The document provides an overview of basic web development concepts including:
- Definitions of terms like the Internet, World Wide Web, URLs, web servers, browsers, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, MySQL, and more.
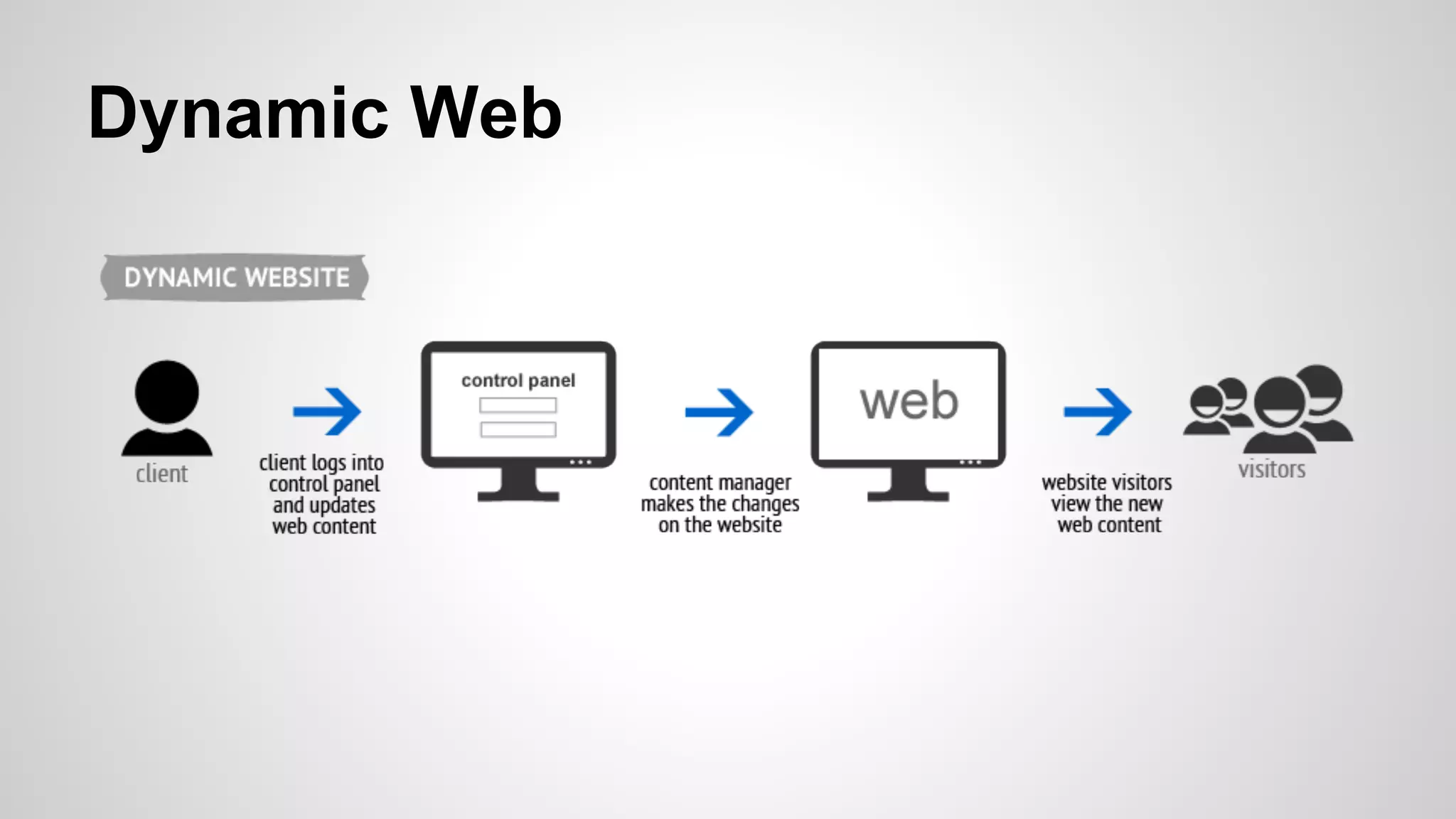
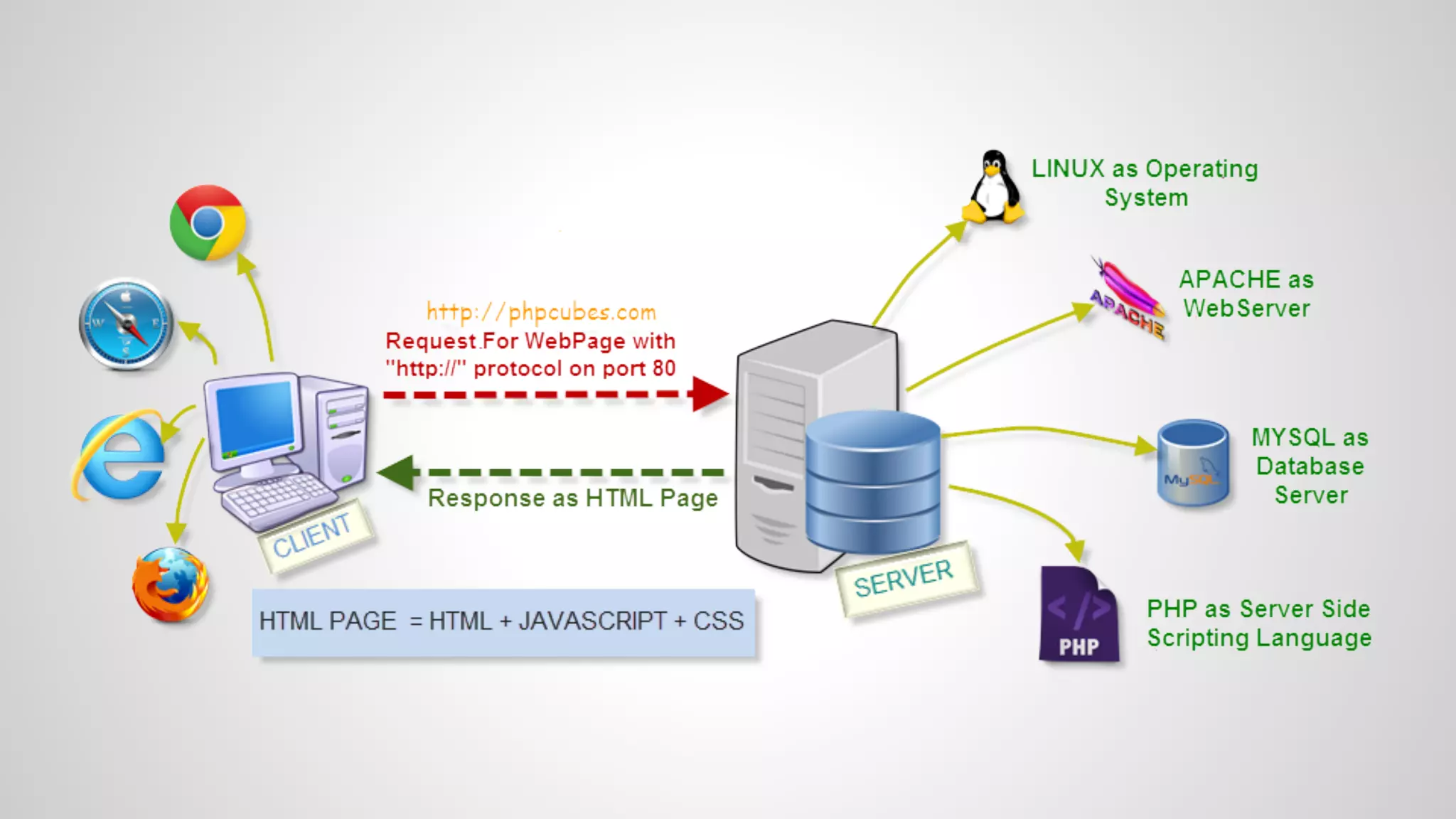
- Explanations of static and dynamic websites, client-server architecture, and how PHP and MySQL can be used to create dynamic sites.
