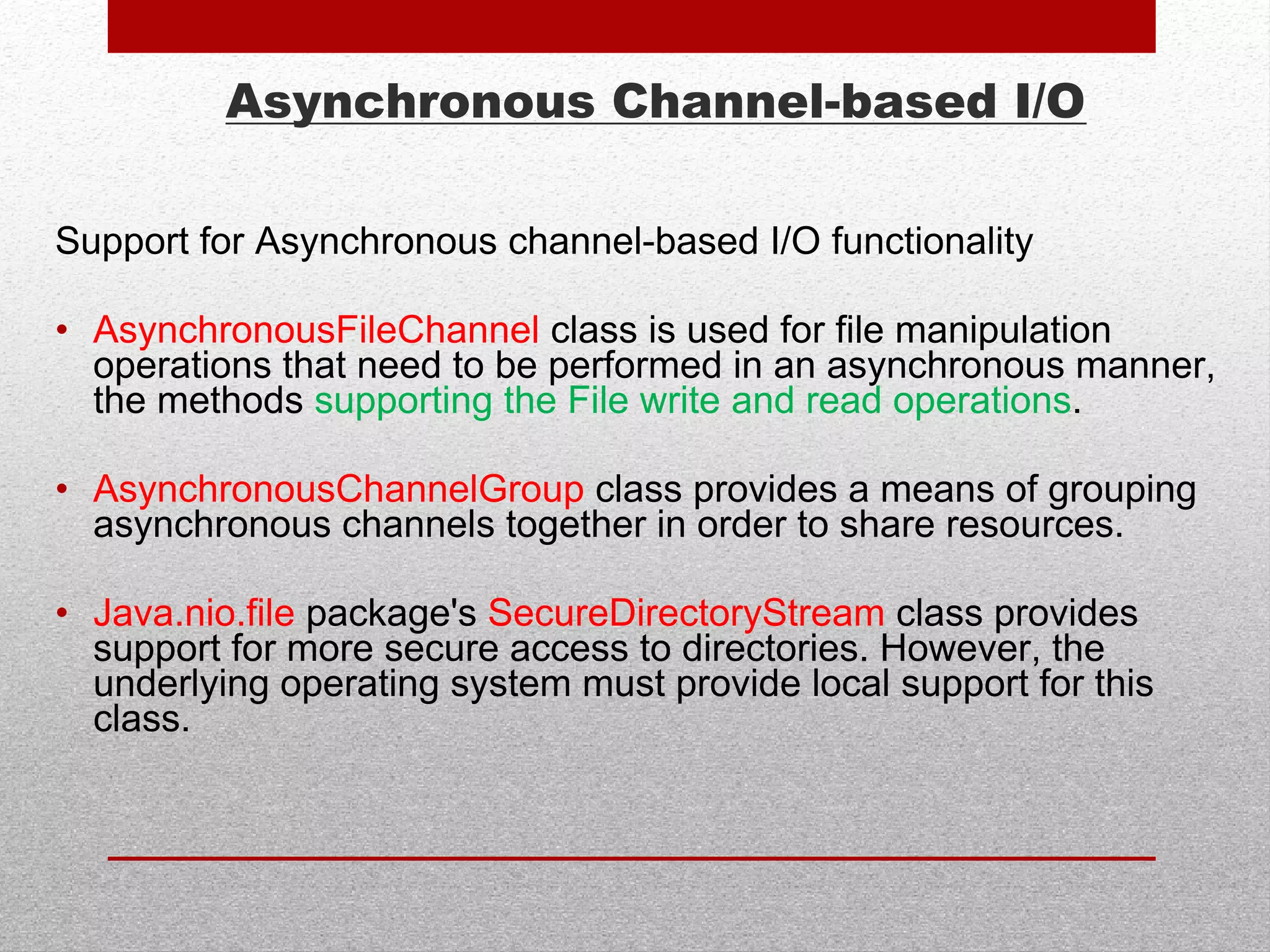
![URLClassLoader Closing
URL url = new URL("file:foo.jar");
URLClassLoader loader = new URLClassLoader (new URL[] {url});
Class cl = Class.forName ("Foo", true, loader);
Runnable foo = (Runnable) cl.newInstance();
foo.run();
loader.close ();
// foo.jar gets updated somehow
loader = new URLClassLoader (new URL[] {url});
cl = Class.forName ("Foo", true, loader);
foo = (Runnable) cl.newInstance();
// run the new implementation of Foo
foo.run();
Eliminates Server restarts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java7features-140206081446-phpapp01/75/Java7-New-Features-and-Code-Examples-21-2048.jpg)
![Varargs
public class VarArgsJavav6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
vaMethod("a", "b", "c");
}
public void vaMethod(String... args) {
for(String s : args)
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Automatically treats Method parameter as an Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java7features-140206081446-phpapp01/75/Java7-New-Features-and-Code-Examples-23-2048.jpg)