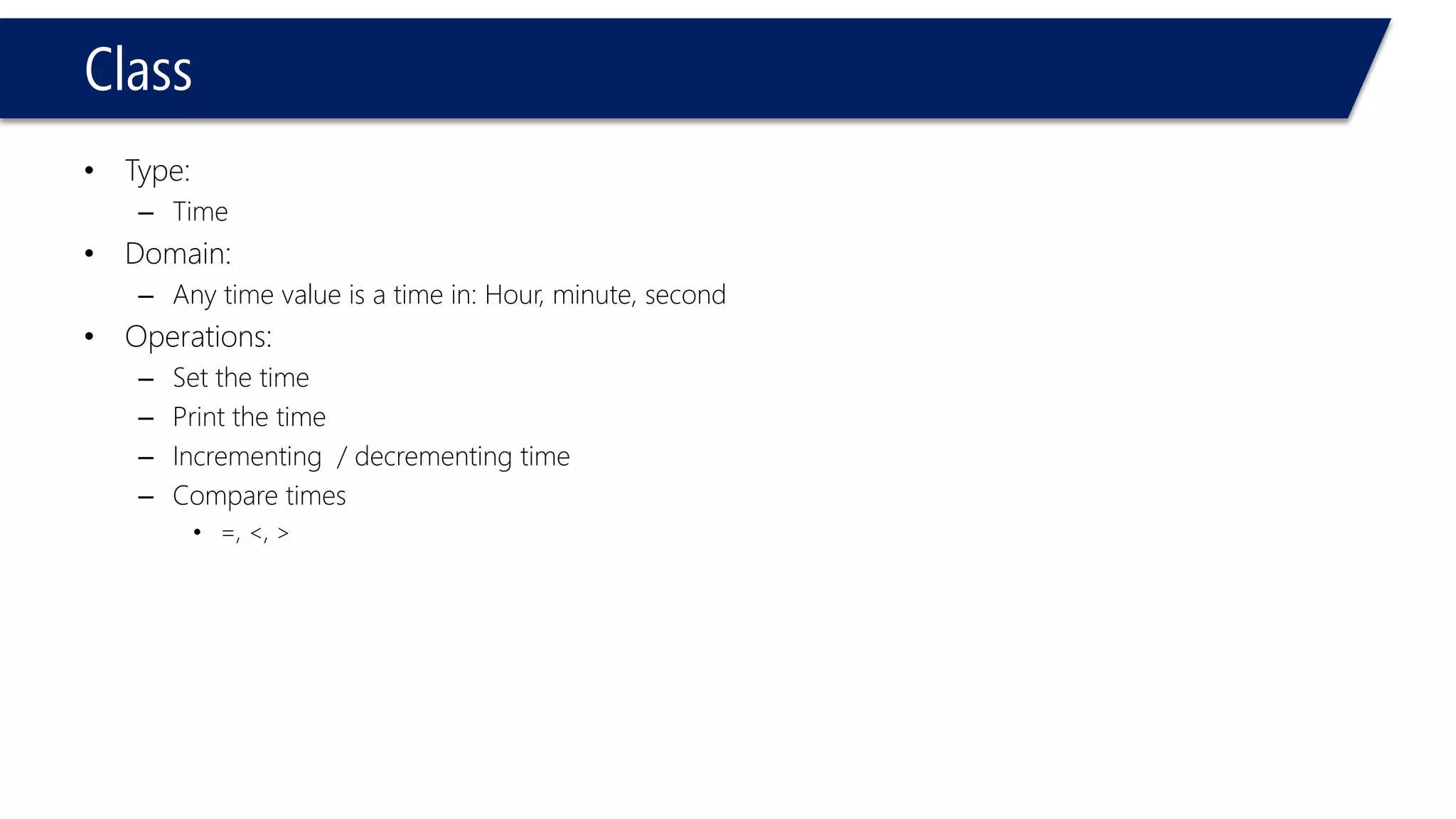
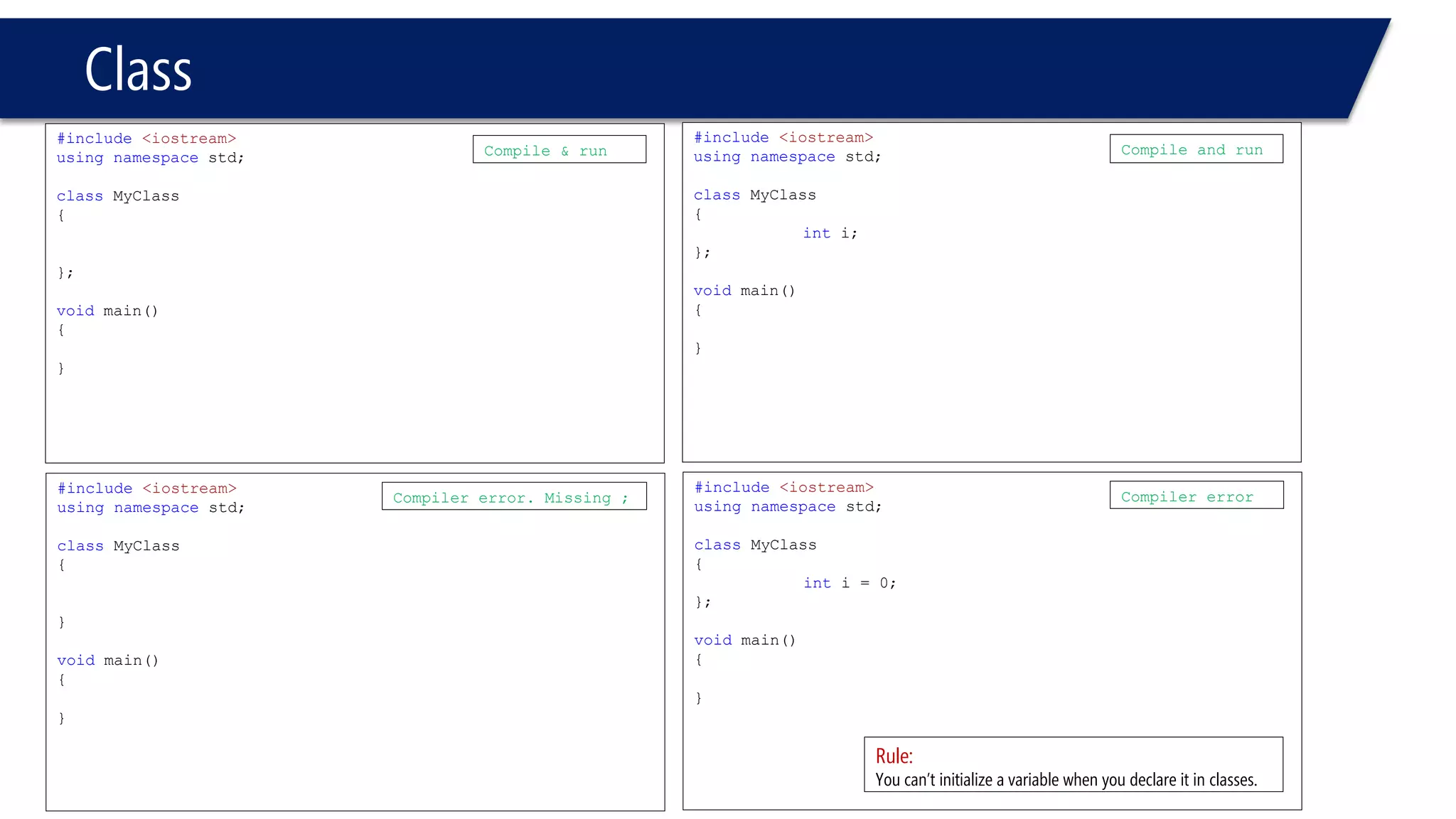
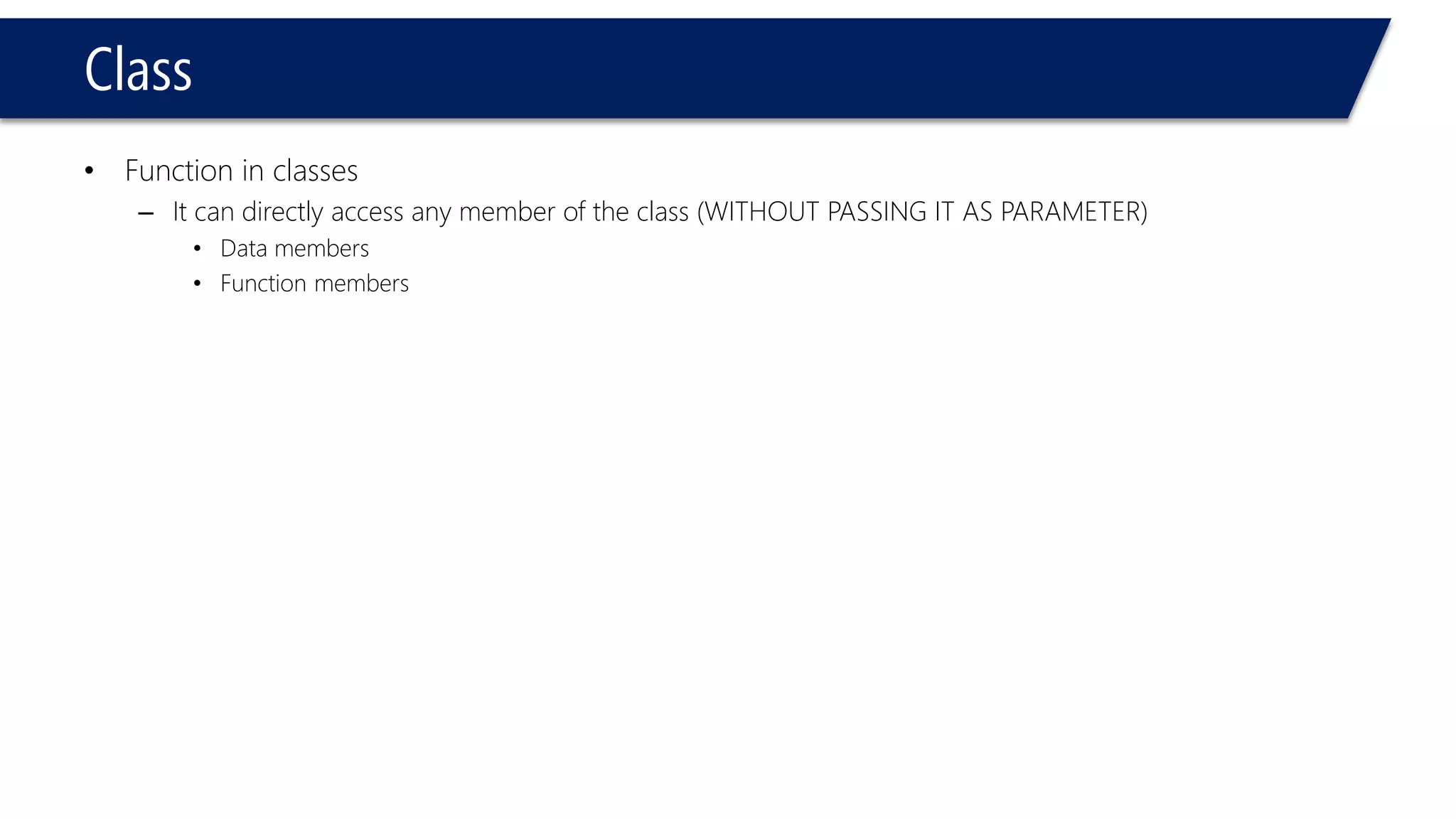
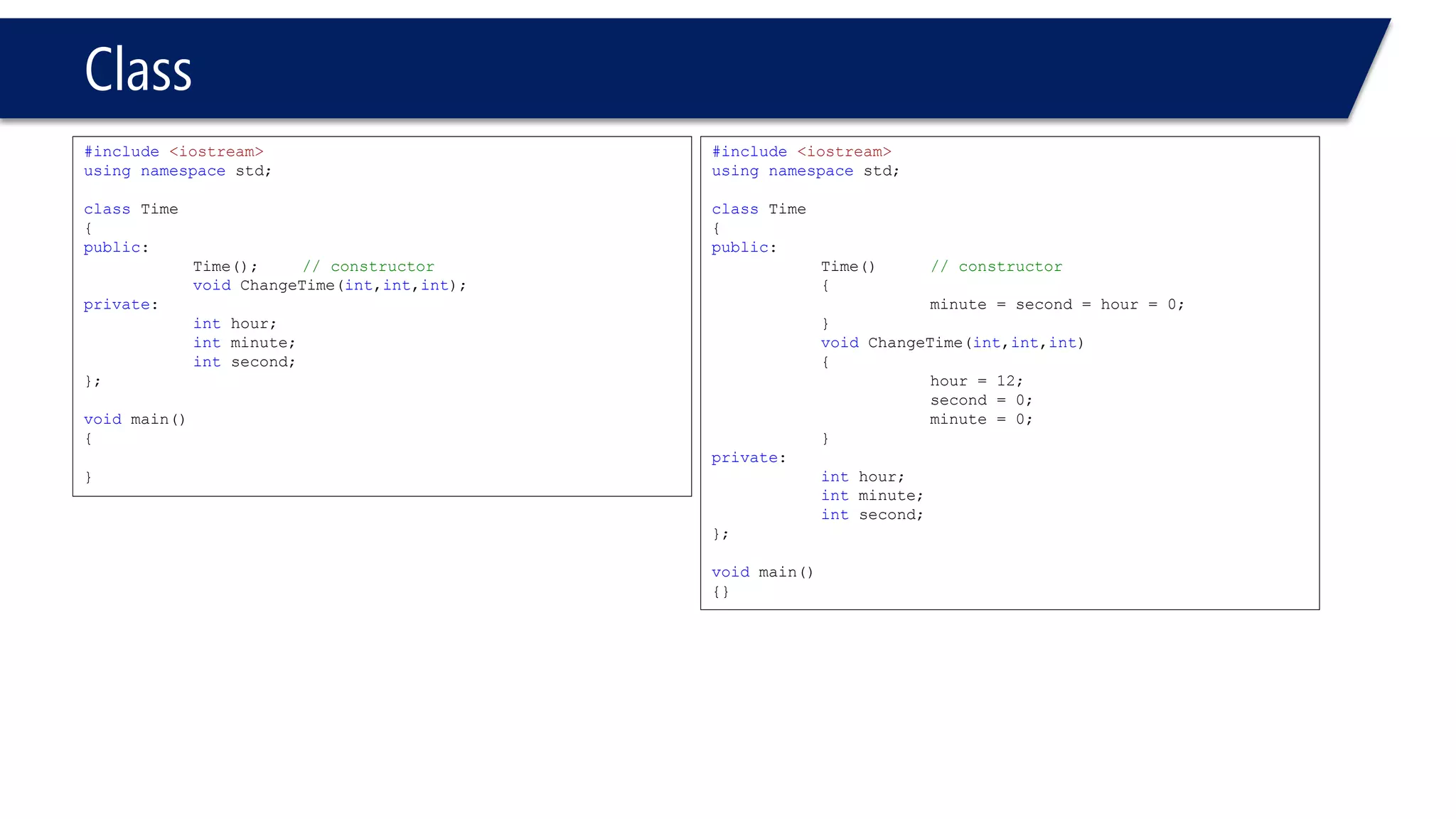
