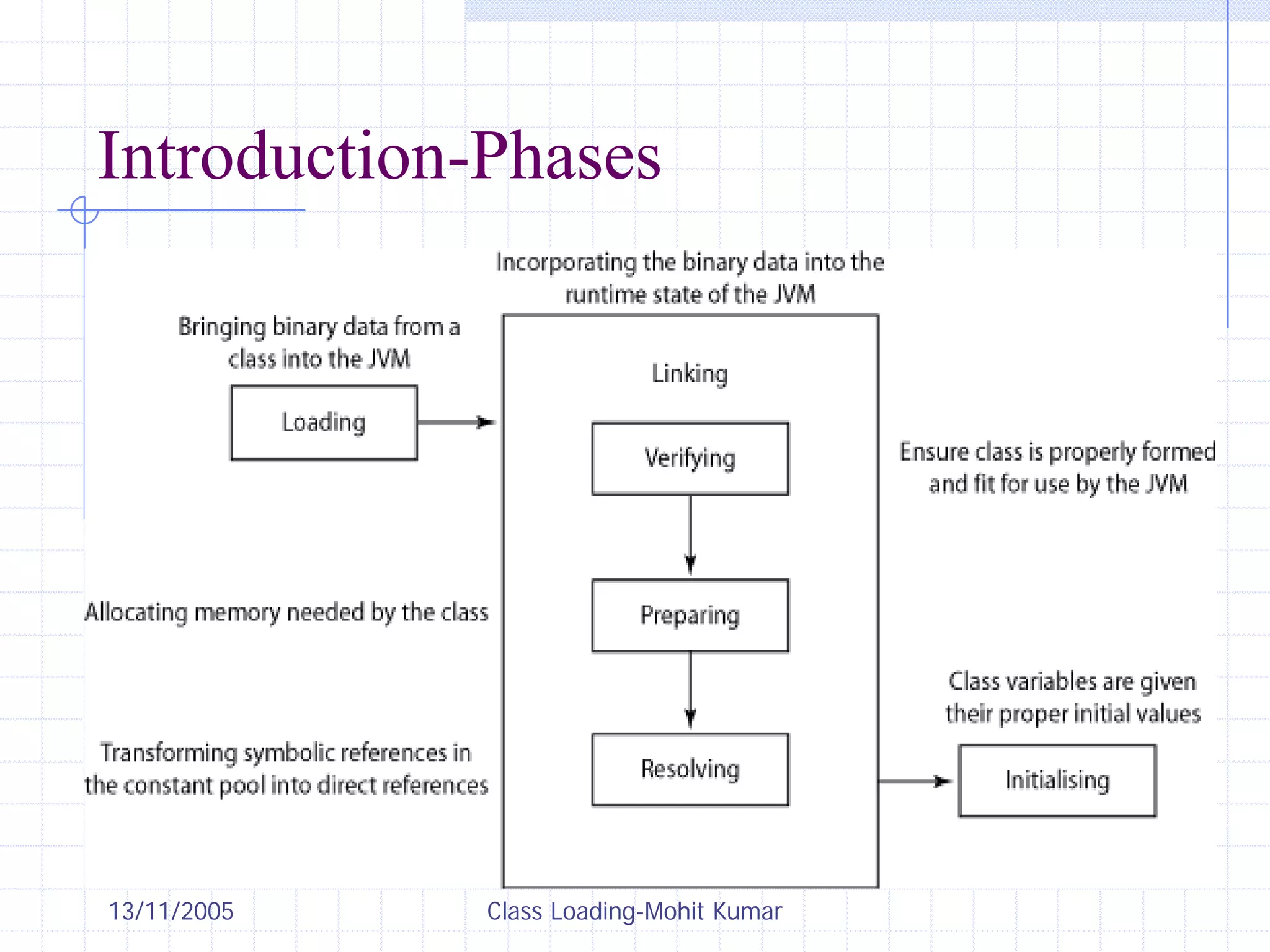
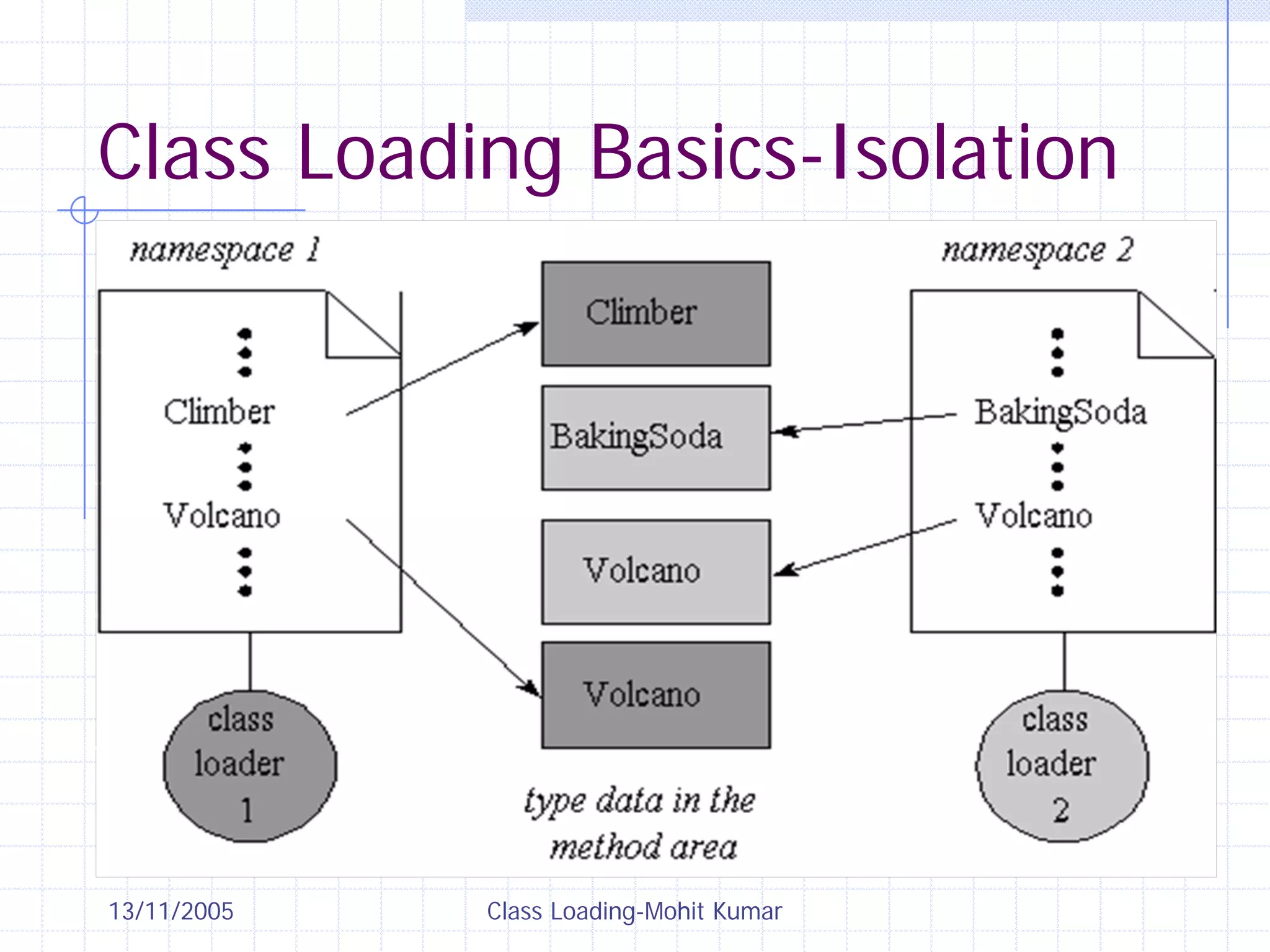
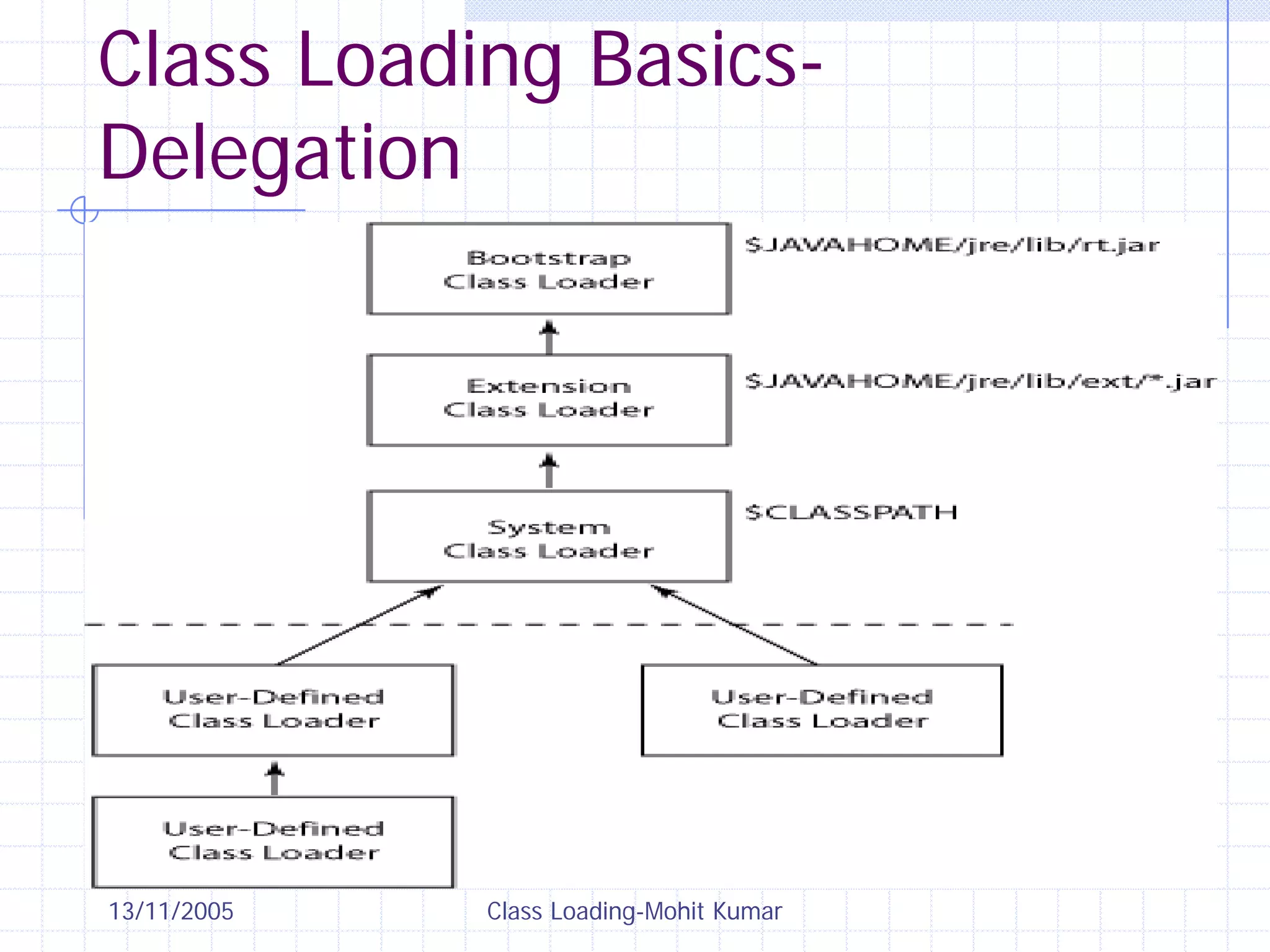
