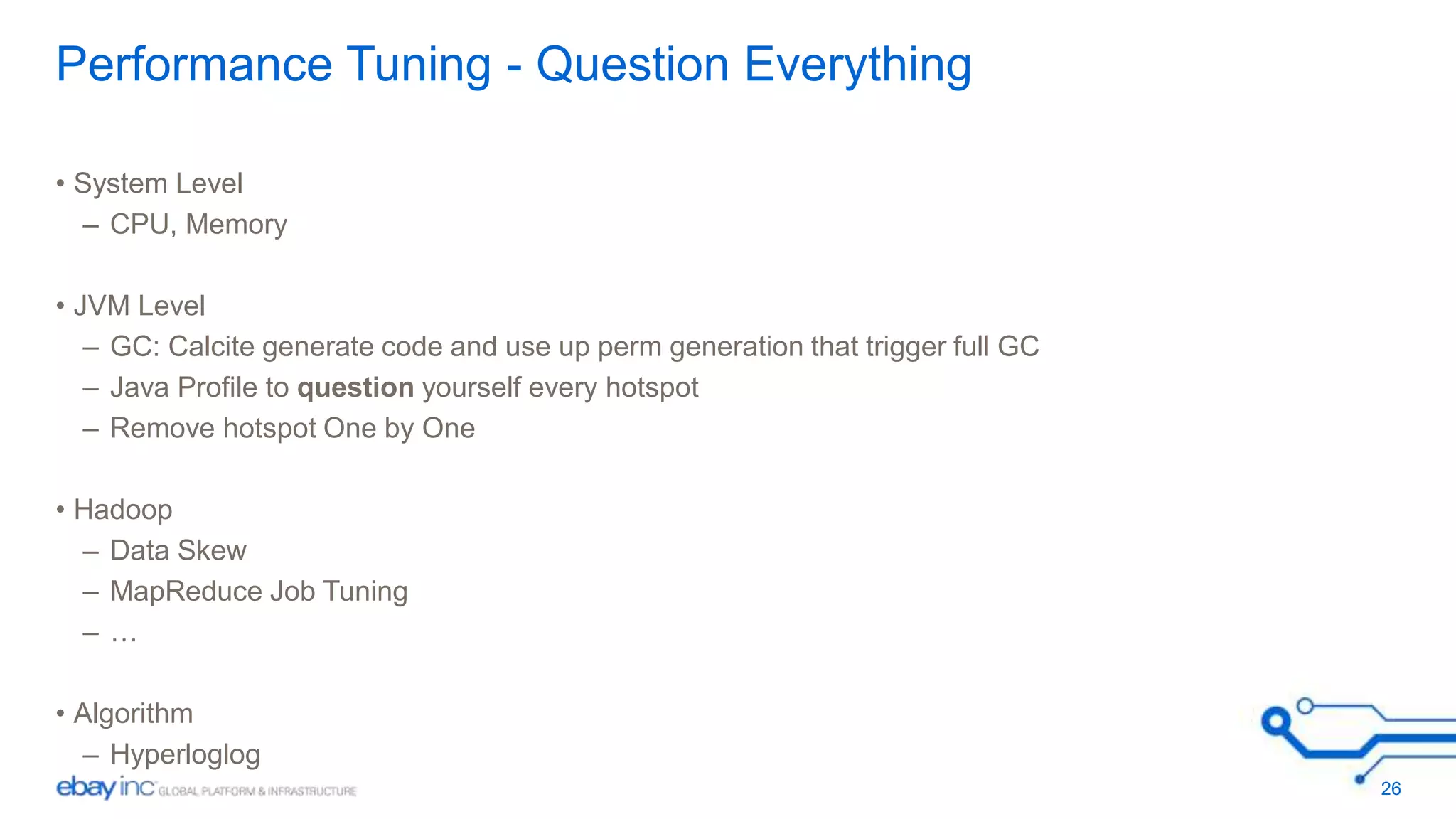
The document outlines engineering principles for product development, emphasizing the importance of deriving ideas from real product issues and focusing on simplicity and feasibility. Key strategies include building a strong team, maximizing automation in testing, and continuously refining the product based on customer feedback. It advocates for a structured approach to design, testing, and onboarding, prioritizing usability and efficient problem-solving.