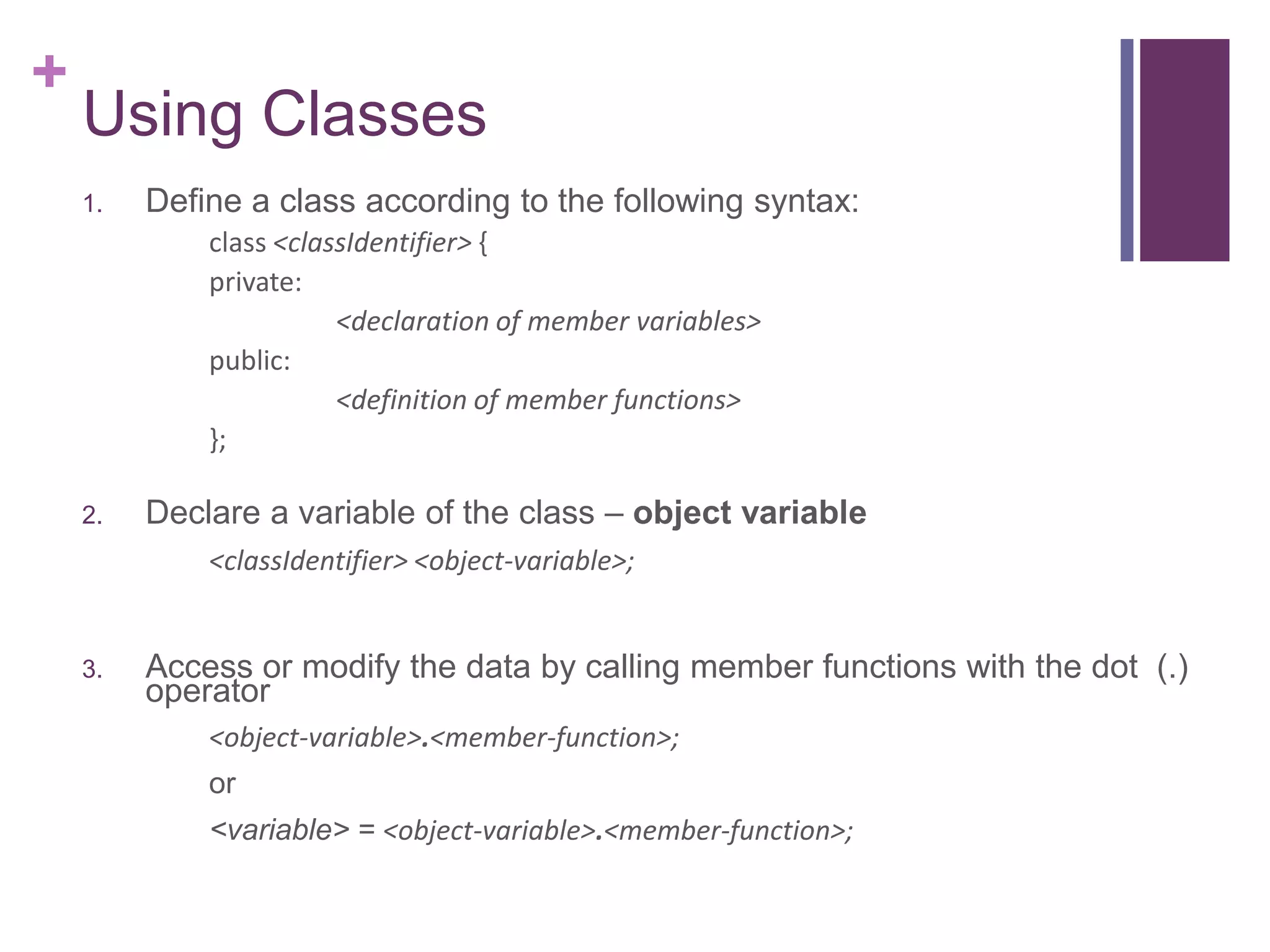
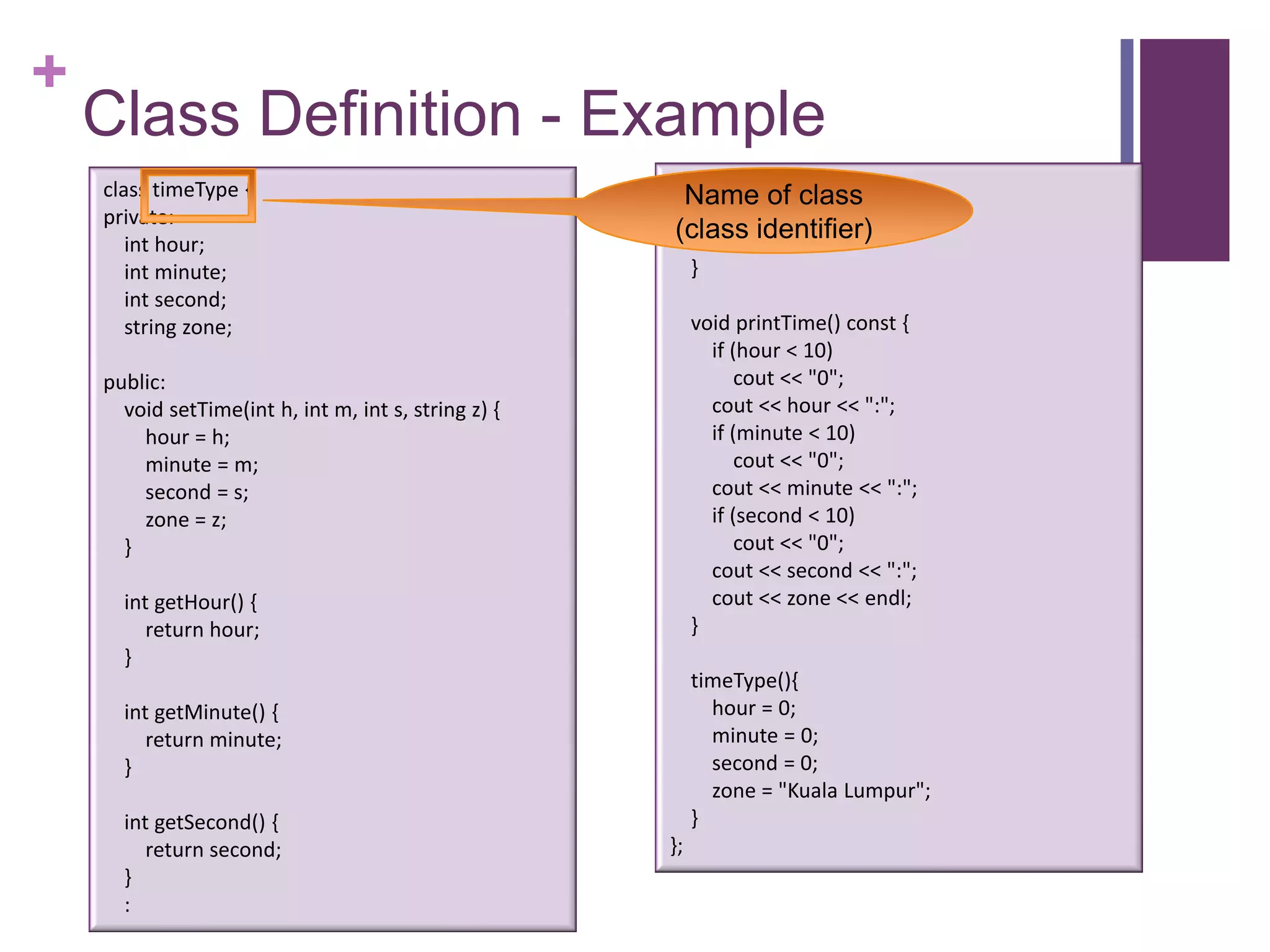
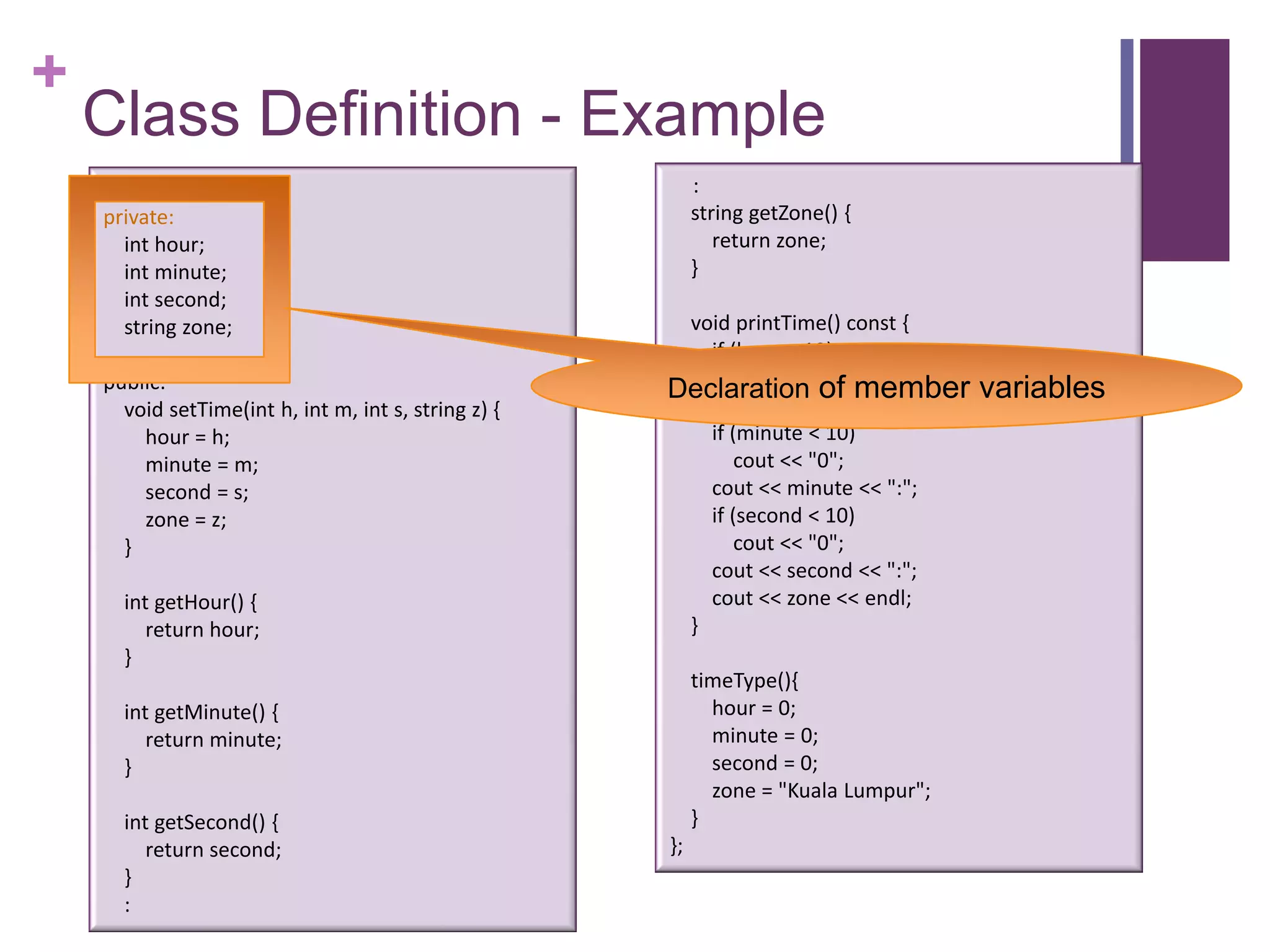
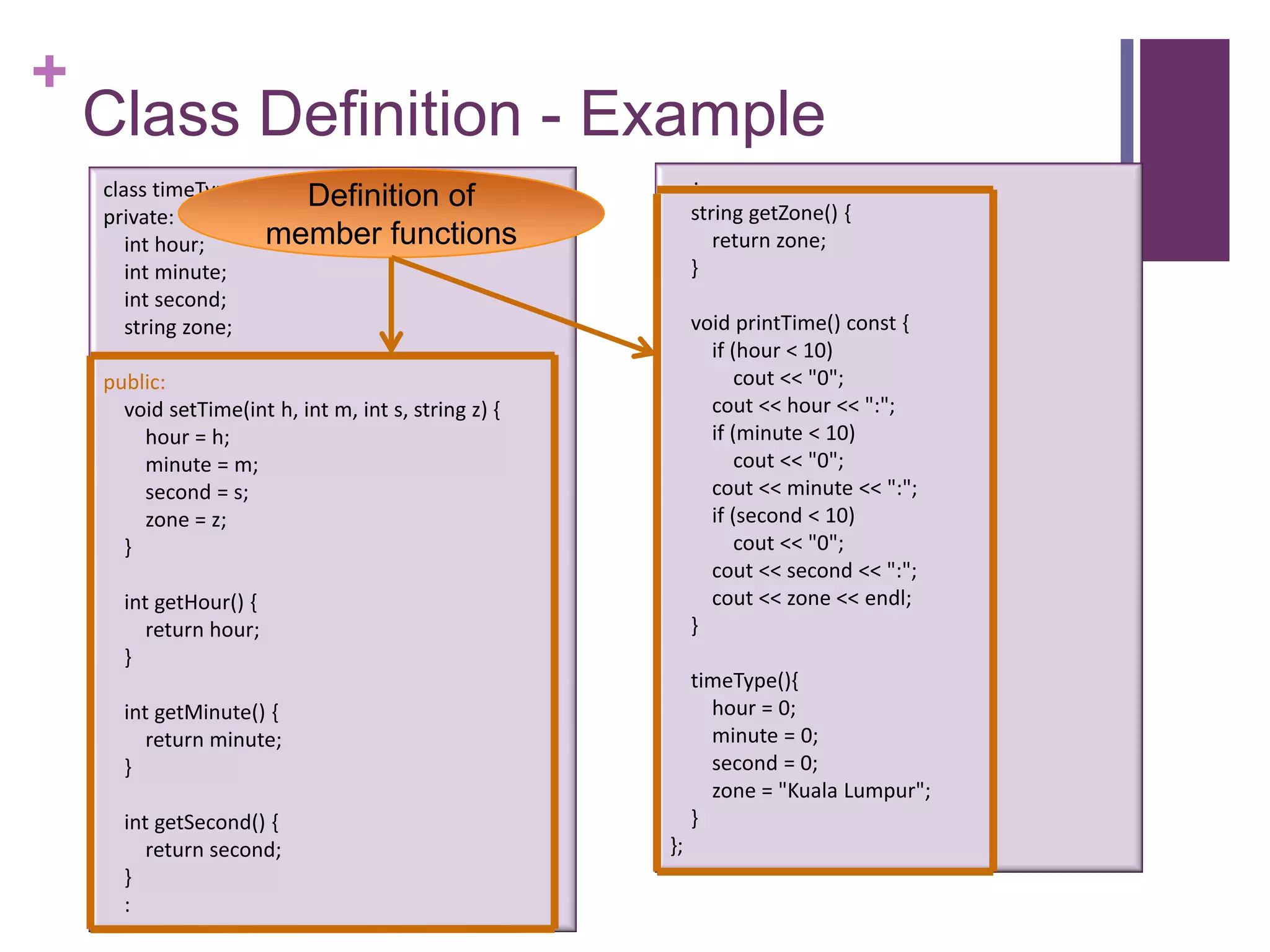
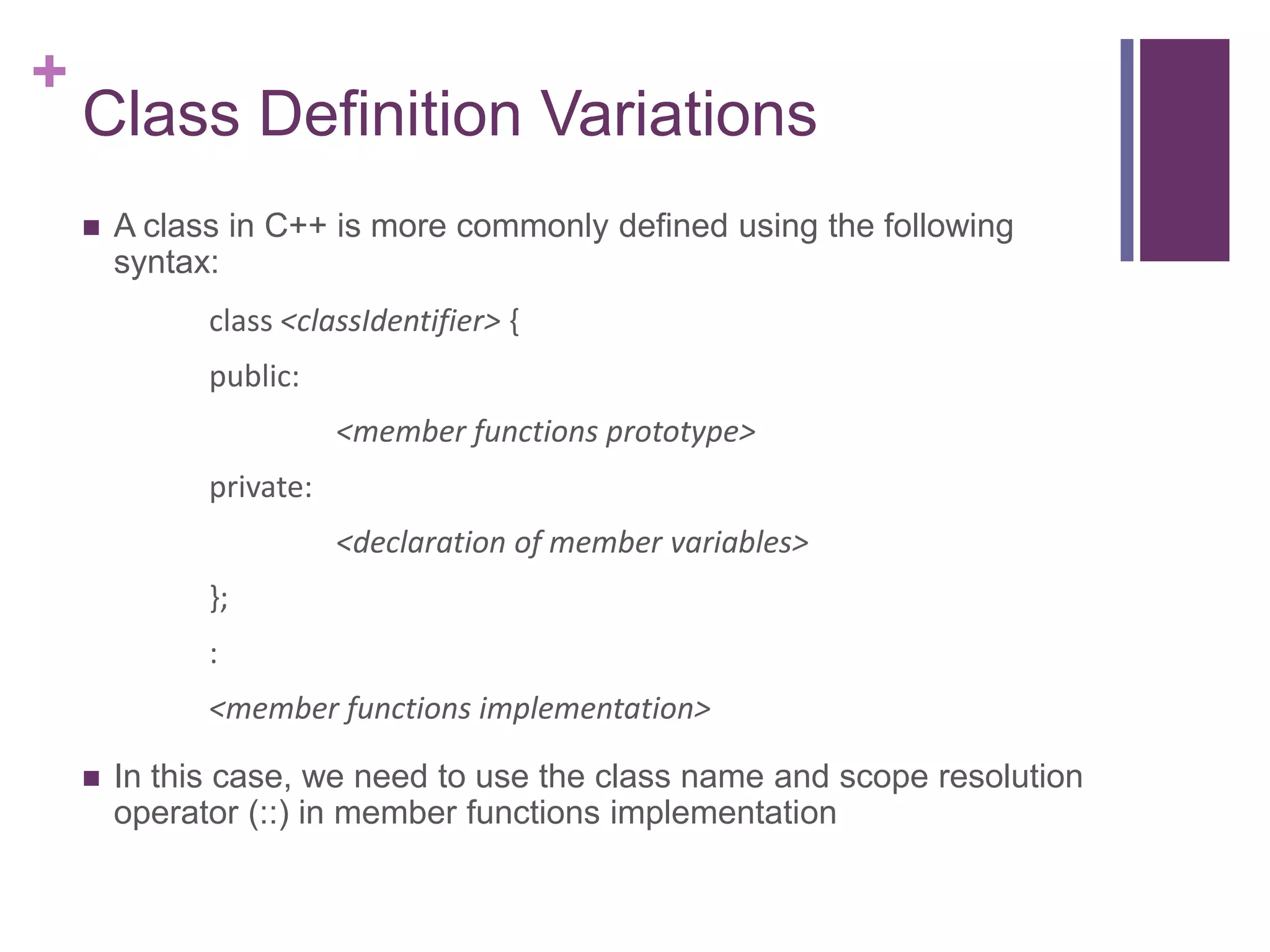
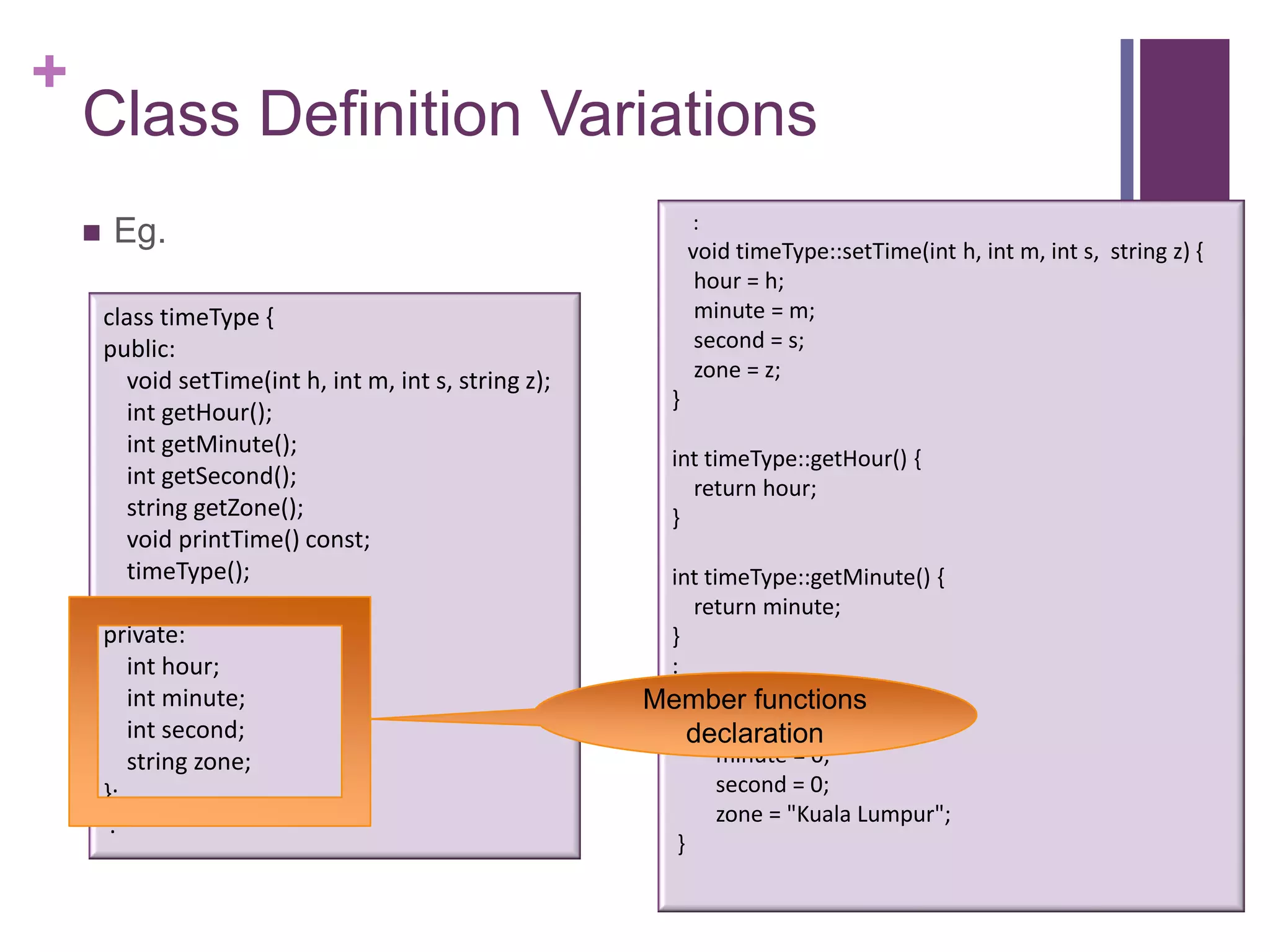
