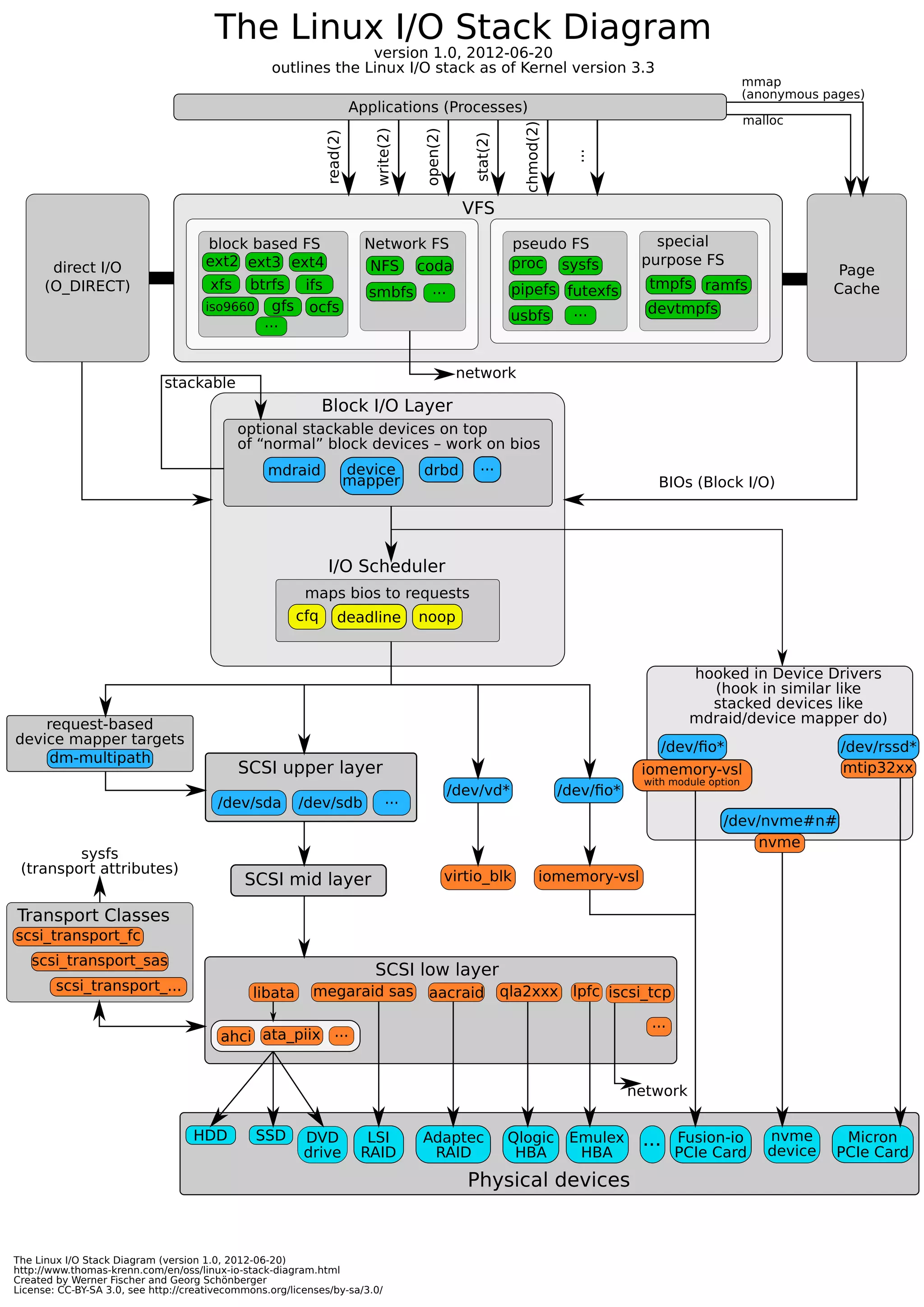
This document outlines the Linux I/O stack as of kernel version 3.3. It shows the path that I/O requests take from applications through the various layers including direct I/O, the page cache, block I/O layer, I/O scheduler, storage devices, filesystems, and network filesystems. Optional components are shown that can be stacked on top of the basic I/O stack like LVM, device mapper targets, multipath, and network transports.