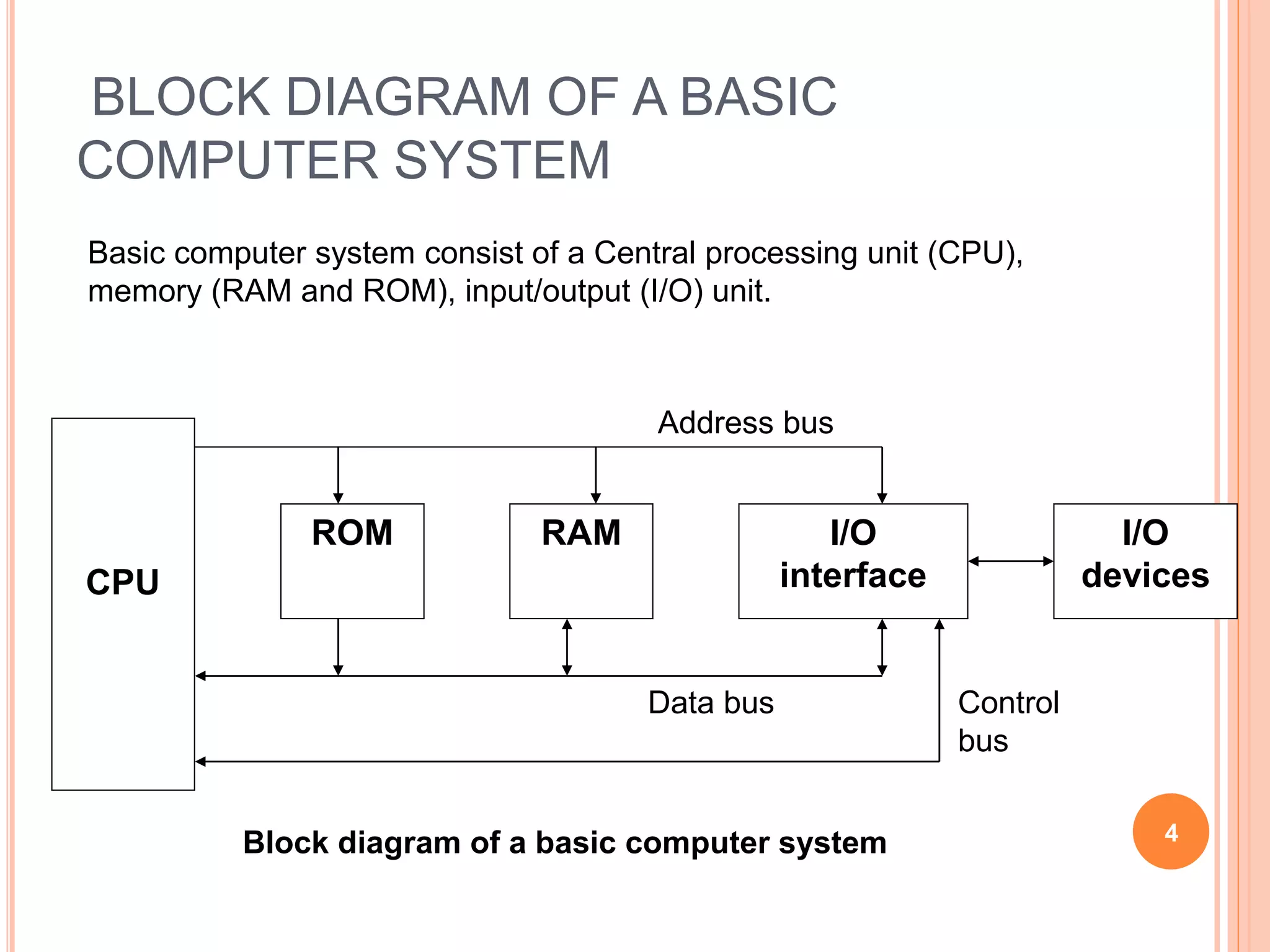
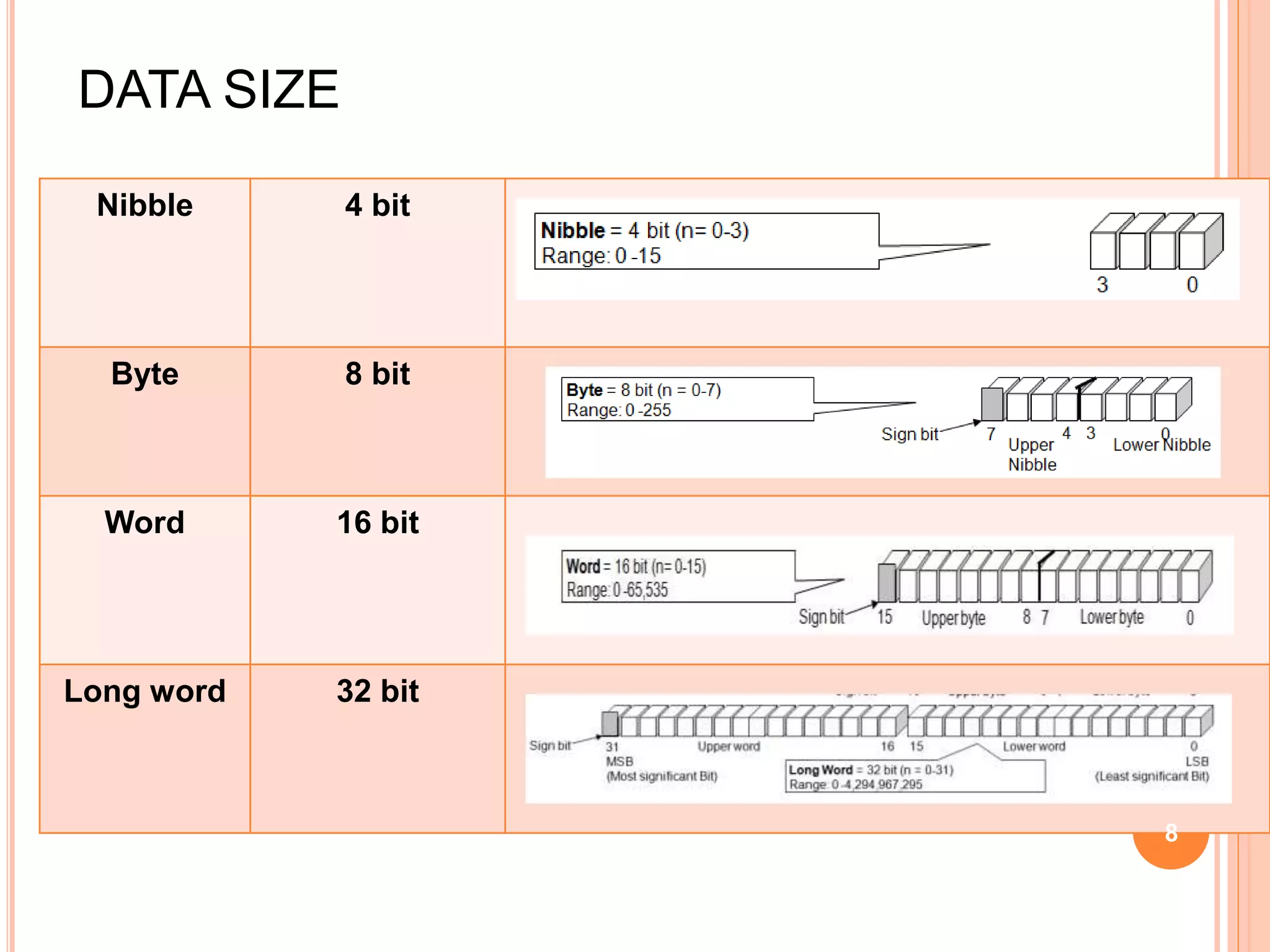
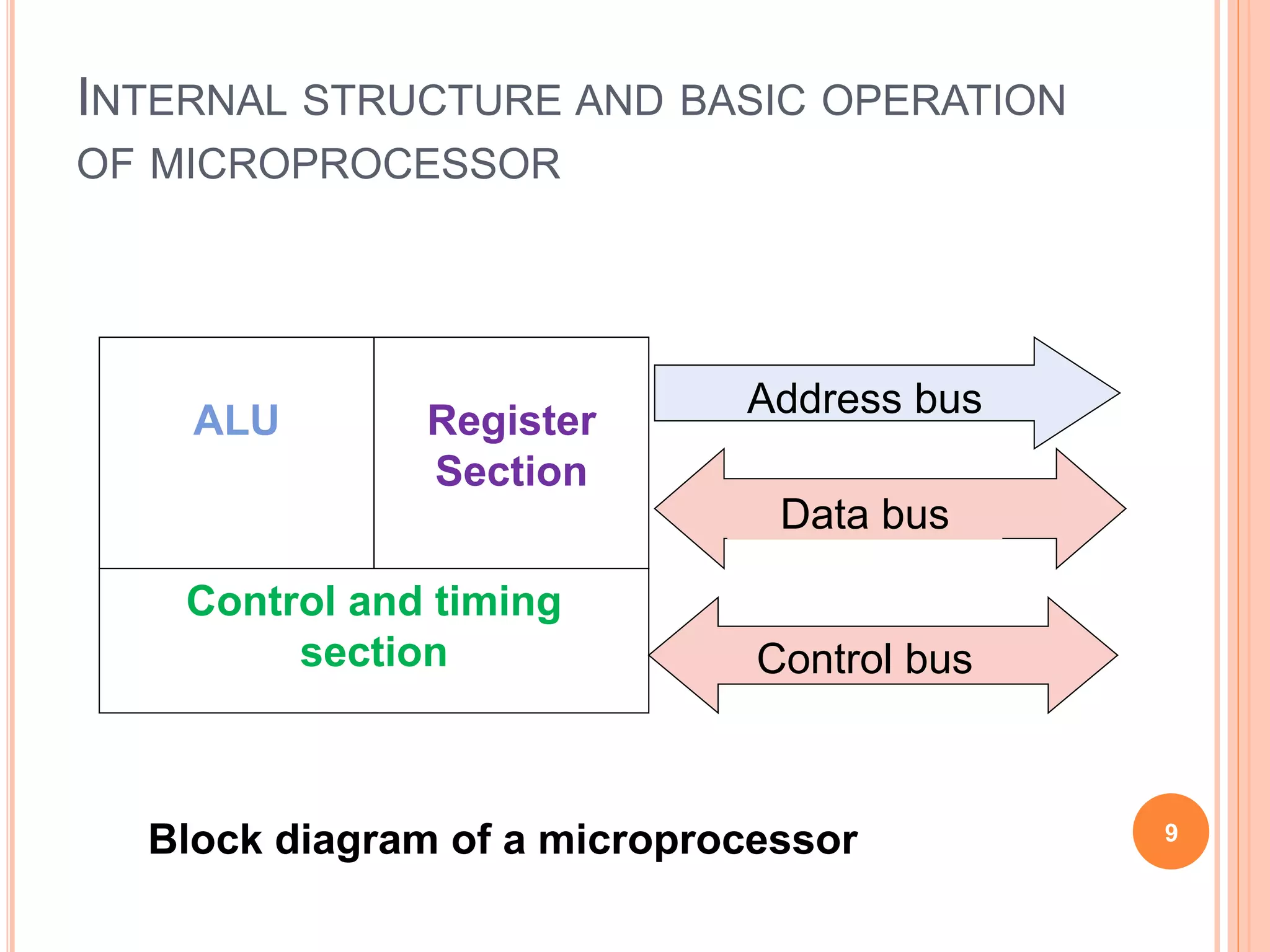