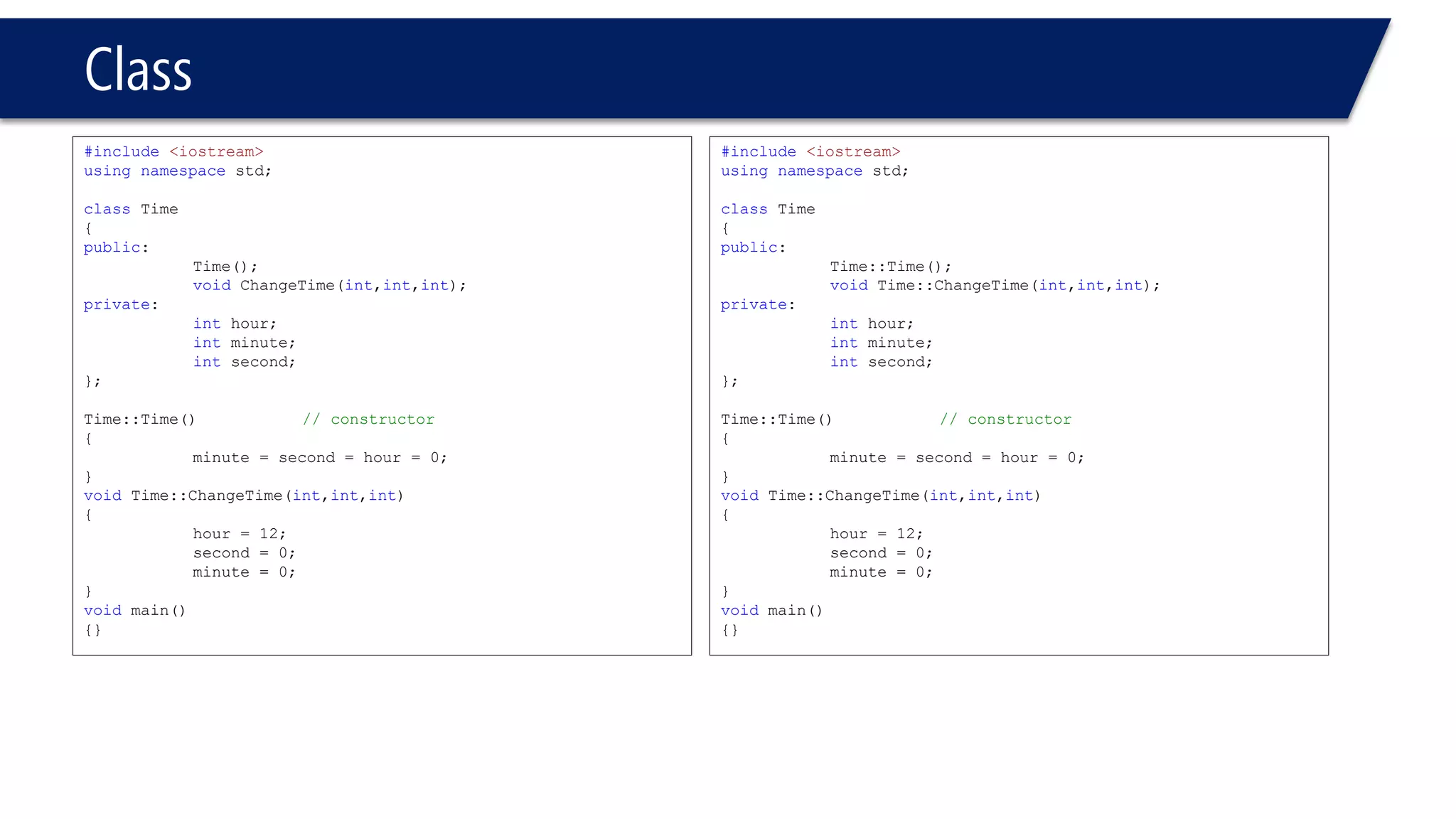
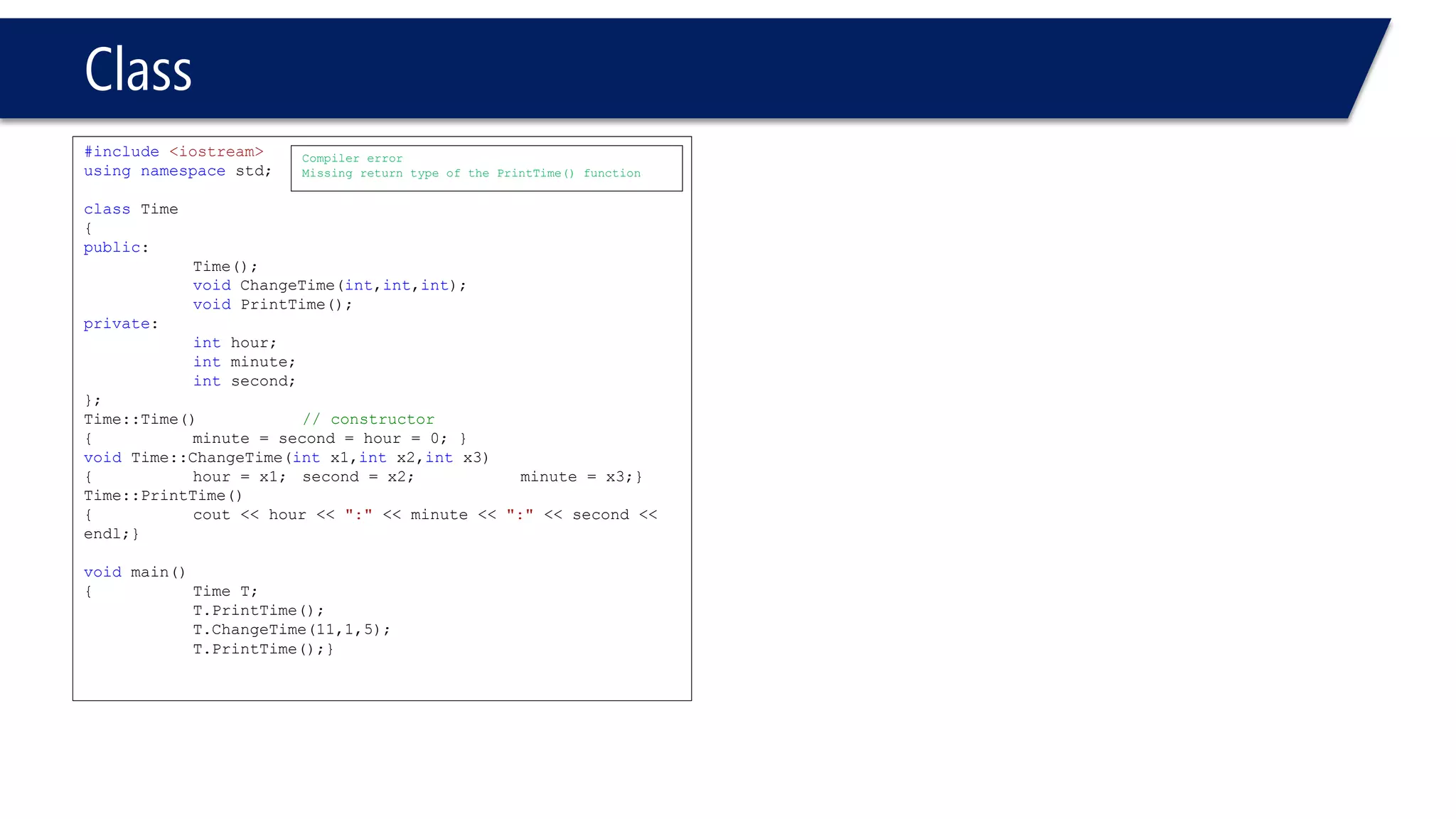
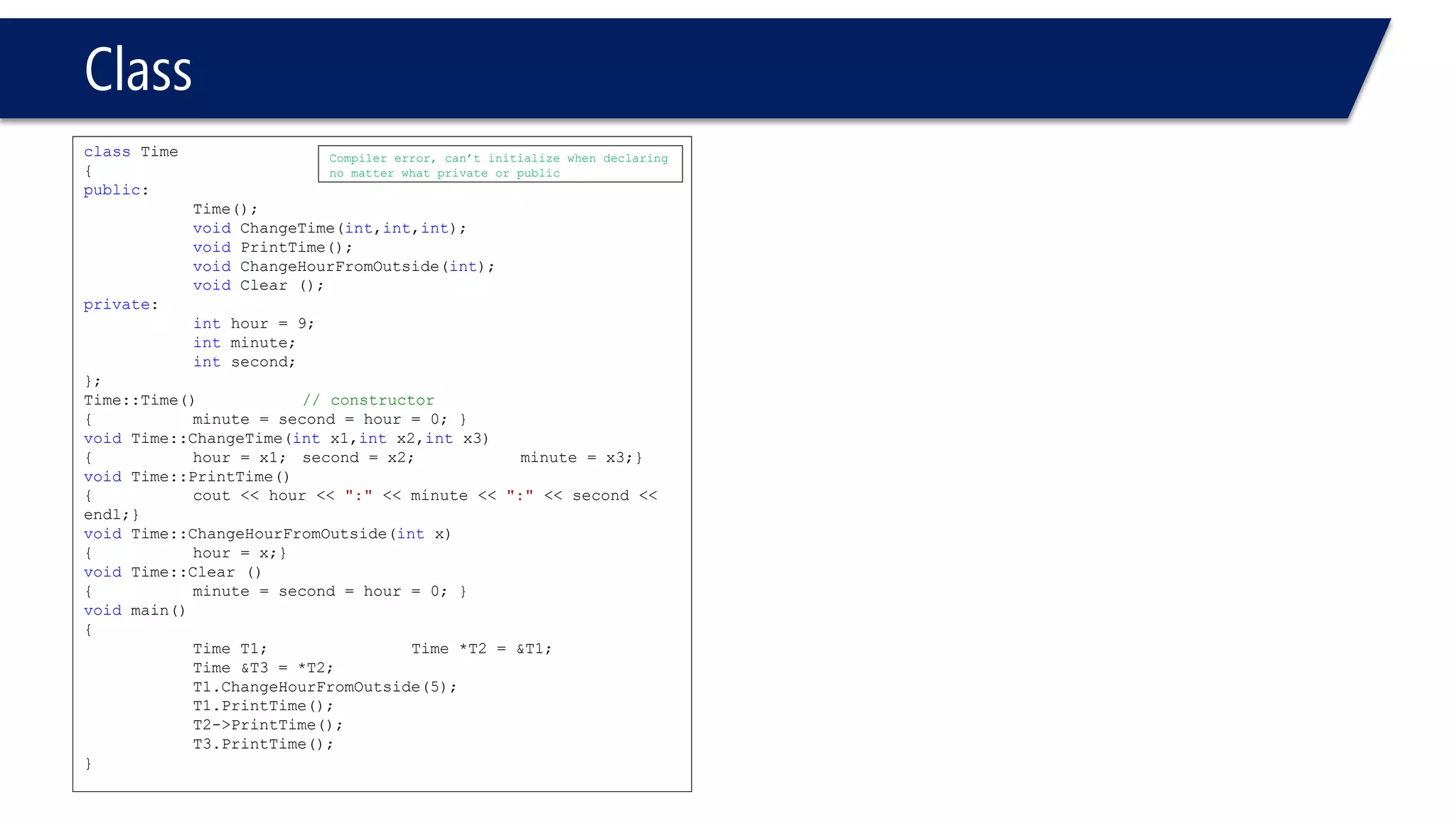
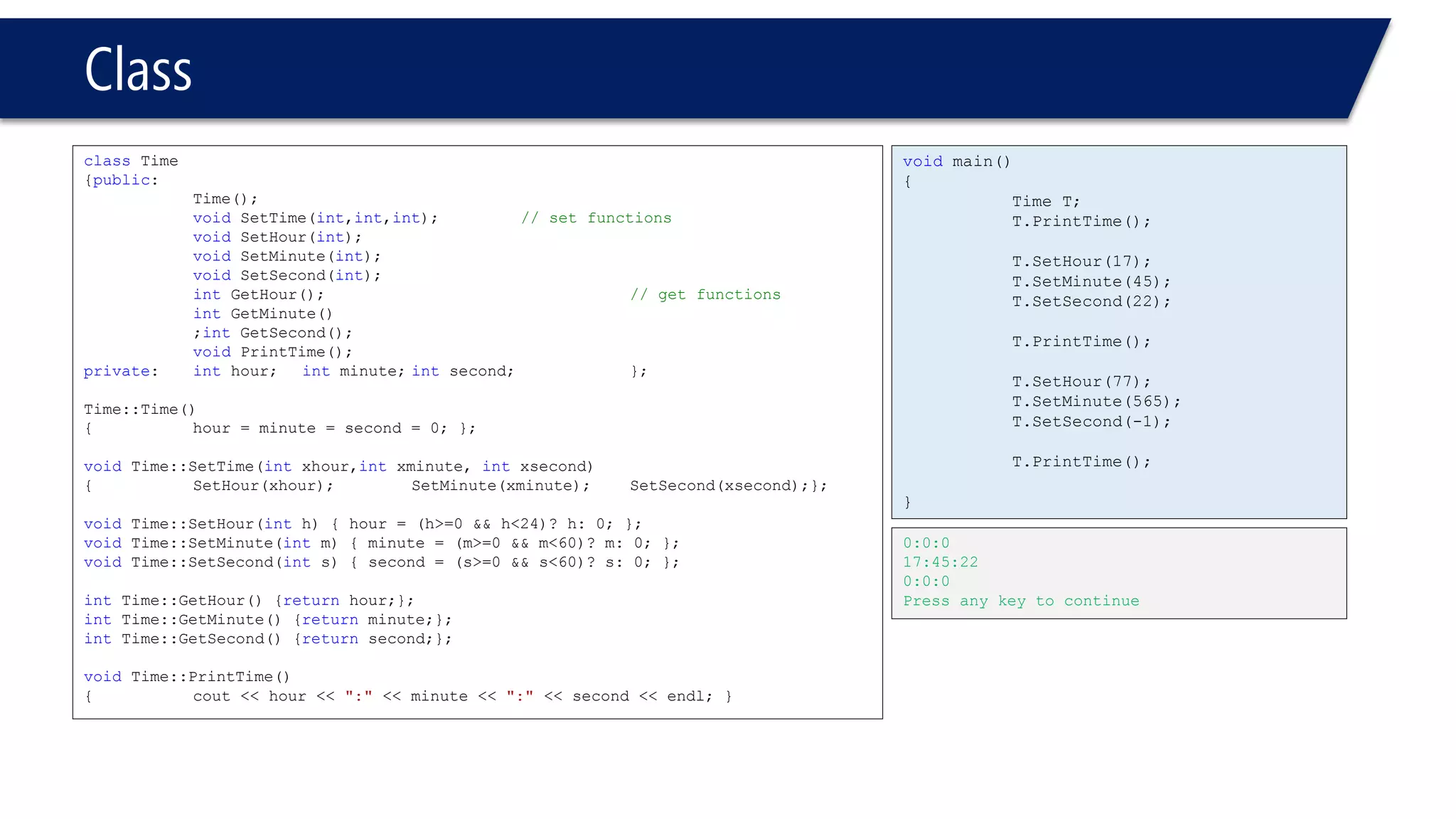
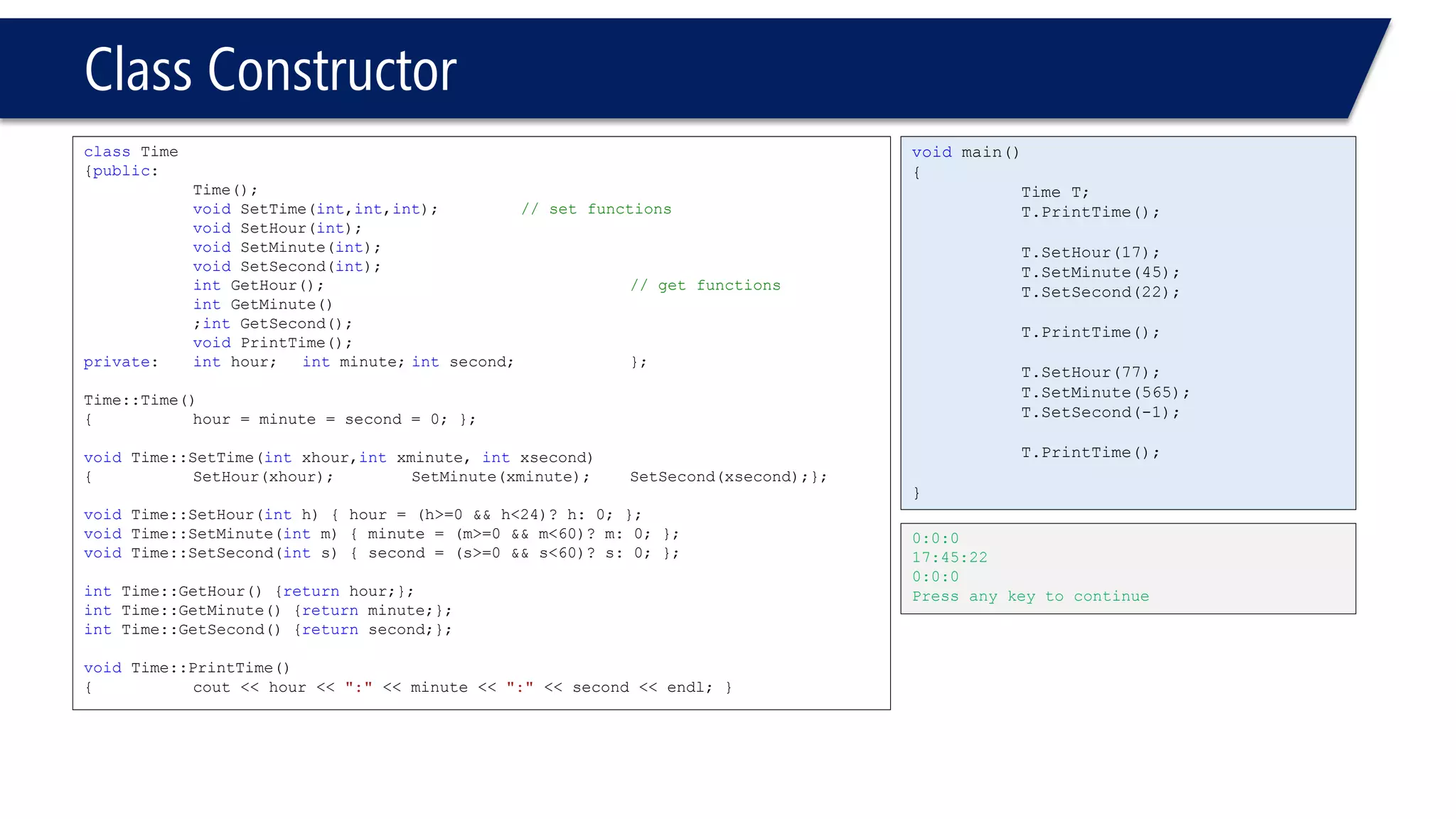
