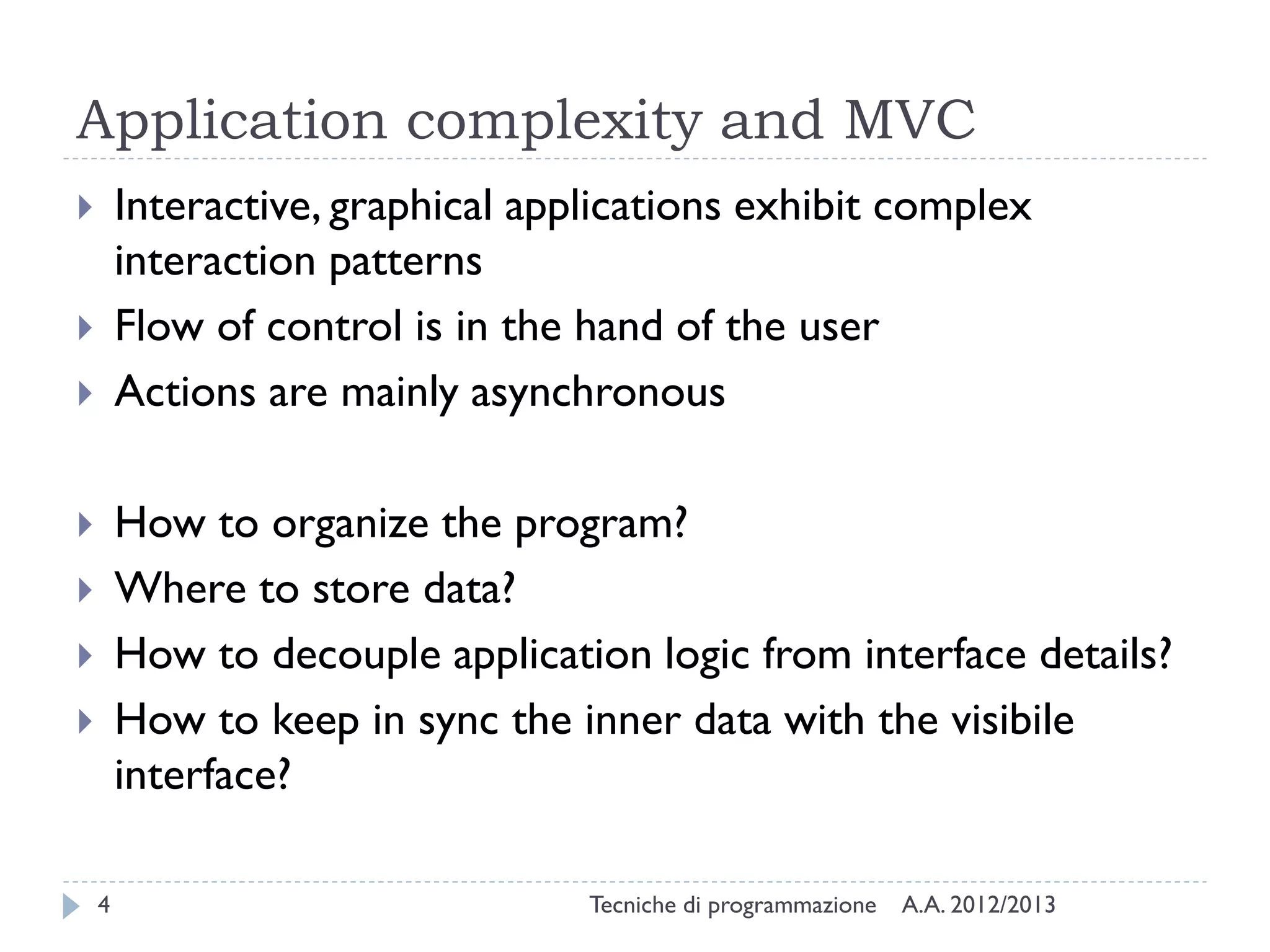
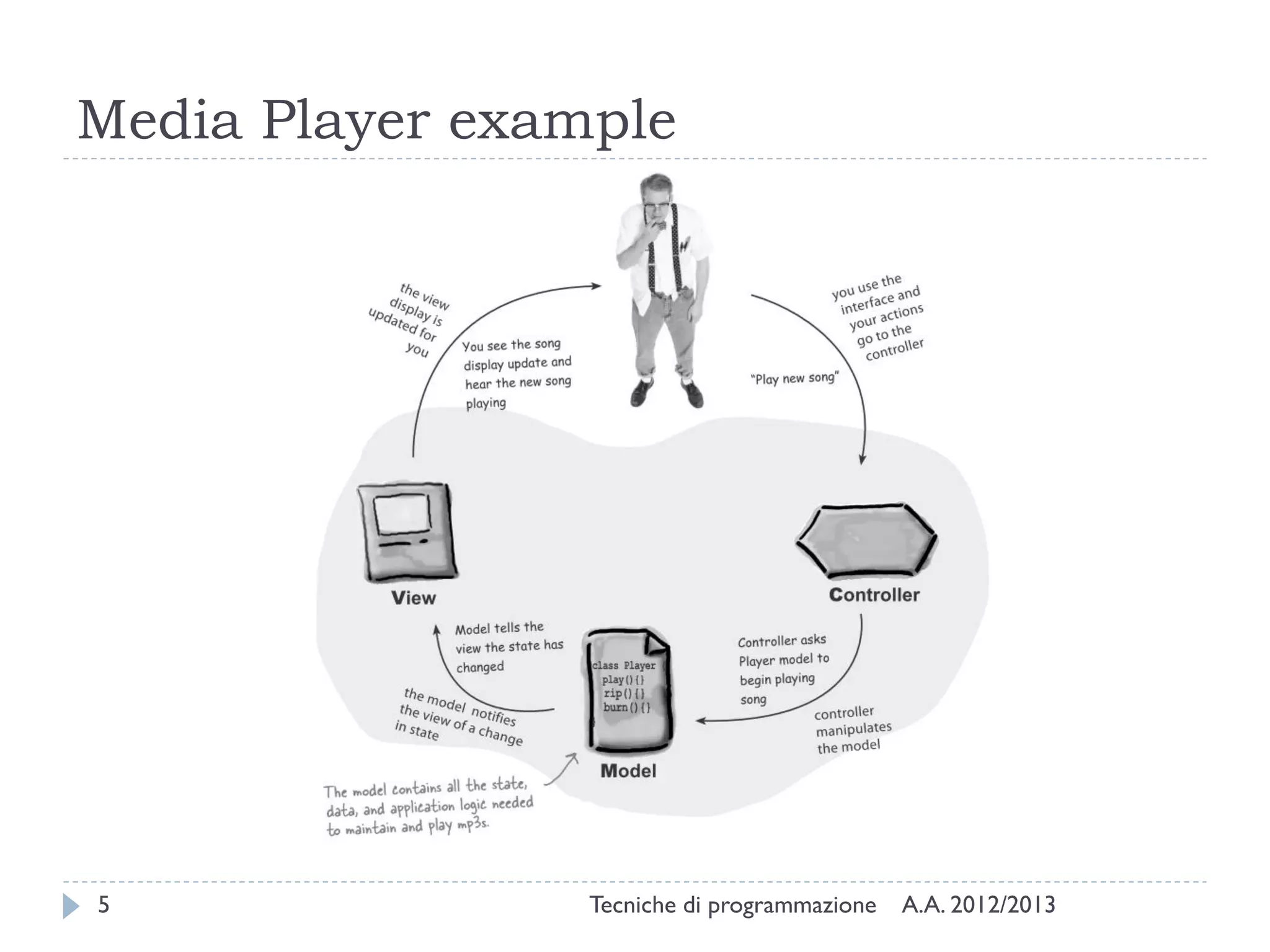
