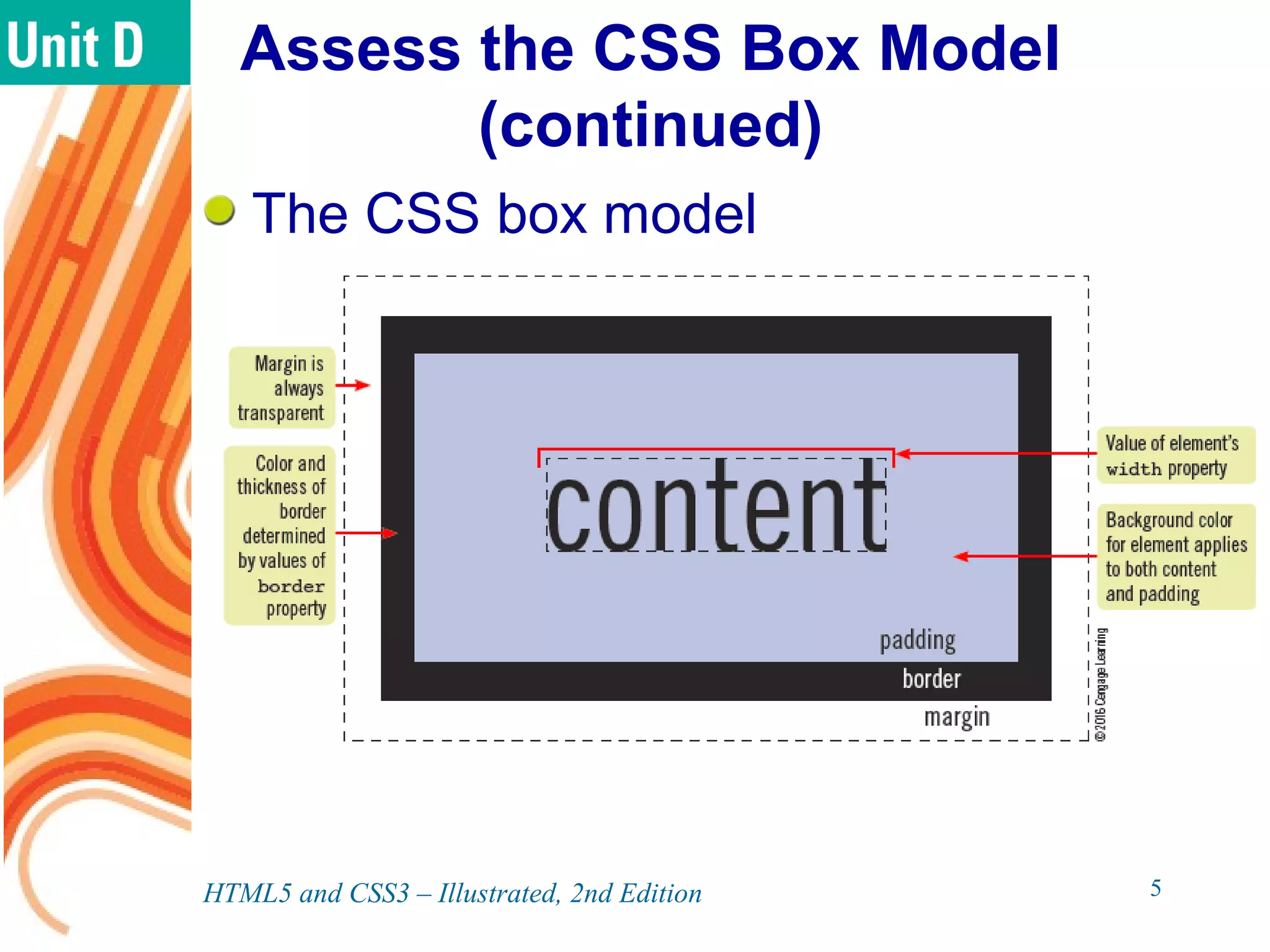
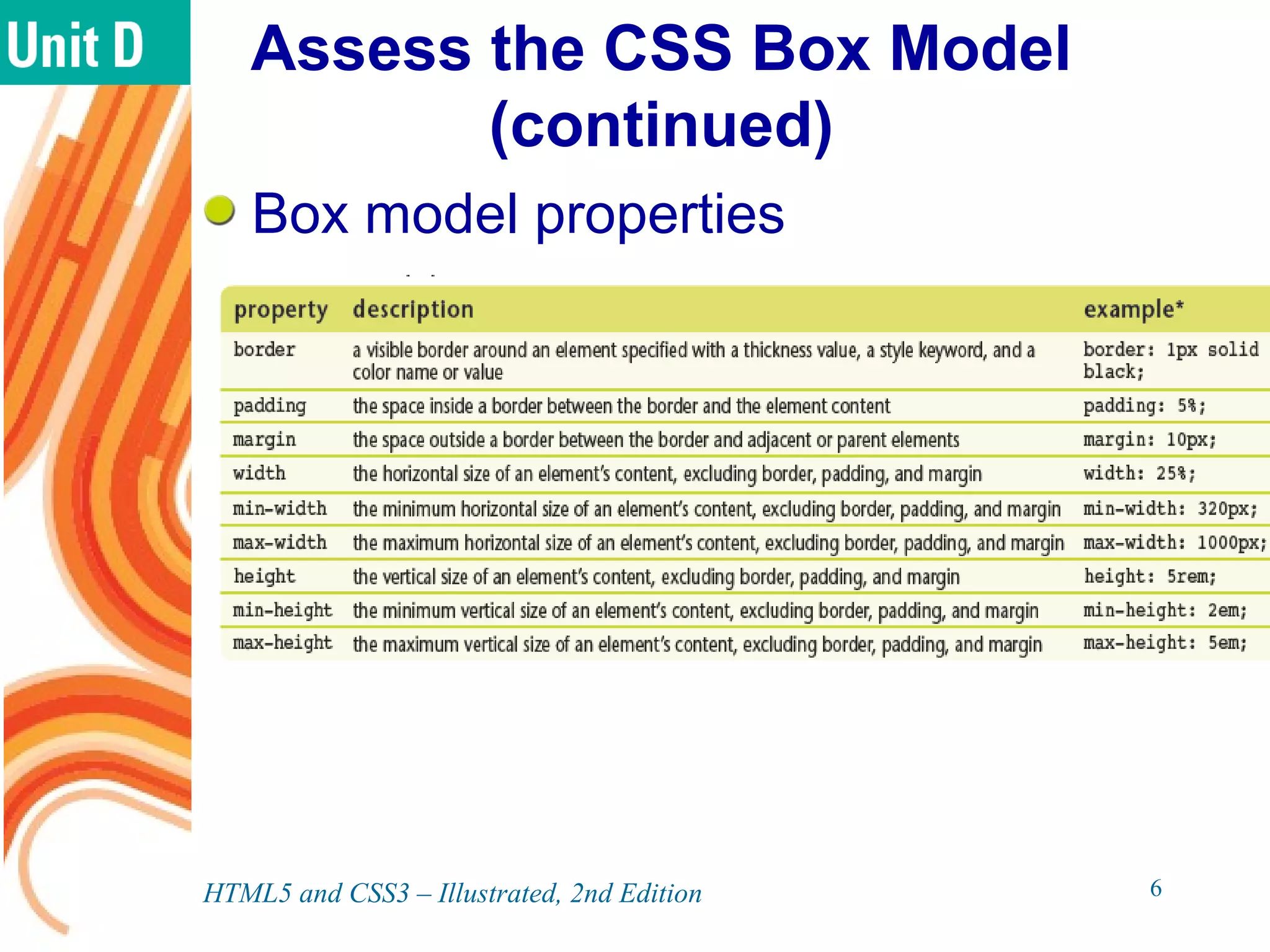
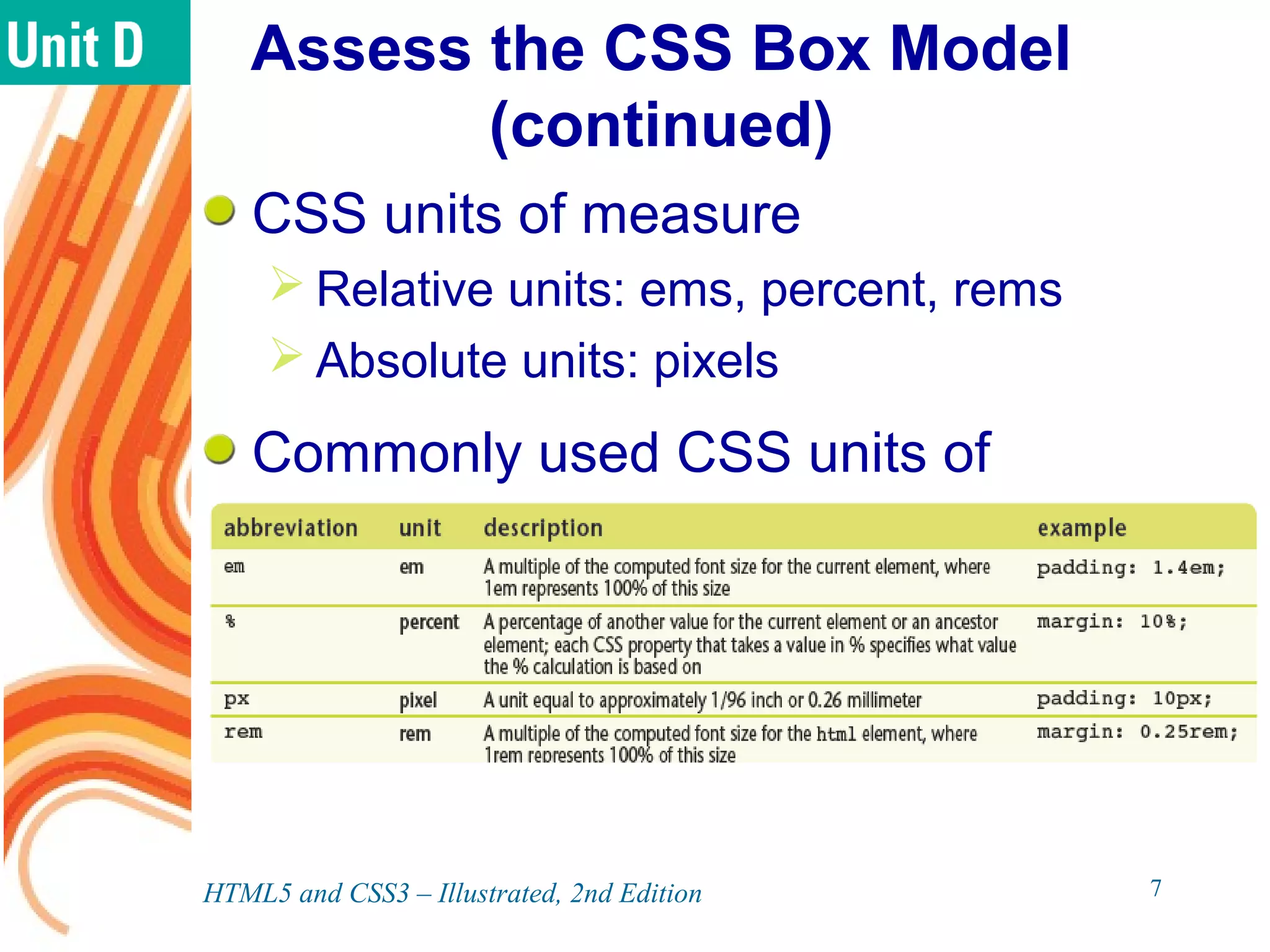
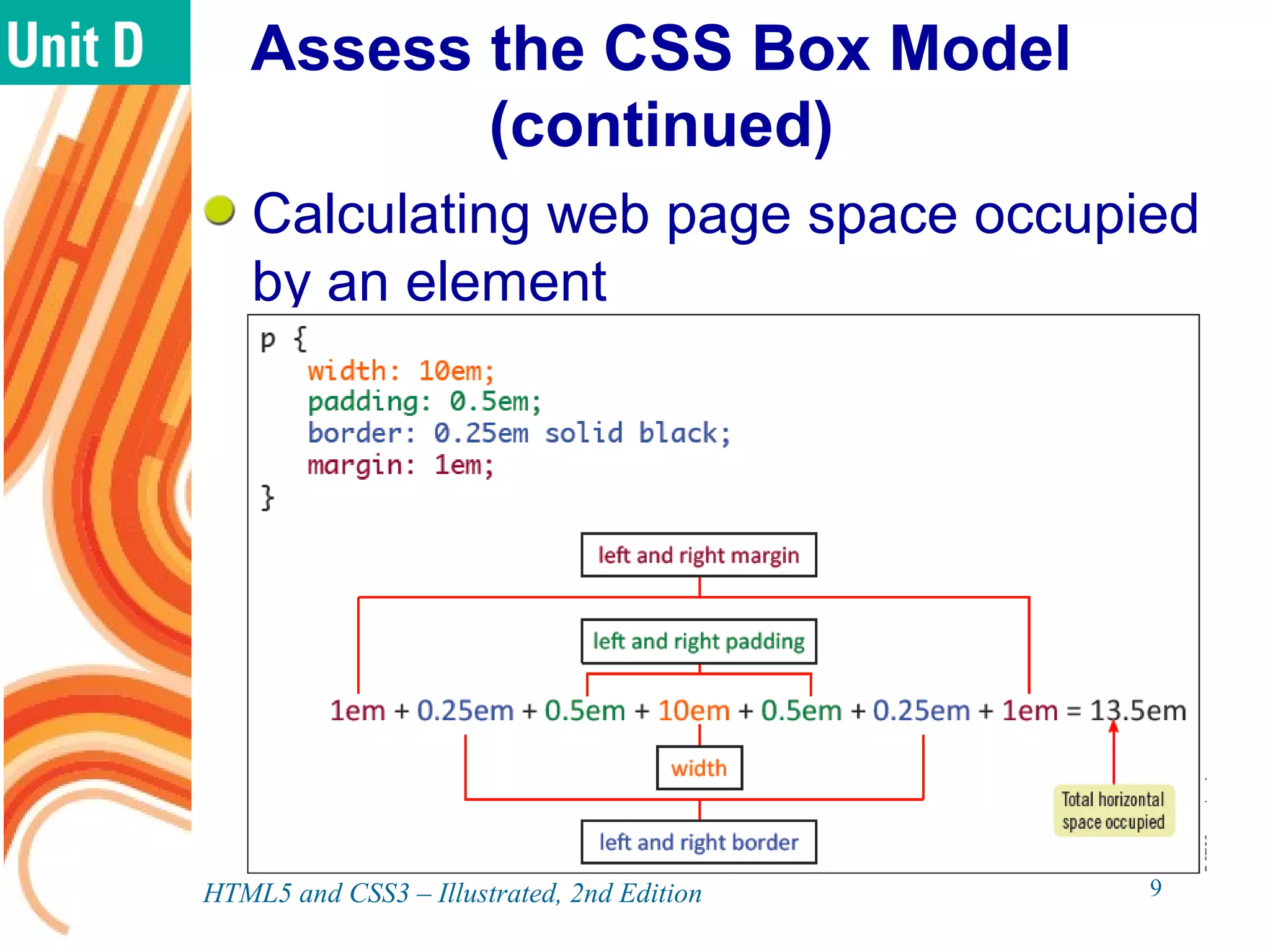
