This PDF lecture material has been specially designed as a complete beginner’s guide to learning the C programming language. It introduces the subject in a simple, clear, and well-structured way so that students with little or no prior programming background can start their journey in computer science with confidence. The purpose of this material is to make programming accessible, understandable, and engaging by focusing on the core foundations of C, one of the most widely used and time-tested programming languages in the world.
C programming is often called the “mother of all programming languages” because many modern languages such as C++, Java, and Python have their roots in it. It is powerful, efficient, and close to the hardware, making it a perfect starting point for understanding how computers work internally. This PDF provides a beginner-friendly overview of C, ensuring that learners not only write code but also develop logical thinking and problem-solving skills.
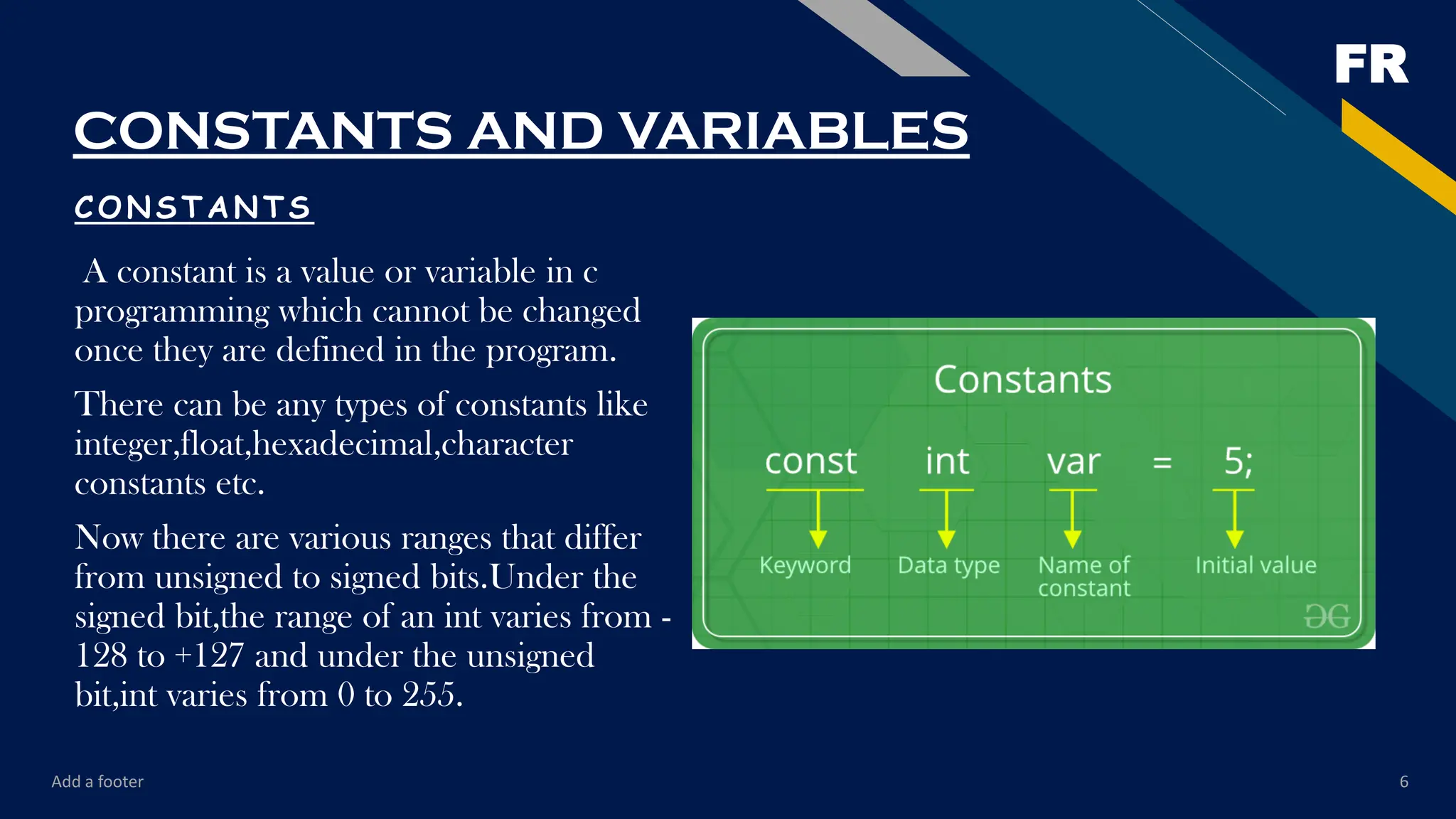
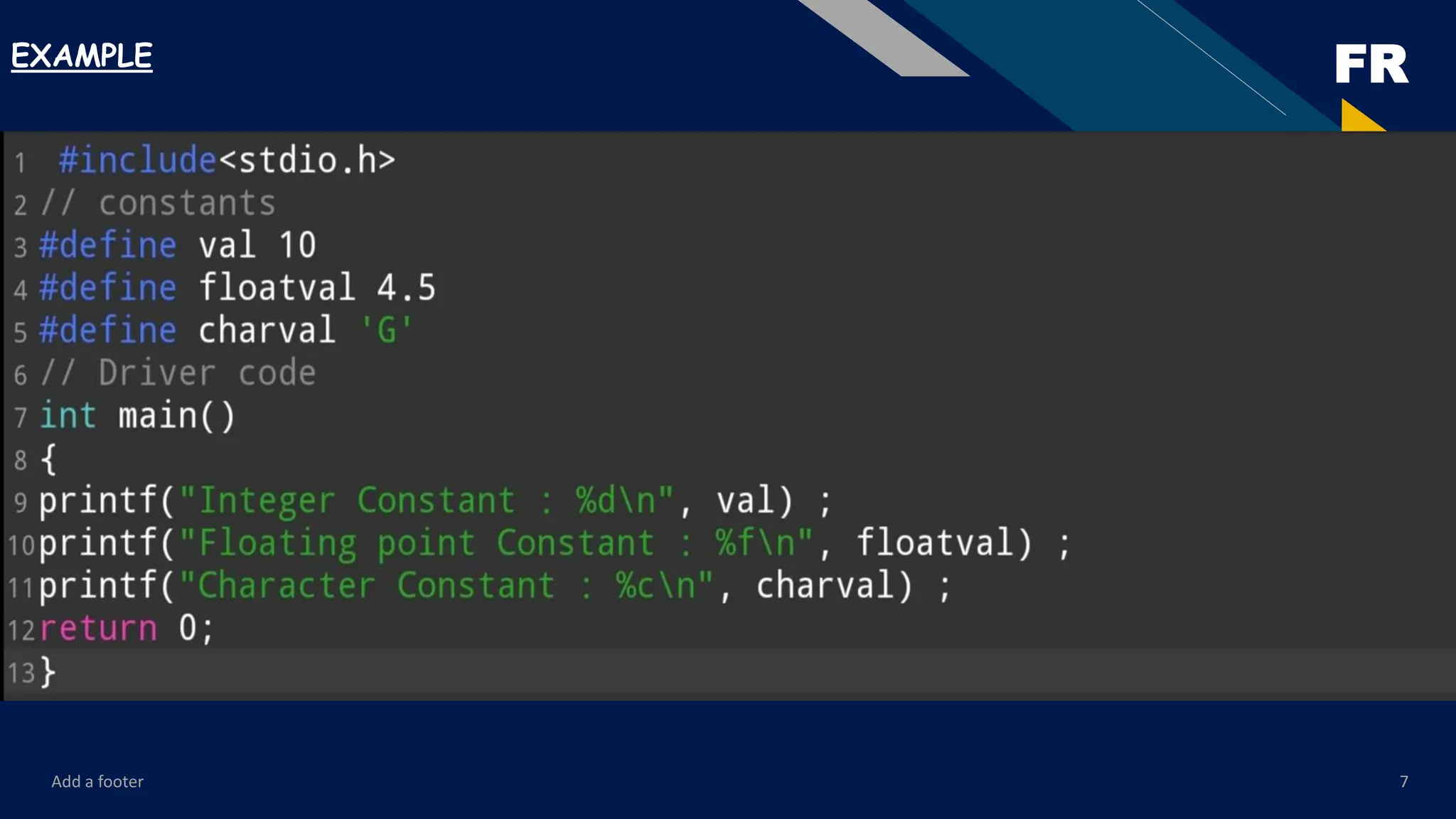
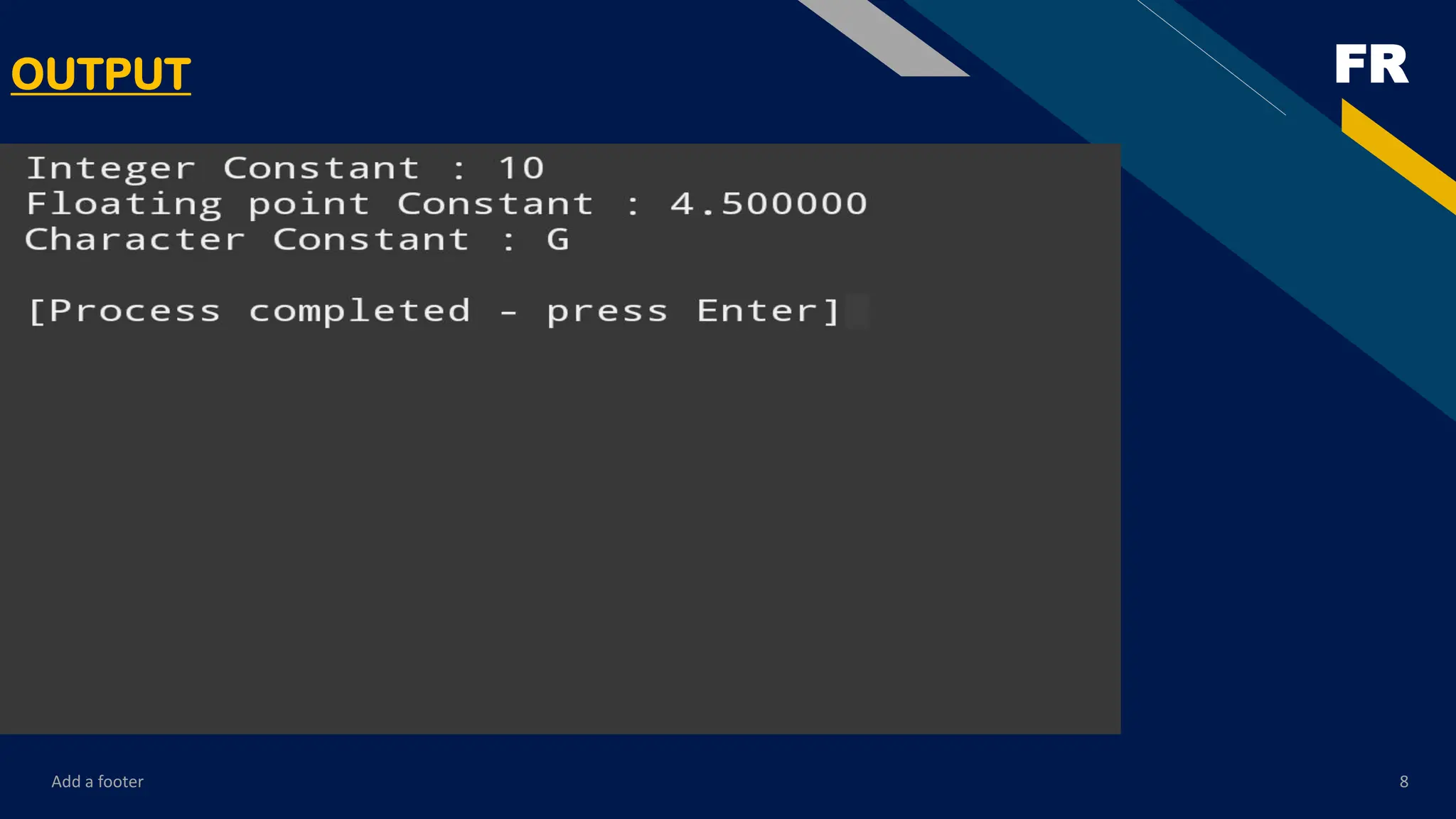
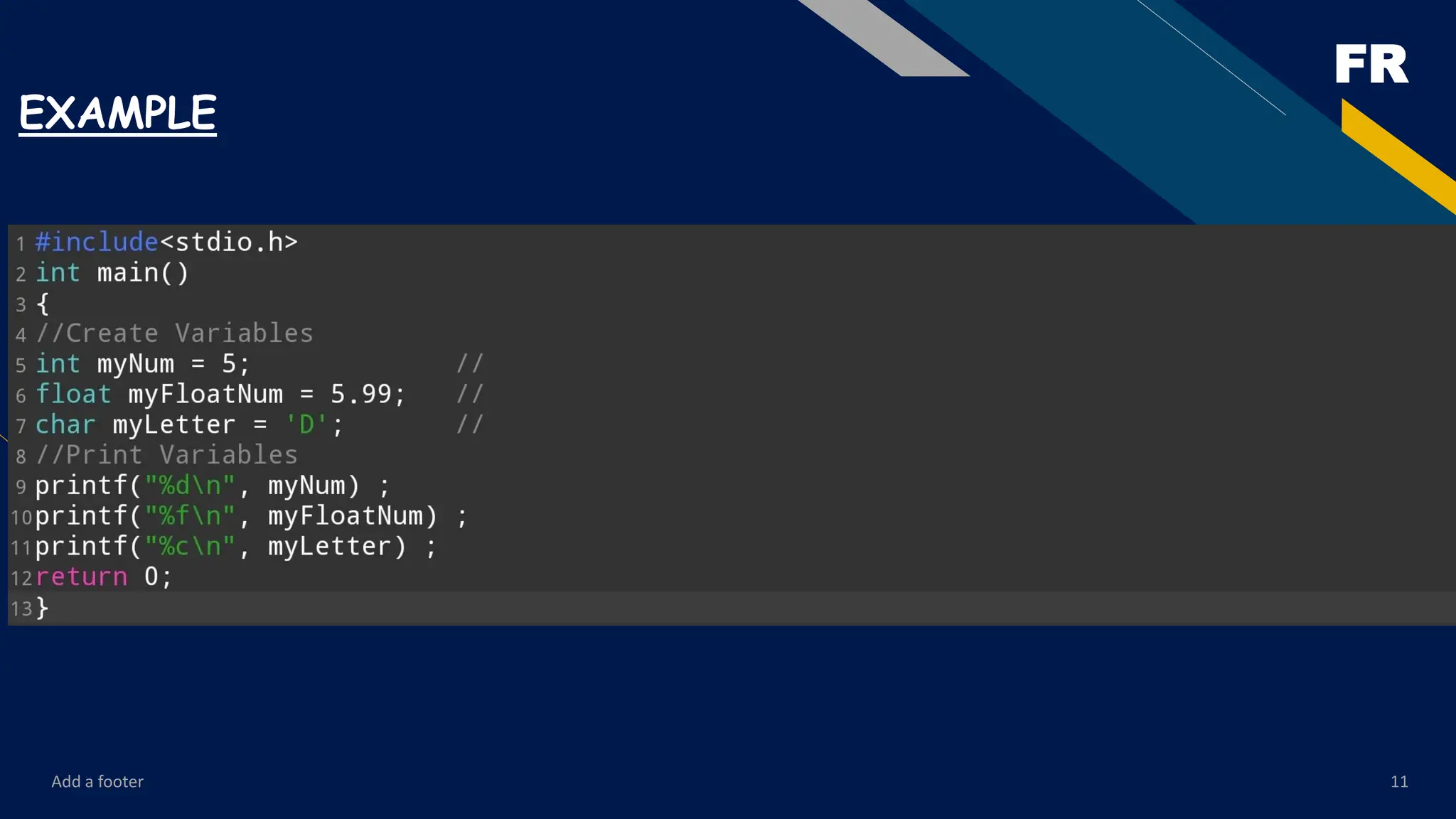
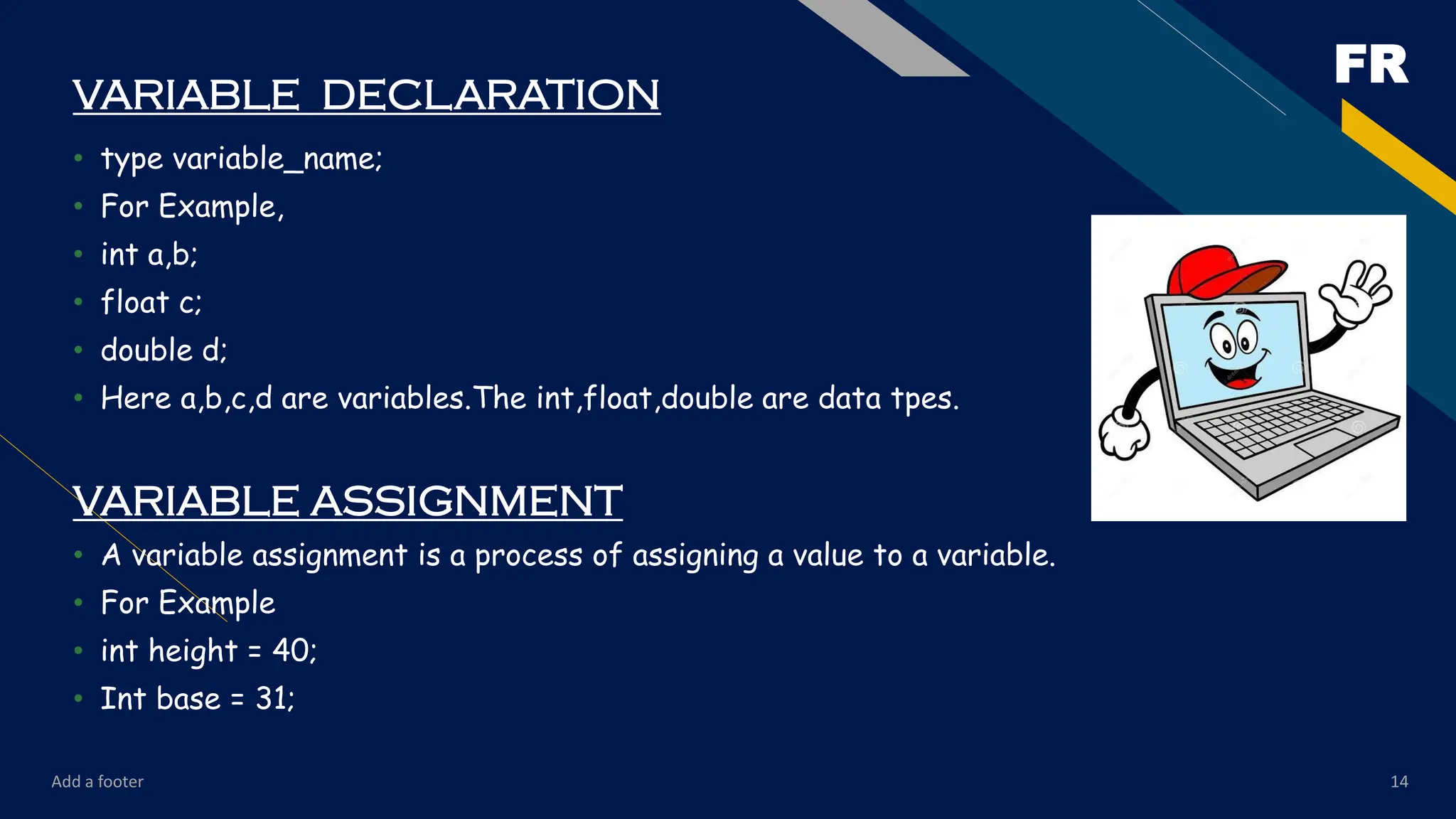
