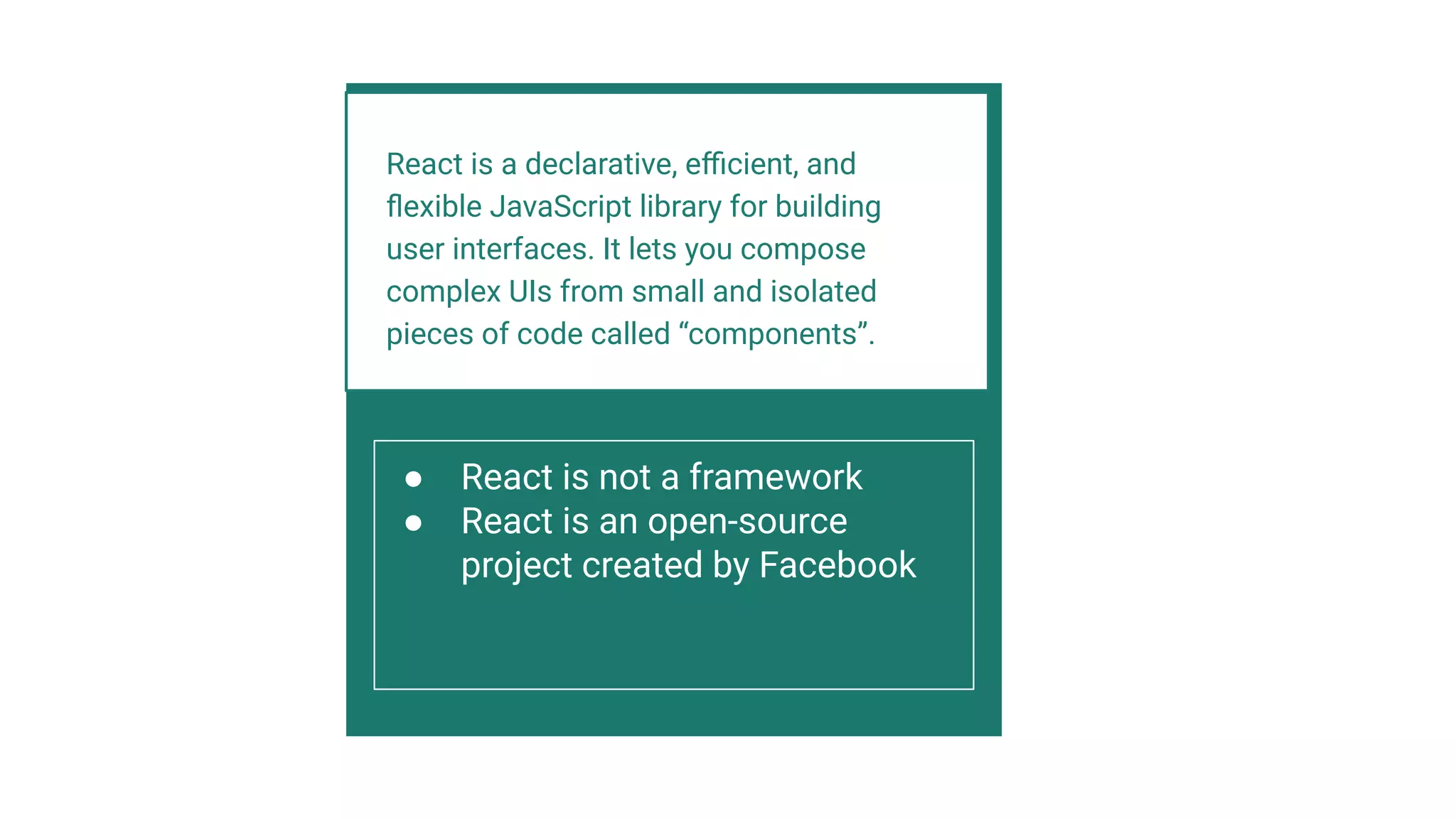
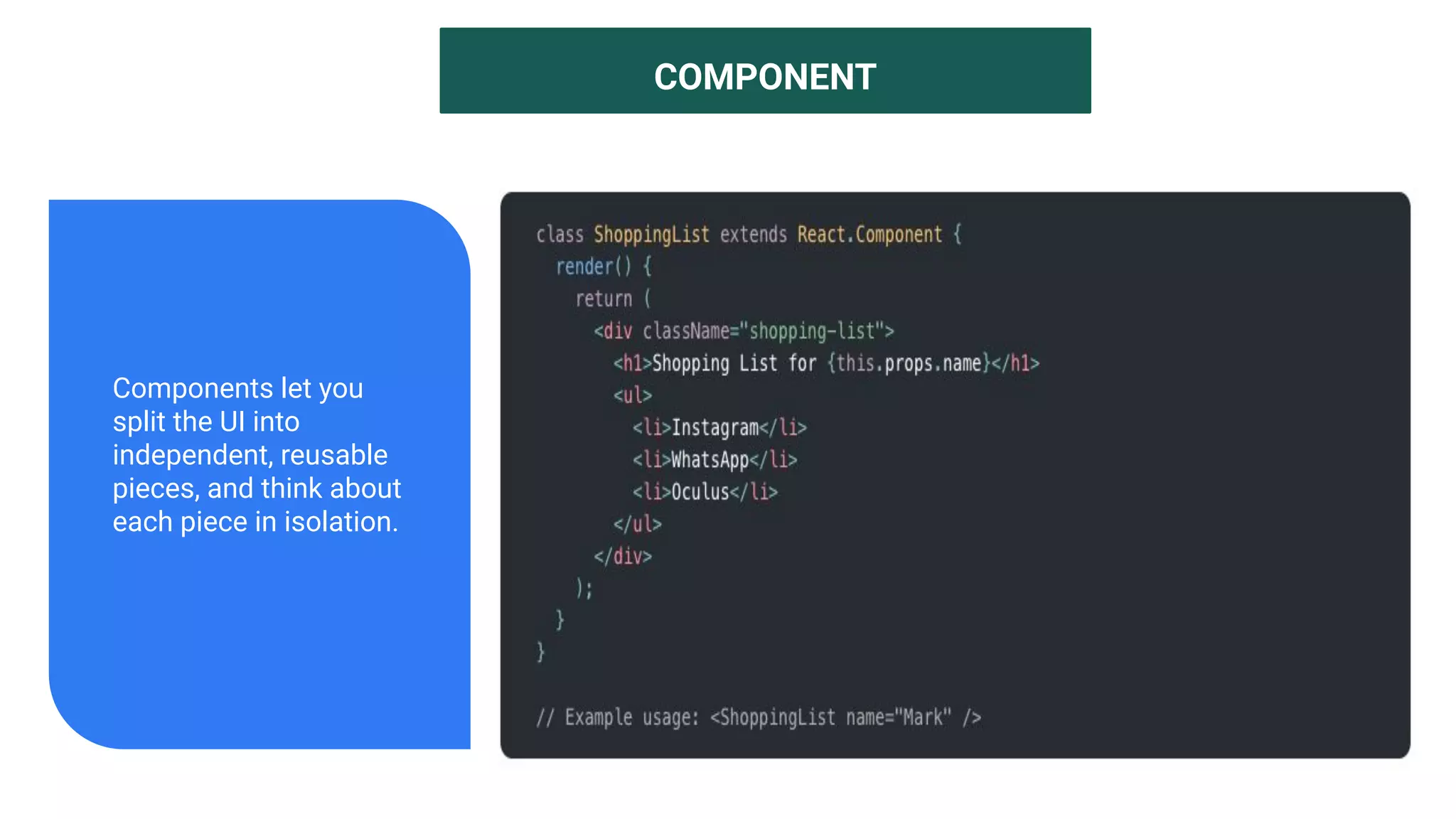
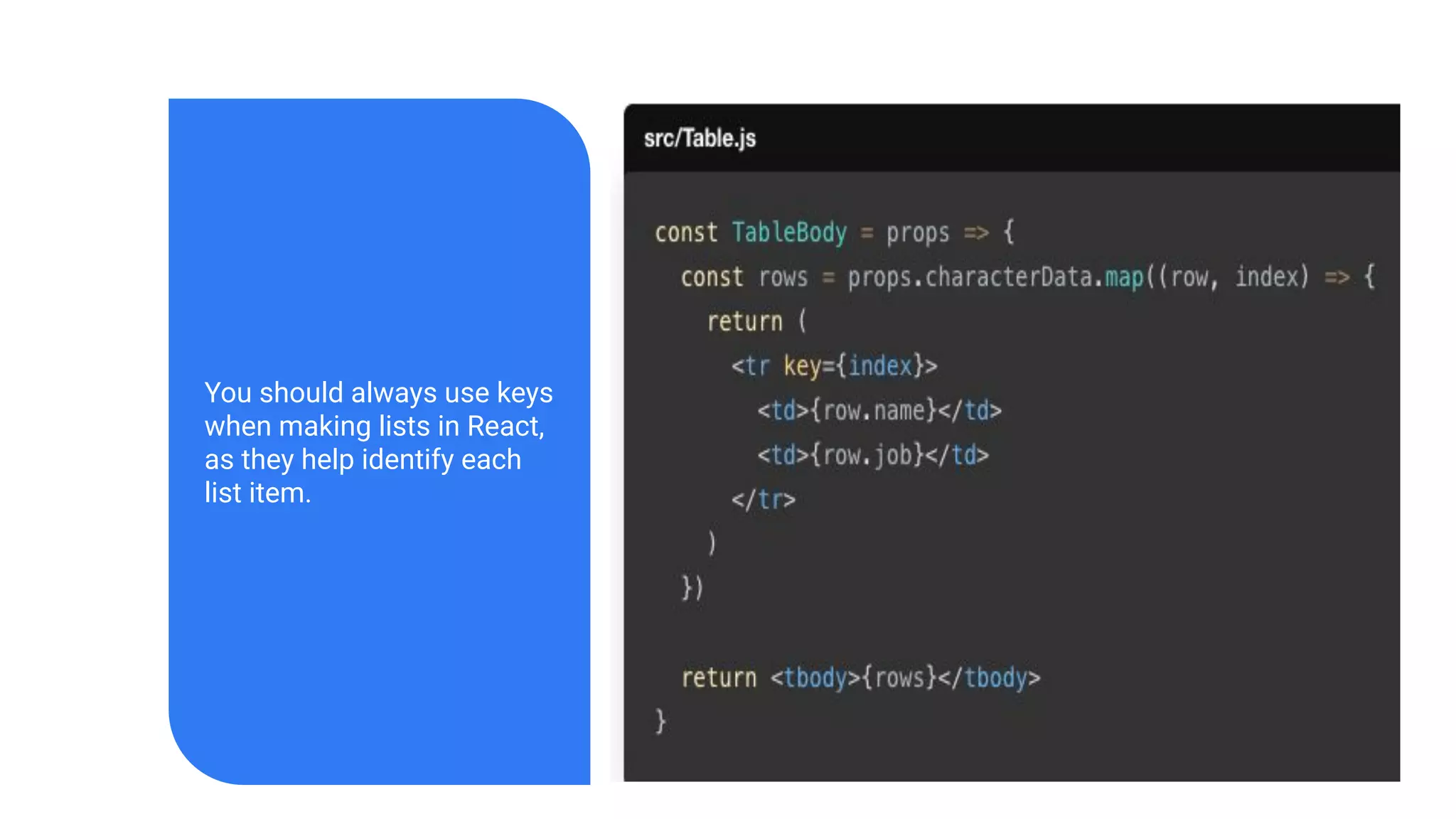
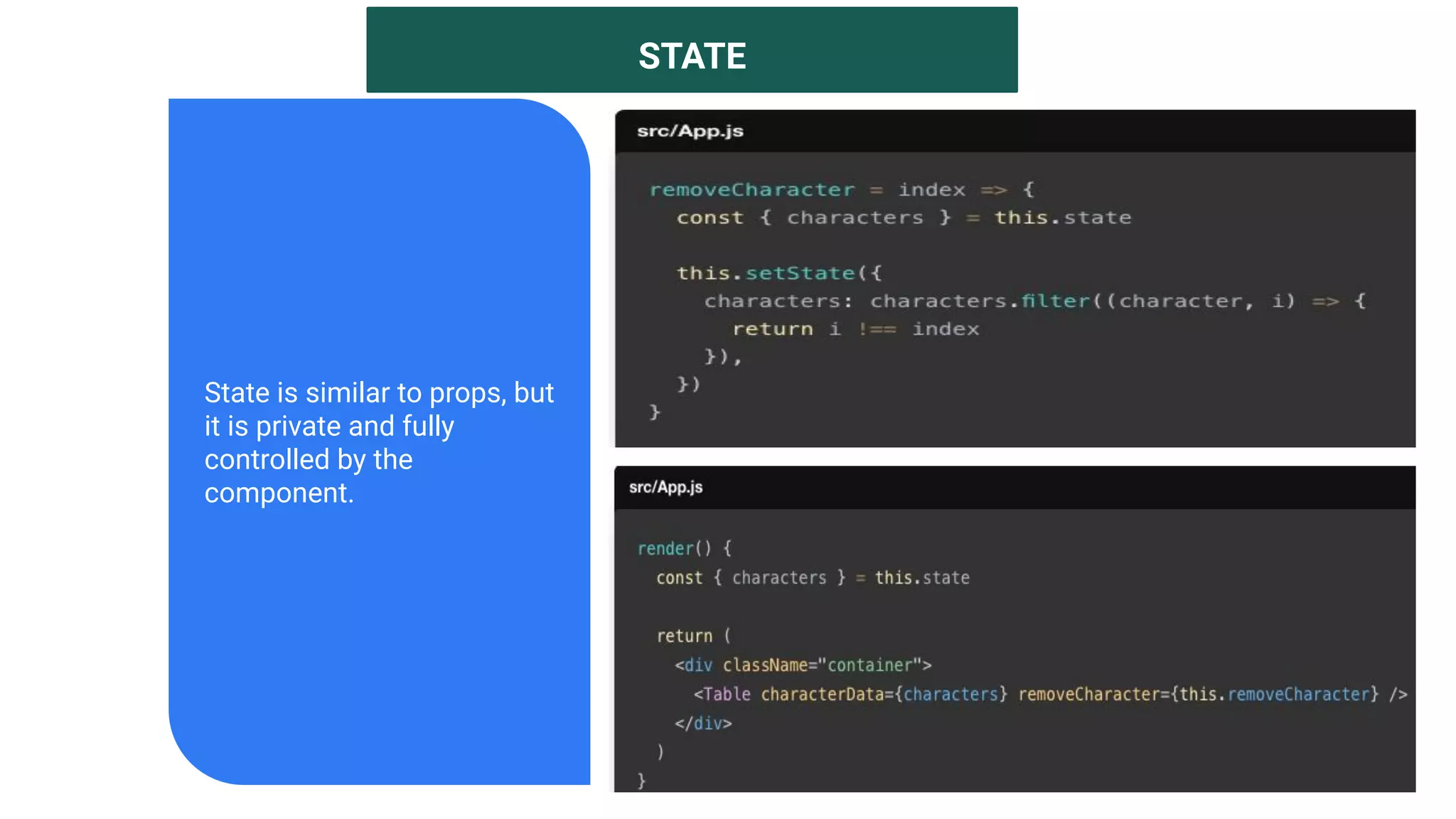
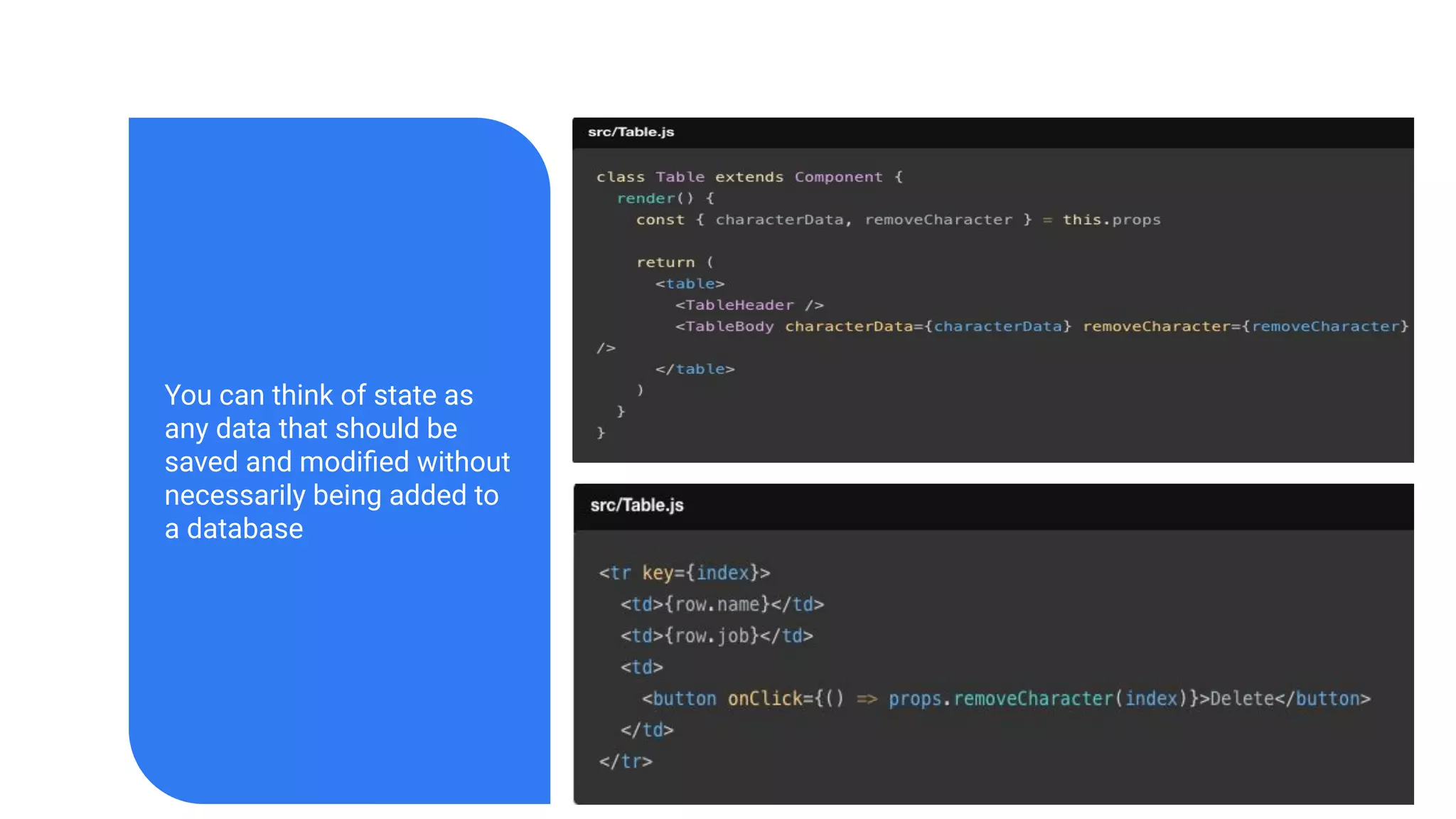