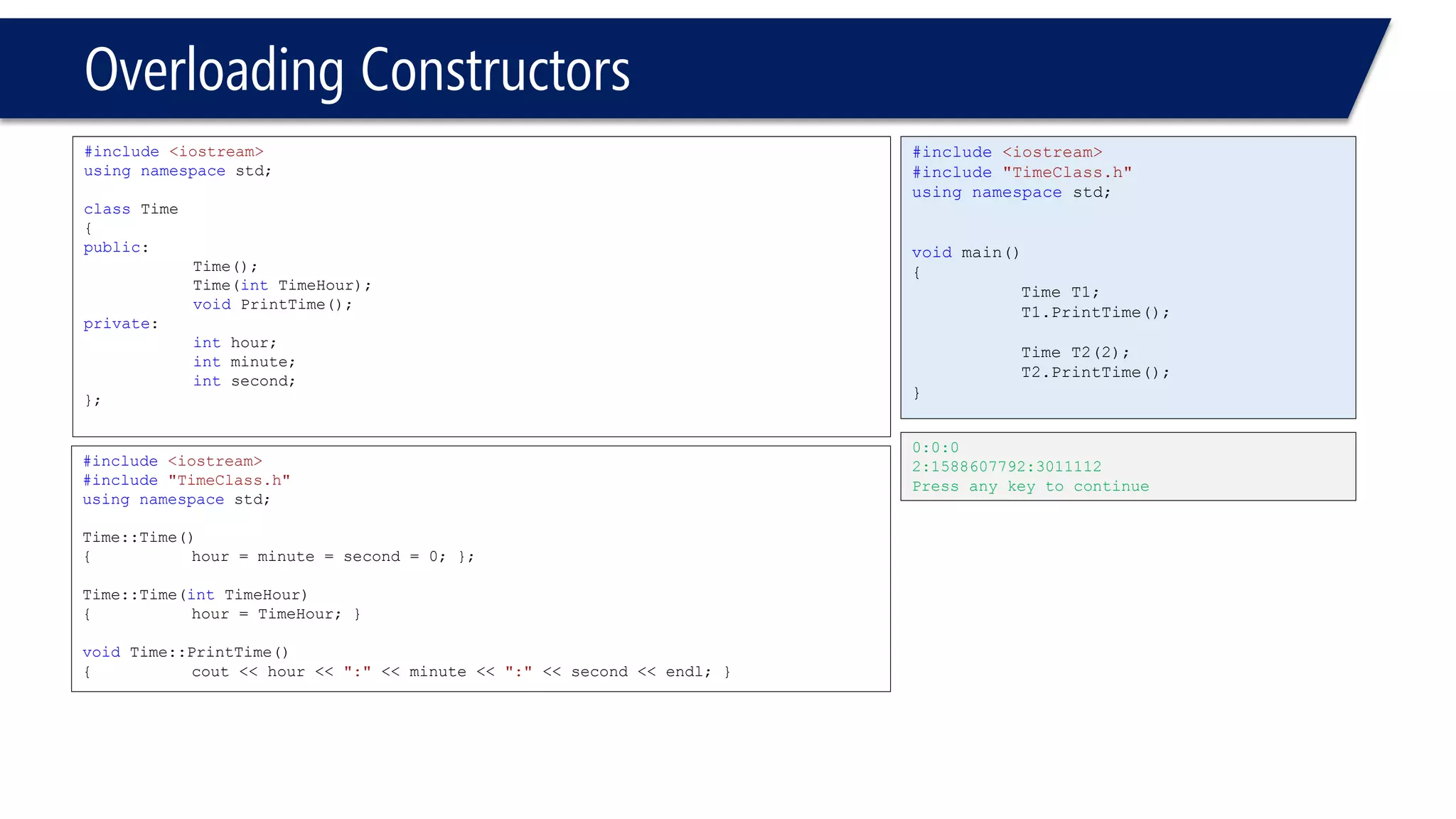
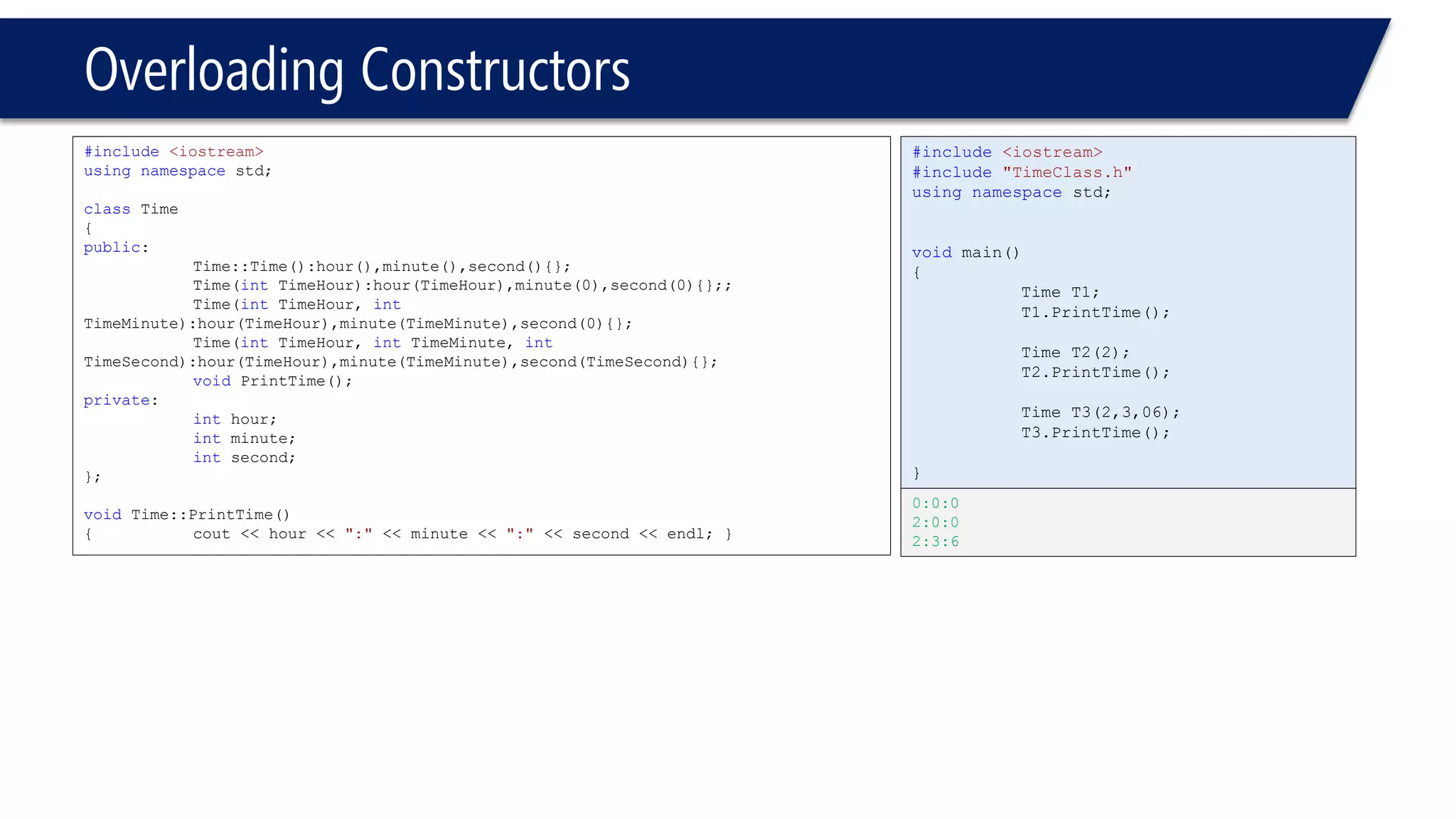
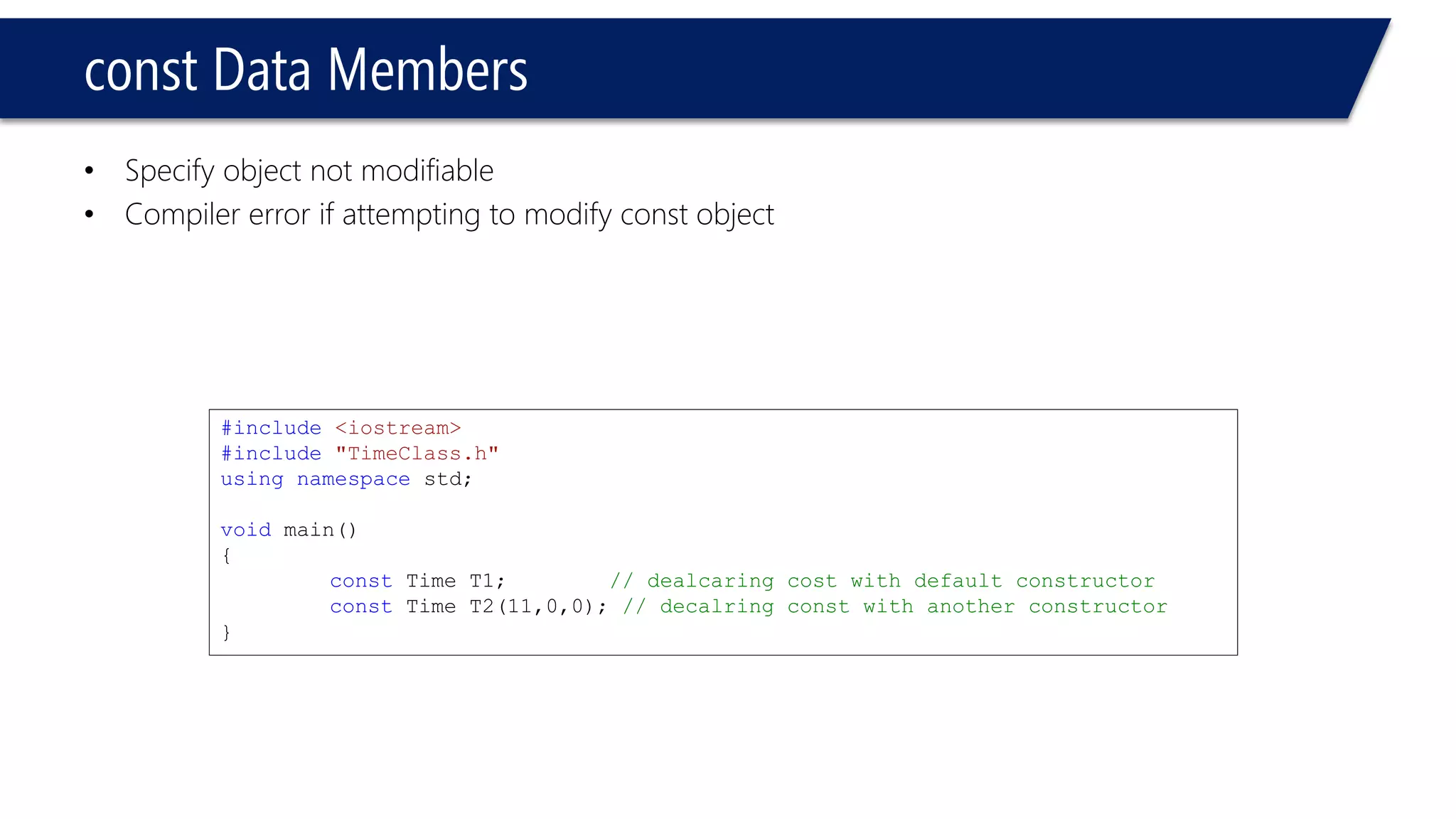
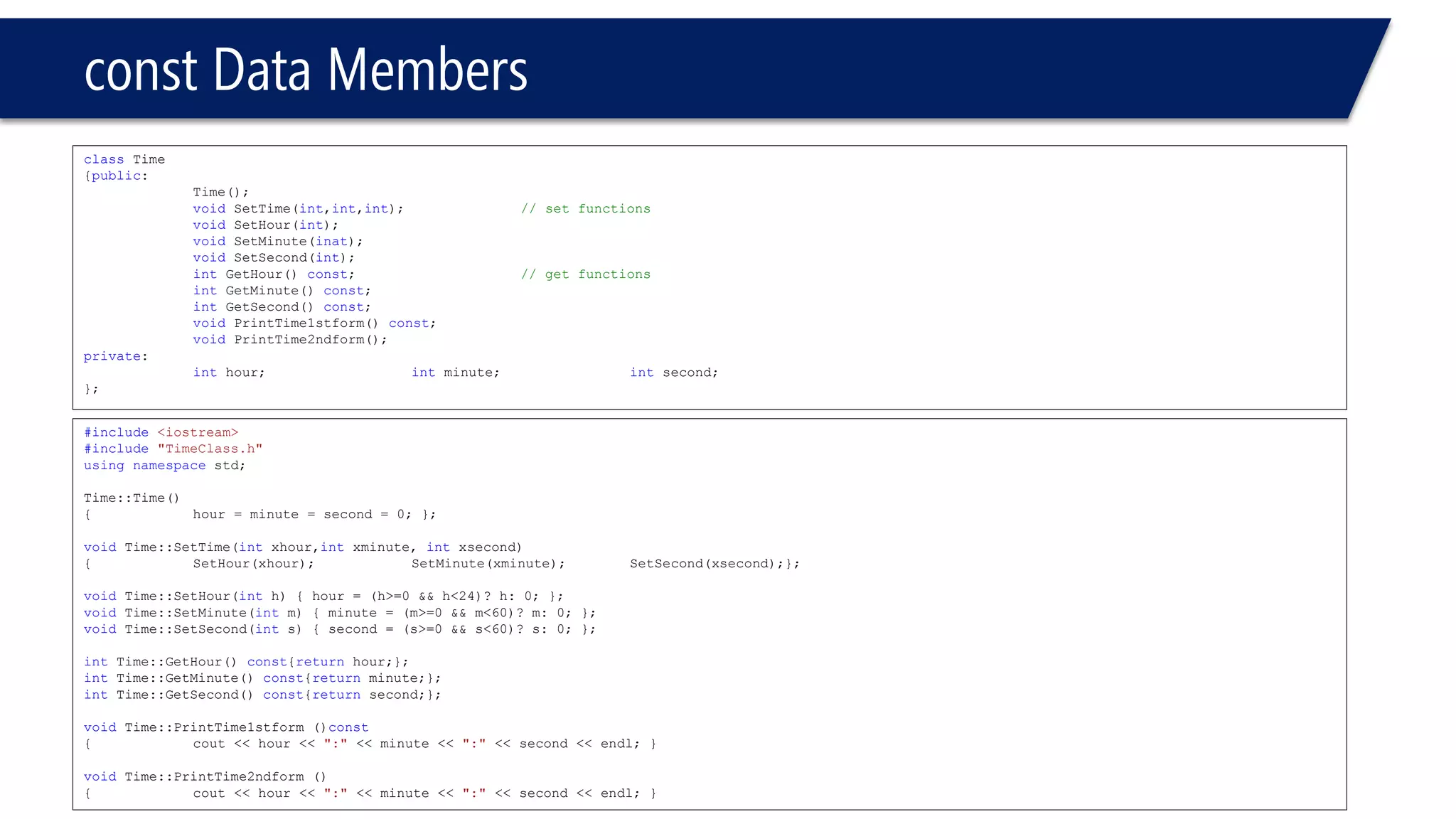
