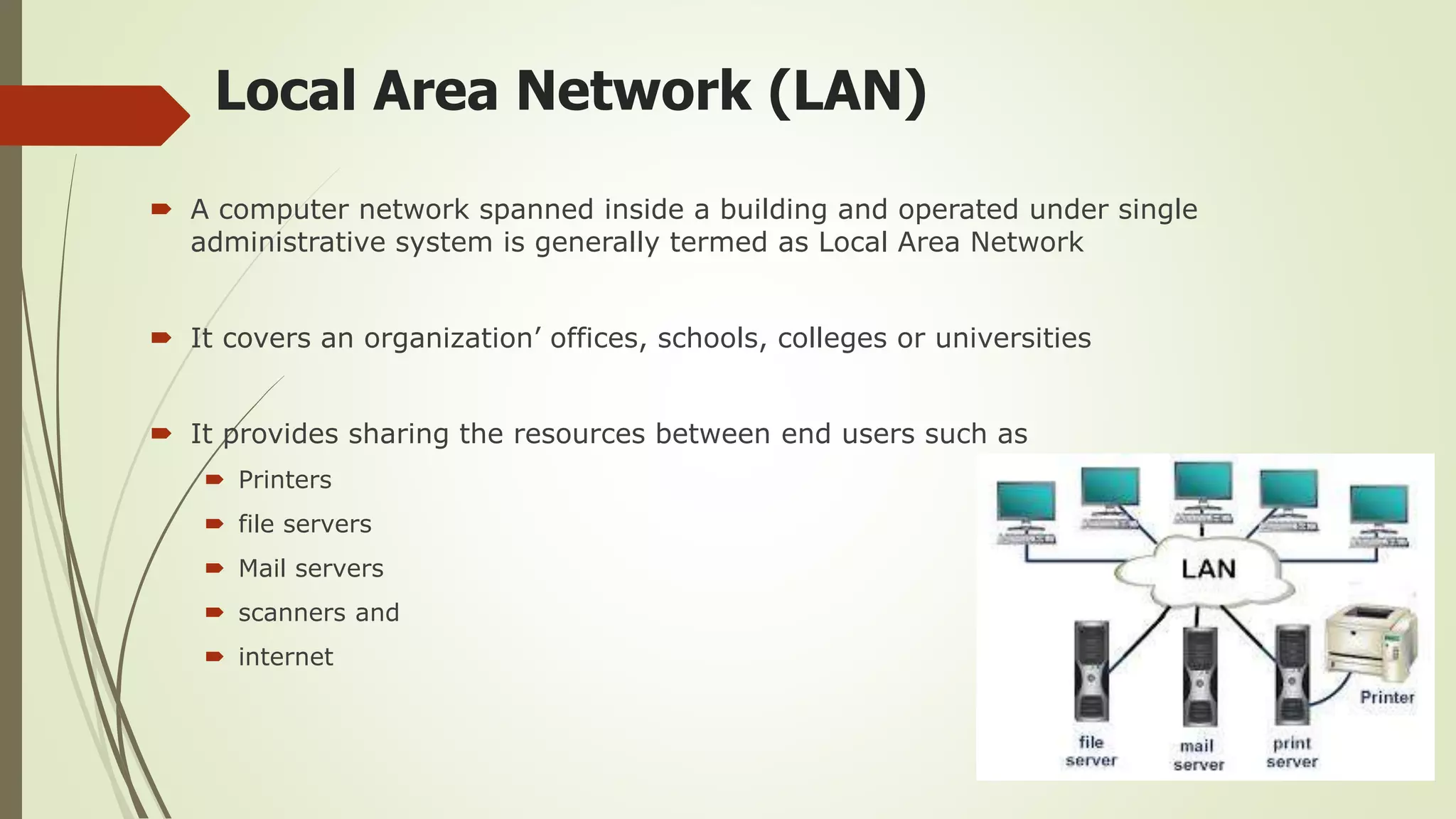
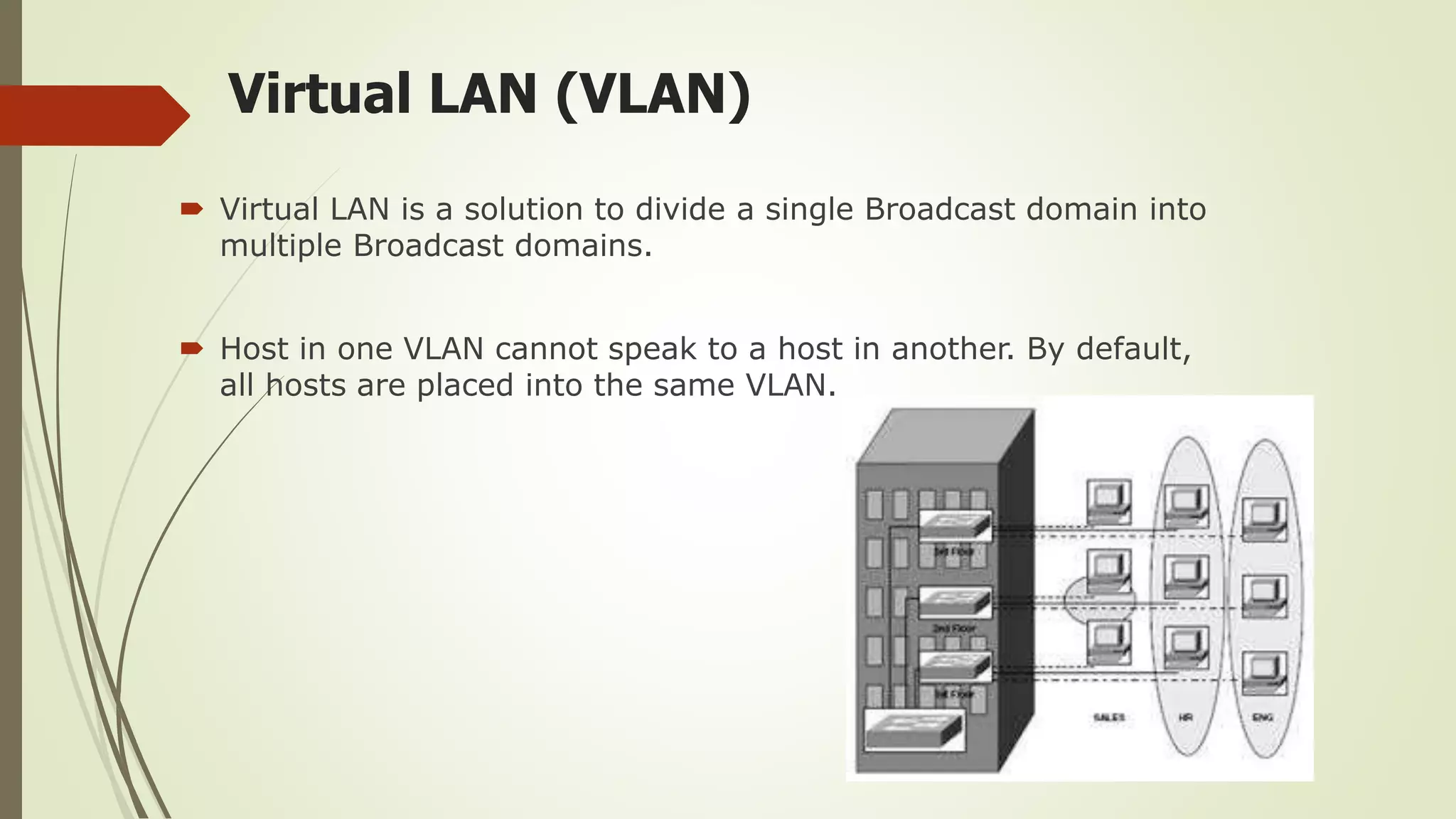
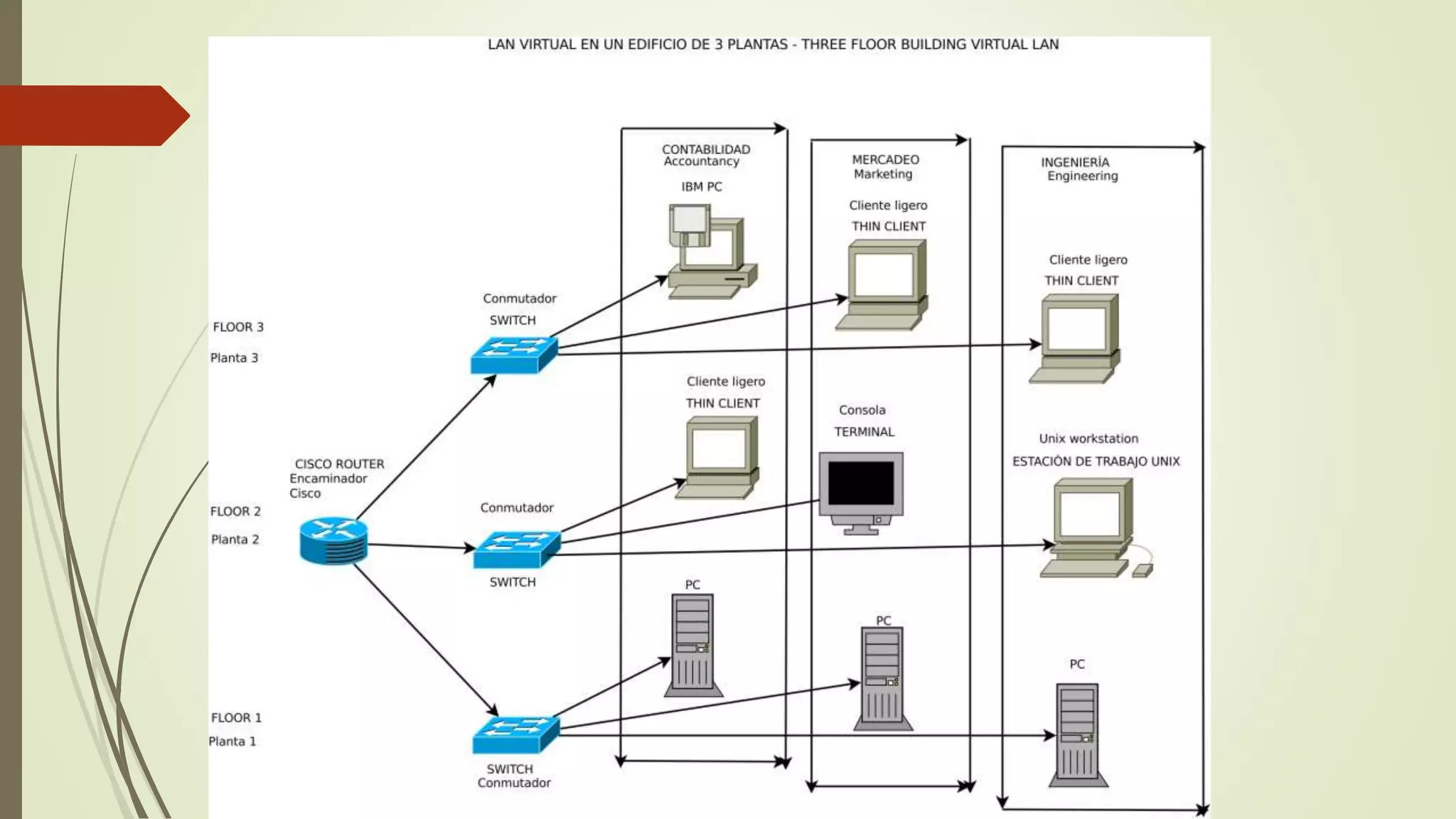
