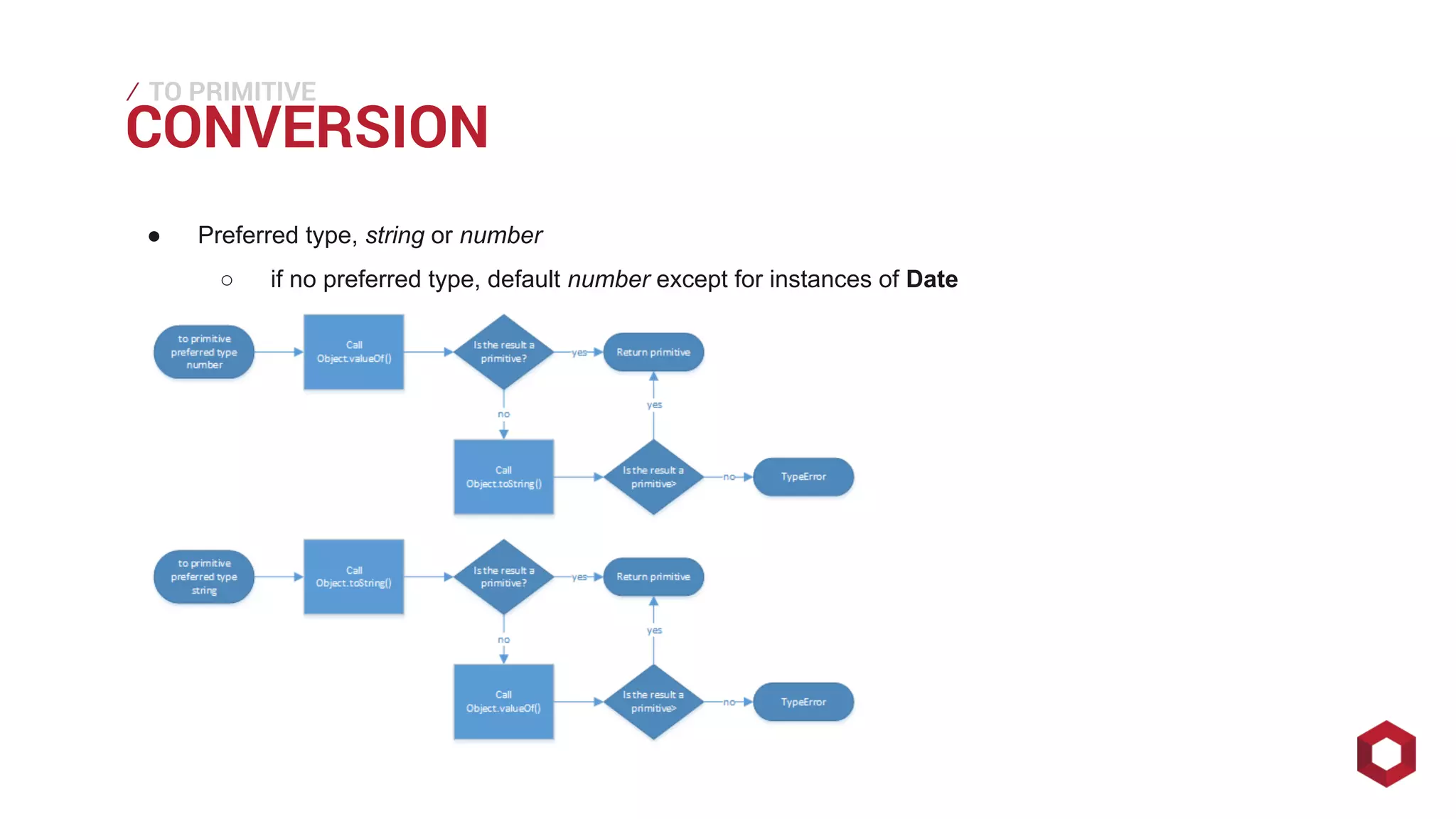
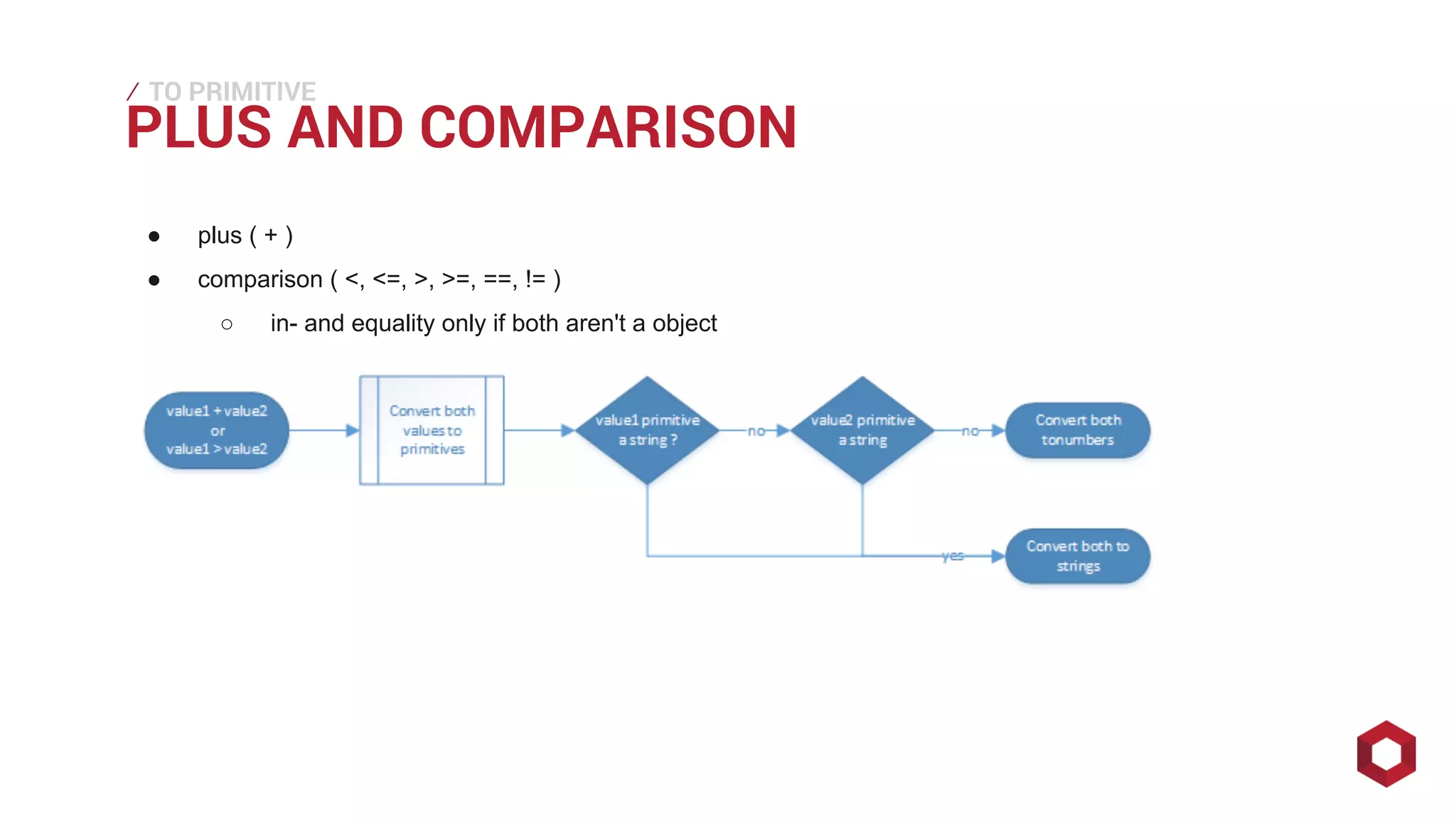
