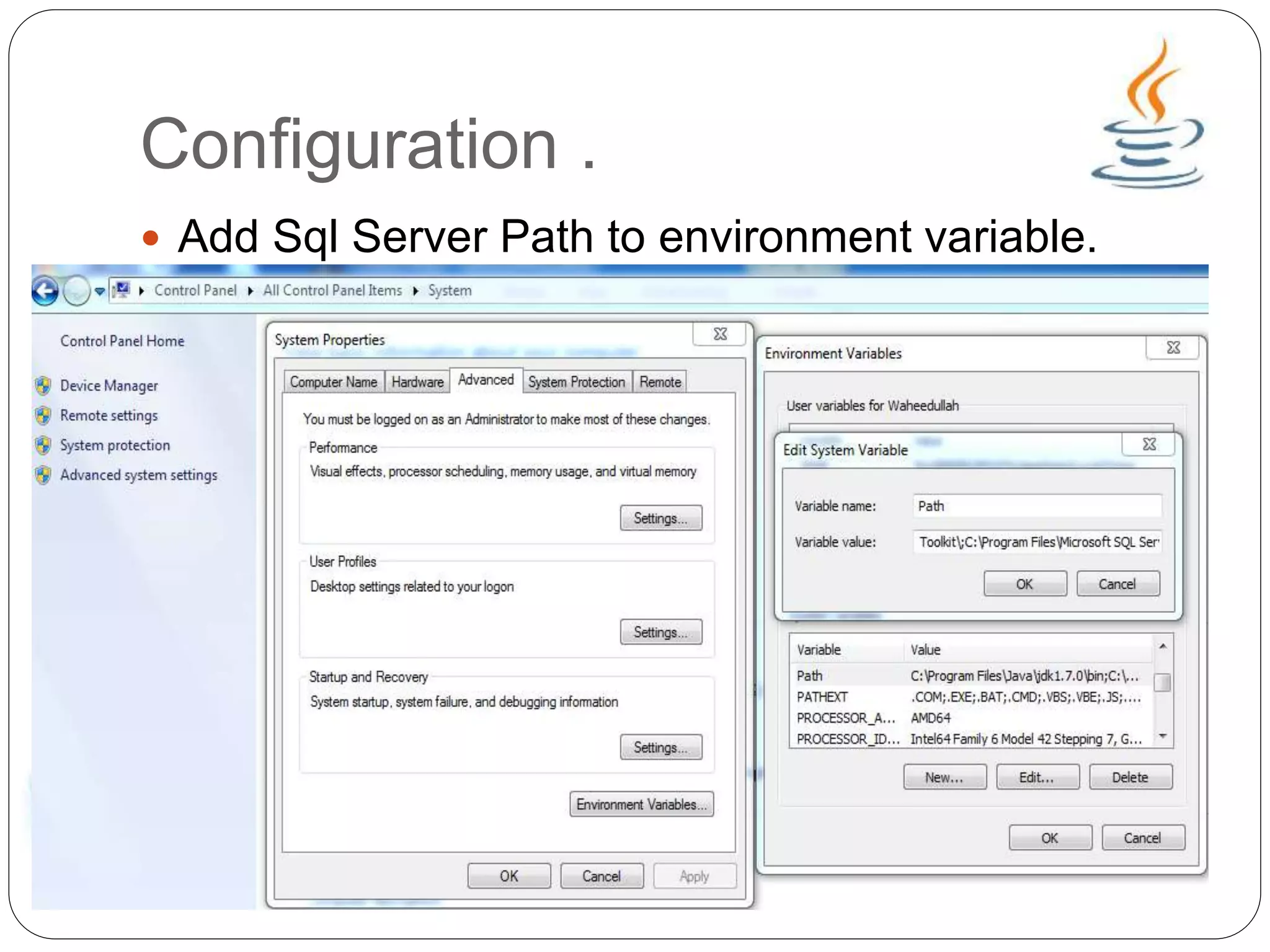
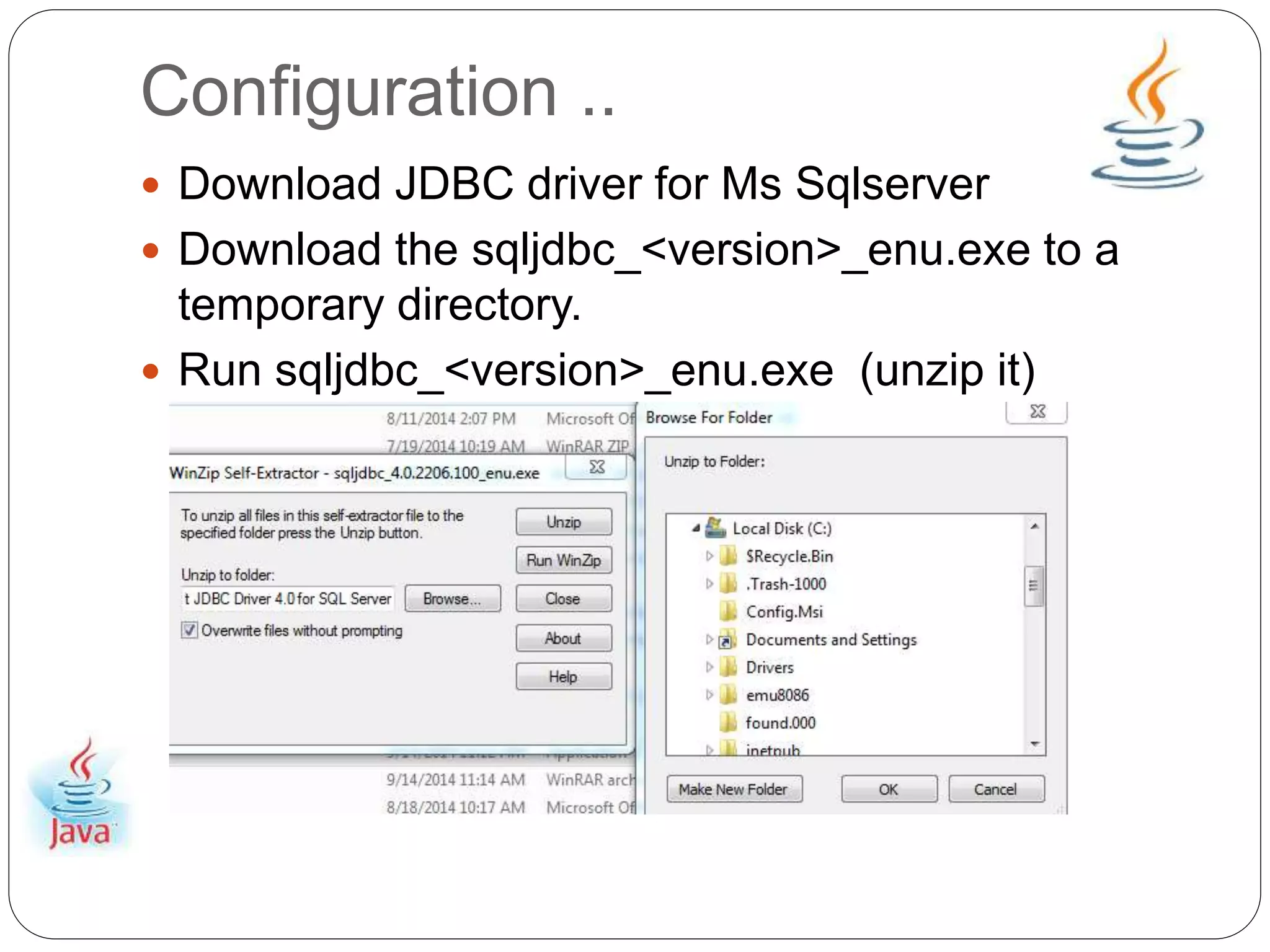
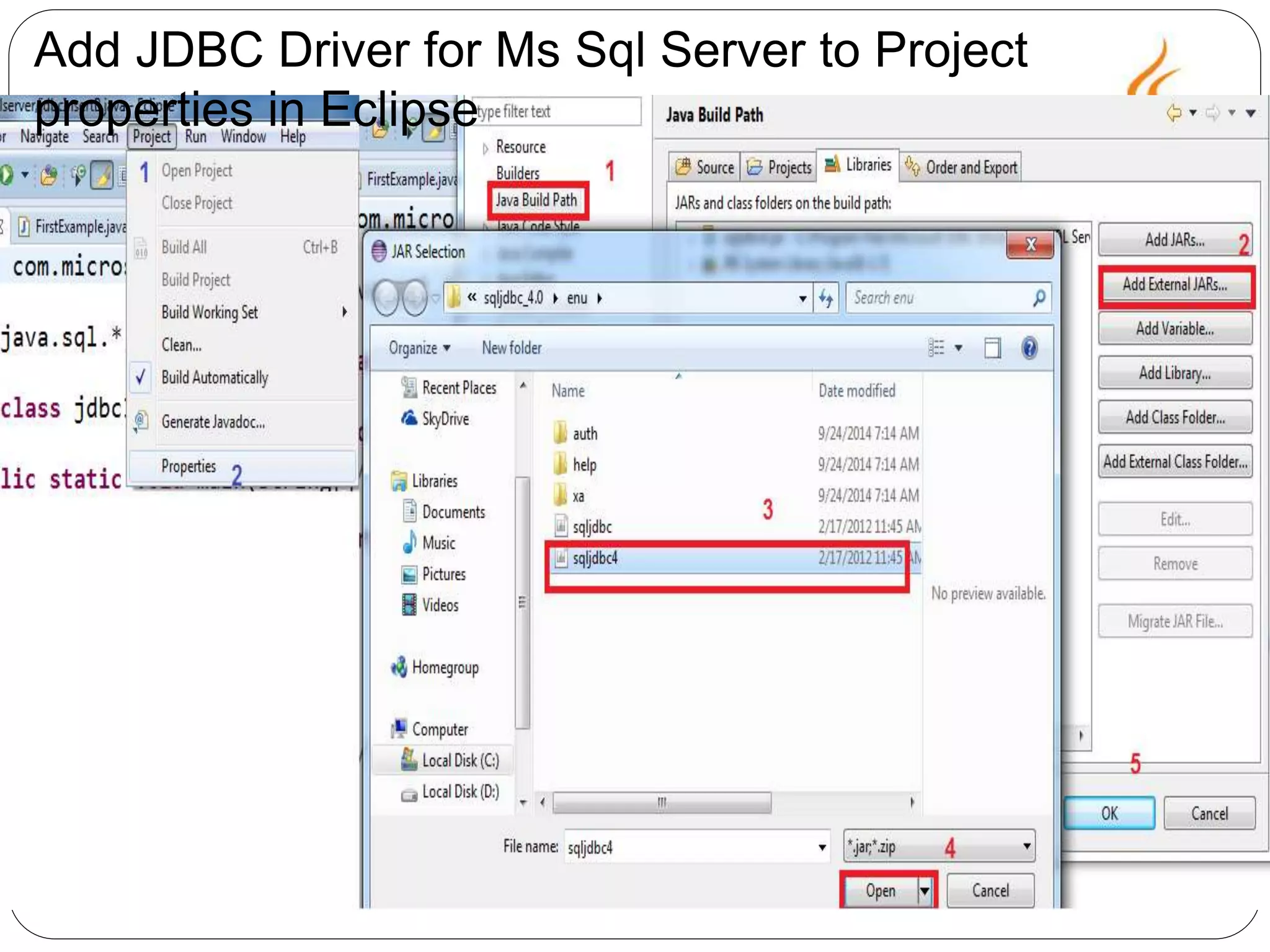
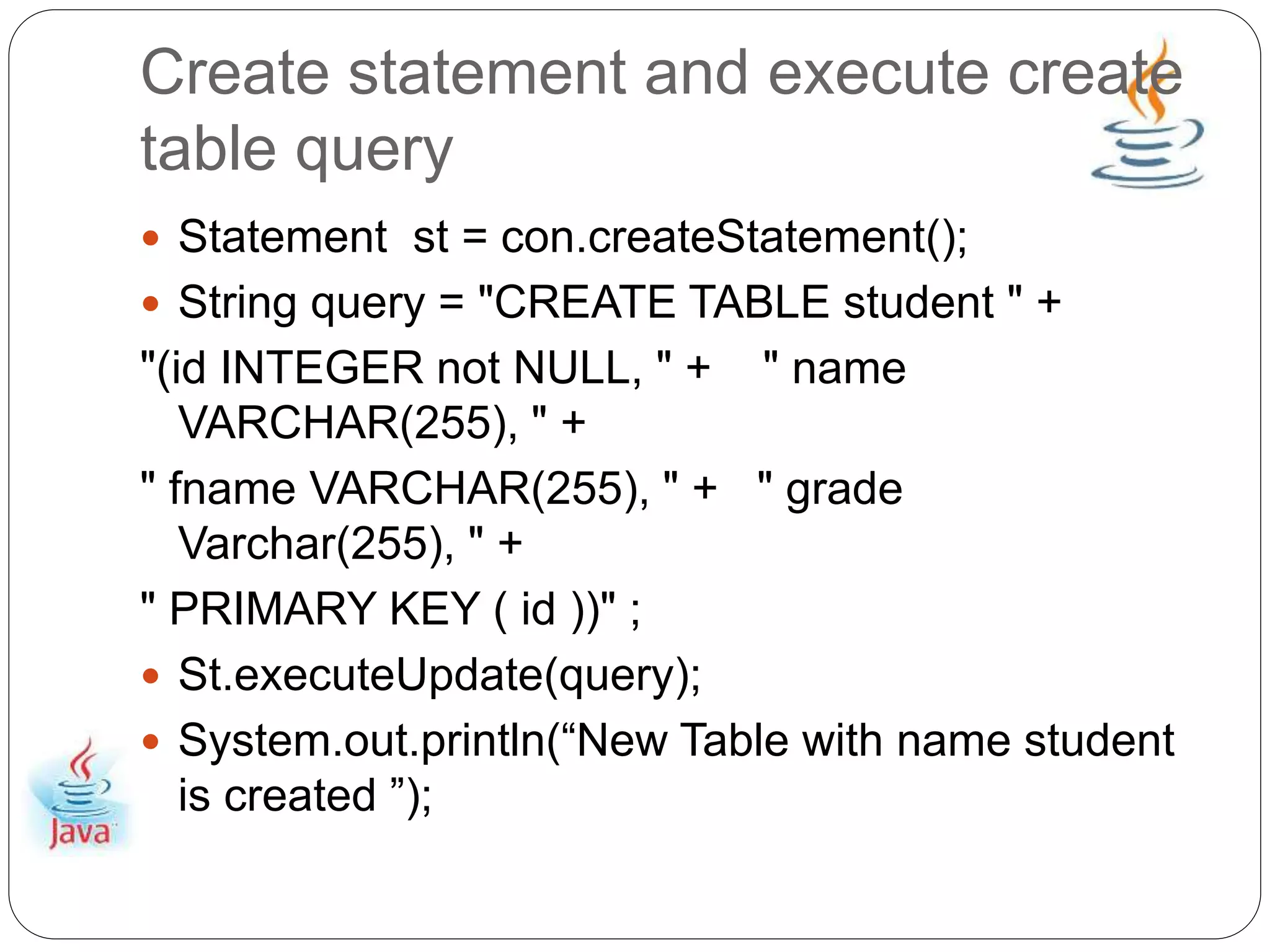
This document provides an overview of Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and how to use it. It discusses how JDBC works by registering drivers, connecting to databases, and executing SQL statements. It also provides steps for configuring JDBC with Eclipse and Microsoft SQL Server, including downloading drivers and copying files. Examples are given for creating tables, executing queries with the Statement interface, and fetching data from the ResultSet. The document concludes by demonstrating how to properly close resources.