The content starts with the very basics—introduction to programming, the history of C, features of the language, and setting up the environment for compiling and running programs. From there, it gradually moves toward fundamental concepts such as data types, variables, constants, operators, and expressions. These form the building blocks of every C program, and the PDF explains them with examples that are easy to follow.
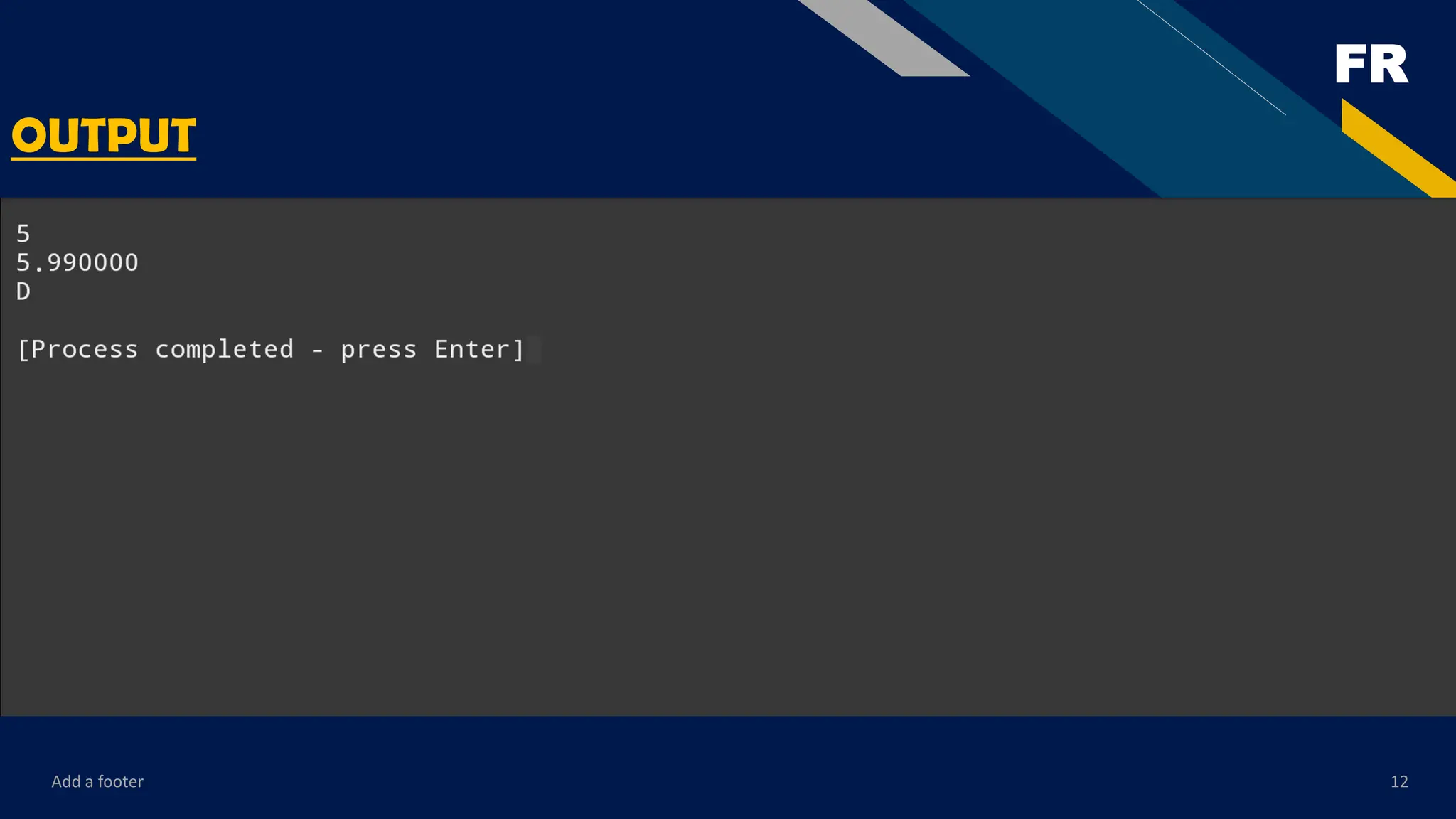
Control structures like decision-making (if, if-else, switch) and looping (for, while, do-while) are explained in detail so that students can understand how to control the flow of