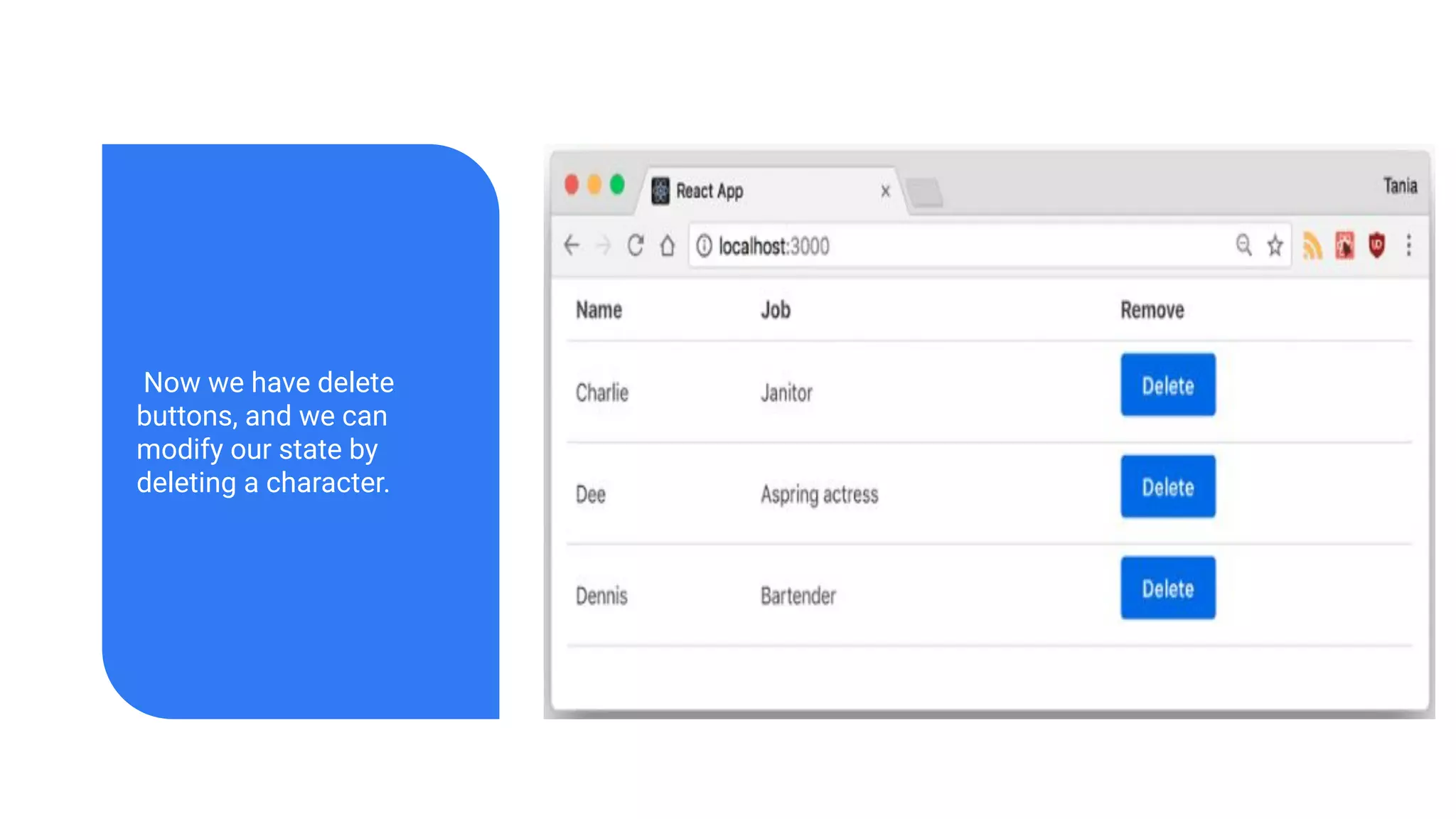
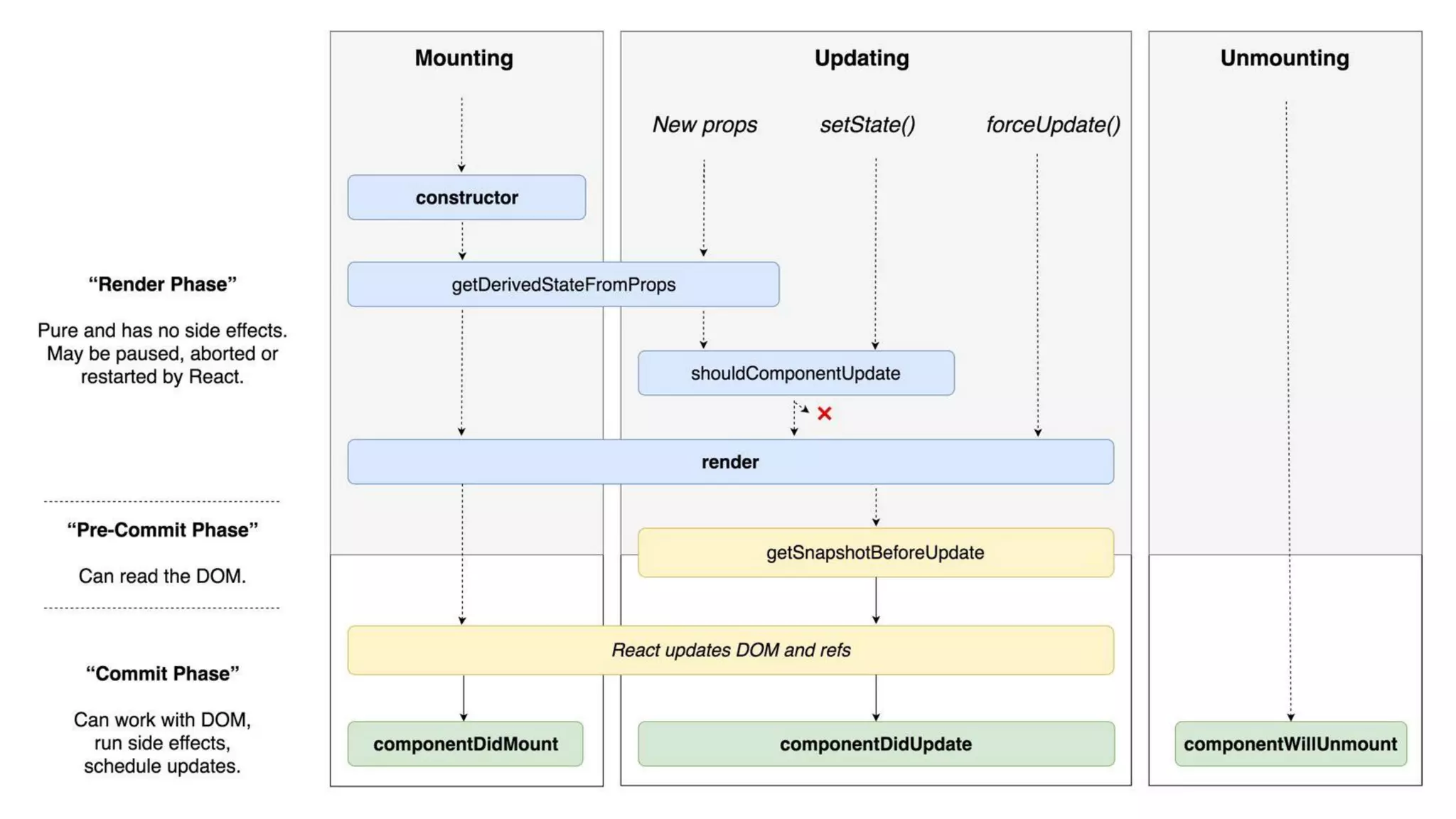
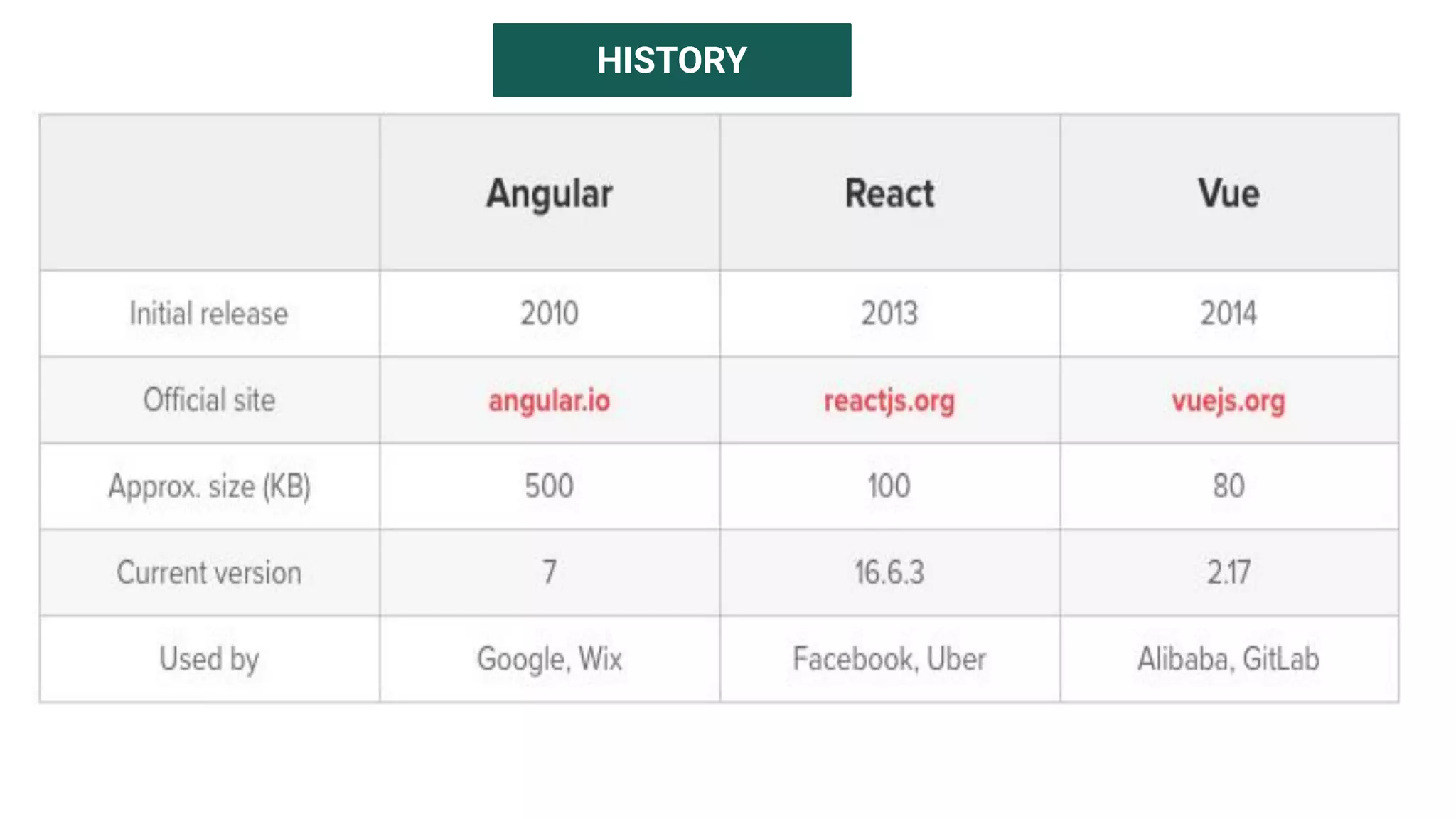
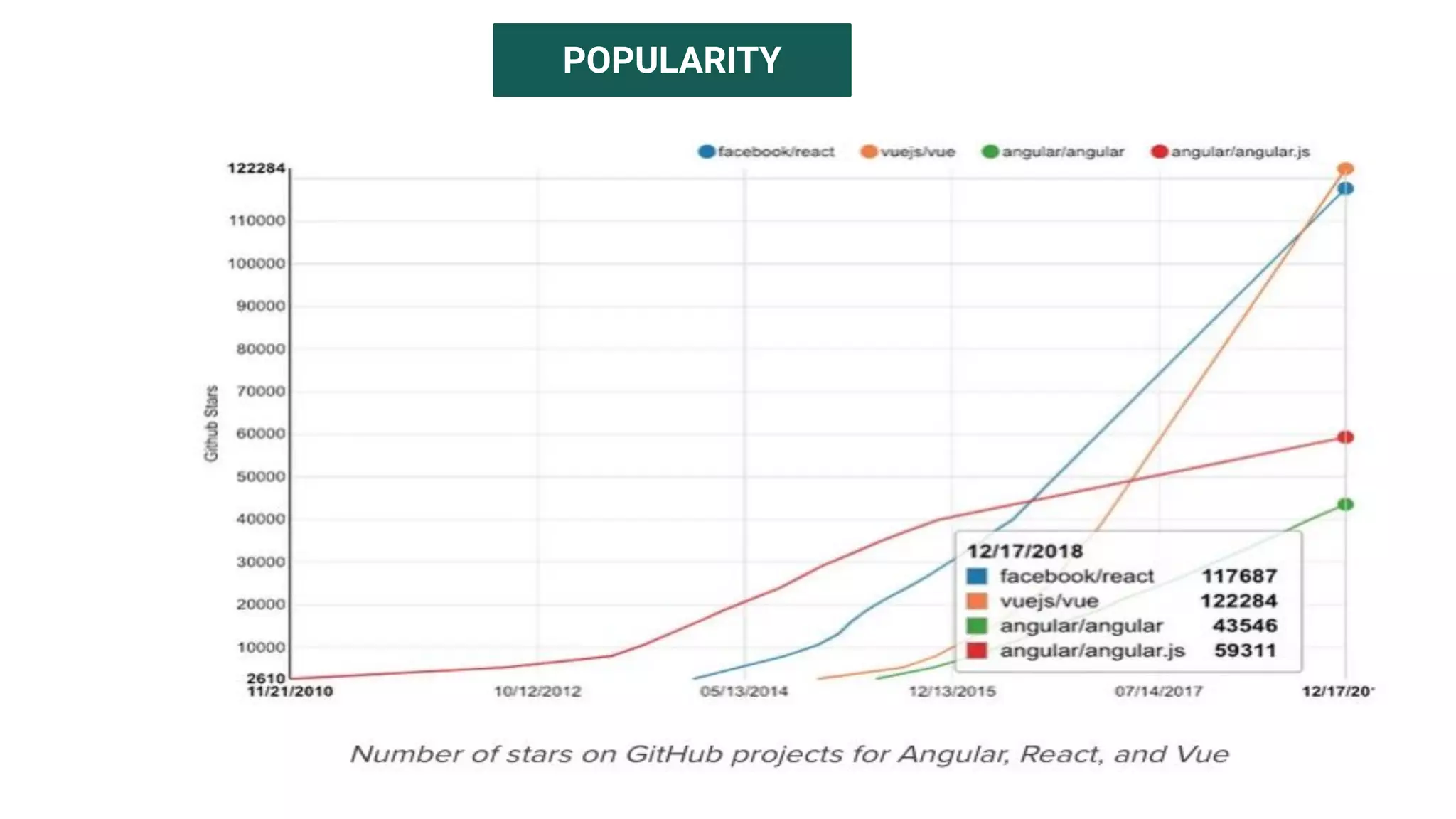
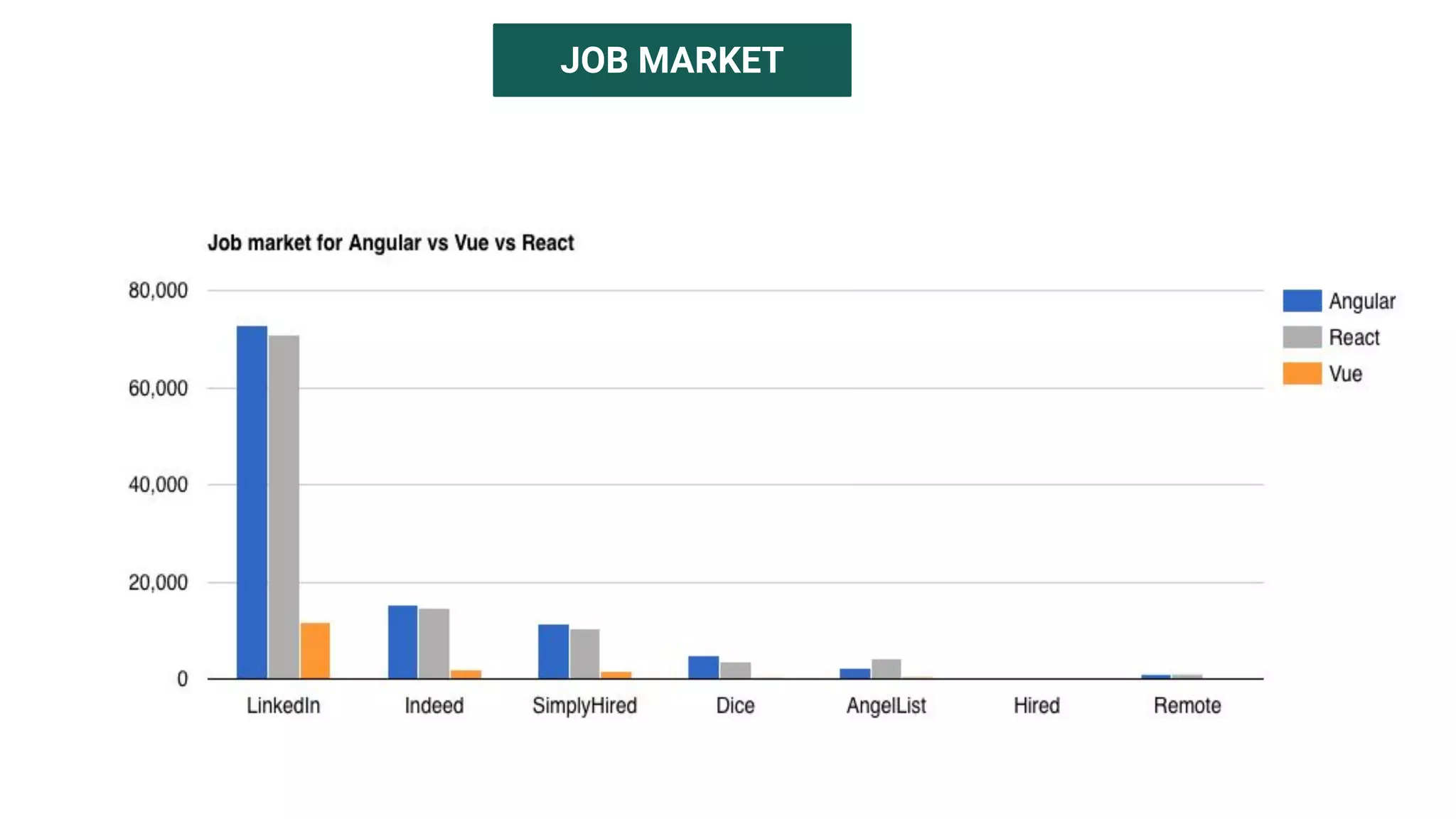
