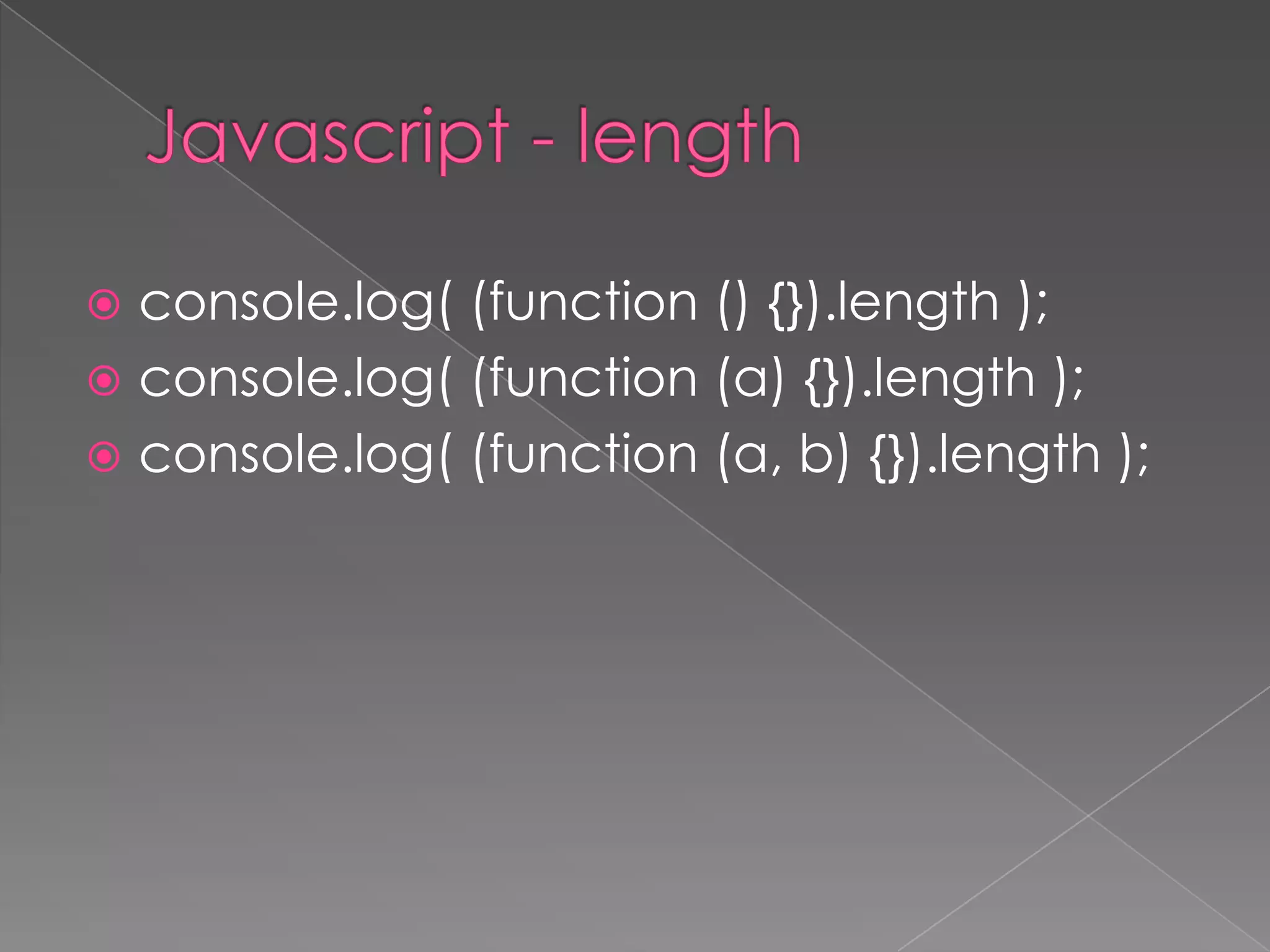
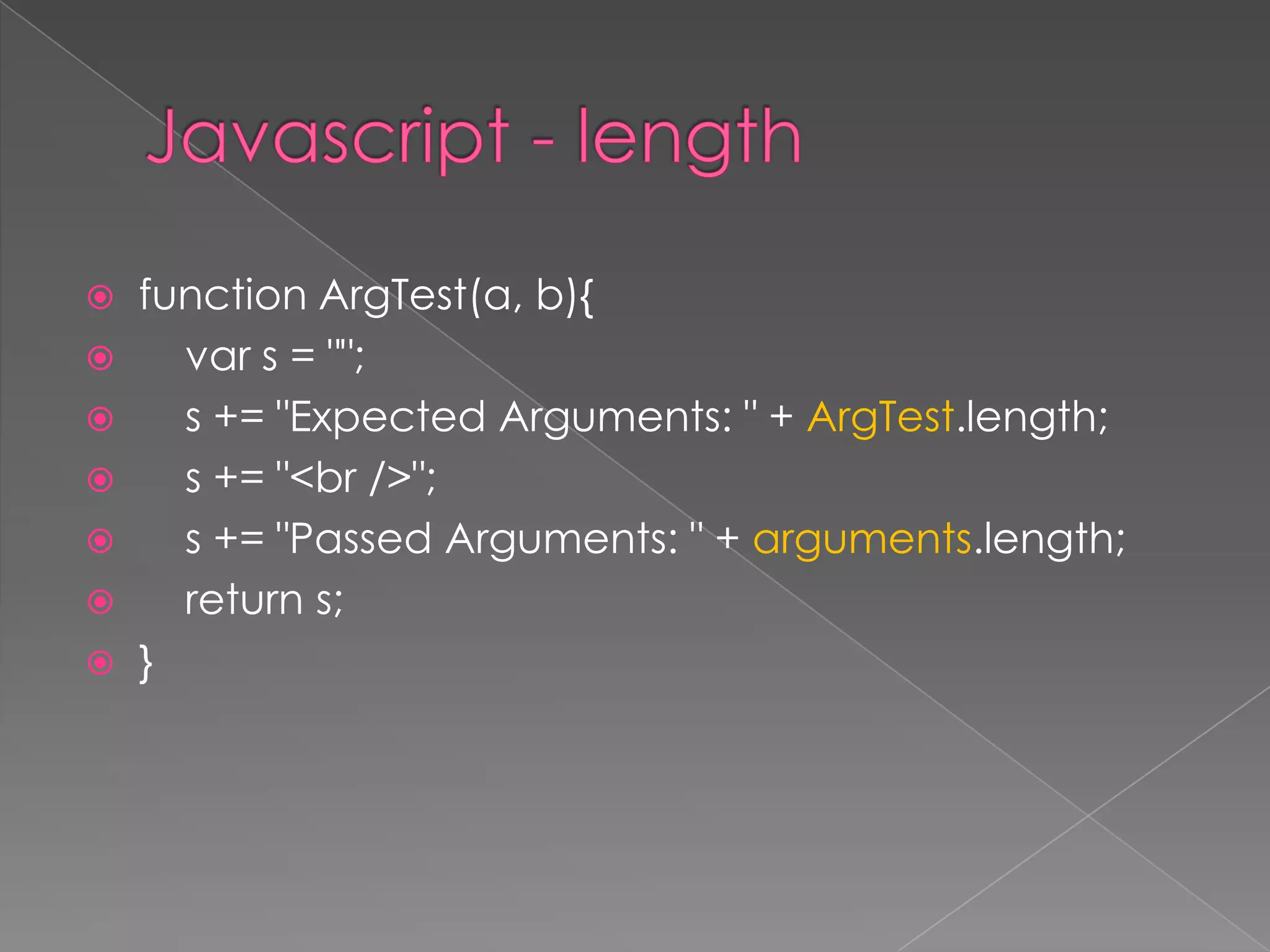
This document discusses JavaScript functions and function methods. It explains function.length to get the number of expected arguments, .call() and .apply() to call a function with a set this value and arguments, arguments.callee to access the currently executing function, .bind() to set the this value and bind arguments when calling a function. Examples are given to demonstrate these function methods.


![ Calls a function with a given this value and
arguments provided individually.
Syntax
› fun.call(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunction-130805062154-phpapp01/75/Javascript-function-5-2048.jpg)

![ Calls a function with a given this value
and arguments provided as an array
Syntax
› fun.apply(thisArg[, argsArray])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunction-130805062154-phpapp01/75/Javascript-function-7-2048.jpg)
![ function diplayInfo(year, month, day){
return "Name:" + this.name + ";birthday:" + year +
"." + month + "." + day;
}
var p = { name: "Jason" };
console.log(diplayInfo.apply(p, [1985, 11, 5]));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunction-130805062154-phpapp01/75/Javascript-function-8-2048.jpg)
![ Specifies the currently executing function
callee is a property of the arguments object.
