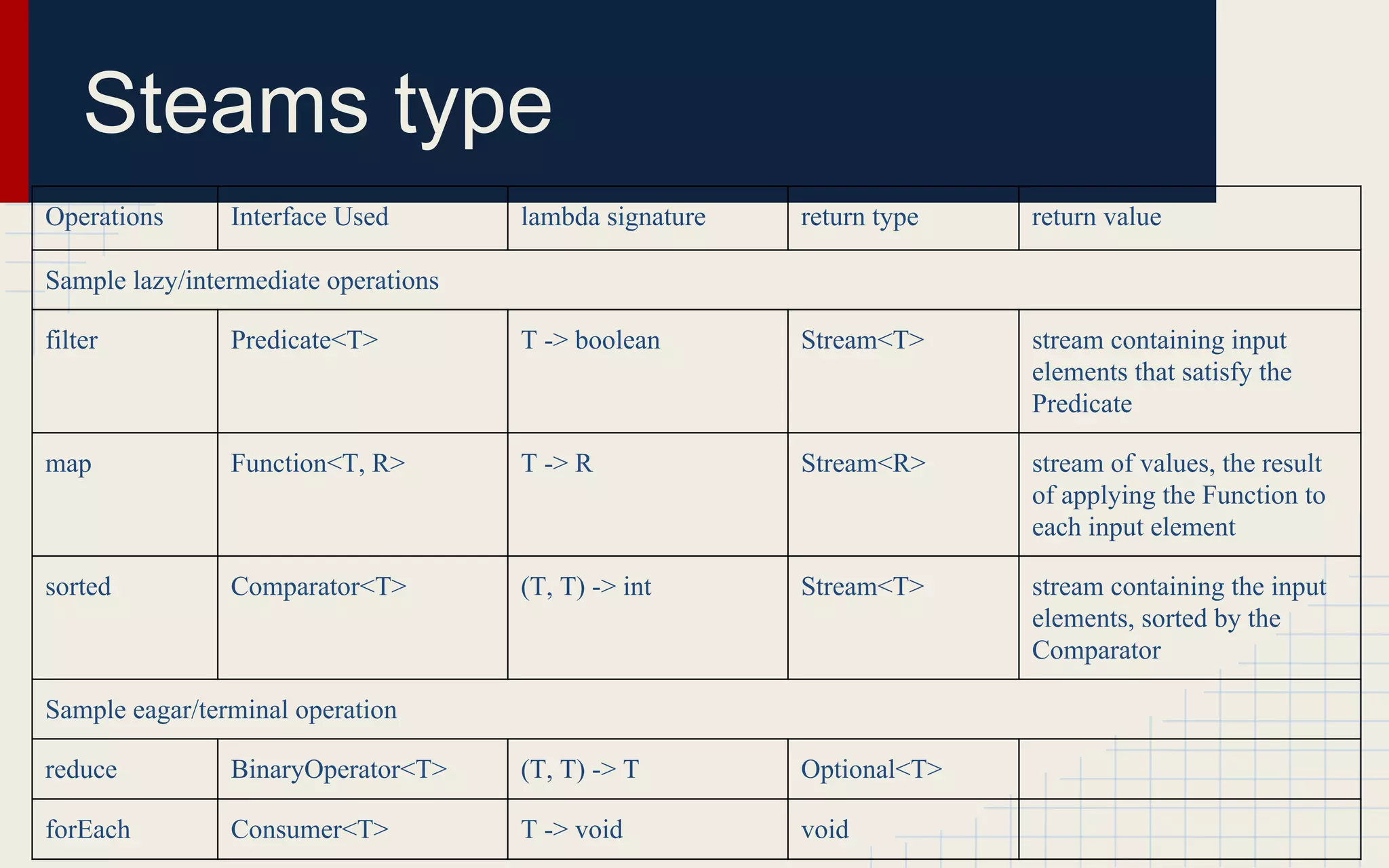
This document provides an overview of new features in Java 8 including lambda expressions, interface improvements, and streams. Lambda expressions allow for anonymous functions and method references in Java. Functional interfaces define a single abstract method that lambda expressions can implement. Interface changes allow interfaces to define static and default methods. Streams provide a functional-style way to process collections of objects through intermediate and terminal operations like filter, map, reduce, and forEach.



