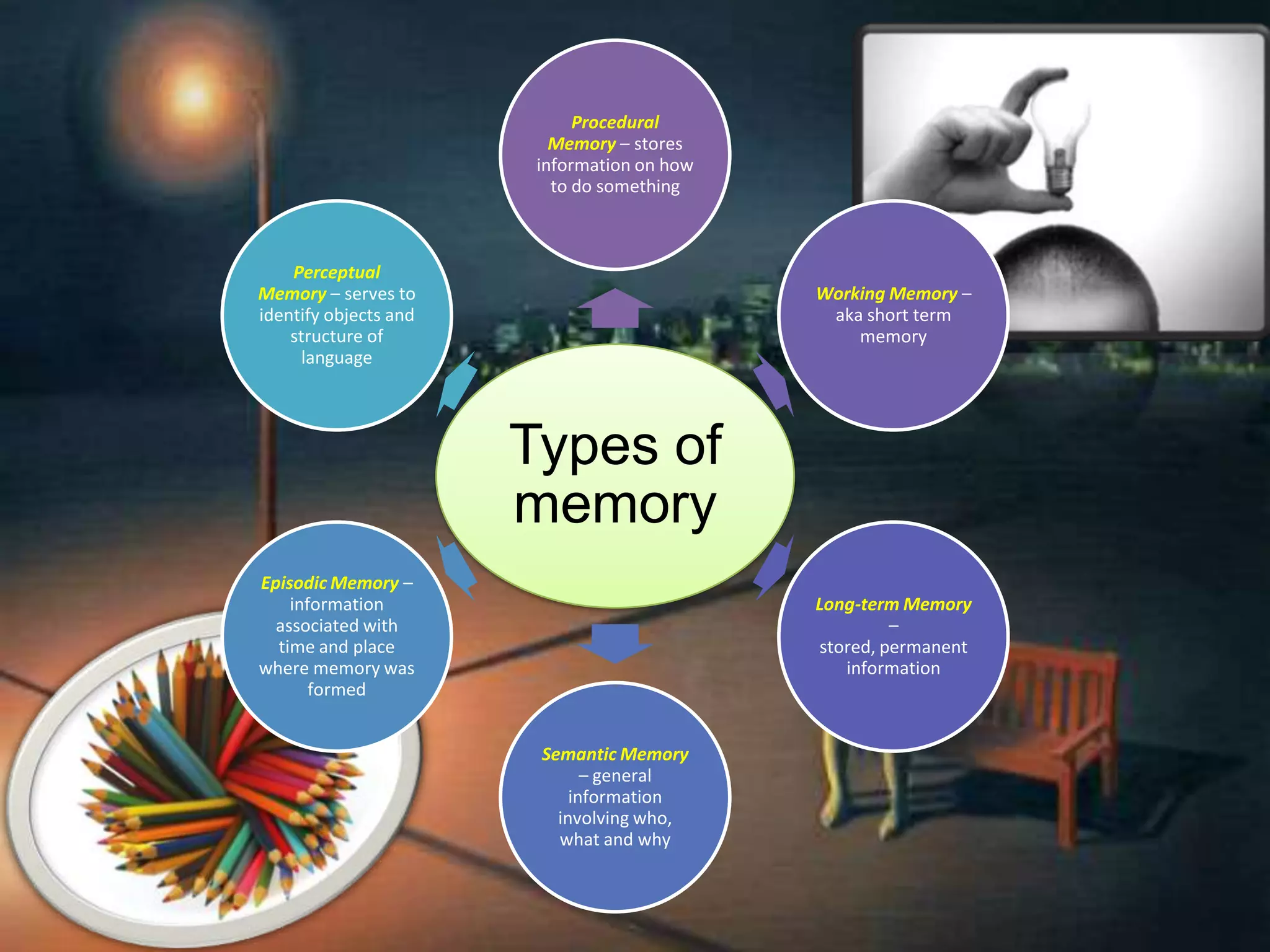
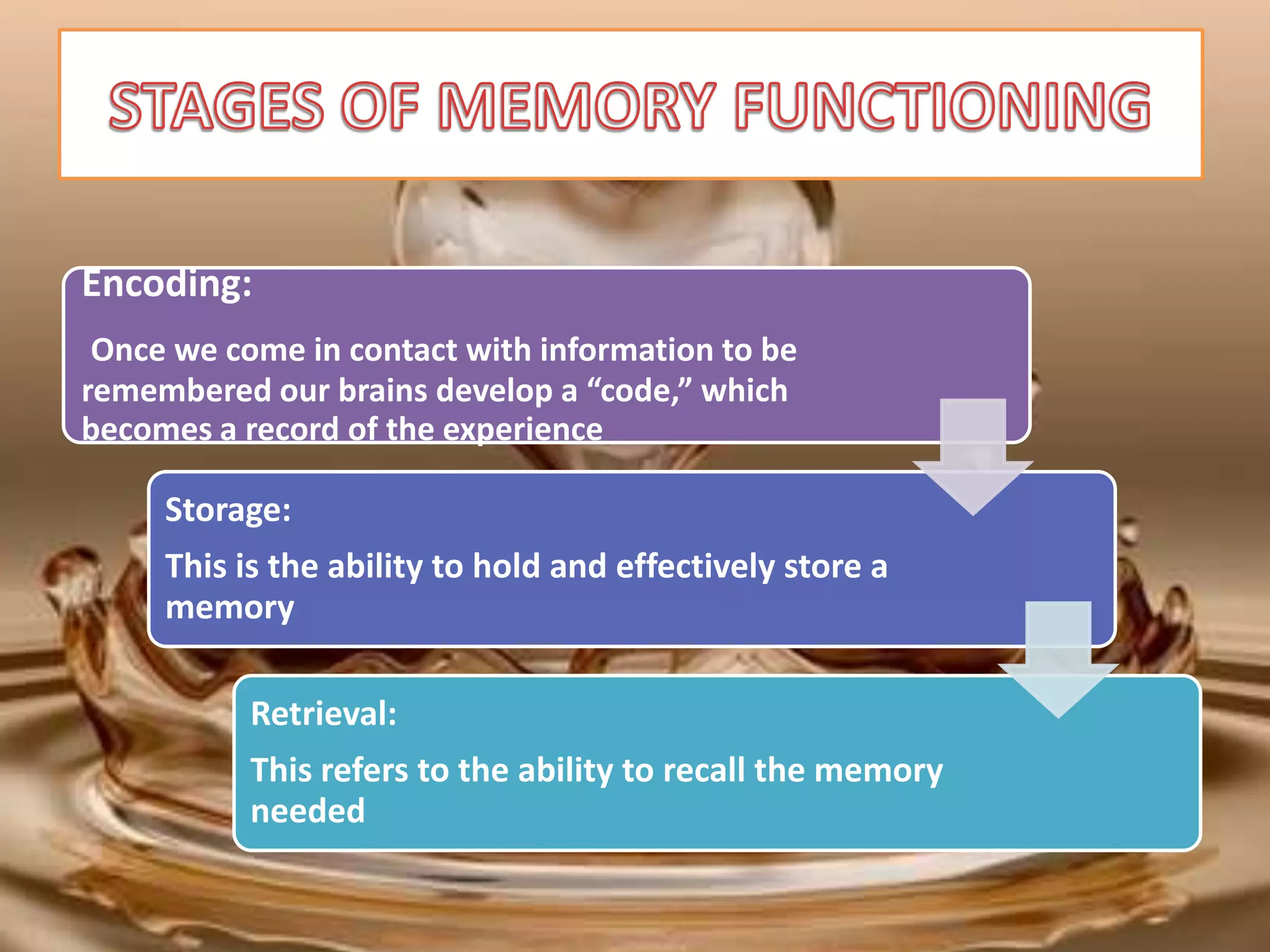
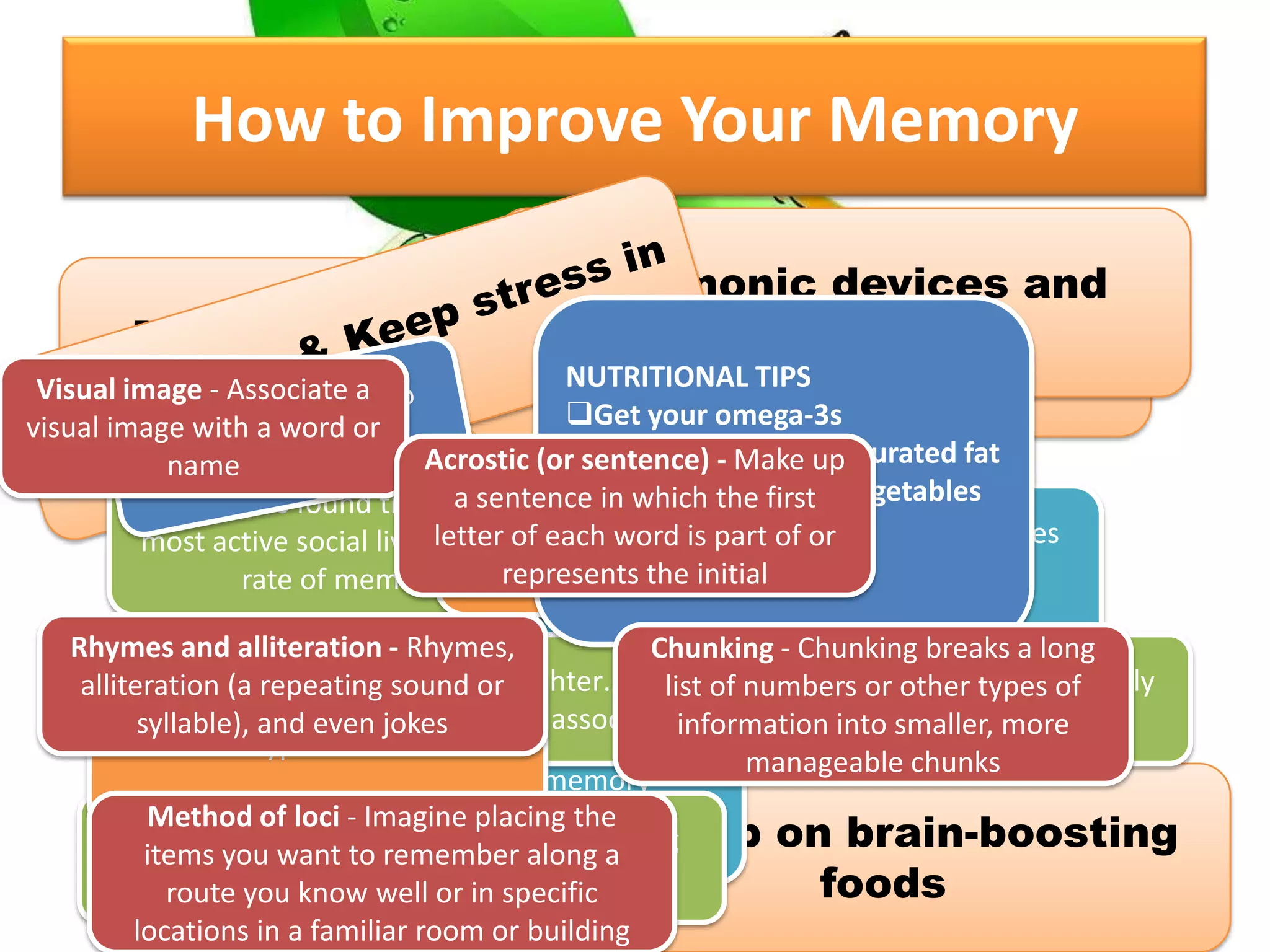