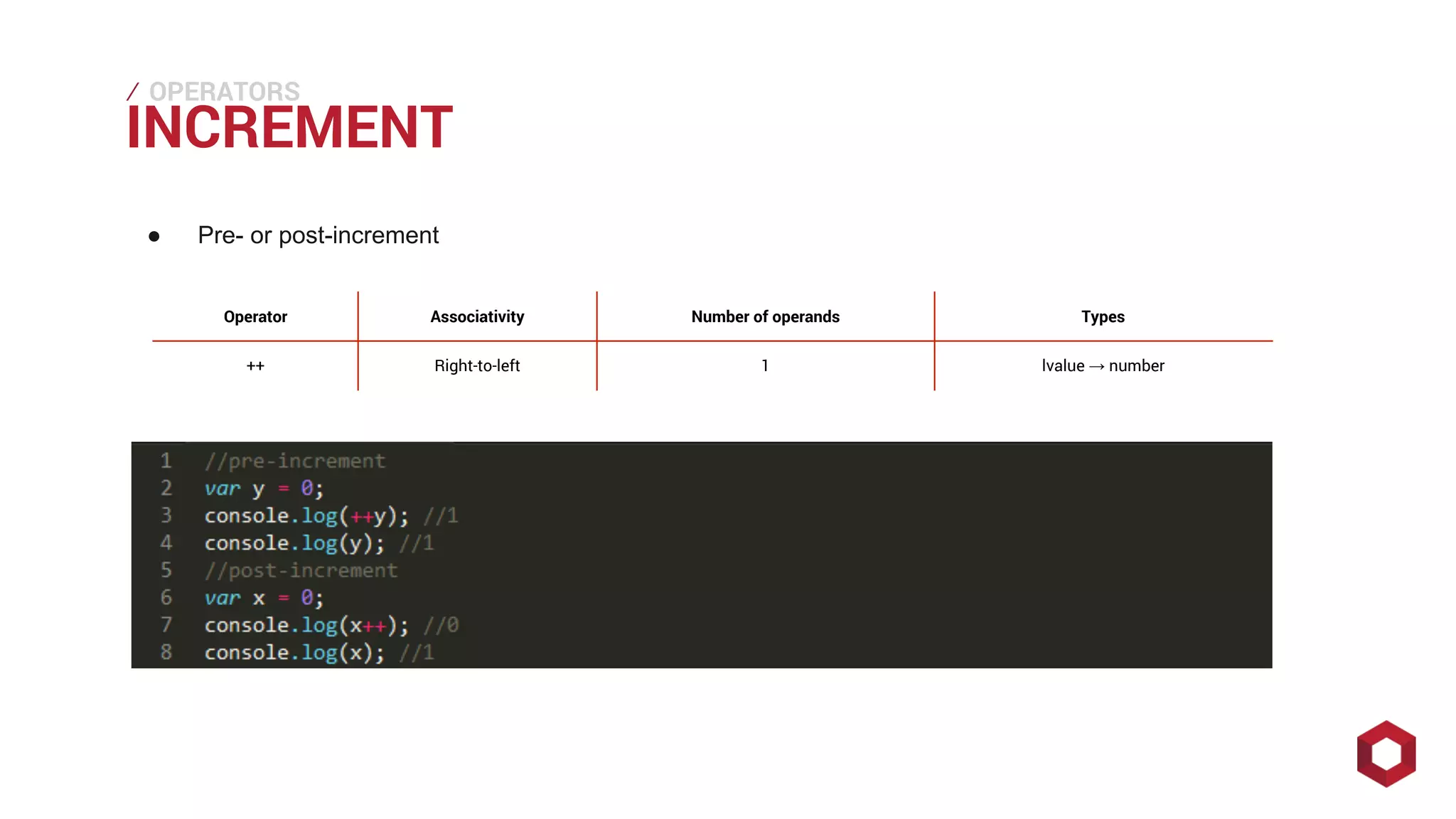
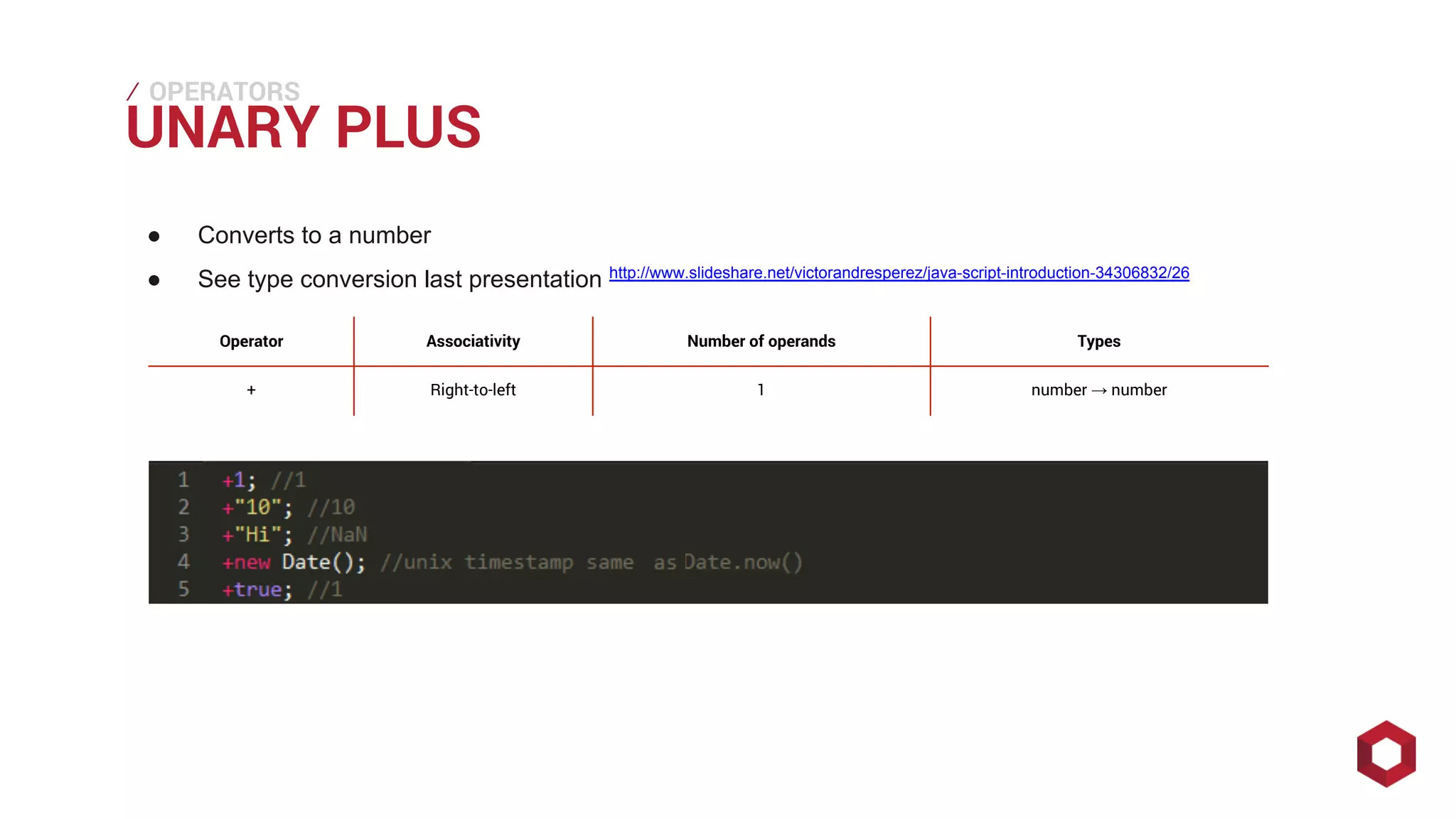
