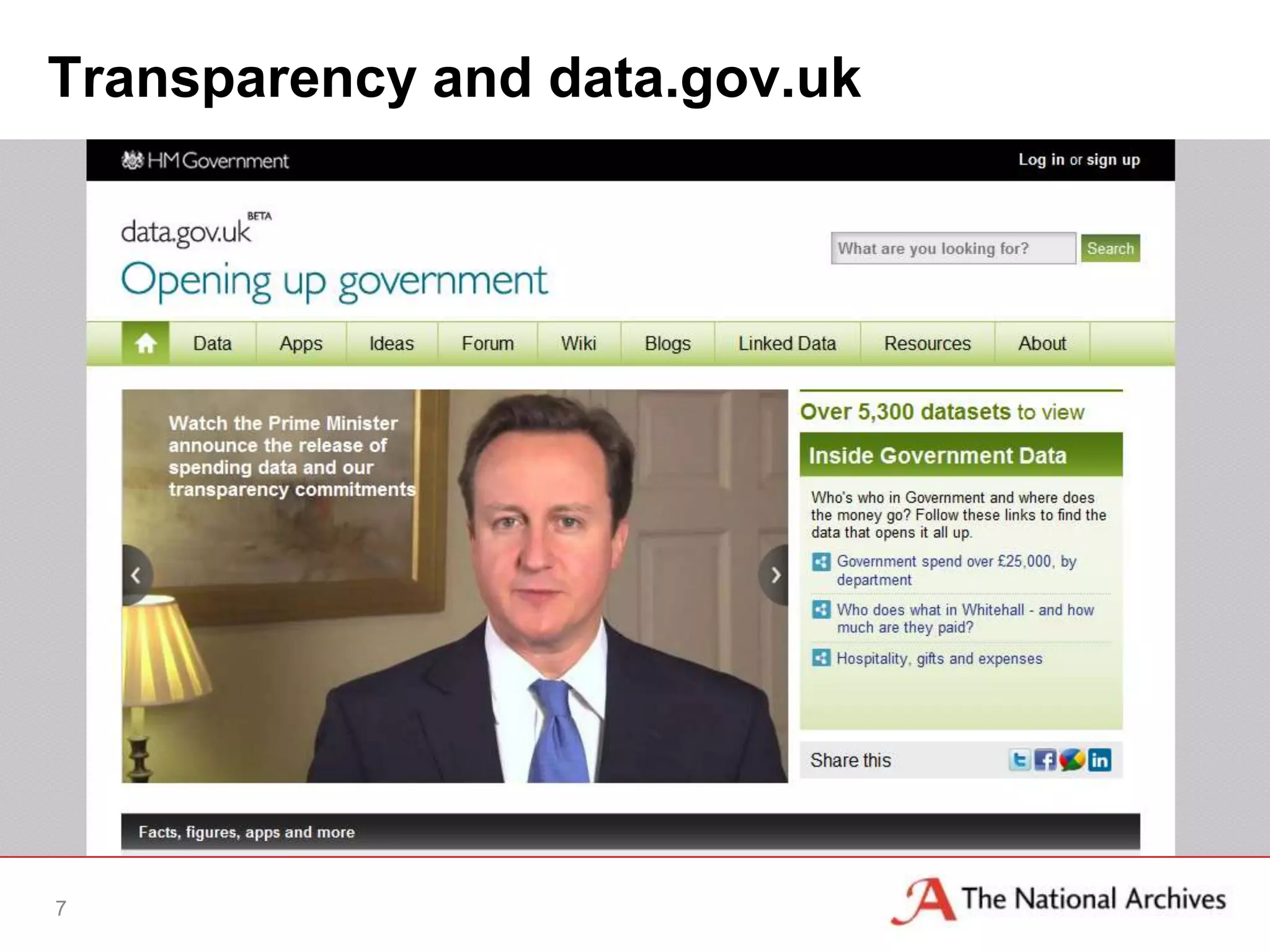
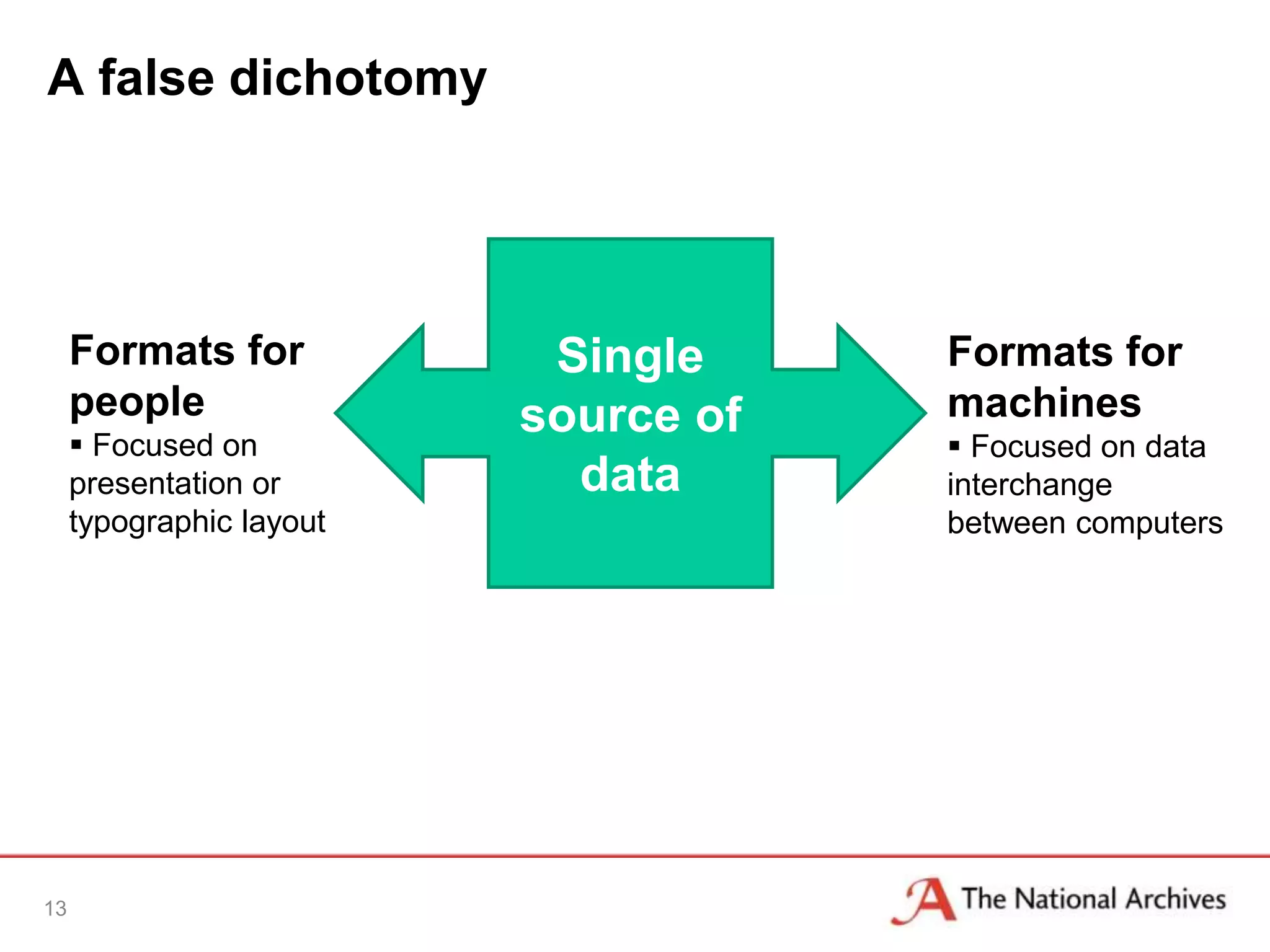
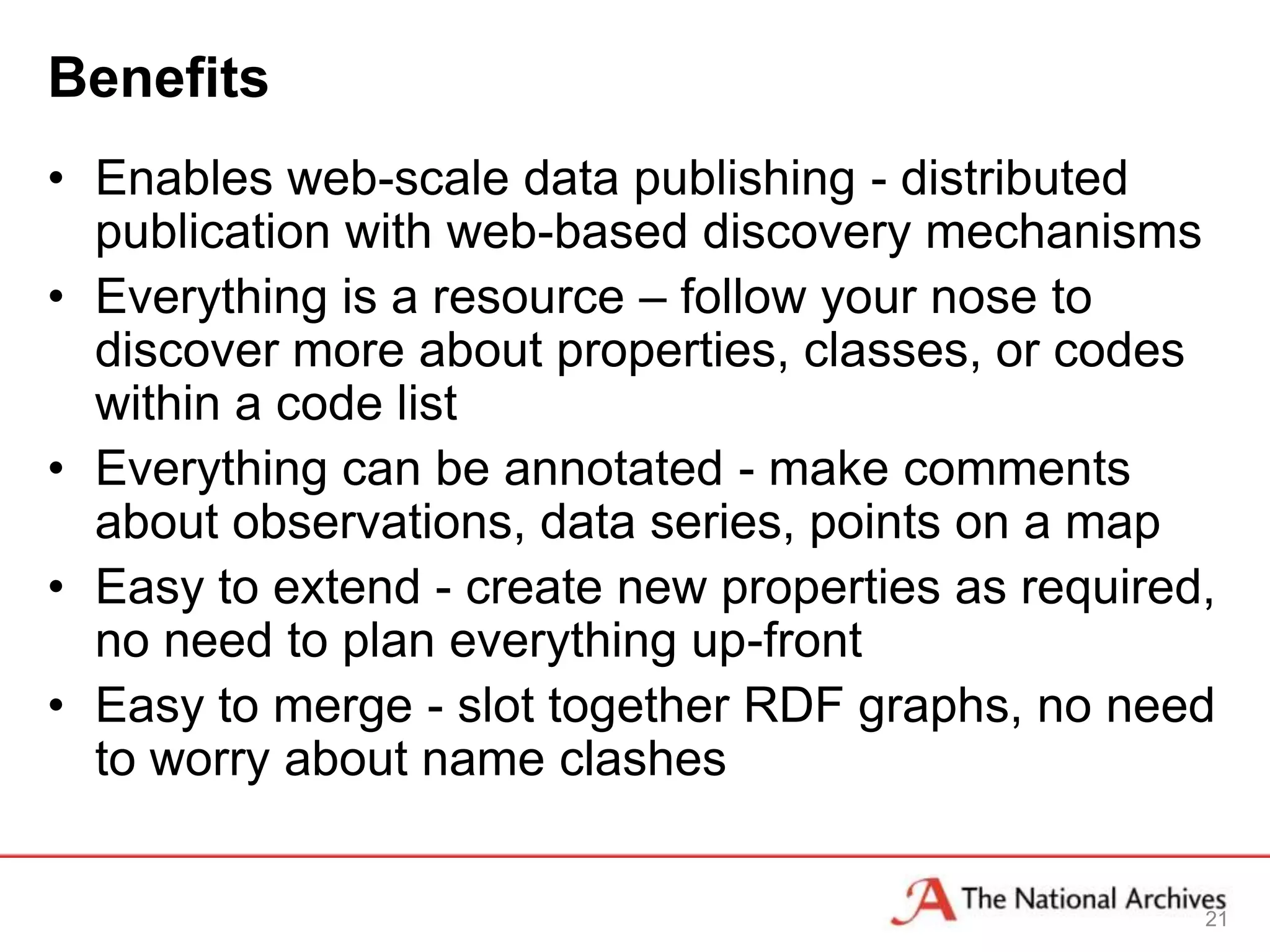
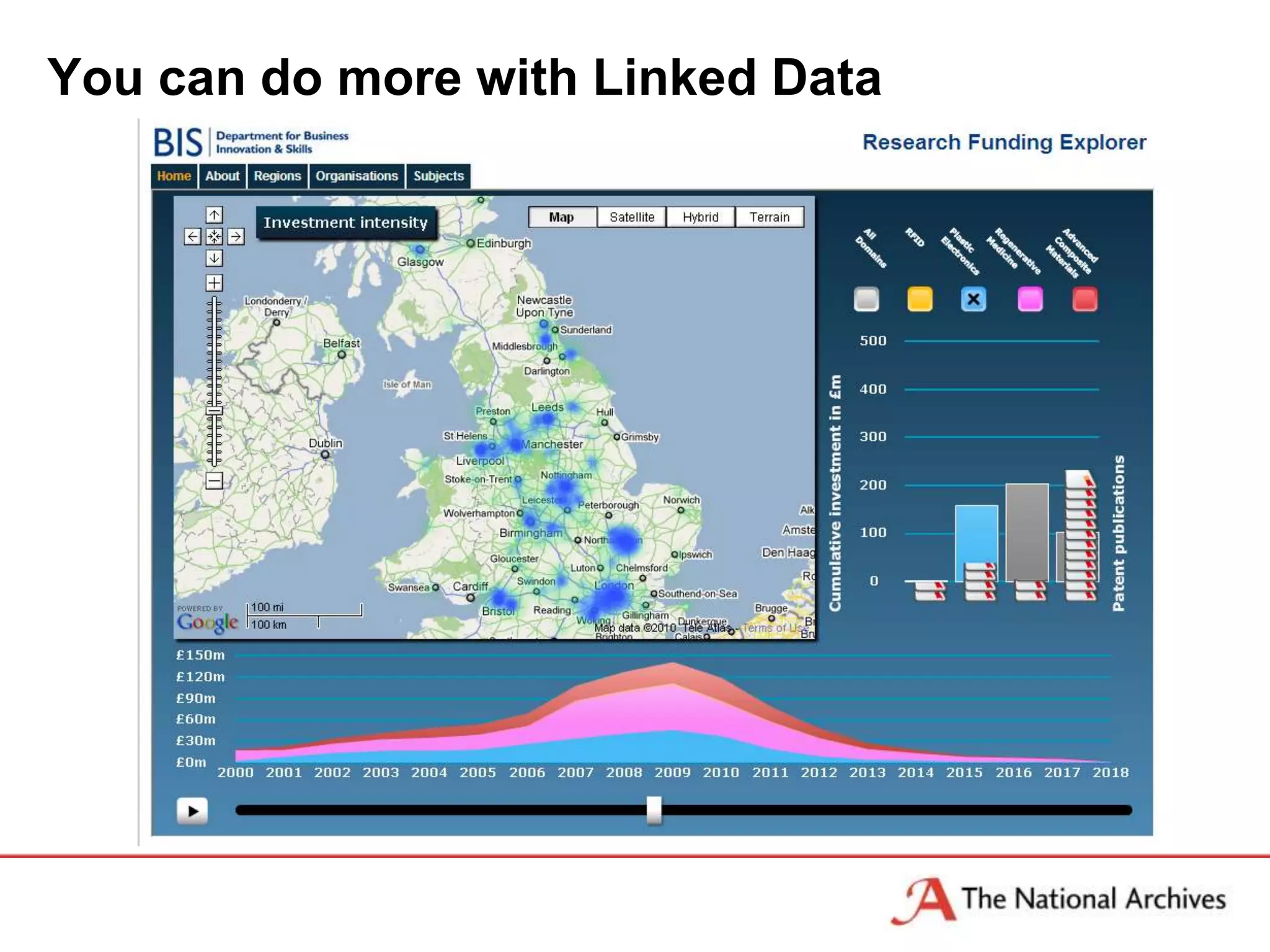