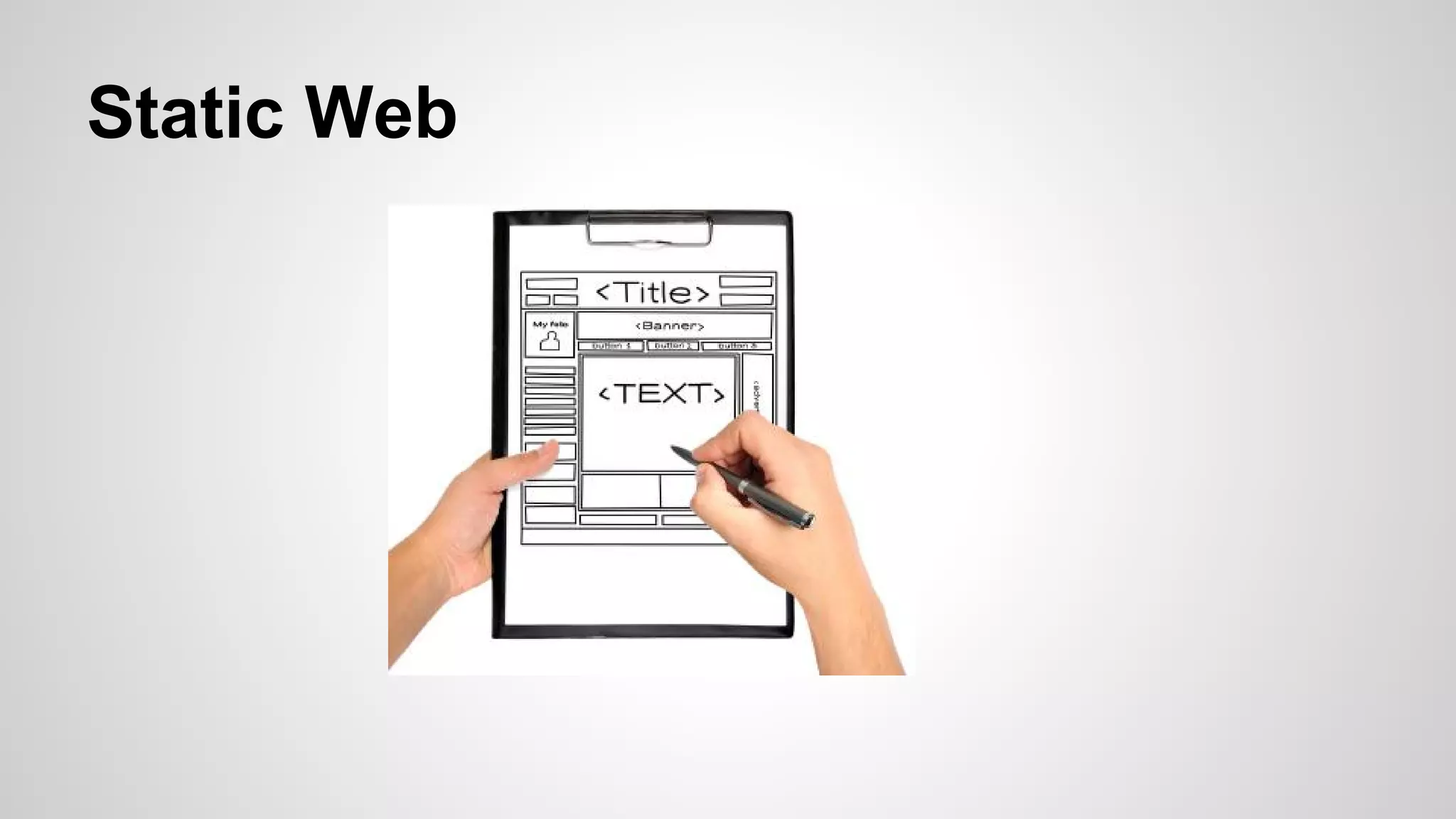
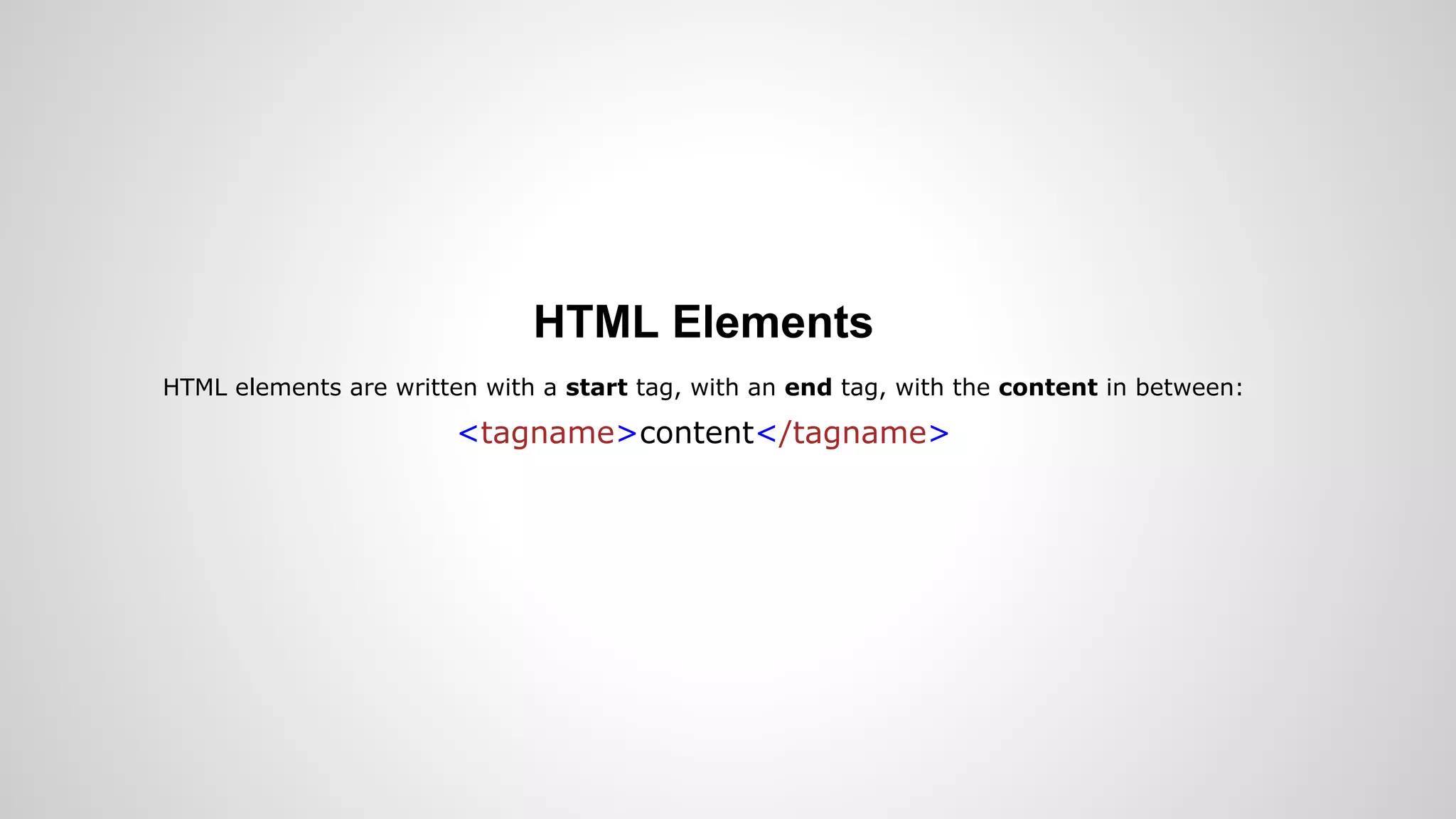