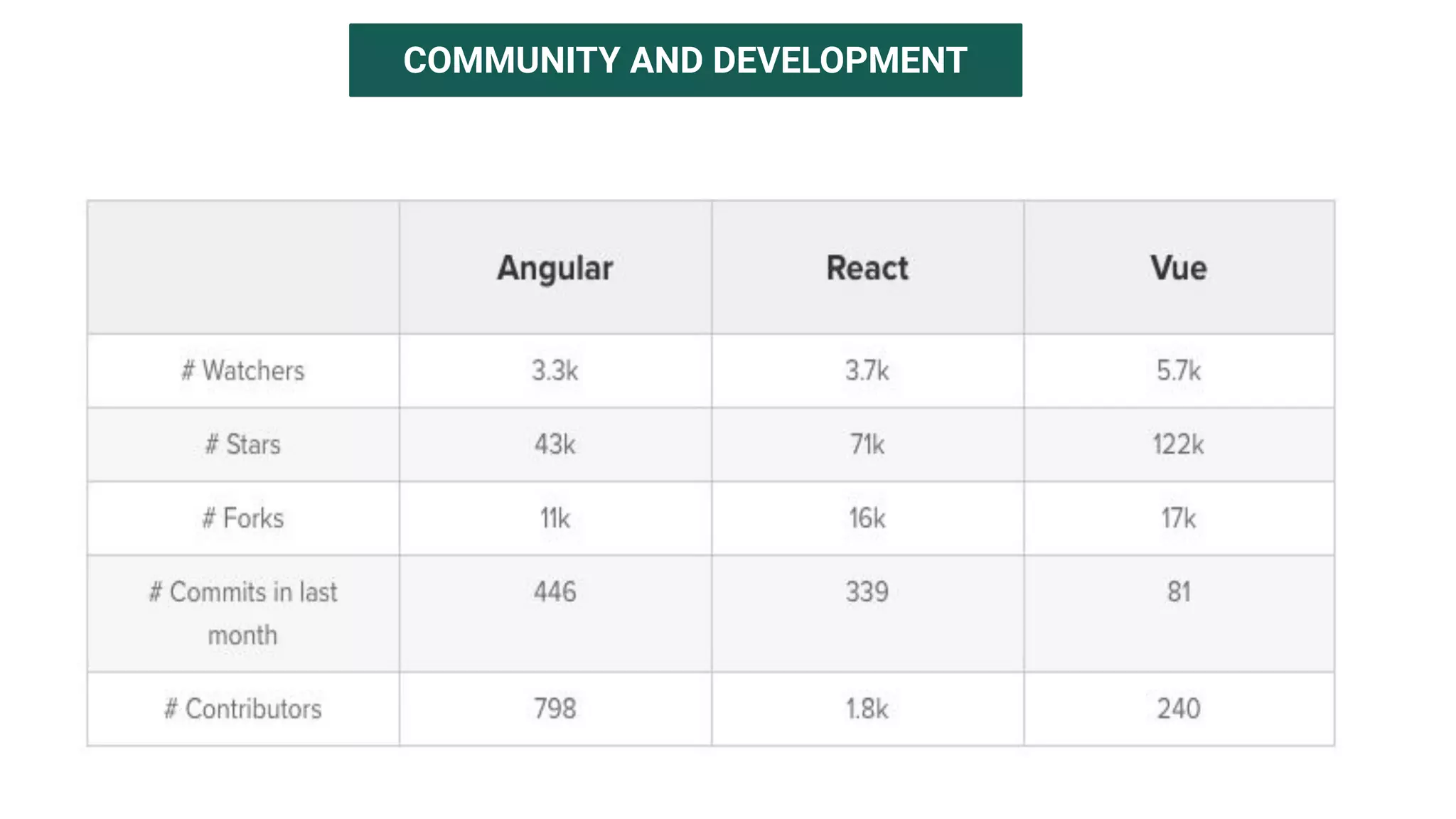
The document introduces several new features in ES10 including BigInt as a new primitive type, String trim methods, optional catch binding, and dynamic imports. It also covers Array flat/flatMap methods for flattening nested arrays. React is summarized as a declarative library for building user interfaces with isolated reusable components, using JSX syntax and component state/props. Key concepts like components, JSX, state, props and lifecycle are defined.


![BigInt is the 7th primitive type.
With BigInteger, you don't have that problem, because once the
assigned bits are not enough to store the exact value, BigInteger
will just add some bits so it can handle the value again.
● const b = 1n
● typeof 10n == 'bigint'
● 10n === BigInt(10)
● 10n == 10
● 200n / 20
--Uncaught TypeError
Flattening of a multi-dimensional array:
The flat() method creates a new array with all sub-array elements
concatenated into it recursively up to the specified depth.