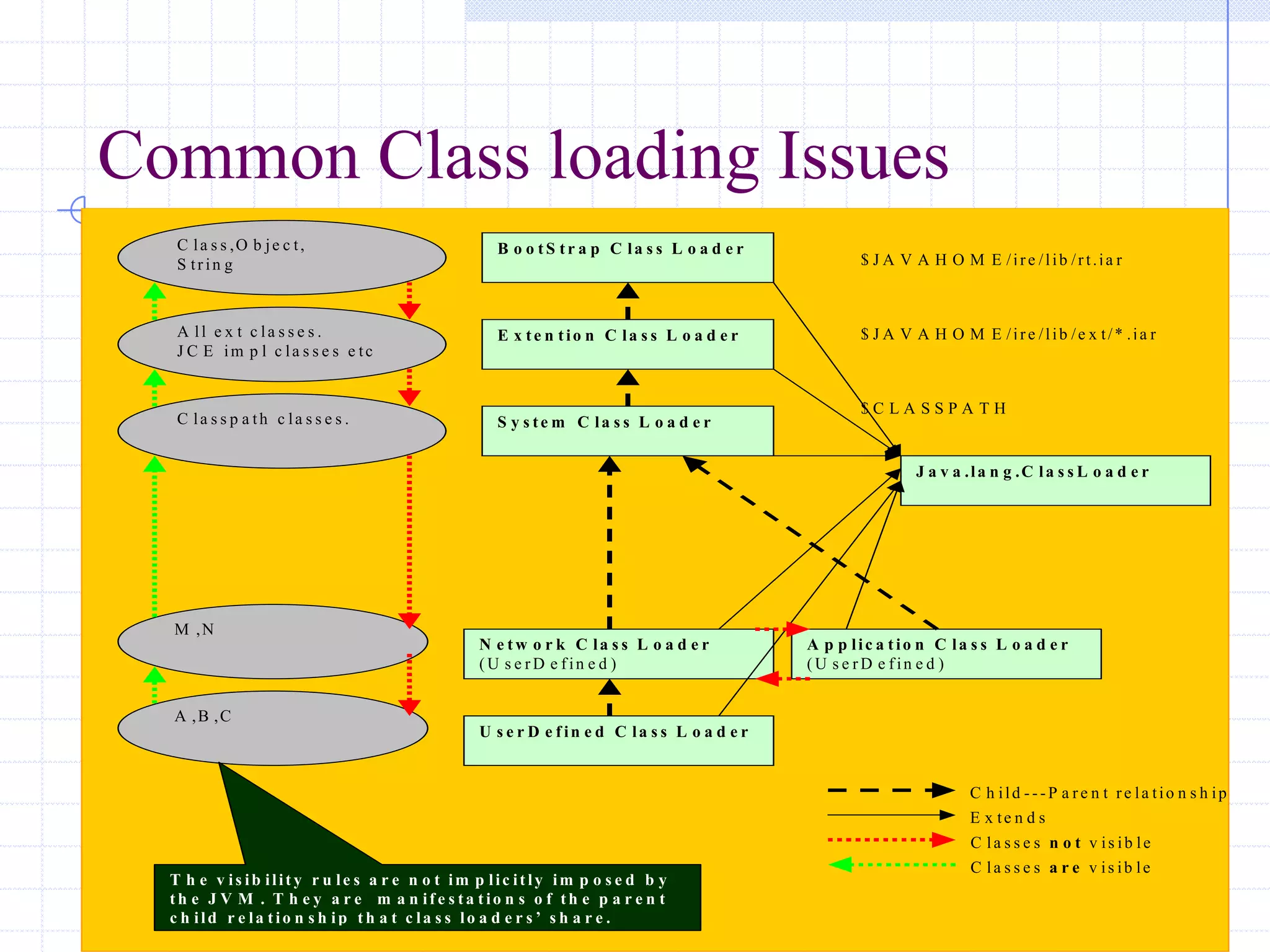
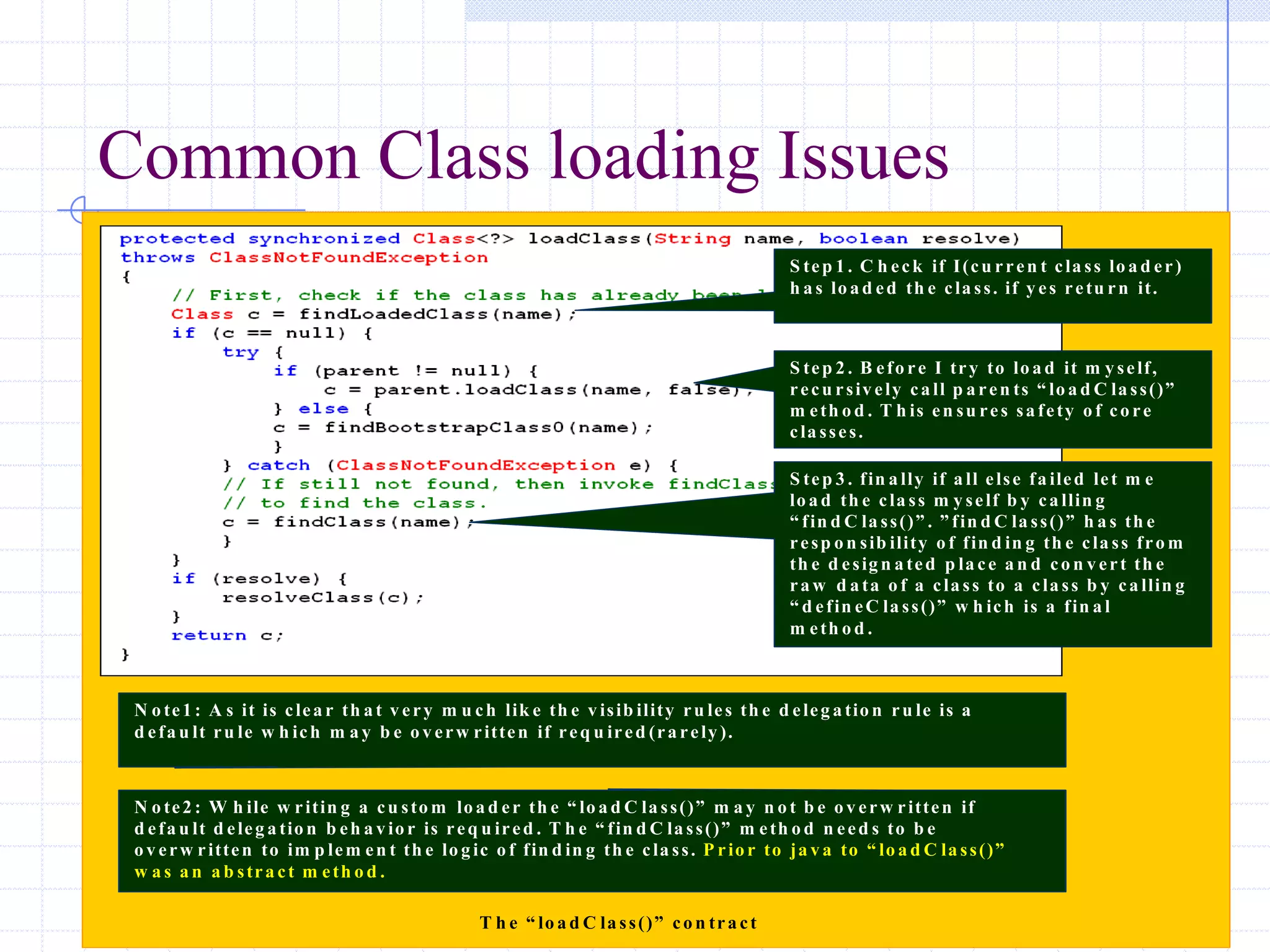
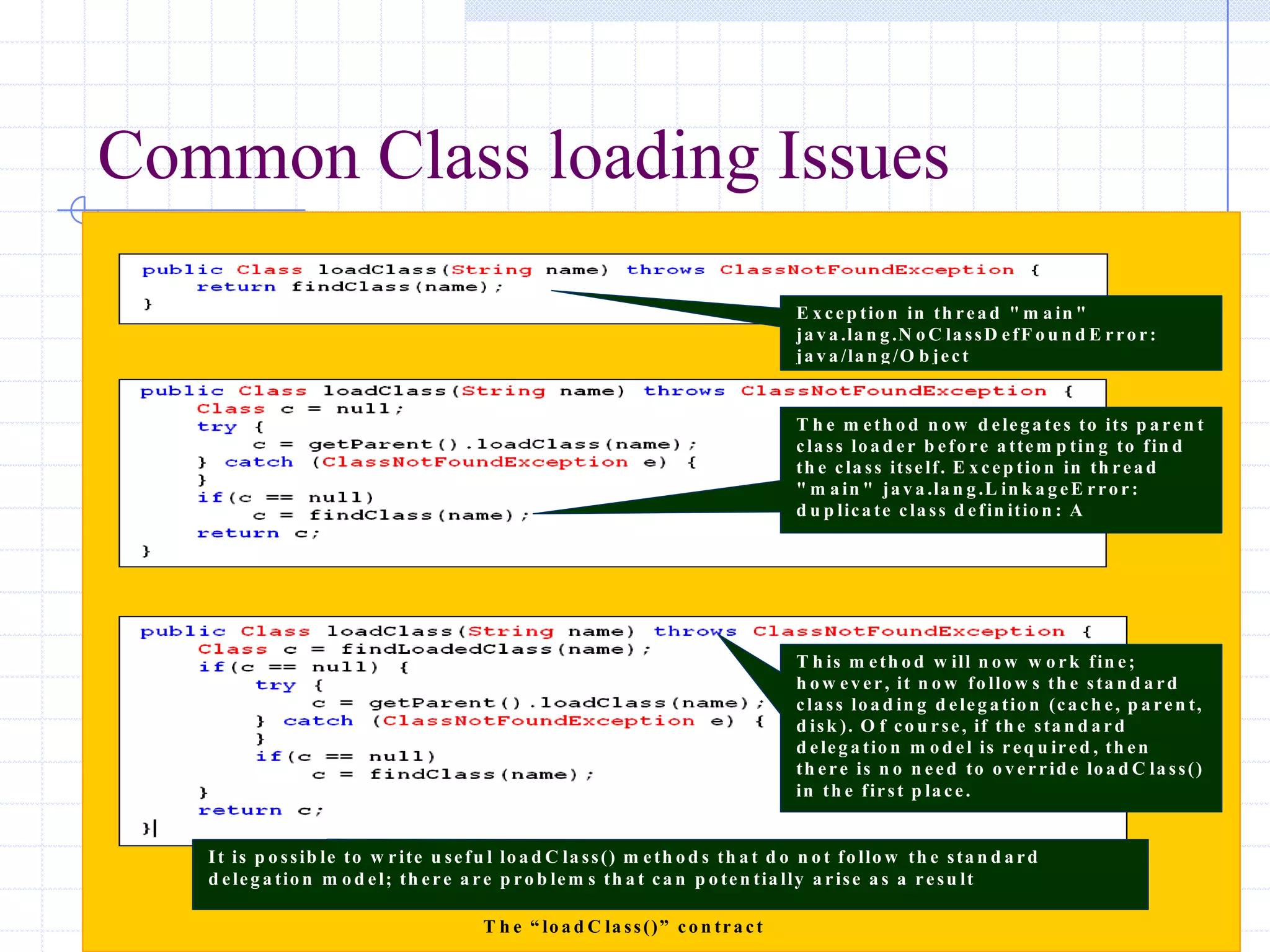
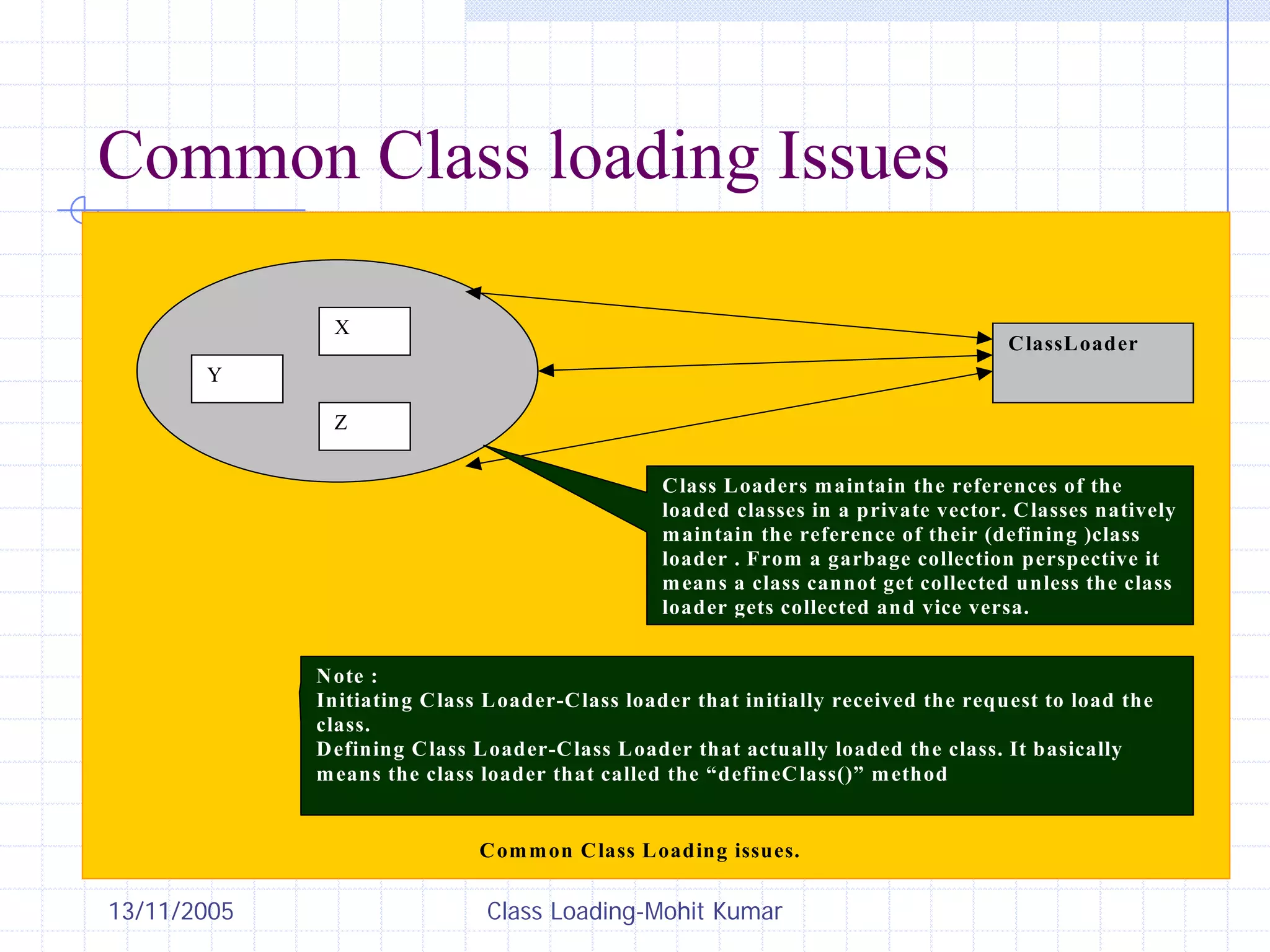