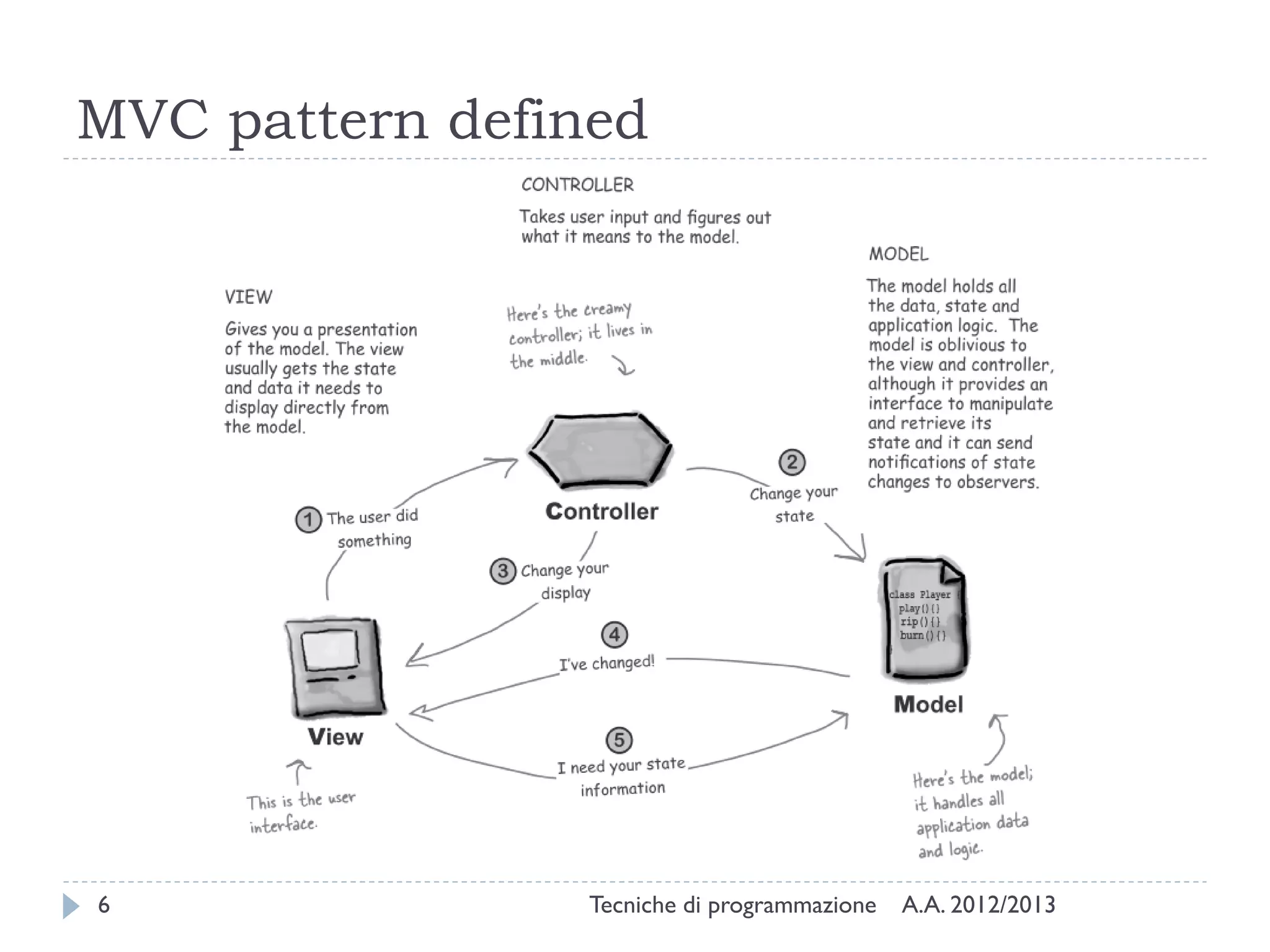
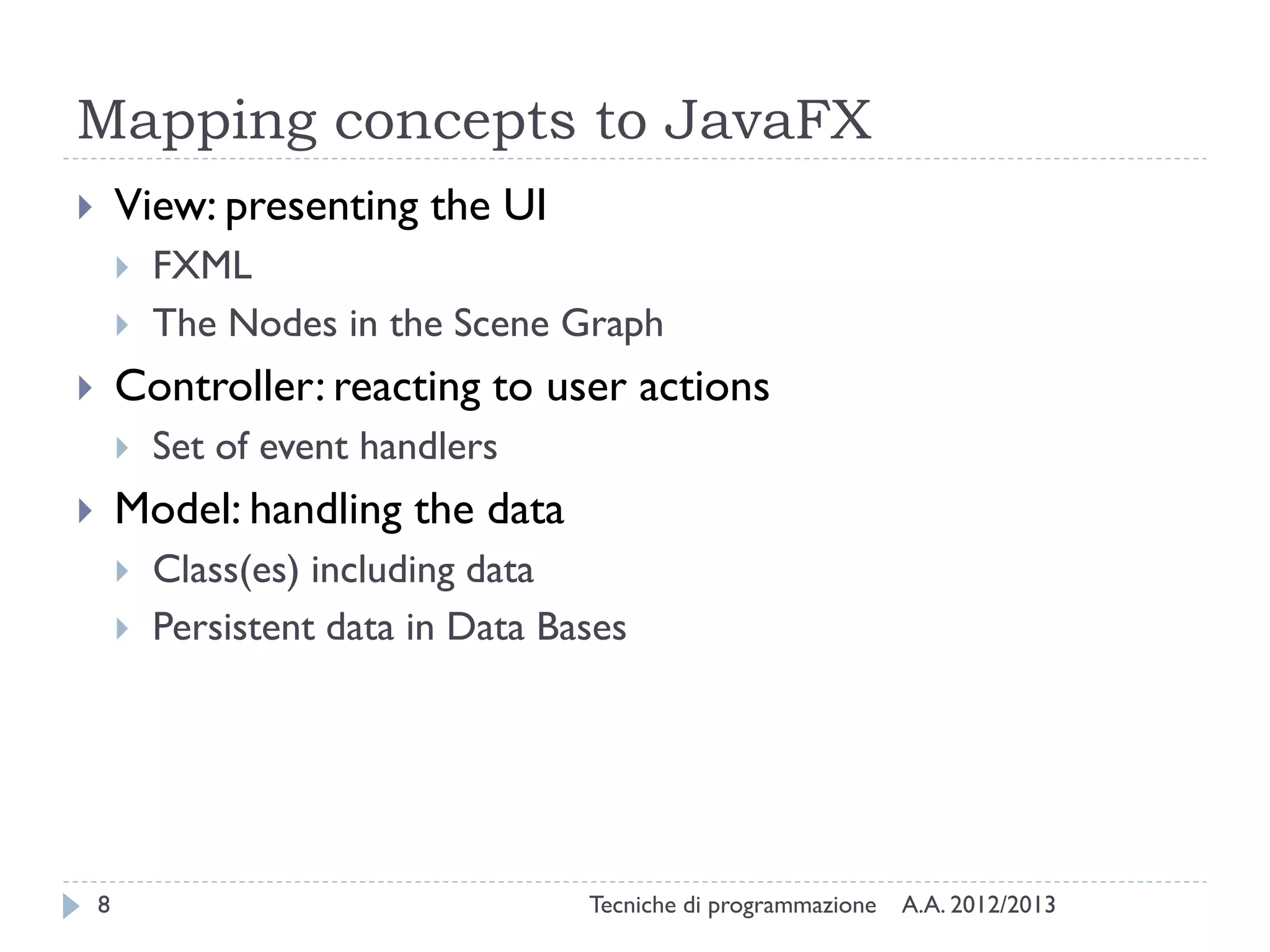
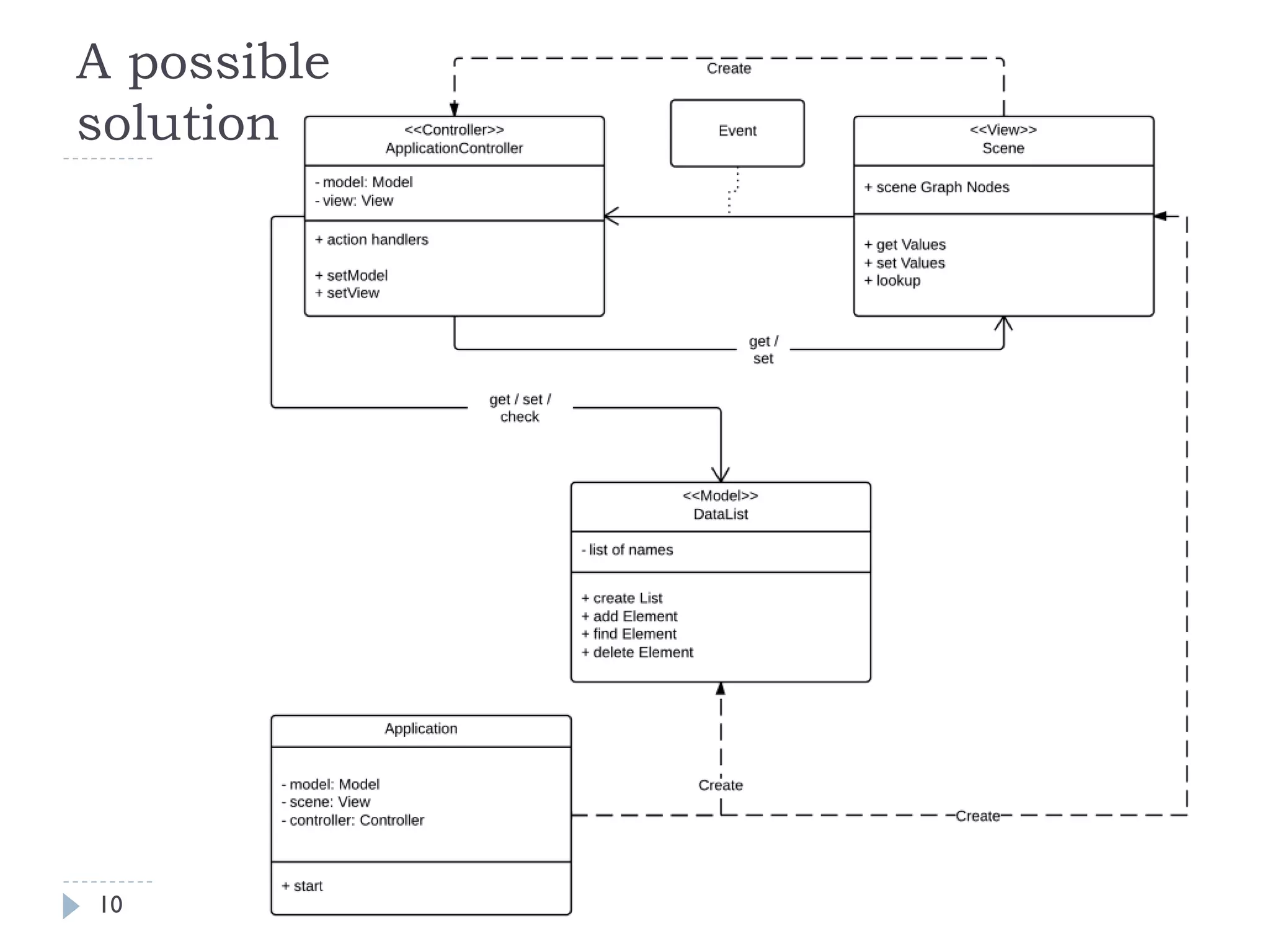