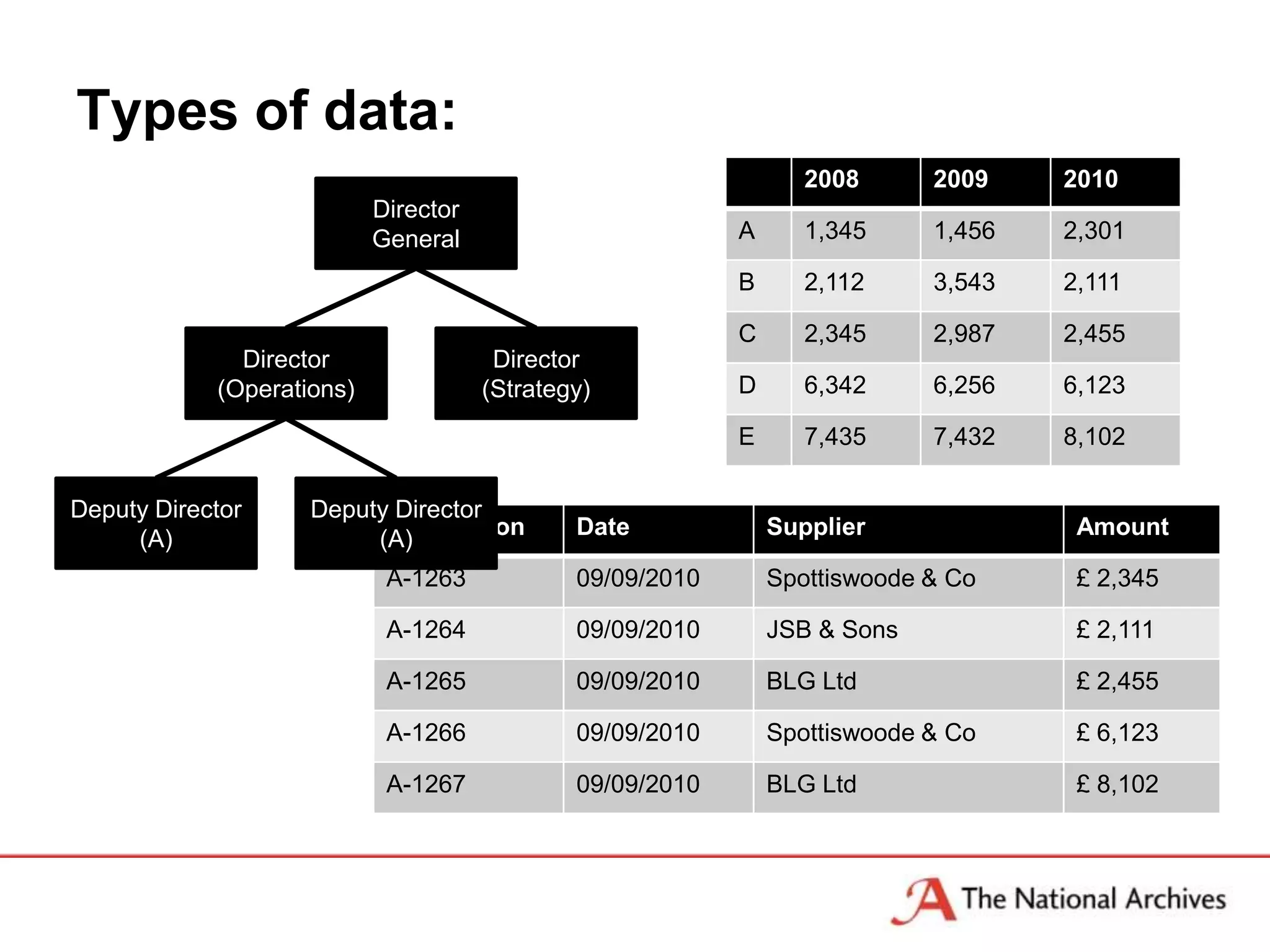
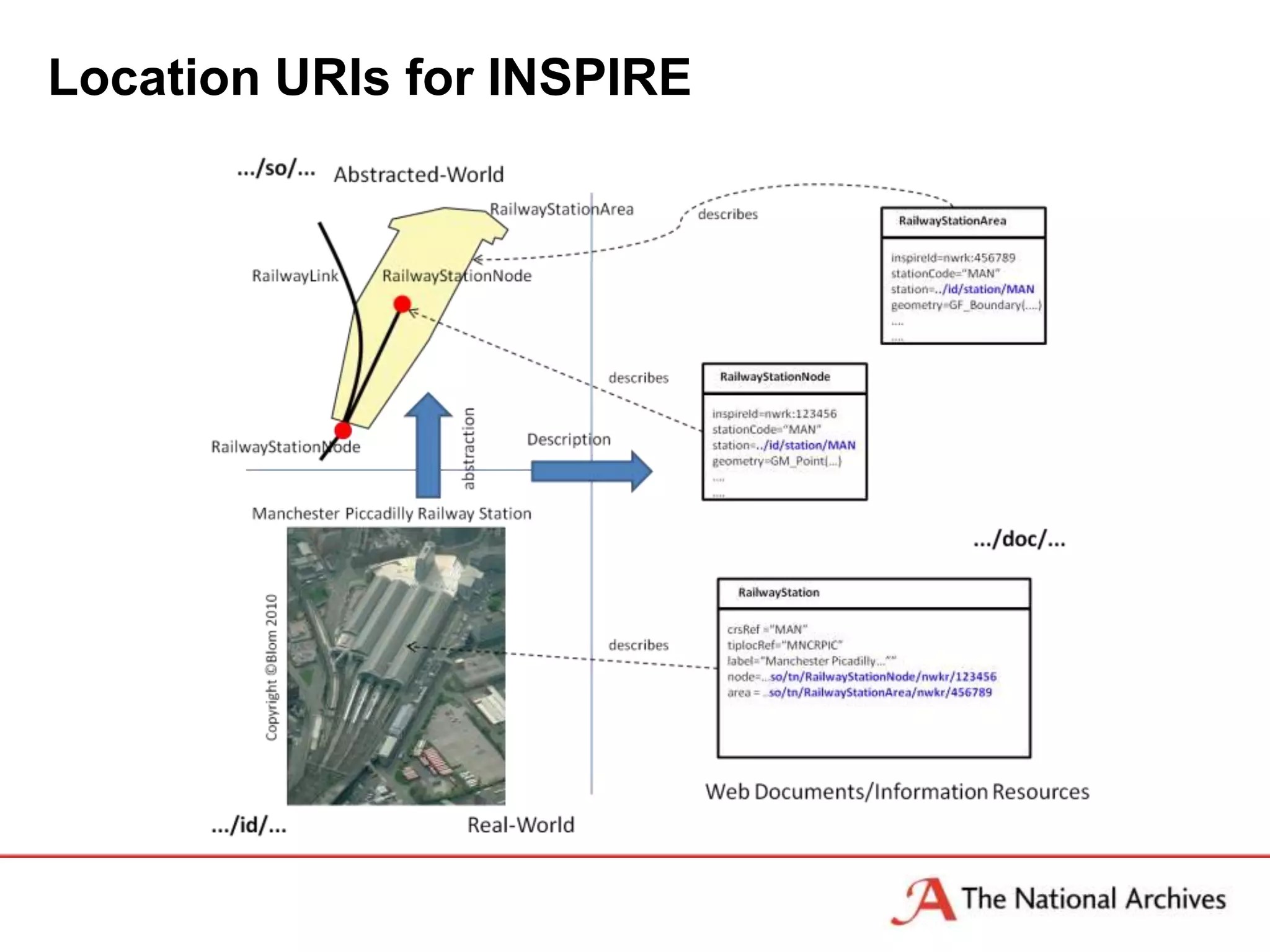
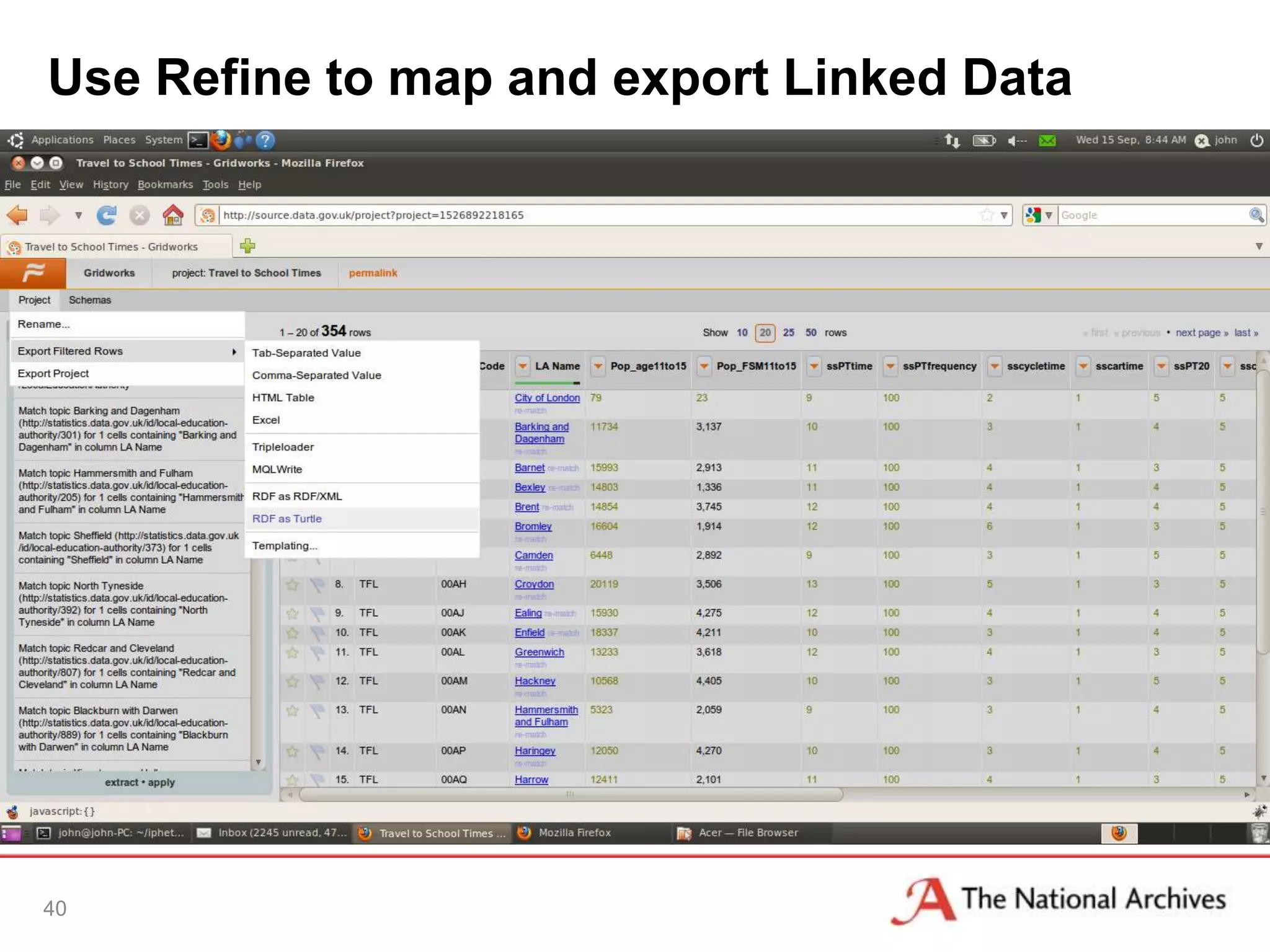