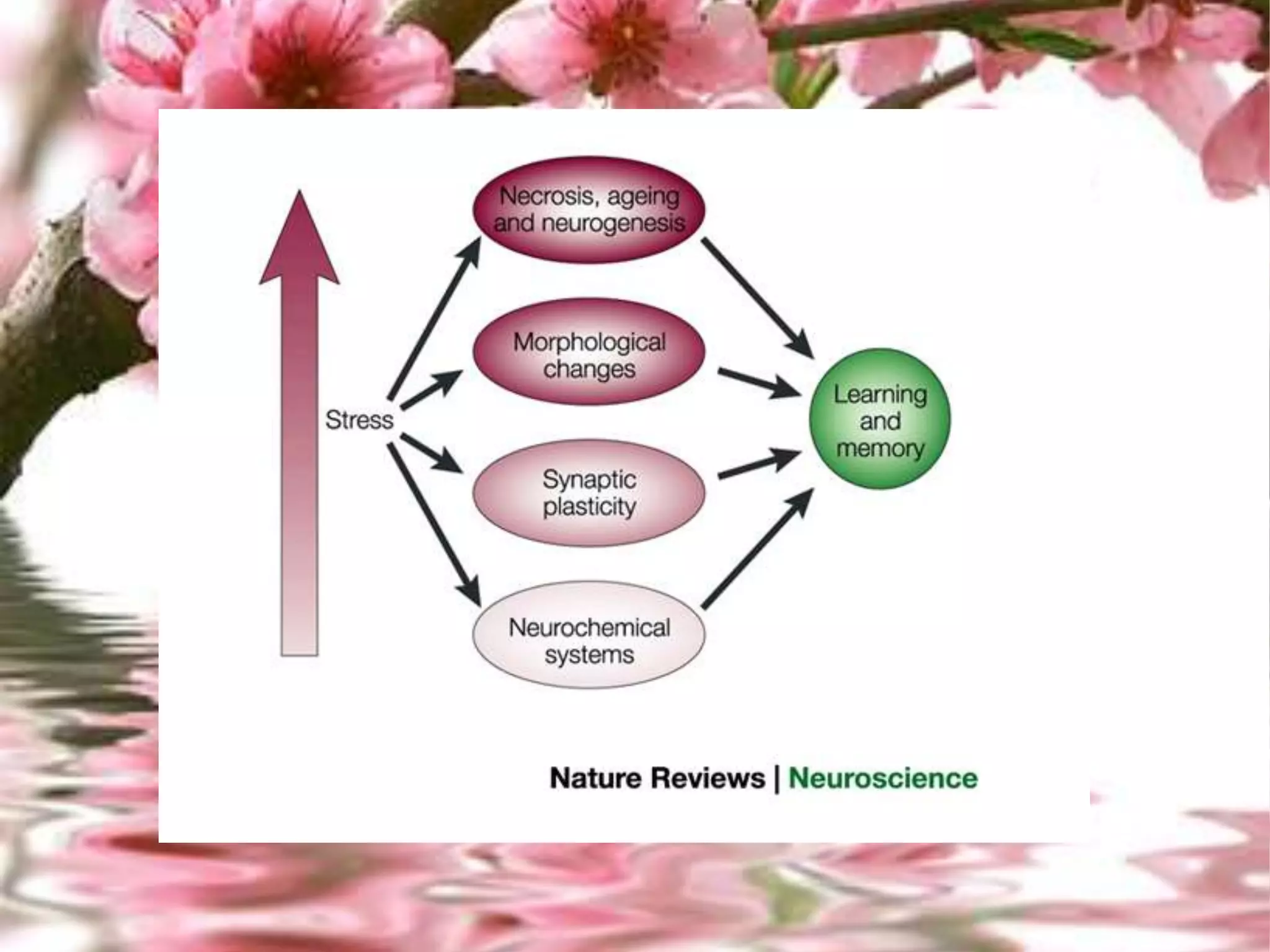
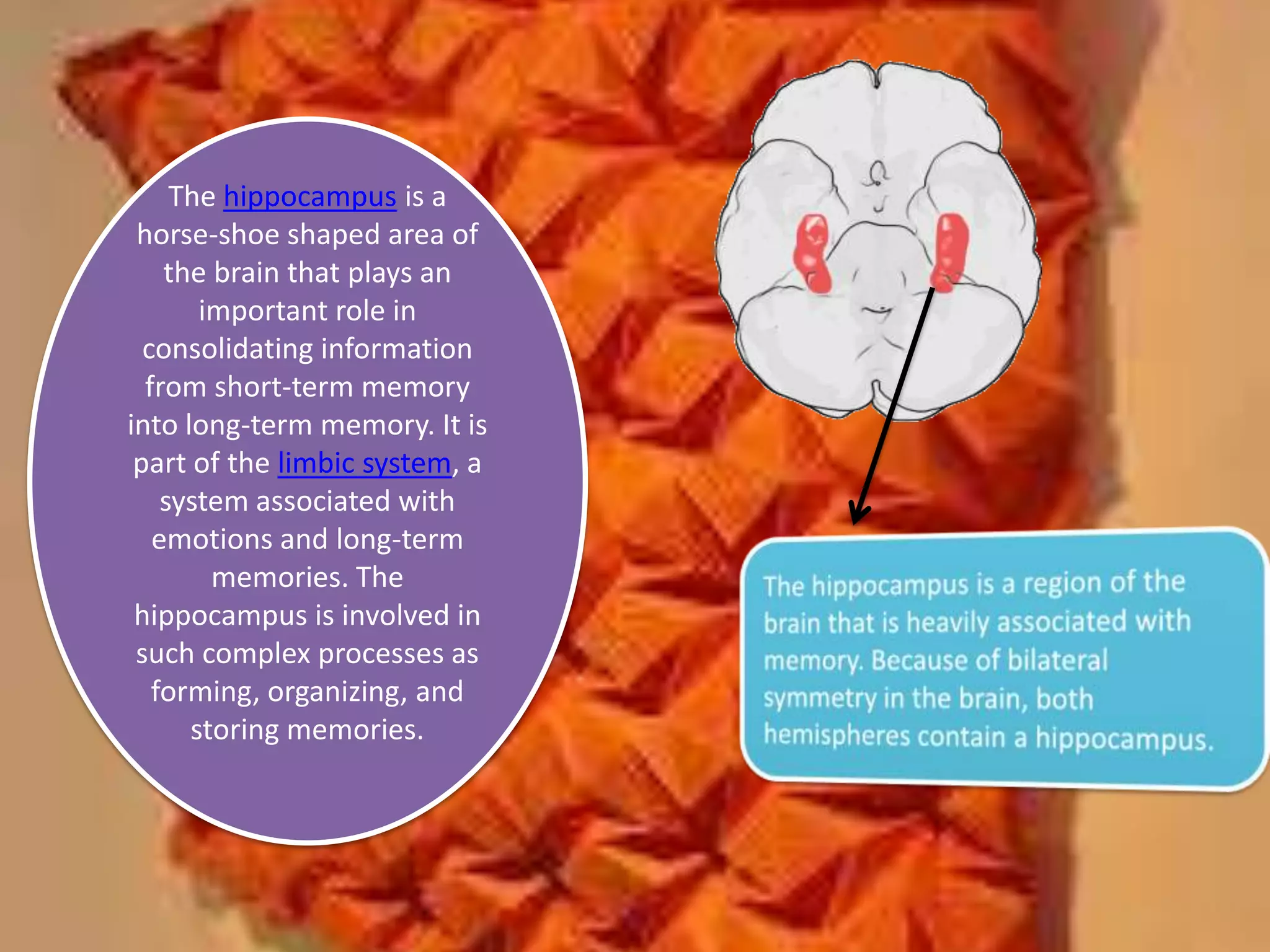
The document outlines different types of memory, including procedural, working, long-term, semantic, episodic, and perceptual memory, explaining their functions and characteristics. It discusses the processes of encoding, storage, and retrieval, as well as strategies for improving memory through lifestyle choices, mnemonic devices, and cognitive techniques. Additionally, it highlights the significance of the hippocampus in memory consolidation and provides tips for enhancing learning and retention.