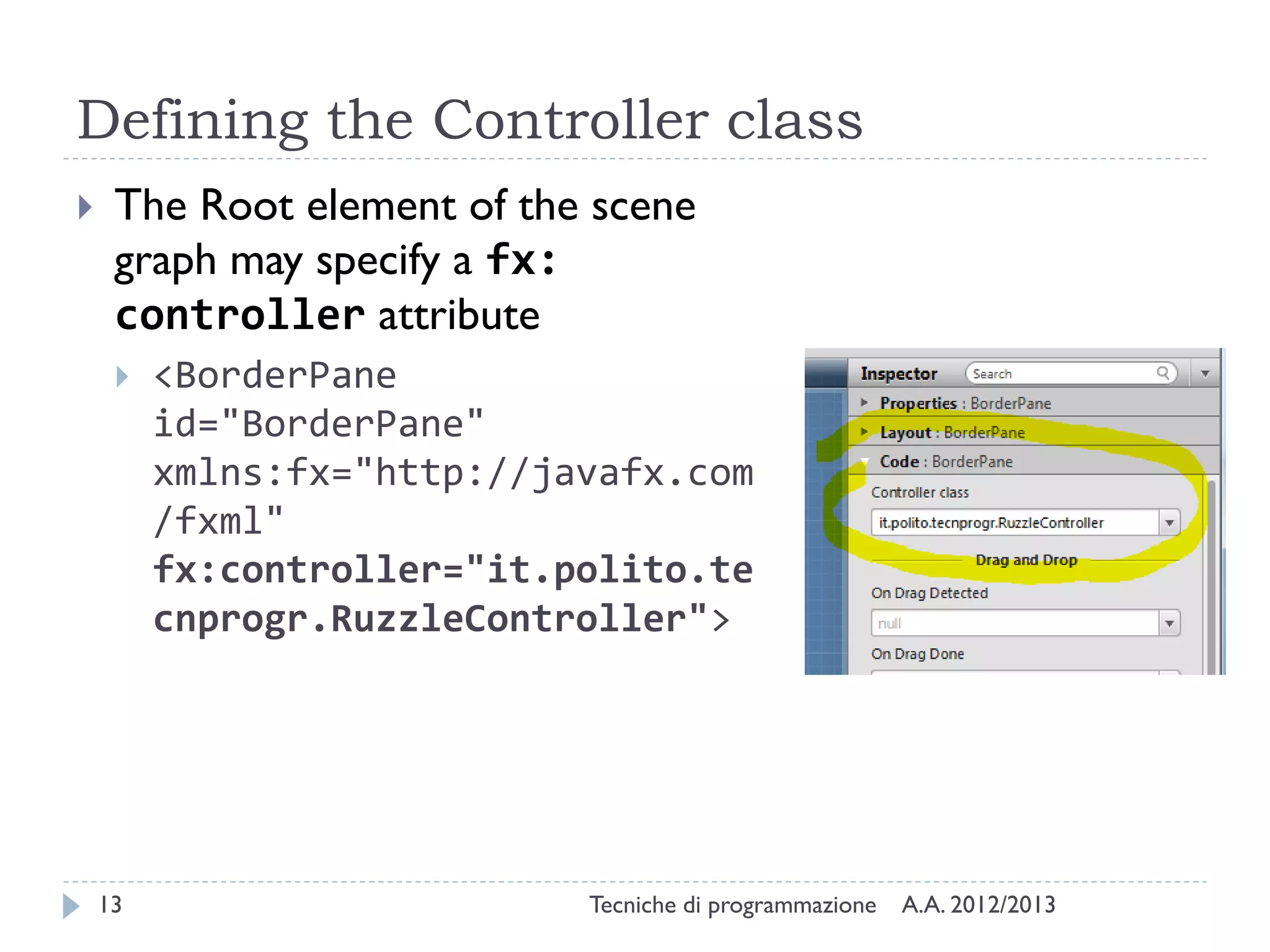
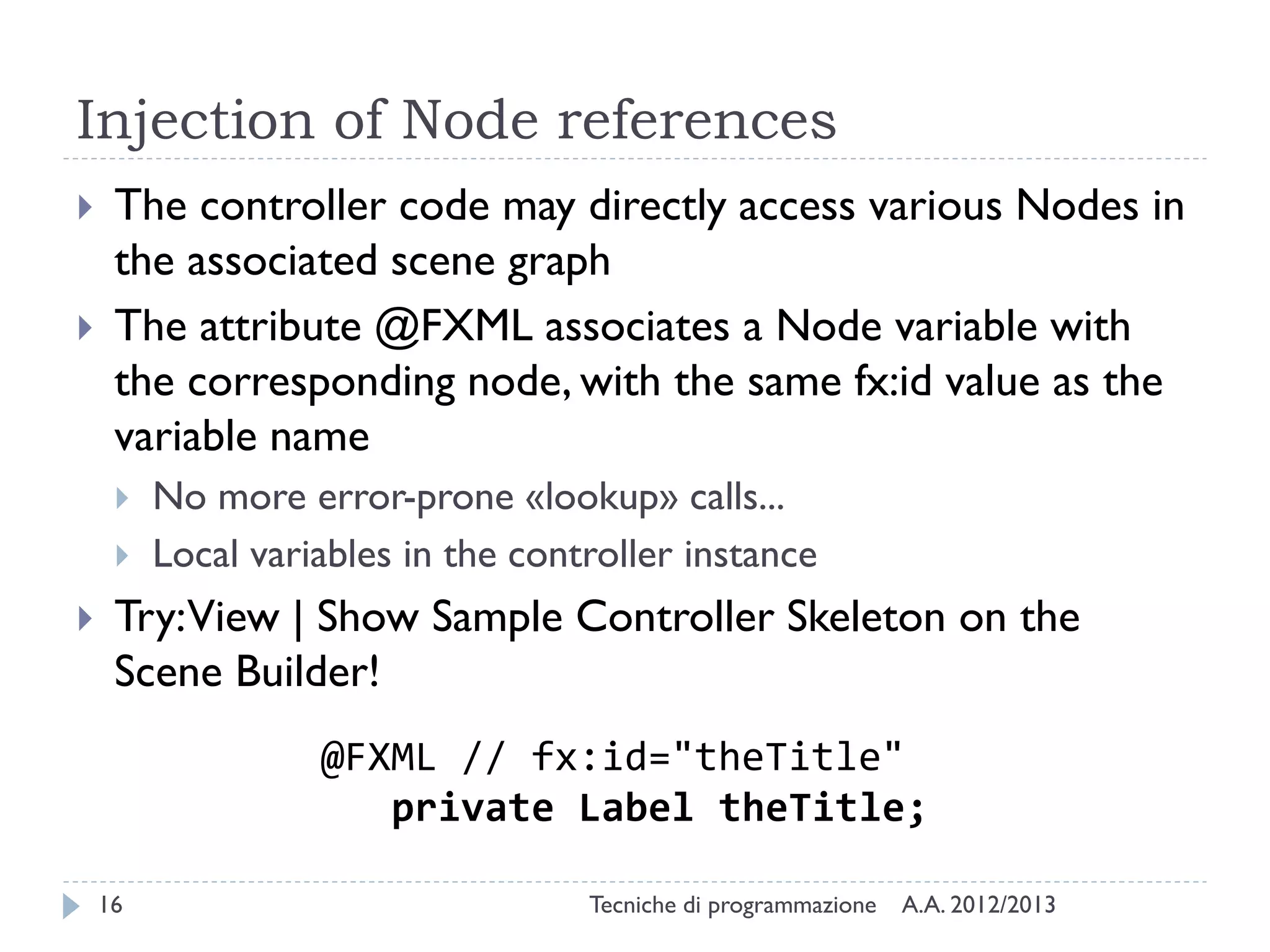