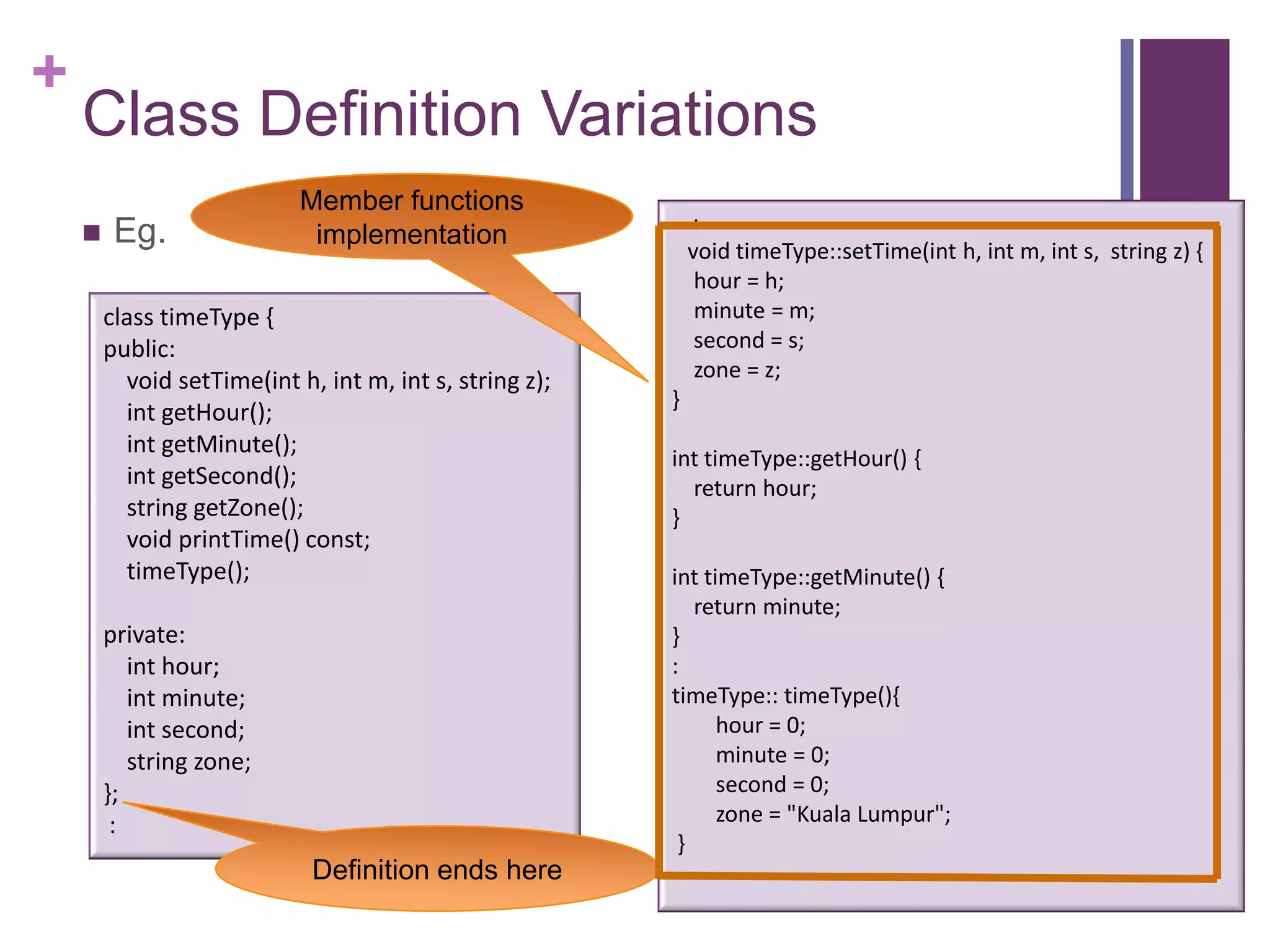
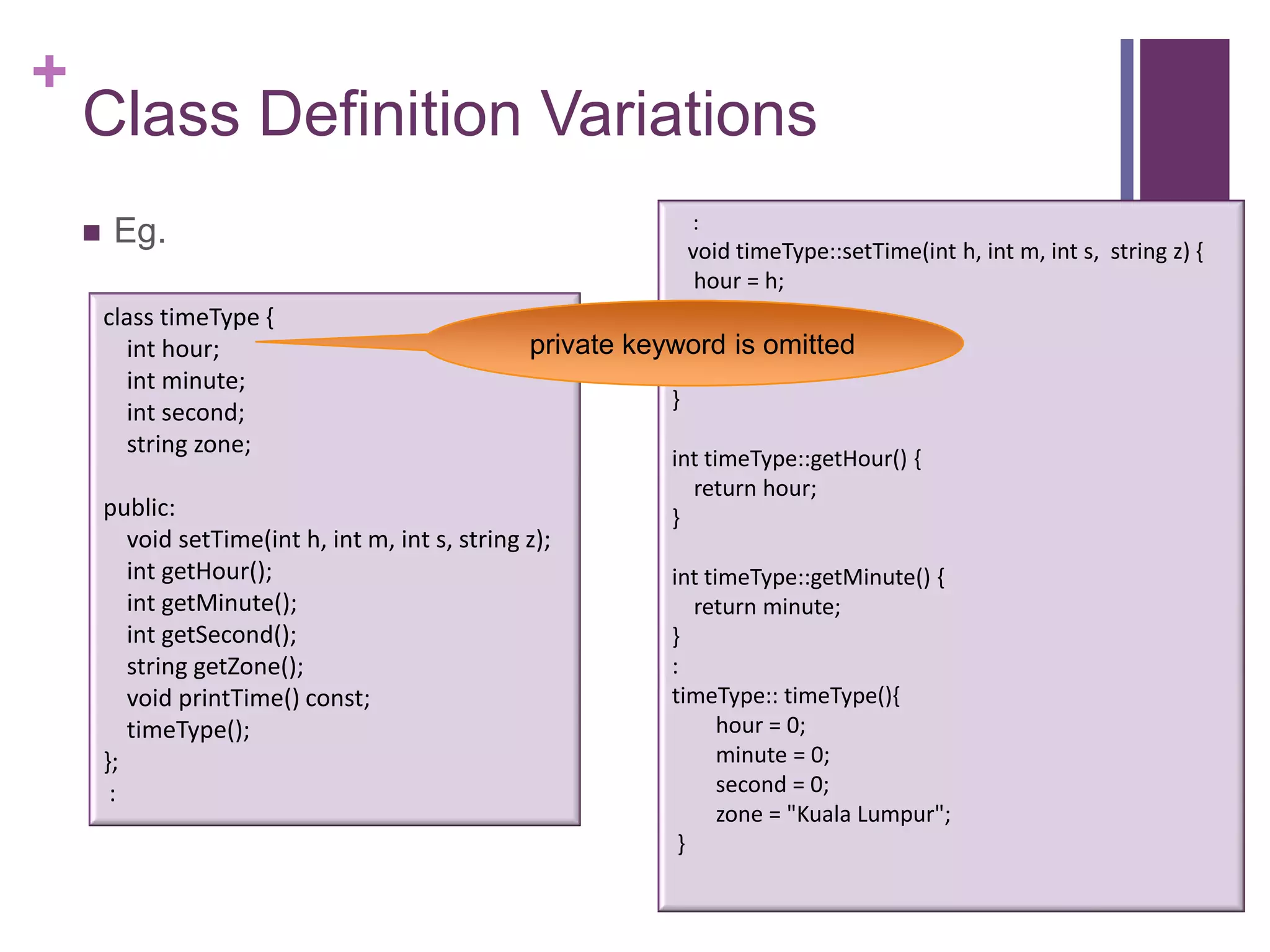
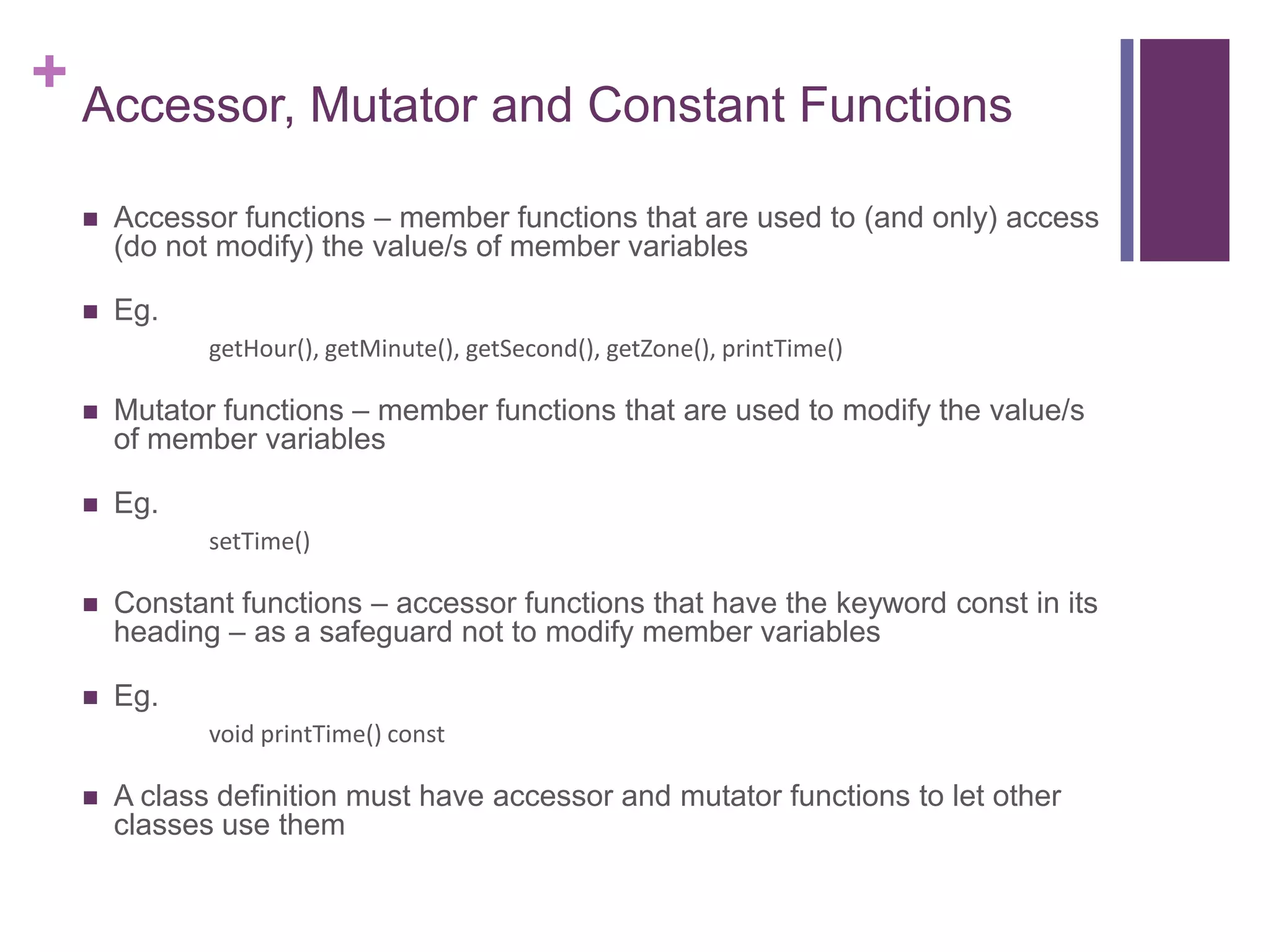
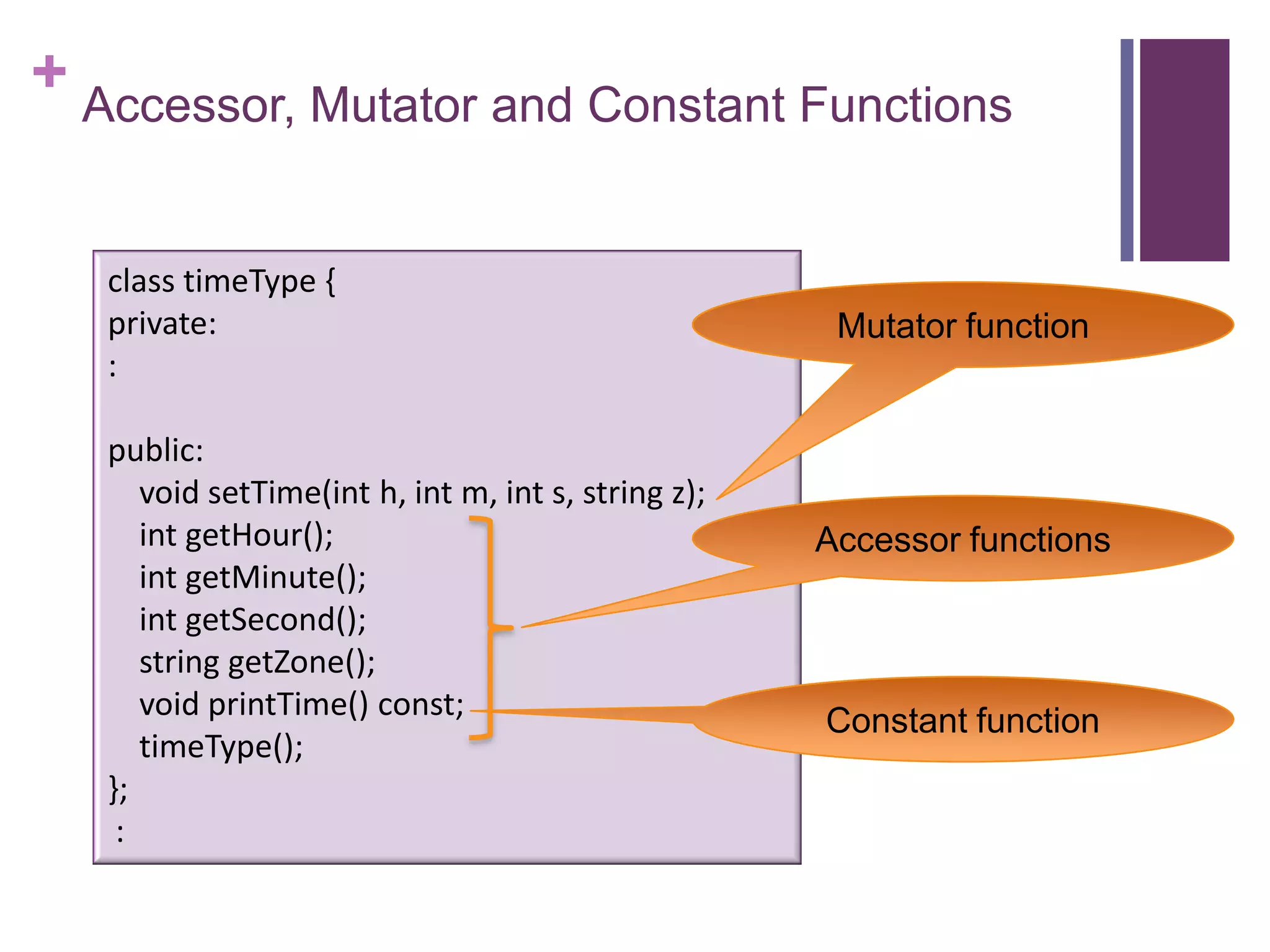
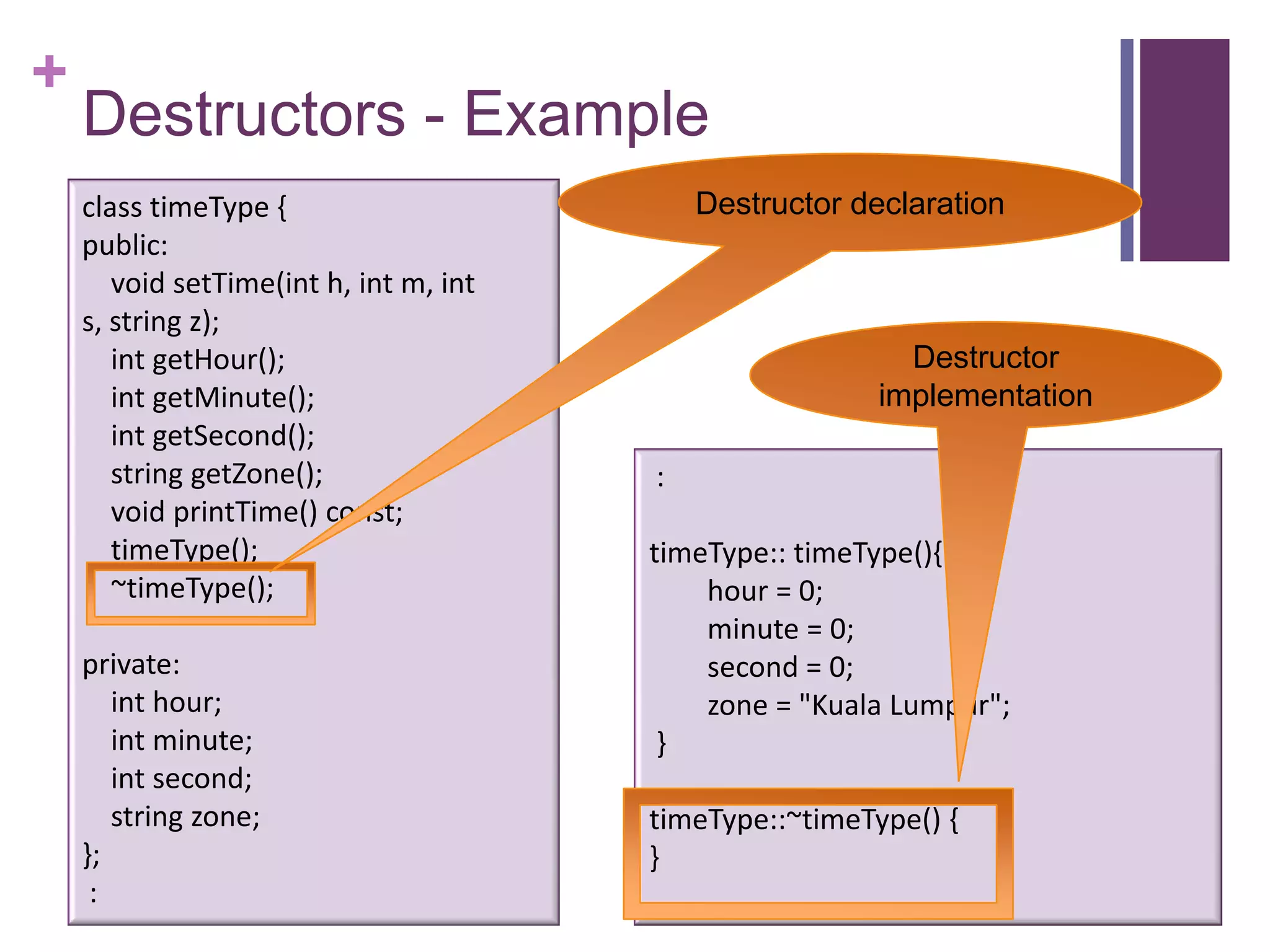