Syntax
› [function.]arguments.callee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunction-130805062154-phpapp01/75/Javascript-function-9-2048.jpg)

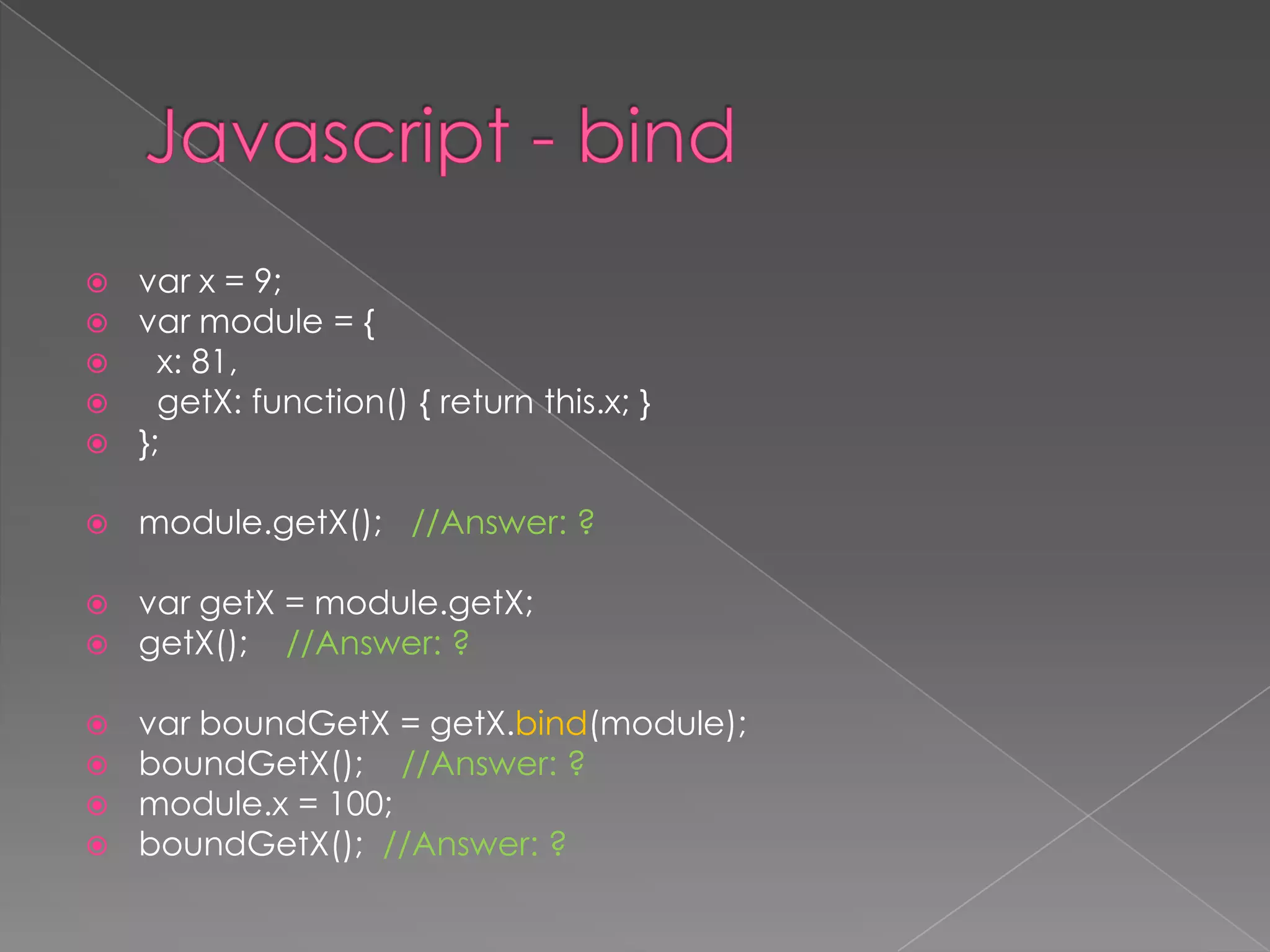
![ Creates a new function that, when
called, has its this keyword set to the
provided value, with a given sequence
of arguments preceding any provided
when the new function is called.
Syntax
fun.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptfunction-130805062154-phpapp01/75/Javascript-function-11-2048.jpg)