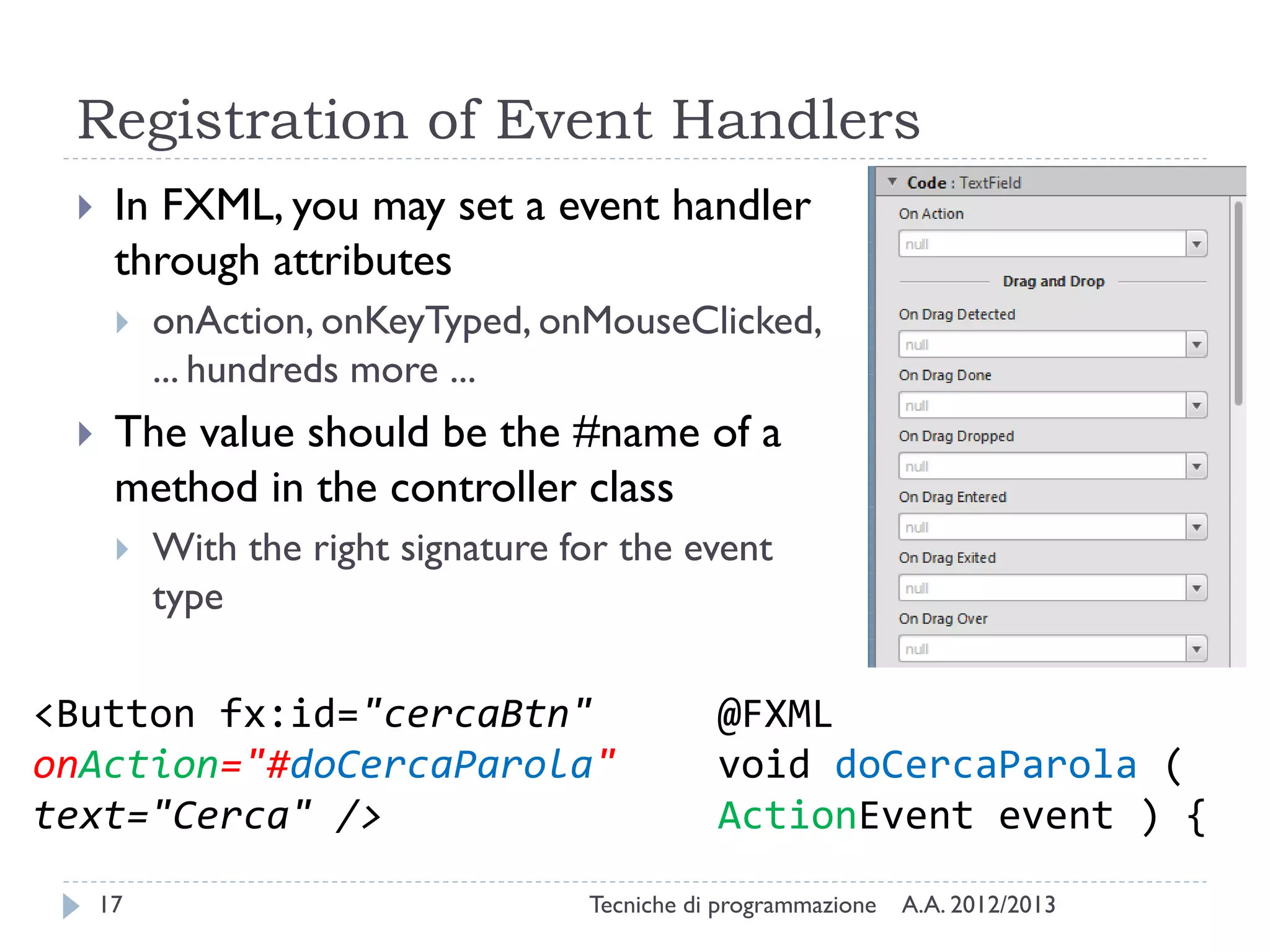
The document discusses JavaFX programming techniques focusing on the model-view-controller (MVC) architecture, detailing the role of controllers in FXML and application design. It explains how to manage complex user interactions in graphical applications using MVC principles, including mapping concepts to JavaFX components. Additionally, it covers FXML attributes for controller definition, event handler registration, and accessing controller instances for efficient data handling.