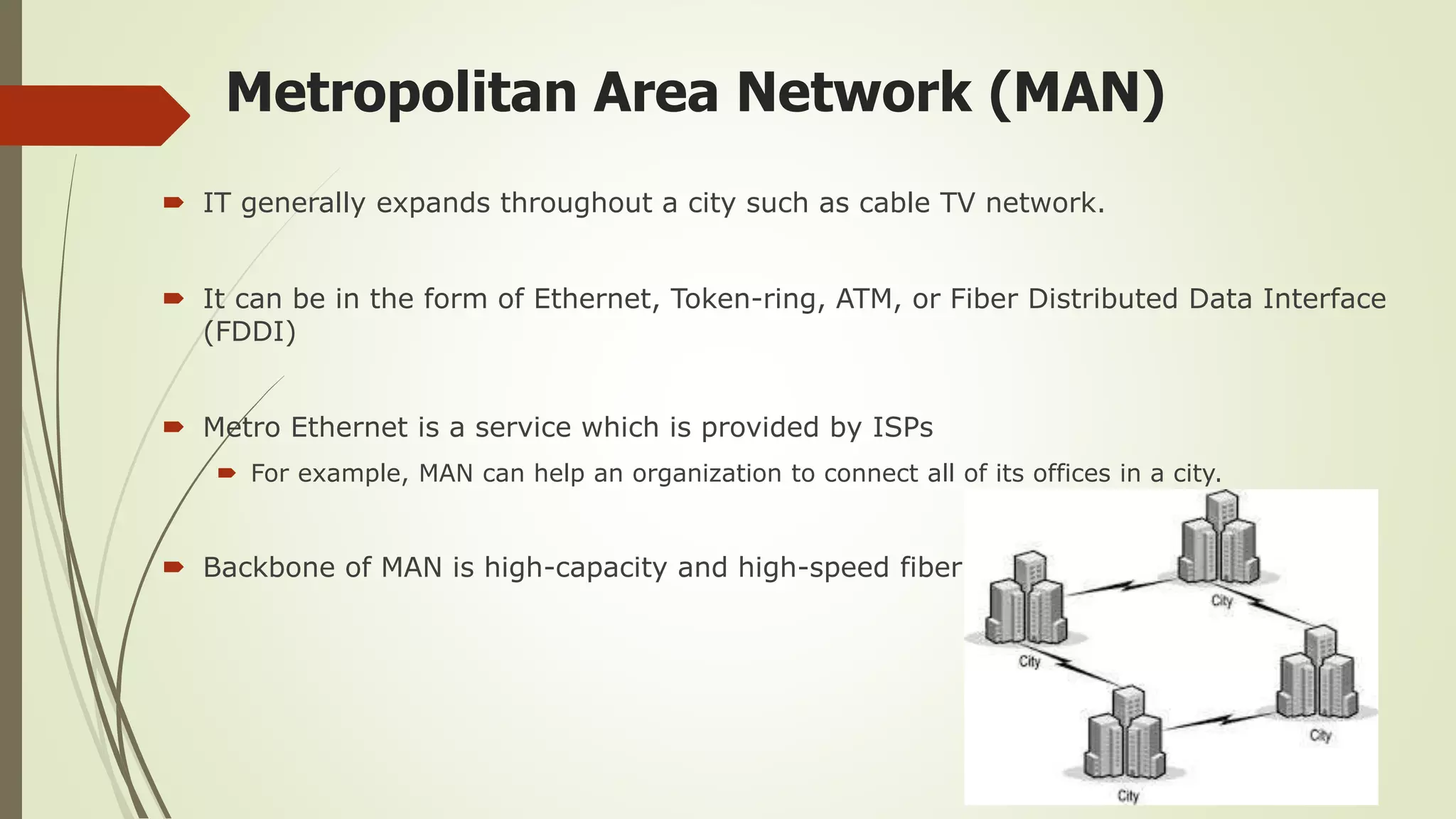
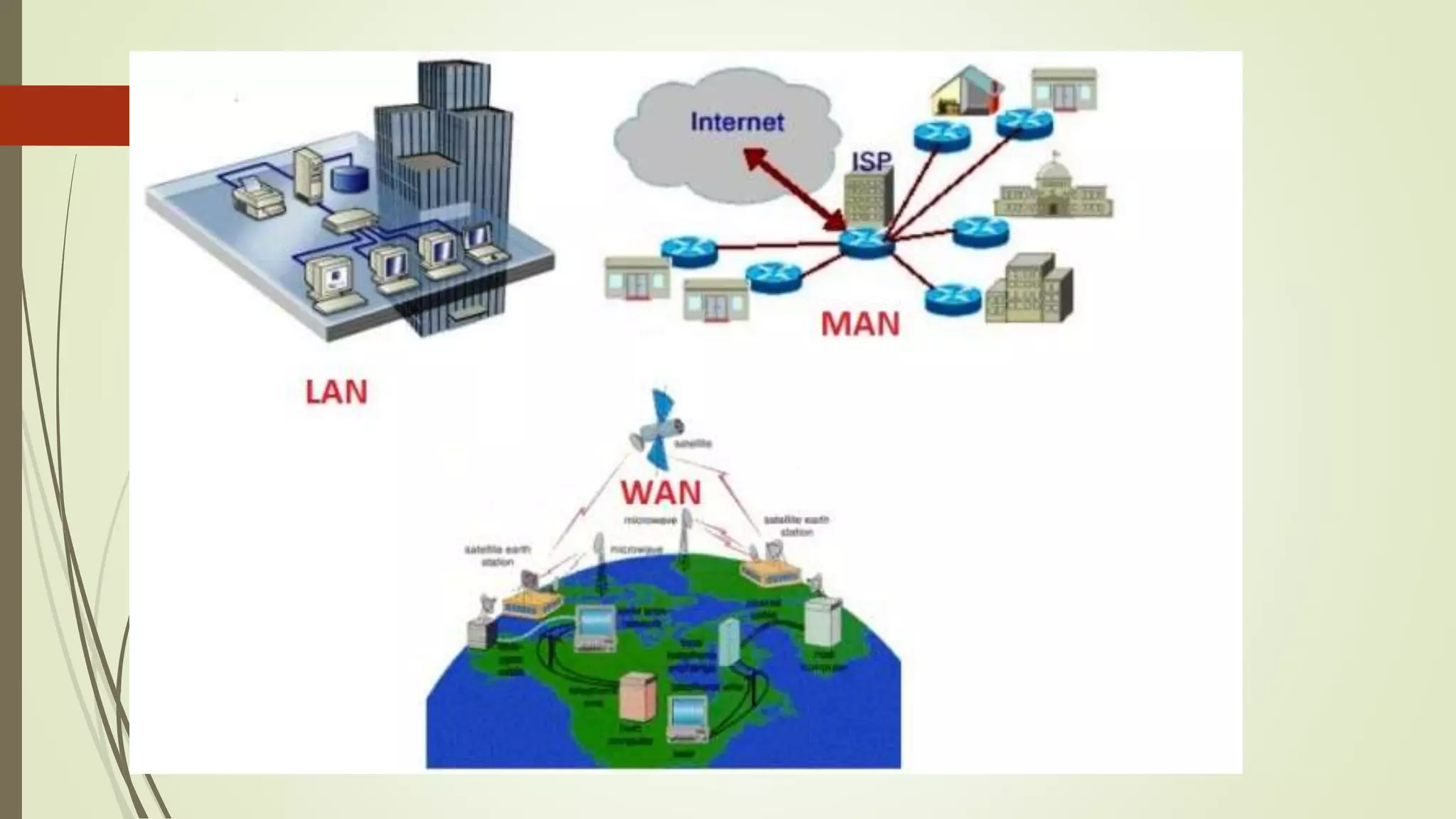
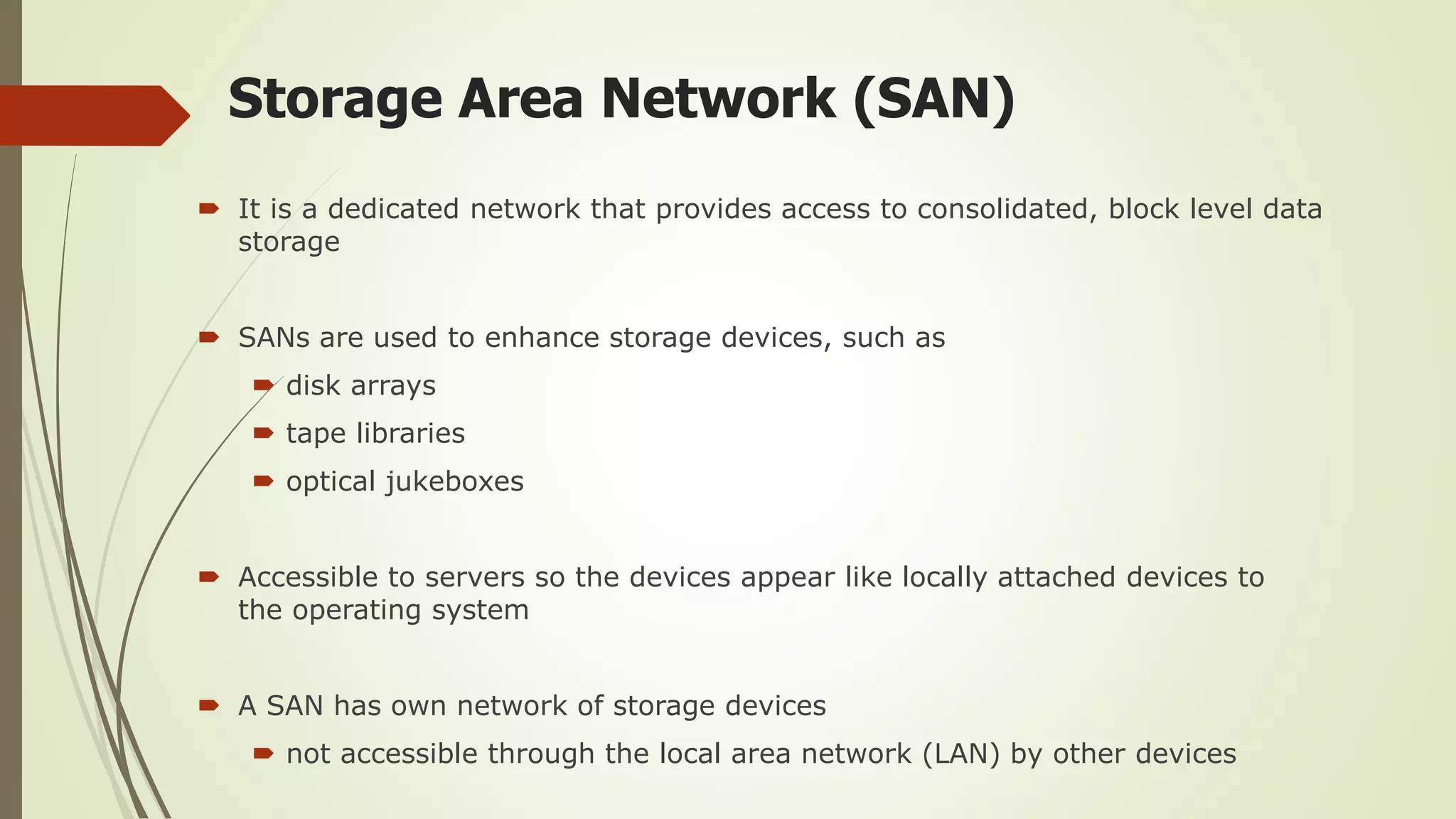