The document discusses C++ classes. It provides:
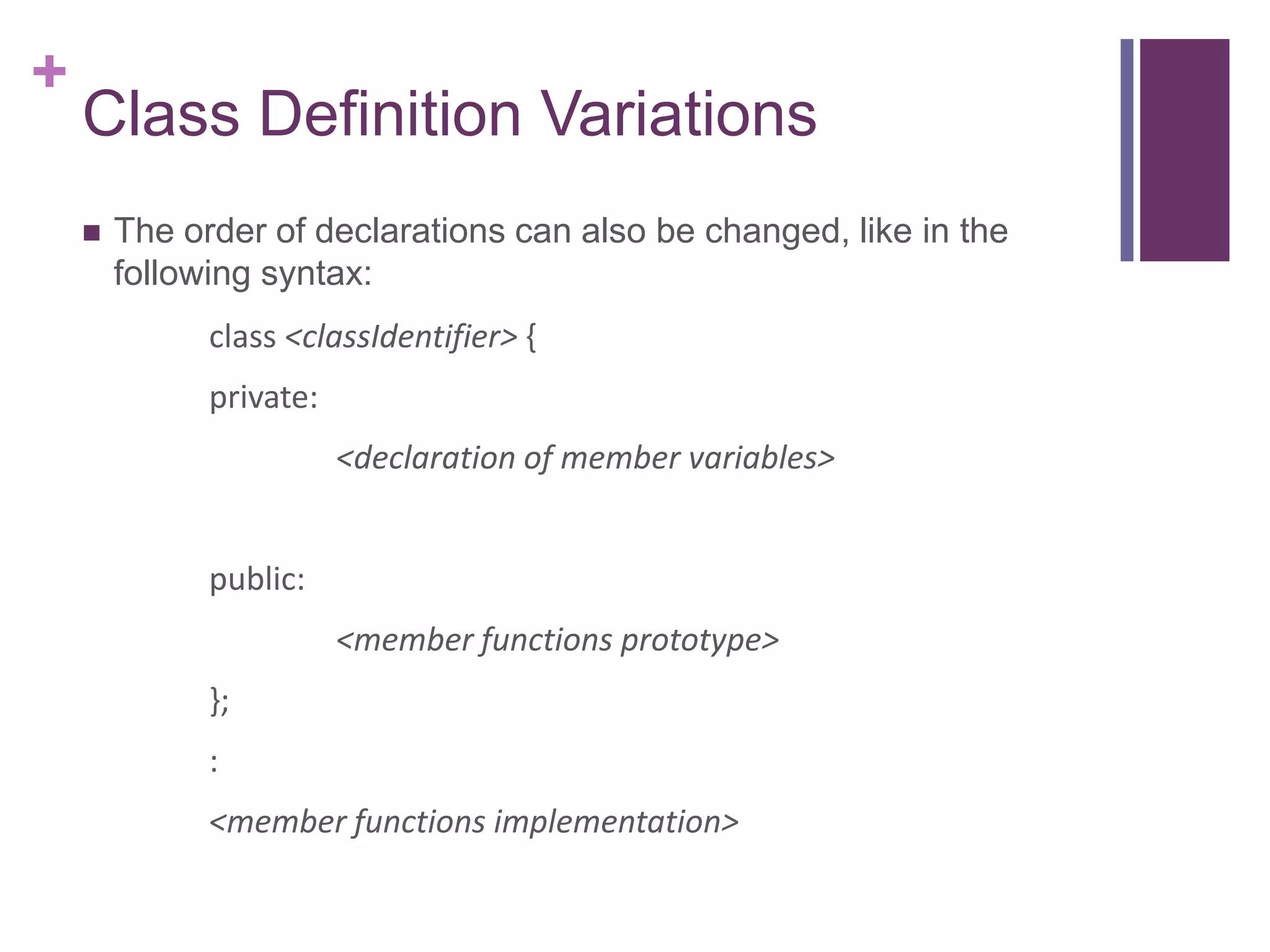
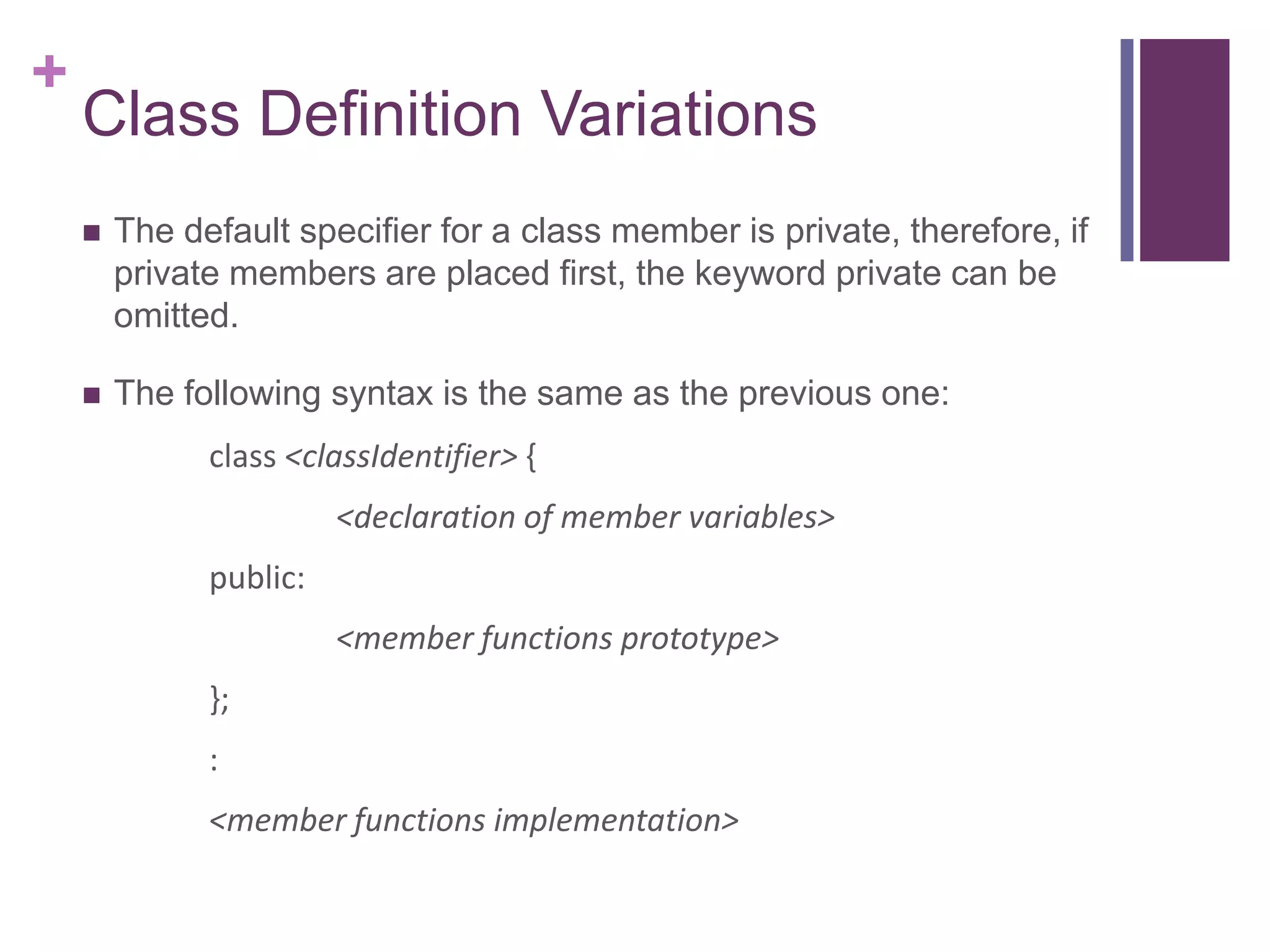
1) The syntax for defining a class with private member variables and public member functions.