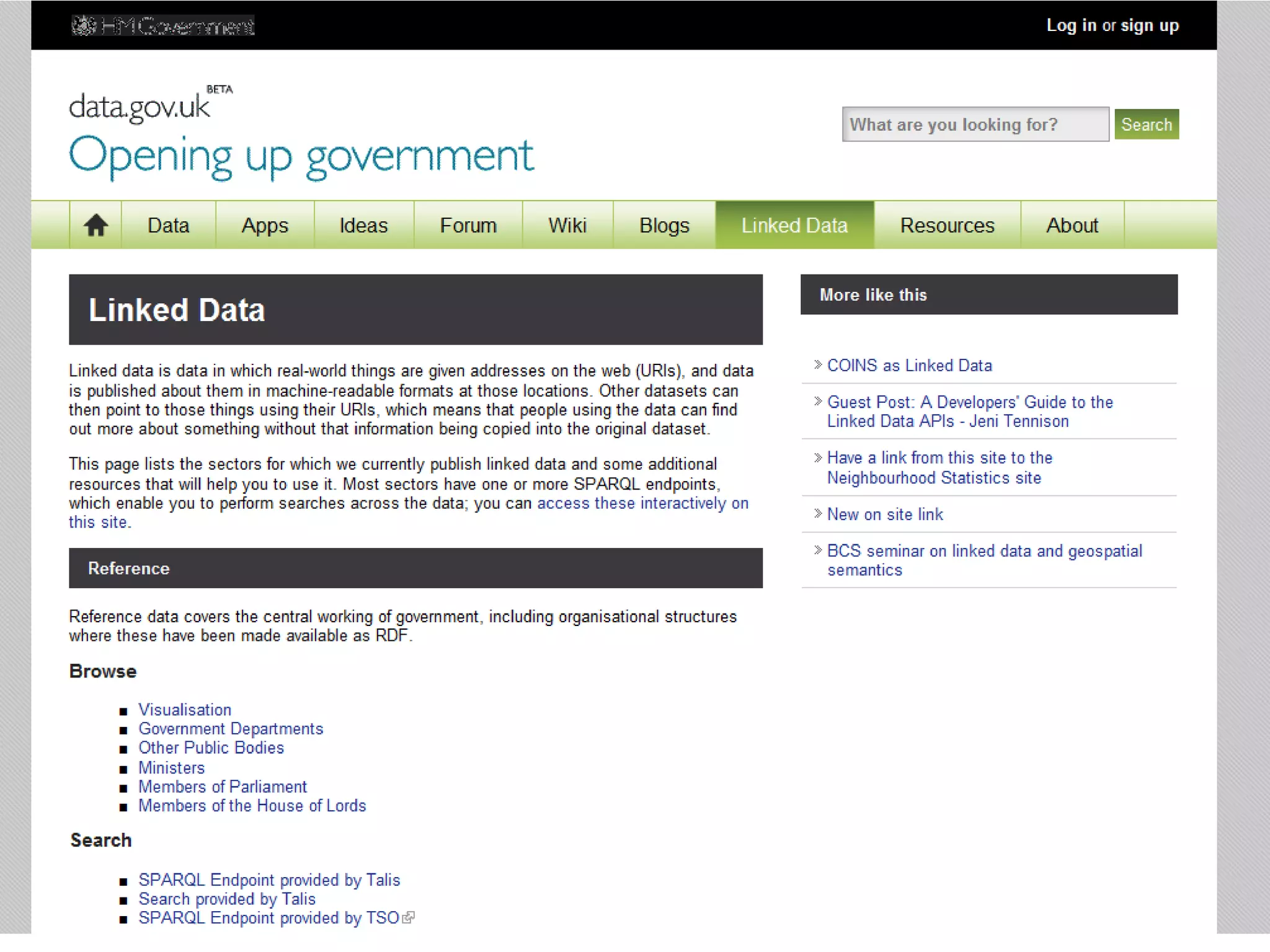
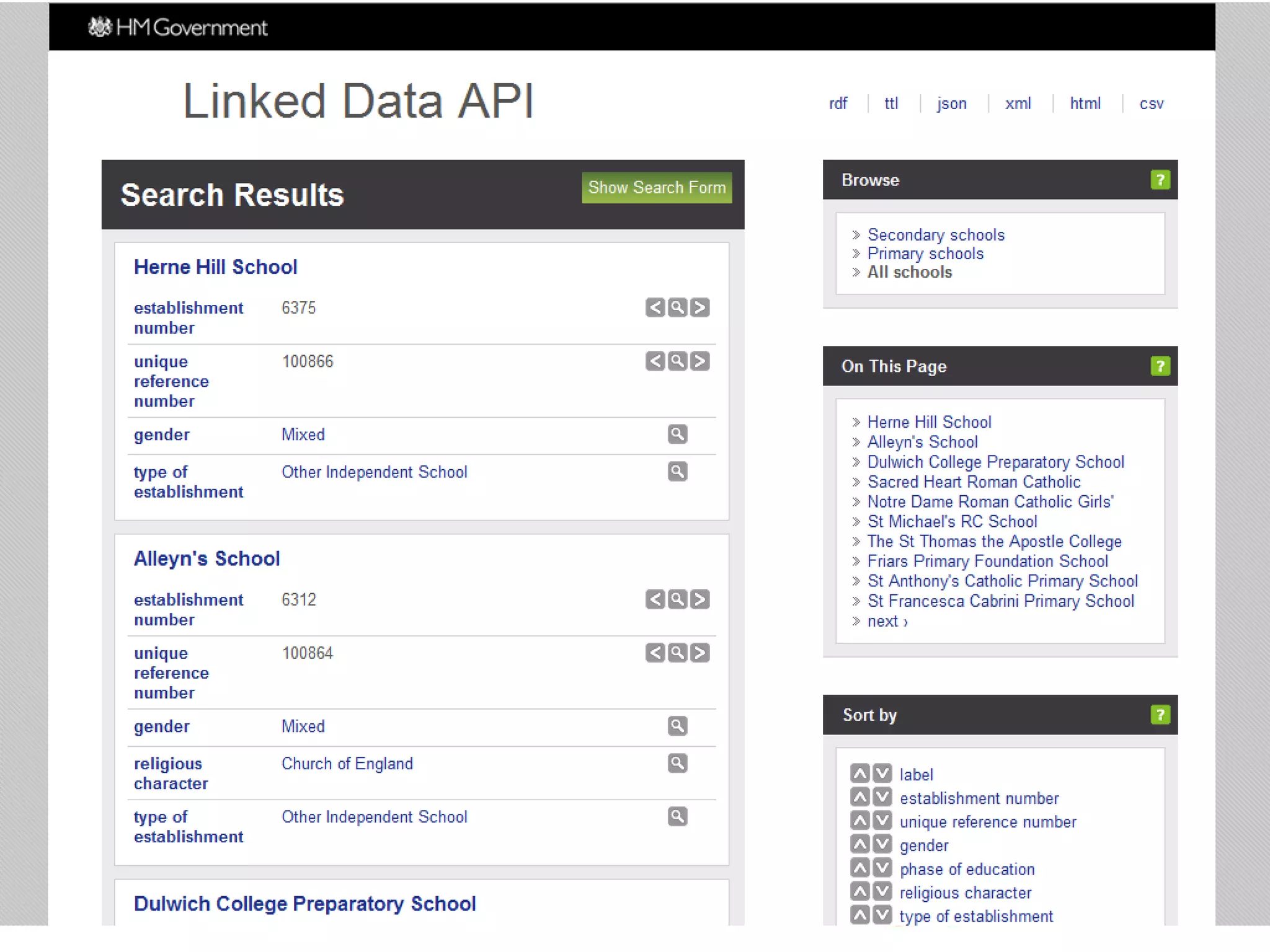
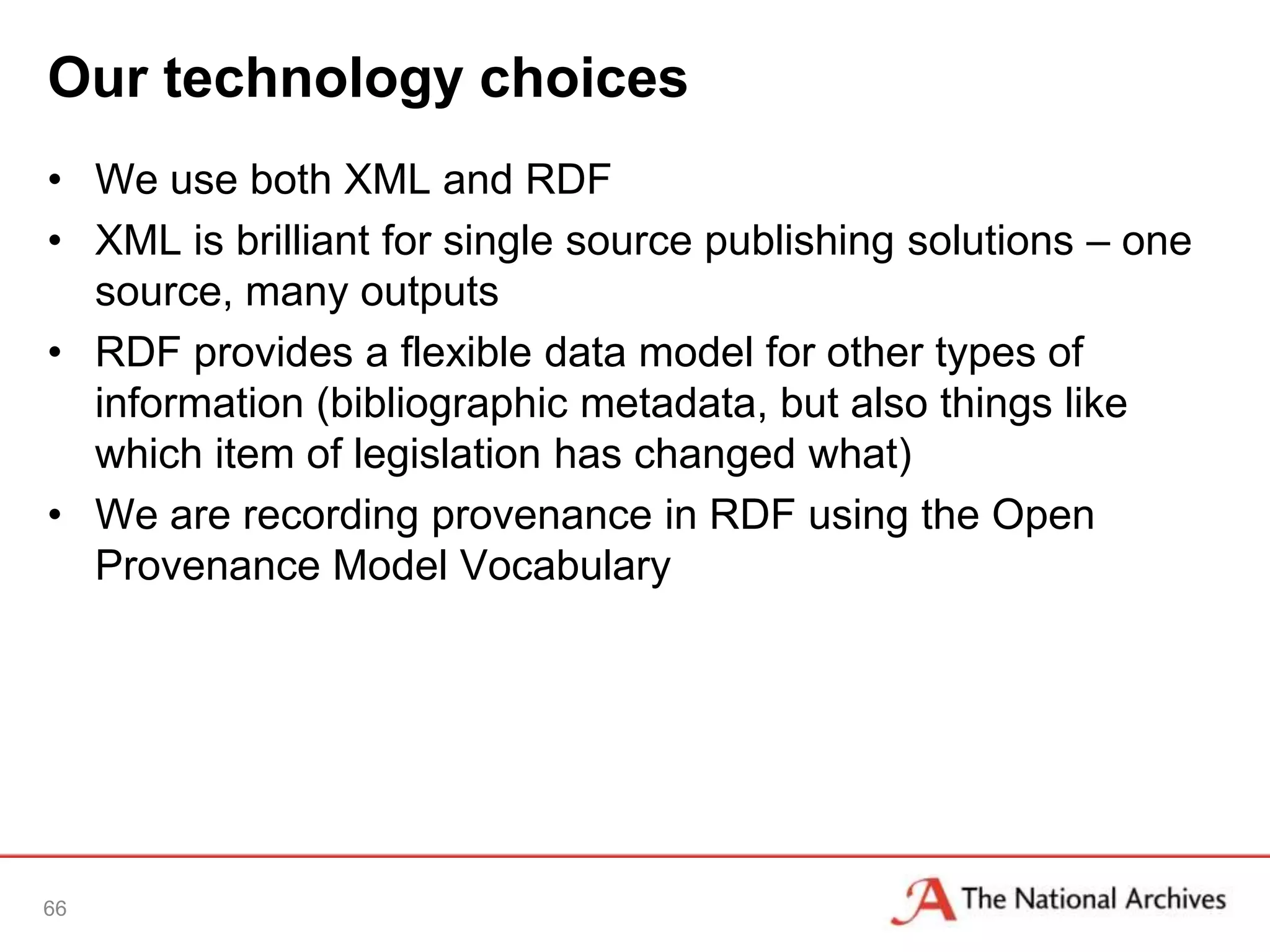
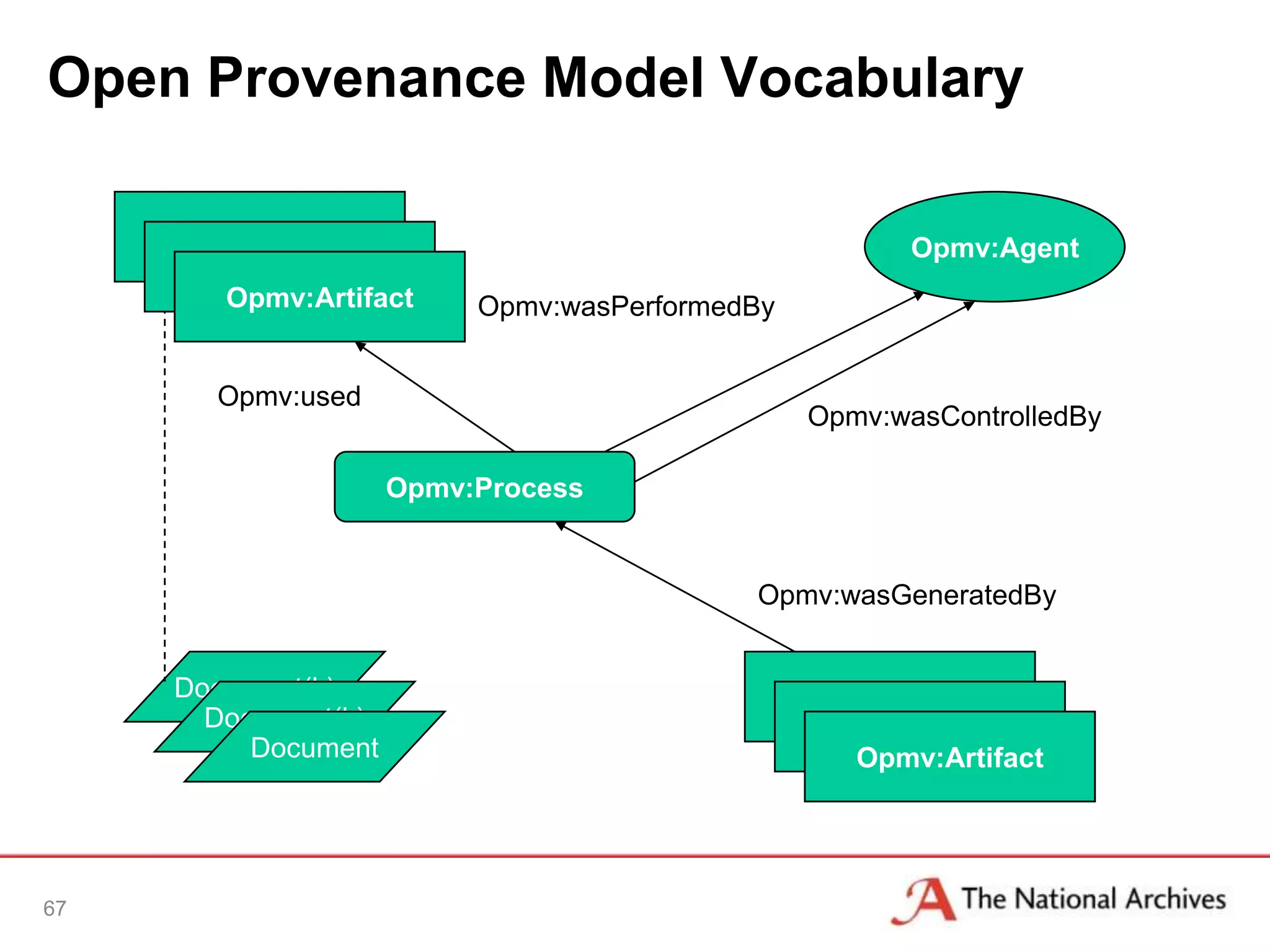
