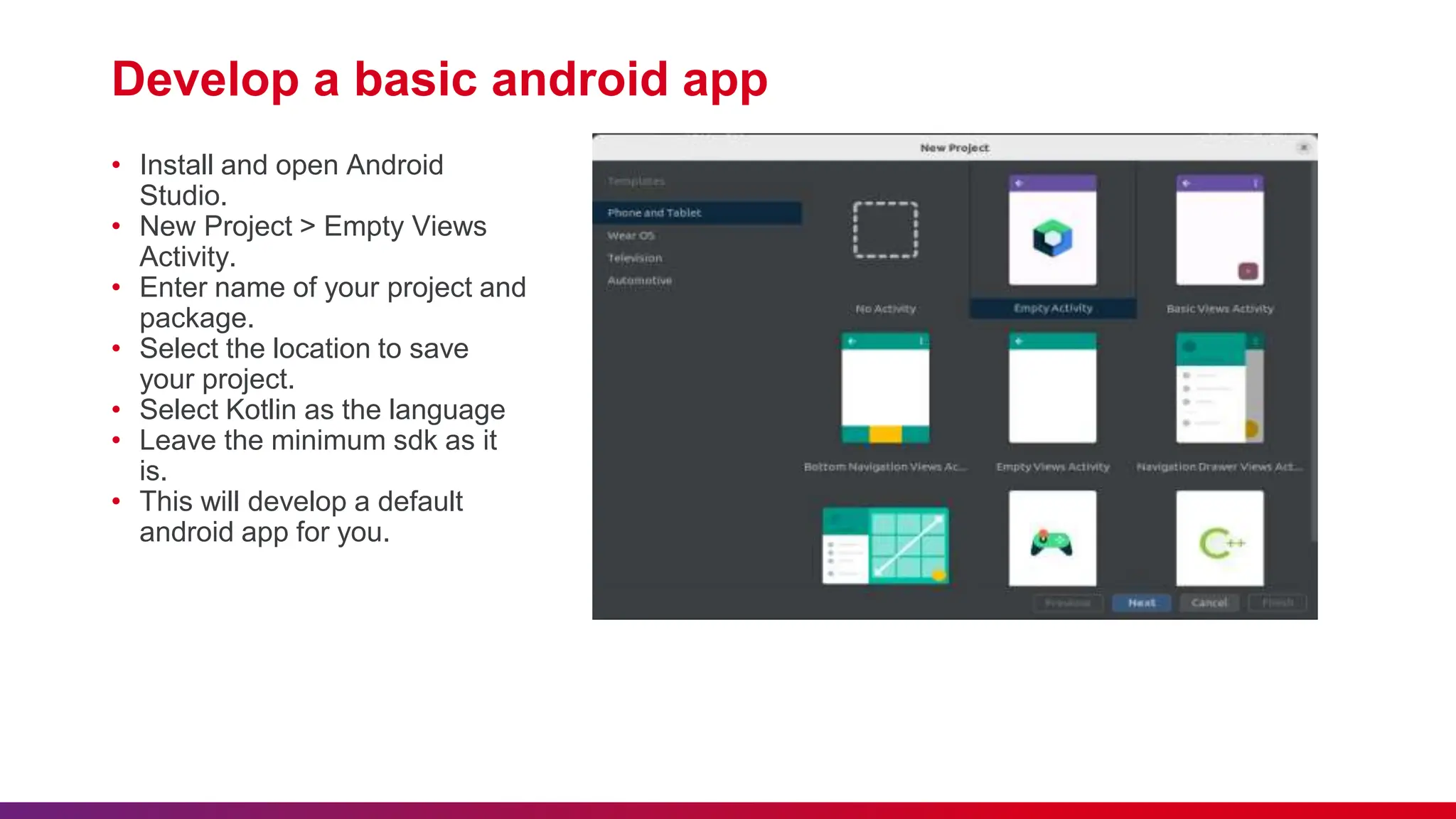
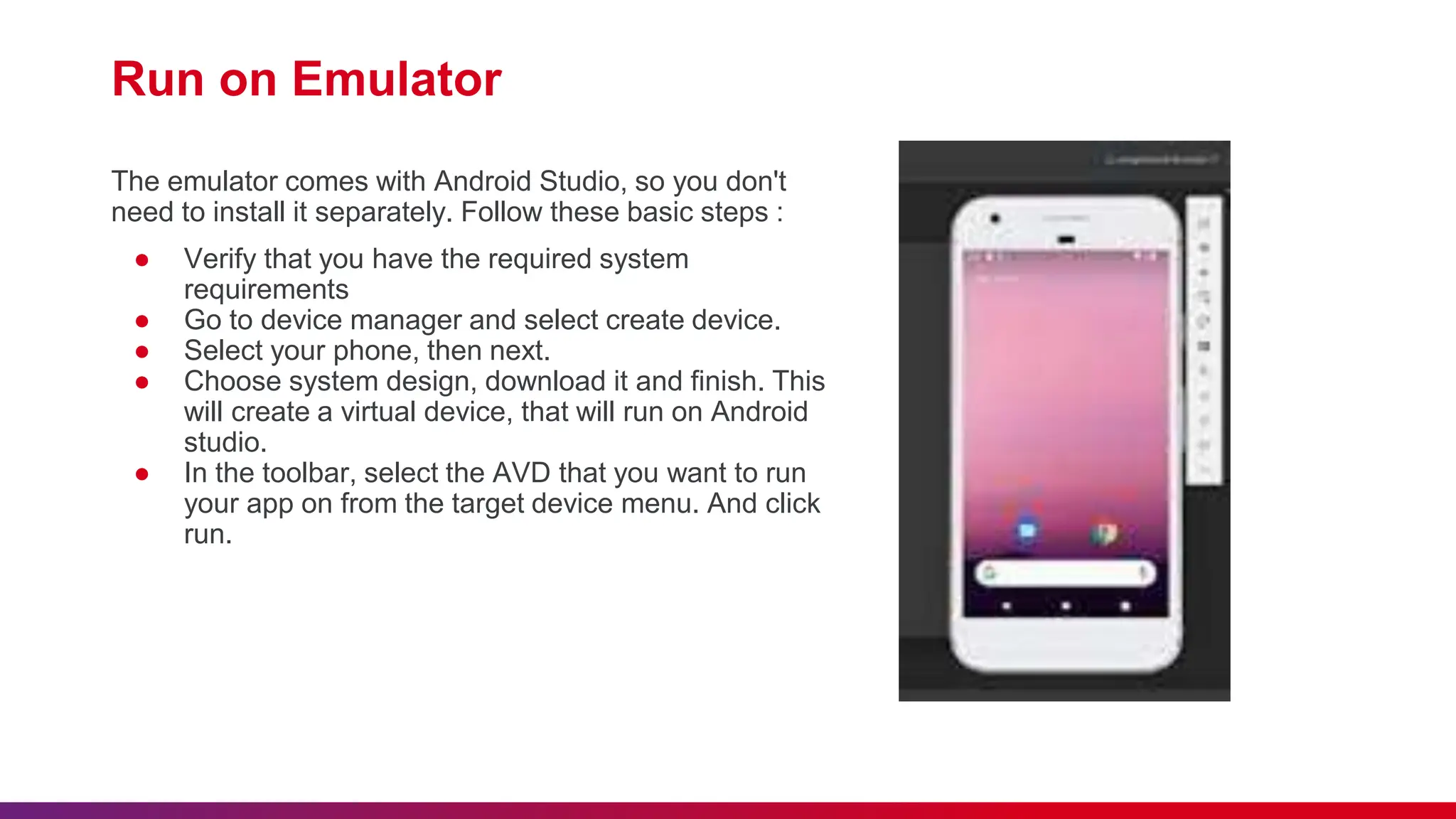
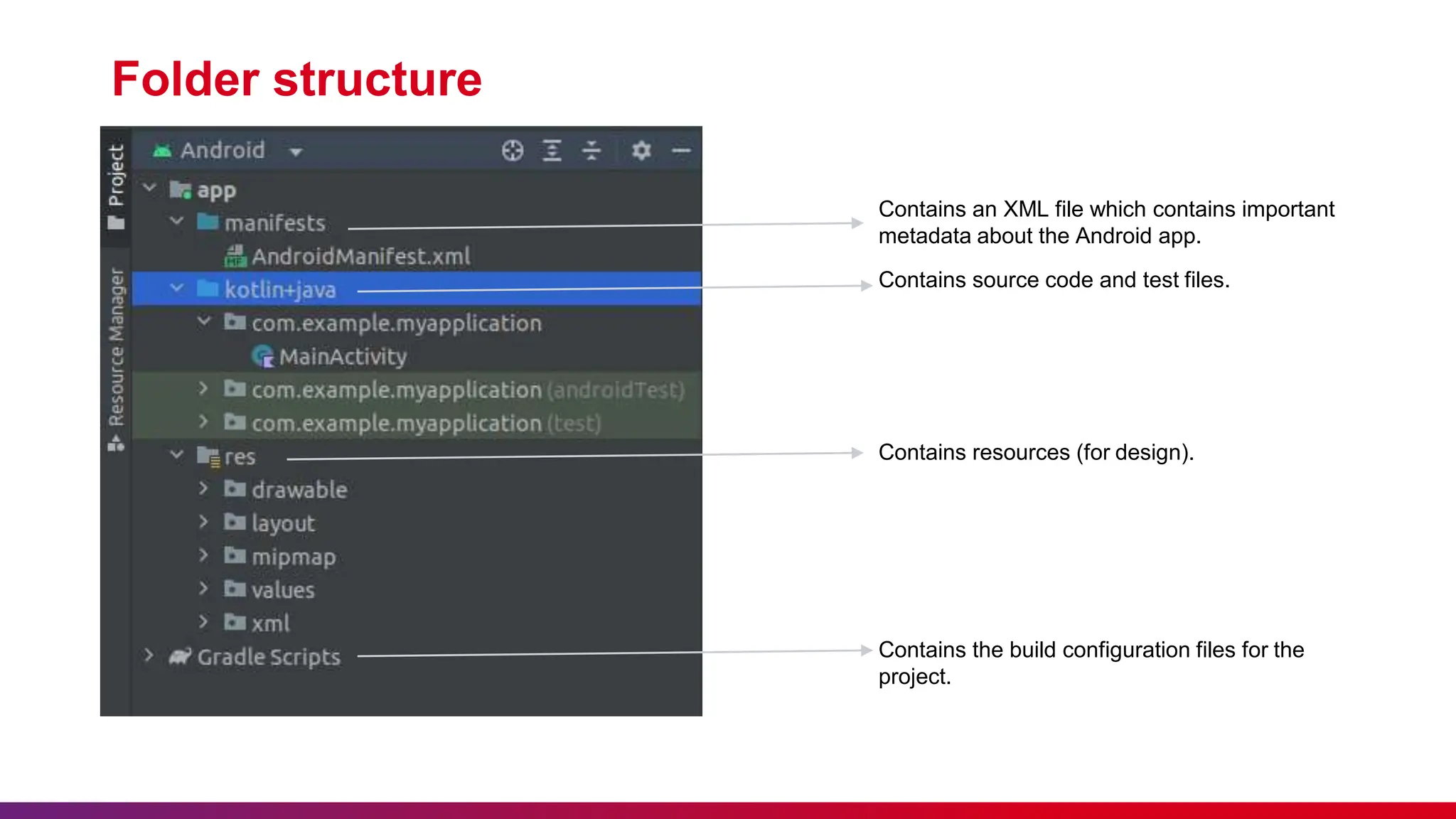