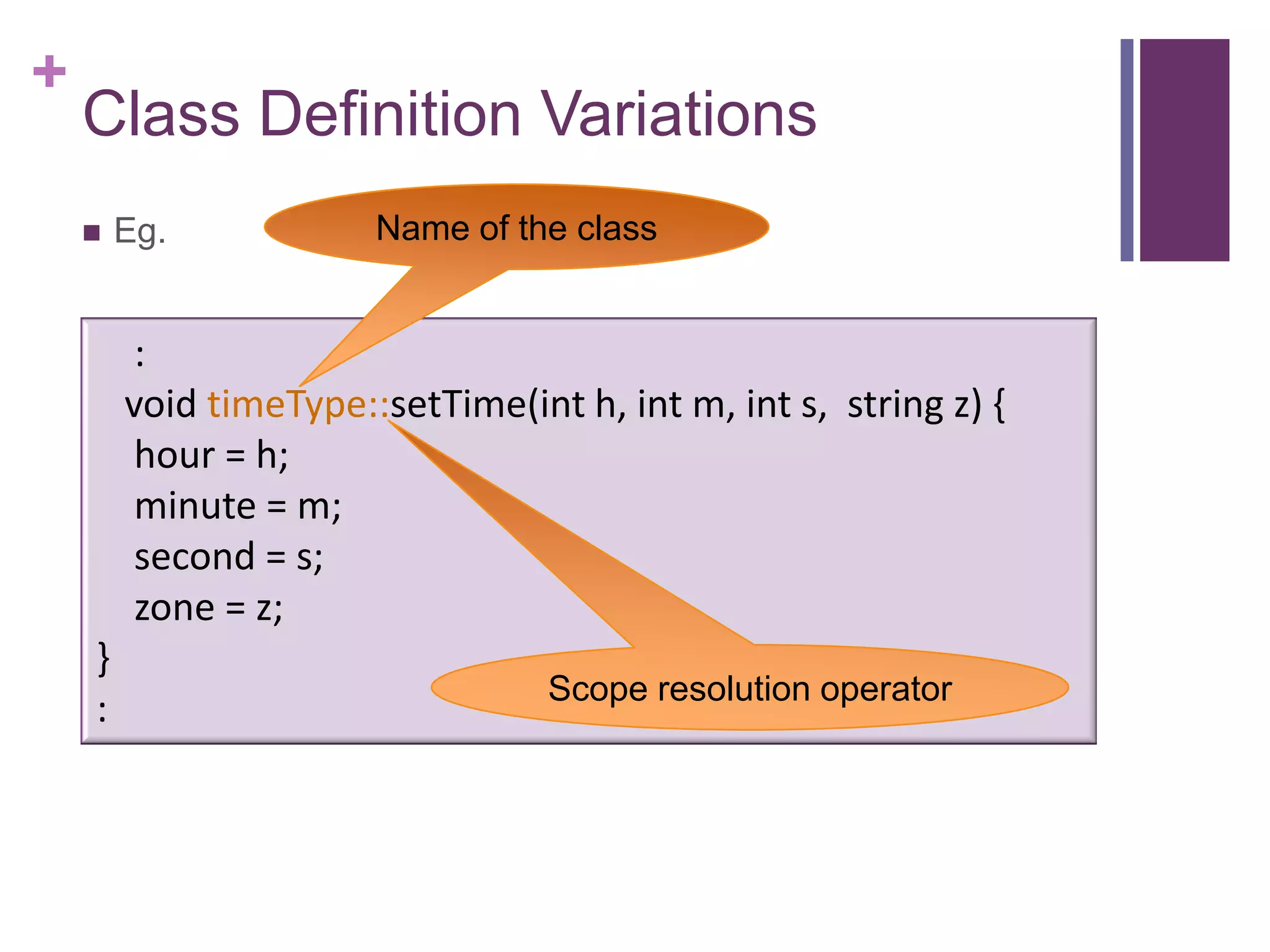
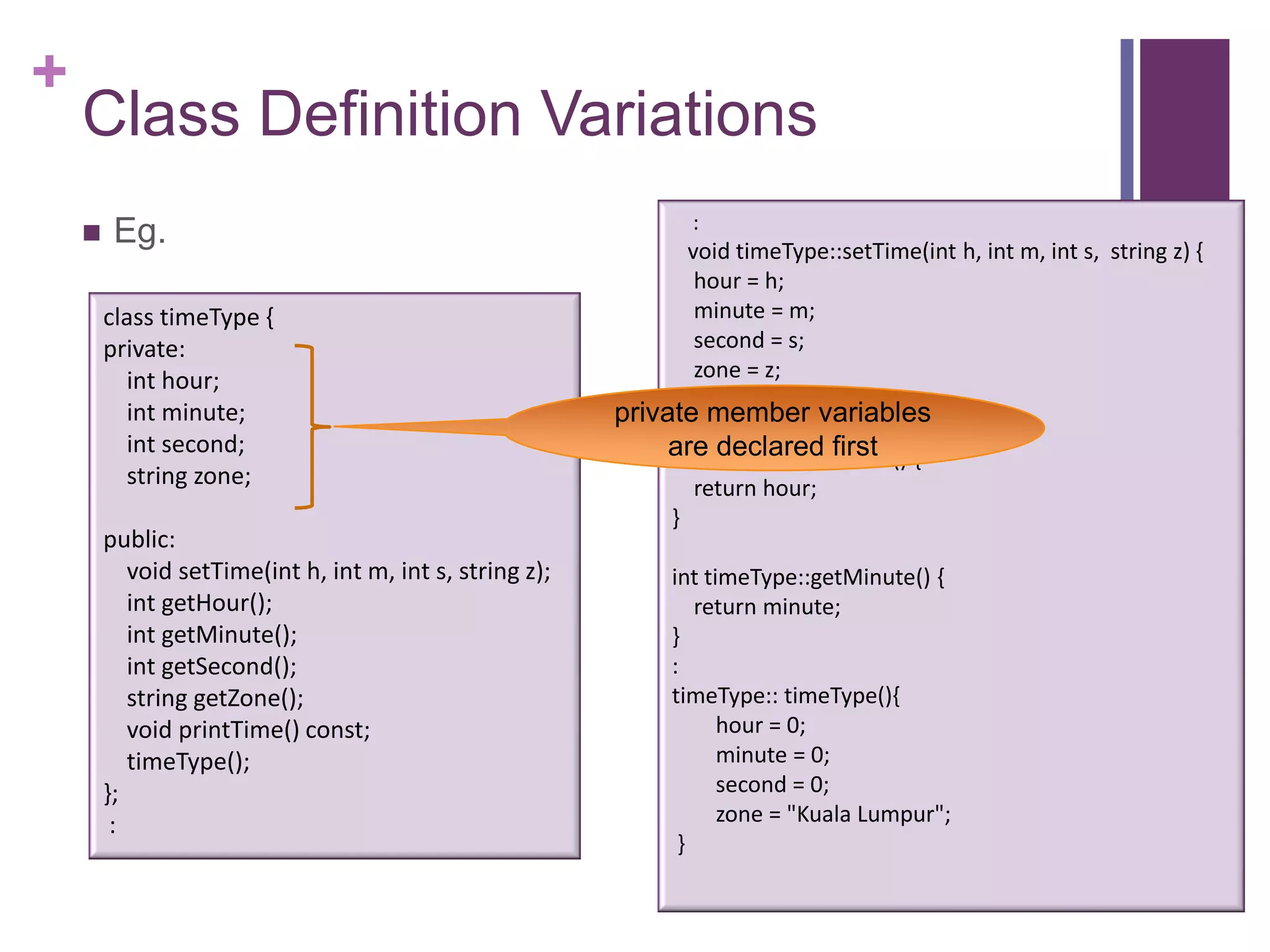
2) An example class definition for a timeType class that stores hour, minute, second as private variables and includes public functions to set/get/print the time.