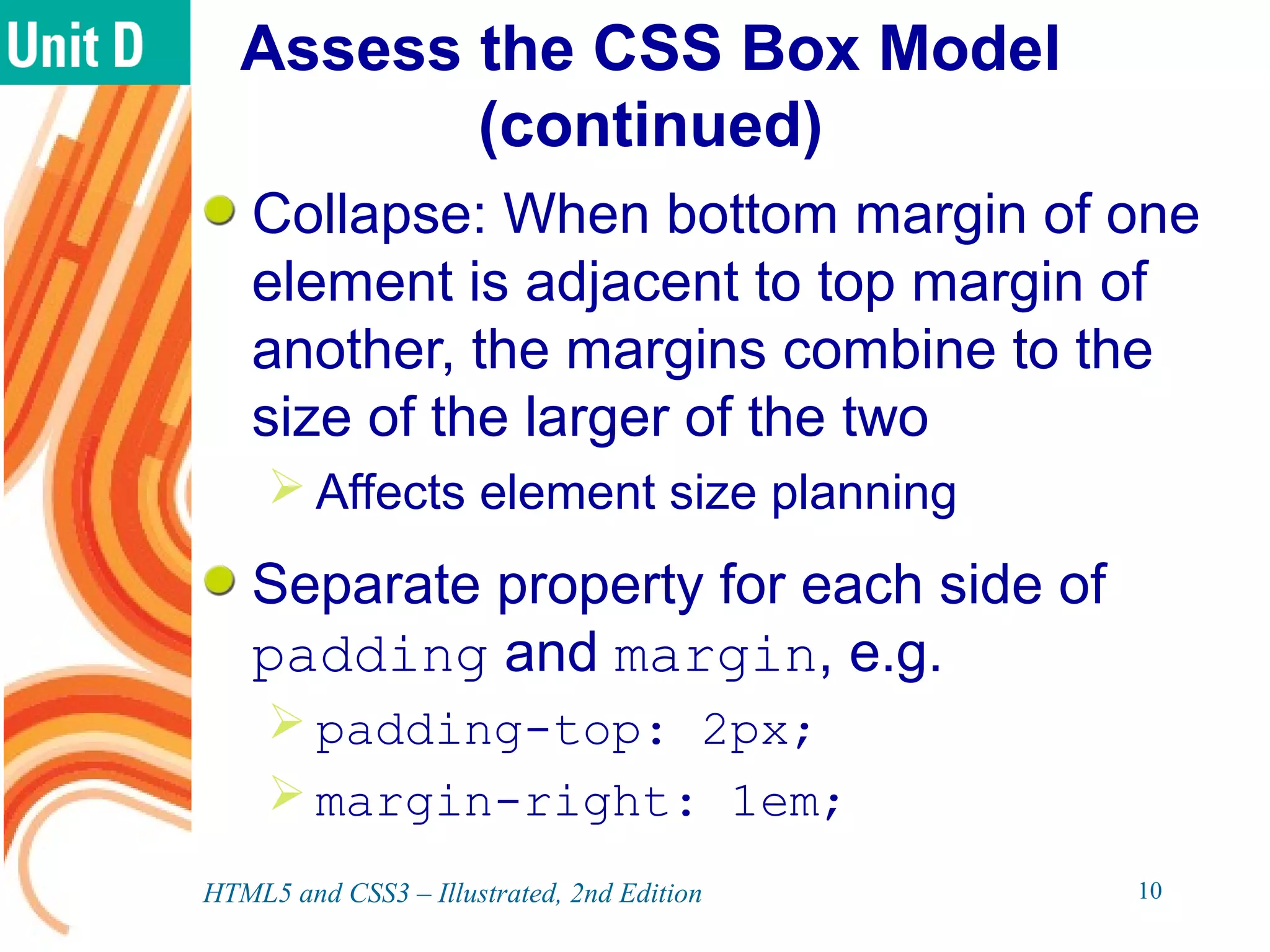
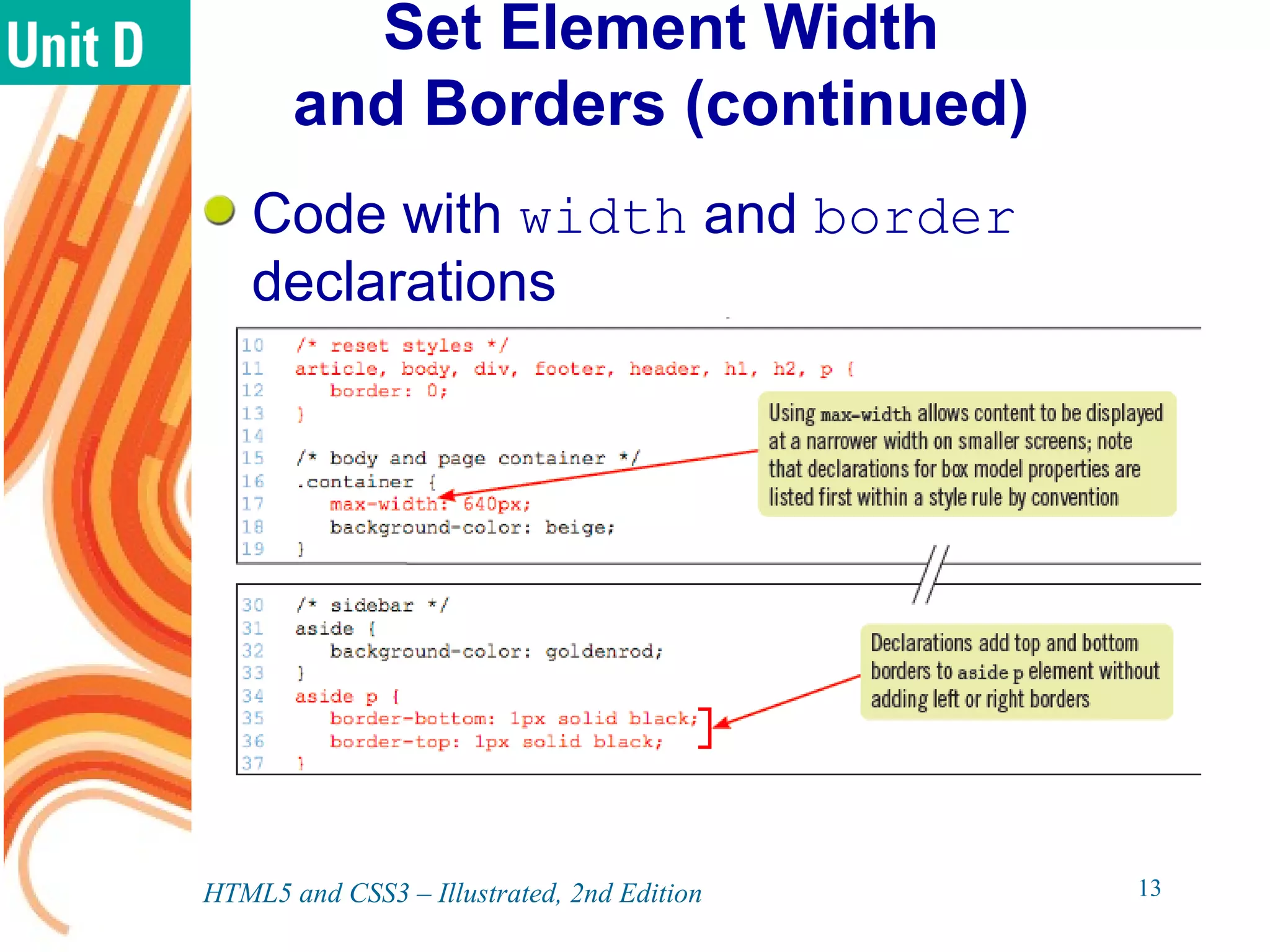
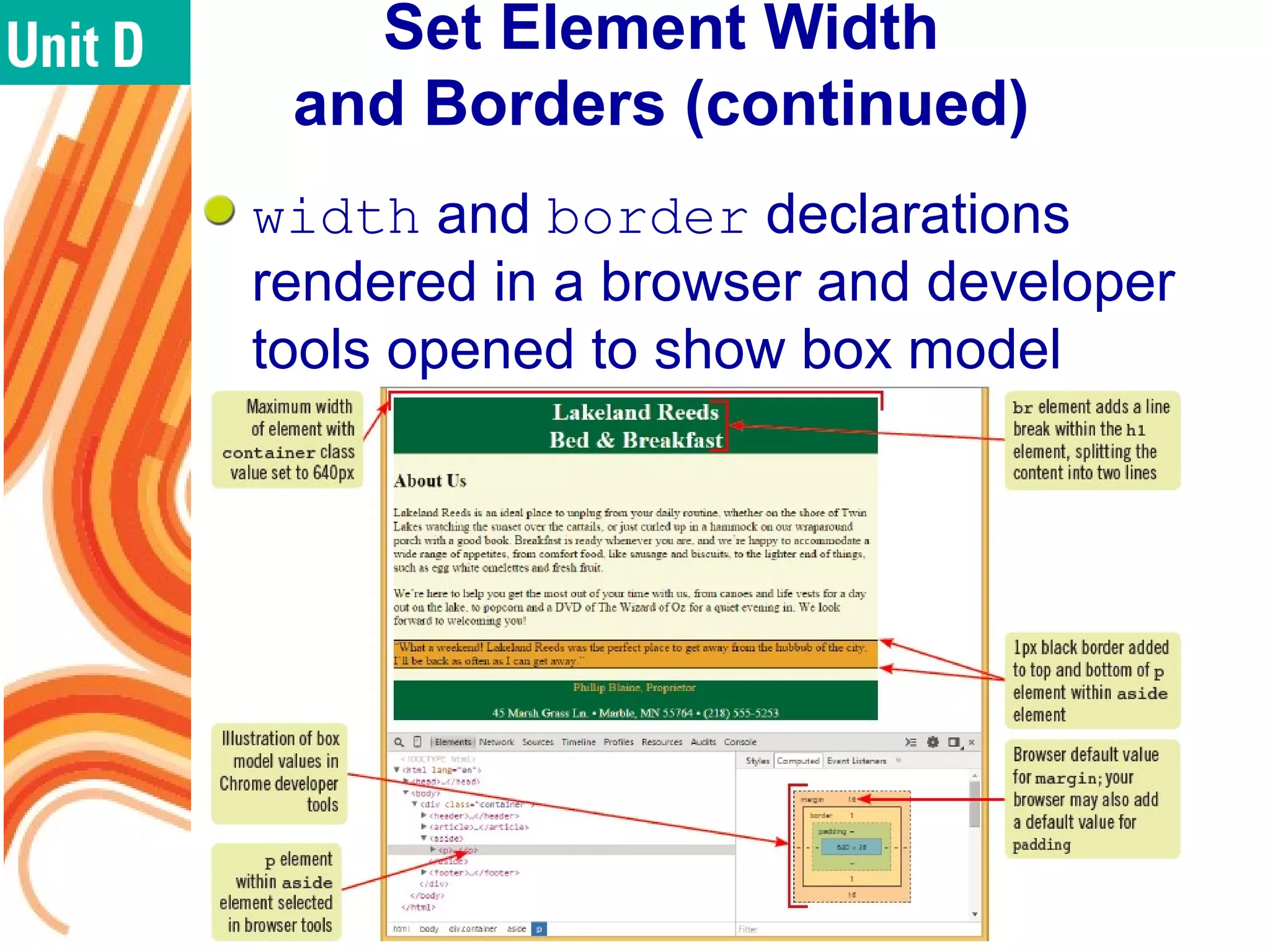
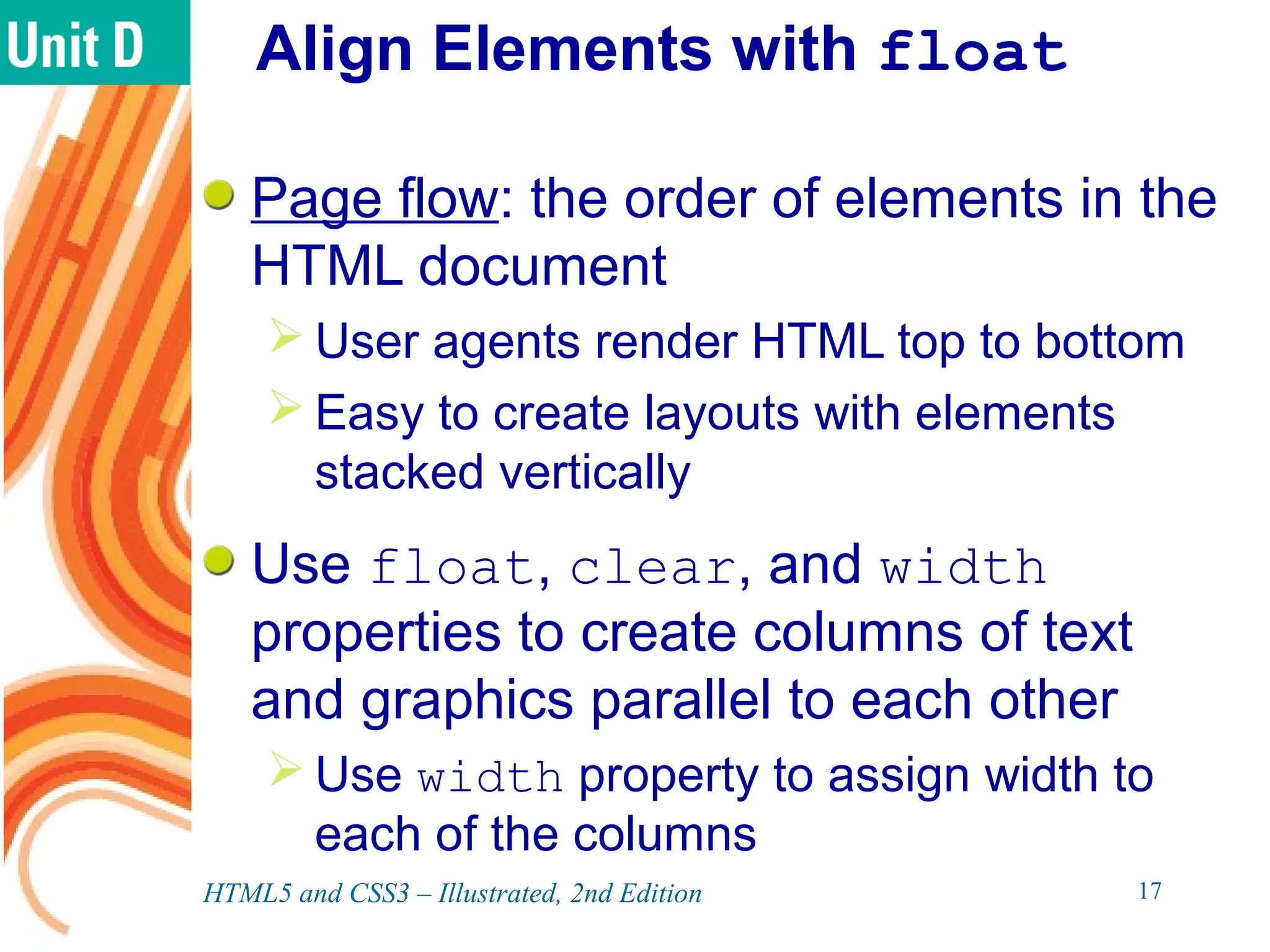