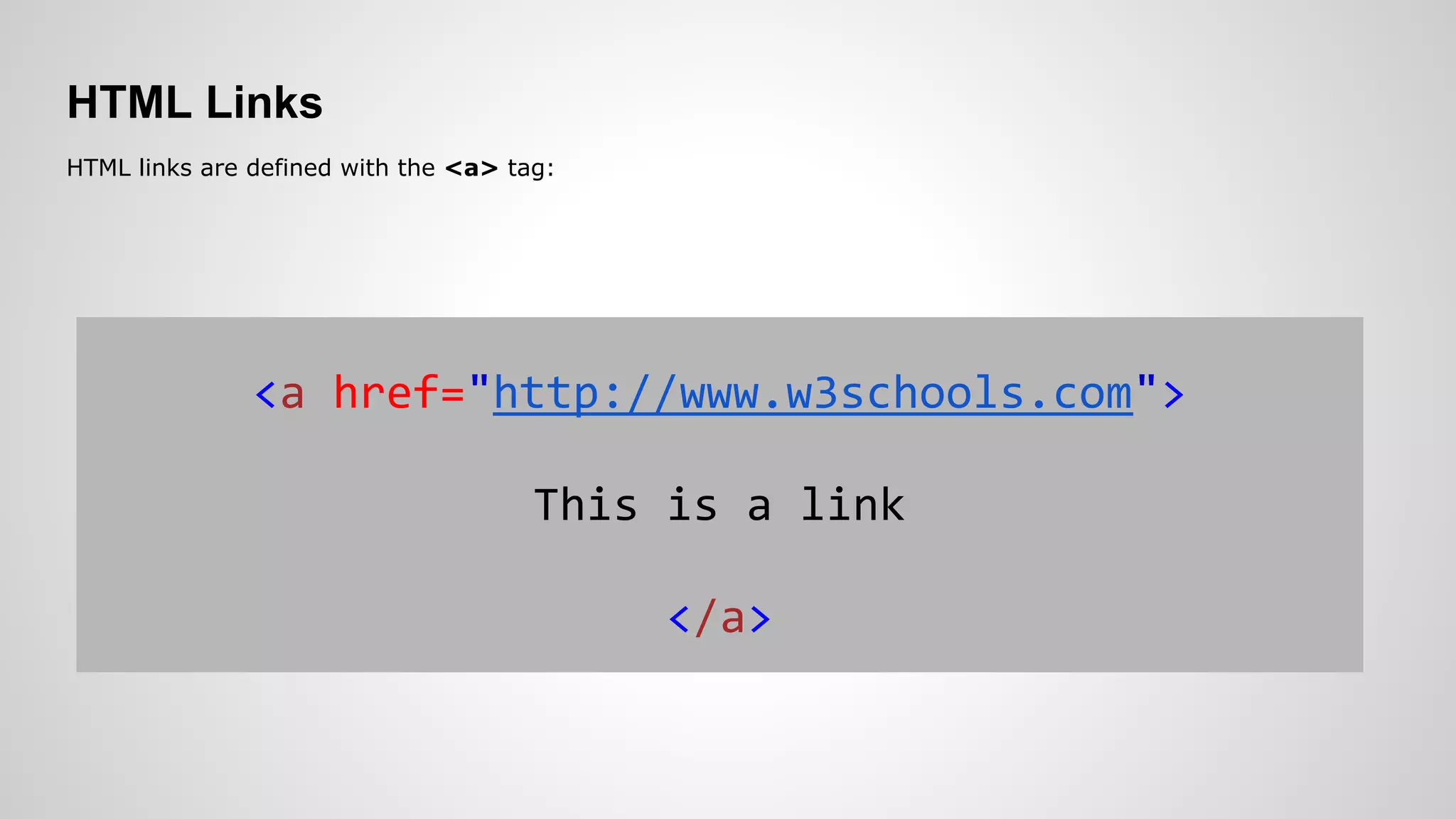
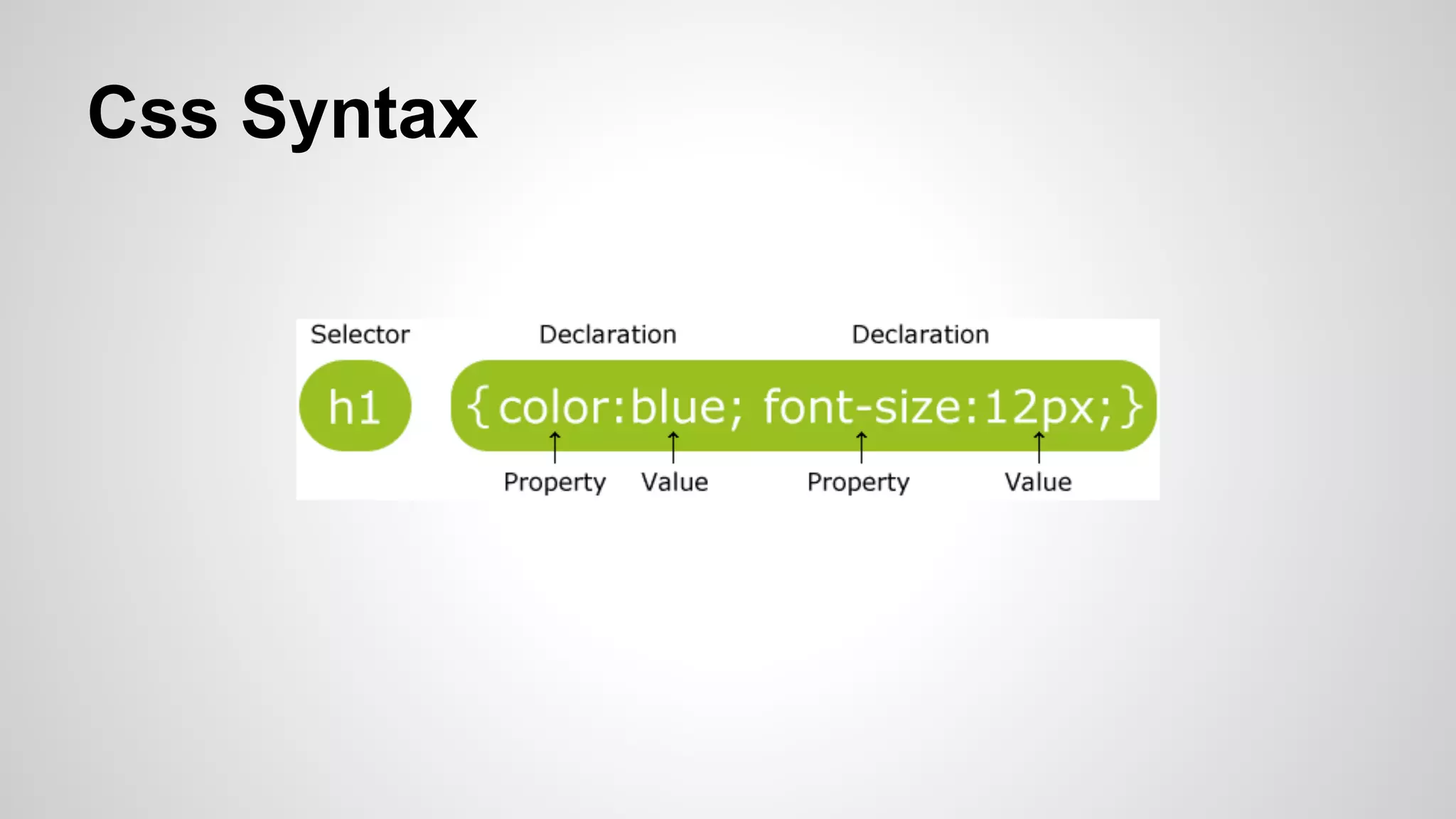
- Introductions to HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and how they are used to build static sites, along with examples of common tags and functions.