their program logically. The material also covers input and output functions, enabling learners to interact with users by reading values and displaying results. Each concept is presented with sample programs, step-by-step explanations, and practice exercises to encourage hands-on learning.
As the material progresses, it introduces more advanced but essential topics such as arrays, strings, functions, pointers, and structures. Arrays and strings teach how to handle collections of data efficiently, while functions help in breaking down big problems into smaller modules. Pointers, one of the most powerful features of C, are explained with diagrams and examples so that beginners can overcome fear and gain clarity. Structures are introduced to help students understand how to organize complex data in real-world applications.
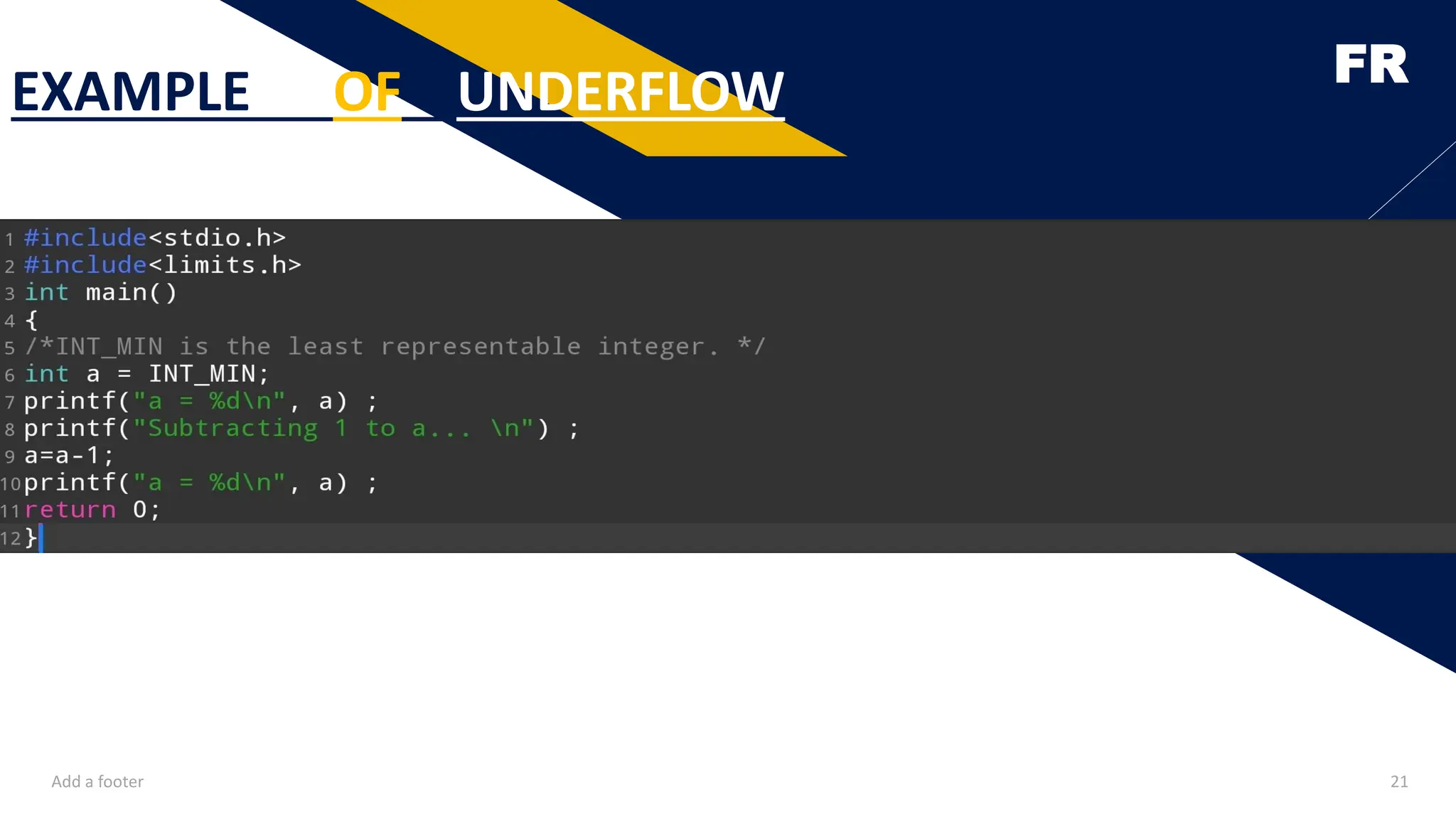
Memory management, file handling, and an overview of dynamic data structures are also included to give learners a complete beginner-level picture of what C can do. The focus is not only on syntax but also on developing an analytical approach to solving problems. Every topic is explained with clear definitions, examples, and illustrations, making it easy for students to grasp the concepts even if they are encountering programming for the first time.
By going through this PDF, students will:
Gain a solid foundation in the fundamentals of programming.




















![Array Declaration
While declaring a one-dimensional array in
C, the data type can be of any type, and
also, we can give any name to the array, just
like naming a random variable.
Syntax:
int arr[5]; //arr is the array name of type integer, and 5 is the size of the array
Array Initialization
In static uninitialized arrays, all the elements
initially contain garbage values, but we can
explicitly initialize them at their declaration.
SYNTAX:
<data_type> <arr_name> [arr_size]={value1, value2, value3,…};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2cprogamming-250916141900-cac49371/75/Lecture-2-c-progamming-pdf-helpful-for-beginners-30-2048.jpg)
![Array Accessing
In one-dimensional arrays in C, elements are accessed by specifying the
array name and the index value within the square brackets. Array
indexing starts from 0 and ends with size-1. If we try to access array
elements out of the range, the compiler will not show any error message;
rather, it will return some garbage value.