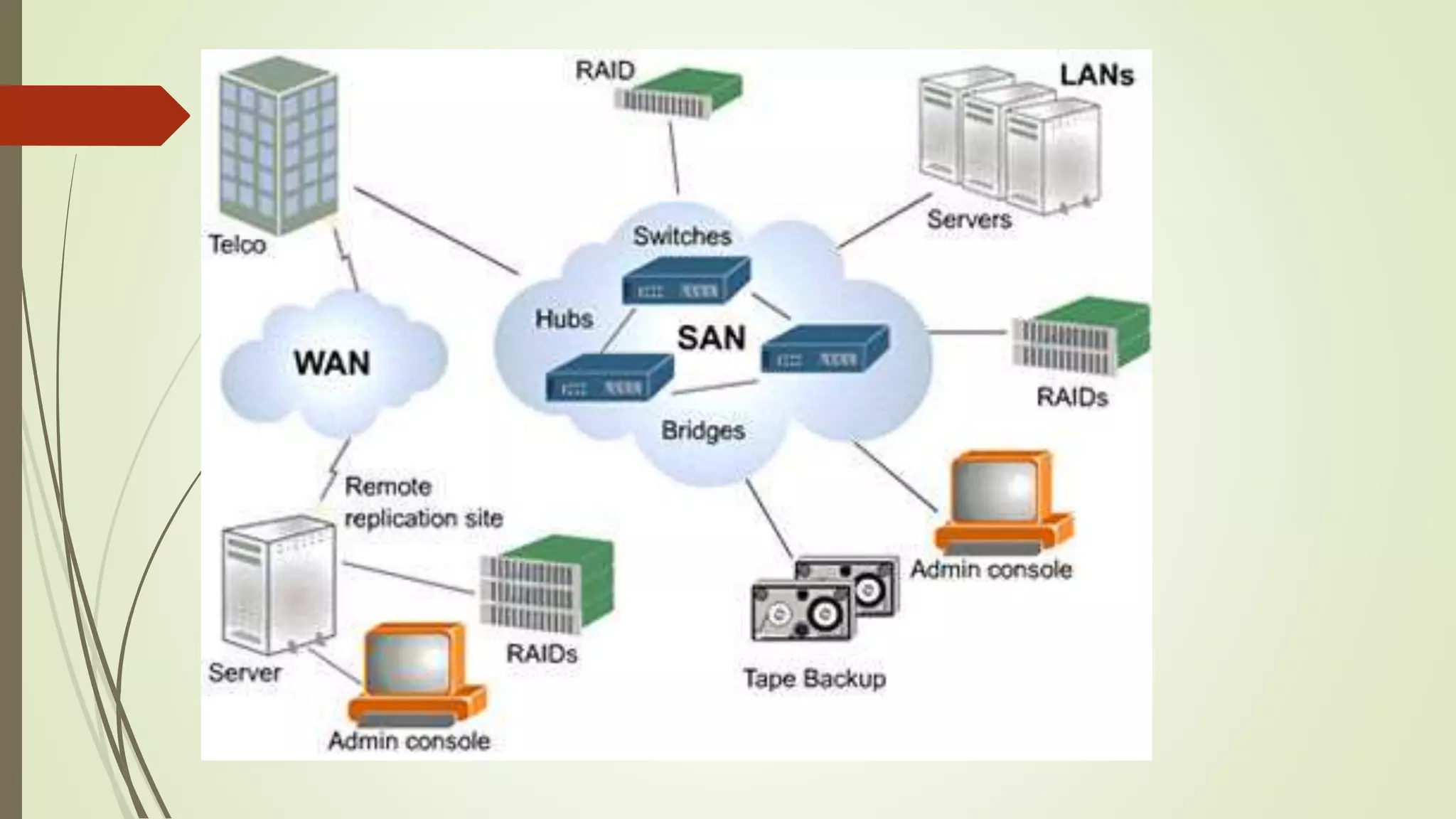
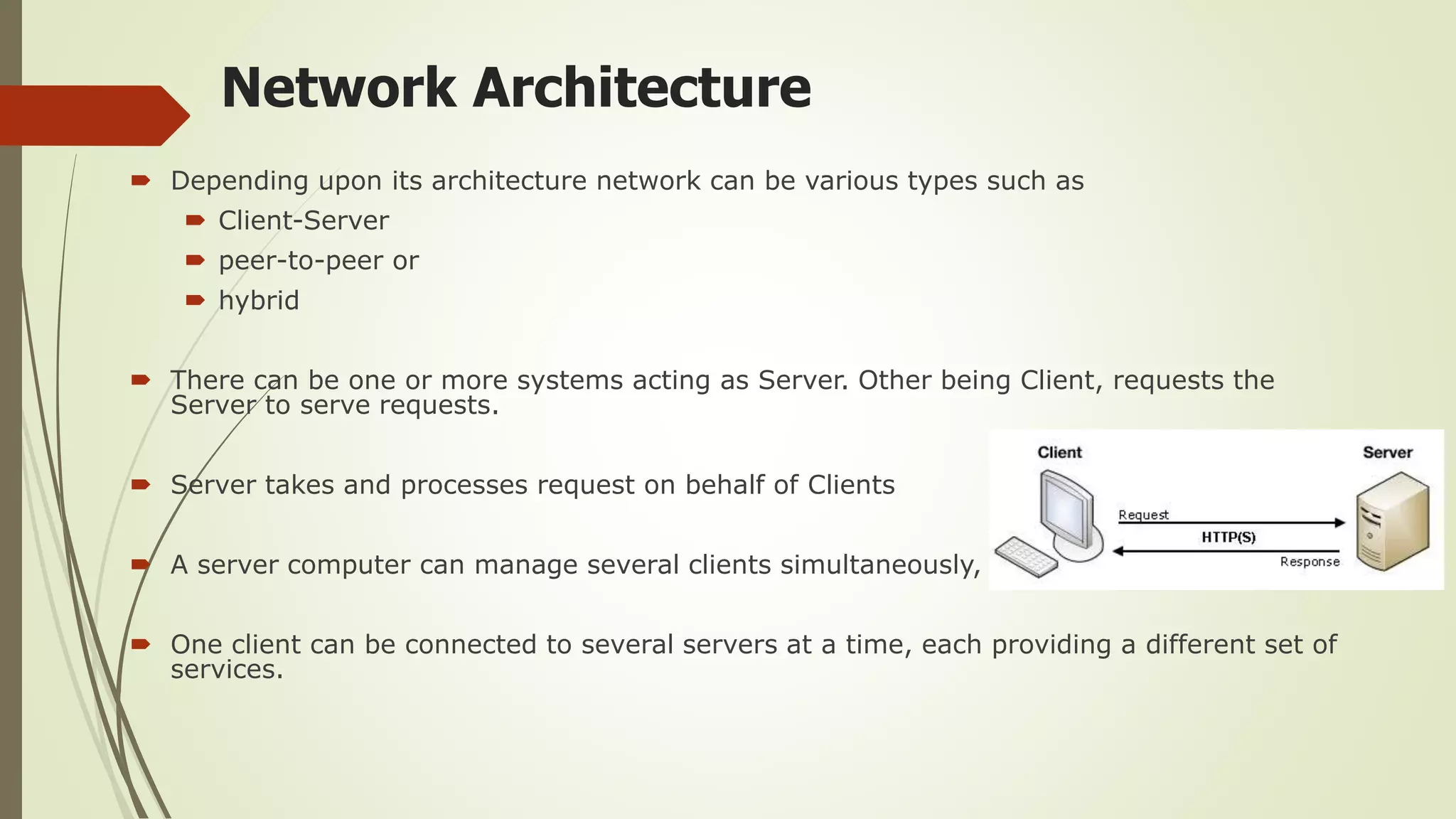
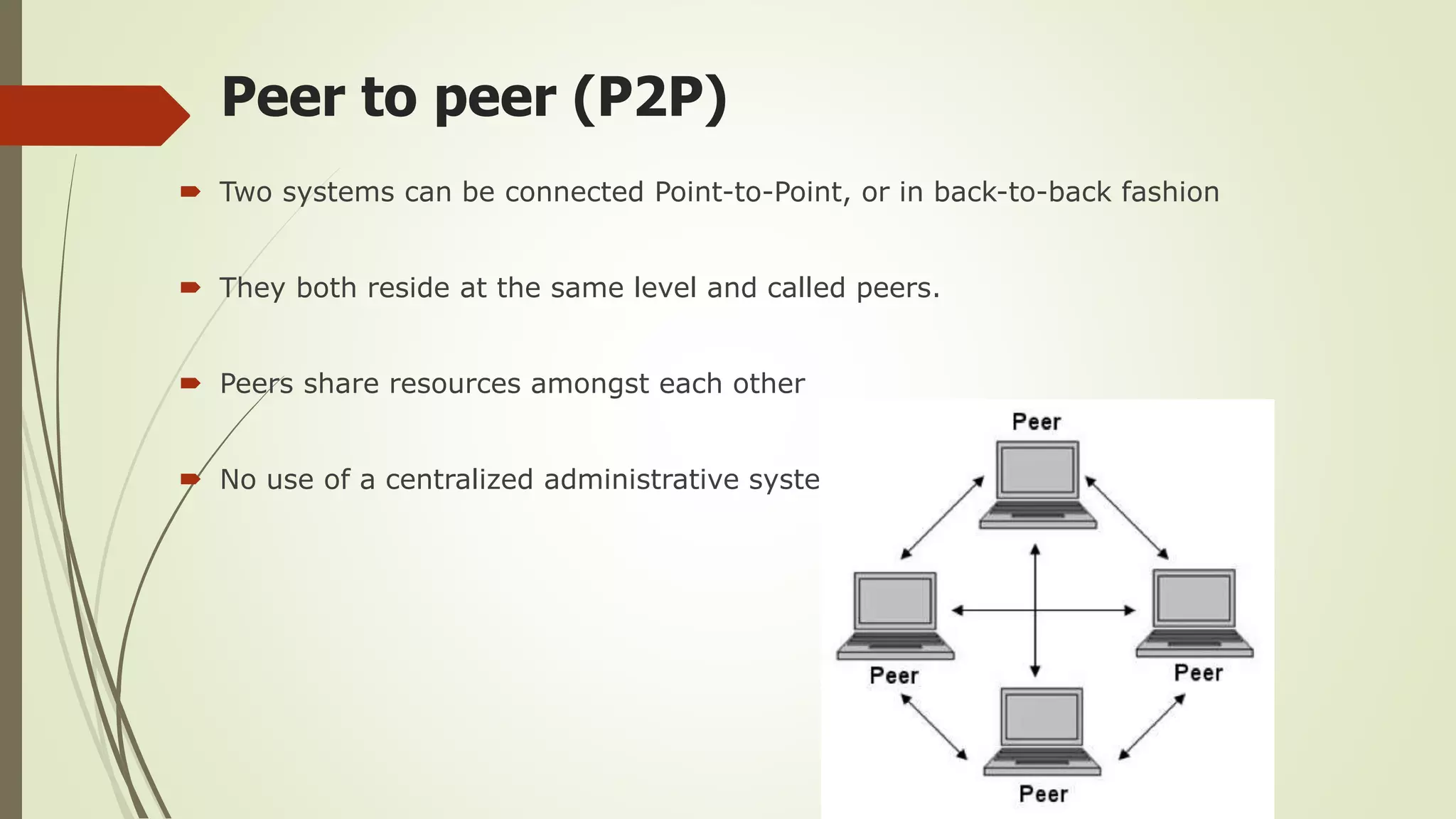