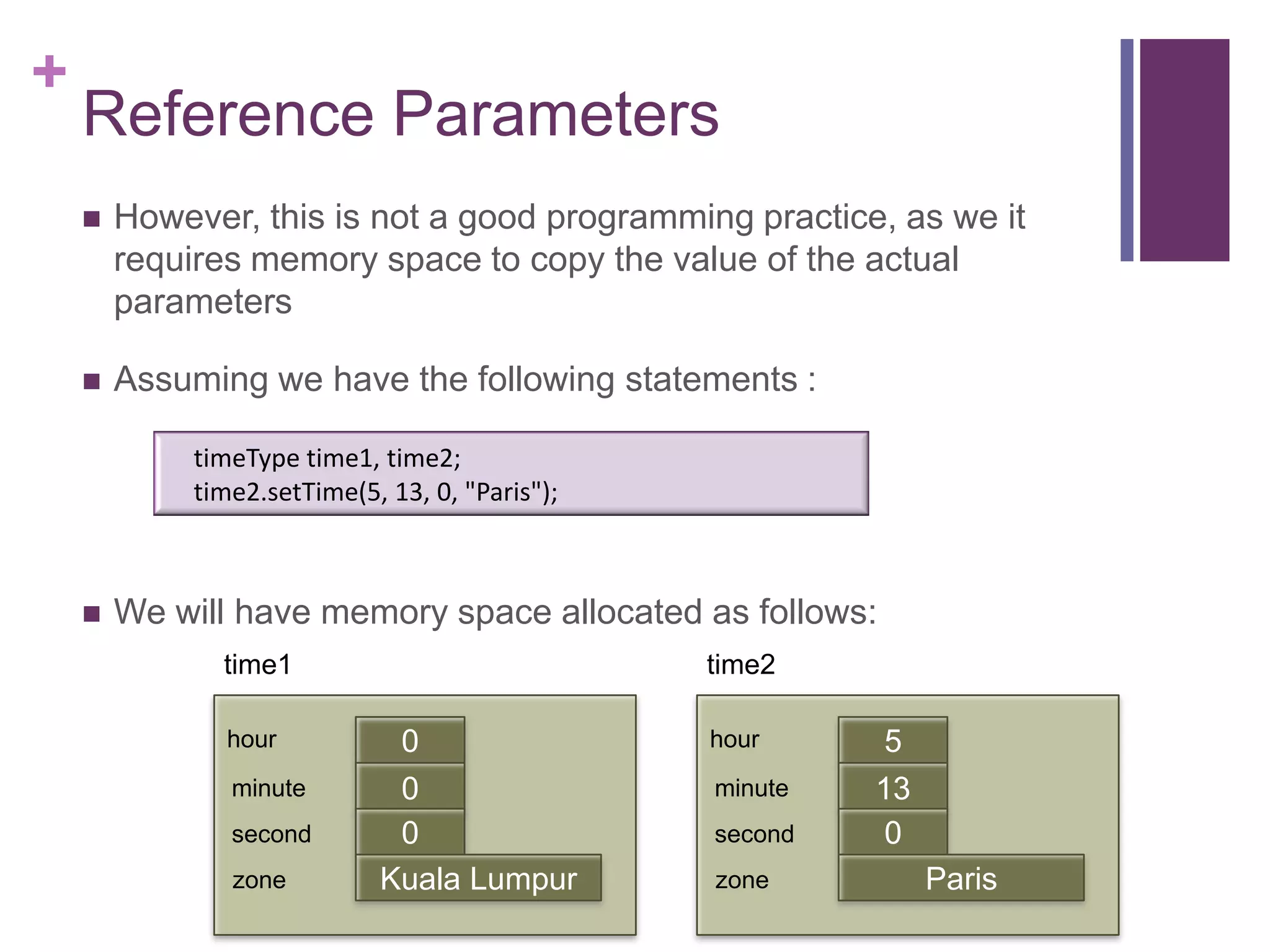
3) An example of how to use the defined timeType class by declaring a timeType object, calling member functions to set/get/print the time values.




![+
Using Classes - Example
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-9-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime; Declaration of
currentTime.printTime(); object variable
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-10-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
Accessing member variables using
member functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-11-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
Modifying member variables
using member functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-12-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes – Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime(); :
timeType(){
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
hour = 0;
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute() = 0;
minute
<< endl; second = 0;
return 0; zone = "Kuala Lumpur";
} }
currentTime };
hour 0
minute 0
first
second 0
zone Kuala Lumpur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-13-2048.jpg)
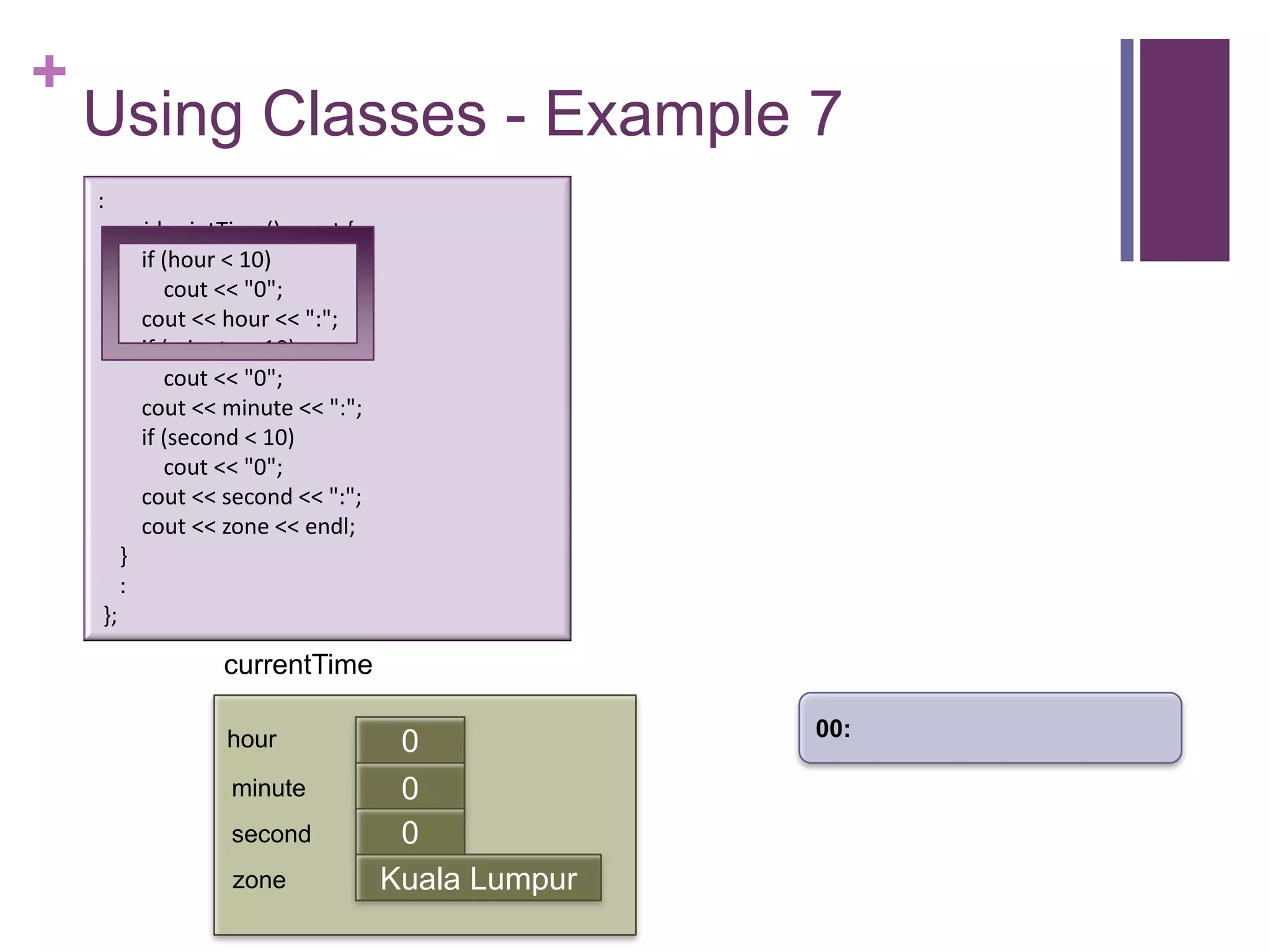
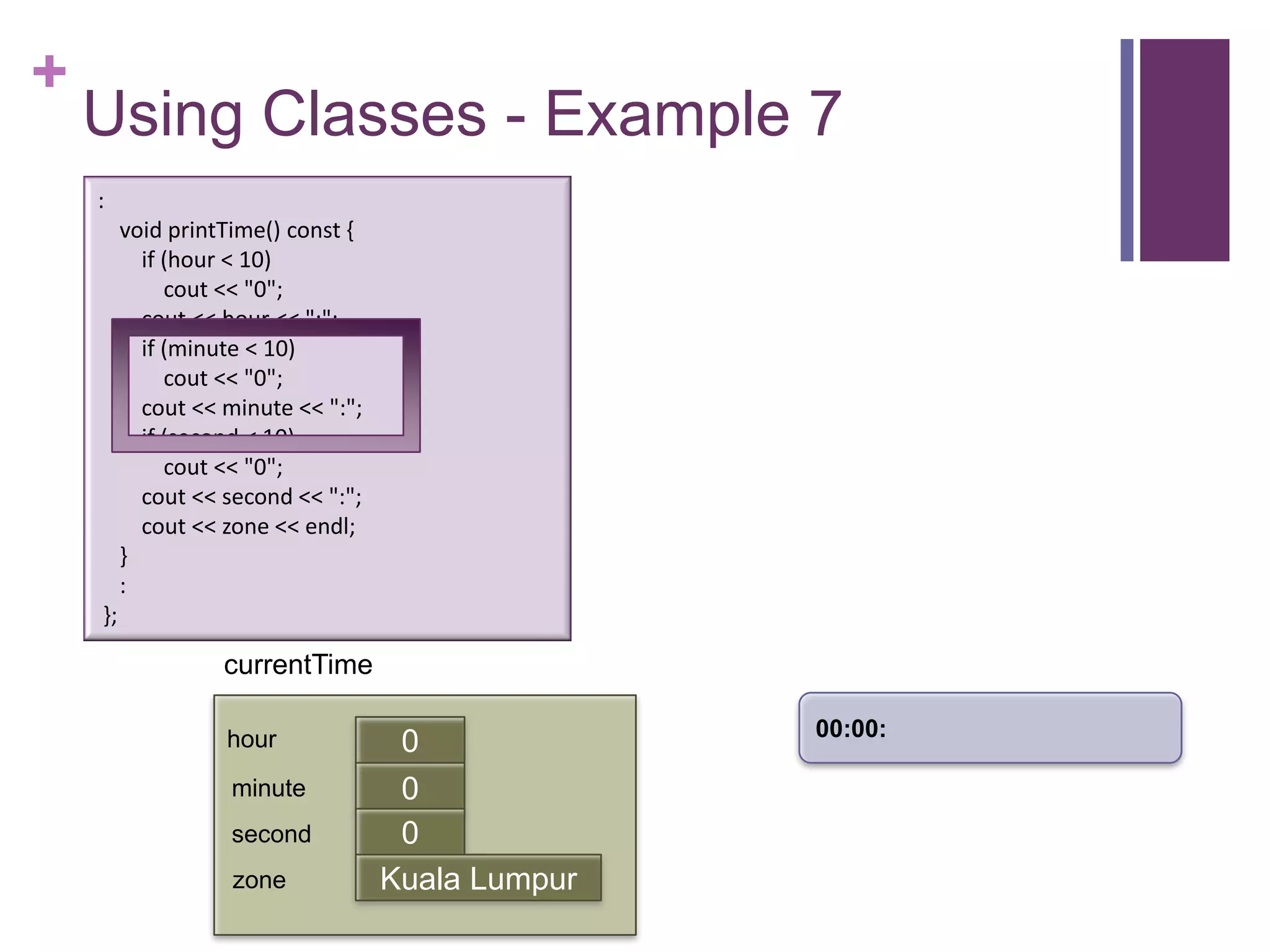
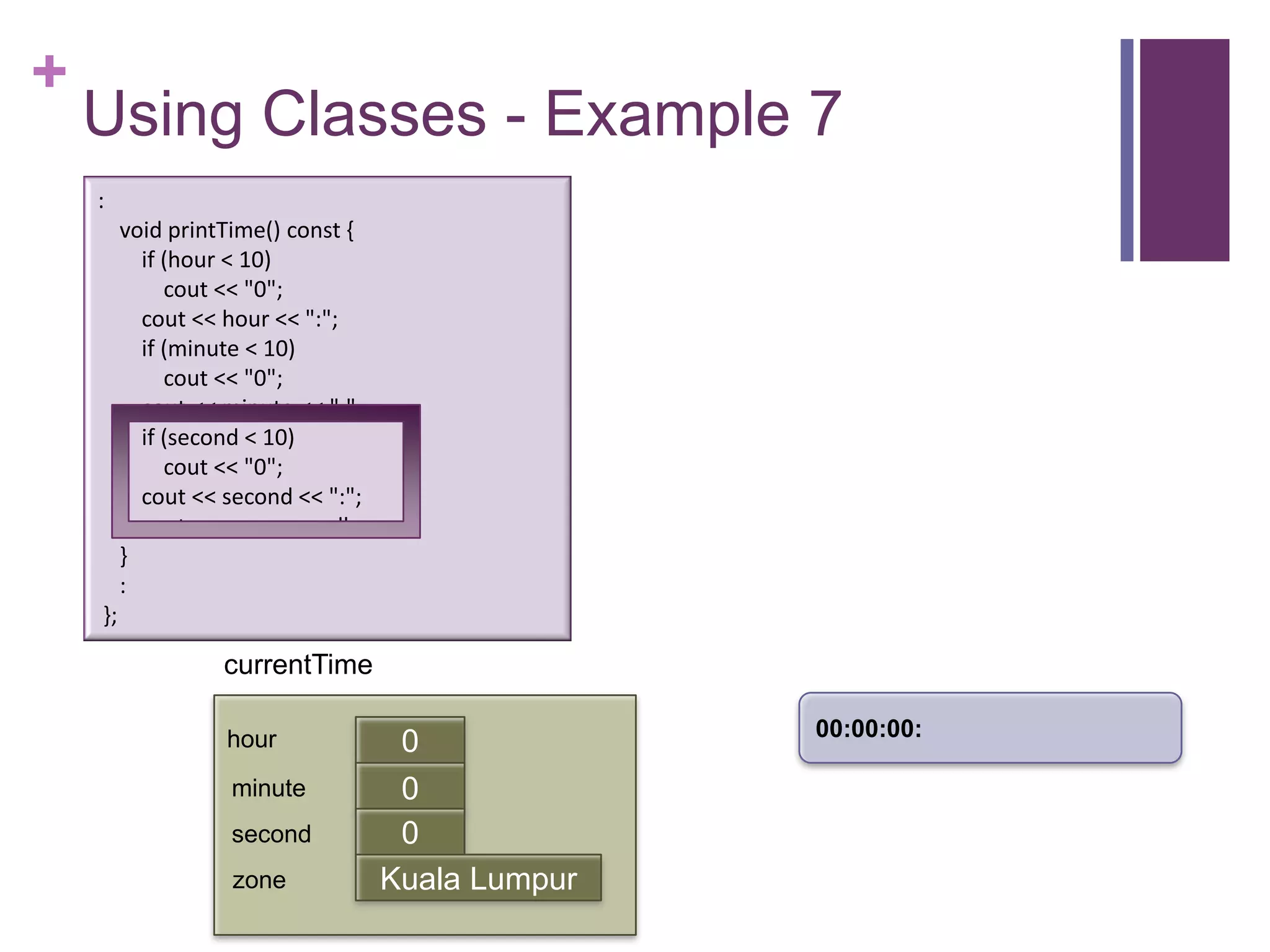
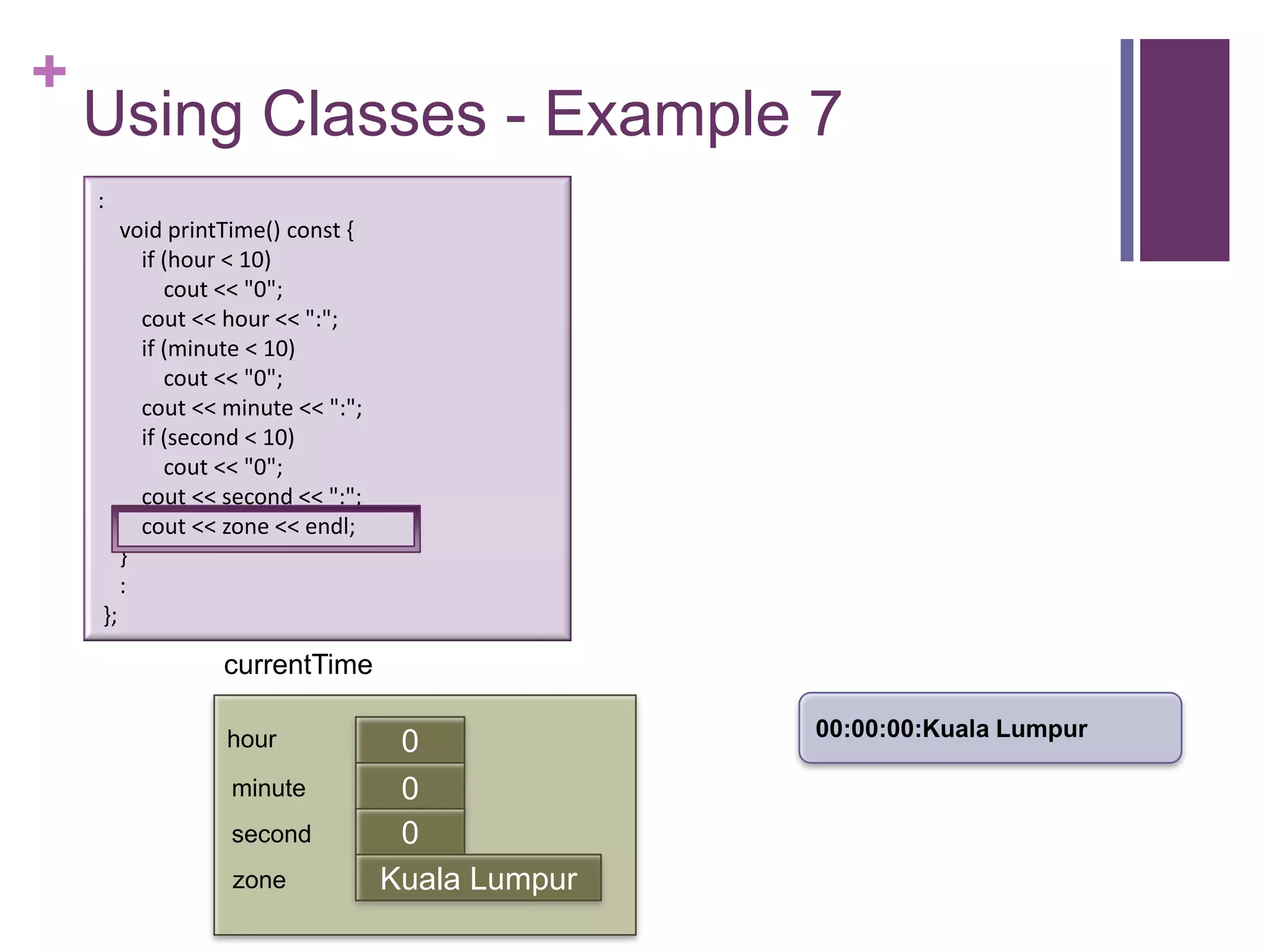
![+
Using Classes – Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime(); :
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is " printTime() const {
void
if (hour < 10)
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute() << "0";
cout
<< endl; cout << hour << ":";
return 0; if (minute < 10)
} cout << "0";
cout << minute << ":";
currentTime if (second < 10)
cout << "0";
cout << second << ":";
hour 0
cout << zone << endl;
minute 0 }
first
second 0 :
zone Kuala Lumpur };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-14-2048.jpg)
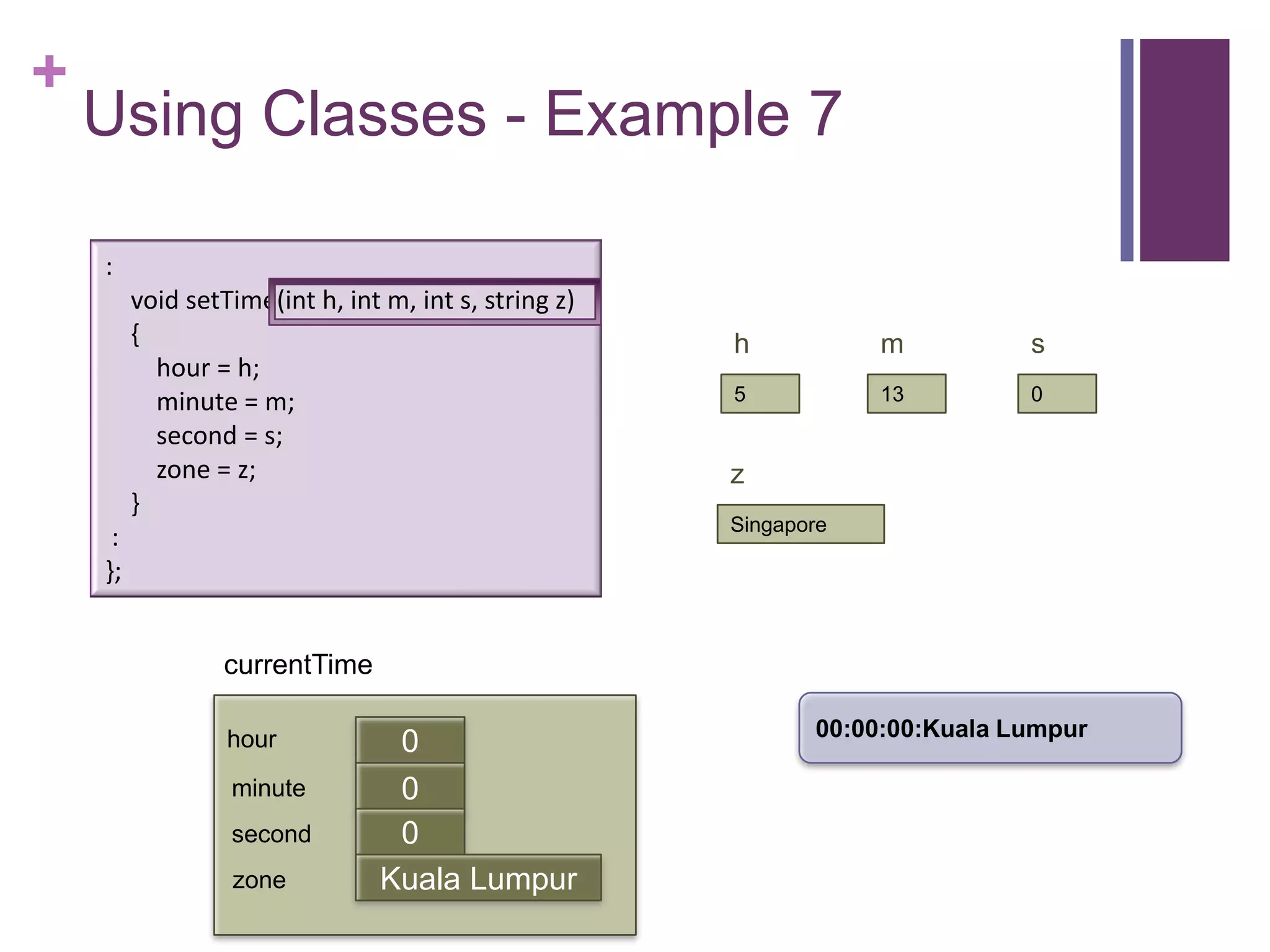
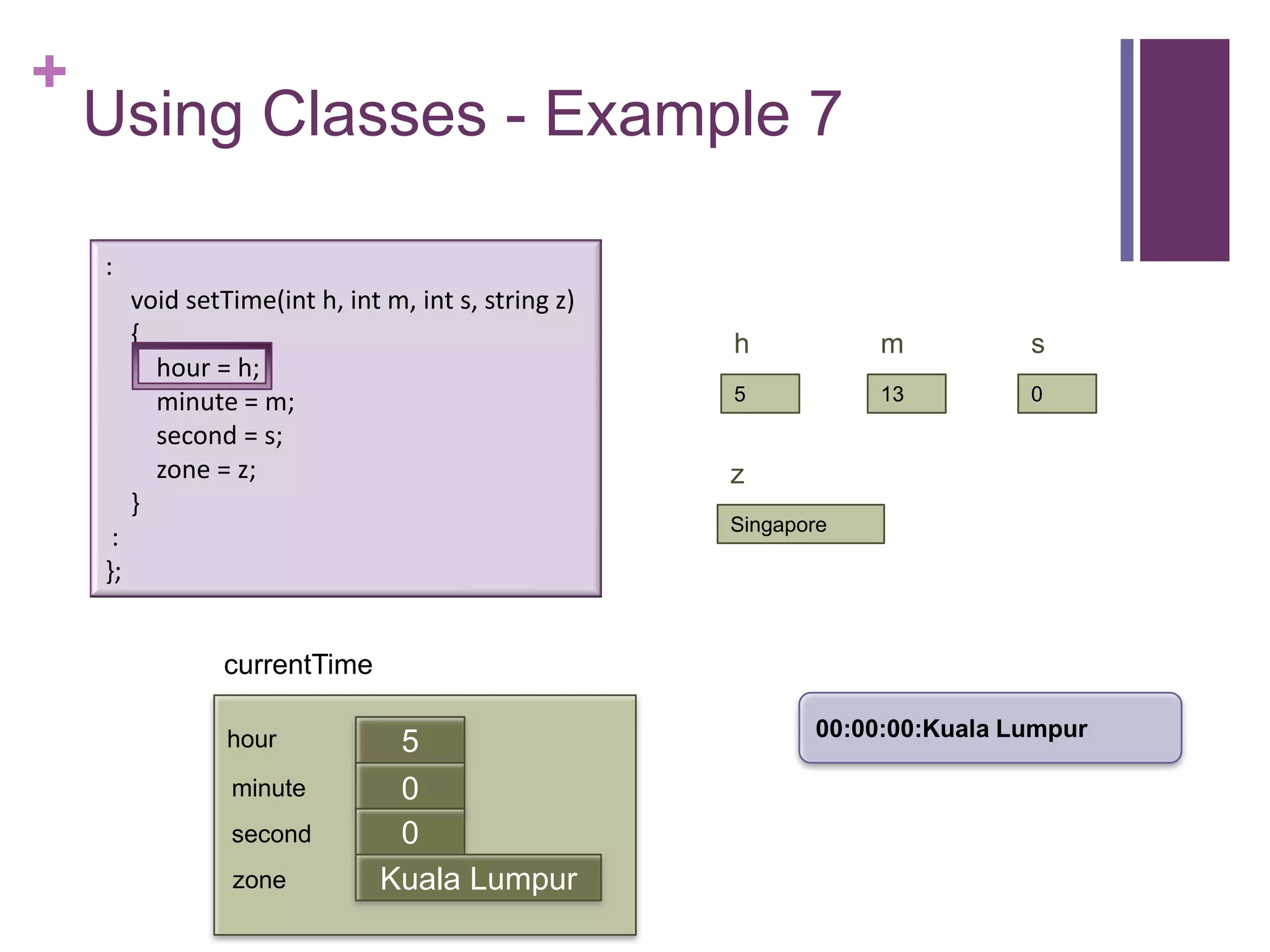
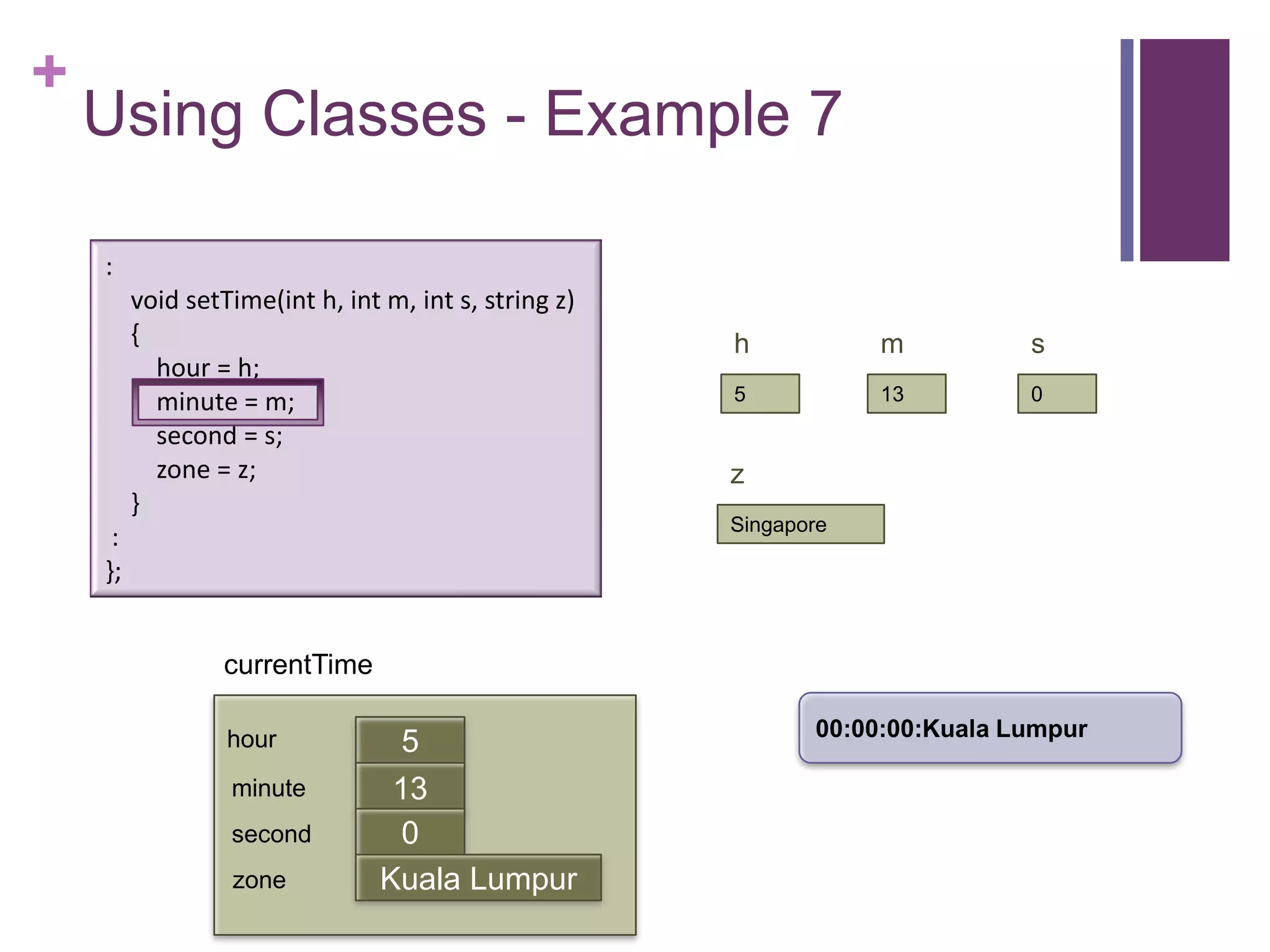
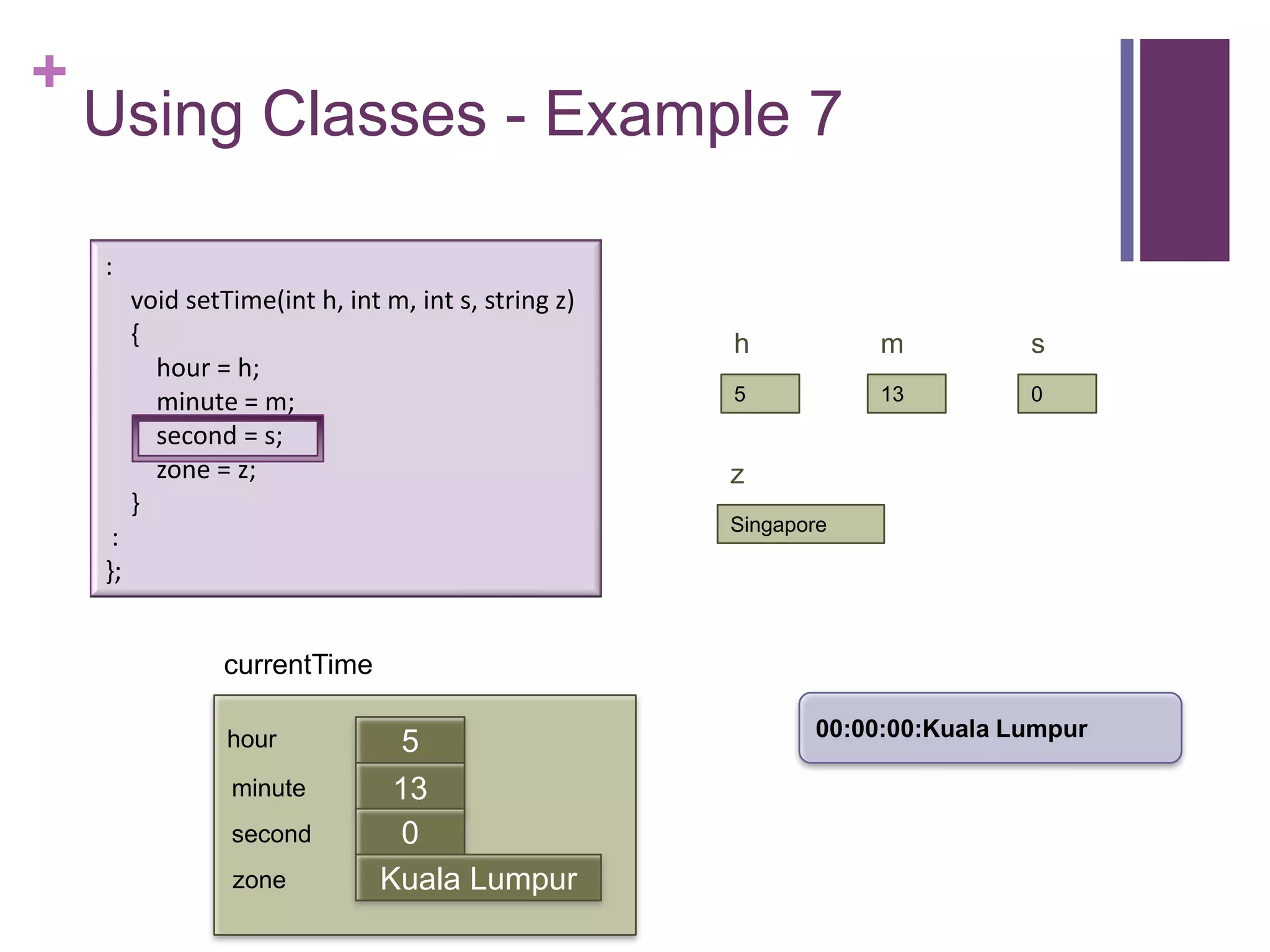
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime(); :
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore"); void setTime(int h, int m, int s, string z)
currentTime.printTime(); {
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is " = h;