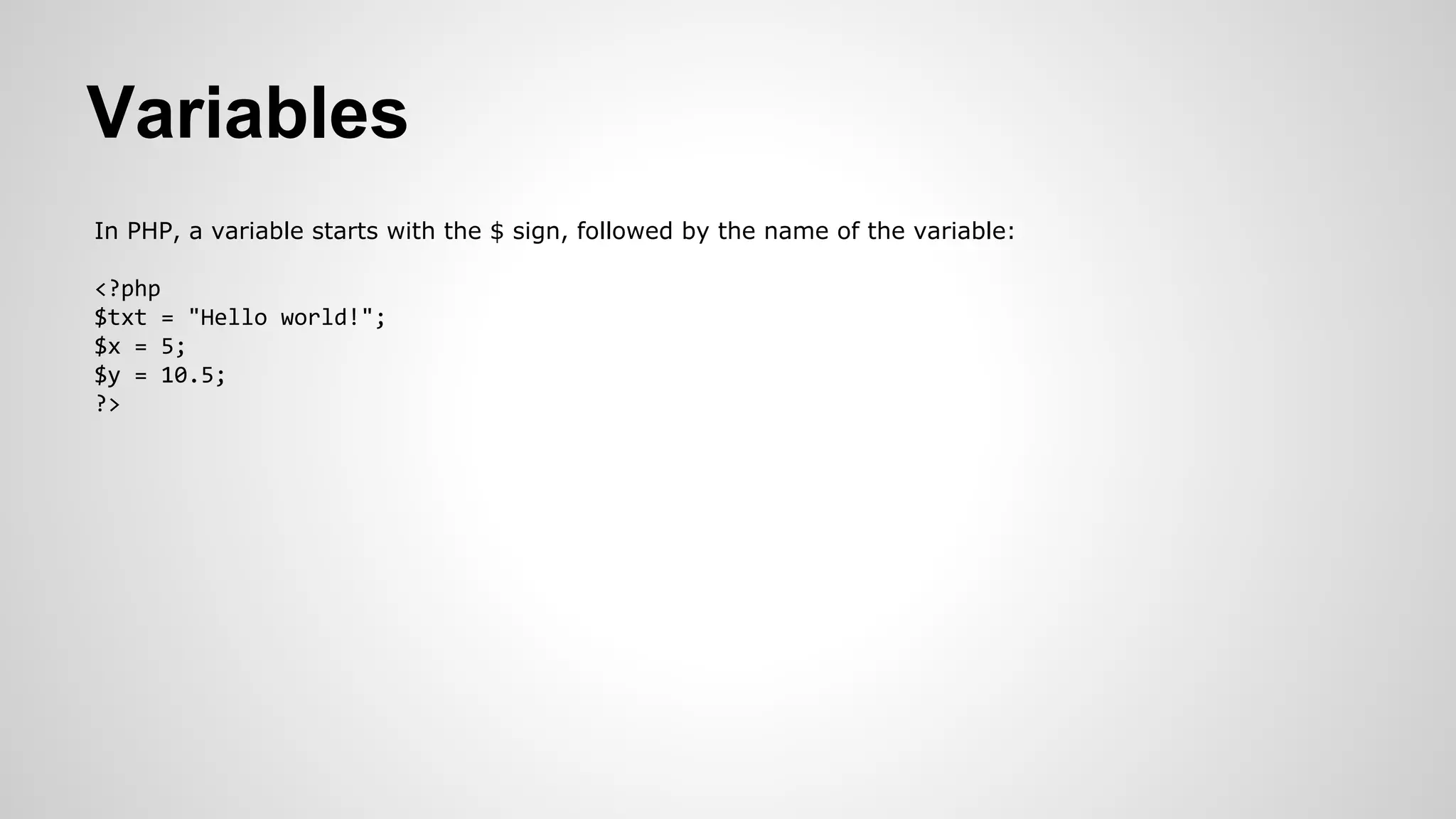
- An overview of how PHP, MySQL, and a LAMP/WAMP stack can be used to create dynamic, database-driven websites.




















































![Fetch Data
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password,
$dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn-
>connect_error);
}
$sql = "SELECT id, firstname, lastname FROM MyGuests";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
// output data of each row
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "id: " . $row["id"]. " - Name: " . $row
["firstname"]. " " . $row["lastname"]. "<br>";
}
} else {
echo "0 results";
}
$conn->close();
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webdevloppement-151011000250-lva1-app6891/75/Les-Basiques-Web-Developpement-HTML5-CSS3-JS-et-PHP-67-2048.jpg)