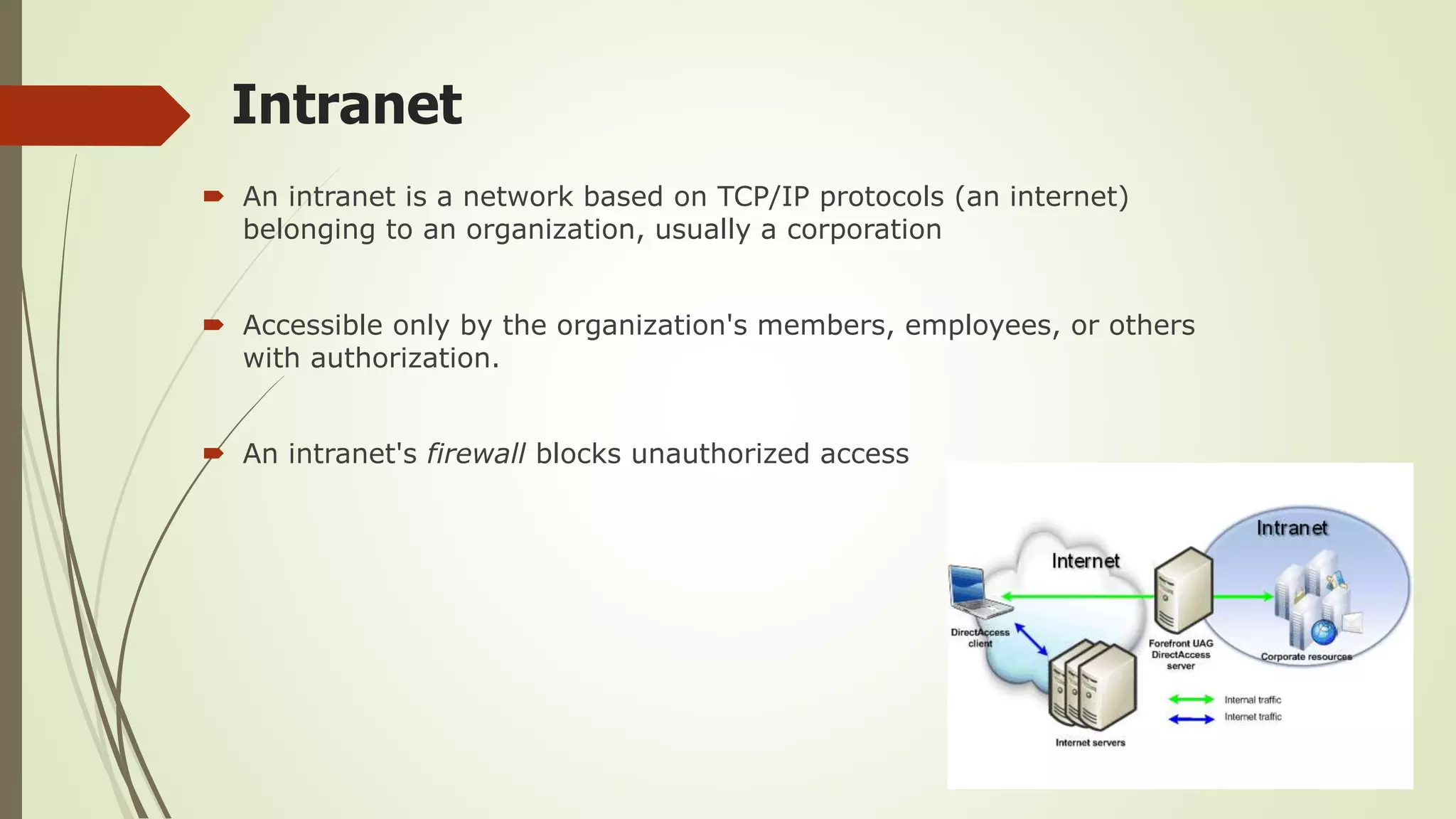
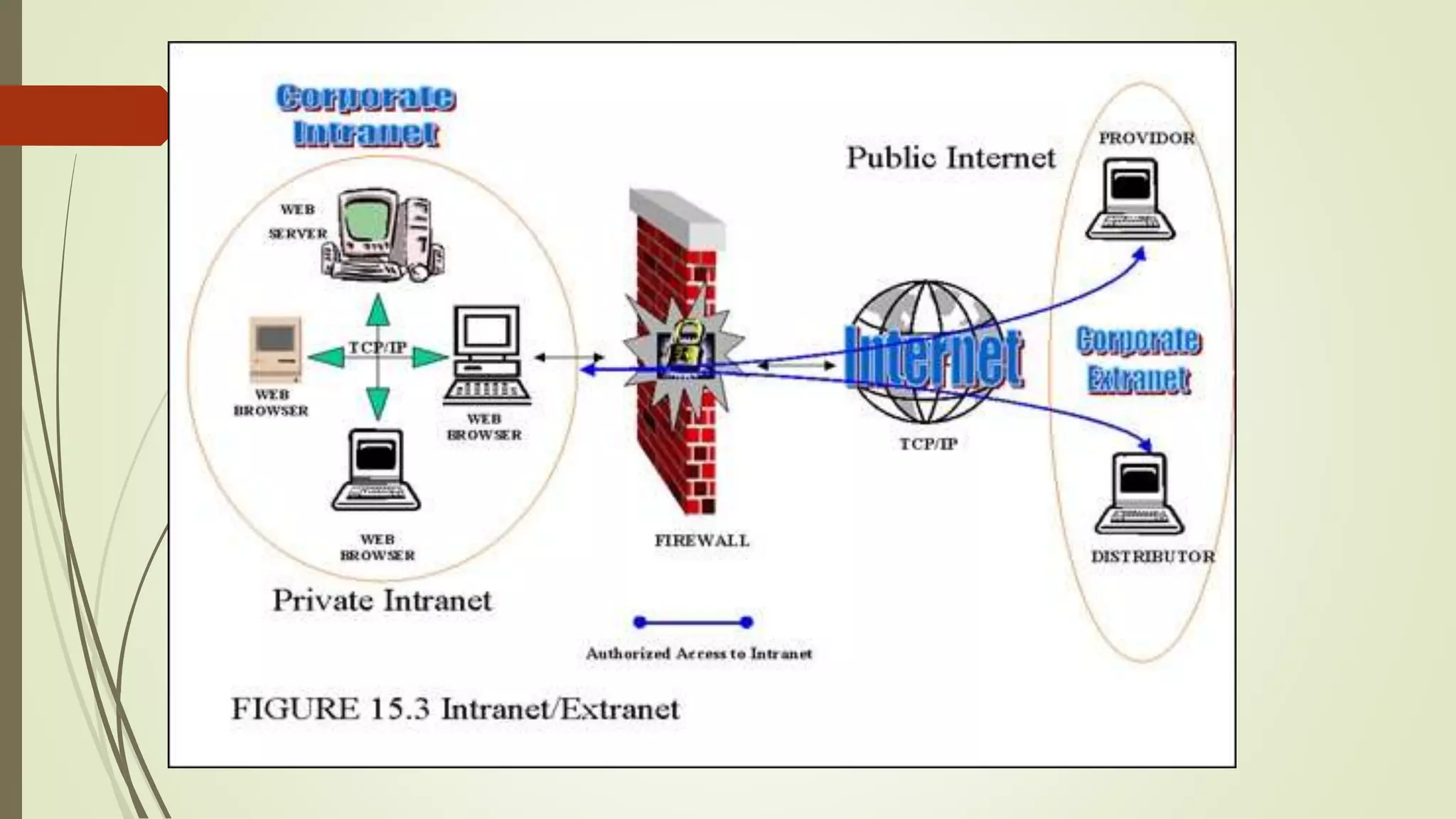
This document defines and classifies different types of computer networks. It describes networks based on their geographical span, including personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), wide area networks (WANs), and storage area networks (SANs). The document also discusses network architecture types like client-server, peer-to-peer, and hybrid networks. Additionally, it provides brief explanations of internetworks, intranets, extranets, and virtual private networks (VPNs).