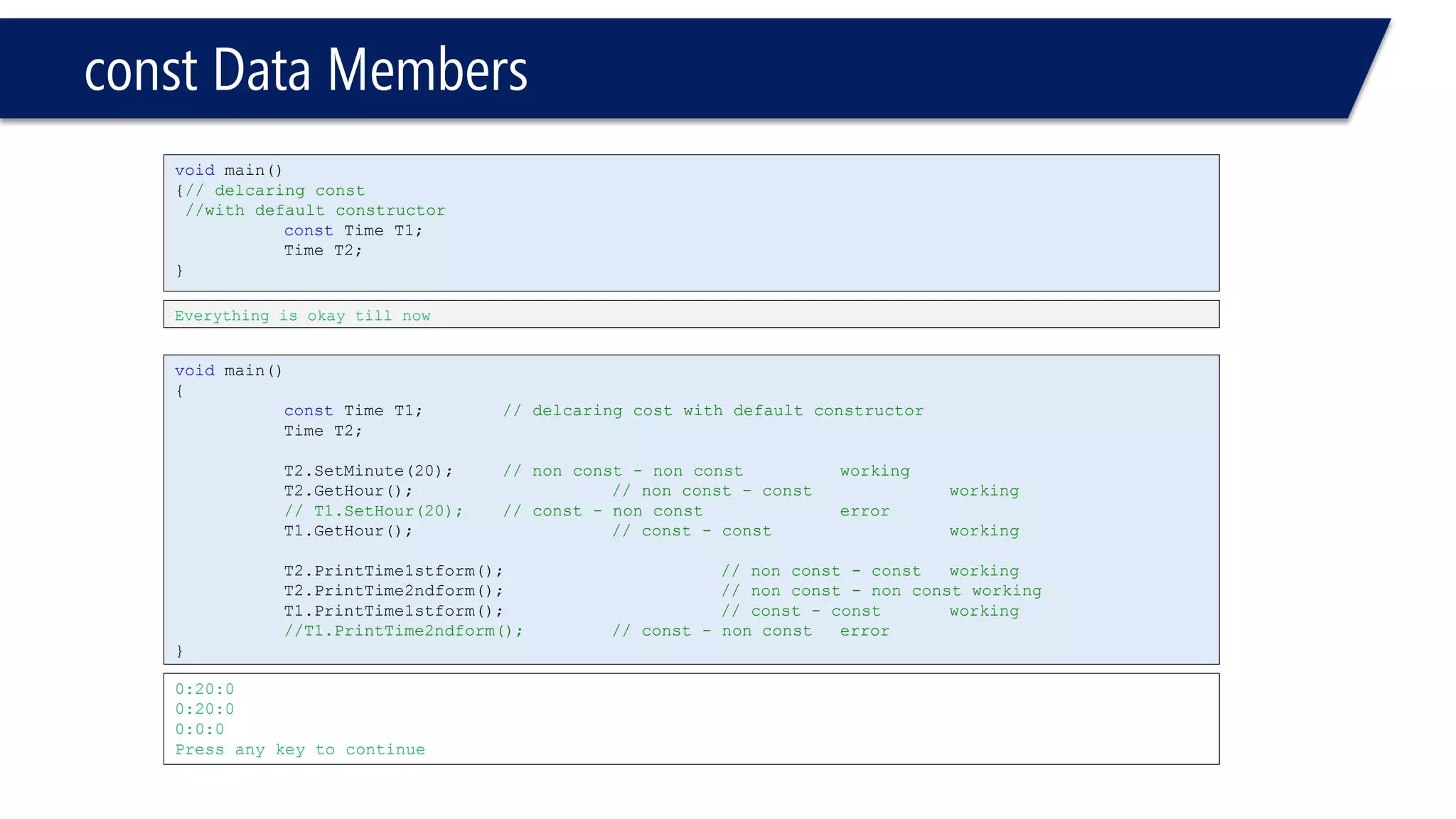
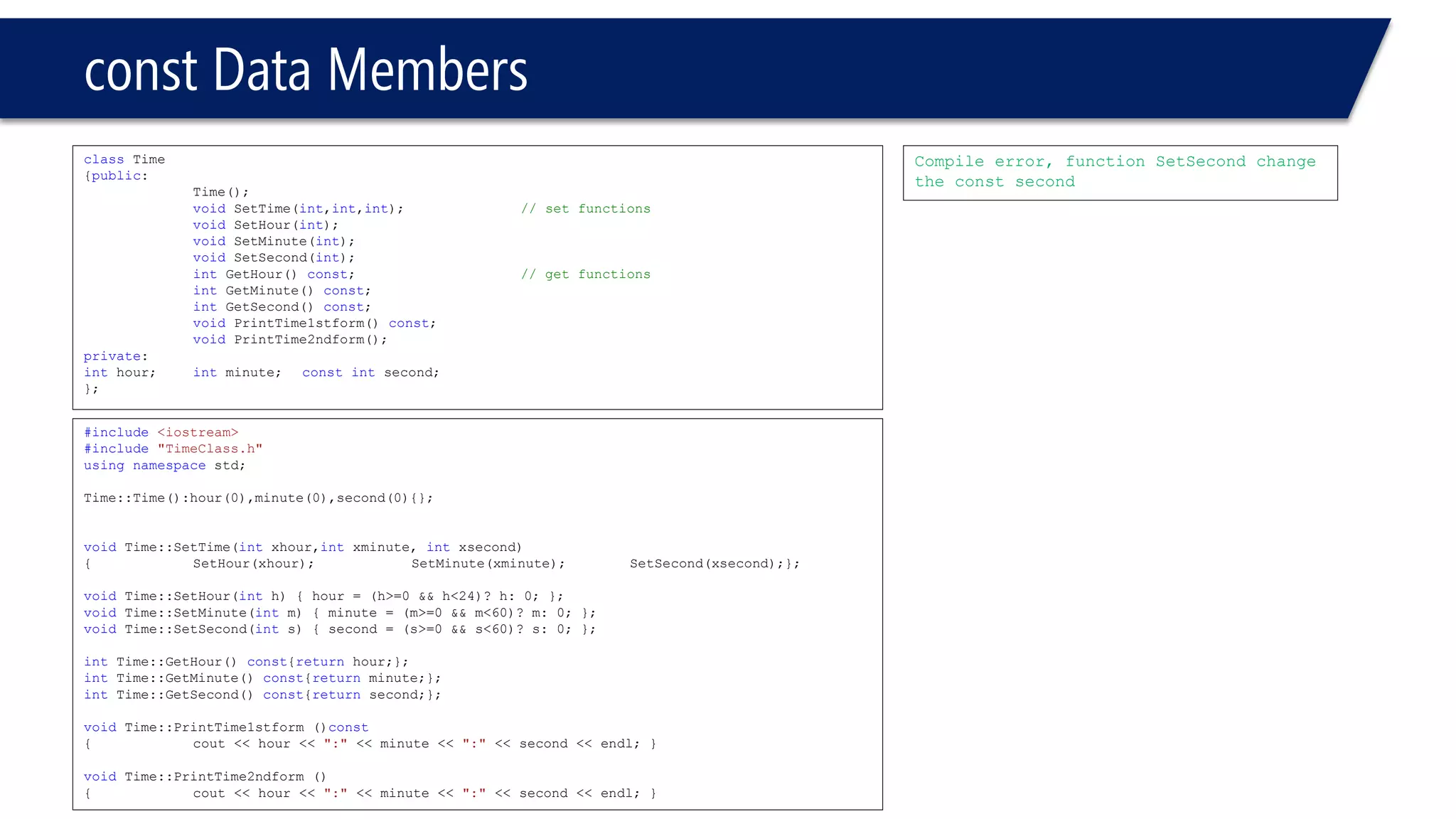
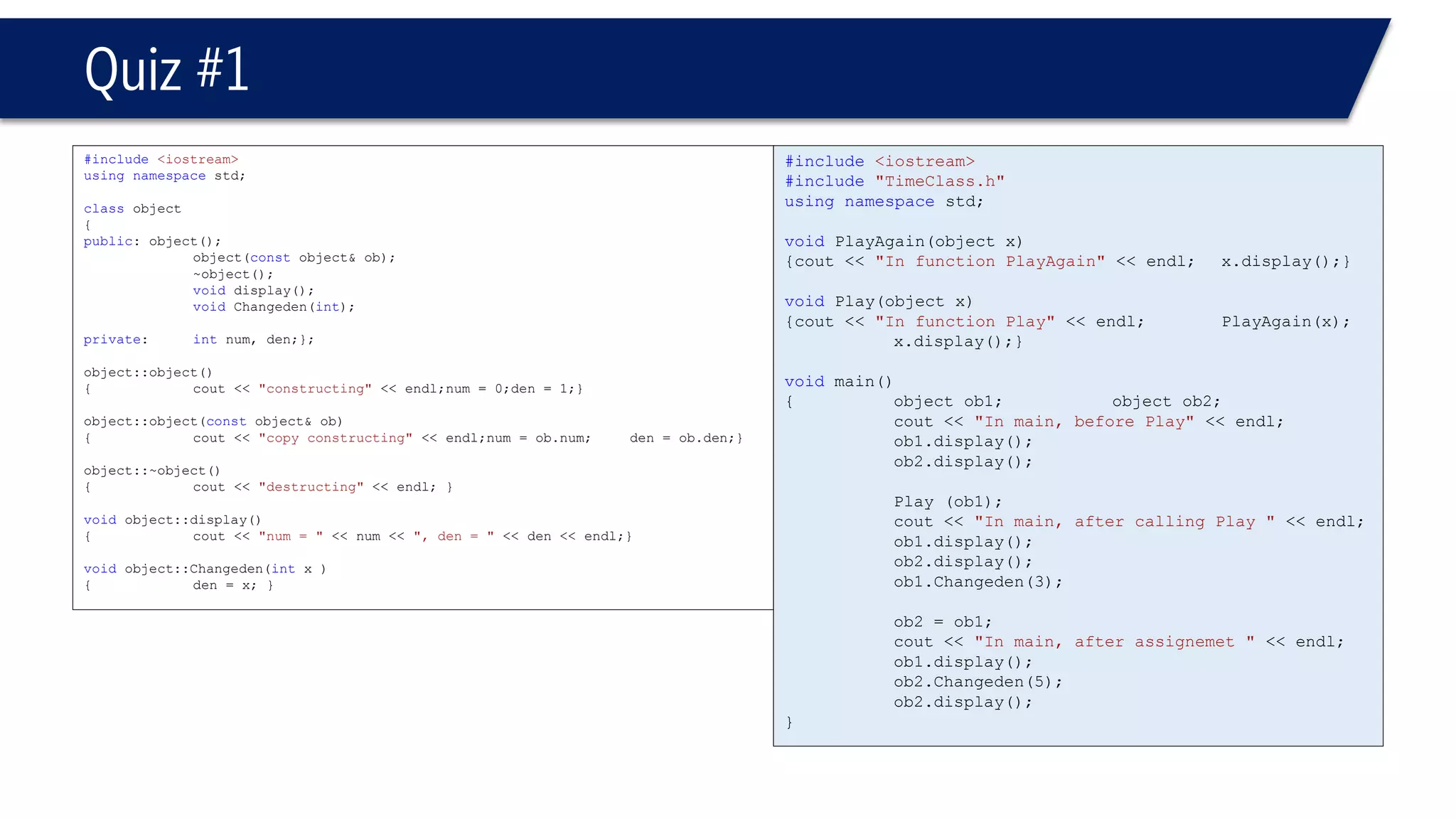
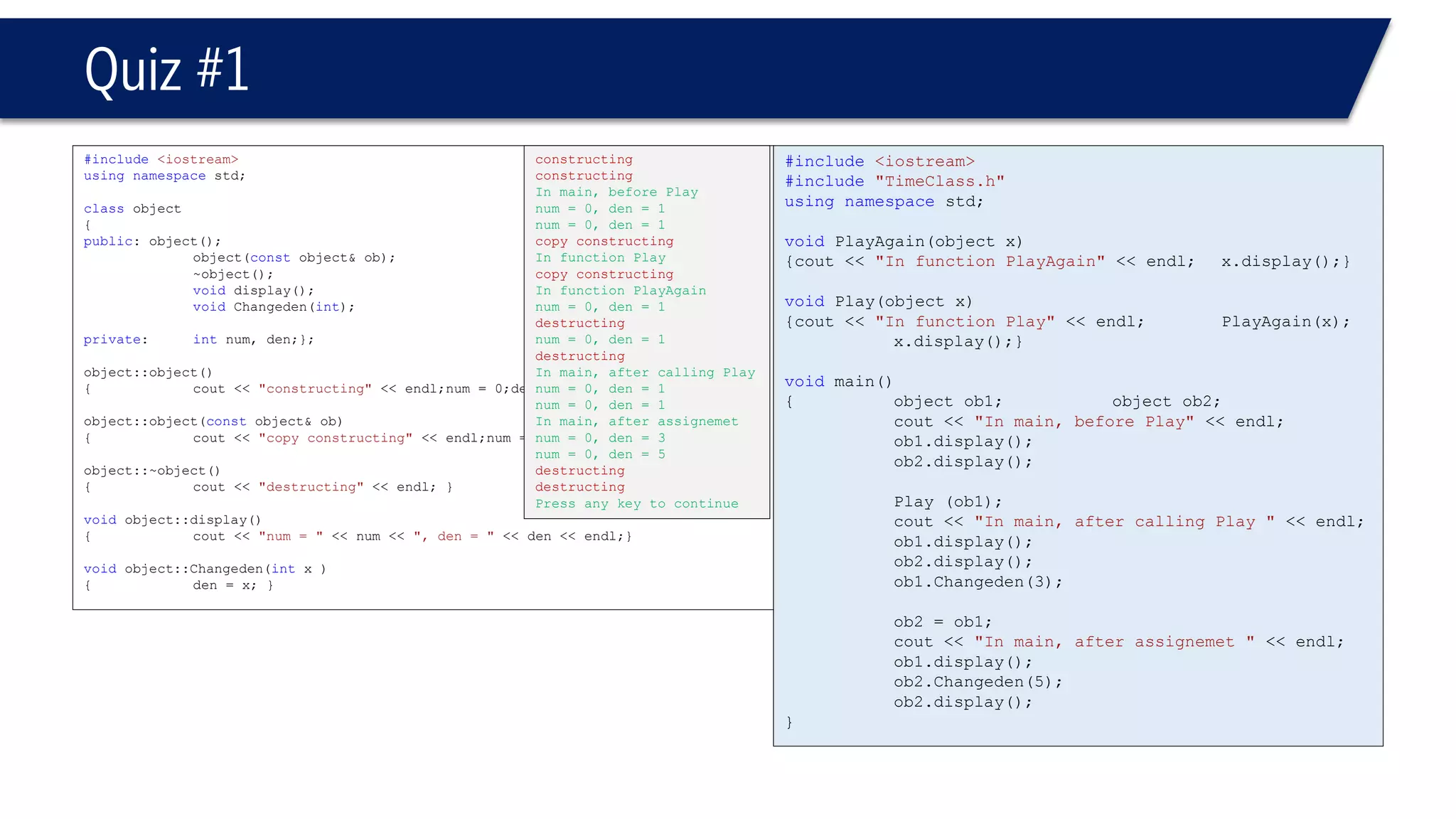