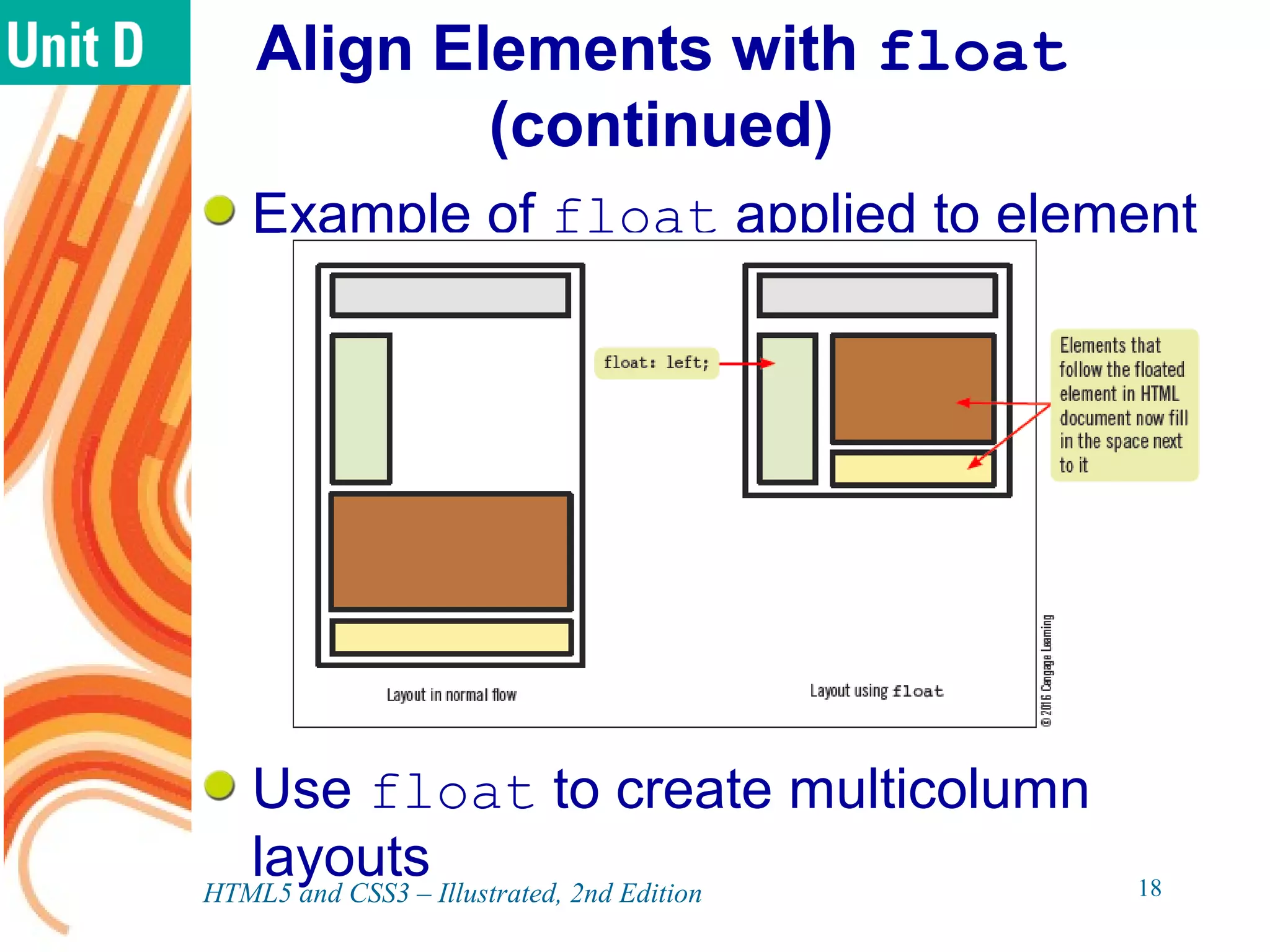
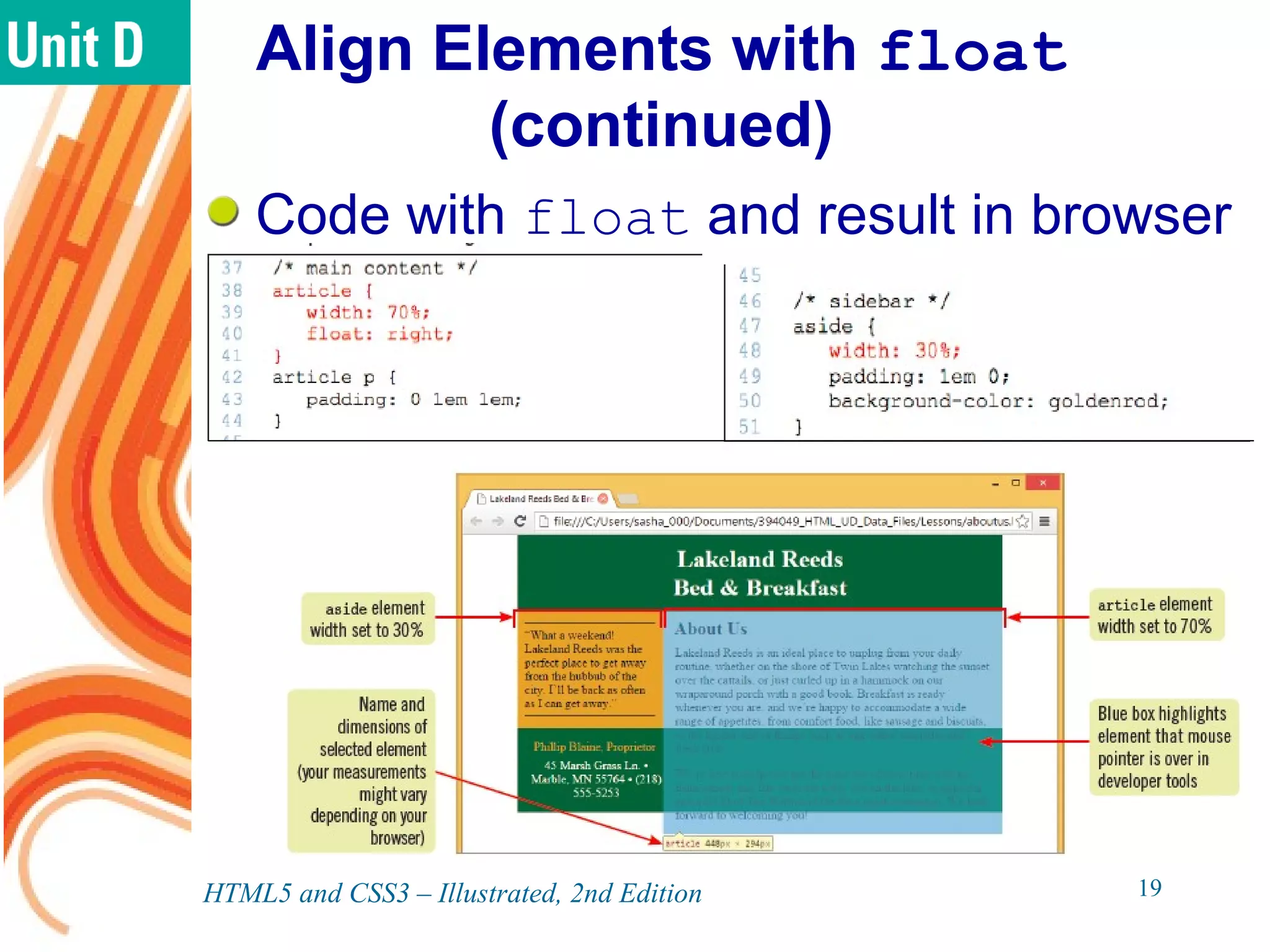
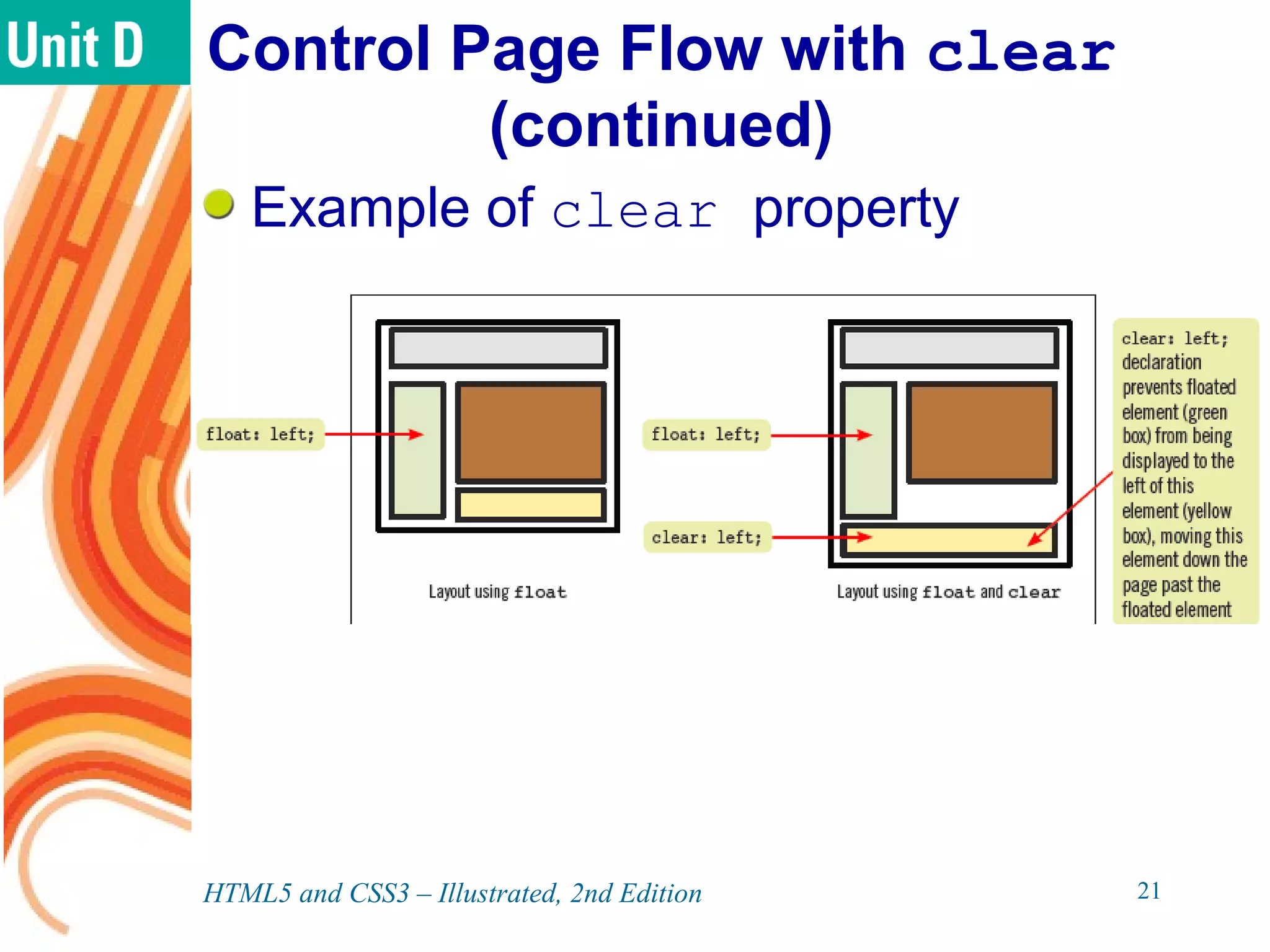
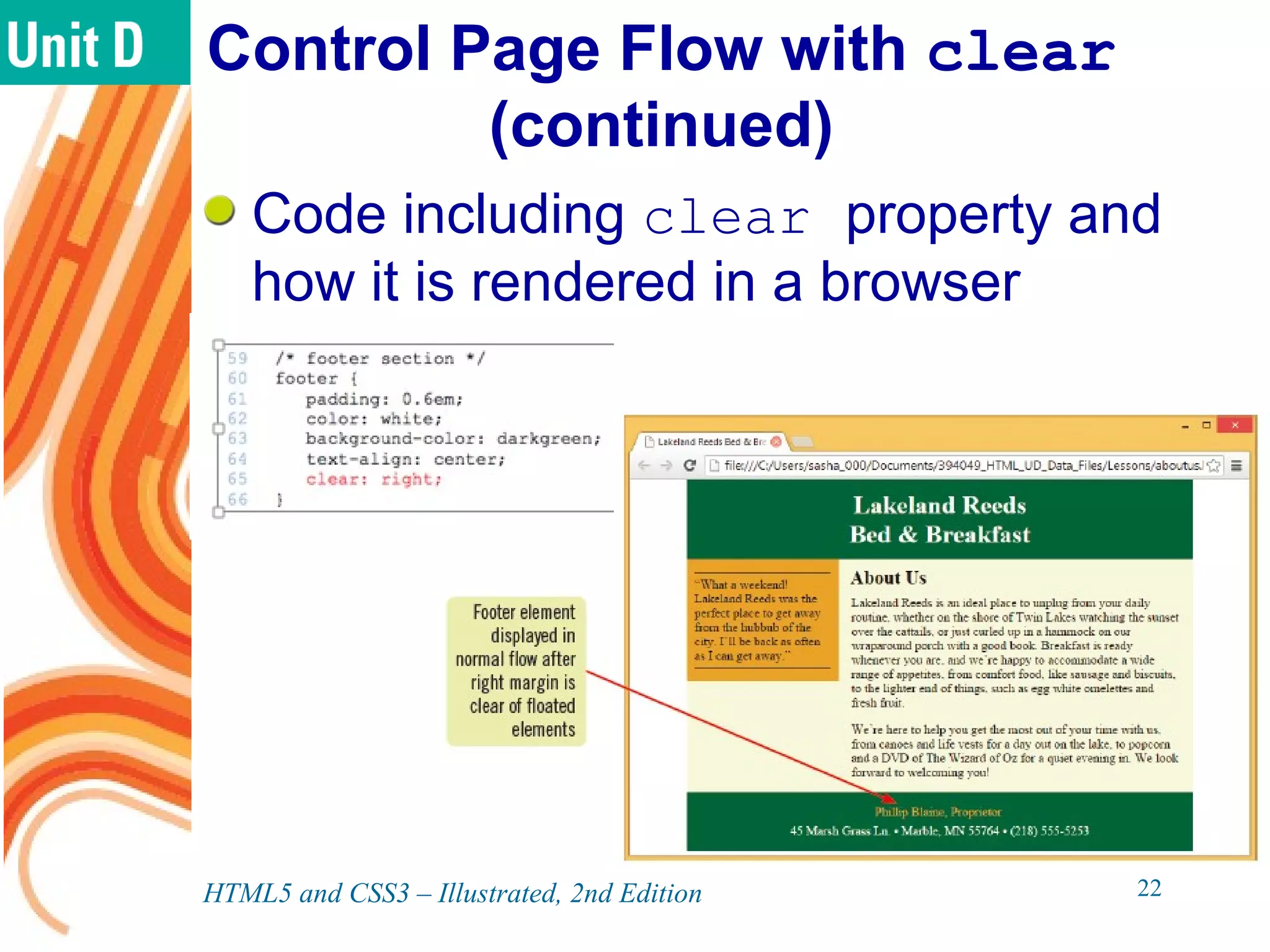