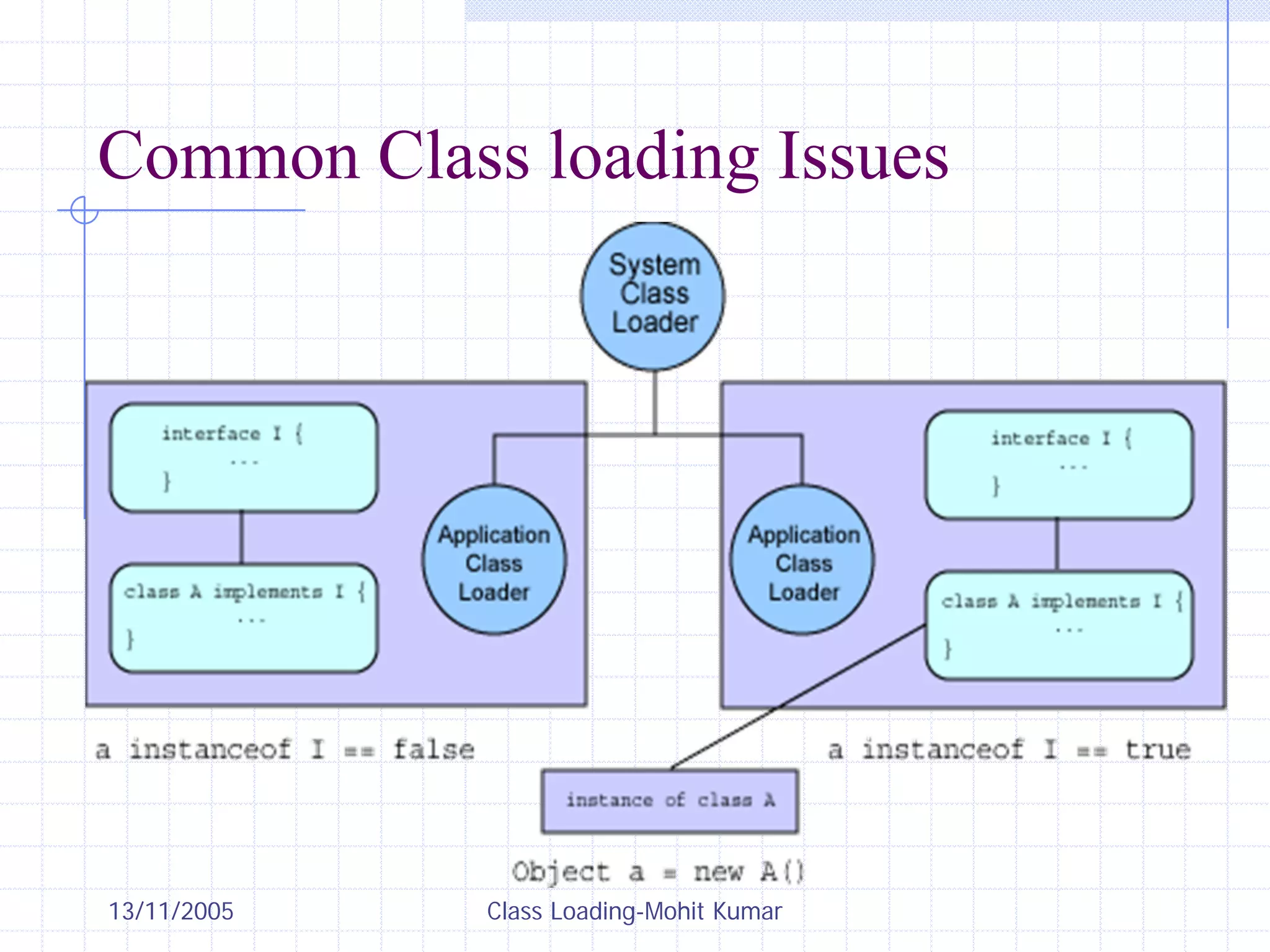
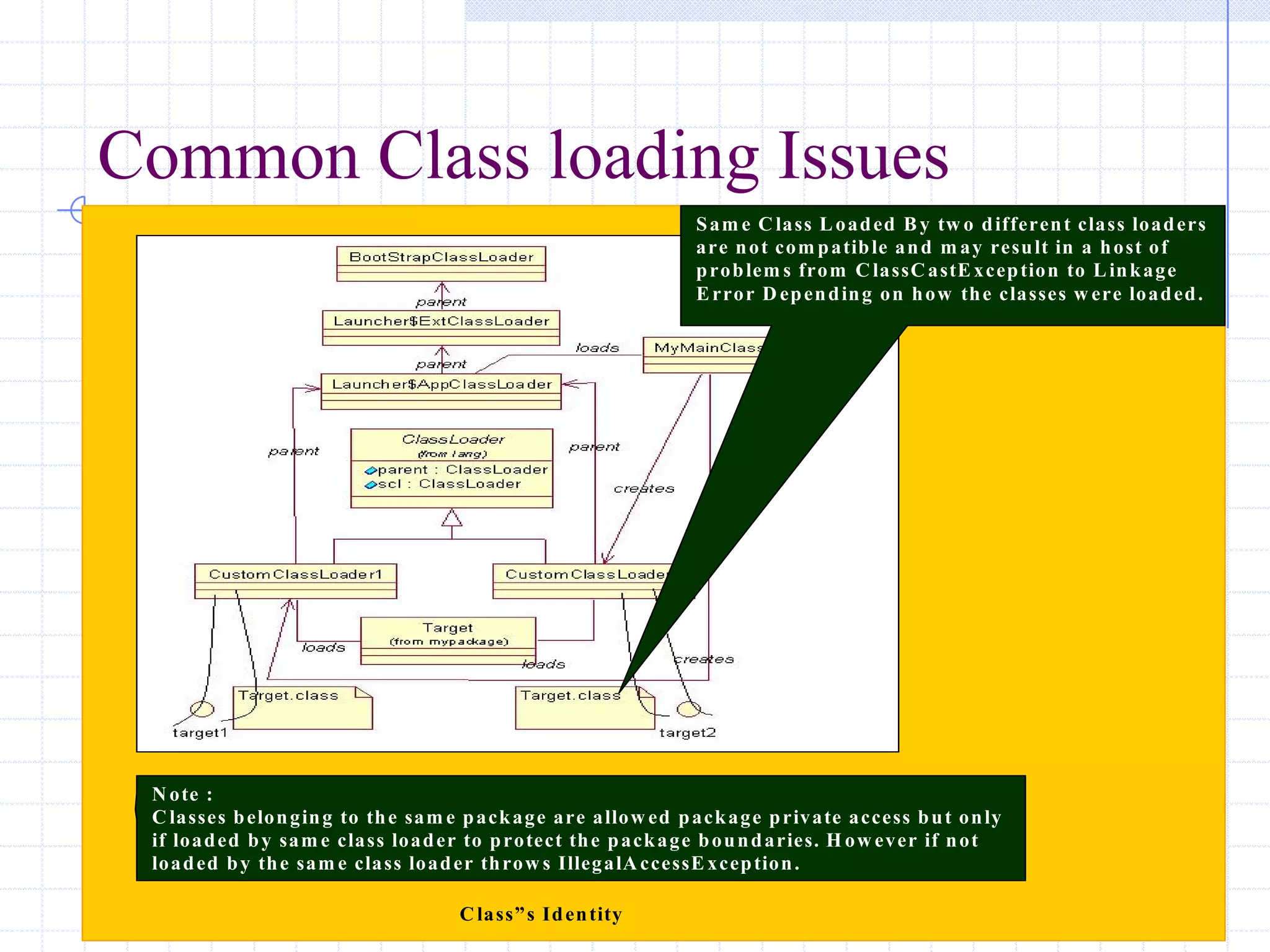
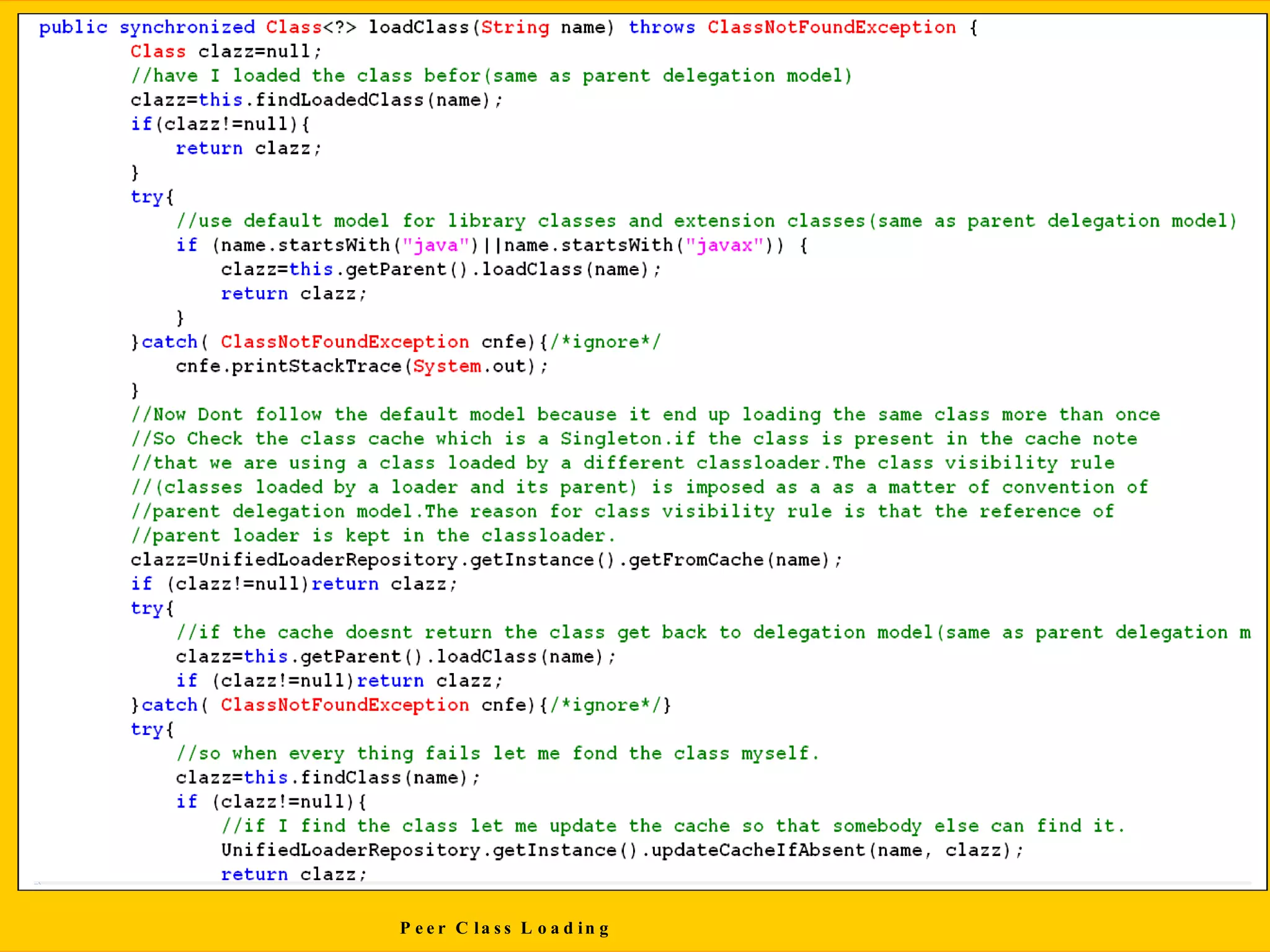