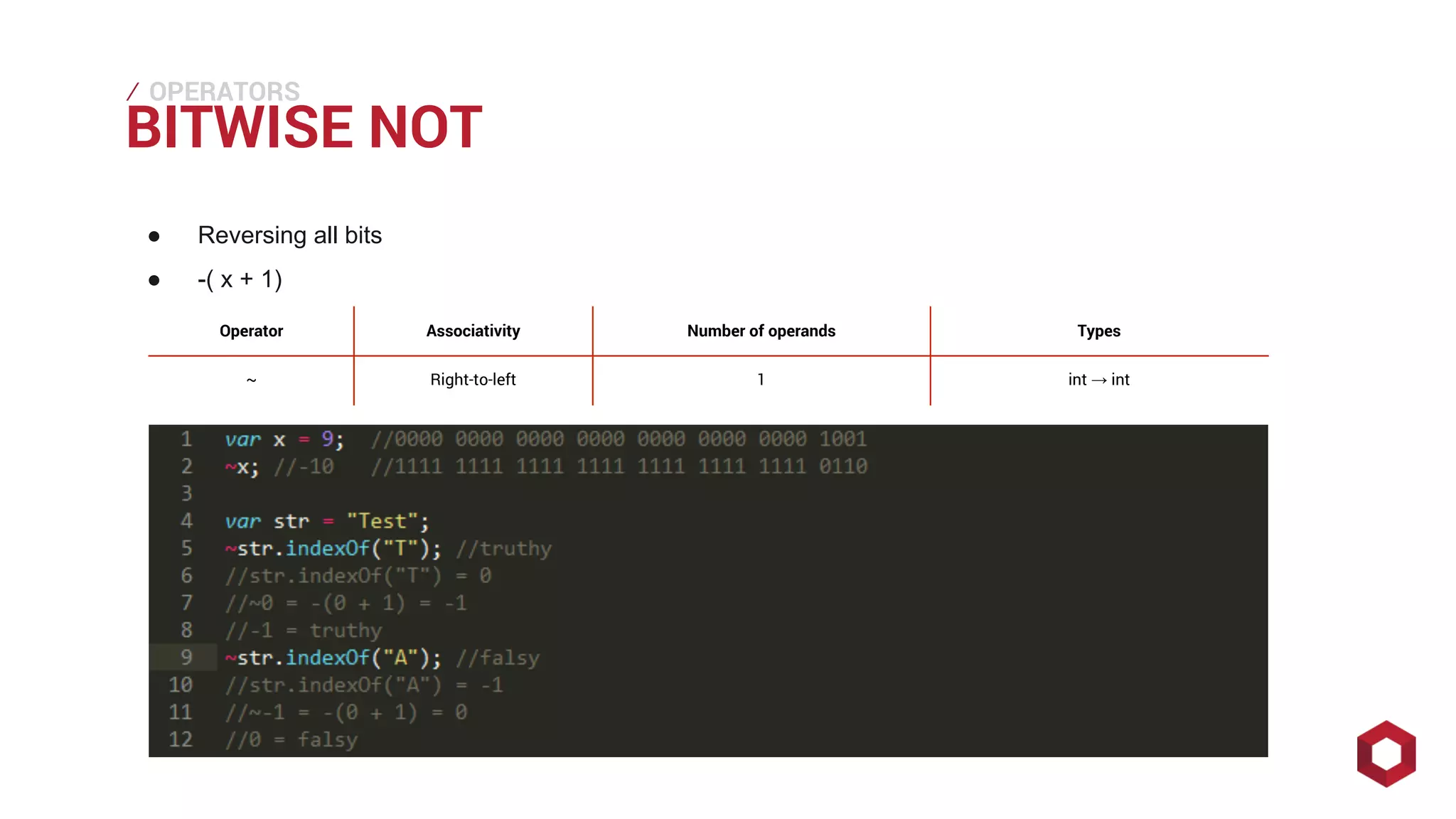
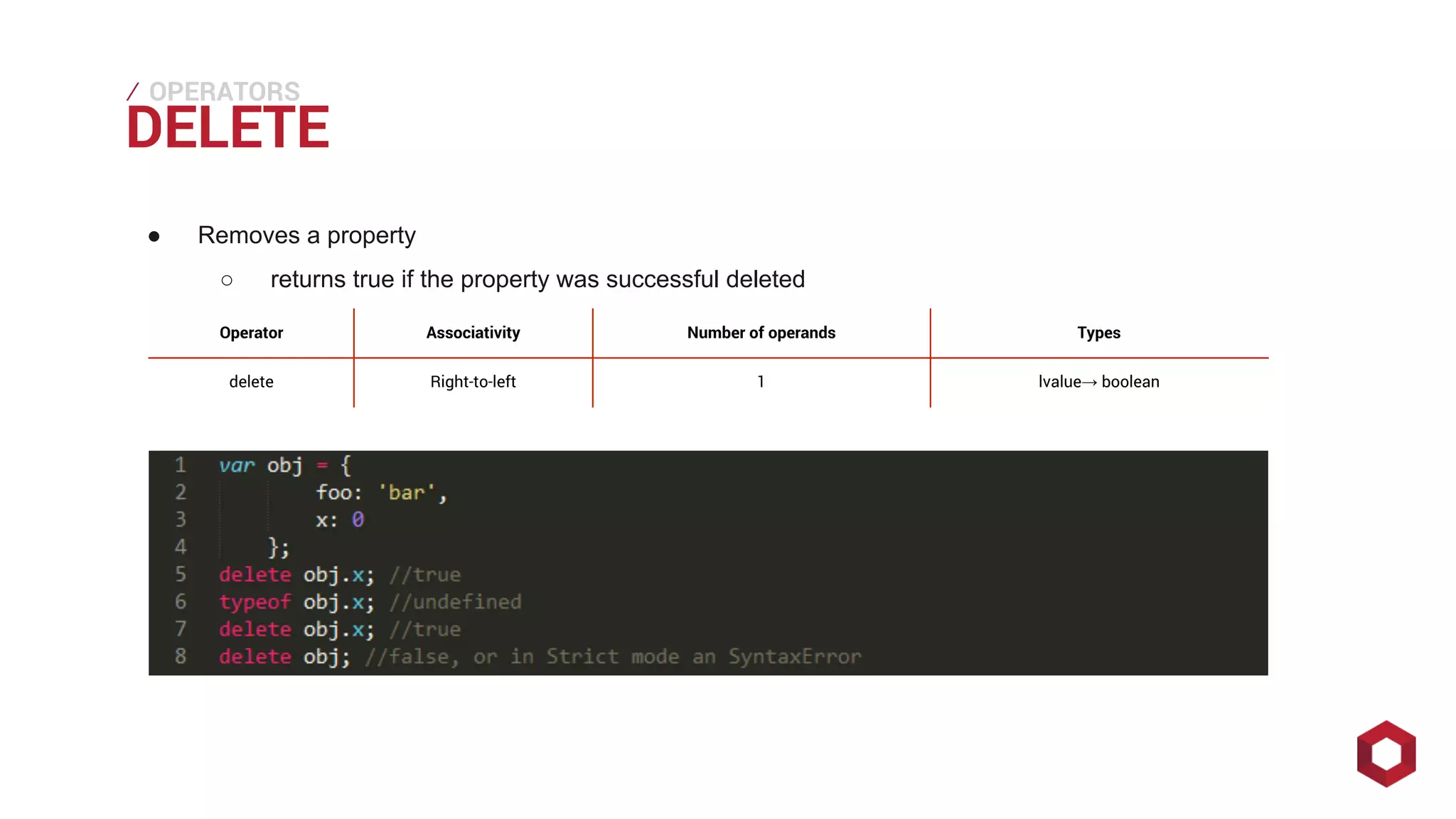
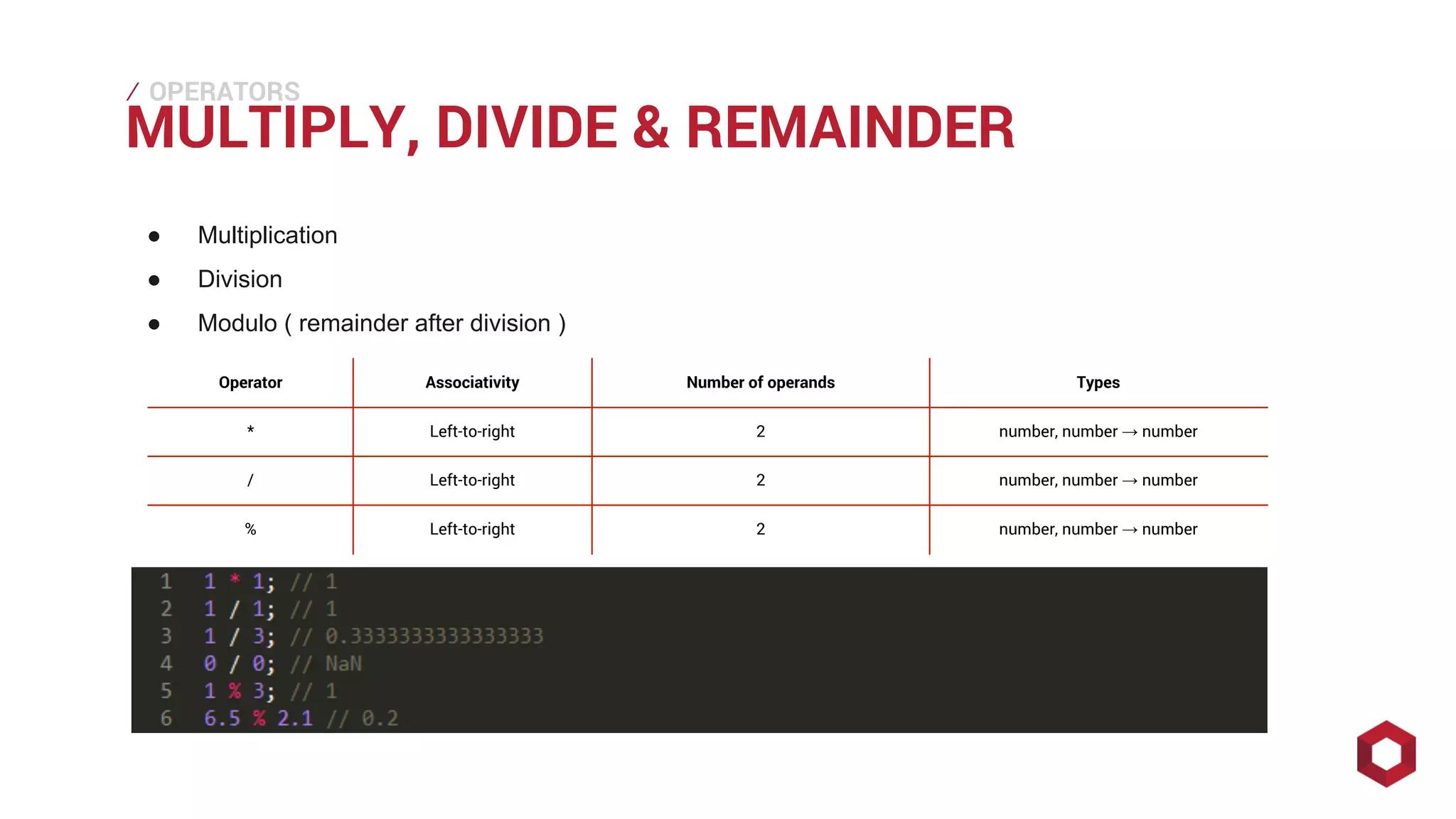