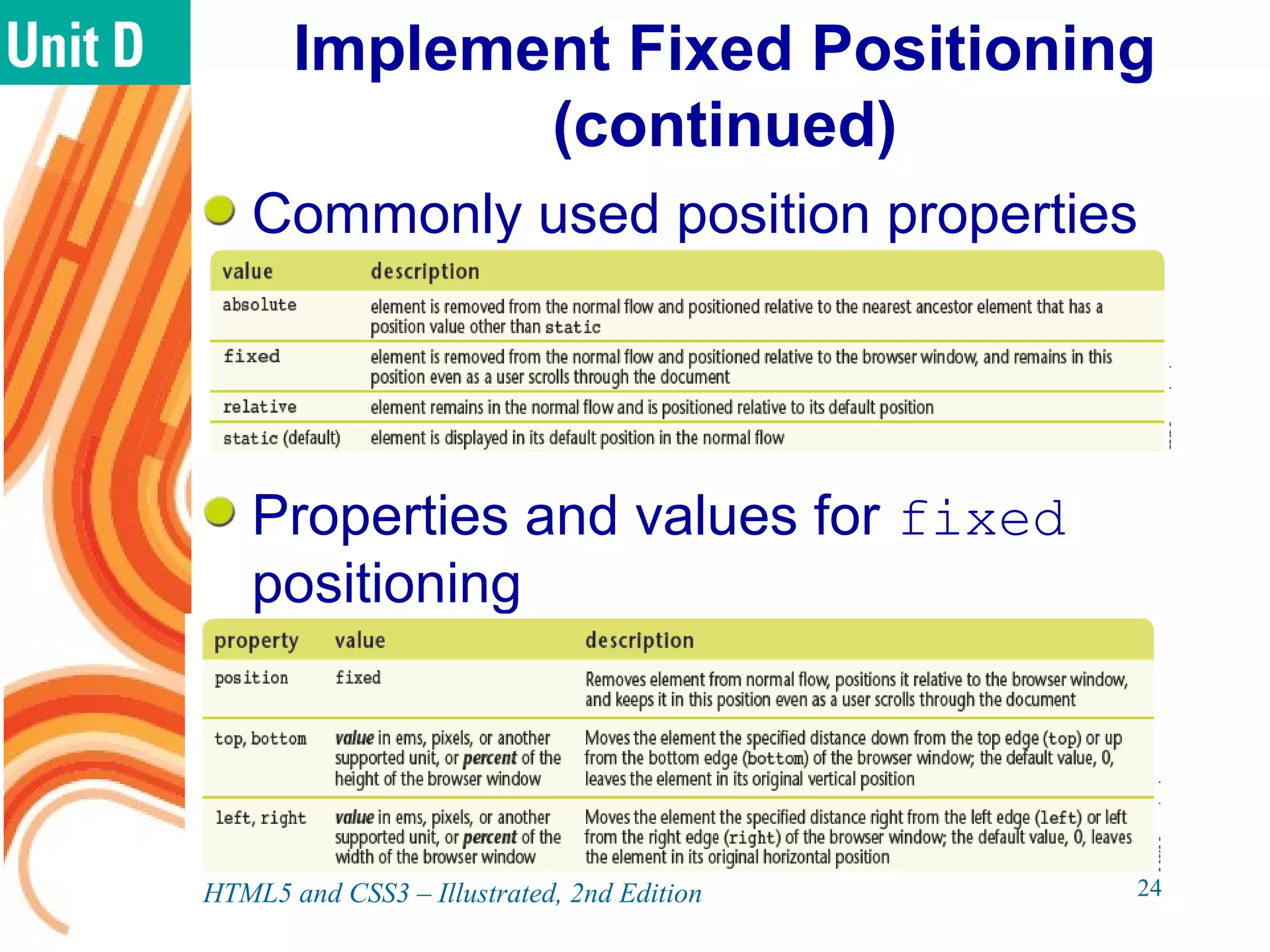
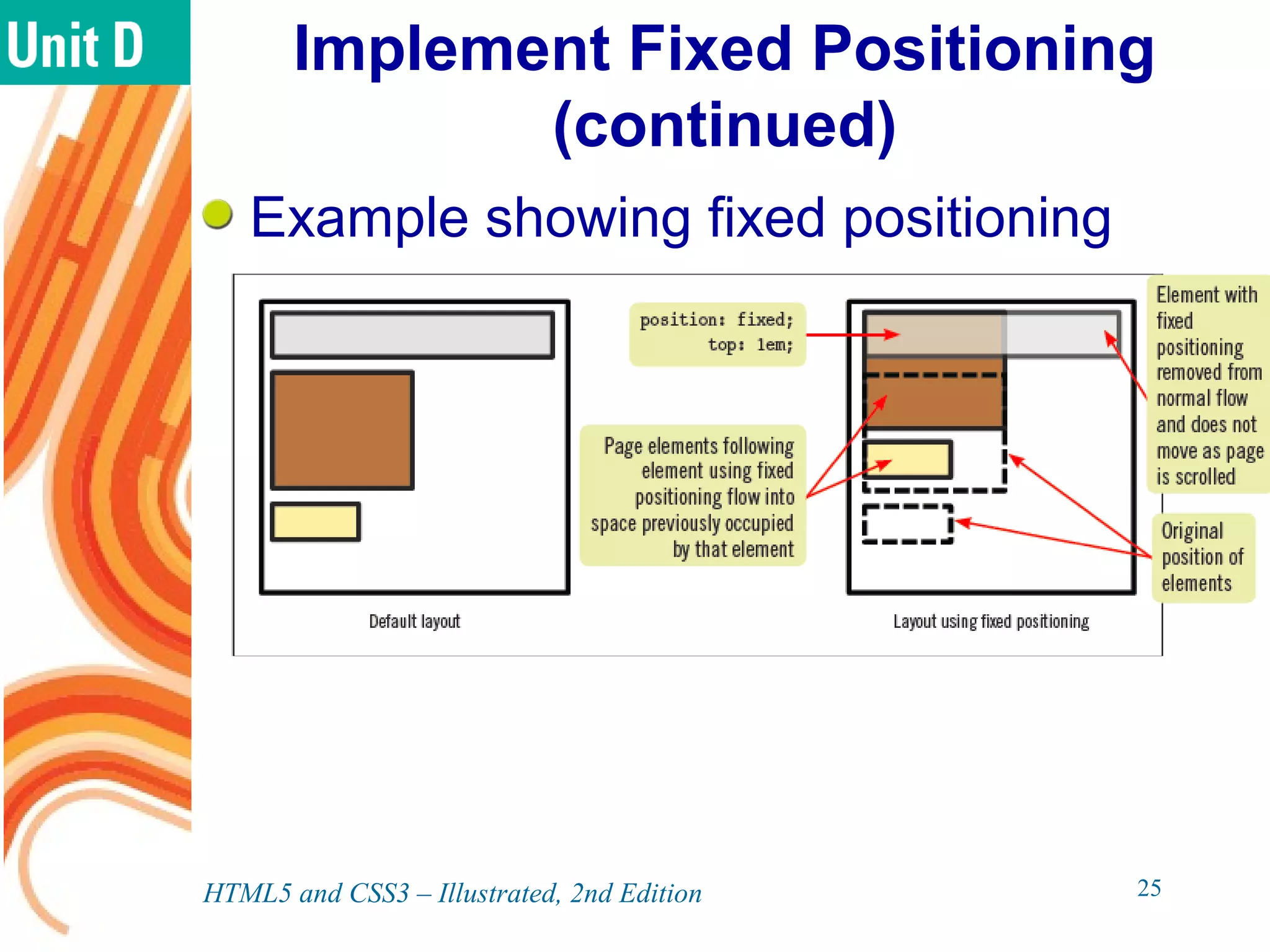
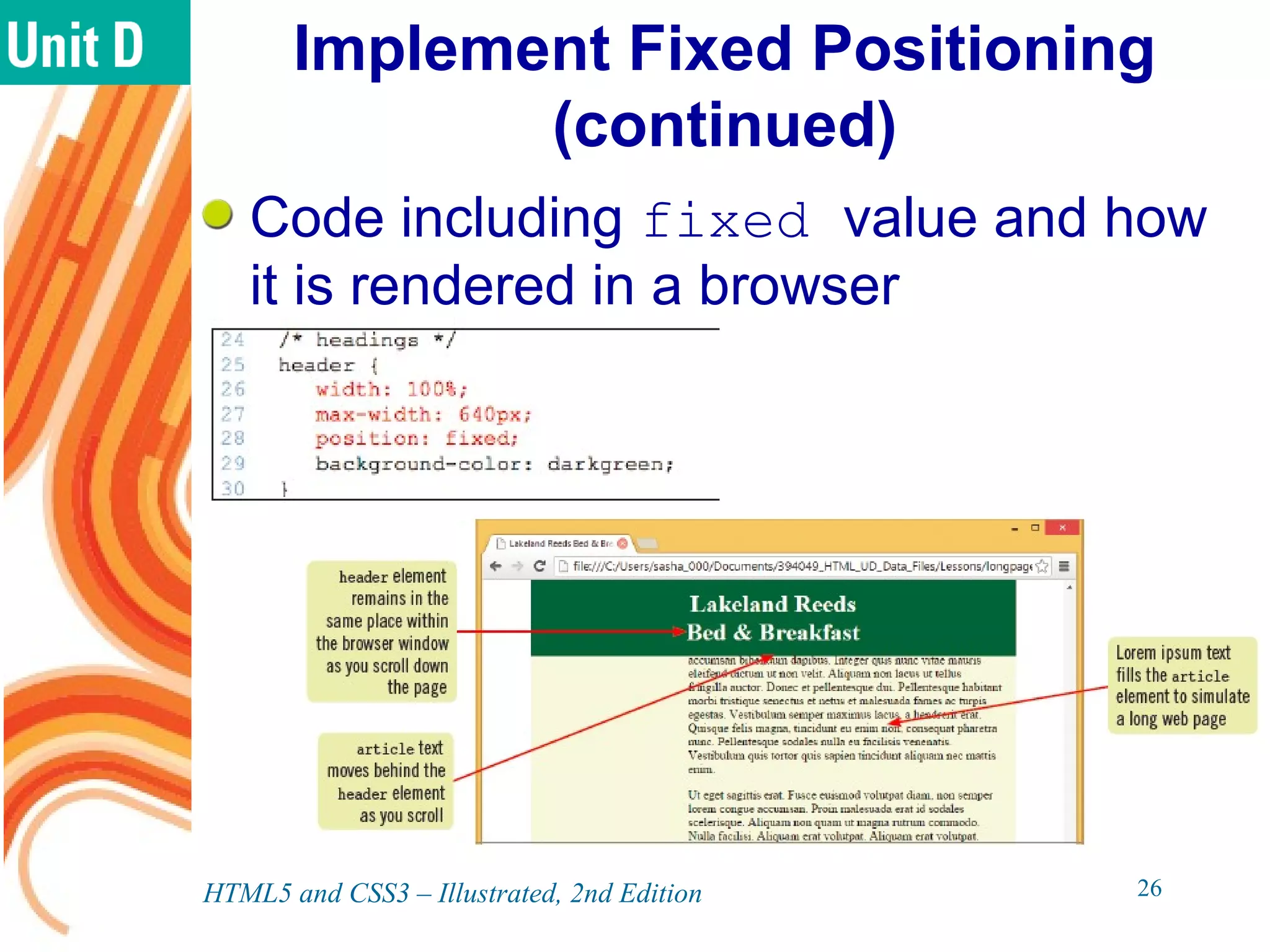
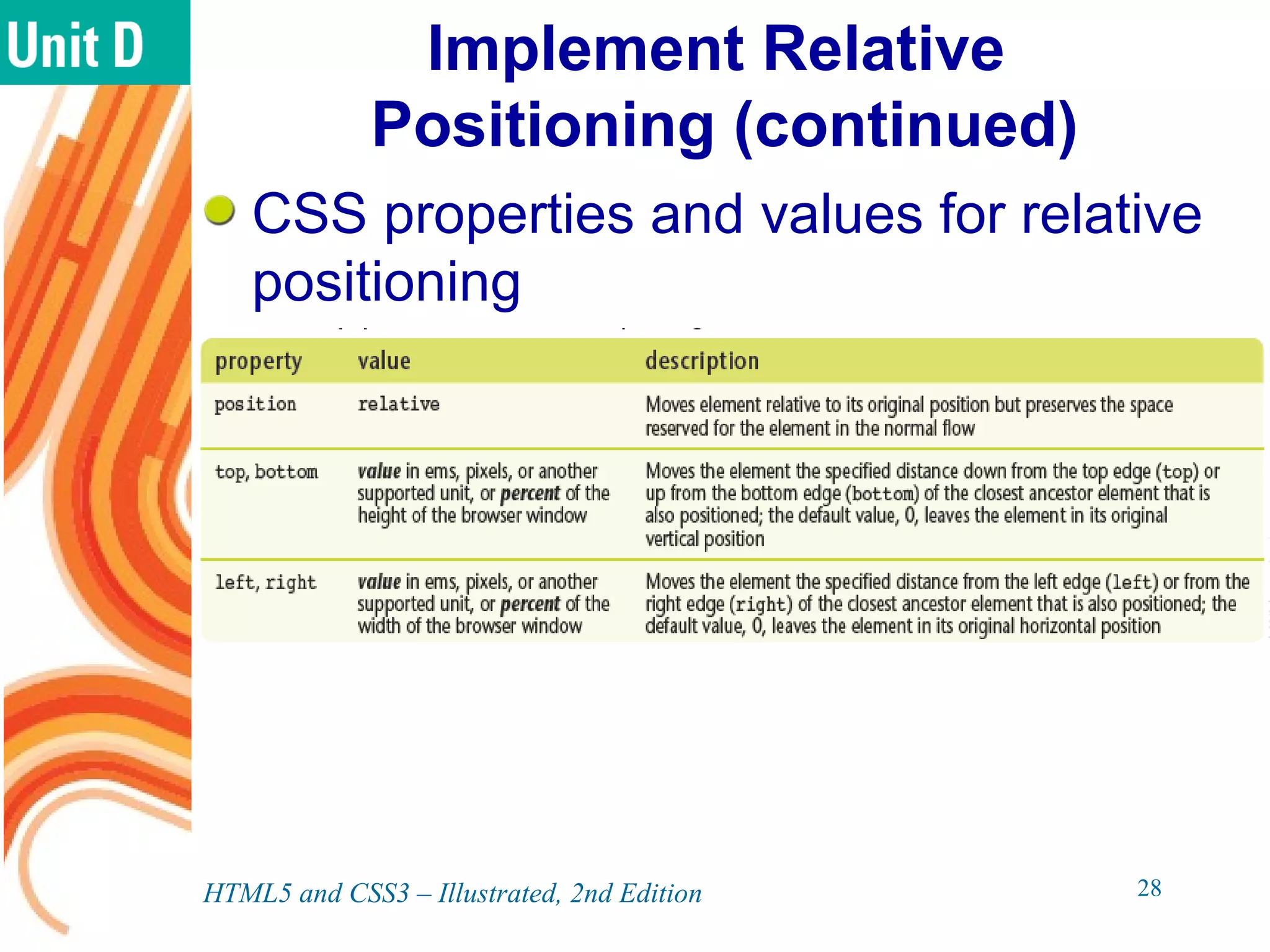
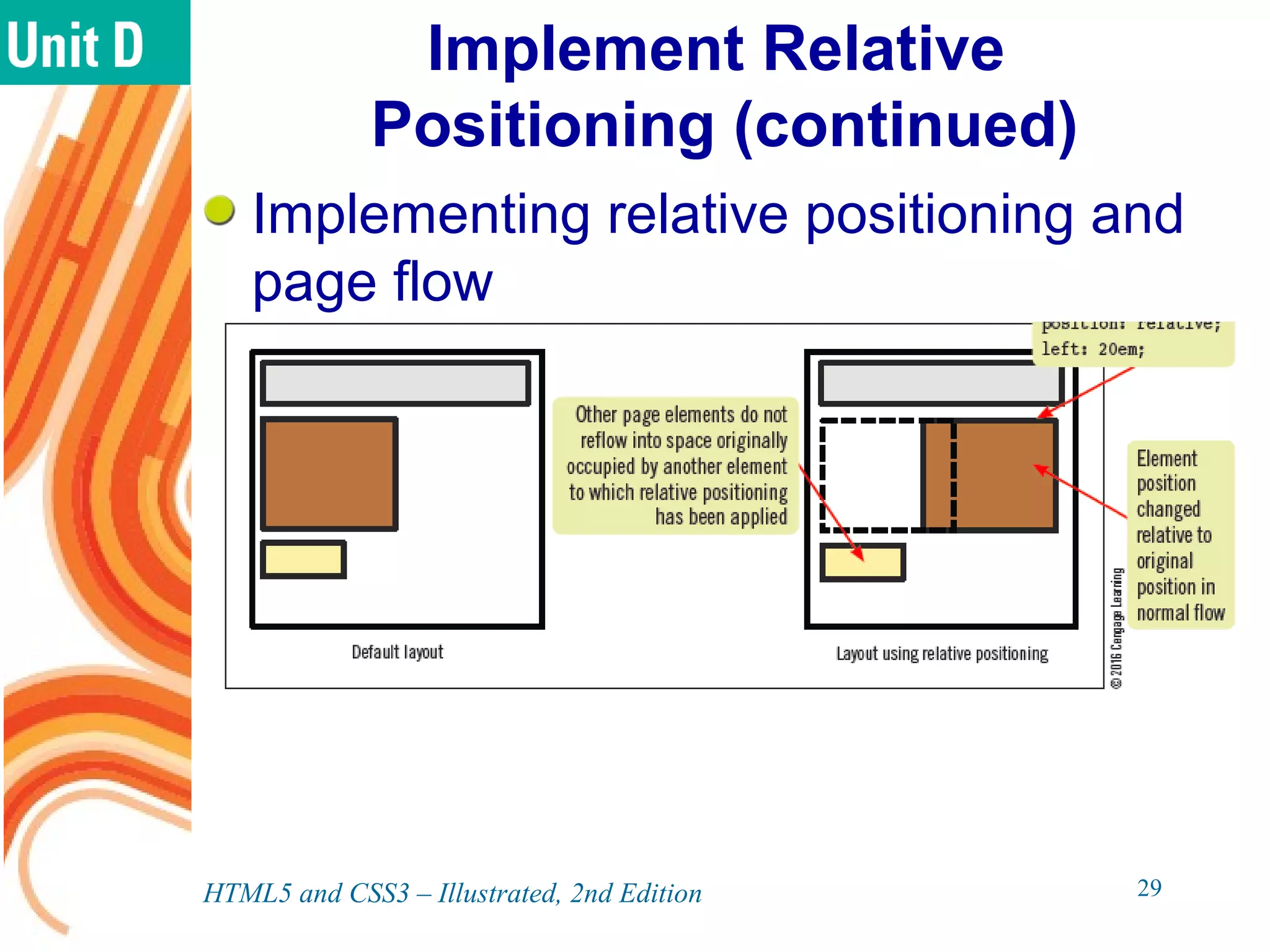