Syntax:
<arr_name>[index];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2cprogamming-250916141900-cac49371/75/Lecture-2-c-progamming-pdf-helpful-for-beginners-32-2048.jpg)
![FR
Add a footer 33
EXAMPLE
#include < stdio.h >
int main() {
//declaring and initializing one-dimensional array in C
int arr[3] = {10, 20, 30};
// After declaration, we can also initialize the array as:
// arr[0] = 10; arr[1] = 20; arr[2] = 30;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// accessing elements of array
printf(" Value of arr[%d]: %dn", i, arr[i]);
}
}
OUTPUT
Value of arr[0]: 10
Value of arr[1]: 20
Value of arr[2]: 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2cprogamming-250916141900-cac49371/75/Lecture-2-c-progamming-pdf-helpful-for-beginners-33-2048.jpg)

![FR
Add a footer 36
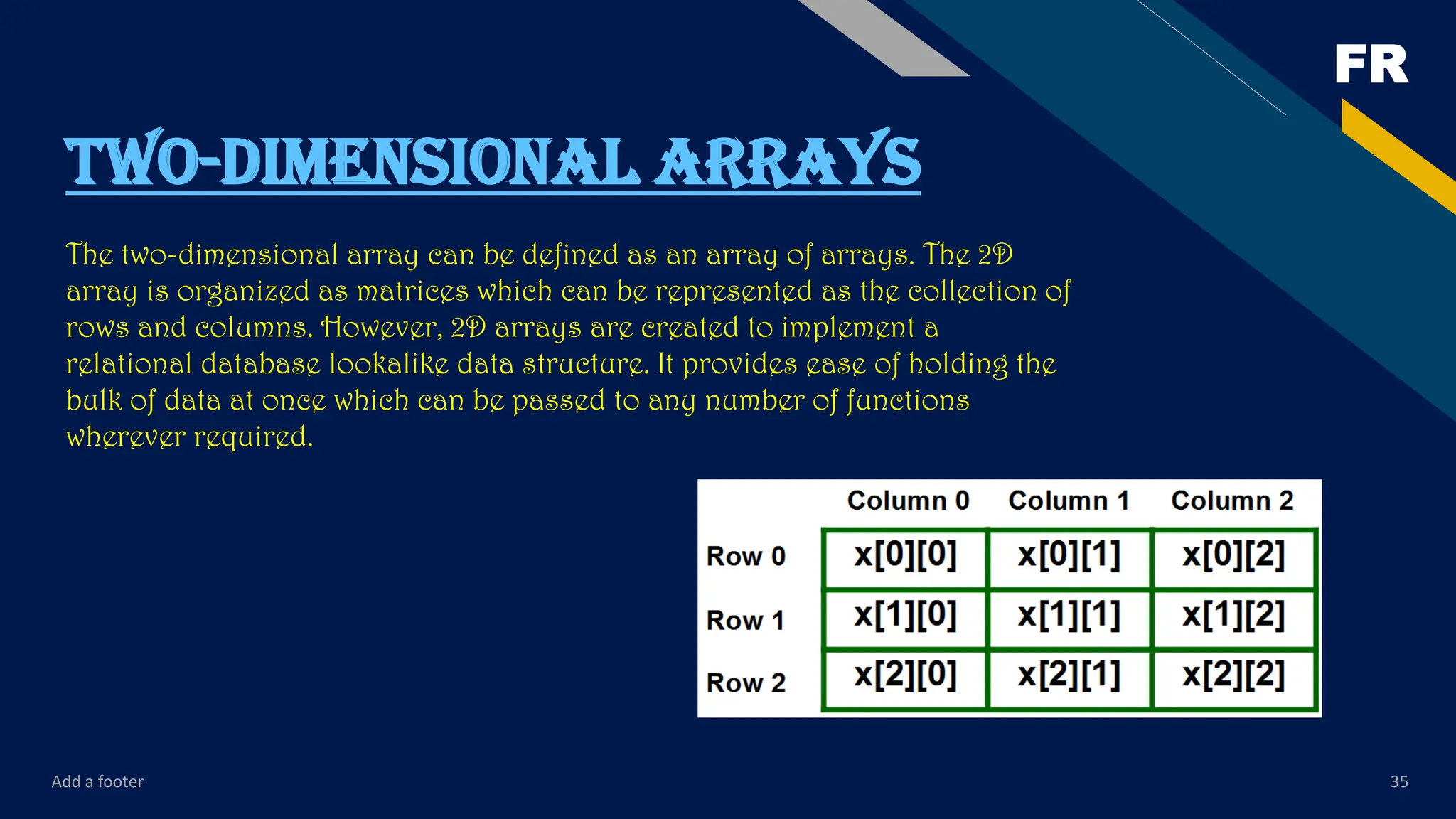
Declaration of two dimensional Array in C
The syntax to declare the 2D array is given below.
data_type array_name[rows][columns];
Consider the following example.
int twodimen[4][3];
Here, 4 is the number of rows, and 3 is the number of columns.
Initialization of 2D Array in C
The two-dimensional array can be initialized and defined in the following way.
int arr[4][3]={{1,2,3},{2,3,4},{3,4,5},{4,5,6}};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2cprogamming-250916141900-cac49371/75/Lecture-2-c-progamming-pdf-helpful-for-beginners-36-2048.jpg)