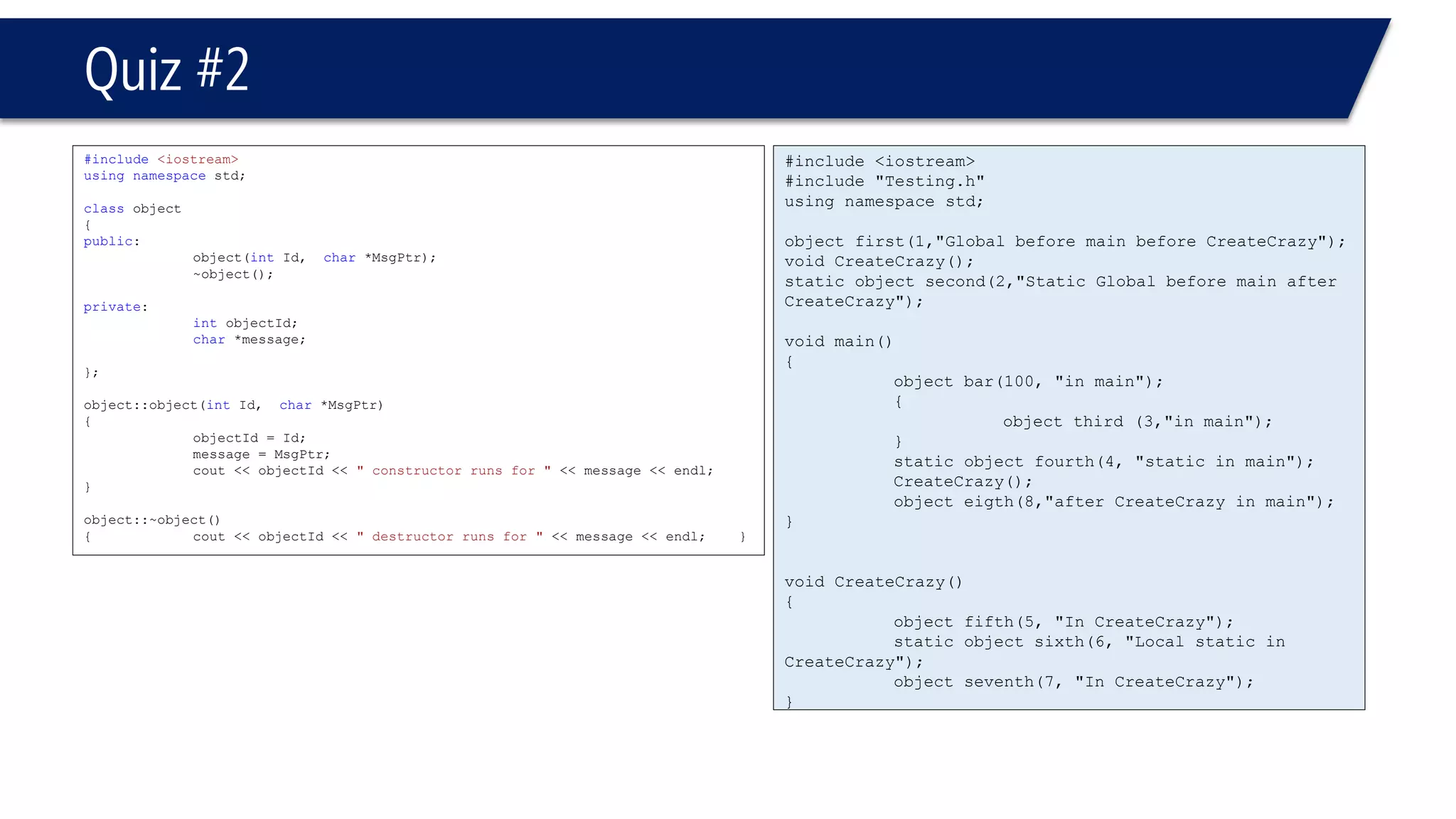
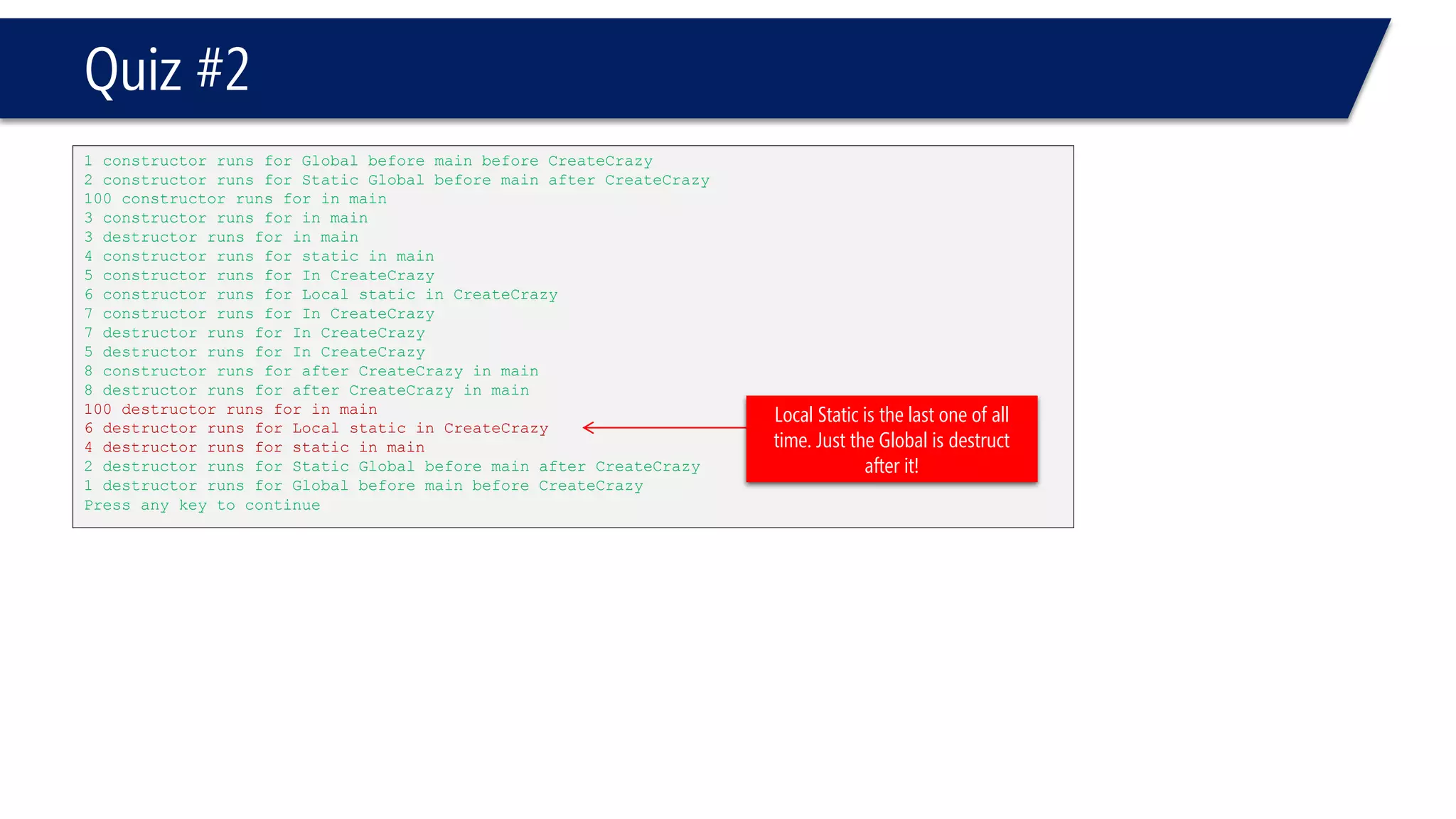
This document provides an overview of classes in C++. It begins with definitions and concepts related to classes, such as encapsulation and user-defined types. It then provides examples of declaring and defining a simple Time class with attributes like hours, minutes, seconds and methods to set, get, print and change the time. The document also discusses class members, access specifiers, constructors, pointers and references to class objects, and getter and setter methods. It concludes with brief mentions of utility functions, separating interface from implementation, and organizing classes across header and source files.