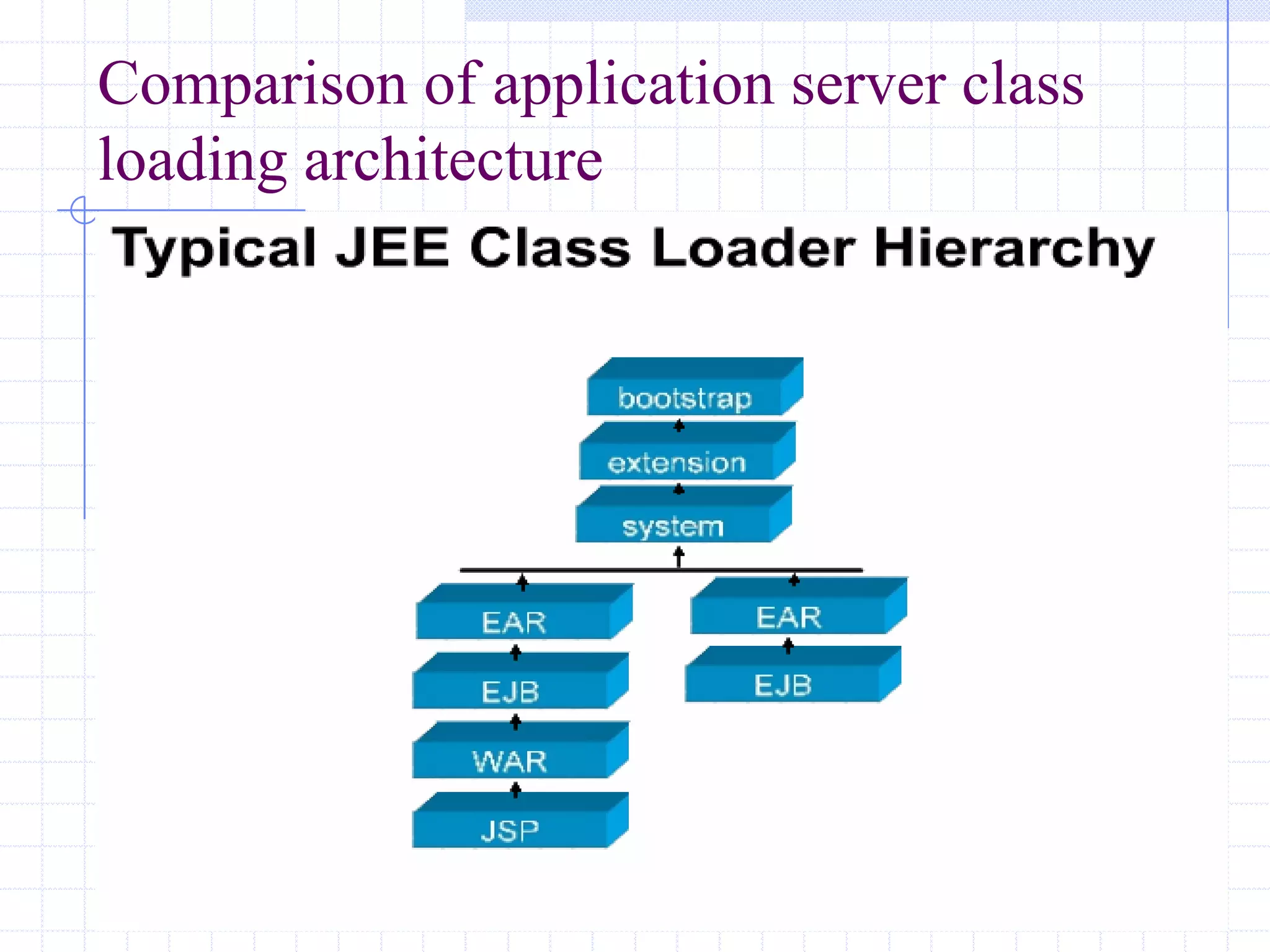
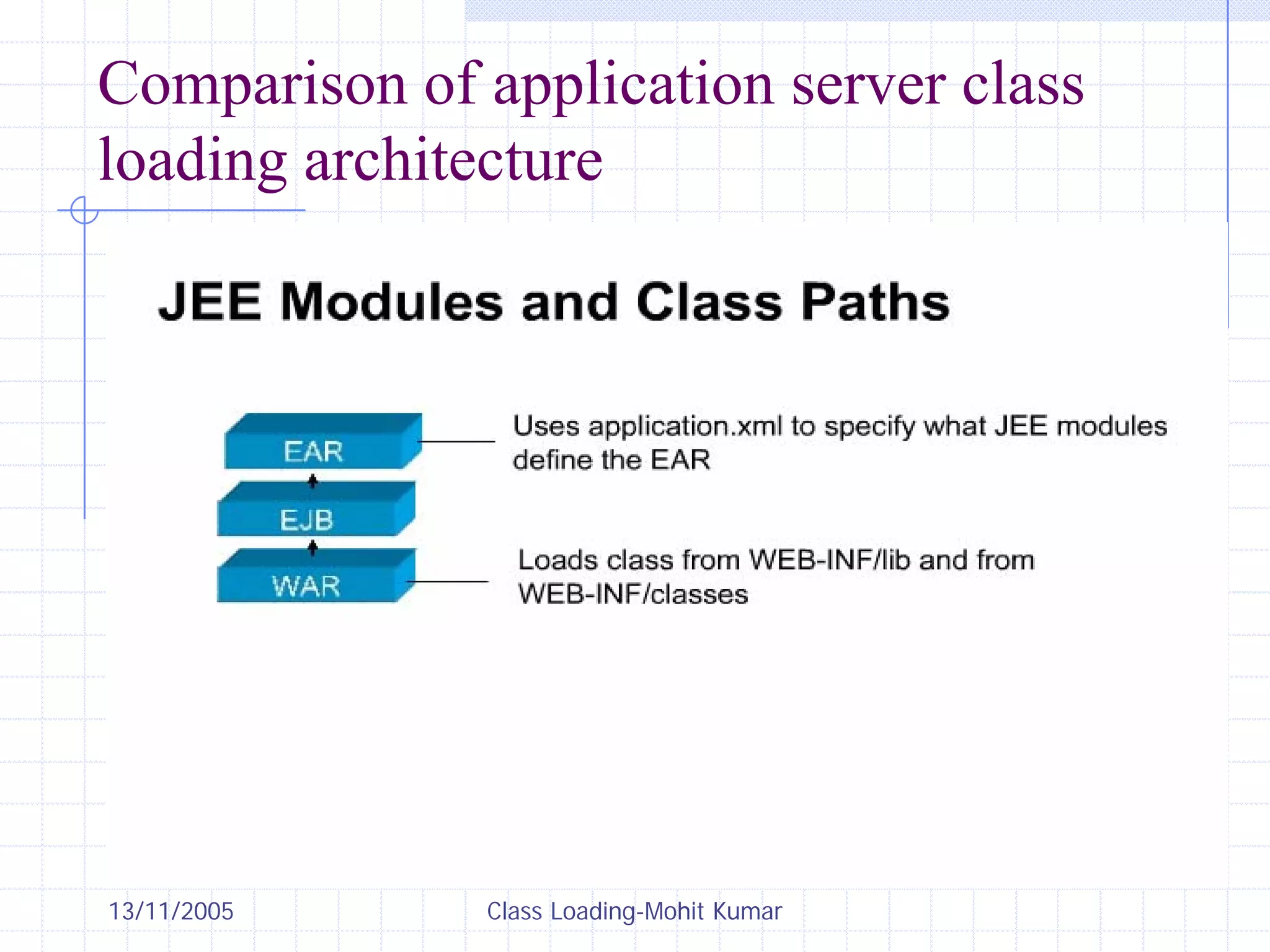
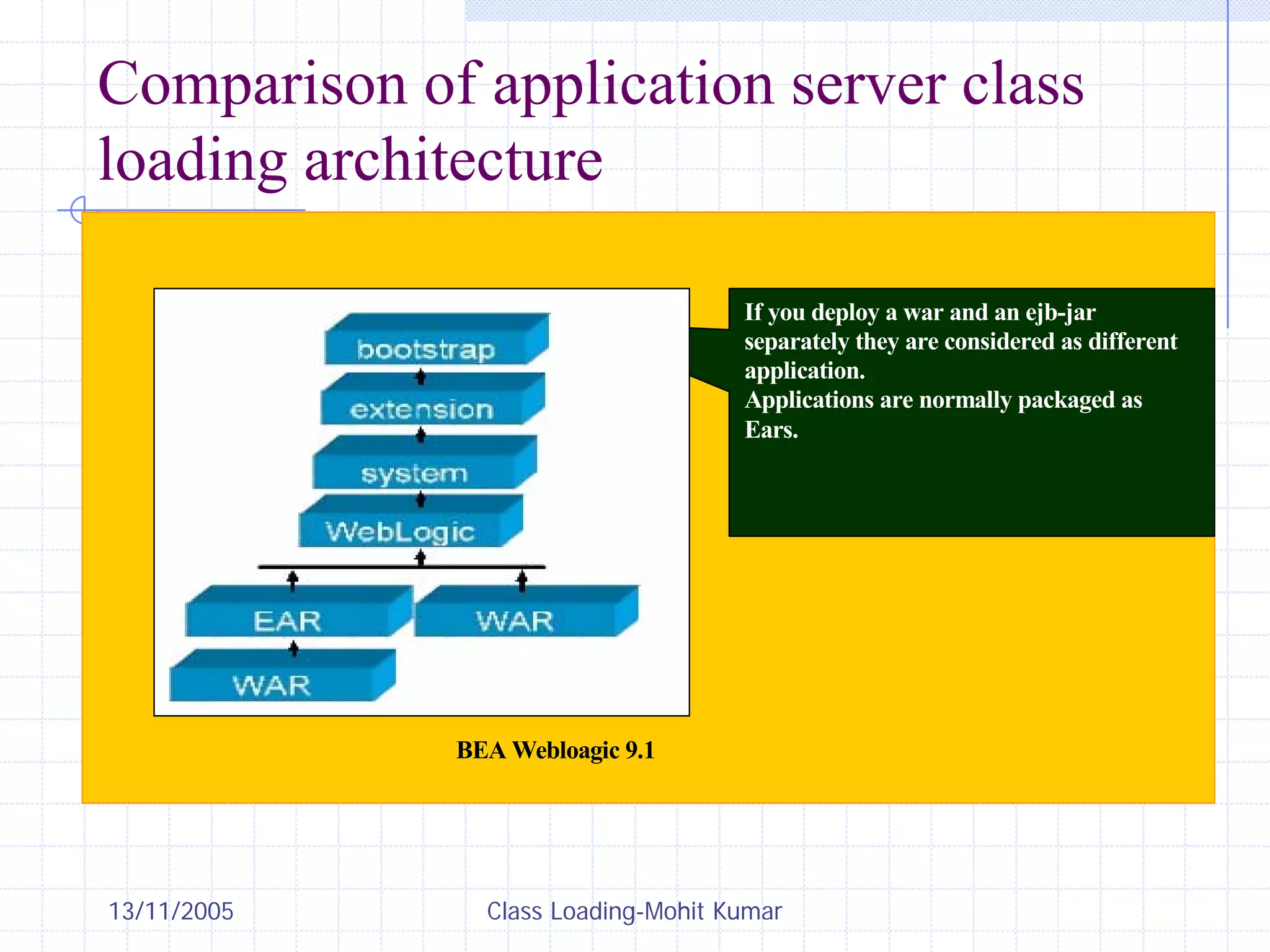
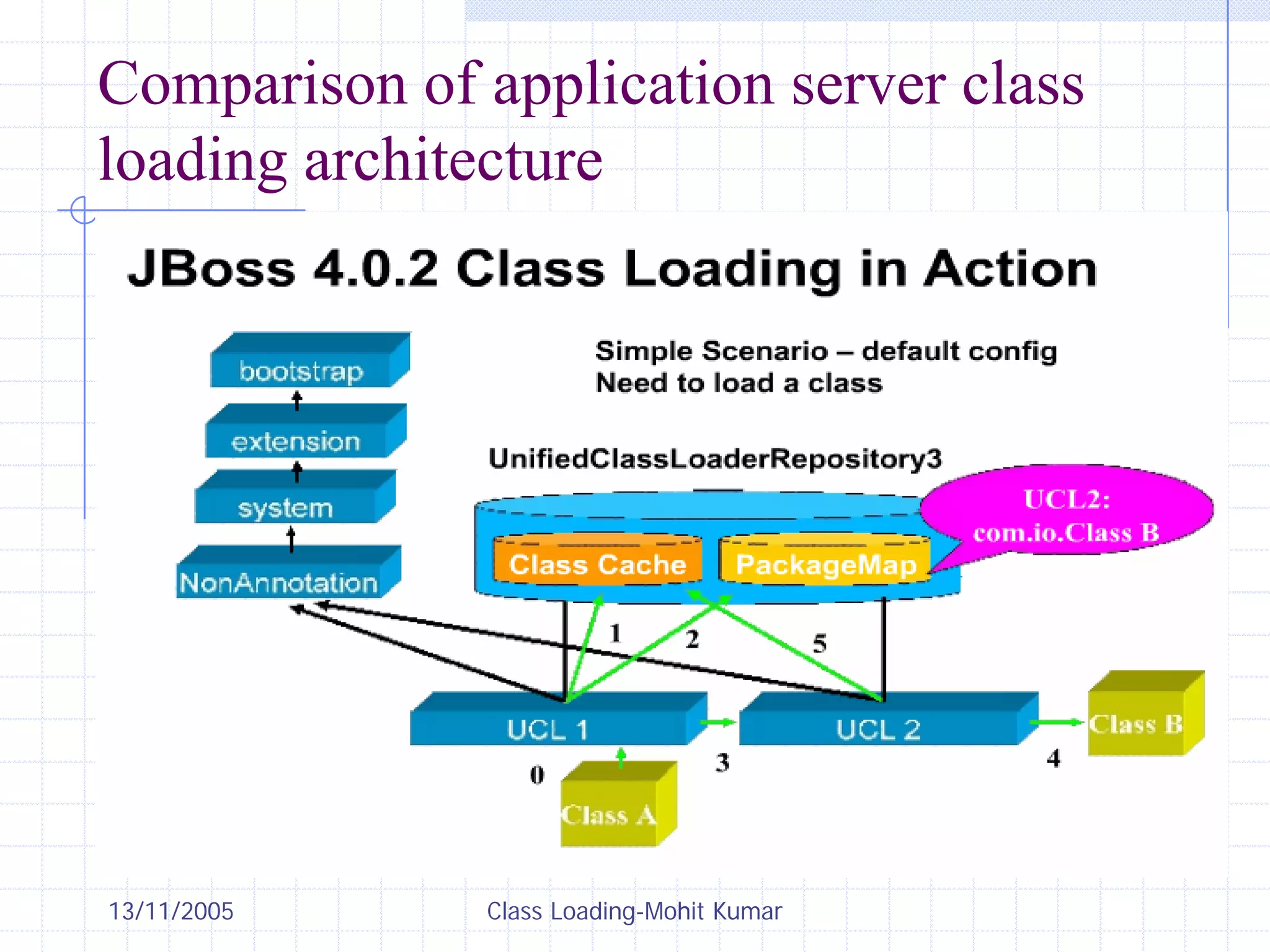
This document discusses Java class loading, including the phases of class loading, class loading basics like isolation and delegation, common class loading issues, diagnosing class loading problems, and peer class loading. It provides details on the loading, linking, and initialization phases, how class loaders maintain class references, issues that can arise from having the same class loaded by multiple class loaders, and common errors like ClassFormatError and UnsatisfiedLinkError. Peer class loading is introduced as an alternative to the standard delegation model.