hour
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute() = m;
minute
<< endl; second = s;
return 0; zone = z;
} }
currentTime :
};
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 0
minute 0
first
second 0
zone Kuala Lumpur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-19-2048.jpg)
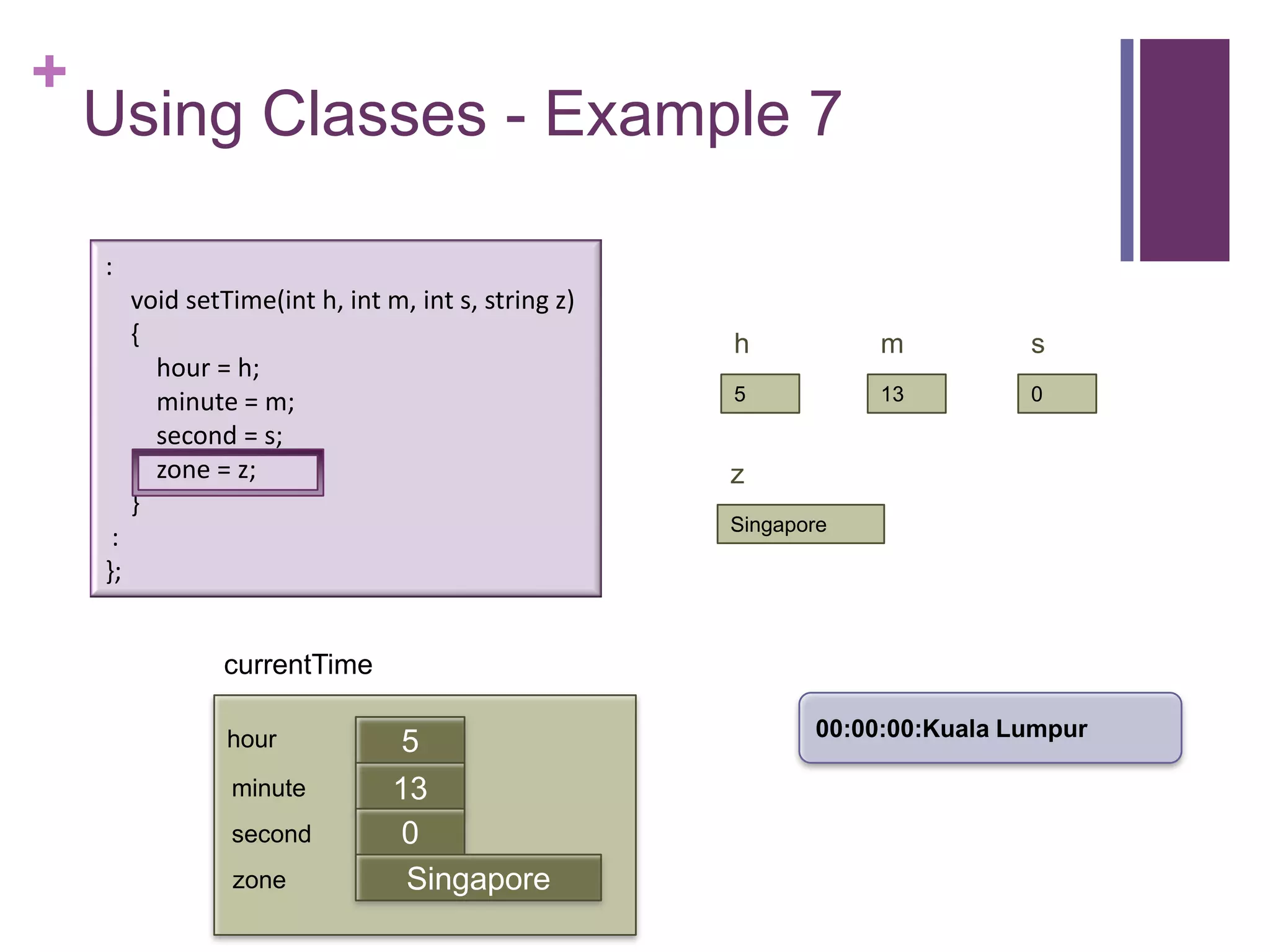
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime(); :
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is " printTime() const {
void
if (hour < 10)
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute() << "0";
cout
<< endl; cout << hour << ":";
return 0; if (minute < 10)
} cout << "0";
cout << minute << ":";
currentTime if (second < 10)
cout << "0";
cout << second << ":";
hour 5
cout << zone << endl;
minute 13 }
first
second 0 :
zone Singapore };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-25-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
currentTime
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 5 05:13:00:Singapore
minute 13
first
second 0
zone Singapore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-26-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
currentTime
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 5 05:13:00:Singapore
minute 13 The time in
first
second 0
zone Singapore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-27-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{ :
timeType currentTime; string getZone() const {
currentTime.printTime(); return zone;
}
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
:
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
currentTime
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 5 05:13:00:Singapore
minute 13 The time in Singapore
first
second 0
zone Singapore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-28-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
currentTime
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 5 05:13:00:Singapore
minute 13 The time in Singapore now is
first
second 0
zone Singapore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-29-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{ :
timeType currentTime; int getHour() const {
currentTime.printTime(); return hour;
}
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
:
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
