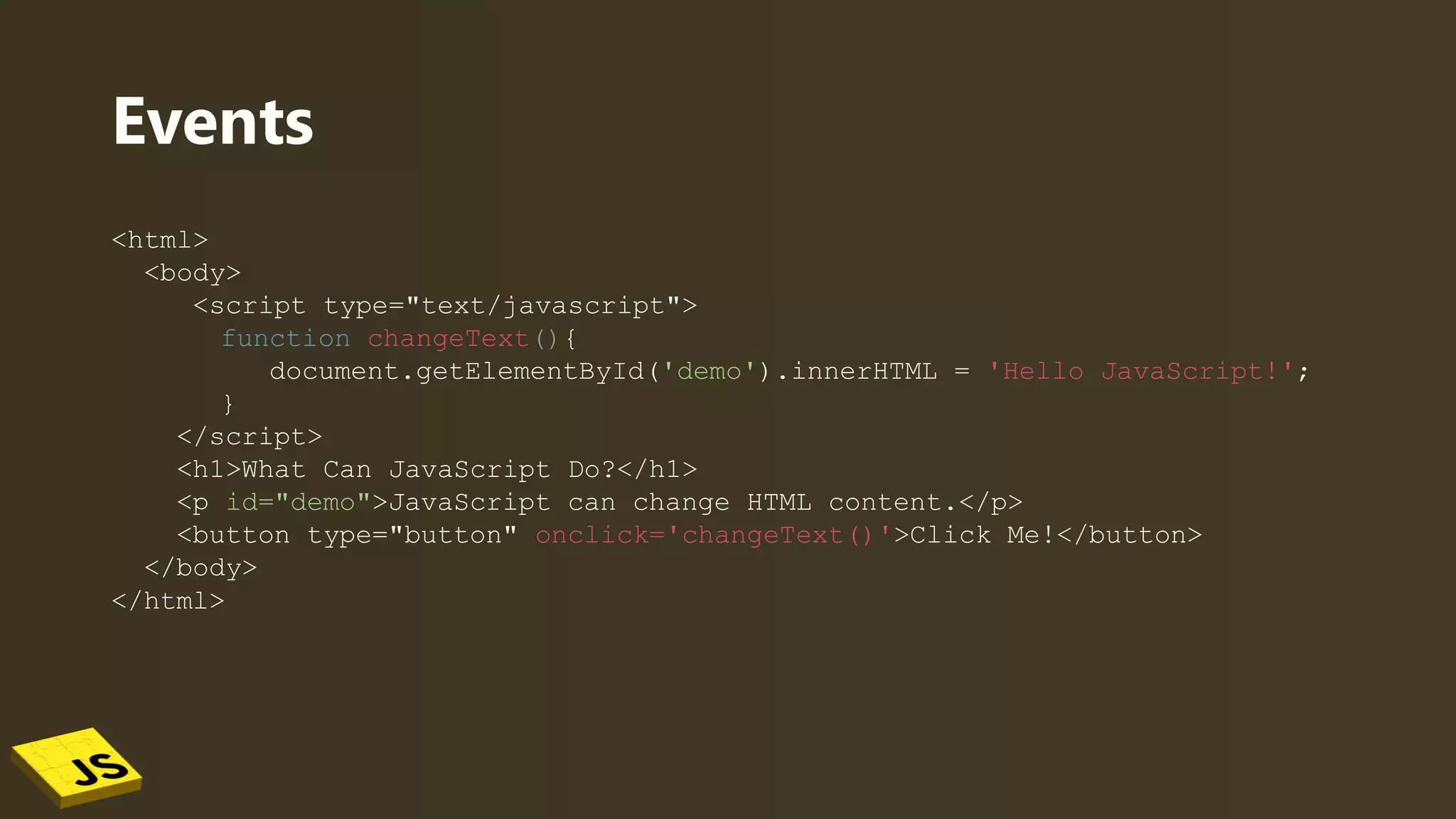
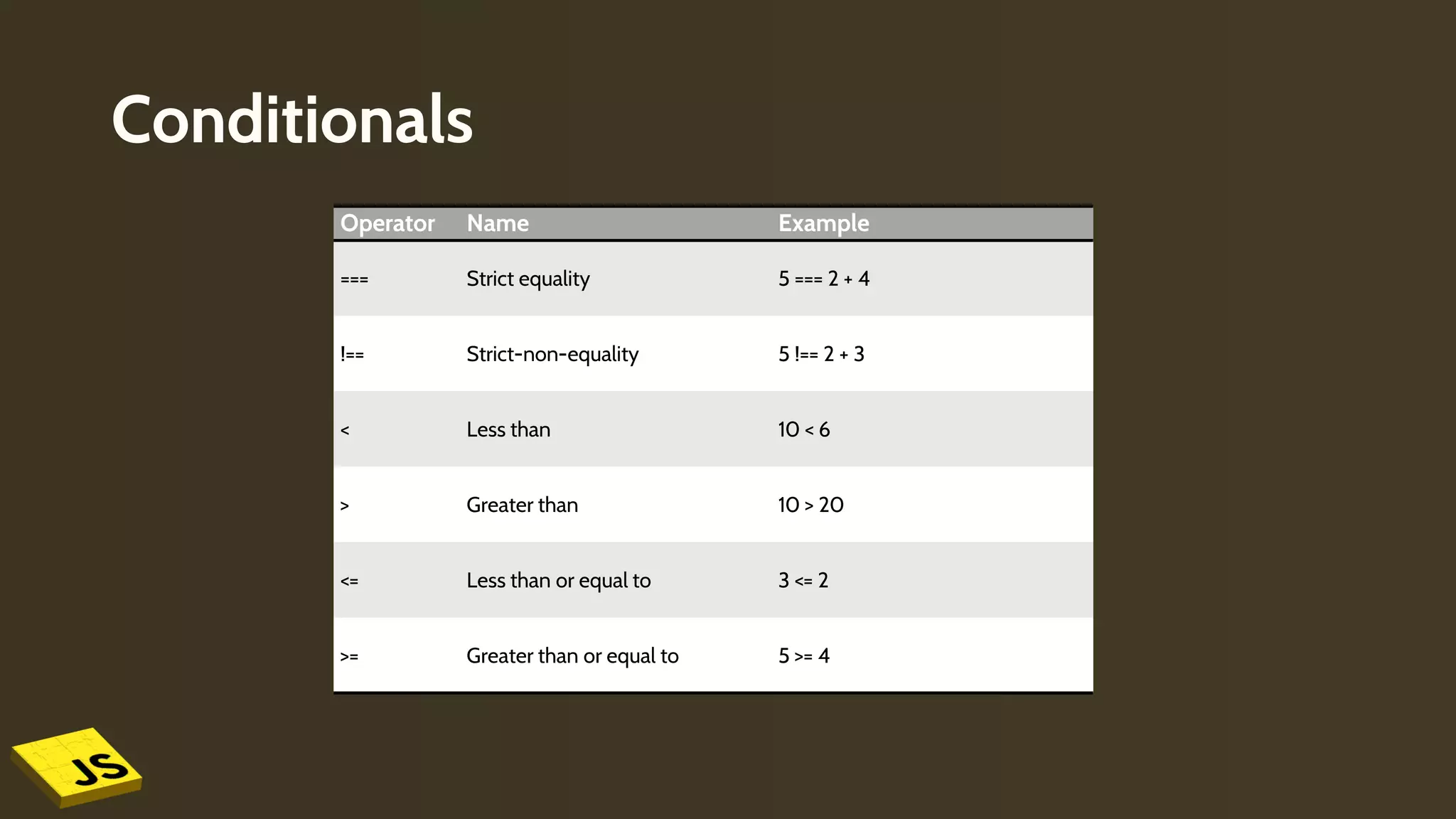
This document provides an overview of JavaScript, detailing its role in web development alongside HTML and CSS. It covers fundamental concepts such as variables, data types, operators, conditionals, loops, functions, and events. The document also includes examples of how to implement JavaScript in HTML for interactive web pages.





![Data Types
Variable Example
String var myVariable = 'Bob';
Number var myVariable = 10;
Boolean var myVariable = true;
Array
var myVariable = [1,'Bob','Steve',10];
Refer to each member of the array like this:
myVariable[0], myVariable[1], etc.
Object
var myVariable = document.querySelector('h1');
All of the above examples too.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-180303053655/75/Javascript-A-sneak-preview-6-2048.jpg)





![Functions
• Special functions
• alert(“Hi”);
• confirm(“Are you gonna eat that?”);
• prompt(“Enter your age [male only]:”);
• getElementById(“elementId”);
• String functions
• split()
• Array functions
• find()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-180303053655/75/Javascript-A-sneak-preview-13-2048.jpg)