Array.flat()
let multi = [1,2,3,[4,5,6,[7,8,9,[10,11,12]]]];
multi.flat(); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,Array(4)]
multi.flat().flat(); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,Array(3)]
multi.flat().flat().flat(); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]
multi.flat(Infinity); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]
BigInt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techtalk-191122182637/75/JavaScript-ES10-and-React-Js-Introduction-4-2048.jpg)
![The flatMap() method first maps each element using a
mapping function, then flattens the result into a new array.
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
arr.map(x => [x, x*2])
// [Array(2), Array(2), Array(2), Array(2), Array(2)]
// 0: (2) [1, 2]
// 1: (2) [2, 4]
// 2: (2) [3, 6]
// 3: (2) [4, 8]
// 4: (2) [5, 10]
arr.flatMap(x => [x,x*2])
// [1, 2, 2, 4, 3, 6, 4, 8, 5, 10]
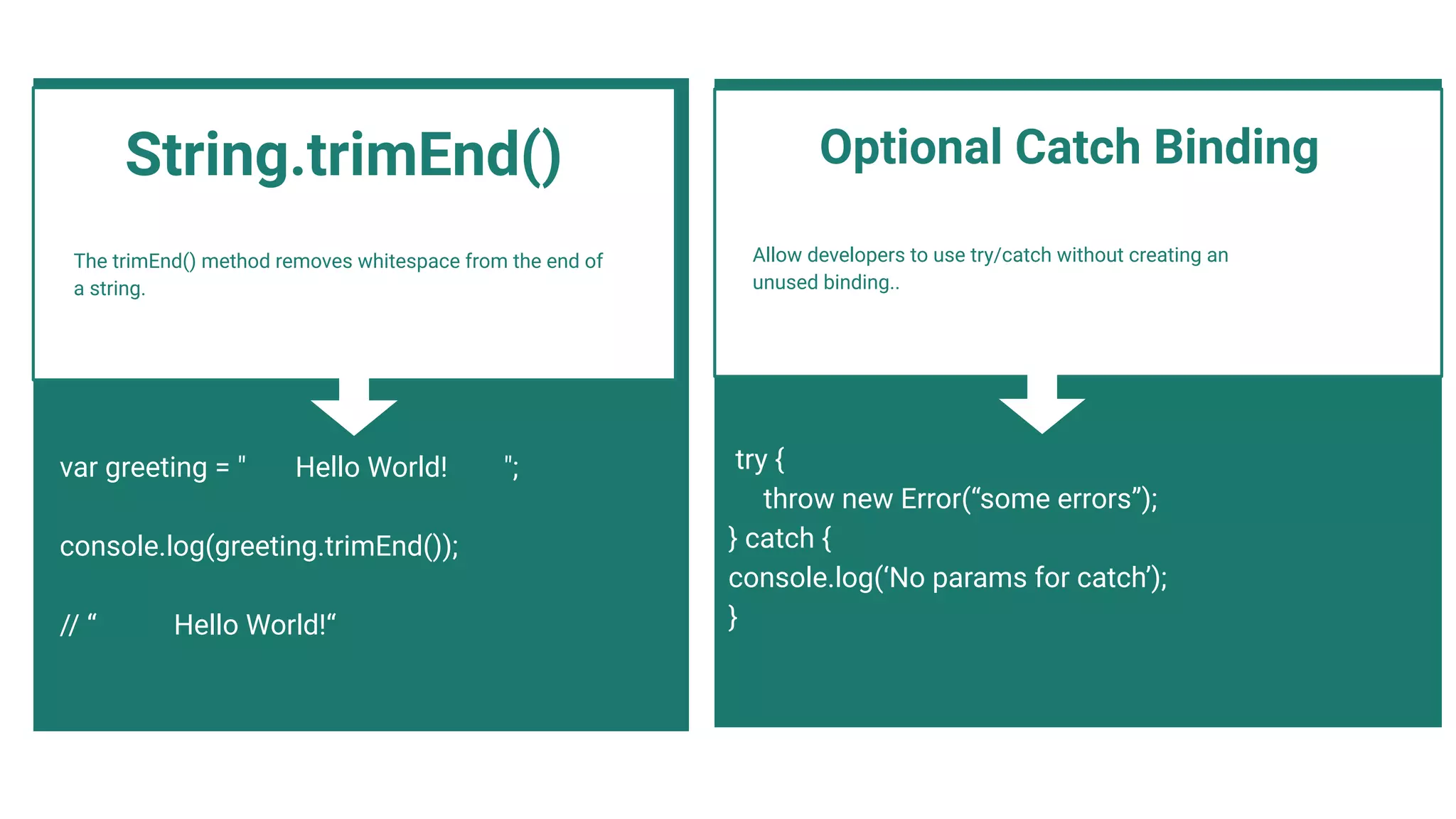
The trimStart() method removes whitespace from the
beginning of a string.
String.trimStart()
var greeting = " Hello World! ";
console.log(greeting.trimStart());
// “Hello World! “
Array.flatMap()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techtalk-191122182637/75/JavaScript-ES10-and-React-Js-Introduction-5-2048.jpg)
![The Object.fromEntries() method transforms a list of
key-value pairs into an object
.
Note: Object.fromEntries only accept iterable (i.e)
Object.fromEntries(iterable)
var entries = new Map([
[‘name’,’aman’],
[‘exp’,’3’]])
Object.fromEntries(entries)
The toString() method returns a string representing the
source code of the function.
Function.toString()
function sayHi(){
console.log(‘say Hi’);
}
console.log(sayHI.toString());
// function sayHI(){
// console.log(‘say Hi’);
// }
Object.fromEntries()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techtalk-191122182637/75/JavaScript-ES10-and-React-Js-Introduction-7-2048.jpg)
![The import(module) expression loads the module and
returns a promise that resolves into a module object that
contains all its exports. It can be called from any place in the
code.
let modulePath = prompt("Which module to load?");
import(modulePath)
.then(obj => <module object>)
.catch(err => <loading error, e.g. if no such
module>)
It returns an iterator instead of array. Iterators on their own
are useful.
It avoids regular expressions with /g flag
string.prototype.matchAll()
// Match all occurrences of the letters: "e" or "l"
let iterator = "hello".matchAll(/[el]/);
for (const match of iterator)
console.log(match);
Dynamic import](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techtalk-191122182637/75/JavaScript-ES10-and-React-Js-Introduction-8-2048.jpg)