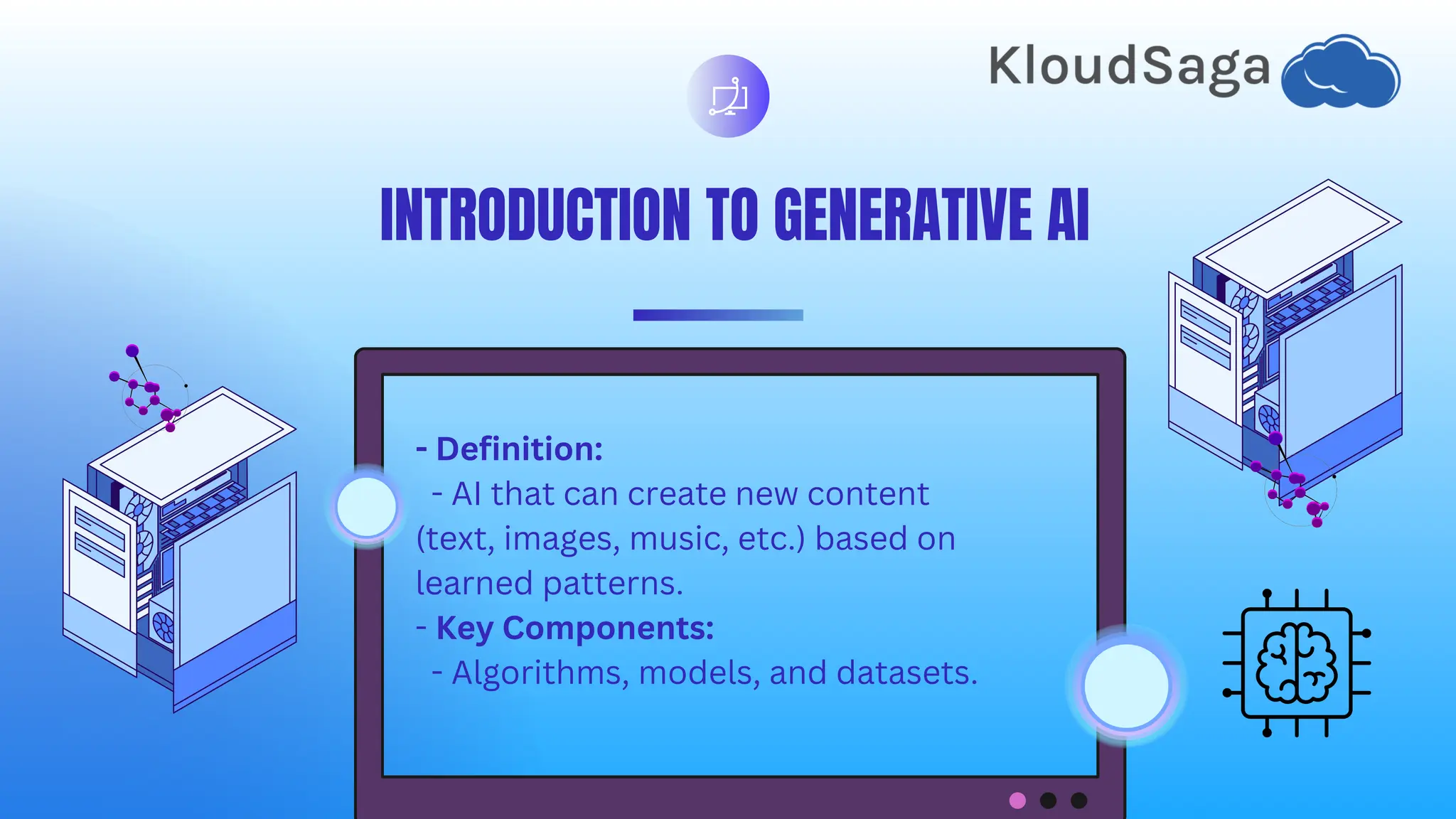
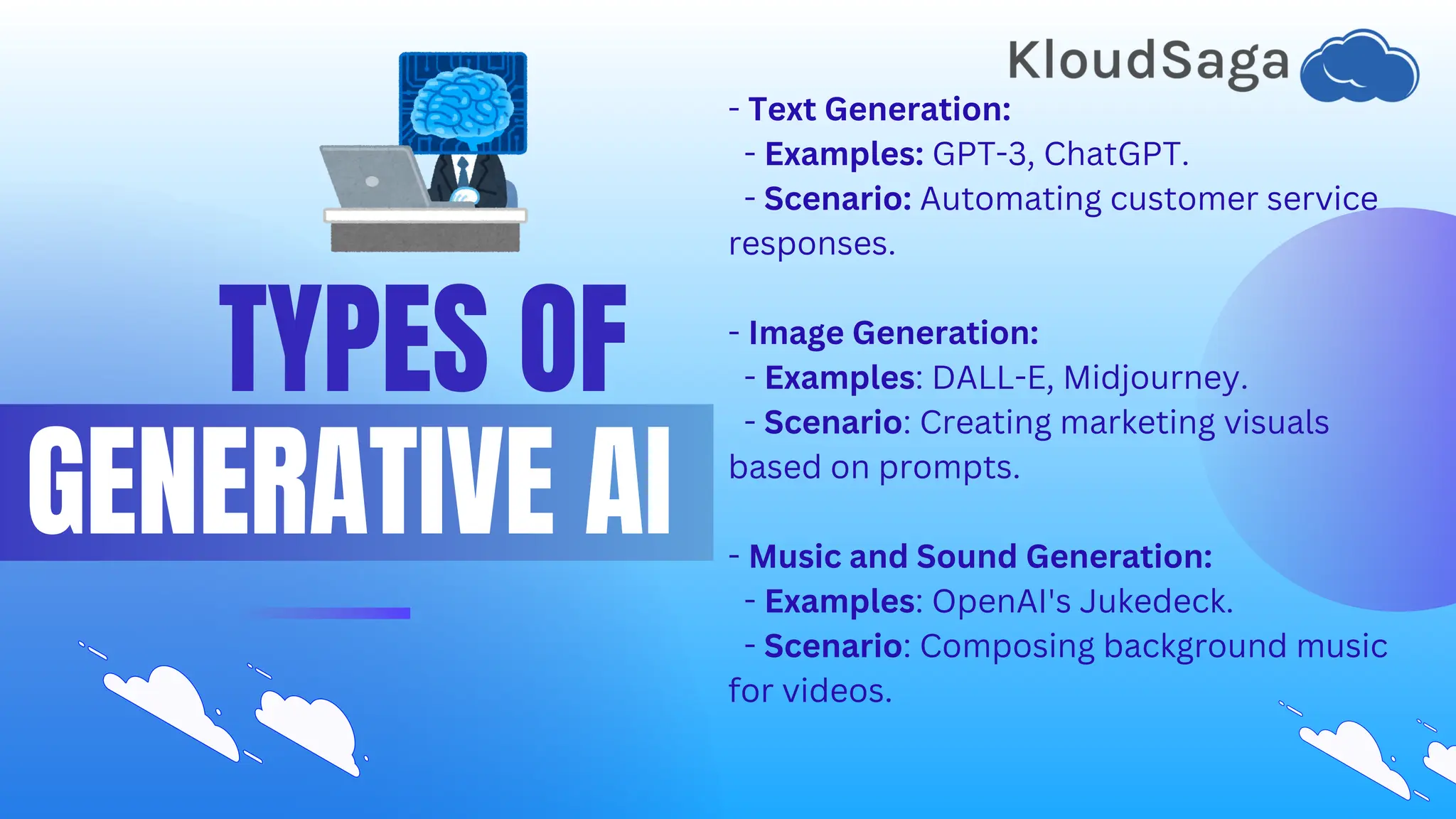
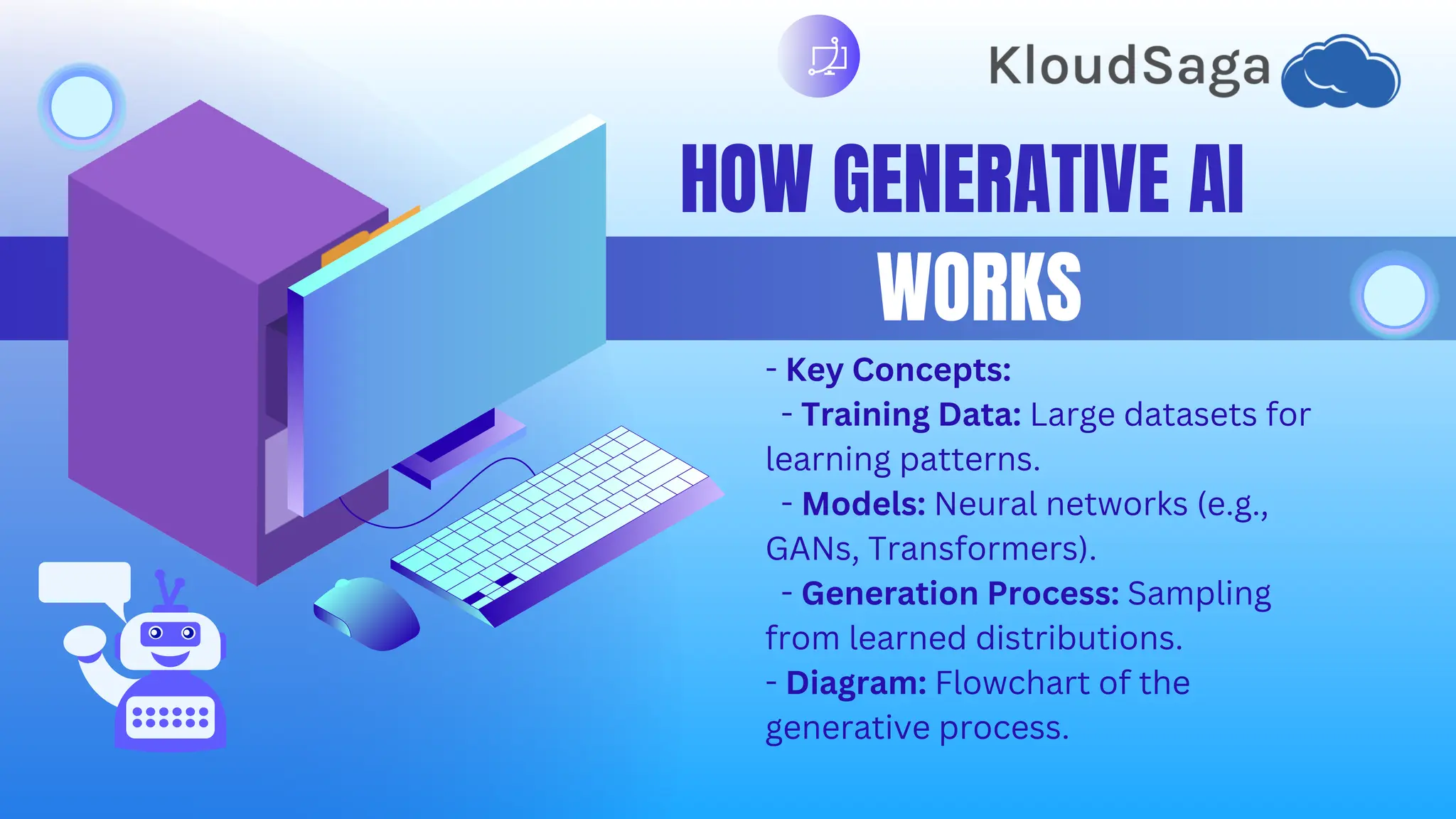
This document provides a beginner's guide to generative AI, outlining its definition, components, and various types, such as text, image, and music generation. It explains key concepts like training data, models (GANS, transformers), and applications in content creation, art, and gaming while addressing ethical considerations including bias and intellectual property. Additionally, it offers resources for getting started, real-world case studies, and trends pointing toward increased personalization and accessibility in generative AI.