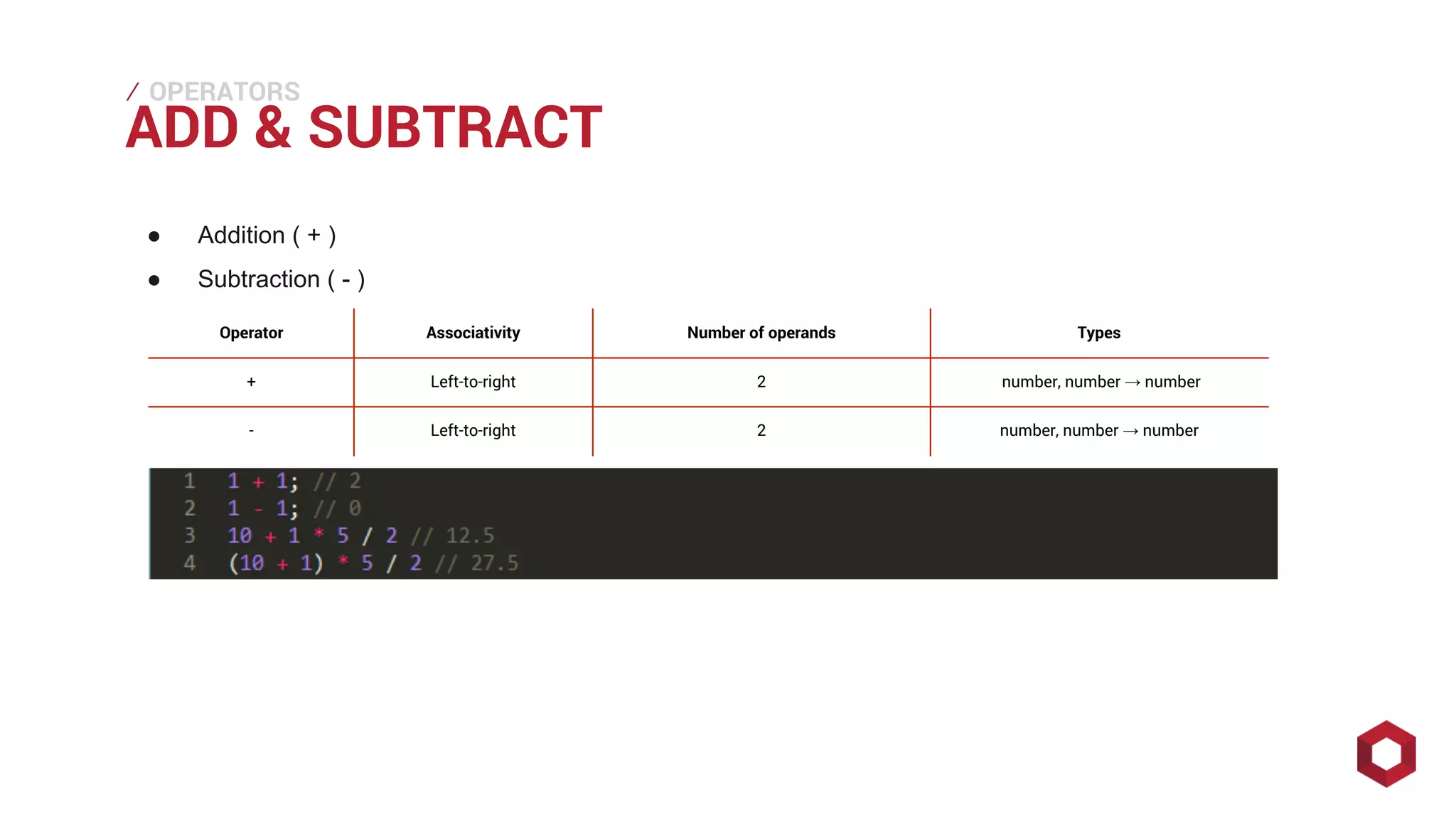
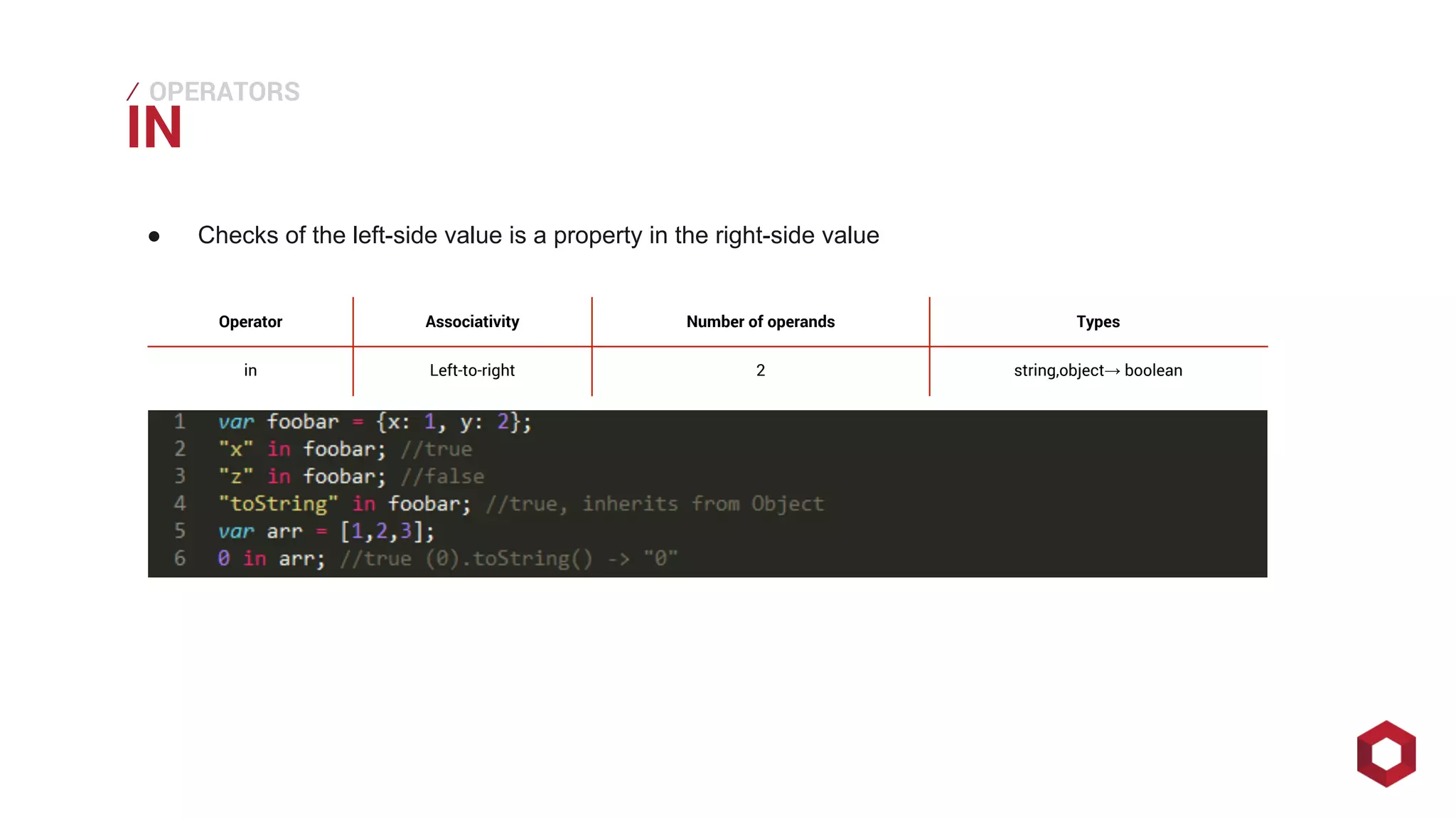