currentTime
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 5 05:13:00:Singapore
minute 13 The time in Singapore now is 5
first
second 0
zone Singapore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-30-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
timeType currentTime;
currentTime.printTime();
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime();
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
currentTime
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 5 05:13:00:Singapore
minute 13 The time in Singapore now is 5:
first
second 0
zone Singapore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-31-2048.jpg)
![+
Using Classes - Example 7
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{ :
timeType currentTime; int getMinute() const {
currentTime.printTime(); return minute;
}
currentTime.setTime(5, 13, 0, "Singapore");
currentTime.printTime(); :
cout << "The time in " << currentTime.getZone() << " now is "
<< currentTime.getHour() << ":" << currentTime.getMinute()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
currentTime
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
hour 5 05:13:00:Singapore
minute 13 The time in Singapore now is 5:13
first
second 0
zone Singapore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-32-2048.jpg)





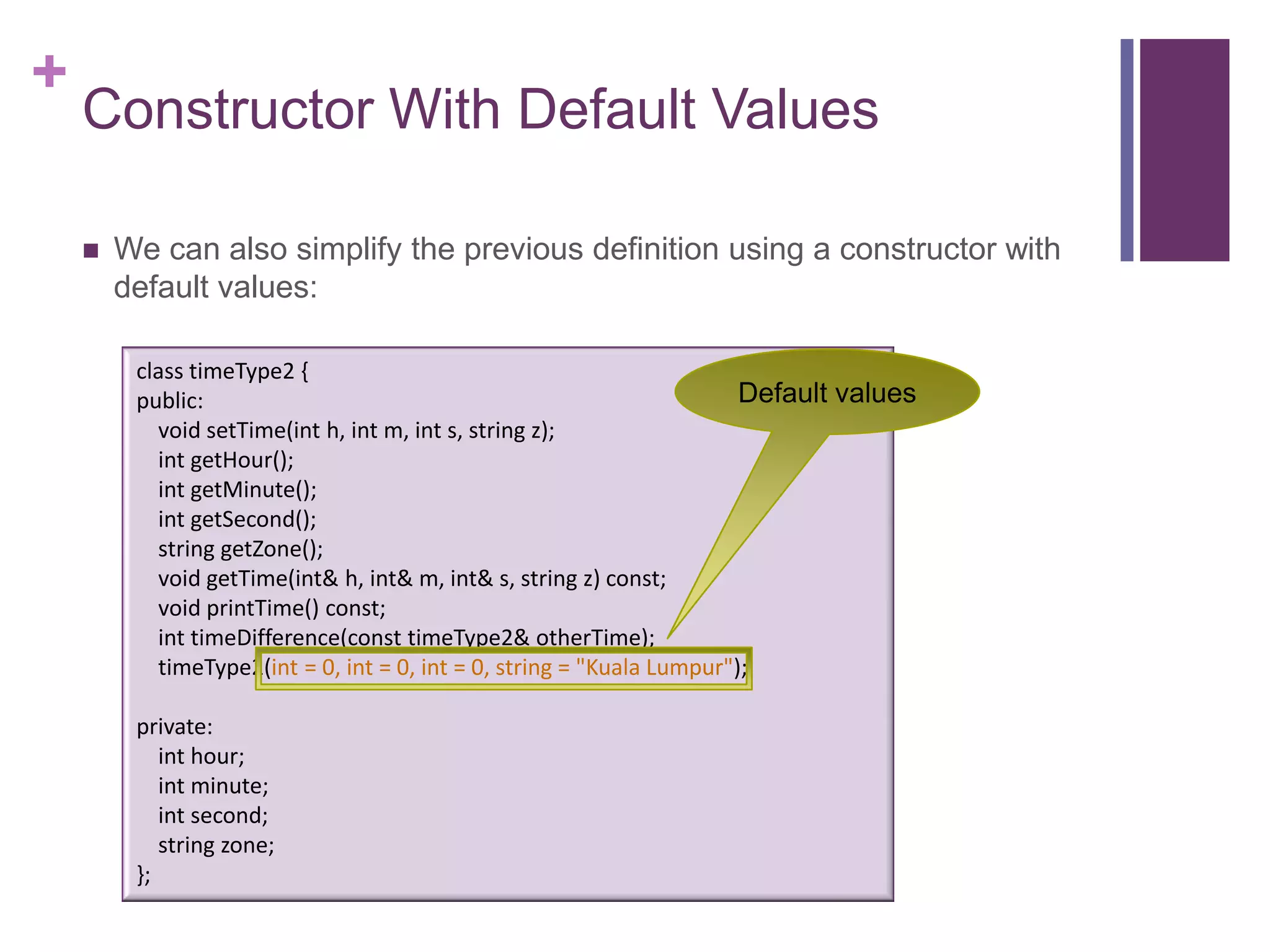
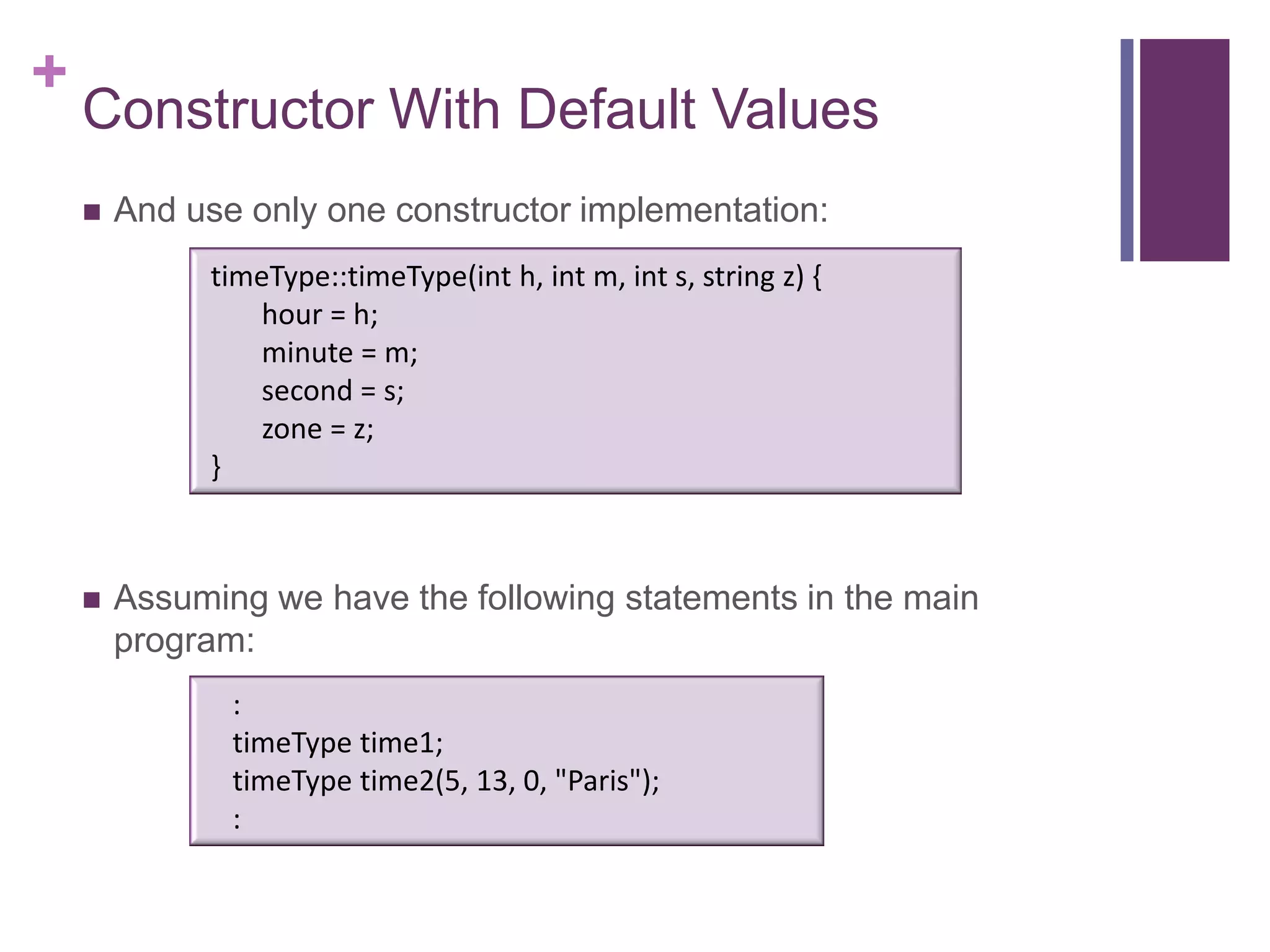
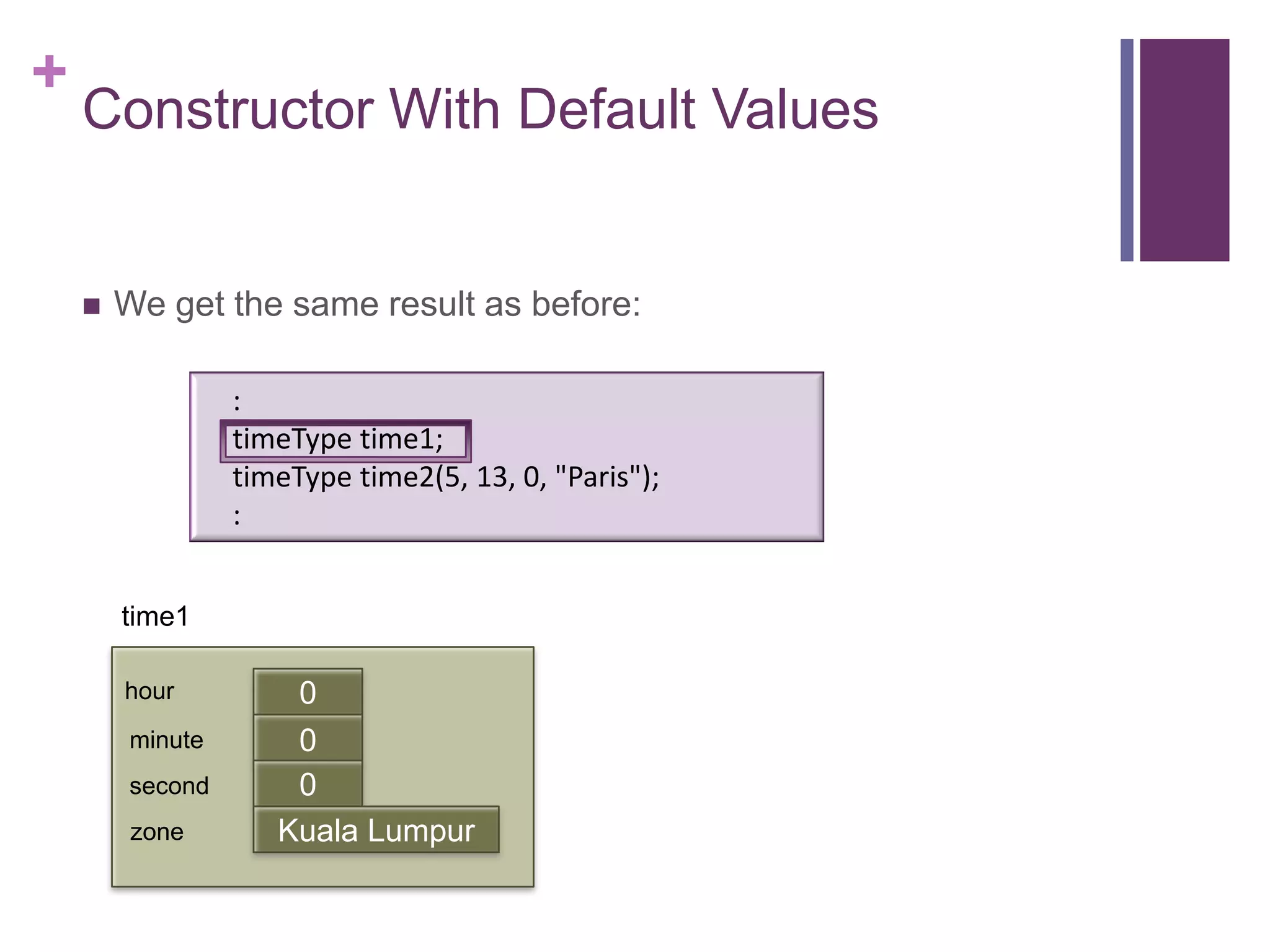
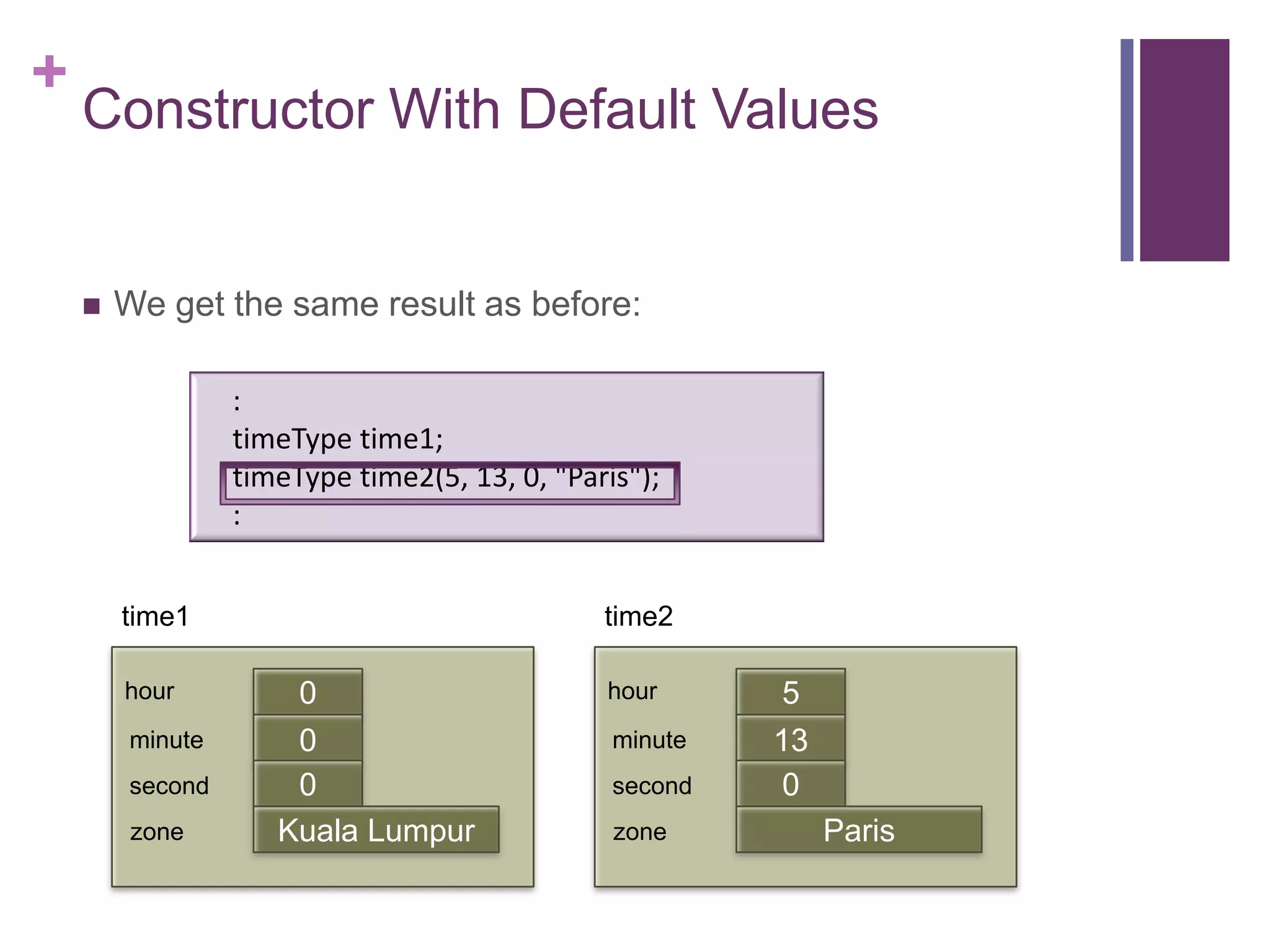

![+
Array of Class Objects (Variables)
Just like other types of data, we can declare an array of object
variables
Eg.
timeType2 time[5];
time[1].setTime(1, 0, 0, "Tokyo");
time[2].setTime(5, 0, 0, "Paris");
time[3].setTime(11, 0, 0, "New York");
time[4].setTime(3, 0, 0, "Sydney");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
time[i].printTime();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-59-2048.jpg)
![+
Array of Class Objects (Variables)
timeType2 time[5];
time[1].setTime(1, 0, 0, "Tokyo");
time[2].setTime(5, 0, 0, "Paris");
time[3].setTime(11, 0, 0, "New York");
time[4].setTime(3, 0, 0, "Sydney");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
time[i].printTime();
time time[0]
time[1]
hour time[2] 0
hour time[3] 0
minute 0
minute first
secondhour time[4] 0
0 0
second hour first0 0
zone minute 0
Kuala Lumpur