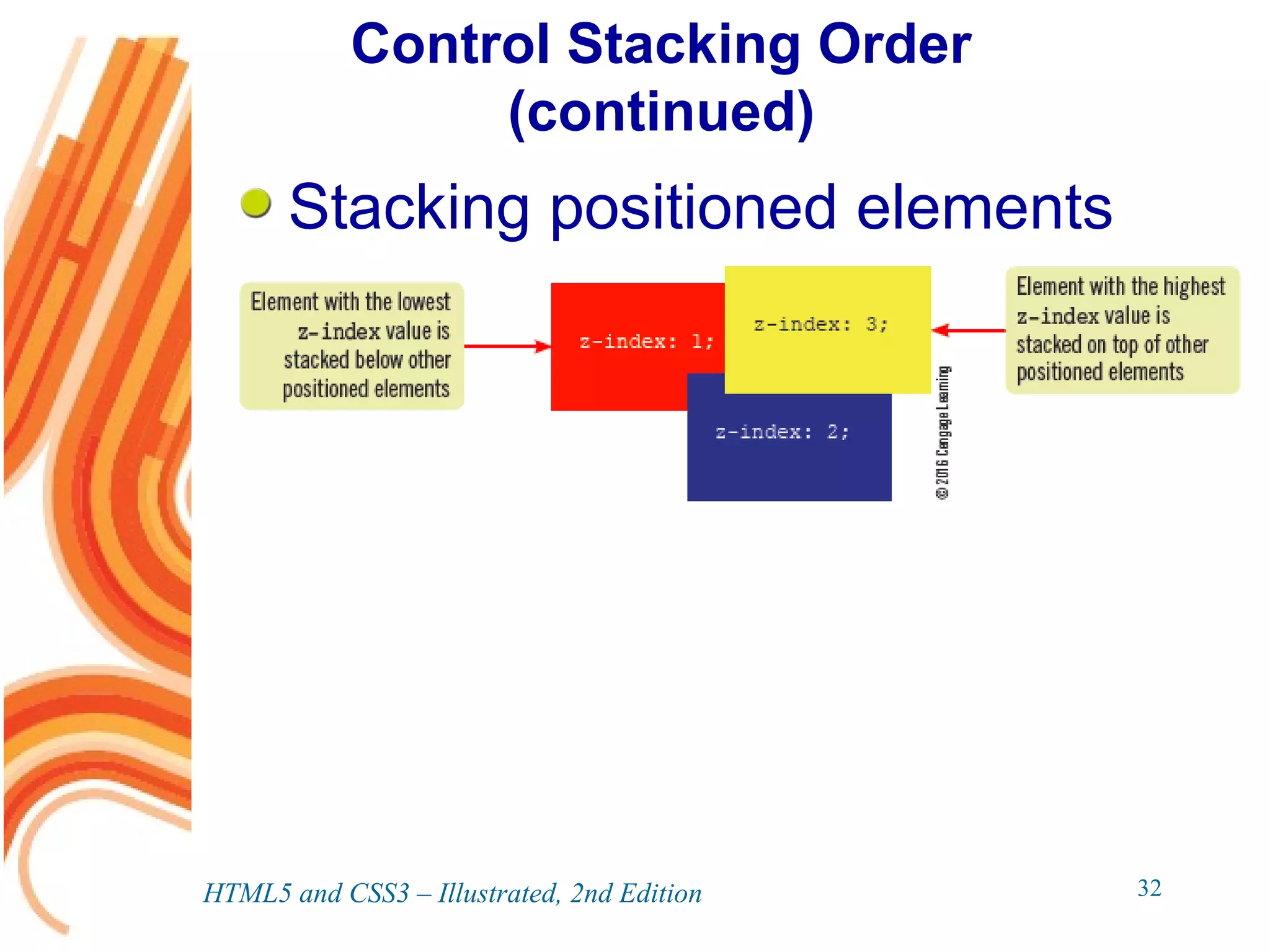
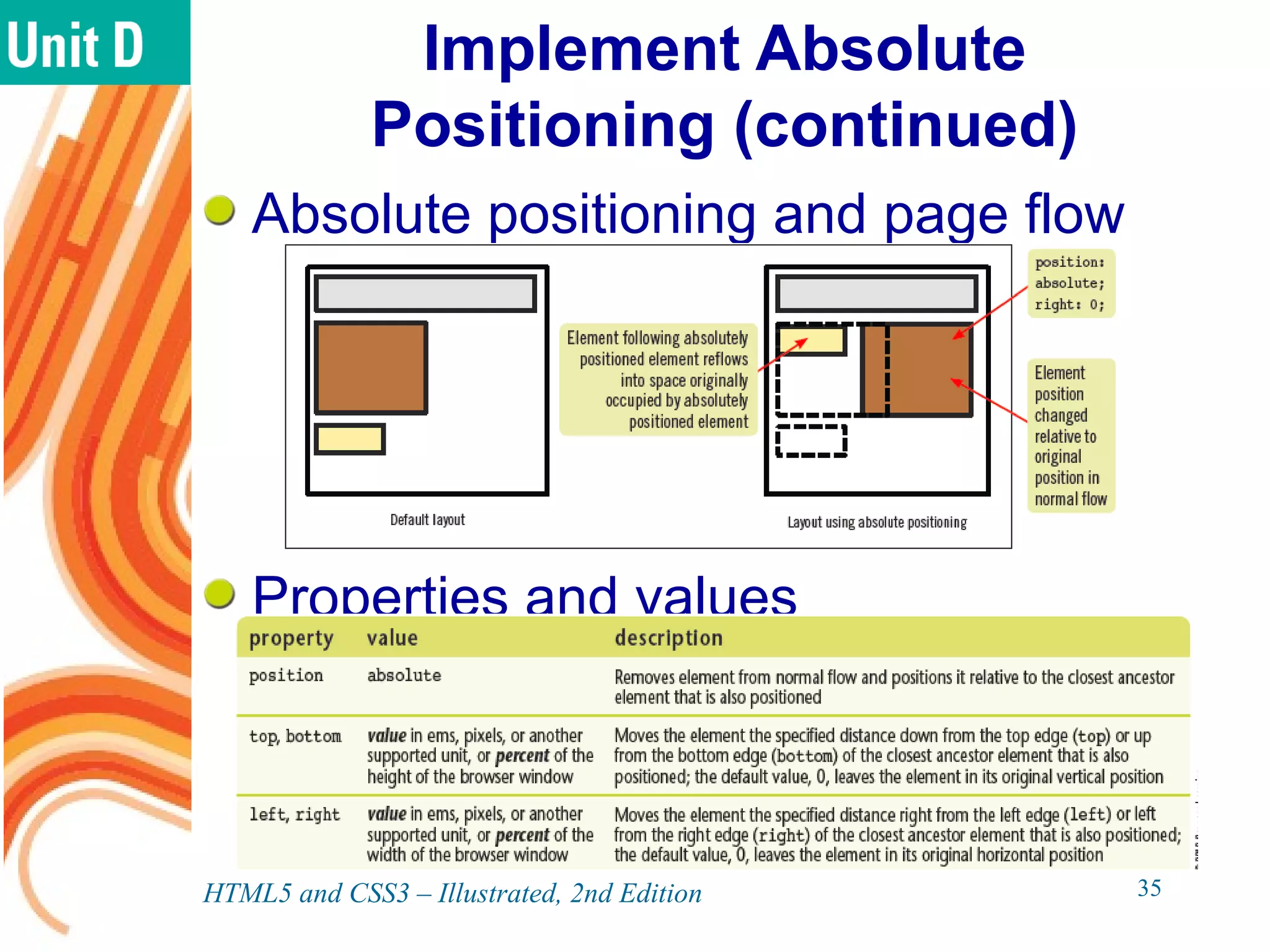
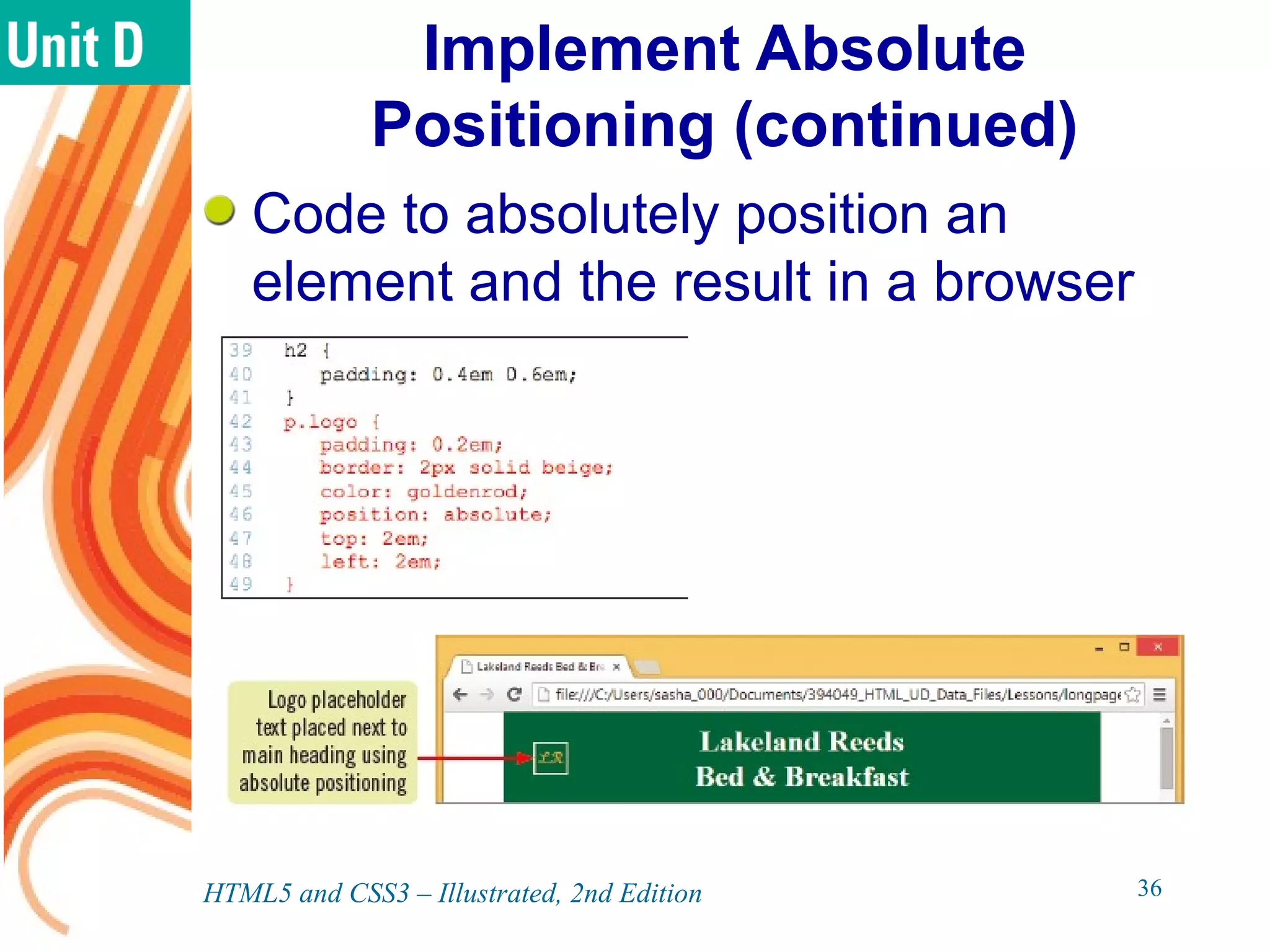
The document discusses various CSS positioning techniques including the box model, setting widths and borders, margins and padding, floats, clearing flows, and fixed, relative, and absolute positioning. The box model treats elements as boxes with properties for borders, margins, padding, and content. Floats and clearing can be used to create multi-column layouts. Fixed positioning keeps elements visible during scrolling while relative and absolute positioning adjust element locations without and within the normal flow, respectively.