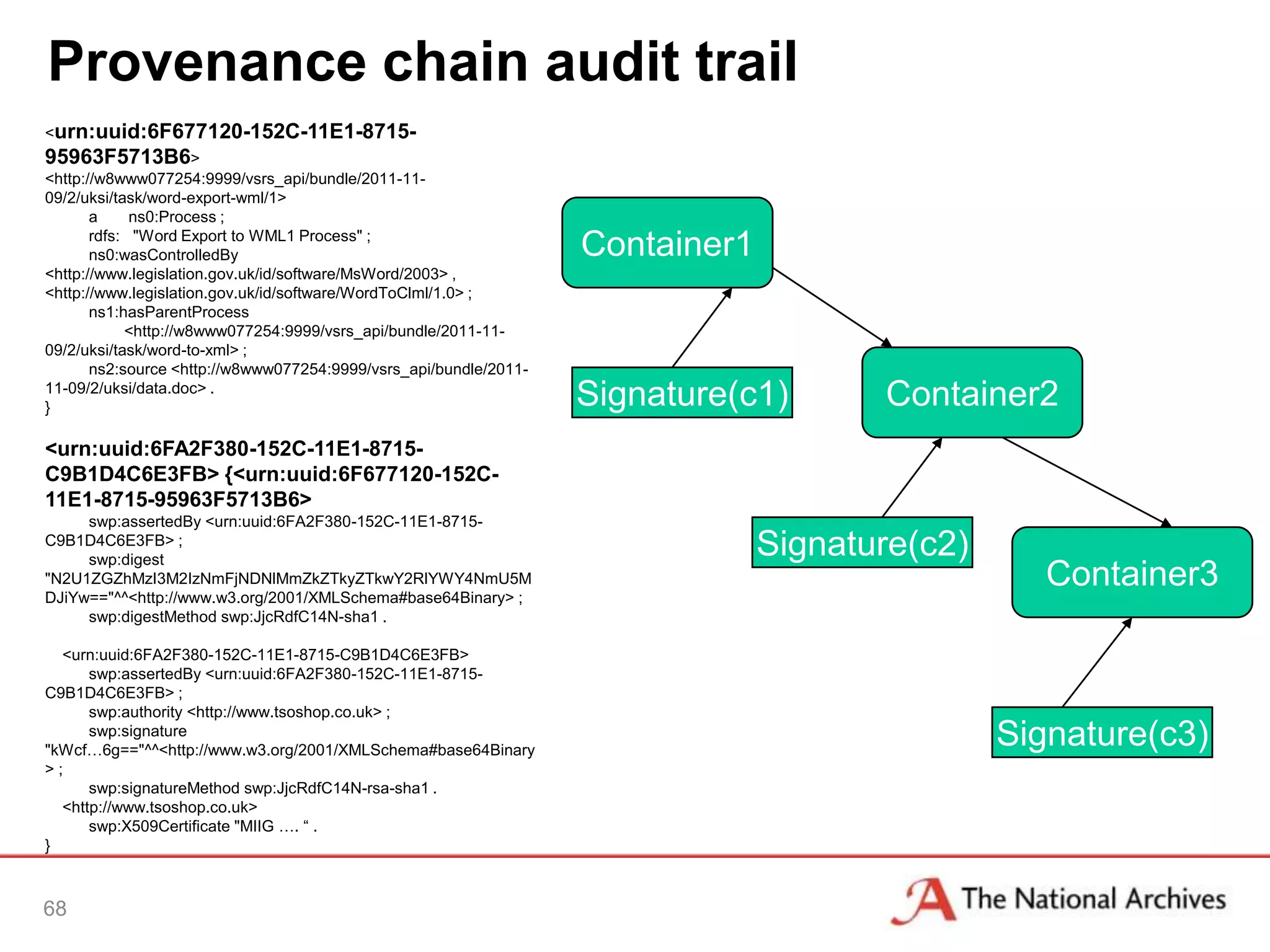
The document discusses the importance of linked data in enhancing government transparency and efficiency in public services, emphasizing the need for open data policies and standards. It outlines the UK government's commitment to making data available in accessible formats to promote accountability and innovation. Additionally, it describes the technologies and methodologies for publishing and linking data to facilitate better interactions and insights.



![Interoperability with the world?
• [DN: insert picture of globe]
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lod-workshop-johnlinkeddataandlowcarbon-120123055626-phpapp01/75/Linked-Open-Government-Data-in-UK-5-2048.jpg)