hour first 0
zone minute 0 0
second Kuala Lumpur
first
zone minute 0 0
second Kuala Lumpur
first
0
second Kuala Lumpur
zone
zone Kuala Lumpur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-60-2048.jpg)
![+
Array of Class Objects (Variables)
timeType2 time[5];
time[1].setTime(1, 0, 0, "Tokyo");
time[2].setTime(5, 0, 0, "Paris");
time[3].setTime(11, 0, 0, "New York");
time[4].setTime(3, 0, 0, "Sydney");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
time[i].printTime();
time
time[1]
hour 1
minute 0
first
second 0
zone Tokyo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-61-2048.jpg)
![+
Array of Class Objects (Variables)
timeType2 time[5];
time[1].setTime(1, 0, 0, "Tokyo");
time[2].setTime(5, 0, 0, "Paris");
time[3].setTime(11, 0, 0, "New York");
time[4].setTime(3, 0, 0, "Sydney");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
time[i].printTime();
time
time[2]
hour 5
minute 0
first
second 0
zone Paris](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-62-2048.jpg)
![+
Array of Class Objects (Variables)
timeType2 time[5];
time[1].setTime(1, 0, 0, "Tokyo");
time[2].setTime(5, 0, 0, "Paris");
time[3].setTime(11, 0, 0, "New York");
time[4].setTime(3, 0, 0, "Sydney");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
time[i].printTime();
time
time[3]
hour 11
minute 0
first
second 0
zone New York](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-63-2048.jpg)
![+
Array of Class Objects (Variables)
timeType2 time[5];
time[1].setTime(1, 0, 0, "Tokyo");
time[2].setTime(5, 0, 0, "Paris");
time[3].setTime(11, 0, 0, "New York");
time[4].setTime(3, 0, 0, "Sydney");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
time[i].printTime();
time
time[4]
hour 3
minute 0
first
second 0
zone Sydney](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-64-2048.jpg)
![+
Array of Class Objects (Variables)
timeType2 time[5];
time[1].setTime(1, 0, 0, "Tokyo");
time[2].setTime(5, 0, 0, "Paris");
time[3].setTime(11, 0, 0, "New York");
time[4].setTime(3, 0, 0, "Sydney");
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
time[i].printTime();
00:00:00:Kuala Lumpur
01:00:00:Tokyo
05:00:00:Paris
11:00:00:New York
03:00:00:Sydney](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1classes3-130217014426-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-classes3-65-2048.jpg)
