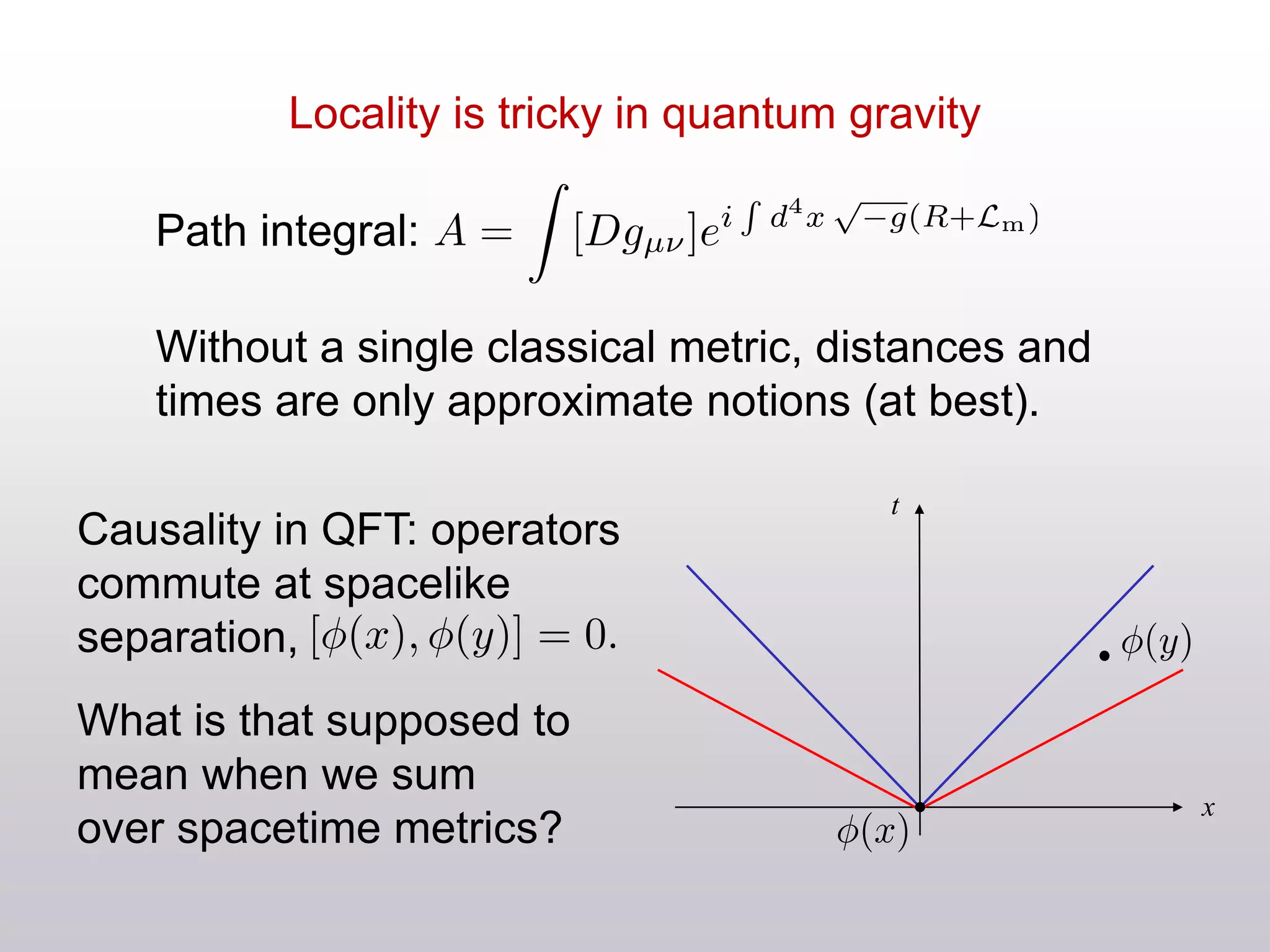
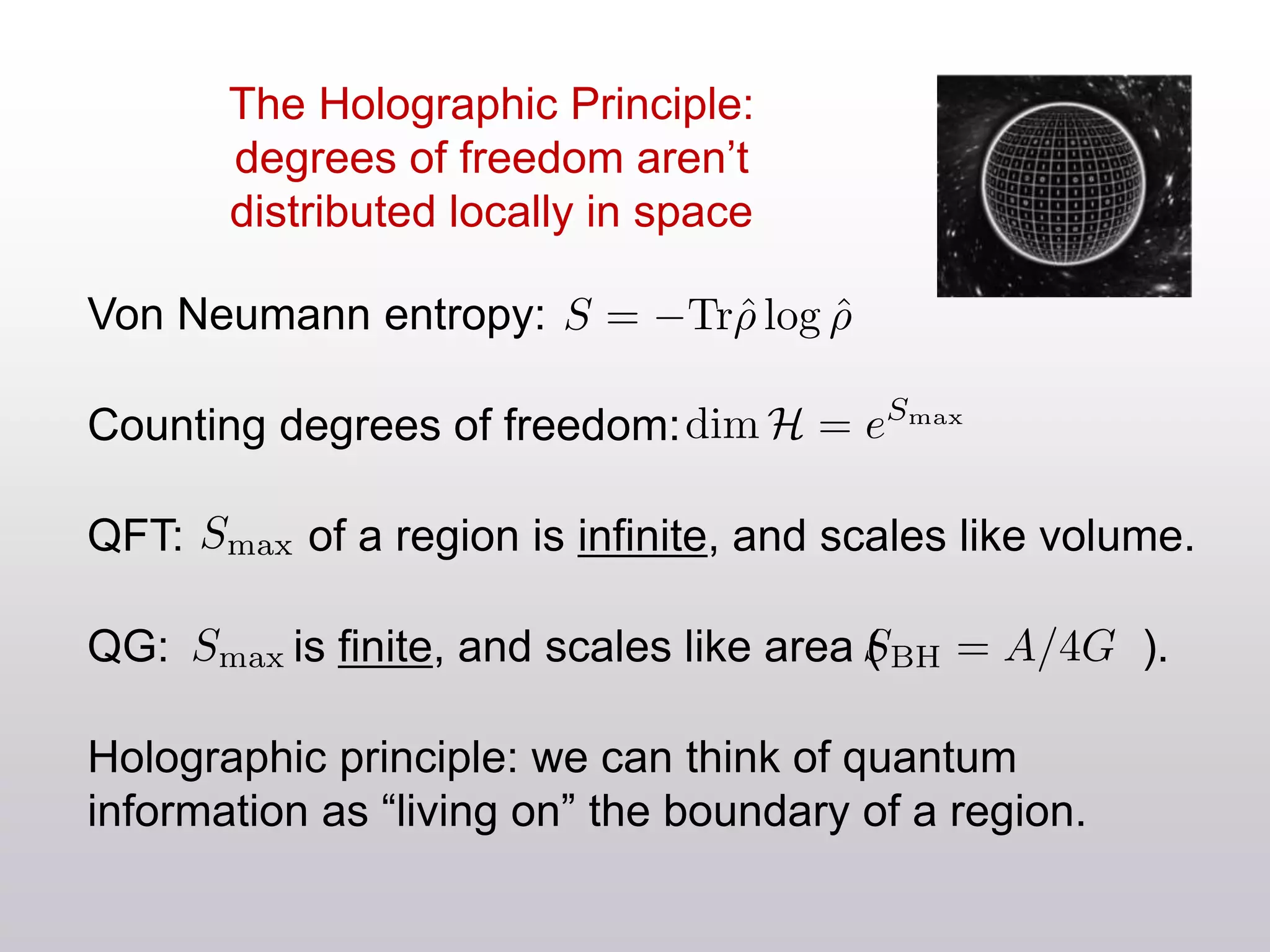
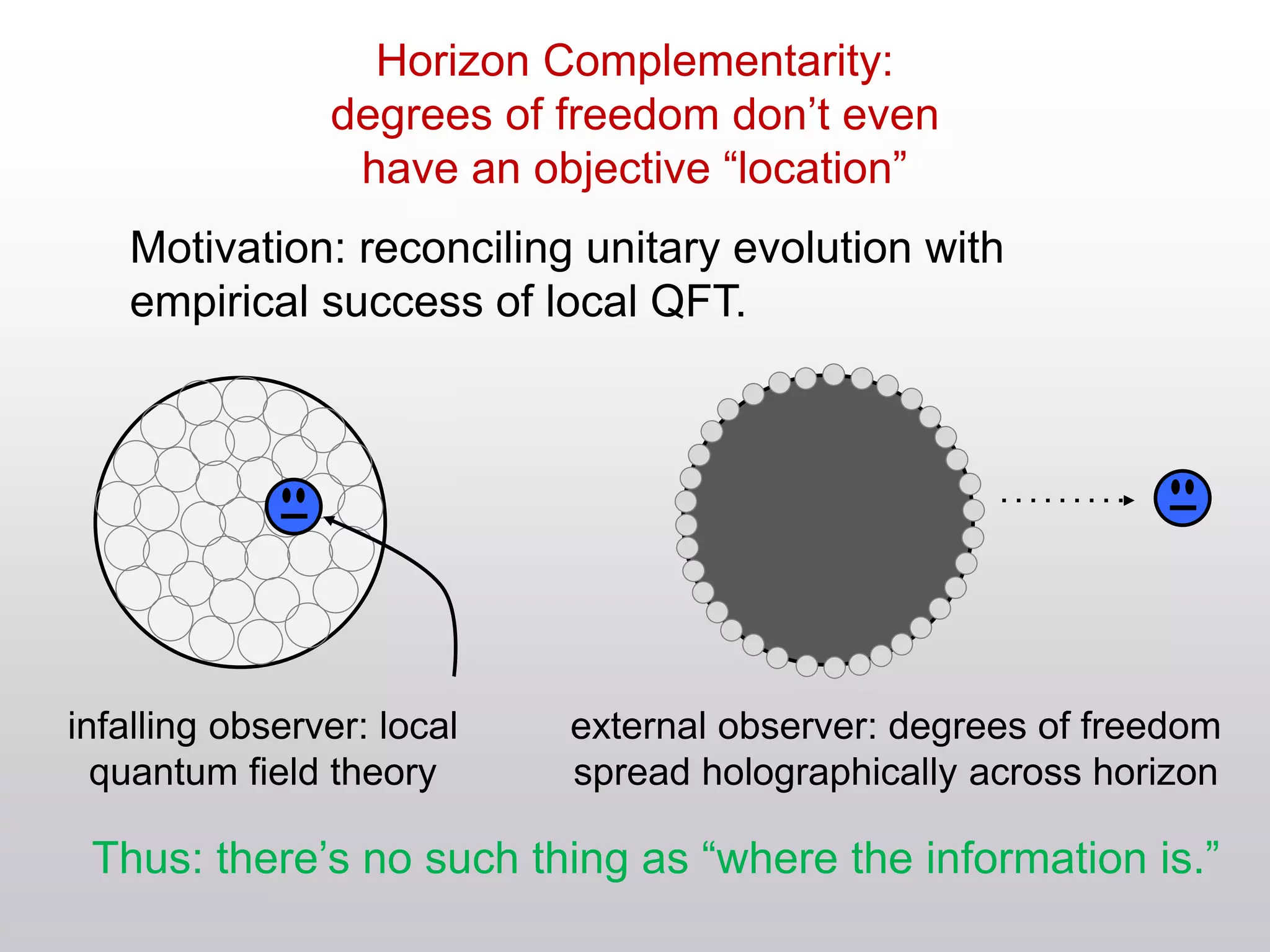
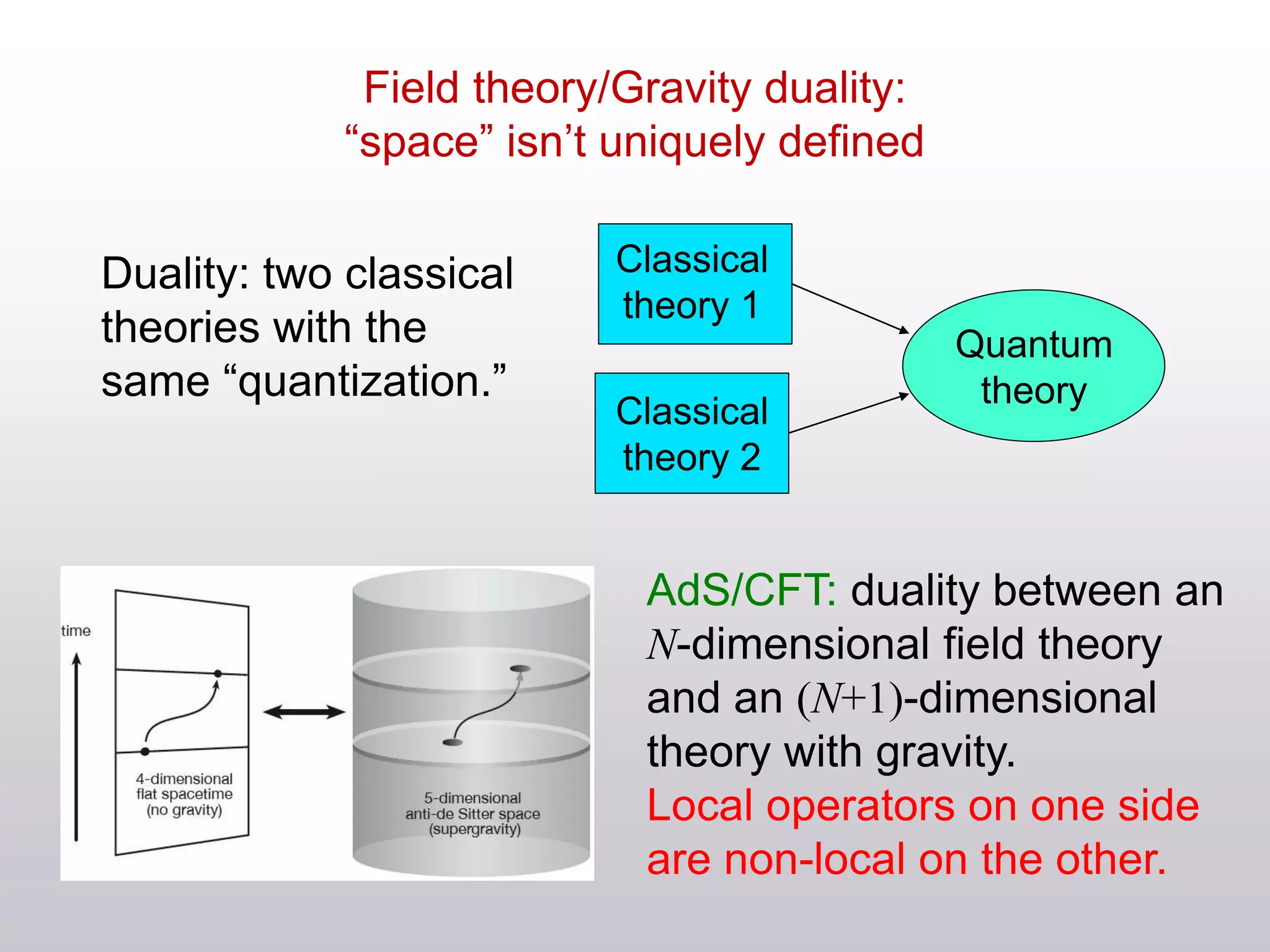
The document discusses the complexities of locality and spacetime in the context of quantum gravity and quantum theory. Key concepts include the holographic principle, which suggests that quantum information is not confined to a specific location but rather distributed across boundaries, and the dualities between classical theories in quantum field theory and gravity. It emphasizes the need to rethink traditional notions of spacetime while exploring ideas like wormholes and horizon complementarity.

![Senses of Locality
Measurement locality: measurement outcomes
are independent of events outside the light cone.
Ontological locality –
Dynamical locality:
[no]
[unclear]
[probably not]
[probably not
even that]
Strong form: local beables.
Weak form:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/harvard-quantum-lessons-210221220341/75/Letting-Go-of-Spacetime-2-2048.jpg)
![Wormholes?
The black-hole information
puzzle has led to a resurgence
of interest in wormholes, in
two different contexts:
• Real but microscopic wormholes relating entangled
particles inside & outside the BH (ER=EPR).
• Imaginary “Euclidean” wormholes used in the
gravitational path integral to calculate properties
of Hawking radiation.
A modern version of “quantum foam.”
[Quanta]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/harvard-quantum-lessons-210221220341/75/Letting-Go-of-Spacetime-7-2048.jpg)