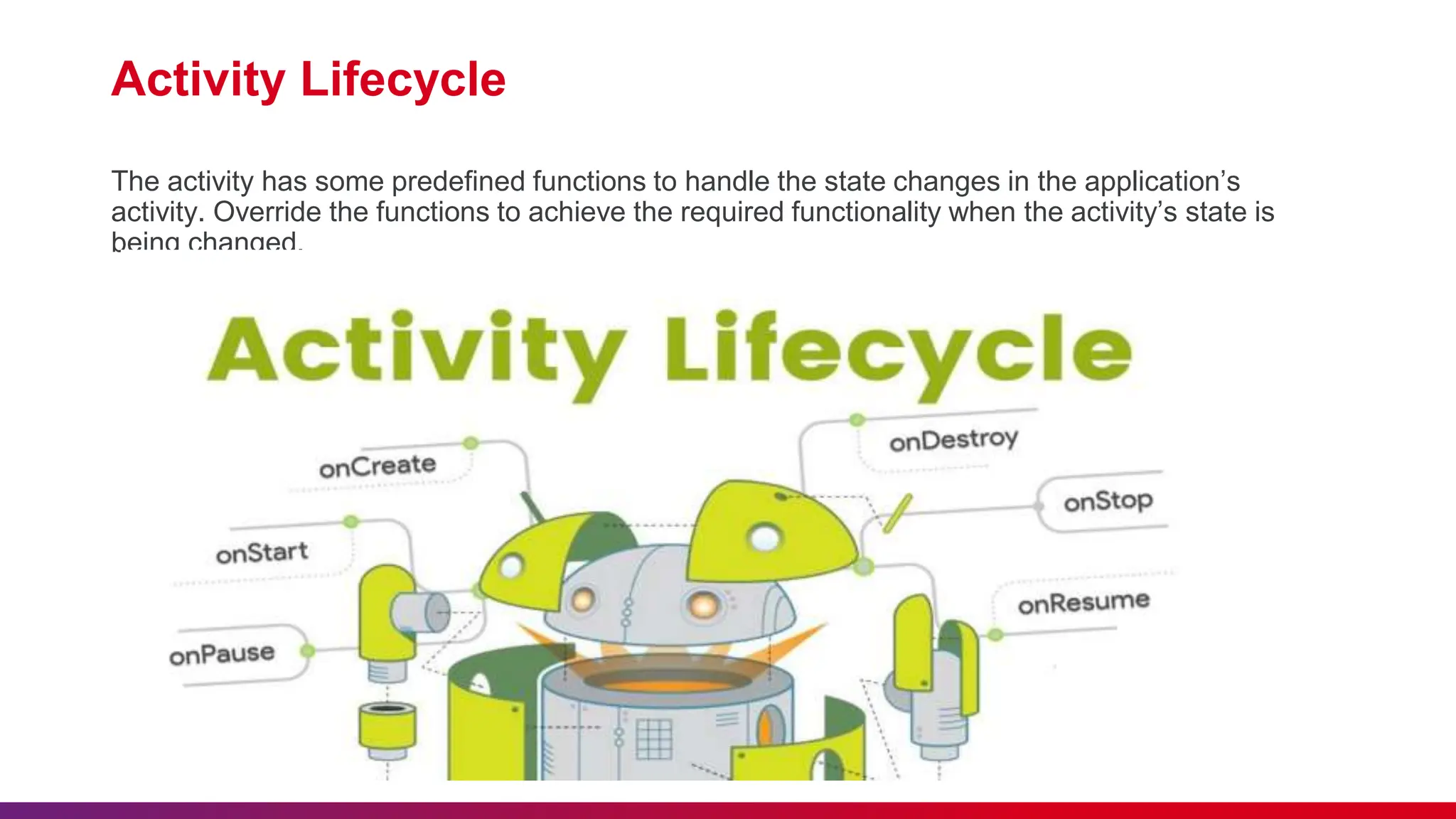
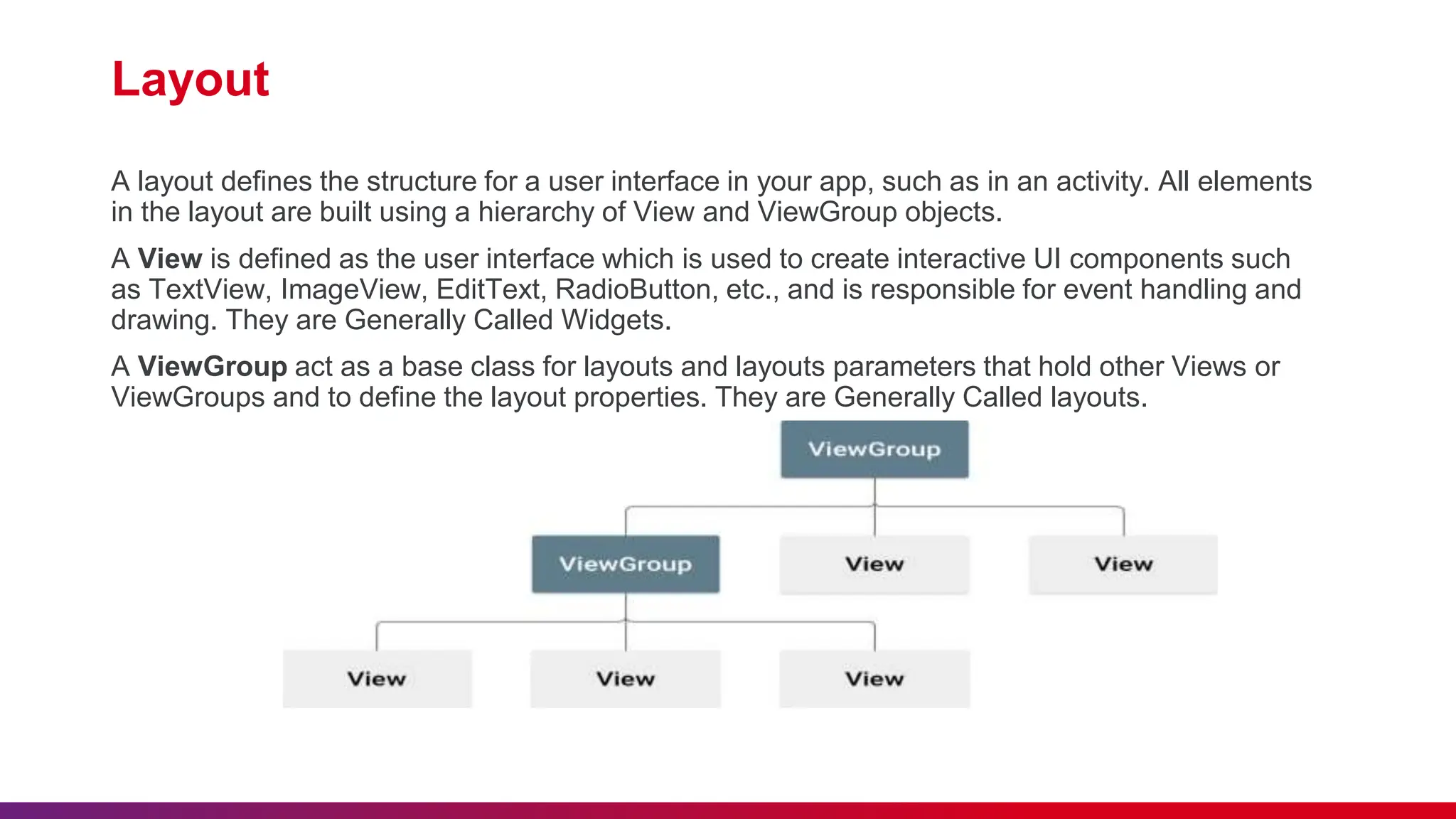
The document outlines best practices for etiquette during a Kotlin Android development session, such as punctuality and maintaining silent mode. It details the structure of Android applications, including folders for manifests, Java code, resources, and Gradle scripts, as well as essential components like activities and intents. Additionally, it provides instructions for setting up Android Studio, developing a basic app, and managing UI layouts with XML.