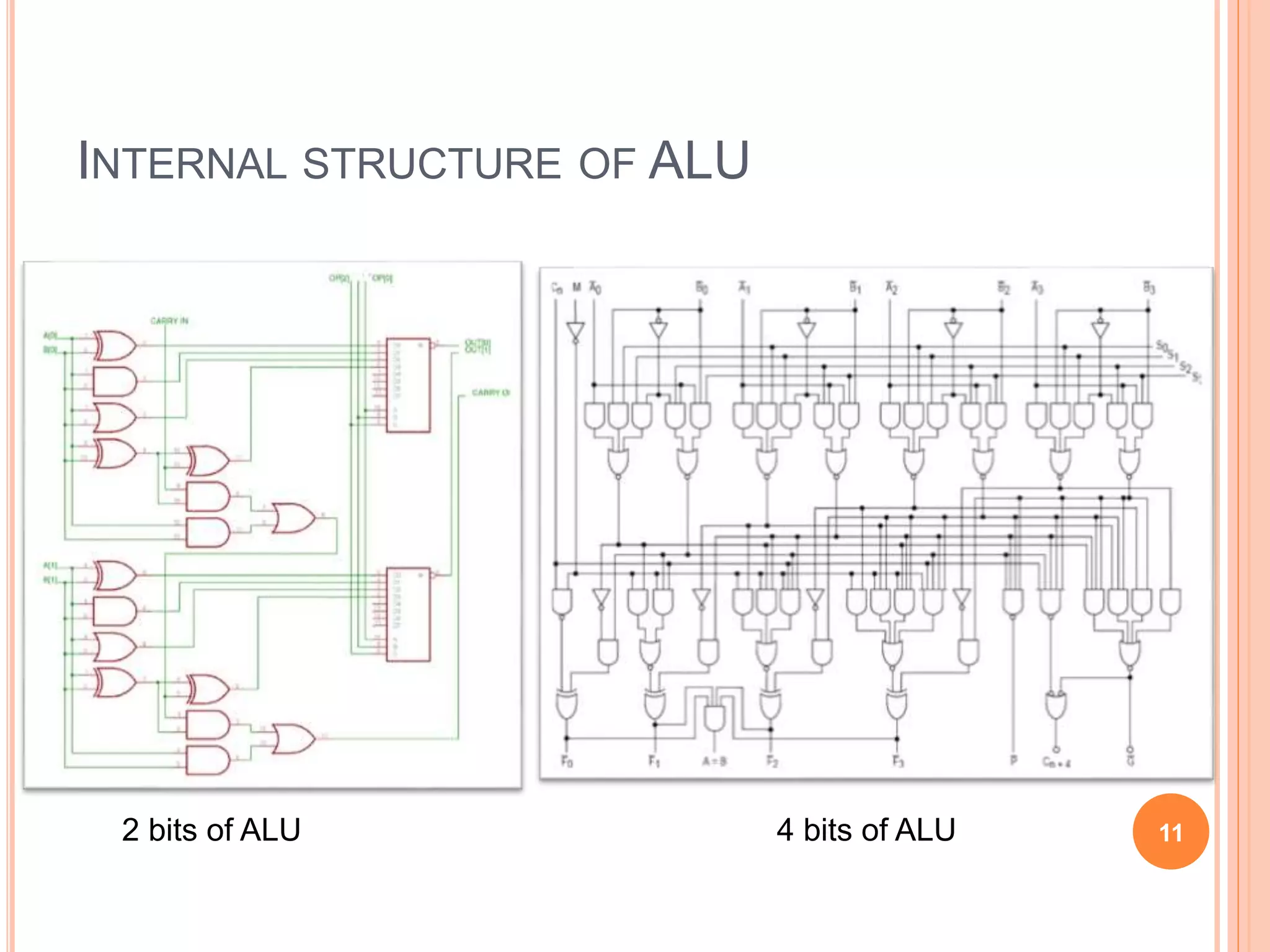
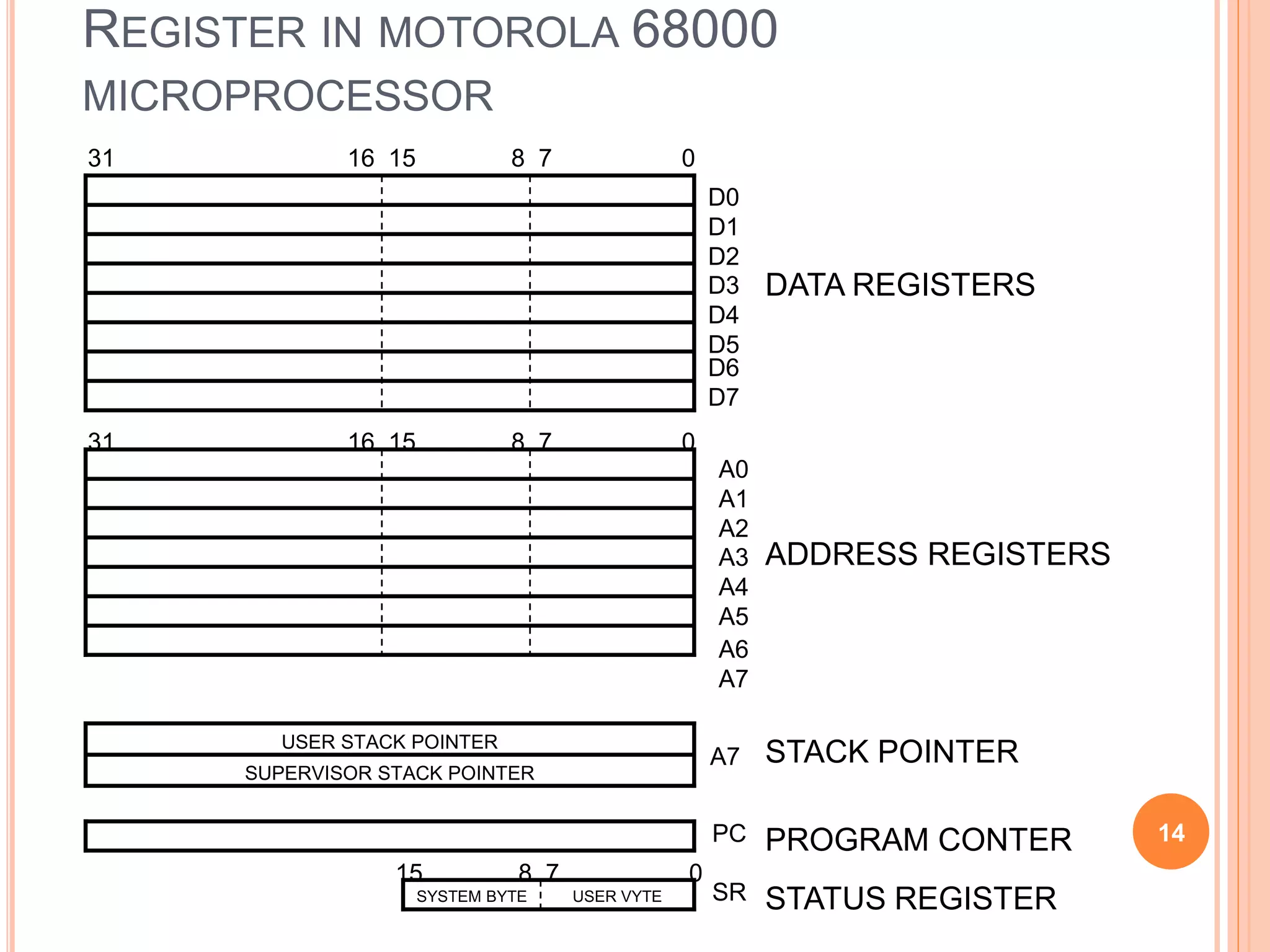
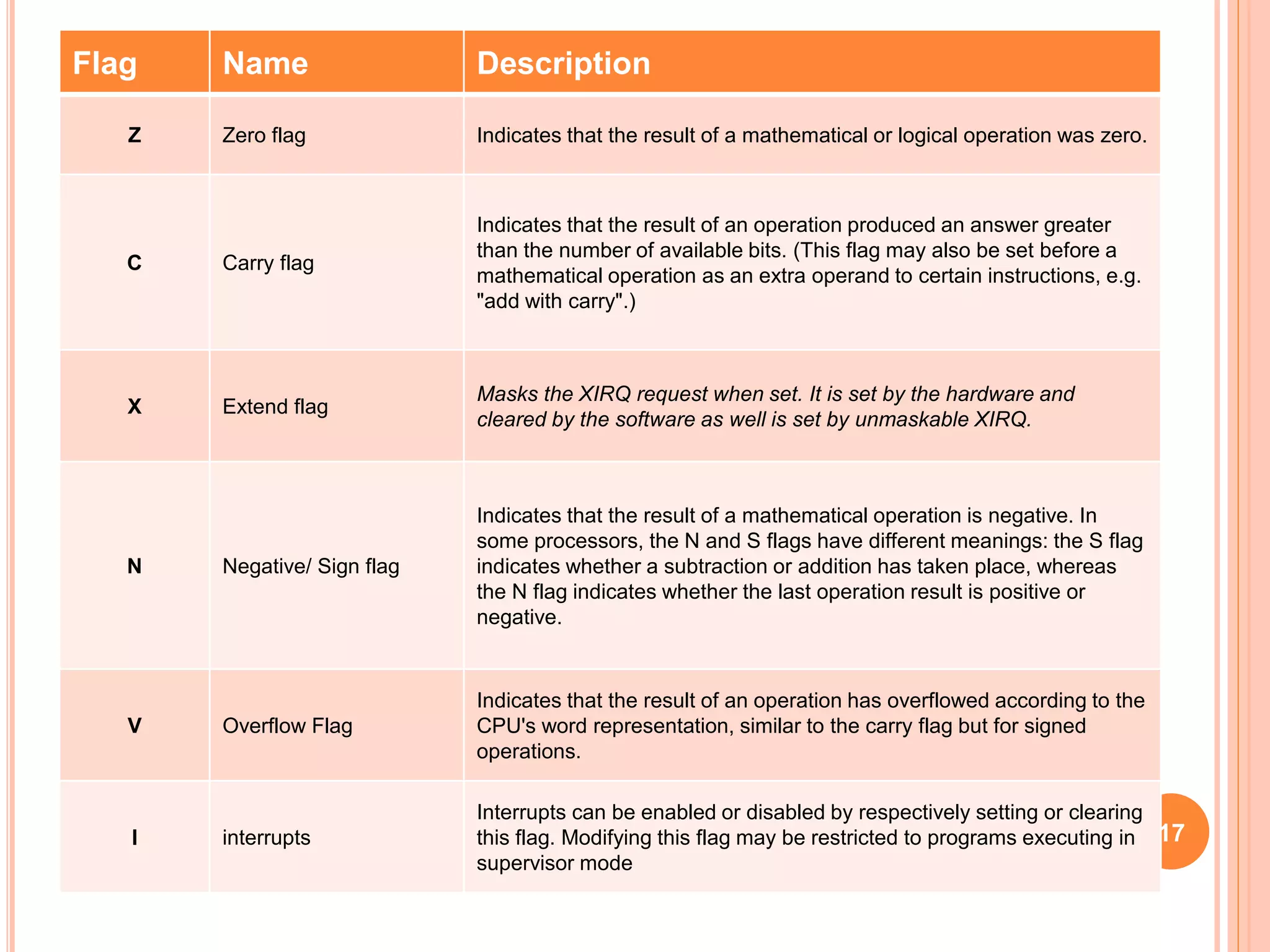
A computer system consists of a central processing unit (CPU), memory, and input/output devices connected via buses. The CPU contains an arithmetic logic unit to perform calculations, registers to store data and instructions, a control unit to coordinate operations, and a program counter. Data is transferred over the data bus in nibbles, bytes, words or long words. The CPU fetches and executes instructions in cycles. Examples of early microprocessors include the Intel 8085 and 8086.