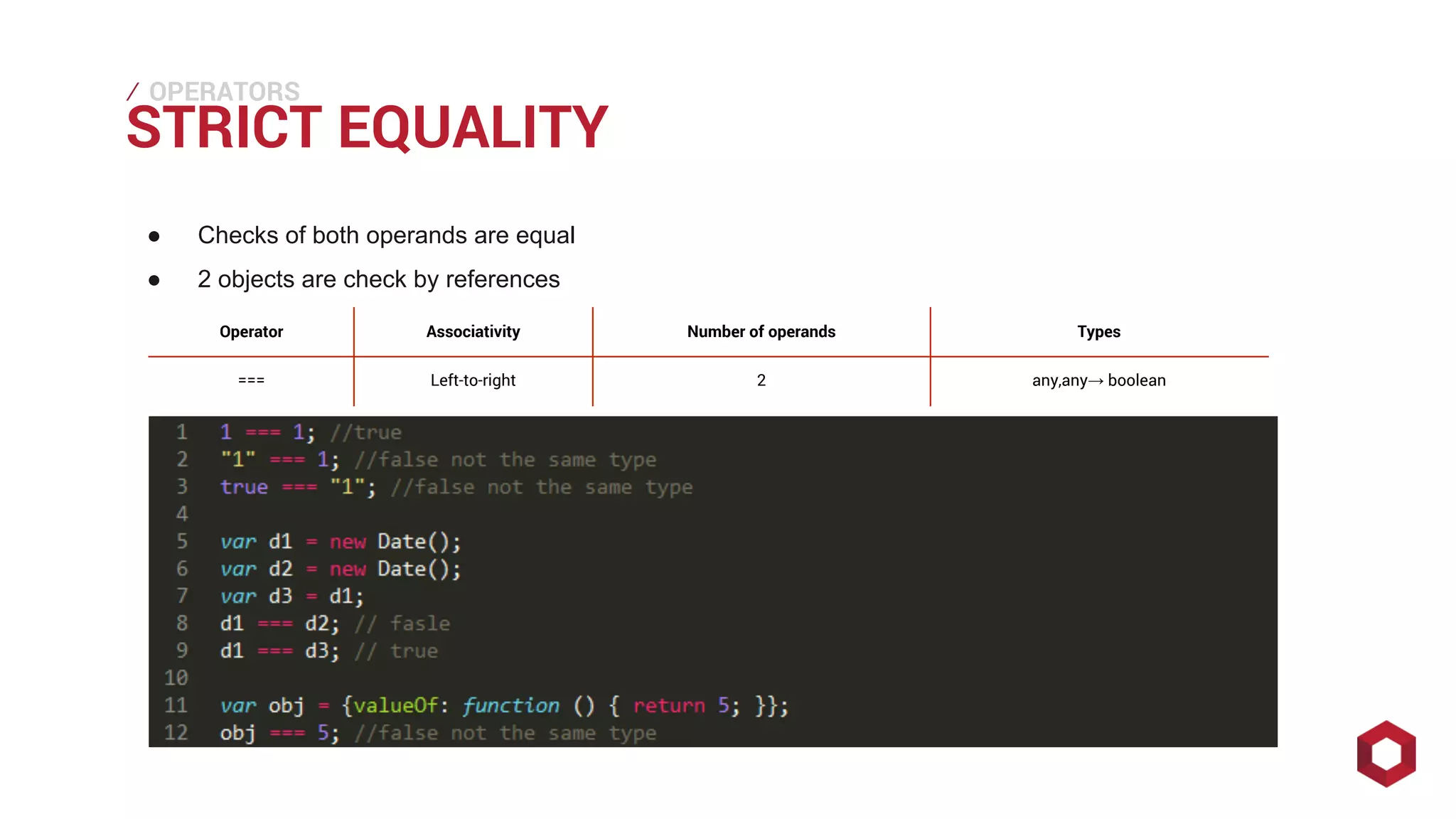
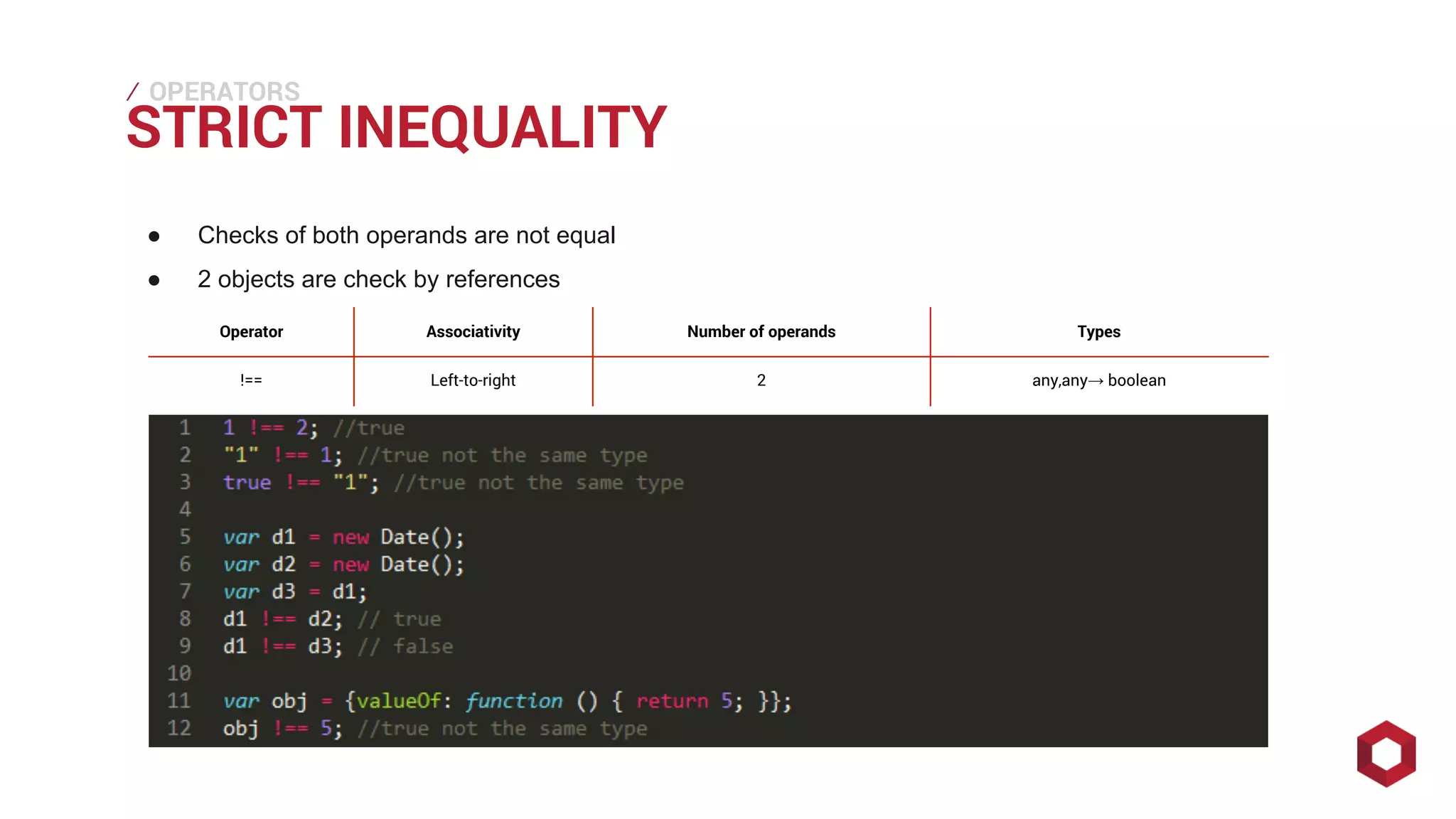
This document discusses JavaScript operators. It covers unary, binary, and ternary operators. It describes each operator's associativity, number of operands, and operand and result types. Common operators covered include arithmetic, comparison, logical, bitwise, assignment, and more.