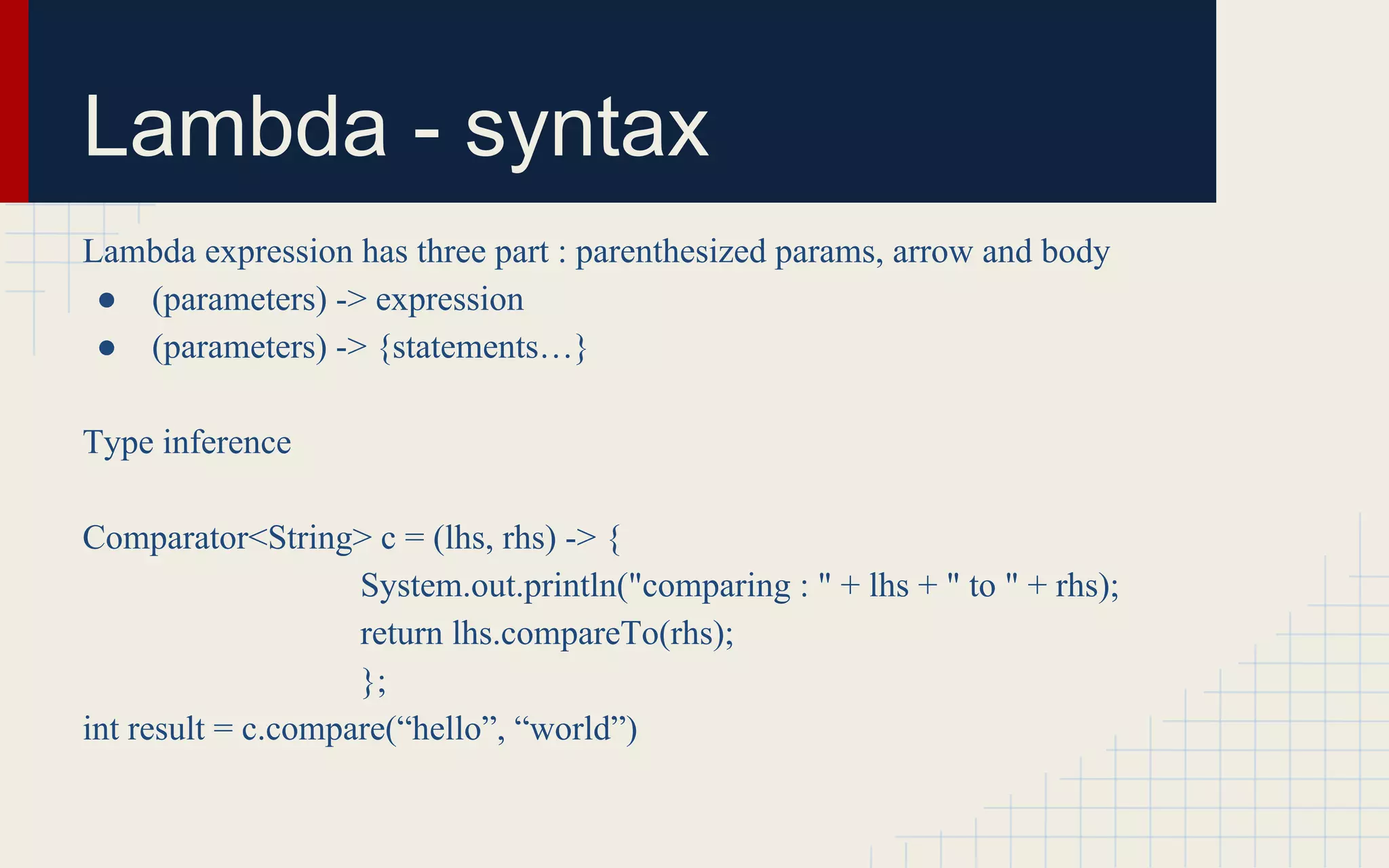
![More examples
List<Apple> inventory = Arrays.asList(new Apple(80,"green"),
new Apple(155, "green"),
new Apple(120, "red"));
// [Apple{color='green', weight=80}, Apple{color='green', weight=155}]
List<Apple> greenApples2 = filterApples(inventory, (Apple a) -> "green".equals(a.getColor()));
System.out.println(greenApples2);
// [Apple{color='green', weight=155}]
List<Apple> heavyApples2 = filterApples(inventory, (Apple a) -> a.getWeight() > 150);
System.out.println(heavyApples2);
public static List<Apple> filterApples(List<Apple> inventory, Predicate<Apple> p){
List<Apple> result = new ArrayList<>();
for(Apple apple : inventory){
if(p.test(apple)){
result.add(apple);
}}
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java81-141212140313-conversion-gate01/75/Java8-5-2048.jpg)